Immune Parameters in Chickens Treated with Antibiotics and Probiotics during Early Life
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chicken Experiment
2.2. Sampling Procedures
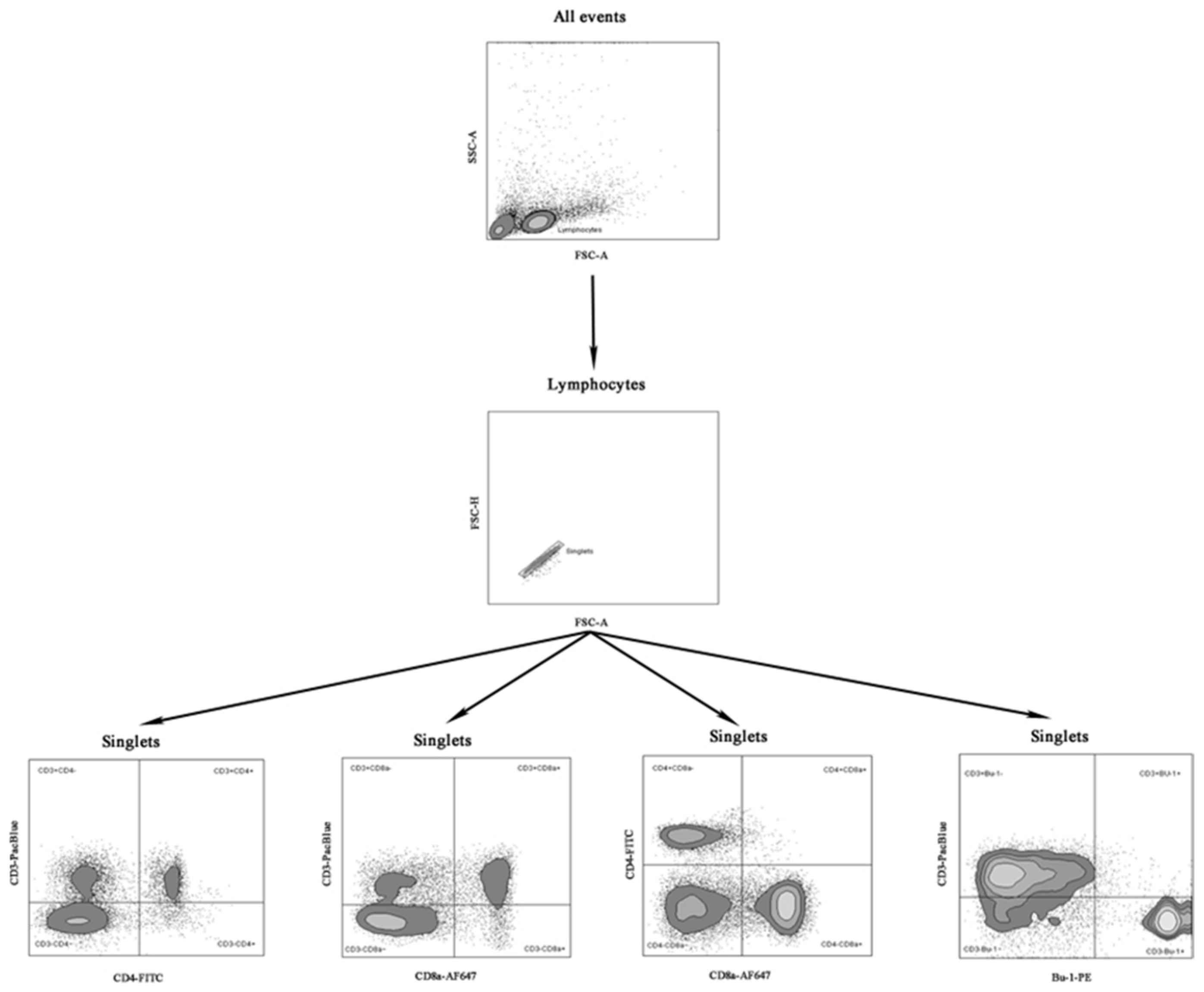
2.3. Isolation of Mononuclear Cells and Flow Cytometry
2.4. Ethical Statement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarradas, J.; Tous, N.; Esteve-Garcia, E.; Brufau, J. The control of intestinal inflammation: A major objective in the research of probiotic strains as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters in poultry. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. In Antimicrobial Resistance; HM Government and Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chrząstek, K.; Wieliczko, A. The influence of enrofloxacin. florfenicol. ceftiofur and E. coli LPS interaction on T and B cells subset in chicks. Vet. Res. Commun. 2015, 39, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chrząstek, K.; Madej, J.P.; Mytnik, E.; Wieliczko, A. The influence of antibiotics on B-cell number, percentage, and distribution in the bursa of Fabricius of newly hatched chicks. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellakany, H.F.; Abu El-Azm, I.M.; Bekhit, A.A.; Shehawy, M.M. Studies on the effects of enrofloxacin overdose on different health parameters in broiler chickens. J. Vet. Med. Res 2008, 18, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, M.S.; Amawi, M.M.; Abu-Basha, E.A.; Yonis, I.B. Assessment of humoral and cellular-mediated immune response in chickens treated with tilmicosin, florfenicol, or enrofloxacin at the time of Newcastle disease vaccination. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarzewski, S. Influence of enrofloxacin and chloramphenicol on the level of IgY in serum and egg yolk after immunostimulation of hens with Salmonella enteritidis antigens. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2002, 5, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Dalhoff, A.; Shalit, I. Immunomodulatory effects of quinolones. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyghebaert, G.; Ducatelle, R.; Van Immerseel, F. An update on alternatives to antimicrobial growth promoters for broilers. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, H.K.; Levine, U.Y.; Looft, T.; Bandrick, M.; Casey, T.A. Treatment, promotion, commotion: Antibiotic alternatives in food-producing animals. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ognik, K.; Cholewińska, E.; Krauze, M.; Abramowicz, K.; Matusevicius, P. The effect of a probiotic preparation containing Enterococcus faecium DSM 7134 for chickens on growth performance, immune status, and the histology and microbiological profile of the jejunum. Anim. Product. Sci. 2017, 59, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognik, K.; Konieczka, P.; Stępniowska, A.; Jankowski, J. Oxidative and epigenetic changes and gut permeability response in early-treated chickens with antibiotic or probiotic. Animals 2020, 10, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze, M.; Abramowicz, K.; Ognik, K. The effect of addition of probiotic bacteria (Bacillus subtilis or Enterococcus faecium) or phytobiotic containing cinnamon oil to drinking water on the health and performance of broiler. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2020, 20, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramowicz, K.; Krauze, M.; Ognik, K. Use of Bacillus subtilis PB6 enriched with choline to improve growth performance, immune status, histological parameters and intestinal microbiota of broiler chickens. Anim. Product. Sci. 2020, 60, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hidayat, M.N.; Malaka, R.; Agustina, L.; Pakiding, W. Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei on hematology and relative weight of lymphoid organs of broiler. