Development of a Bead-Based Multiplex Fluorescent Immunoassay to Detect Antibodies against Maedi-Visna Virus in Sheep
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Commercial Antigens
2.3. Production of Recombinant Proteins Based on the Norwegian Viral Strain
2.4. Serum Samples
2.5. Coupling of Antigen to Beads
2.6. Bead-Based Immunoassay
2.7. Coupling Confirmation
2.8. Assay Optimisation
2.9. Validation of Analytical Characteristics
2.10. Additional Testing of Samples
3. Results
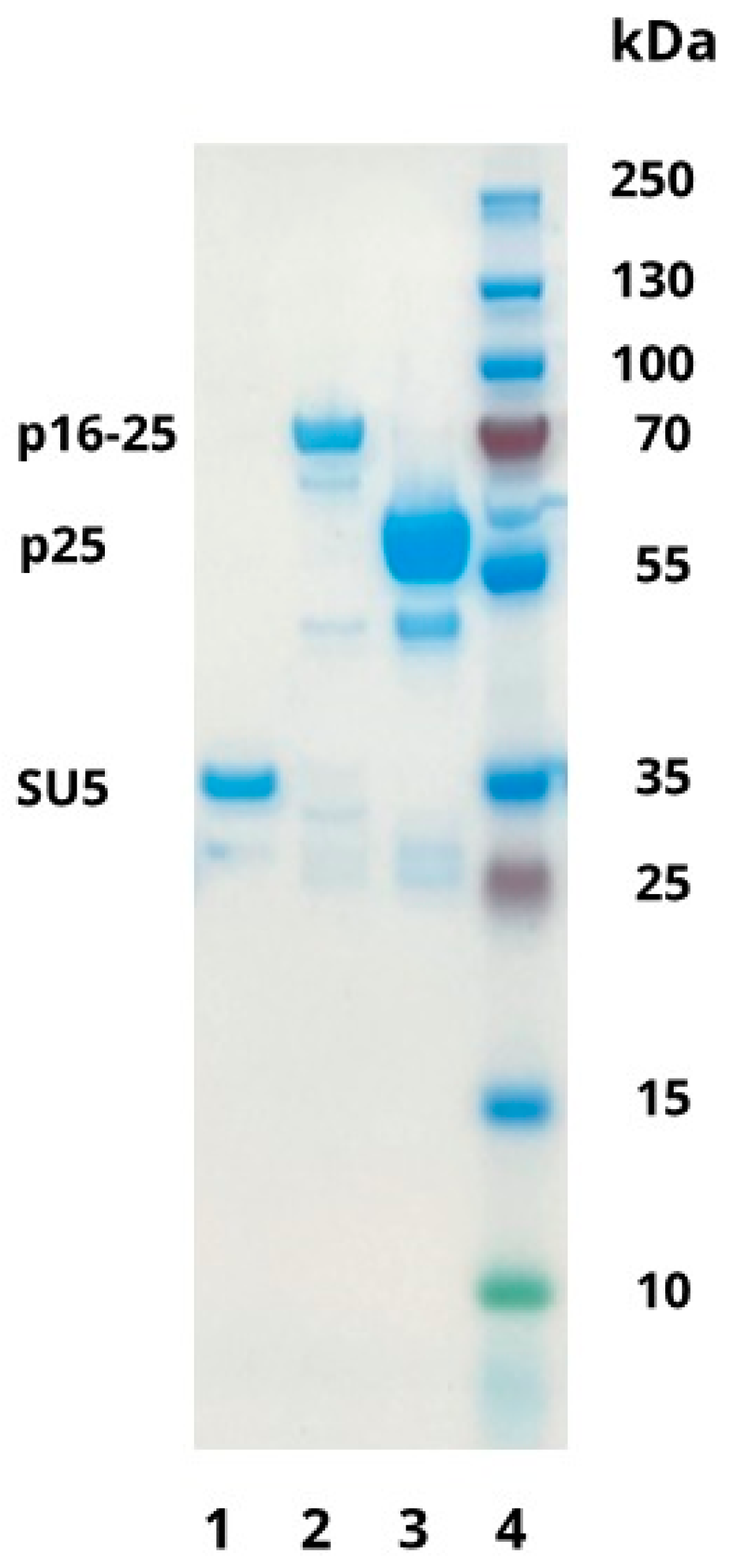
3.1. Production of Recombinant Proteins
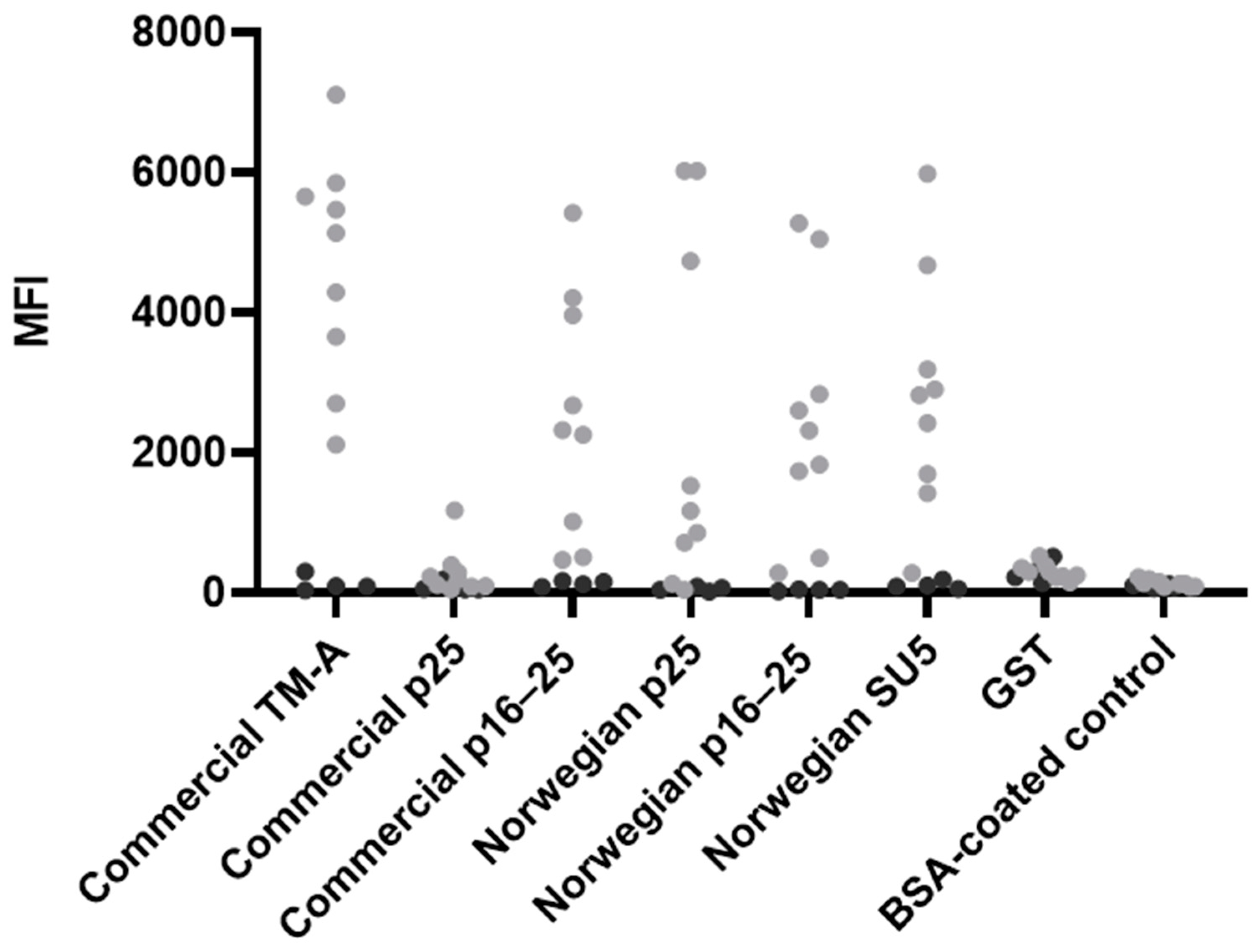
3.2. Development and Optimisation of the Bead-Based Multiplex Immunoassay
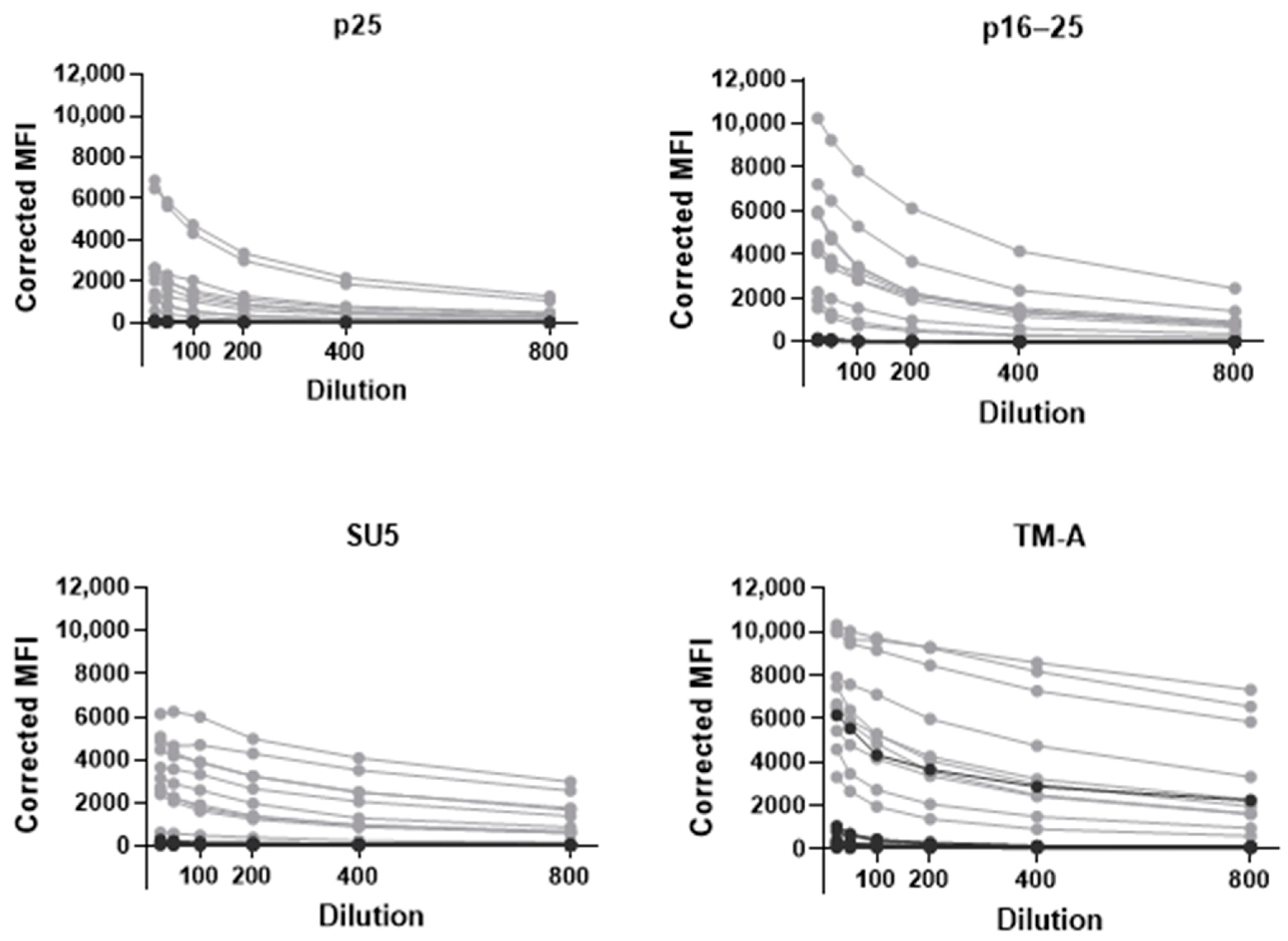
3.3. Analytical Characteristics
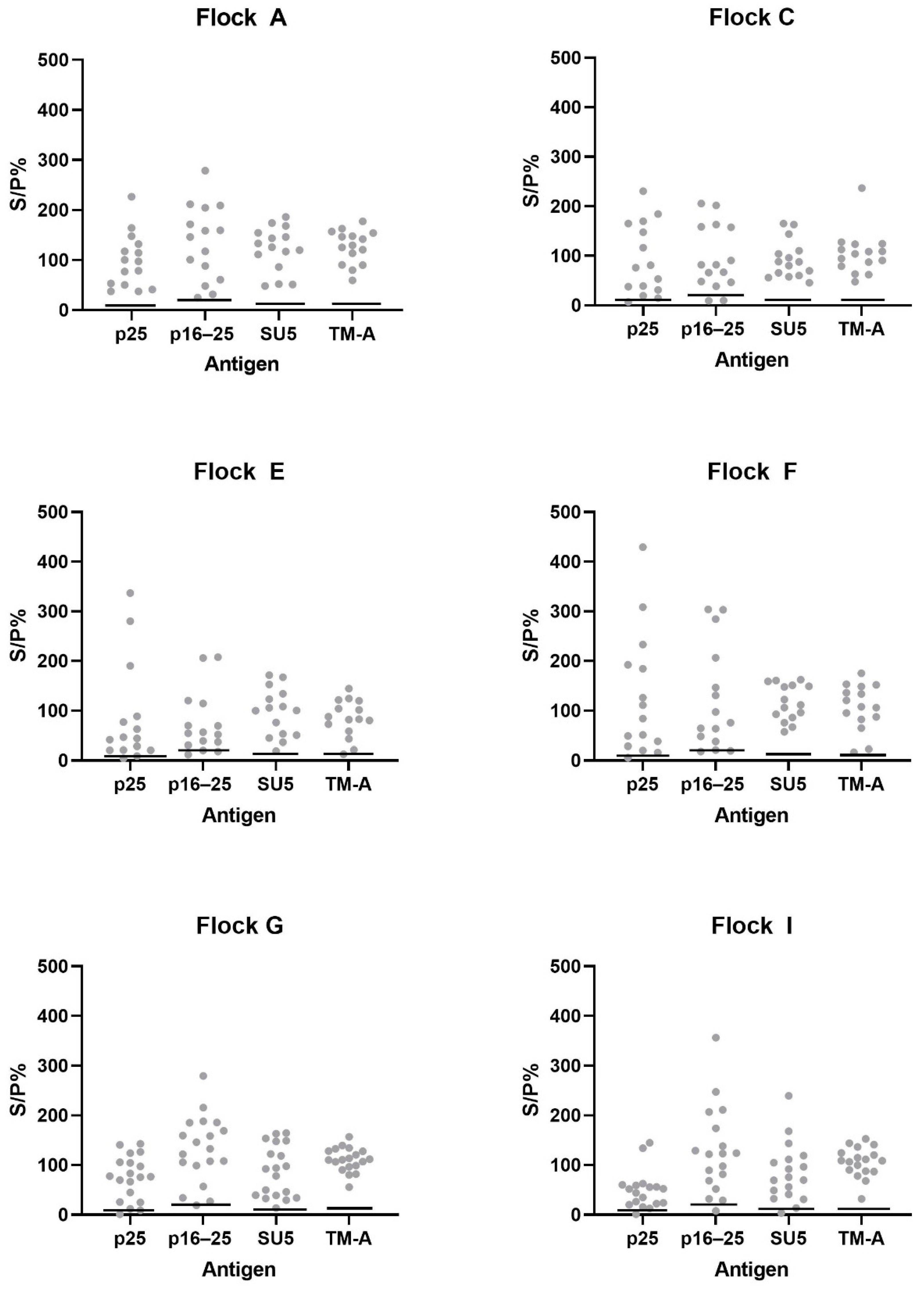
3.4. Additional Testing of Samples from High Prevalence Flocks
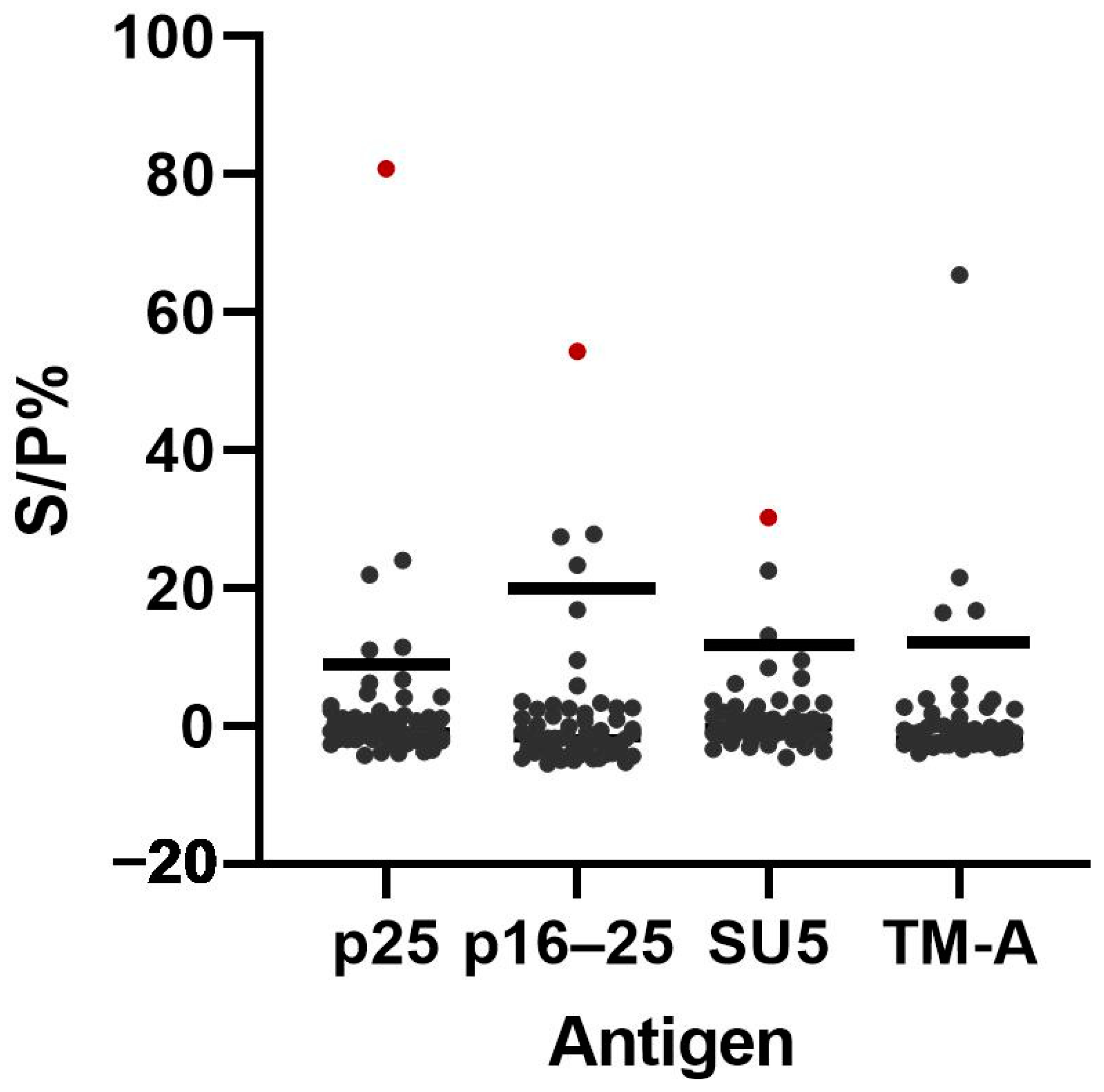
3.5. Additional Testing of Samples with Discrepant ELISA Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pétursson, G.; Hoff-Jørgensen, R. Maedi-Visna and Related Diseases, 1st ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Norwell, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Peterhans, E.; Greenland, T.; Badiola, J.; Harkiss, G.; Bertoni, G.; Amorena, B.; Eliaszewicz, M.; Juste, R.A.; Krassnig, R.; Lafont, J.P.; et al. Routes of transmission and consequences of small ruminant lentiviruses (SRLVs) infection and eradication schemes. Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, A.H.; Åkerstedt, J.; Klevar, S. The Surveillance Programme for Small Ruminant Lentivirus Infections in Sheep and Goats in Norway 2021; Norwegian Veterinary Institute: Ås, Norway, 2022; Available online: https://www.vetinst.no/overvaking/maedi-cae-sau-geit (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- de Andrés, D.; Klein, D.; Watt, N.J.; Berriatua, E.; Torsteinsdottir, S.; Blacklaws, B.A.; Harkiss, G.D. Diagnostic tests for small ruminant lentiviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 107, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogianni, A.I.; Stavropoulos, I.; Chaintoutis, S.C.; Bossis, I.; Gelasakis, A.I. Serological, Molecular and Culture-Based Diagnosis of Lentiviral Infections in Small Ruminants. Viruses 2021, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiels, R.; Van Mael, E.; Quinet, C.; Adjadj, N.R.; Cay, A.B.; De Regge, N. Comparative Analysis of Different Serological and Molecular Tests for the Detection of Small Ruminant Lentiviruses (SRLVs) in Belgian Sheep and Goats. Viruses 2018, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalberts, M.; Peterson, K.; Moll, L.; Vellema, P.; van Maanen, C. Evaluation of five SRLV ELISAs for fitness for purpose in sheep and goat accreditation schemes in the Netherlands. Small Rumin. Res. 2021, 202, 106452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Veterinary Institute (SVA). Surveillance of Infectious Diseases in Animals and Humans in Sweden 2022; National Veterinary Institute (SVA): Uppsala, Sweden, 2023; Available online: https://www.sva.se/amnesomraden/smittlage/sjukdomsrapporter-om-sva-s-overvakning/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Shah, C.; Böni, J.; Huder, J.B.; Vogt, H.-R.; Mühlherr, J.; Zanoni, R.; Miserez, R.; Lutz, H.; Schüpbach, J. Phylogenetic analysis and reclassification of caprine and ovine lentiviruses based on 104 new isolates: Evidence for regular sheep-to-goat transmission and worldwide propagation through livestock trade. Virology 2004, 319, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguijón, E.; Reina, R.; Pérez, M.; Polledo, L.; Villoria, M.; Ramírez, H.; Leginagoikoa, I.; Badiola, J.J.; García-Marín, J.F.; de Andrés, D.; et al. Small ruminant lentivirus infections and diseases. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houwers, D.J.; Nauta, I.M. Immunoblot analysis of the antibody response to ovine lentivirus infections. Vet. Microbiol. 1989, 19, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang, J.; Keen, J.; Cutlip, R.C.; Littledike, E.T. Evaluation of an ELISA for Detection of Ovine Progressive Pneumonia Antibodies using a Recombinant Transmembrane Envelope Protein. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1993, 5, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, G.; Hertig, C.; Zahno, M.-L.; Vogt, H.-R.; Dufour, S.; Cordano, P.; Peterhans, E.; Cheevers, W.P.; Sonigo, P.; Pancino, G. B-cell epitopes of the envelope glycoprotein of caprine arthritis–encephalitis virus and antibody response in infected goats. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2929–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang, J.; Torres, J.V. Oligopeptide-based enzyme immunoassay for ovine lentivirus antibody detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1813–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordasini, F.; Vogt, H.R.; Zahno, M.L.; Maeschli, A.; Nenci, C.; Zanoni, R.; Peterhans, E.; Bertoni, G. Analysis of the antibody response to an immunodominant epitope of the envelope glycoprotein of a lentivirus and its diagnostic potential. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, S.; Mannelli, A.; Merlo, T.; Ponti, N. Characterization of the immunodominant cross-reacting epitope of visna maedi virus and caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus capsid antigen. Virus Res. 1999, 61, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwang, J.; Rosati, S.; Yang, S.; Juste, R.A.; de la Concha-Bermejillo, A. Recognition of ovine lentivirus gag gene products by serum from infected sheep. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 55, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher-Hennings, J.; Araujo, K.P.; Souza, C.J.; Fang, Y.; Lawson, S.; Nelson, E.A.; Clement, T.; Dunn, M.; Lunney, J.K. Opportunities for bead-based multiplex assays in veterinary diagnostic laboratories. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragan, I.K.; Davis, A.S.; McVey, D.S.; Richt, J.A.; Rowland, R.R.; Wilson, W.C. Evaluation of Fluorescence Microsphere Immunoassay for Detection of Antibodies to Rift Valley Fever Virus Nucleocapsid Protein and Glycoproteins. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, R.L.; Ouellette, I.; Lindsay, R.W.; Parks, C.L.; King, C.R.; McDermott, A.B.; Morrow, G. A Multiplex Microsphere-Based Immunoassay Increases the Sensitivity of SIV-Specific Antibody Detection in Serum Samples and Mucosal Specimens Collected from Rhesus Macaques Infected with SIVmac239. Biores Open Access 2013, 2, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, B.; Freer, H. Development of a bead-based multiplex assay for simultaneous quantification of cytokines in horses. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 127, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, H.N.; Murphy, R.; Lopez, E.; Garcia, C. Conversion of a capture ELISA to a Luminex xMAP assay using a multiplex antibody screening method. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 65, e4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WOAH. Terrestrial Manual 2023—Chapter 1.1.6. Validation of Diagnostic Assays for Infectious Diseases of Terrestrial Animals; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2023; Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/1.01.06_VALIDATION.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Grego, E.; Bertolotti, L.; Quasso, A.; Profiti, M.; Lacerenza, D.; Muz, D.; Rosati, S. Genetic characterization of small ruminant lentivirus in Italian mixed flocks: Evidence for a novel genotype circulating in a local goat population. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerre, A.; Rømo, G.; Klevar, S.; Åkerstedt, J.; Kampen, A.H.; Hektoen, L.; Nordstoga, A.B. Challenges using serological diagnostics in elimination of visna/maedi: Serological results from two outbreaks in Norwegian sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2023, 229, 107149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorius. Instructions for Use Vivaspin® 500 and 2. Available online: https://www.vivaproducts.com/downloads/vivaspin-2-500-operating-instructions.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2023).
