To Be, or Not to Be: That Is the Hamletic Question of Cryptic Evolution in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Raja miraletus Species Complex
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Genetic Data Analysis
2.2.1. Genetic Diversity
2.2.2. Population Connectivity and Phylogenetic Signals
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity
3.2. Population Connectivity and Phylogenetic Signals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, R.G. Linking evolutionary pattern and process. In Endless Forms; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, J. Hybridization, ecological races and the nature of species: Empirical evidence for the ease of speciation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 2971–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, R.G.; Larson, E.L. Hybridization, introgression, and the nature of species boundaries. J. Hered. 2014, 105, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norris, R.D. Pelagic species diversity, biogeography, and evolution. Paleobiology 2000, 26, 236–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, H.T.; Bernardi, G.; Simon, T.; Joyeux, J.-C.; Macieira, R.M.; Gasparini, J.L.; Rocha, C.; Rocha, L.A. Island biogeography of marine organisms. Nature 2017, 549, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbi, S.R.; Lessios, H.A. Evolutionary animation: How do molecular phylogenies compare to Mayr’s reconstruction of speciation patterns in the sea? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6566–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynghammar, A.; Christiansen, J.S.; Griffiths, A.M.; Fevolden, S.-E.; Hop, H.; Bakken, T. DNA barcoding of the Northern Northeast Atlantic skates (Chondrichthyes, Rajiformes), with remarks on the widely distributed starry ray. Zool. Scr. 2014, 43, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palumbi, S.R. Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, and marine speciation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1994, 25, 547–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C.; Neigel, J.E.; Arnold, J. Demographic influences on mitochondrial DNA lineage survivorship in animal populations. J. Mol. Evol. 1984, 20, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasolini, P.; Ragazzini, C.; Zaccaro, Z.; Cariani, A.; Ferrara, G.; Gonzalez, E.G.; Landi, M.; Milano, I.; Stagioni, M.; Guarniero, I.; et al. Quaternary geographical sibling speciation and population structuring in the eastern Atlantic skates (Suborder Rajoidea) Raja clavata and R. straeleni. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 2173–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milá, B.; Van Tassell, J.L.; Calderón, J.A.; Rüber, L.; Zardoya, R. Cryptic lineage divergence in marine environments: Genetic differentiation at multiple spatial and temporal scales in the widespread intertidal goby Gobiosoma bosc. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 5514–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Ingram, K.K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, E. Systematics and the Origin of Species from the Viewpoint of a Zoologist; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1942; p. 372. ISBN 9780674862500. [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton, N. Sibling species in the sea. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1993, 24, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, A. Cryptic polychaete diversity: A Review. Zool. Scr. 2014, 43, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellono, N.W.; Leitch, D.B.; Julius, D. Molecular tuning of electroreception in sharks and skates. Nature 2018, 558, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEachran, J.D.; Dunn, K.A. Phylogenetic analysis of skates, a morphologically conservative clade of Elasmobranchs (Chondrichthyes: Rajidae). Copeia 1998, 1998, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinti, F.; Ungaro, N.; Pasolini, P.; De Panfilis, M.; Garoia, F.; Guarniero, I.; Sabelli, B.; Marano, G.; Piccinetti, C. Development of molecular and morphological markers to improve species-specific monitoring and systematics of Northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean skates (Rajiformes). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 288, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglésias, S.P.; Toulhoat, L.; Sellos, D.Y. Taxonomic confusion and market mislabelling of threatened skates: Important consequences for their conservation status. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carugati, L.; Melis, R.; Cariani, A.; Cau, A.; Crobe, V.; Ferrari, A.; Follesa, M.C.; Geraci, M.L.; Iglésias, S.P.; Pesci, P.; et al. Combined COI barcode-based methods to avoid mislabelling of threatened species of deep-sea skates. Anim. Conserv. 2022, 25, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, A.M.; Sims, D.W.; Cotterell, S.P.; El Nagar, A.; Ellis, J.R.; Lynghammar, A.; McHugh, M.; Neat, F.C.; Pade, N.G.; Queiroz, N.; et al. Molecular markers reveal spatially segregated cryptic species in a critically endangered fish, the common skate (Dipturus batis). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannas, R.; Follesa, M.C.; Cabiddu, S.; Porcu, C.; Salvadori, S.; Iglésias, S.P.; Deiana, A.M.; Cau, A. Molecular and morphological evidence of the occurrence of the norwegian skate Dipturus nidarosiensis (Storm, 1881) in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2010, 6, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonara, P.; Bellodi, A.; Zupa, W.; Donnaloia, M.; Gaudio, P.; Neglia, C.; Follesa, M.C. Morphological traits and capture depth of the Norwegian skate (Dipturus nidarosiensis (Storm, 1881)) from two Mediterranean populations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.R.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; Gadig, O.B.F. The importance of considering genetic diversity in shark and ray conservation policies. Conserv. Genet. 2018, 19, 501–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serena, F.; Mancusi, C.; Barone, M. Field identification guide to the skates (Rajidae) of the Mediterranean Sea. Guidelines for data collection and analysis. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2010, 17, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Cariani, A.; Messinetti, S.; Ferrari, A.; Arculeo, M.; Bonello, J.J.; Bonnici, L.; Cannas, R.; Carbonara, P.; Cau, A.; Charilaou, C.; et al. Improving the conservation of Mediterranean Chondrichthyans: The ELASMOMED DNA barcode reference library. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebert, D.A.; Compagno, L.J. Biodiversity and systematics of skates (Chondrichthyes: Rajiformes: Rajoidei). Biol. Skates 2007, 27, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Last, P.R.; White, W.T.; de Carvalho, M.R.; Séret, B.; Stehmann, M.F.W.; Naylor, G.J.P. (Eds.) Rays of the World; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia; Comstock Publishing Associates: Sacramento, CA, USA; pp. i–ix + 1–790. ISBN 978-0-643-10914-8.
- Serena, F.; Abella, A.J.; Bargnesi, F.; Barone, M.; Colloca, F.; Ferretti, F.; Fiorentino, F.; Jenrette, J.; Moro, S. Species diversity, taxonomy and distribution of Chondrichthyes in the Mediterranean and Black Sea. Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 497–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, V. The systematic and geographical distribution of hawkmoth flowers in the temperate North American flora. Bot. Gaz. 1983, 144, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, I.; Keil, P.; Jetz, W.; Crawford, F.W. Historical biogeography using species geographical ranges. Syst. Biol. 2015, 64, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriques, S.; Guilhaumon, F.; Villéger, S.; Amoroso, S.; França, S.; Pasquaud, S.; Cabral, H.N.; Vasconcelos, R.P. Biogeographical region and environmental conditions drive functional traits of estuarine fish assemblages worldwide. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 752–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neat, F.; Pinto, C.; Burrett, I.; Cowie, L.; Travis, J.; Thorburn, J.; Gibb, F.; Wright, P.J. Site fidelity, survival and conservation options for the threatened flapper skate (Dipturus cf. intermedia). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2015, 25, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisk, M.G.; Jordaan, A.; Miller, T.J. Moving beyond the current paradigm in marine population connectivity: Are adults the missing link? Fish Fish. 2014, 15, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearmouth, V.J.; Sims, D.W. Movement and behaviour patterns of the critically endangered common skate Dipturus batis revealed by electronic tagging. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 380, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, E.; Buckley, A.A.; Stewart, C.; Metcalfe, J.D. Repeated seasonal migration by a thornback ray in the southern North Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, E.; Buckley, A.A.; Stewart, C.; Metcalfe, J.D. Migratory behaviour of the thornback ray, Raja clavata, in the southern North Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musick, J.A.; Ellis, J.K.; Hamlett, W. Reproductive evolution of chondrichthyans. In HAMLETT, WC, Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes, Sharks, Batoids and Chimaeras; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 45–71. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, L.J.V.; Ebert, D.A. Southern African Skate Biodiversity and Distribution. In Biology of Skates; Ebert, D.A., Sulikowski, J.A., Eds.; Developments in Environmental Biology of Fishes 27; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 19–39. ISBN 978-1-4020-9703-4. [Google Scholar]
- Stehmann, M.F.W.; Bürkel, D.L. Rajidae. In Fishes of the North-Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean; Whitehead, P.J.P., Bauchot, M., Hureau, J., Nielsen, J., Eds.; Unesco: Paris, France, 1984; Volume 1, ISBN 9789230022150. [Google Scholar]