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 492, 012127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalaifah, H.S. Benefits of probiotics and/or prebiotics for antibiotic-reduced poultry. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, A.A. Can probiotics improve the environmental microbiome and resistome of commercial poultry production? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4534–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Hao, H.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Dai, M.; Huang, L.; Yuan, Z. Antibiotic alternatives: The substitution of antibiotics in animal husbandry? Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teo, A.Y.; Tan, H.M. Evaluation of the performance and intestinal gut microflora of broilers fed on corn-soy diets supplemented with Bacillus subtilis PB6 (CloSTAT). J. Appl. Poul. Res. 2007, 16, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Cao, G.T.; Ferket, P.R.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.P.; Chen, A.G. Effects of probiotic, Clostridium butyricum, on growth performance, immune function, and cecal microflora in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.M.; Ebeid, T.A.; Al-Homidan, I.; Soliman, N.K.; Abou-Emera, O.K. Influence of probiotic supplementation on immune response in broilers raised under hot climate. Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mountzouris, K.C.; Balaskas, C.; Xanthakos, I.; Tzivinikou, A.; Fegeros, K. Effects of a multi-species probiotic on biomarkers of competitive exclusion efficacy in broilers challenged with Salmonella enteritidis. Br. Poult. Sci. 2009, 50, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviagen 2014 Ross 308 Broiler: Performance Objectives. Available online: http://en.aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Ross308BroilerNutritionSpecs2014-EN.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Koncicki, A.; Tykałowski, B.; Stenzel, T.; Śmiałek, M.; Pestka, D. Effect of infection of turkeys with haemorrhagic enteritis adenovirus isolate on the selected parameters of cellular immunity and the course of colibacillosis. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 5, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B. The bursa of Fabricius: The evolution of a discovery. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Cui, H.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Guo, H. Toxic effect of NiCl2 on development of the bursa of Fabricius in broiler chickens. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heckert, R.A.; Estevez, I.; Russek-Cohen, E.; Pettit-Riley, R. Effects of density and perch availability on the immune status of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2002, 81, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, J.P.; Stefaniak, T.; Bednarczyk, M. Effect of in ovo delivered prebiotics and symbiotic on lymphoid organs’ morphology in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikandar, A.H.; Zaneb, H.; Younus, M.; Masood, S.; Aslam, A.; Shah, M.; Rehman, H. Growth performance, immune status and organ morphometry in broilers fed Bacillus subtilis-supplemented diet. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 47, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.; Abdel-Megeid, N.S.; Abou-Elnaga, M.K.; Mahmoud, S.F. Early nutrition with different diets composition versus fasting on immunity-related gene expression and histomorphology of digestive and lymphoid organs of layer-type chicks. Animals 2021, 11, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Jia, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, Y. Supplementation of probiotics in water beneficial growth performance, carcass traits, immune function, and antioxidant capacity in broiler chickens. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepaniak, J.A.; Shuster, J.E.; Hu, W.; Sundick, R.S. Production and in vitro characterization of recombinant chicken interleukin-2. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999, 19, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staeheli, P.; Puehler, F.; Schneider, K.; Gobel, T.W.; Kaspers, B. Cytokines of birds: Conserved functions--a largely different look. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2001, 21, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Cornelissen, J.B.W.J.; Mevius, D.J.; Smits, M.A.; Smidt, H.; Rebel, J.M. Antibiotics in 16-day-old broilers temporarily affect microbial and immune parameters in the gut. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3068–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labro, M.T. Interference of antibacterial agents with phagocyte functions: Immunomodulation or “immuno-fairy tales”? Clin. Microbial. Rev. 2000, 13, 615–650. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer, J.W. Immunomodulation by antimicrobial drugs. Neth. J. Med. 2003, 61, 233–234. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.C.; Galley, H.F.; Watt, A.M.; Webster, N.R. Differential effects of three antibiotics on T helper cell cytokine expression. J. Antimicrob. Chemotherap. 2005, 56, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, V.; Saratchandra, G.; Ramesh, J. Effect of enrofloxacin on zootechnical performance, behaviour and immunohistopathological response in broiler chicken. Vet. World 2013, 6, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madubuike, K.G.; Okoroafor, O.N.; Asuzu, I.U. Effects of early-life antibiotics administration on the immune response to Newcastle disease lasota vaccination and weight indices of broiler chicken. Folia 2020, 64, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, M.; Ya, T.; Huang, W.; Gao, P.; Zhang, H. A novel Lactobacillus plantarum strain P-8 activates beneficial immune response of broiler chickens. Int. Immunopharm. 2015, 29, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.M.; Yamanishi, S.; Sohn, J.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Leung, J.M.; Cho, I.; Kim, S.G.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Mahana, D.; et al. Altering the intestinal microbiota during a critical developmental window has lasting metabolic consequences. Cell 2014, 158, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Kim, I.H. Effects of multistrain probiotics on growth performance, apparent ileal nutrient digestibility, blood characteristics, cecal microbial shedding, and excreta odor contents in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, K.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Supplemental effects of probiotic Bacillus subtilis fmbJ on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul-Madsen, H.R.; Viertlböeck, B.; Härtle, S.; Smith, A.L.; Göbel, T.W. Chapter 7—Innate Immune Responses. In Avian Immunology, 2nd ed.; Schat, K.A., Kaspers, B., Kaiser, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 121–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sohail, M.U.; Ijaz, A.; Yousaf, M.S.; Ashraf, K.; Zaneb, H.; Aleem, M.; Rehman, H. Alleviation of cyclic heat stress in broilers by dietary supplementation of mannan-oligosaccharide and Lactobacillus-based probiotic: Dynamics of cortisol, thyroid hormones, cholesterol, C-reactive protein, and humoral immunity. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; Thorburn, A.N.; Mackay, C.R.; Macia, L. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar]
- Usami, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Ohata, A.; Miyoshi, M.; Aoyama, M.; Fueda, Y.; Kotani, J. Butyrate and trichostatin A attenuate nuclear factor κB activation and tumor necrosis factor α secretion and increase prostaglandin E2 secretion in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | BW kg | Spleen Weight g | Spleen Index 2 | BF Weight g | BF Index 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 days of age | |||||
| GC 1 | 0.152 | 0.102 b | 0.067 | 0.249 b | 0.163 b |
| GP | 0.156 | 0.121 a | 0.078 | 0.313 a | 0.200 a |