- Mattilsynet. Retningslinje for Lentivirus (Mædi/CAE) Hos Småfe [Guidelines for Small Ruminant Lentiviruses]. Available online: https://mattilsynet-xp7prod.enonic.cloud/api/_/attachment/inline/c1d91206-89f3-4c2d-bd26-284631cd946f:37d49bb086b0ebb4aac61f12af78c1e701c5766c/Retningslinje_lentivirus_samlet.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Innovative Diagnostics. Internal Validation Report ID Screen® MVV-CAEV Indirect; Innovative Diagnostics: Grabels, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aira, C.; Penning, M.; Eiden, M.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; Blome, S.; Strutzberg-Minder, K.; López, L.; Rueda, P.; Sastre, P. A multiplex assay for the detection of antibodies to relevant swine pathogens in serum. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.S.; Riber, U.; Jensen, V.F.; Lauritsen, K.T.; Andresen, L.O. Development and evaluation of a bead-based Multiplexed Fluorescent ImmunoAssay (MFIA) for detection of antibodies to Salmonella enterica serogroup B and C1 in pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wagner, B.; Freer, H.; Schilling, M.; Bannantine, J.P.; Campo, J.J.; Katani, R.; Grohn, Y.T.; Radzio-Basu, J.; Kapur, V. Early detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection in cattle with multiplex-bead based immunoassays. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nájera-Rivera, H.D.; Rodríguez-Cortez, A.D.; Anaya-Santillán, M.G.; Díaz-Aparicio, E.; Ramos-Rodríguez, A.V.; Siliceo-Cantero, I.J.; Vázquez-Franco, N.C.; Nieto-Patlán, E.; De las Peñas, A.; Valdés-Vázquez, L.M.; et al. Multiplex assay for the simultaneous detection of antibodies against small ruminant lentivirus, Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis, and Brucella melitensis in goats. Vet. World 2023, 16, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torfason, E.G.; Gudnadóttir, M.; Löve, A. Comparison of immunoblots with neutralizing and complement fixing antibodies in experimental and natural cases of visna-maedi. Arch. Virol. 1992, 123, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, J.; Kwang, J.; Rosati, S. Comparison of ovine lentivirus detection by conventional and recombinant serological methods. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995, 47, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOAH. Terrestrial Manual 2023—Chapter 2.2.1. Development and Optimisation of Antibody Detection Assays; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2014; Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/2.02.01_ANTIBODY_DETECT.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Jerre, A.; Nordstoga, A.B.; Dean, K.R.; Holmøy, I.H. Evaluation of three commercial ELISA tests for serological detection of maedi-visna virus using Bayesian latent class analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 208, 105765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valas, S.; Le Ven, A.; Croise, B.; Maquigneau, M.; Perrin, C. Interference of vaccination against bluetongue virus serotypes 1 and 8 with serological diagnosis of small-ruminant lentivirus infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattilsynet, O. Veileder for Flytting av Småfe [Guidelines for Moving Small Ruminants]; Mattilsynet [Norwegian Food Safety Authority]: Oslo, Norway, 2022; Available online: https://www.mattilsynet.no/om_mattilsynet/gjeldende_regelverk/veiledere/veileder_for_flytting_av_smaafe.32357/binary/Veileder%20for%20flytting%20av%20sm%C3%A5fe (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Boshoff, C.H.; Dungu, B.; Williams, R.; Vorster, J.; Conradie, J.D.; Verwoerd, D.W.; York, D.F. Detection of Maedi-Visna virus antibodies using a single fusion transmembrane-core p25 recombinant protein ELISA and a modified receiver-operating characteristic analysis to determine cut-off values. J. Virol. Methods 1997, 63, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogarol, C.; Bertolotti, L.; Klevar, S.; Profiti, M.; Gjerset, B.; Rosati, S. Serological characterization of small ruminant lentiviruses: A complete tool for serotyping lentivirus infection in goat. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 176, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft, N.; Åkerstedt, J.; Tharaldsen, J.; Hopp, P. Evaluation of three serological tests for diagnosis of Maedi-Visna virus infection using latent class analysis. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 120, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Panel | Samples | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Panel 1 | 1 positive pooled sample (30 animals positive in screening and verification ELISA) 1 negative pooled sample (30 animals negative in screening ELISA) | Optimisation (antigen concentrations) |
