Secretory IgA as Biomarker for Gastrointestinal Nematodes Natural Infection in Different Breed Sheep
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Selection
2.2. Animal Sampling
2.3. Antigen Production
2.3.1. Somatic Antigen from Third-Stage Larvae of T. circumcincta
2.3.2. Recombinant Protein Disulfide Isomerase of T. circumcincta
2.4. Indirect ELISA against Gastrointestinal Nematodes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
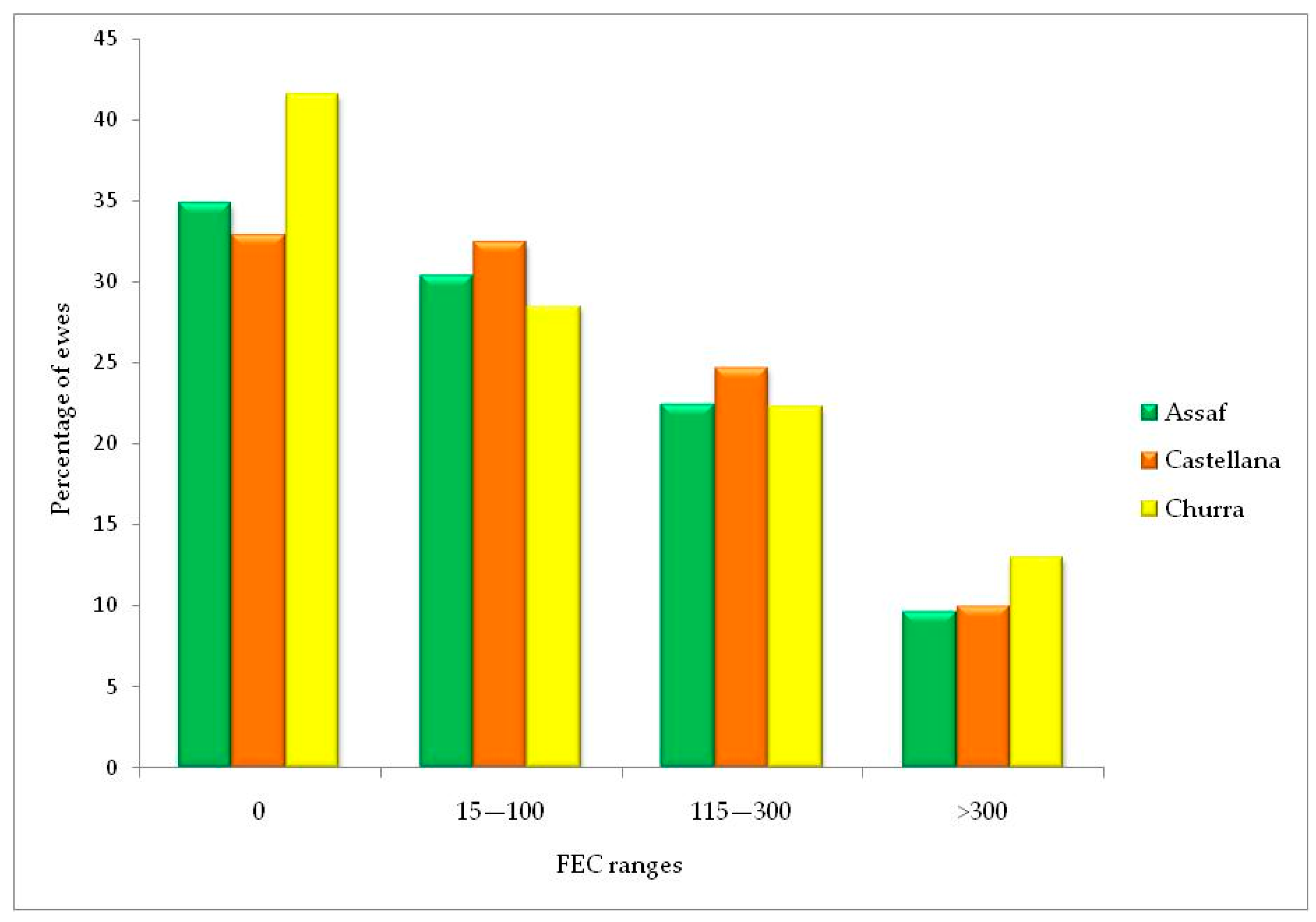
3.1. Fecal Egg Count and Risk of Infections Depending on the Breed
3.2. Prediction of Infection Risk
3.3. IgA Levels against GIN as a Marker of Infection Level
3.4. Association between IgA Levels for the Different Biological Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terrill, T.H.; Miller, J.E.; Burke, J.M.; Mosjidis, J.A.; Kaplan, R.M. Experiences with Integrated Concepts for the Control of Haemonchus contortus in Sheep and Goats in the United States. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRae, K.M.; Good, B.; Hanrahan, J.P.; McCabe, M.S.; Cormican, P.; Sweeney, T.; O’Connell, M.J.; Keane, O.M. Transcriptional Profiling of the Ovine Abomasal Lymph Node Reveals a Role for Timing of the Immune Response in Gastrointestinal Nematode Resistance. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 224, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, D.; Bosco, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; Kaulfuß, K.H.; Kellermann, M.; Fischer, J.; Wang, H.; Kley, K.; Mayr, S.; et al. Eprinomectin Pour-on (EPRINEX® Pour-on, Merial): Efficacy against Gastrointestinal and Pulmonary Nematodes and Pharmacokinetics in Sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossner, A.G.; Venturina, V.M.; Shaw, D.J.; Pemberton, J.M.; Hopkins, J. Relationship between Susceptibility of Blackface Sheep to Teladorsagia circumcincta Infection and an Inflammatory Mucosal T Cell Response. Vet. Res. 2012, 224, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Valladares, M.; Robles-Pérez, D.; Martínez-Pérez, J.M.; Cordero-Pérez, C.; Famularo, M.D.R.; Fernández-Pato, N.; González-Lanza, C.; Castañón-Ordóñez, L.; Rojo-Vázquez, F.A. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Nematodes and Fasciola hepatica in Sheep in the Northwest of Spain: Relation to Climatic Conditions and/or Man-Made Environmental Modifications. Parast. Vectors 2013, 6, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturina, V.M.; Gossner, A.G.; Hopkins, J. The Immunology and Genetics of Resistance of Sheep to Teladorsagia circumcincta. Vet. Res. Commun. 2013, 37, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Valladares, M.; Valderas-García, E.; Gandasegui, J.; Skuce, P.; Morrison, A.; Castilla Gómez De Agüero, V.; Cambra-Pellejà, M.; Balaña-Fouce, R.; Rojo-Vázquez, F.A. Teladorsagia circumcincta Beta Tubulin: The Presence of the E198L Polymorphism on Its Own Is Associated with Benzimidazole Resistance. Parast. Vectors 2020, 13, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.M. Drug Resistance in Nematodes of Veterinary Importance: A Status Report. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, I.; Pomroy, W.E.; Kenyon, P.R.; Smith, G.; Adlington, B.; Moss, A. Lack of Efficacy of Monepantel against Teladorsagia circumcincta and Trichostrongylus colubriformis. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederos, A.E.; Ramos, Z.; Banchero, G.E. First Report of Monepantel Haemonchus contortus Resistance on Sheep Farms in Uruguay. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stear, M.J.; Doligalska, M.; Donskow-Schmelter, K. Alternatives to Anthelmintics for the Control of Nematodes in Livestock. Parasitol. 2007, 134, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, J.; Morgan, E.R.; Rinaldi, L.; Van Dijk, J.; Demeler, J.; Höglund, J.; Hertzberg, H.; Van Ranst, B.; Hendrickx, G.; Vercruysse, J.; et al. Practices to Optimise Gastrointestinal Nematode Control on Sheep, Goat and Cattle Farms in Europe Using Targeted (Selective) Treatments. Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, S.; Piedrafita, D.; Sandeman, M.; Cotton, S. The Current Status of Anthelmintic Resistance in a Temperate Region of Australia; Implications for Small Ruminant Farm Management. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 17, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewc, M.; De Waal, T.; Zintl, A. Biological Methods for the Control of Gastrointestinal Nematodes. Vet. J. 2021, 268, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunia, M.; Phocas, F.; Gourdine, J.L.; Bijma, P.; Mandonnet, N. Simulated Selection Responses for Breeding Programs Including Resistance and Resilience to Parasites in Creole Goats. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Valladares, M.; Vara-Del Río, M.P.; Cruz-Rojo, M.A.; Rojo-Vázquez, F.A. Genetic Resistance to Teladorsagia circumcincta: IgA and Parameters at Slaughter in Churra Sheep. Parasite Immunol. 2005, 27, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eady, S.J.; Woolaston, R.R.; Mortimer, S.I.; Lewer, R.P.; Raadsma, H.W.; Swan, A.A.; Ponzoni, R.W. Resistance to Nematode Parasites in Merino Sheep: Sources of Genetic Variation. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1996, 47, 895–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollott, G.E.; Karlsson, L.J.E.; Eady, S.; Greefft, J.C. Genetic Parameters for Indicators of Host Resistance to Parasites from Weaning to Hogget Age in Merino Sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 2852–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, P.B. Faecal Egg Counts as a Guide for Drench Use. N. Z. Vet. J. 2002, 50, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.J.; Morris, C.A.; Wheeler, M.; Tate, M.; Sutherland, I.A. Salivary IgA: A Suitable Measure of Immunity to Gastrointestinal Nematodes in Sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stear, M.J.; Strain, S.; Bishop, S.C. How Lambs Control Infection with Ostertagia circumcincta. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 72, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stear, M.J.; Abuagob, O.; Benothman, M.; Bishop, S.C.; Innocent, G.; Kerr, A.; Mitchell, S. Variation among Faecal Egg Counts Following Natural Nematode Infection in Scottish Blackface Lambs. Parasitology 2006, 132, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinski, E.; Bairden, K.; Duncan, J.L.; Eisler, M.C.; Holmes, P.H.; McKellar, Q.A.; Murray, M.; Stear, M.J. Local and Plasma Antibody Responses to the Parasitic Larval Stages of the Abomasal Nematode Ostertagia circumcincta. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 59, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cisneros, J.P.J.; Stear, M.J.; Mair, C.; Singleton, D.; Stefan, T.; Stear, A.; Marion, G.; Matthews, L. An Explicit Immunogenetic Model of Gastrointestinal Nematode Infection in Sheep. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, S.A.J.; Bishop, S.C.; Henderson, N.G.; Kerr, A.; McKellar, Q.A.; Mitchell, S.; Stear, M.J. The Genetic Control of IgA Activity against Teladorsagia circumcincta and Its Association with Parasite Resistance in Naturally Infected Sheep. Parasitoloy 2002, 124, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stear, M.J.; Bairden, K.; Innocent, G.T.; Mitchell, S.; Strain, S.; Bishop, S.C. The Relationship between IgA Activity against 4th-Stage Larvae and Density-Dependent Effects on the Number of 4th-Stage Larvae of Teladorsagia circumcincta in Naturally Infected Sheep. Parasitoloy 2004, 129, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie-Clarke, K.; Kaseja, K.; Sotomaior, C.; Brady, N.; Moore, K.; Stear, M. Salivary IgA: A Biomarker for Resistance to Teladorsagia circumcincta and a New Estimated Breeding Value. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 269, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo-Couoh, J.G.; Aguilar-Caballero, A.J.; Torres-Acosta, J.F.J.; González-Garduño, R. Comparing the Phenotypic Susceptibility of Pelibuey and Katahdin Female Lambs against Natural Gastrointestinal Nematode Infections under Hot Humid Tropical Conditions. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, B.; Back, J.W.; Klaren, V.N.A.; Speijer, D.; Peek, R. Conserved Regions of Protein Disulfide Isomerase Are Targeted by Natural IgA Antibodies in Humans. Int. Immunol. 2002, 14, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Secretory IgA: Designed for Anti-Microbial Defense. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowdridge, S.; MacKinnon, K.; McCann, J.C.; Zajac, A.M.; Notter, D.R. Hair-Type Sheep Generate an Accelerated and Longer-Lived Humoral Immune Response to Haemonchus contortus Infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, J.M.; Robinson, N.A.; Meeusen, E.N.T.; Piedrafita, D.M. The Relationship between the Rapid Rejection of Haemonchus contortus Larvae with Cells and Mediators in Abomasal Tissues in Immune Sheep. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, C.; Saravia, A.; Costa, M.; Castells, D.; Ciappesoni, G.; Riet-Correa, F.; Freire, T. Resistance to Haemonchus contortus in Corriedale Sheep Is Associated to High Parasite-Specific IgA Titer and a Systemic Th2 Immune Response. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H.; Wastling, J.M.; Knox, D.P. A Preliminary Proteomic Survey of the in Vitro Excretory/Secretory Products of Fourth-Stage Larval and Adult Teladorsagia circumcincta. Parasitoloy 2006, 132, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Valladares, M.; Godio-Fernández, R.; Vara-Del Río, M.P.; Martín, J.F.; Rojo-Vázquez, F.A. Expression of the Recombinant Protein Disulphide Isomerase of Teladorsagia circumcincta. Parasite Immunol. 