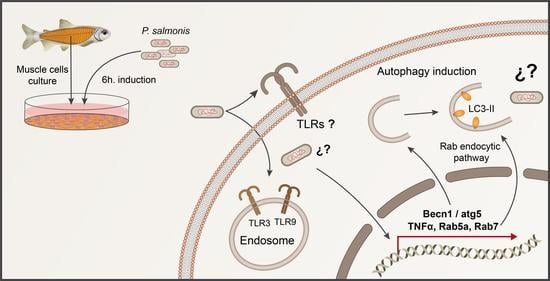
Evidence of the Autophagic Process during the Fish Immune Response of Skeletal Muscle Cells against Piscirickettsia salmonis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Fish Husbandry
2.3. Primary Culture of Muscle Cells
2.4. Piscirickettsia salmonis Culture and Infection Protocol
2.5. Quantitative Real Time PCR (qPCR)
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
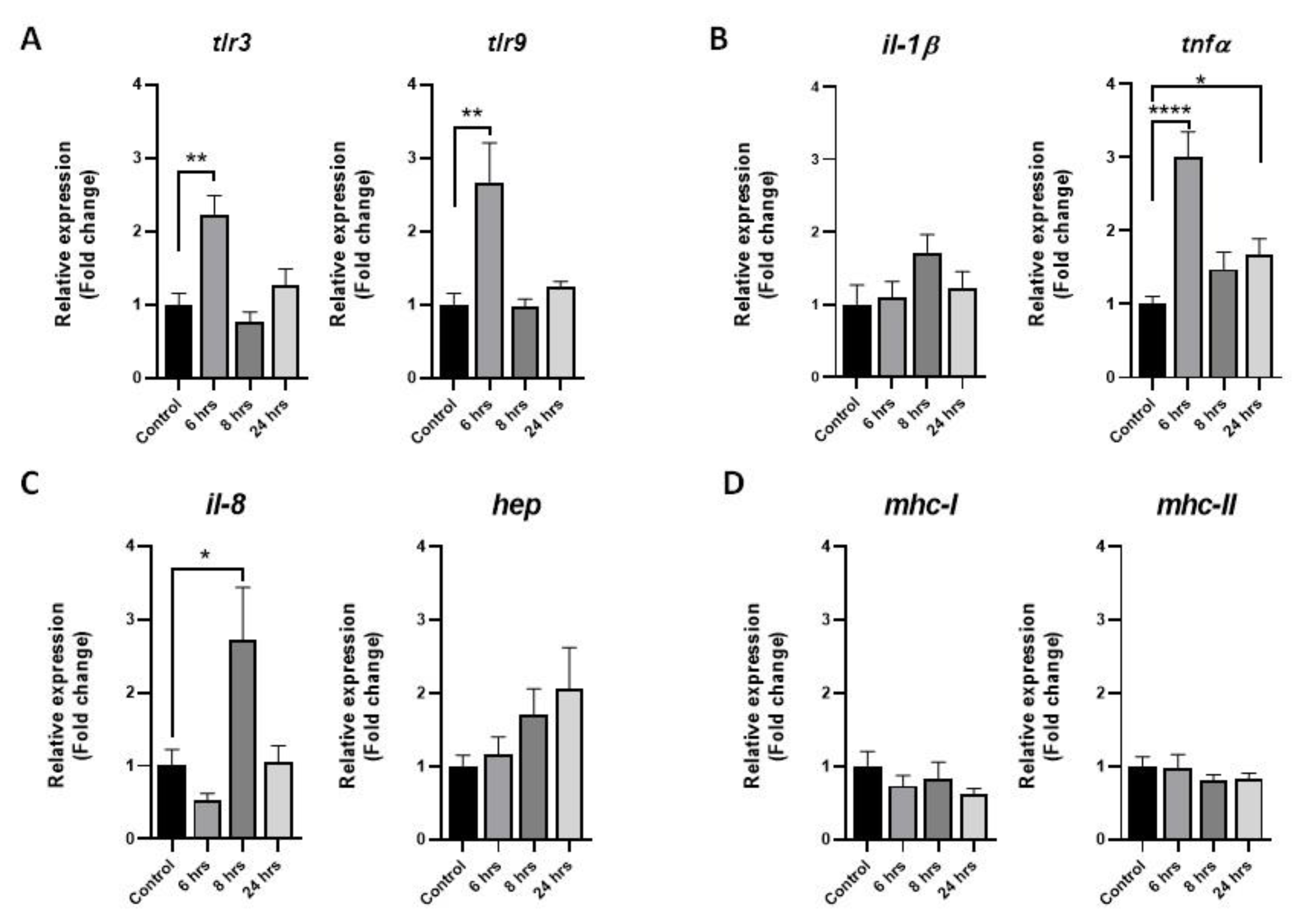
3.1. Immune-like Response of Skeletal Muscle Cells after P. salmonis Challenge
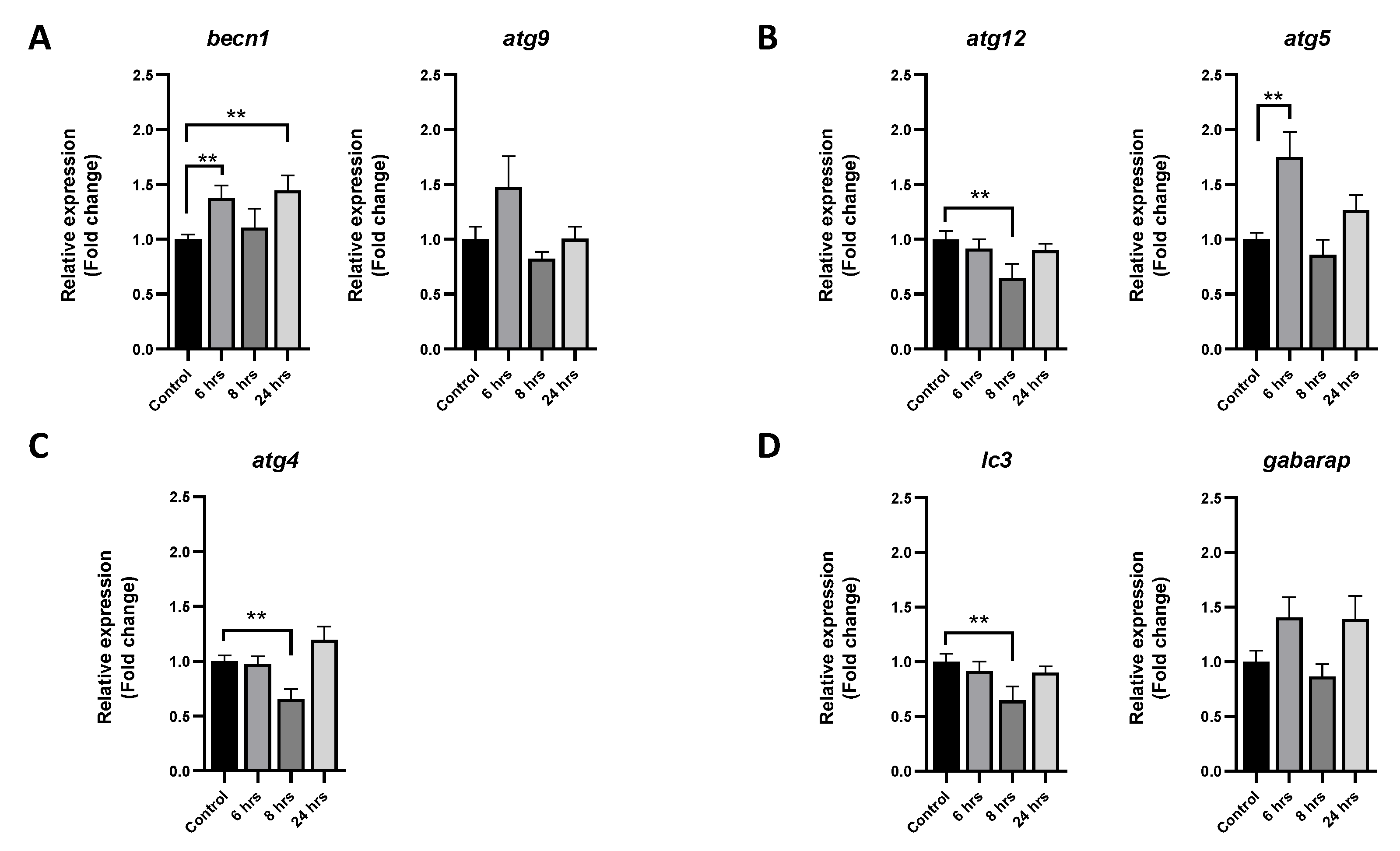
3.2. Autophagic Modulation in Muscle Cells after P. salmonis Challenge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jagannath, C.; McBride, J.W.; Vergne, I. The autophagy pathway: Bacterial pathogen immunity and evasion. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 768935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Levine, B.; Cuervo, A.M.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy fights disease through cellular selfdigestion. Nature 2008, 451, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belghit, I.; Panserat, S.; Sadoul, B.; Dias, K.; Skiba-Cassy, S.; Seiliez, I. Macronutrient composition of the diet affects the feeding-mediated down regulation of autophagy in muscle of Rainbow Trout (O. mykiss). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, D.; Münz, C. Innate and adaptive immunity through autophagy. Immunity 2007, 27, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgin, H.W.; Levine, B. Autophagy genes in immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya, P.; Reggiori, F.; Codogno, P. Emerging regulation and functions of autophagy. Nature 2013, 15, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Dancourt, J.; Shteyn, V.; Puente, G.; Fong, W.M.; Nag, S.; Bewersdorf, J.; Yamamoto, A.; Antonny, B.; Melia, T.J. Lipidation of the LC3/GABARAP family of autophagy proteins relies on a membrane-curvature-sensing domain in Atg3. Nature 2014, 16, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puleston, D.J.; Simon, A.K. Autophagy in the immune system. Immunology 2014, 141, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.A.; Deretic, V. Toll-like receptors in control of immunological autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.H.; Fleuri, A.K.; Pellison, N.C.; Quirino, G.F.; Horta, C.V.; de Carvalho, R.V.; Oliveira, S.C.; Zamboni, D.S. Autophagy downstream of endosomal Toll-like receptor signaling in macrophages is a key mechanism for resistance to Leishmania major infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13087–13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Into, T.; Inomata, M.; Takayama, E.; Takigawa, T. Autophagy in regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.A.; Elmaoued, R.A.; Davis, A.S.; Kyei, G.; Deretic, V. Toll-like receptors control autophagy. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J. Autophagy and cytokines. Cytokine 2011, 56, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Qin, W.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, L. Emerging regulatory mechanisms and functions of autophagy in fish. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmori-Cedeño, J.; Liu, J.; Misk, E.; Lillie, B.N.; Lumsden, J.S. Autophagy-related genes in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) gill epithelial cells and their role in nutrient restriction. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pham, P.H.; Lumsden, J.S. Autophagy modulation in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss L. and resistance to experimental infection with Flavobacterium psychrophilum. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, V.; Valenzuela, C.A.; Zuloaga, R.; Aros, C.; Altamirano, C.; Valdés, J.A.; Molina, A. Effect of cortisol on the immune-like response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) myotubes challenged with Piscirickettsia salmonis. Veter-Immunol. Immunopathol. 2021, 237, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, A.M.; Müntefering, T.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Ruck, T. Skeletal muscle cells actively shape (auto)immune responses. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiendl, H.; Hohlfeld, R.; Kieseier, B.C. Immunobiology of muscle: Advances in understanding an immunological microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Huang, T.; Zhu, R.; Gu, R.; Shi, D.; Xiao, J.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Liao, H. Immunological behavior analysis of muscle cells under IFN-γ stimulation in vitro and in vivo. Anat. Rec. 2018, 301, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiendl, H.; Lautwein, A.; Mitsdörffer, M.; Krause, S.; Erfurth, S.; Wienhold, W.; Morgalla, M.; Weber, E.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Lochmüller, H.; et al. Antigen processing and presentation in human muscle: Cathepsin S is critical for MHC class II expression and upregulated in inflammatory myopathies. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 138, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Dabur, R. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in regulation of skeletal muscle metabolism: A systematic review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2161–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahuja, A.; Dabur, R. Dynamics of toll-like receptors signaling in skeletal muscle atrophy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 5831–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidball, J.G.; Villalta, S.A. Regulatory interactions between muscle and the immune system during muscle regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R1173–R1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues-Faria, C.; Vasson, M.-P.; Goncalves-Mendes, N.; Boirie, Y.; Walrand, S. Skeletal muscle regeneration and impact of aging and nutrition. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 26, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, J.K.; Raida, M.K.; Kania, P.W.; Buchmann, K. Differential immune response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) at early developmental stages (larvae and fry) against the bacterial pathogen Yersinia ruckeri. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 36, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, C.A.; Zuloaga, R.; Poblete-Morales, M.; Vera-Tobar, T.; Mercado, L.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Valdés, J.A.; Molina, A. Fish skeletal muscle tissue is an important focus of immune reactions during pathogen infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 73, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, V.; Valenzuela, C.A.; Aros, C.; Dettleff, P.