- Kadri, H.; Marouani, S.; Bradai, M.N.; Bouaïn, A. Food habits of the brown ray Raja miraletus (Chondrichthyes: Rajidae) from the Gulf of Gabès (Tunisia). Mar. Biol. Res. 2014, 10, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šantić, M.; Radja, B.; Pallaoro, A. Feeding habits of brown ray (Raja miraletus Linnaeus, 1758) from the eastern central Adriatic Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2013, 9, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikliras, A.C.; Stergiou, K.I. Age at maturity of Mediterranean marine fishes. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulvy, N.K. Raja miraletus. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T124569516A124512700.en (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Dulvy, N.K.; Walls, R.H.L.; Abella, A.; Serena, F.; Bradai, M.N. Raja miraletus (Mediterranean Assessment). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T124569516A176535719.en (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Ebert, D.A.; Wintner, S.P.; Kynes, P.M. An annotated checklist of the chondrichthyans of South Africa. Zootaxa 2021, 4947, 1–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, L.J.V.; Ebert, D.A.; Smale, M.J. Guide to the Sharks and Rays of Southern Africa; Struik: Cape Town, South Africa, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- McEachran, J.D.; Séret, B.; Miyake, T. Morphological variation within Raja miraletus and status of R. ocellifera (Chondrichthyes, Rajoidei). Copeia 1989, 1989, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, G.; Caira, J.; Jensen, K.; Rosana, K.; Straube, N.; Lakner, C. Elasmobranch phylogeny: A mitochondrial estimate based on 595 species. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 31–56. ISBN 978-1-4398-3924-9. [Google Scholar]
- Caira, J.N.; Rodriguez, N.; Pickering, M. New African species of Echinobothrium (Cestoda: Diphyllidea) and implications for the identities of their skate hosts. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Last, P.R.; Séret, B. A New eastern central Atlantic skate Raja parva sp. nov. (Rajoidei: Rajidae) belonging to the Raja miraletus species complex. Zootaxa 2016, 4147, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; de Waard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knowlton, N. Cryptic and sibling species among the decapod Crustacea. J. Crustac. Biol. 1986, 6, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.A.T.; Harry, A.V.; Welch, D.J.; Street, R.; White, J.; Geraghty, P.T.; Macbeth, W.G.; Tobin, A.; Simpfendorfer, C.A.; Ovenden, J.R. Detection of interspecies hybridisation in Chondrichthyes: Hybrids and hybrid offspring between Australian (Carcharhinus tilstoni) and common (C. limbatus) blacktip shark found in an Australian fishery. Conserv. Genet. 2012, 13, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlyza, I.S.; Shen, K.-N.; Solihin, D.D.; Soedharma, D.; Berrebi, P.; Borsa, P. Species boundaries in the Himantura uarnak species complex (Myliobatiformes: Dasyatidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frodella, N.; Cannas, R.; Velonà, A.; Carbonara, P.; Farrell, E.; Fiorentino, F.; Follesa, M.; Garofalo, G.; Hemida, F.; Mancusi, C.; et al. Population connectivity and phylogeography of the mediterranean endemic skate Raja polystigma and evidence of its hybridization with the parapatric sibling R. montagui. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 554, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siskey, M.R.; Shipley, O.N.; Frisk, M.G. Skating on thin ice: Identifying the need for species-specific data and defined migration ecology of Rajidae Spp. Fish Fish. 2019, 20, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nagar, A.; McHugh, M.; Rapp, T.; Sims, D.W.; Genner, M.J. Characterisation of polymorphic microsatellite markers for skates (Elasmobranchii: Rajidae) from expressed sequence tags. Conserv. Genet. 2010, 11, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spedicato, M.T.; Massutí, E.; Mérigot, B.; Tserpes, G.; Jadaud, A.; Relini, G. The MEDITS trawl survey specifications in an ecosystem approach to fishery management. Sci. Mar. 2019, 83, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Relini, G. Demersal trawl surveys in Italian Seas: A short review. Actes Colloq. IFREMER 2000, 26, 76–93. Available online: https://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00716/82814/87636.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Ivanova, N.V.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Hebert, P.D.N. Universal primer cocktails for fish DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, G.; Crobe, V.; Ferrari, A.; Baino, R.; Massi, D.; Titone, A.; Mancusi, C.; Serena, F.; Cannas, R.; Carugati, L.; et al. Strongly structured populations and reproductive habitat fragmentation increase the vulnerability of the Mediterranean starry ray Raja asterias (Elasmobranchii, Rajidae). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2022, 32, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, M.J.; Song, H.; Whiting, M.F. Assessing the effects of primer specificity on eliminating numt coamplification in DNA barcoding: A case study from Orthoptera (Arthropoda: Insecta). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. Bold: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crobe, V.; Ferrari, A.; Hanner, R.; Leslie, R.W.; Steinke, D.; Tinti, F.; Cariani, A. Molecular taxonomy and diversification of Atlantic skates (Chondrichthyes, Rajiformes): Adding more pieces to the puzzle of their evolutionary history. Life 2021, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, D.; Connell, A.D.; Hebert, P.D.N. Linking adults and immatures of South African marine fishes. Genome 2016, 59, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Bank, H. DNA barcoding results for some Southern African elephantfish, guitarfish, rattails, rays, sharks and skates. Int. J. Oceanogr. Aquac. 