| Panel 2 | 9 positives in screening and verification ELISA 4 negatives in screening ELISA | Optimisation (commercial and Norwegian antigens) |
| Panel 3 | 10 positives in screening and verification ELISA 8 negatives in screening ELISA | Optimisation (serial dilution) |
| Panel 4 | 5 samples with S/P% values ranging from positive to inconclusive and negative in screening ELISA | Repeatability |
| Panel 5 | 40 negatives in screening ELISA 67 positives in screening and verification ELISA | Cut-off determination |
| Panel 6 | 3 samples positive in screening and verification ELISA from panel 3 | Analytical sensitivity |
| Panel 7 | 60 negatives in screening ELISA (50 evenly distributed throughout Norway, 5 haemolytic, and 5 positives in an in-house antibody ELISA for Toxoplasma gondii) | Analytical specificity |
| Panel 8 | 32 positives in screening and verification ELISA from positive flocks | Exploring samples from high prevalence flocks |
| Panel 9 | 15 positives in screening ELISA and Elitest, negative in verification ELISA from positive flocks 14 positives in screening ELISA and Elitest, negative in verification ELISA from negative flocks | Exploring samples with discrepant ELISA results |
| Antigen/Test | Samples Panel 5 1 | IDvet Reference Serum (S/P%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (S/P%) | Sample 2 (S/P%) | Sample 3 (S/P%) | ||
| ELISA | 1:800 (112.9) | 1:400 (87.3) | 1:200 (68.4) | 1:400 (62.2) |
| Multiplex p25 | 1:800 (14.4) | 1:6400 (9.1) | 1:1600 (12.6) | 1:400 (13.9) |
| Multiplex p16–25 | 1:800 (35.5) | 1:1600 (23.5) | 1:400 (29.3) | 1:50 (29.3) |
| Multiplex SU5 | 1:800 (16.5) | 1:6400 (14.8) | 1:6400 (13.6) | 1:100 (12.1) |
| Multiplex TM-A | 1:12,800 (14.0) | 1:3200 (18.9) | 1:800 (17.2) | 1:1600 (18.4) |
| Sample Description | Antigen | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P25 | P16–25 | SU5 | TM-A | |
| Haemolytic | + | − | − | − |
| Haemolytic | − | − | − | + |
| Toxoplasmosis + | − | + | − | − |
| East | − | − | − | + |
| East | + | − | − | − |
| East | − | − | + | − |
| East | + | + | − | − |
| South | + | − | − | − |
| South | − | − | − | + |
| West | + | + | + | − |
| West | − | + | − | − |
| North | − | − | + | − |
| North | − | − | − | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borge, A.J.; Colitti, B.; Rosati, S.; Nordstoga, A.B.; Gjerset, B.; Udjus, K.; Nogarol, C.; Chellappa, S.; Samdal, I.A.; Lybeck, K. Development of a Bead-Based Multiplex Fluorescent Immunoassay to Detect Antibodies against Maedi-Visna Virus in Sheep. Animals 2024, 14, 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101442
Borge AJ, Colitti B, Rosati S, Nordstoga AB, Gjerset B, Udjus K, Nogarol C, Chellappa S, Samdal IA, Lybeck K. Development of a Bead-Based Multiplex Fluorescent Immunoassay to Detect Antibodies against Maedi-Visna Virus in Sheep. Animals. 2024; 14(10):1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101442
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorge, Anniken Jerre, Barbara Colitti, Sergio Rosati, Anne B. Nordstoga, Britt Gjerset, Kristin Udjus, Chiara Nogarol, Stalin Chellappa, Ingunn Anita Samdal, and Kari Lybeck. 2024. "Development of a Bead-Based Multiplex Fluorescent Immunoassay to Detect Antibodies against Maedi-Visna Virus in Sheep" Animals 14, no. 10: 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101442
APA StyleBorge, A. J., Colitti, B., Rosati, S., Nordstoga, A. B., Gjerset, B., Udjus, K., Nogarol, C., Chellappa, S., Samdal, I. A., & Lybeck, K. (2024). Development of a Bead-Based Multiplex Fluorescent Immunoassay to Detect Antibodies against Maedi-Visna Virus in Sheep. Animals, 14(10), 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101442