| GA | 0.157 | 0.121 a | 0.078 | 0.327 a | 0.209 a |
| SEM | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.006 |
| p-value | 0.571 | 0.047 | 0.066 | 0.036 | 0.004 |
| 35 days of age | |||||
| GC 1 | 2.355 | 1.993 | 0.085 | 4.562 | 0.194 |
| GP | 2.450 | 2.269 | 0.092 | 4.394 | 0.180 |
| GA | 2.345 | 2.374 | 0.101 | 4.397 | 0.189 |
| SEM | 0.035 | 0.028 | 0.003 | 0.075 | 0.007 |
| p-value | 0.414 | 0.068 | 0.101 | 0.205 | 0.696 |
| Item | Immunophenotype | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3+CD4+ | CD3+CD8a+ | CD4+CD8a+ | CD3-Bu-1+ | |
| 6 days of age | ||||
| GC 1 | 28.66 a | 43.38 | 3.06 | 19.54 b |
| GP | 22.55 b | 43.42 | 3.17 | 25.30 a |
| GA | 19.40 b | 40.38 | 2.79 | 28.33 a |
| SEM | 1.107 | 1.042 | 0.164 | 1.046 |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.407 | 0.629 | 0.001 |
| 35 days of age | ||||
| GC 1 | 22.09 | 39.23 | 1.85 | 28.46 |
| GP | 20.82 | 45.19 | 2.00 | 25.42 |
| GA | 21.84 | 43.26 | 1.71 | 28.35 |
| SEM | 0.826 | 1.059 | 0.090 | 1.120 |
| p-value | 0.813 | 0.059 | 0.457 | 0.470 |
| Item | Immunophenotype | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3+CD4+ | CD3+CD8a+ | CD4+CD8a+ | CD3-Bu-1+ | |
| 6 days of age | ||||
| GC 1 | 13.63 | 3.12 | 0.985 | 5.72 b |
| GP | 14.05 | 3.28 | 0.759 | 7.56 a |
| GA | 12.13 | 4.08 | 0.680 | 7.75 a |
| SEM | 0.977 | 0.207 | 0.074 | 0.306 |
| p-value | 0.715 | 0.125 | 0.219 | 0.007 |
| 35 days of age | ||||
| GC 1 | 9.44 | 6.15 | 0.687 | 8.58 |
| GP | 8.99 | 7.83 | 0.574 | 8.39 |
| GA | 9.36 | 6.36 | 0.442 | 8.45 |
| SEM | 0.451 | 0.356 | 0.086 | 0.156 |
| p-value | 0.915 | 0.108 | 0.520 | 0.879 |
| Item | ALB g/L | IgA µg/mL | IgY µg/mL | Cp U/L | IL-2 pg/mL | IL-6 ng/L | TNF ng/L | CRP mg/dL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 days of age | ||||||||
| GC 1 | 7.99 | 135.1 ab | 1207.5 a | 5.23 a | 518.9 b | 119.3 a | 164.3 ab | 1.196 a |
| GP | 9.27 | 111.5 b | 1088.8 ab | 4.54 b | 982.3 ab | 92.1 b | 132.8 b | 1.100 b |
| GA | 8.51 | 150.7 a | 928.3 b | 5.37 ab | 1163.6 a | 123.8 a | 189.0 a | 1.260 a |
| SEM | 0.264 | 4.997 | 40.74 | 0.161 | 58.31 | 4.217 | 7.361 | 0.018 |
| p-value | 0.139 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.020 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 | <0.001 |
| 35 days of age | ||||||||
| GC 1 | 17.78 | 250.2 | 576.2 a | 7.08 a | 36.07 b | 119.4 | 215.0 ab | 1.210 a |
| GP | 20.88 | 229.2 | 501.1 ab | 5.82 b | 41.21 ab | 108.6 | 180.9 b | 1.094 b |
| GA | 18.25 | 174.8 | 435.5 b | 5.24 b | 46.52 a | 123.6 | 235.1 a | 1.067 b |
| SEM | 0.762 | 13.44 | 15.91 | 0.202 | 1.605 | 4.336 | 7.247 | 0.018 |
| p-value | 0.206 | 0.056 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | 0.356 | 0.005 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankowski, J.; Tykałowski, B.; Stępniowska, A.; Konieczka, P.; Koncicki, A.; Matusevičius, P.; Ognik, K. Immune Parameters in Chickens Treated with Antibiotics and Probiotics during Early Life. Animals 2022, 12, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091133
Jankowski J, Tykałowski B, Stępniowska A, Konieczka P, Koncicki A, Matusevičius P, Ognik K. Immune Parameters in Chickens Treated with Antibiotics and Probiotics during Early Life. Animals. 2022; 12(9):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091133
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankowski, Jan, Bartłomiej Tykałowski, Anna Stępniowska, Paweł Konieczka, Andrzej Koncicki, Paulius Matusevičius, and Katarzyna Ognik. 2022. "Immune Parameters in Chickens Treated with Antibiotics and Probiotics during Early Life" Animals 12, no. 9: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091133
APA StyleJankowski, J., Tykałowski, B., Stępniowska, A., Konieczka, P., Koncicki, A., Matusevičius, P., & Ognik, K. (2022). Immune Parameters in Chickens Treated with Antibiotics and Probiotics during Early Life. Animals, 12(9), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091133