2019, 3, 000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Pereira, B.; Moura, T.; Griffiths, A.M.; Serrano Gordo, L.; Figueiredo, I. Molecular barcoding of skates (Chondrichthyes: Rajidae) from the Southern Northeast Atlantic. Zool. Scr. 2011, 40, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.O.; Landi, M.; Martins, R.; Costa, M.H.; Costa, M.E.; Carneiro, M.; Alves, M.J.; Steinke, D.; Carvalho, G.R. A ranking system for reference libraries of DNA barcodes: Application to marine fish species from Portugal. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Amaro, S.; Ordines, F.; Picornell, A.; Castro, J.A.; Ramon, C.; Massutí, E.; Terrasa, B. The evolutionary history of mediterranean batoidea (Chondrichthyes: Neoselachii). Zool. Scr. 2018, 47, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Tinti, F.; Maresca, V.B.; Velonà, A.; Cannas, R.; Thasitis, I.; Costa, F.O.; Follesa, M.C.; Golani, D.; Hemida, F.; et al. Natural history and molecular evolution of demersal Mediterranean sharks and skates inferred by comparative phylogeographic and demographic analyses. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landi, M.; Dimech, M.; Arculeo, M.; Biondo, G.; Martins, R.; Carneiro, M.; Carvalho, G.R.; Brutto, S.L.; Costa, F.O. DNA barcoding for species assignment: The case of Mediterranean marine fishes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, A.; Vella, N.; Schembri, S. A molecular approach towards taxonomic identification of elasmobranch species from Maltese fisheries landings. Mar. Genomics 2017, 36, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkafas, G.A.; Megalofonou, P.; Batzakas, G.; Apostolidis, A.P.; Exadactylos, A. Molecular phylogenetic convergence within Elasmobranchii revealed by Cytochrome Oxidase Subunits. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 61, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambounis, A.G.; Ekonomou, G.; Megalofonou, P.; Batzakas, G.; Malandrakis, E.; Martsicalis, P.; Panagiotaki, P.; Neofitou, C.; Exadactylos, A. Molecular Phylogenetic Interrelations between Species of the Elasmobranchii subclass. 2010; unpublished; submitted to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases. [Google Scholar]
- Shirak, A.; Dor, L.; Seroussi, E.; Ron, M.; Hulata, G.; Golani, D. DNA barcoding of fish species from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokes, M.B. DNA Barcoding of Marine Fish Species from Turkish Coastline. 2016; unpublished; submitted to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin Suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. Curr. Contents Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. 1981, 12, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Knebelsberger, T.; Landi, M.; Neumann, H.; Kloppmann, M.; Sell, A.F.; Campbell, P.D.; Laakmann, S.; Raupach, M.J.; Carvalho, G.R.; Costa, F.O. A reliable DNA barcode reference library for the identification of the North European shelf fish fauna. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Wills, D.P.M.; Shipley, P. MICRO-CHECKER: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhir, K.; Borsa, P.; Chikhi, L.; Raufaste, N.; Bonhomme, F. GENETIX 4.05, Logiciel Sous Windows TM Pour la Génétique des Populations. 1996. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/document?_vid=7cfcd230-1958-4cfc-a571-ce0ba003e63f (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Rousset, F. GENEPOP’007: A complete re-implementation of the GENEPOP software for Windows and Linux. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT 2.9.3, a Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices. 2001. Available online: http://www2.unil.ch/popgen/softwares/fstat.htm (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-Feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction Data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Conde, I.; de Uña-Álvarez, J. Sgof: An R package for multiple testing problems. R J. 2014, 6, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.; Connor, T.R.; Sirén, J.; Aanensen, D.M.; Corander, J. Hierarchical and spatially explicit clustering of DNA sequences with BAPS software. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubisz, M.J.; Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopelman, N.M.; Mayzel, J.; Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Mayrose, I. Clumpak: A program for identifying clustering modes and packaging population structure inferences across K. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-L.; Liu, J.-X. StructureSelector: A web-based software to select and visualize the optimal number of clusters using multiple methods. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T.; Devillard, S.; Balloux, F. Discriminant analysis of principal components: A new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team R: A language and environment for statistical computing 2021.