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Gallardo-Escarate, C.; Altamirano, C.; Molina, A.; Valdés, J.A. Transcriptomic analysis reveals a Piscirickettsia salmonis-induced early inflammatory response in rainbow trout skeletal muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D: Genom. Proteom. 2021, 39, 100859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aedo, J.; Reyes, A.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Molina, A.; Valdés, J. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces rainbow trout myotube atrophy via Akt/FoxO1/Atrogin-1 signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2015, 47, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, L.; Nie, G.; Li, X. Toll-like receptor recognition of bacteria in fish: Ligand specificity and signal pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Jeong, E.-K.; Kim, M.-J.; Jung, Y.M.; Jung, Y.-J. Stimulation of toll-like receptor 3 diminishes intracellular growth of Salmonella Typhimurium by enhancing autophagy in murine macrophages. Metabolites 2021, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, C.; Haussmann, D.; Kausel, G.; Figueroa, J. Molecular cloning of Salmo salar Toll-like receptors (TLR1, TLR22, TLR5M and TLR5S) and expression analysis in SHK-1 cells during Piscirickettsia salmonis infection. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas-Serri, M.; Peña, A.; Maldonado, L. Transcriptomic profiles of post-smolt Atlantic salmon challenged with Piscirickettsia salmonis reveal a strategy to evade the adaptive immune response and modify cell-autonomous immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 81, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Wen, H.; Qi, X.; Li, Y.; He, F. Immune correlates of NF-κB and TNFα promoter DNA methylation in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) muscle and immune parameters change response to vibrio anguillarum infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 119, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, S.; Nakano, R.; Kitanaka, T.; Kitanaka, N.; Nakayama, T.; Sugiya, H. ERK2 and JNK1 contribute to TNF-α-induced IL-8 expression in synovial fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, C.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, W.-J. Interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression in the olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV) challenge. Dev. Reprod. 2019, 23, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münz, C. Autophagy in immunity. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 172, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Mizushima, N.; Virgin, H.W. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 2011, 469, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-T.; Balmori-Cedeno, J.; Misk, E.; Lumsden, J.S. Pharmacological and nutritional modulation of autophagy in a rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gill cell line, RTgill-W1. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2020, 56, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, J.J.; Wirth, M.; Tooze, S.A.; Lane, J.D.; Hammond, C.L. Autophagy coordinates chondrocyte development and early joint formation in zebrafish. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e22002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawed, S.A.; Zhang, J.; Ren, F.; He, Y.; Mei, J. atg7 and beclin1 are essential for energy metabolism and survival during the larval-to-juvenile transition stage of zebrafish. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 7, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.-F.; Li, Z.-C.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Mou, C.-Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Chen, D.-D.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.-F.; Li, S. Fish herpesvirus KLP manipulates Beclin1 to selectively degrade MITA through a precise autophagic manner for immune evasion. Water Biol. Secur. 2023, 2, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuma, A.; Mizushima, N.; Ishihara, N.; Ohsumi, Y. Formation of the ∼350-kDa Apg12-Apg5·Apg16 multimeric complex, mediated by Apg16 oligomerization, is essential for autophagy in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18619–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Qin, Q. Fish autophagy protein 5 exerts negative regulation on antiviral immune response against iridovirus and nodavirus. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wen, Q.; Li, W.; Yuan, X.; Fu, Q.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X. ATG12 is involved in the antiviral immune response in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 119, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, Z.; Sass, M. The autophagic roles of Rab small GTPases and their upstream regulators. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitelli, R.; Santillo, M.; Lattero, D.; Chiariello, M.; Bifulco, M.; Bruni, C.B.; Bucci, C. Role of the small GTPase RAB7 in the late endocytic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 4391–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, A.; Wolfson, D.L.; Ahluwalia, B.S.; Jensen, I.; Jørgensen, J.; Iliev, D.B. Intracellular distribution and transcriptional regulation of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) Rab5c, 7a and 27a homologs by immune stimuli. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valenzuela, C.A.; Azúa, M.; Álvarez, C.A.; Schmitt, P.; Ojeda, N.; Mercado, L. Evidence of the Autophagic Process during the Fish Immune Response of Skeletal Muscle Cells against Piscirickettsia salmonis. Animals 2023, 13, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050880
Valenzuela CA, Azúa M, Álvarez CA, Schmitt P, Ojeda N, Mercado L. Evidence of the Autophagic Process during the Fish Immune Response of Skeletal Muscle Cells against Piscirickettsia salmonis. Animals. 2023; 13(5):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050880
Chicago/Turabian StyleValenzuela, Cristián A., Marco Azúa, Claudio A. Álvarez, Paulina Schmitt, Nicolás Ojeda, and Luis Mercado. 2023. "Evidence of the Autophagic Process during the Fish Immune Response of Skeletal Muscle Cells against Piscirickettsia salmonis" Animals 13, no. 5: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050880
APA StyleValenzuela, C. A., Azúa, M., Álvarez, C. A., Schmitt, P., Ojeda, N., & Mercado, L. (2023). Evidence of the Autophagic Process during the Fish Immune Response of Skeletal Muscle Cells against Piscirickettsia salmonis. Animals, 13(5), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050880