2007, 29, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, R.B.; Hirst, T.R.; Tuite, M.F. Protein Disulphide Isomerase: Building Bridges in Protein Folding. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994, 19, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, C.P.; Berneman, A.; Pires, R.; Avrameas, S.; Bouvet, J.P. Natural Polyreactive Secretory Immunoglobulin A Autoantibodies as a Possible Barrier to Infection in Humans. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Valladares, M.; Vara-Del Río, M.P.; Rojo-Vázquez, F.A. Use of a 203 Aα Fragment of Tc-PDI to Detect IgA Activity during Infection by Teladorsagia circumcincta in Sheep. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subdirección General de Producciones Ganaderas y Cinegéticas. Dirección General de Producciones y Mercados Agrarios Caracterización Del Sector Ovino y Caprino de Carne En España; MAGRAMA: Madrid, Spain, 2021.
- MAGRAMA. Caracterización Del Sector Ovino y Caprino En España; MAGRAMA: Madrid, Spain, 2021; pp. 1–25.
- Domke, A.V.M.; Chartier, C.; Gjerde, B.; Leine, N.; Vatn, S.; Stuen, S. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Helminths, Lungworms and Liver Fluke in Sheep and Goats in Norway. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 194, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Bistgani, Z.; Siadat, S.A.; Bakhshandeh, A.; Ghasemi Pirbalouti, A.; Hashemi, M. Interactive Effects of Drought Stress and Chitosan Application on Physiological Characteristics and Essential Oil Yield of Thymus Daenensis Celak. Crop. J. 2017, 5, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hernández, T.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Hernández, J.N.; Machín, C.; Paz-Sánchez, Y.; Hayward, A.D.; Wright, H.W.; Price, D.R.G.; Matthews, J.B.; McNeilly, T.N.; et al. Differences in the Protection Elicited by a Recombinant Teladorsagia circumcincta Vaccine in Weaned Lambs of Two Canarian Sheep Breeds. Vet. Parasitol. 2022, 306, 109722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.C.S.; Oliveira, L.M.; Santos, Y.L.D.C.O.; Dantas, M.C.S.; Walker, C.I.B.; Faria, A.M.C.; Bueno, L.L.; Dolabella, S.S.; Fujiwara, R.T. The Role of IgA in Gastrointestinal Helminthiasis: A Systematic Review. Immunol. Lett. 2022, 249, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husband, A. Perpectives in immunity: A ruminant model. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1987, 17, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Induction of Secretory Immunity and Memory at Mucosal Surfaces. Vaccine 2007, 25, 5467–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolaston, R.R.; Baker, R. Prospects of Breeding Small Ruminants for Resistance to Internal Parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 1996, 26, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante, A.F.T.; Bricarello, P.A.; Rocha, R.A.; Gennari, S.M. Resistance of Santa Ines, Suffolk and Ile de France Sheep to Naturally Acquired Gastrointestinal Nematode Infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 120, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanimisetti, H.B.; Greiner, S.P.; Zajac, A.M.; Notter, D.R. Performance of Hair Sheep Composite Breeds: Resistance of Lambs to Haemonchus contortus. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 82, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.F.; Hernández, A.; Molina, J.M.; Fernández, A.; Raadsma, H.W.; Meeusen, E.N.T.; Piedrafita, D. Comparative Experimental Haemonchus contortus Infection of Two Sheep Breeds Native to the Canary Islands. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 153, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, K.P.; Miller, J.E.; Lomax, L.G.; Burnett, D.D. Evaluation of Immune Response to Artificial Infections of Haemonchus contortus in Gulf Coast Native Compared with Suffolk Lambs. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 181, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.N.; Hernández, A.; Stear, M.J.; Conde-Felipe, M.; Rodríguez, E.; Piedrafita, D.; González, J.F. Potential Role for Mucosal IgA in Modulating Haemonchus contortus Adult Worm Infection in Sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 223, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Robertos, N.F.; Torres-Acosta, J.F.J.; González-Garduño, R.; Notter, D.R. Phenotypic Expression of Parasite Susceptibility to Haemonchus contortus in Pelibuey Sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 239, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.; Jackson, F.; Jackson, E.; Williams, J. Age Immunity to Ostertagia circumcincta: Comparison of the Local Immune Response of L4 and 10 Months Old Lambs. J. Comp. Pathol. 1985, 9, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcrae, K.M.; Stear, M.J.; Good, B.; Keane, O.M. The Host Immune Response to Gastrointestinal Nematode Infection in Sheep. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beraldi, D.; Craig, B.H.; Bishop, S.C.; Hopkins, J.; Pemberton, J.M. Phenotypic Analysis of Host-Parasite Interactions in Lambs Infected with Teladorsagiacircumcincta. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, C.; Paim, T.D.P.; De Melo, C.B.; Brasil, B.S.A.F.; Paiva, S.R. Selection Methods for Resistance to and Tolerance of Helminths in Livestock. Parasite 2014, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, K.A.; Nussey, D.H.; Maclellan, R.; Pilkington, J.G.; McNeilly, T.N. Fecal Antibody Levels as a Noninvasive Method for Measuring Immunity to Gastrointestinal Nematodes in Ecological Studies. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castilla-Gómez de Agüero, V.; González, J.F.; Hernández, J.N.; Valderas-García, E.; Rojo Vázquez, F.A.; Arranz, J.J.; Gutiérrez-Gil, B.; Martínez-Valladares, M. Differences within Churra Breed Sheep in the Early Immune Response to the Infection by Teladorsagiacircumcincta. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.J.; Morris, C.A.; Wheeler, M. Genetic and Phenotypic Relationships between Carbohydrate Larval Antigen (CarLA) IgA, Parasite Resistance and Productivity in Serial Samples Taken from Lambs after Weaning. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Chevrotère, C.; Bambou, J.C.; Arquet, R.; Jacquiet, P. Genetic Analysis of the Potential Role of IgA and IgE Responses against Haemonchus contortus in Parasite Resistance of Creole Goats Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 186, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Moors, E.; Sohnrey, B.; Gauly, M. Gastrointestinal Nematode Infections in German Sheep. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, J.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Bartley, D.J.; Skuce, P.J.; Kenyon, F.; Geurden, T.; Hoste, H.; Williams, A.R.; Sotiraki, S.; Höglund, J.; et al. Mind the Gaps in Research on the Control of Gastrointestinal Nematodes of Farmed Ruminants and Pigs. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafuna, T.; Soma, P.; Tsotetsi-Khambule, A.M.; Hefer, C.A.; Muchadeyi, F.C.; Thekisoe, O.M.M.; Pierneef, R.E. Bacterial Profiling of Haemonchus contortus Gut Microbiome Infecting Dohne Merino Sheep in South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schallig, H.D.F.H.; Hornok, S.; Cornelissen, J.B.W.J. Comparison of Two Enzyme Immunoassays for the Detection of Haemonchus contortus Infections in Sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 57, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, J.; Rakhshandehroo, E.; Yektaseresht, A. Development and Evaluation of an Indirect ELISA for Detection of Teladorsagia circumcincta Infection in Sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuquerella, M.; Gómez-Muñoz, M.T.; Carrera, L.; de la Fuente, C.; Alunda, J.M. Cross Antigenicity among Ovine Trichostrongyloidea. Preliminary Report. Vet. Parasitol. 1994, 53, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.D.; Pettit, D.; Smith, S.K. Cross-Protection Studies with Gut Membrane Glycoprotein Antigens from Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta. Parasite Immunol. 2001, 23, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, G.B.L.; Pulford, H.D.; Hein, W.R.; Severn, W.B.; Shoemaker, C.B. Characterization of a 35-KDA Carbohydrate Larval Antigen (CarLA) from Trichostrongylus colubriformis; a Potential Target for Host Immunity. Parasite Immunol. 2003, 25, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Flock | Breed | N | Type of Pasture |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Churra | 42 | CL |
| 2 | Churra | 40 | CL |
| 3 | Assaf | 13 | OL |
| 4 | Assaf | 40 | CL |
| 5 | Assaf | 24 | OL |
| 6 | Assaf | 46 | CL |
| 7 | Churra | 48 | CL |
| 8 | Castellana | 40 | CL |
| 9 | Castellana | 40 | CL |
| 10 | Assaf | 40 | CL |
| 11 | Castellana | 53 | CL |
| 12 | Assaf | 36 | OL |
| 13 | Castellana | 40 | CL |
| 14 | Castellana | 41 | CL |
| 15 | Castellana | 43 | OL |
| Total | 589 |
| L3SE-Tc | PDI-Tc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Antibody | Sample | Antibody | |
| ELISA-Saliva | 1/3 | 1/500 | 1/2 | 1/500 |
| ELISA-Nasal secretions | 1/4 | 1/500 | 1/2 | 1/500 |
| ELISA-Serum | 1/1 | 1/500 | 1/2 | 1/250 |
| FEC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breed | Total Ewes | Young Ewes | Adult Ewes | |
| Assaf | Mean ± SD Range | 132 ± 180 (0–975) | 122 ± 159 0–825 | 128 ± 181 0–975 |
| % positive FEC | 64.97% | 62.22% | 65.79% | |
| N | 197 | 45 | 152 | |
| Castellana | Mean ± SD Range | 108 ± 162 0–915 | 99 ± 140 0–735 | 113 ± 164 0–915 |
| % positive FEC | 67.06% | 58.76% | 75.19% | |
| N | 255 | 126 | 129 | |
| Churra | Mean ± SD Range | 151 ± 181 0–945 | 155 ± 157 0–735 | 151 ± 181 0–945 |
| % positive FEC | 59.68% | 81.81% | 54.63% | |
| N | 129 | 22 | 108 | |
| Total ewes | Mean ± SD | 113 ± 173 | 108 ± 164 | 113 ± 173 |