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; aki Yano, T. Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, J.H. The batoid fishes of the east coast of southern Africa. Part III: Skates and electric rays. S. Afr. Assoc. Mar. Biol. Res. Investig. Rep. 1967, 17, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschfeld, M.; Dudgeon, C.; Sheaves, M.; Barnett, A. Barriers in a sea of elasmobranchs: From fishing for populations to testing hypotheses in population genetics. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Castillo, J.; Beheregaray, L.B. Oceanographic heterogeneity influences an ecological radiation in elasmobranchs. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, R.; Potts, W.M.; Sauer, W.H.; Santos, C.V.; Kruger, J.; Thomas, J.A.; Shaw, P.W. Molecular genetic, life-history and morphological variation in a coastal warm-temperate sciaenid fish: Evidence for an upwelling-driven speciation event. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriques, R.; Potts, W.M.; Santos, C.V.; Sauer, W.H.; Shaw, P.W. Population connectivity and phylogeography of a coastal fish, Atractoscion aequidens (Sciaenidae), across the Benguela current region: Evidence of an ancient vicariant event. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chevolot, M.; Hoarau, G.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Stam, W.T.; Olsen, J.L. Phylogeography and population structure of thornback ray (Raja clavata L., Rajidae). Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 3693–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, E.; Pasolini, P.; Bertozzi, M.; Garoia, F.; Ungaro, N.; Vacchi, M.; Sabelli, B.; Tinti, F. Rapid Miocene-Pliocene dispersal and evolution of mediterranean rajid fauna as inferred by mitochondrial gene variation. J. Evol. Biol. 2005, 18, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patarnello, T.; Volckaert, F.A.M.J.; Castilho, R. Pillars of Hercules: Is the Atlantic–Mediterranean transition a phylogeographical break? Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 4426–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, R.; Vacca, L.; Cariani, A.; Carugati, L.; Charilaou, C.; Di Crescenzo, S.; Ferrari, A.; Follesa, M.C.; Mancusi, C.; Pinna, V.; et al. Baseline genetic distinctiveness supports structured populations of thornback ray in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2023, 33, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serena, F. Field Identification Guide to the Sharks and Rays of the Mediterranean and Black Sea; Food & Agriculture Organisation of The United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2005; 97 pp. + 11 colour plates + egg cases. [Google Scholar]

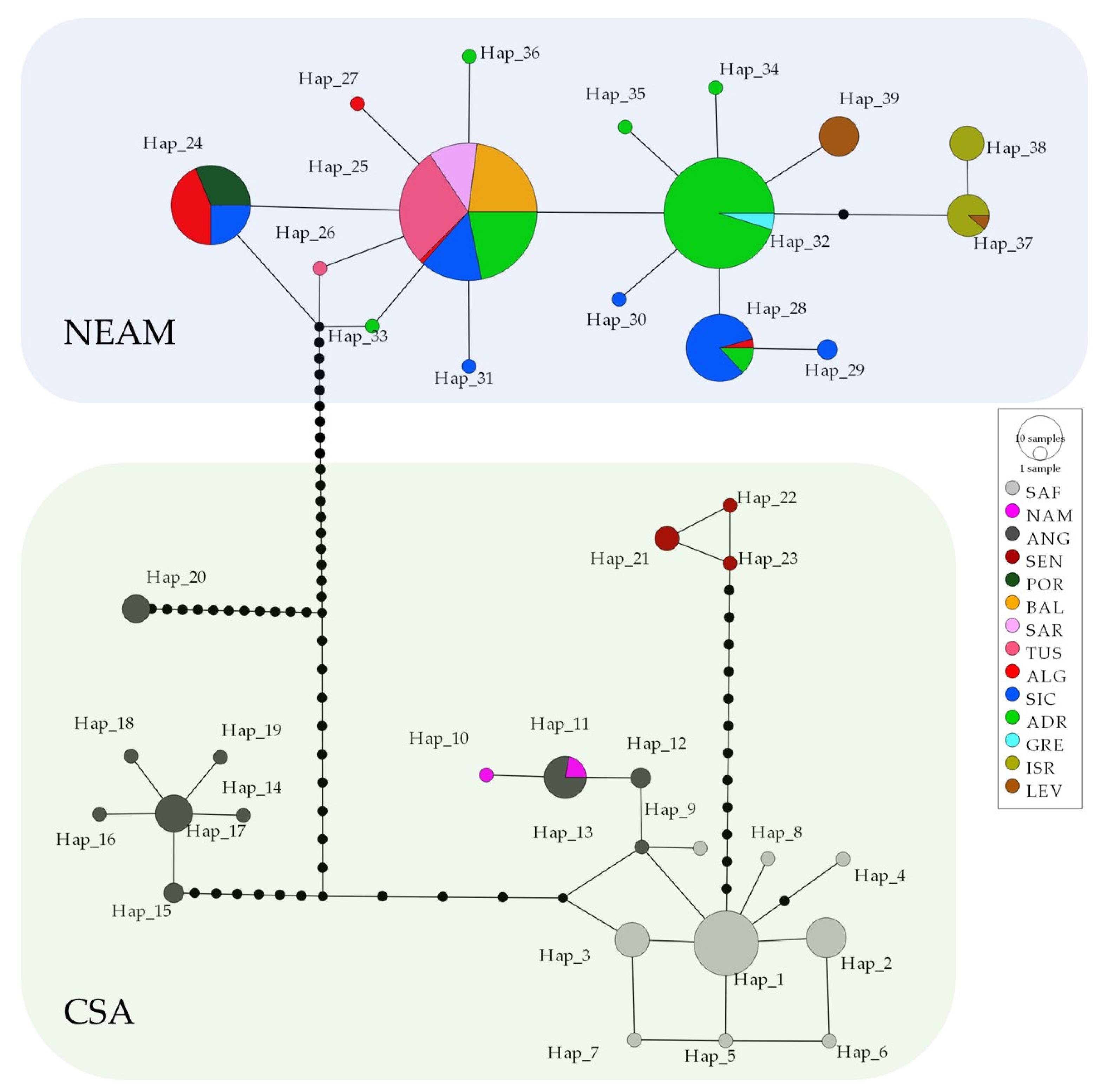

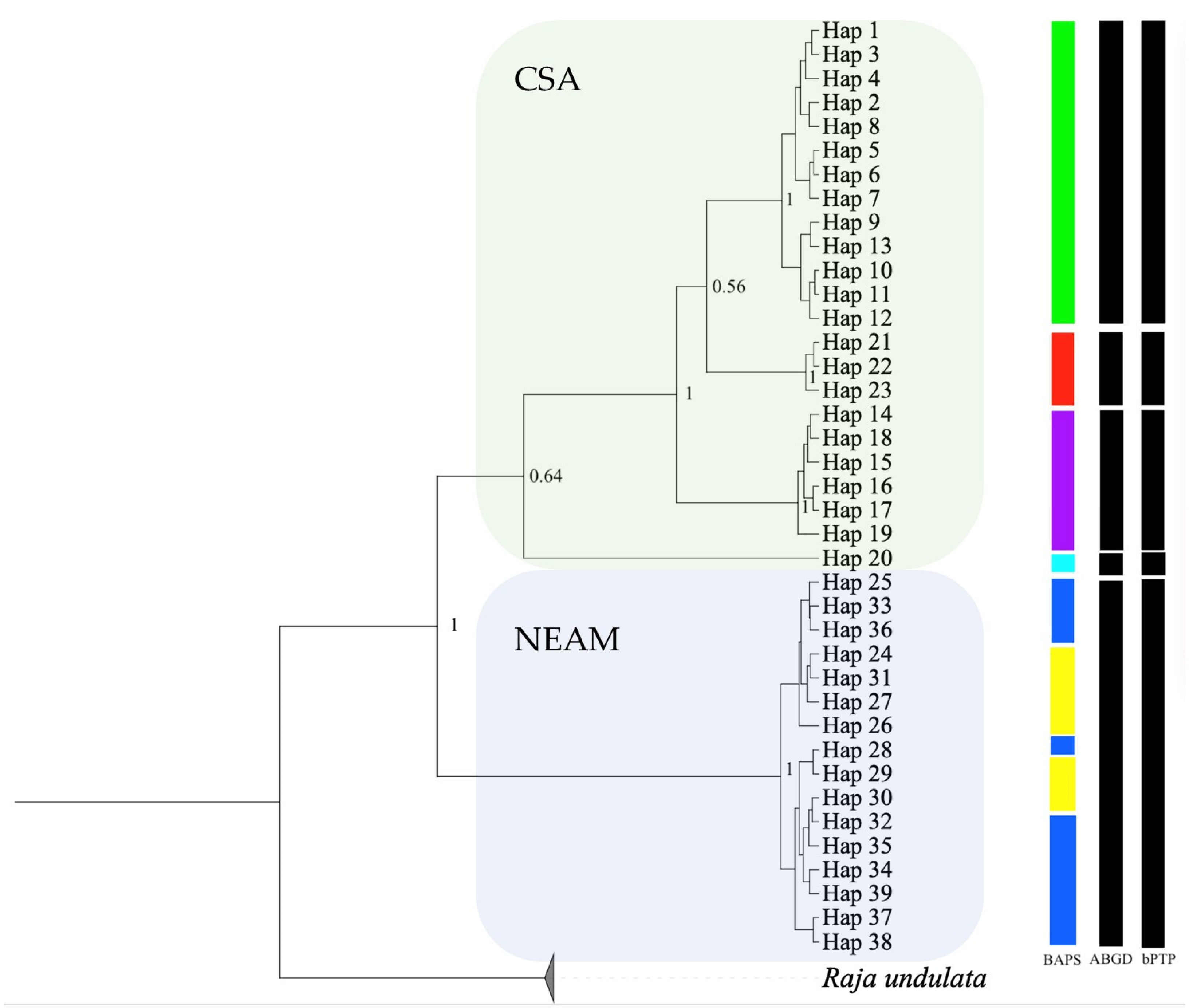
| Sampling Area | Macro Area Code | N (tot) | N (COI) | N (EST-SSRs) | Years | Source (Trawl Survey Program) | McEachran et al., 1989 [48] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central-Southern Africa (CSA) | |||||||
| South Africa—South Coast | SAF | 8 | 6 | 8 | 2006 | ST (Africana) | 5 |
| South Africa—South Coast | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2007, 2012 | GB/BOLD | 5 | |
| South Africa—South Coast | 32 | 30 | 31 | 2011 | ST (Africana) | 5 | |
| Namibia | NAM | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2009, 2010 | GB/BOLD | 5 |
| Angola | ANG | 27 | 27 | 26 | 2006 | ST (Nansen) | 4 |
| Senegal | SEN | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2007 | CF | 2 |
| Northeastern Atlantic–Mediterranean Sea (NEAM) | |||||||
| Portugal | POR | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2007 | ST (IPIMAR) | n.a. |
| Portugal | 0 | 7 | 0 | 2005, 2007 | GB/BOLD | n.a. | |
| Balearic Islands | BAL | 19 | 19 | 16 | 2006 | ST (MedITS) | 1 |
| Balearic Islands | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2013 | ST (MedITS) | 1 | |
| Sardinia | SAR | 11 | 11 | 8 | 2002, 2005 | ST (MedITS) | 1 |
| Tuscany | TUS | 26 | 22 | 21 | 2005, 2006 | ST (MedITS) | 1 |
| Tuscany | 16 | 6 | 13 | 2008, 2010 | ST (MedITS) | 1 | |
| Algeria | ALG | 8 | 8 | 5 | 2002, 2003 | FM (Algiers) | 1 |
| Algeria | 10 | 9 | 8 | 2009, 2010 | FM (Algiers) | 1 | |
| Strait of Sicily—Adventura Bank | SIC | 22 | 22 | 22 | 2014 | ST (MedITS) | 1 |
| Strait of Sicily—Maltese Bank | 16 | 12 | 8 | 2000, 2002 | ST (MedITS) | 1 | |