| Range | 0–975 | 0–825 | 0–975 | |
| % positive FEC | 64.43% | 85.50% | 54.24% | |
| N | 582 | 193 | 389 | |
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Estimated Prevalence 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breed | |||
| Assaf | Reference | 0.5976 | |
| Castellana | 0.76 (0.46–1.24) | 0.2684 | 0.5285 |
| Churra | 0.69 (0.33–1.44) | 0.3221 | 0.5053 |
| Castellana | 1.10 (0.56–2.13) 2 | 0.7835 | |
| Age | |||
| Adult ewes | Reference | 0.4354 | |
| Young ewes | 2.39 (1.37–4.19) | 0.0022 * | 0.6488 |
| Breed × Age | |||
| AdultAssaf | Reference | 0.4550 | |
| Young Assaf | 3.16 (1.35–7.43) | 0.0083 * | 0.7255 |
| Adult Castellana | Reference | 0.5391 | |
| Young Castellana | 0.92 (0.51–1.67) | 0.7806 | 0.5180 |
| Adult Churra | Reference | 0.3197 | |
| Young Churra | 4.72 (1.42–15.7) | 0.0115 * | 0.6895 |
| Pasture type | |||
| Farm pastures | Reference | 0.3113 | |
| Communal pastures | 6.97 (3.84–12.6) | 0.0001 ** | 0.7592 |
| Young Ewes (N = 193) | Adult Ewes (N = 389) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L3SE-Tc | PDI-Tc | L3SE-Tc | PDI-Tc | |
| Serum | Rho = 0.306 ** p = 0.000 | Rho = 0.107 p = 0.159 | Rho = 0.123 ** p = 0.000 | Rho = 0.091 p = 0.077 |
| Nasal | Rho = 0.504 ** p = 0.000 | Rho = 0.498 ** p = 0.000 | Rho = 0.031 p = 0.554 | Rho = 0.179 ** p = 0.000 |
| Saliva | Rho = 0.058 p = 0.137 | Rho = 0.295 ** p = 0.000 | Rho = 0.059 p = 0.246 | Rho = 0.001 p = 0.989 |
| (A) | L3SE-Tc | |||
| Serum | Nasal secretions | Saliva | ||
| L3SE-Tc | Serum | 1 | ||
| Nasal secretions | Rho = 0.05 p = 0.205 | 1 | ||
| Saliva | Rho = 0.183 ** p = 0.000 | Rho = 0.178 ** p = 0.000 | 1 | |
| (B) | PDI-Tc | |||
| Serum | Nasal secretions | Saliva | ||
| PDI-Tc | Serum | 1 | ||
| Nasal secretions | Rho = 0.110 ** p = 0.000 | 1 | ||
| Saliva | Rho = 0.146 ** p = 0.000 | Rho = 0.255 ** p = 0.000 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castilla Gómez de Agüero, V.; Valderas-García, E.; González del Palacio, L.; Giráldez, F.J.; Balaña-Fouce, R.; Martínez-Valladares, M. Secretory IgA as Biomarker for Gastrointestinal Nematodes Natural Infection in Different Breed Sheep. Animals 2023, 13, 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132189
Castilla Gómez de Agüero V, Valderas-García E, González del Palacio L, Giráldez FJ, Balaña-Fouce R, Martínez-Valladares M. Secretory IgA as Biomarker for Gastrointestinal Nematodes Natural Infection in Different Breed Sheep. Animals. 2023; 13(13):2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132189
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastilla Gómez de Agüero, Verónica, Elora Valderas-García, Laura González del Palacio, F. Javier Giráldez, Rafael Balaña-Fouce, and María Martínez-Valladares. 2023. "Secretory IgA as Biomarker for Gastrointestinal Nematodes Natural Infection in Different Breed Sheep" Animals 13, no. 13: 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132189
APA StyleCastilla Gómez de Agüero, V., Valderas-García, E., González del Palacio, L., Giráldez, F. J., Balaña-Fouce, R., & Martínez-Valladares, M. (2023). Secretory IgA as Biomarker for Gastrointestinal Nematodes Natural Infection in Different Breed Sheep. Animals, 13(13), 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132189