| Strait of Sicily—Maltese Bank | 0 | 11 | 0 | 2007 | GB/BOLD | 1 | |
| Adriatic Sea—Northern Italian coast | ADR | 39 | 31 | 20 | 2006, 2007 | ST (MedITS; GruND) | 1 |
| Adriatic Sea—Croatian coast | 24 | 24 | 8 | 2002, 2004 | ST (MedITS; GruND) | 1 | |
| Adriatic Sea—Southern Italian coast | 19 | 16 | 19 | 2004 | ST (MedITS; GruND) | 1 | |
| Adriatic Sea—Albanian coast | 19 | 13 | 17 | 2004 | ST (MedITS; GruND) | 1 | |
| Ionian Sea | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2004 | ST (MedITS; GruND) | 1 | |
| Greece—Aegean coast | GRE | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2014 | GB/BOLD | 1 |
| Israel | ISR | 8 | 7 | 7 | 2009 | CF | 1 |
| Israel | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2012 | BOLD | 1 | |
| Israel | 0 | 4 | 0 | 2014 | GB/BOLD | 1 | |
| Levantine Sea | LEV | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2016 | GB/BOLD | 1 |
| Levantine Sea | 7 | 7 | 7 | 2009 | CF | 1 | |
| Raja asterias | Raja brachyura | Raja clavata | Raja microocellata | Raja montagui | Raja polystigma | Raja radula | Raja straeleni | Raja undulata | Raja miraletus (CSA) | Raja miraletus (NEAM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raja asterias | 0.0025 ± 0.0012 | 0.0139 | 0.0106 | 0.0132 | 0.0135 | 0.0121 | 0.0095 | 0.0111 | 0.0121 | 0.0155 | 0.0189 |
| Raja brachyura | 0.0863 | 0.0030 ± 0.0016 | 0.0107 | 0.0094 | 0.0119 | 0.0114 | 0.0121 | 0.0125 | 0.0136 | 0.0141 | 0.0172 |
| Raja clavata | 0.0591 | 0.0514 | 0.0038 ± 0.0000 | 0.0115 | 0.0103 | 0.0113 | 0.0070 | 0.0059 | 0.0141 | 0.0133 | 0.0169 |
| Raja microocellata | 0.0877 | 0.0465 | 0.0598 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0125 | 0.0107 | 0.0114 | 0.0115 | 0.0127 | 0.0140 | 0.0172 |
| Raja montagui | 0.0829 | 0.0606 | 0.0511 | 0.0638 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0066 | 0.0126 | 0.0116 | 0.0128 | 0.0132 | 0.0172 |
| Raja polystigma | 0.0748 | 0.0526 | 0.0514 | 0.0596 | 0.0229 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0108 | 0.0112 | 0.0123 | 0.0119 | 0.0164 |
| Raja radula | 0.0487 | 0.0685 | 0.0280 | 0.0648 | 0.0646 | 0.0564 | 0.0010 ± 0.0012 | 0.0071 | 0.0119 | 0.0137 | 0.0173 |
| Raja straeleni | 0.0593 | 0.0593 | 0.0150 | 0.0601 | 0.0590 | 0.0558 | 0.0282 | 0.0019 ± 0.0010 | 0.0122 | 0.0131 | 0.0174 |
| Raja undulata | 0.0767 | 0.0736 | 0.0733 | 0.0799 | 0.0790 | 0.0711 | 0.0742 | 0.0735 | 0.0009 ± 0.0010 | 0.0122 | 0.0170 |
| Raja miraletus (CSA) | 0.1053 | 0.0857 | 0.0861 | 0.0947 | 0.0830 | 0.0778 | 0.0908 | 0.0907 | 0.0770 | 0.0183 ± 0.0029 | 0.0117 |
| Raja miraletus (NEAM) | 0.1072 | 0.1020 | 0.0989 | 0.1007 | 0.0921 | 0.0897 | 0.0974 | 0.1033 | 0.0959 | 0.0733 | 0.0025 ± 0.0010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrari, A.; Crobe, V.; Cannas, R.; Leslie, R.W.; Serena, F.; Stagioni, M.; Costa, F.O.; Golani, D.; Hemida, F.; Zaera-Perez, D.; et al. To Be, or Not to Be: That Is the Hamletic Question of Cryptic Evolution in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Raja miraletus Species Complex. Animals 2023, 13, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132139
Ferrari A, Crobe V, Cannas R, Leslie RW, Serena F, Stagioni M, Costa FO, Golani D, Hemida F, Zaera-Perez D, et al. To Be, or Not to Be: That Is the Hamletic Question of Cryptic Evolution in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Raja miraletus Species Complex. Animals. 2023; 13(13):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132139
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrari, Alice, Valentina Crobe, Rita Cannas, Rob W. Leslie, Fabrizio Serena, Marco Stagioni, Filipe O. Costa, Daniel Golani, Farid Hemida, Diana Zaera-Perez, and et al. 2023. "To Be, or Not to Be: That Is the Hamletic Question of Cryptic Evolution in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Raja miraletus Species Complex" Animals 13, no. 13: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132139
APA StyleFerrari, A., Crobe, V., Cannas, R., Leslie, R. W., Serena, F., Stagioni, M., Costa, F. O., Golani, D., Hemida, F., Zaera-Perez, D., Sion, L., Carbonara, P., Fiorentino, F., Tinti, F., & Cariani, A. (2023). To Be, or Not to Be: That Is the Hamletic Question of Cryptic Evolution in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Raja miraletus Species Complex. Animals, 13(13), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13132139











