Comparative Study of the Expression Profiles of miRNAs of Milk-Derived Exosomes of Yak and Jeryak
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Milk
2.2. Determination of Milk Quality
2.3. Extraction and Identification of Milk Exosomes from Yak and Jeryak Samples
2.3.1. Extraction of Exosomes by Density Gradient Centrifugation
2.3.2. Identification of Exosome
2.4. Extraction of Exosome RNA
2.5. Construction and Sequencing of Small RNA Library
2.6. Preprocessing of Sequencing Data
2.7. Differential miRNA Expression Analysis
2.8. Prediction of Target Genes and GO, KEGG Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the Yak and Jeryak Milk Quality
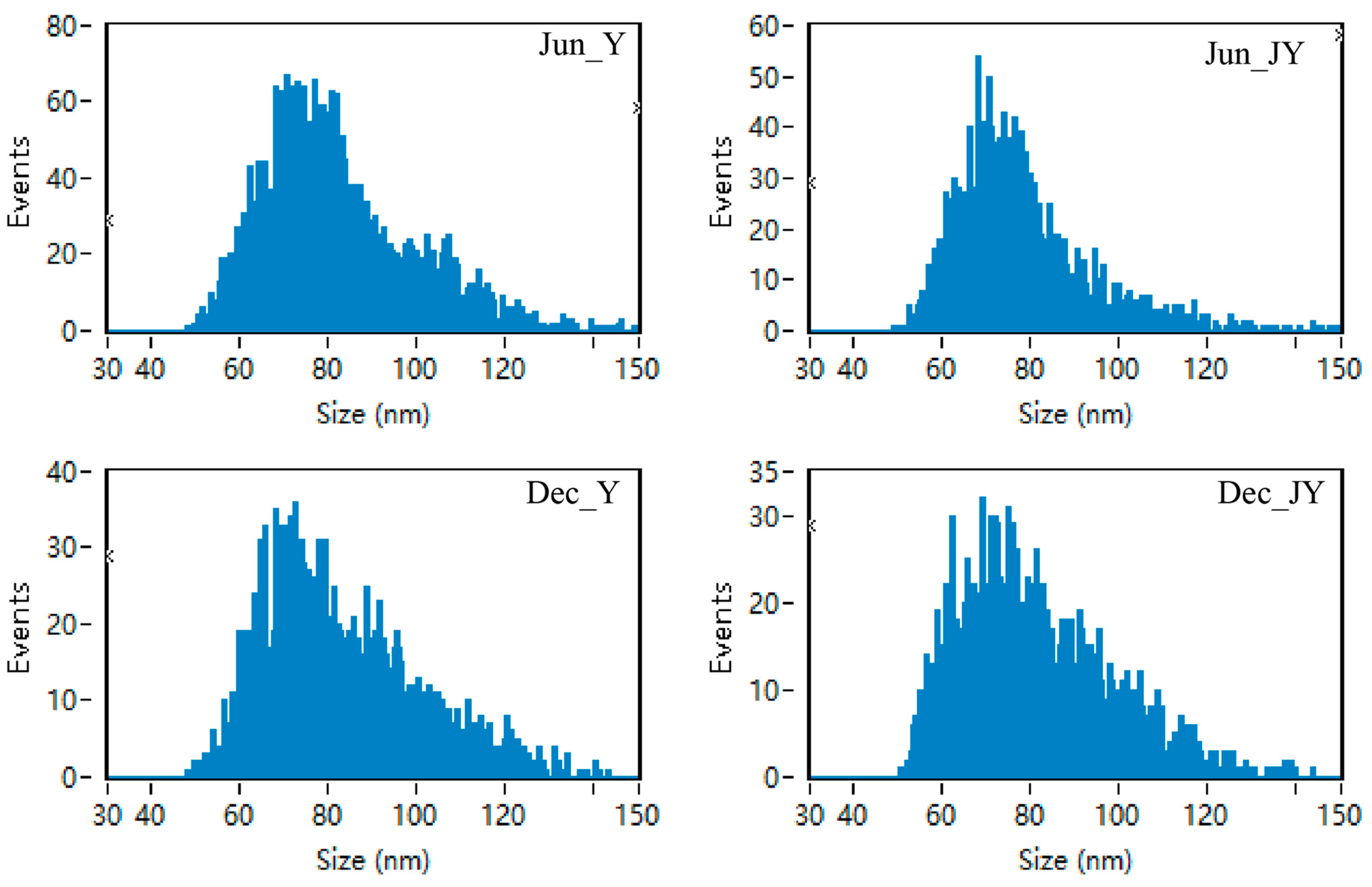
3.2. Identification of Milk Exosomes from Yak and Jeryak Milk Collected in June and December
3.3. Characteristic Analysis of Yak and Jeryak Milk Exosome miRNAs Obtained in June and December
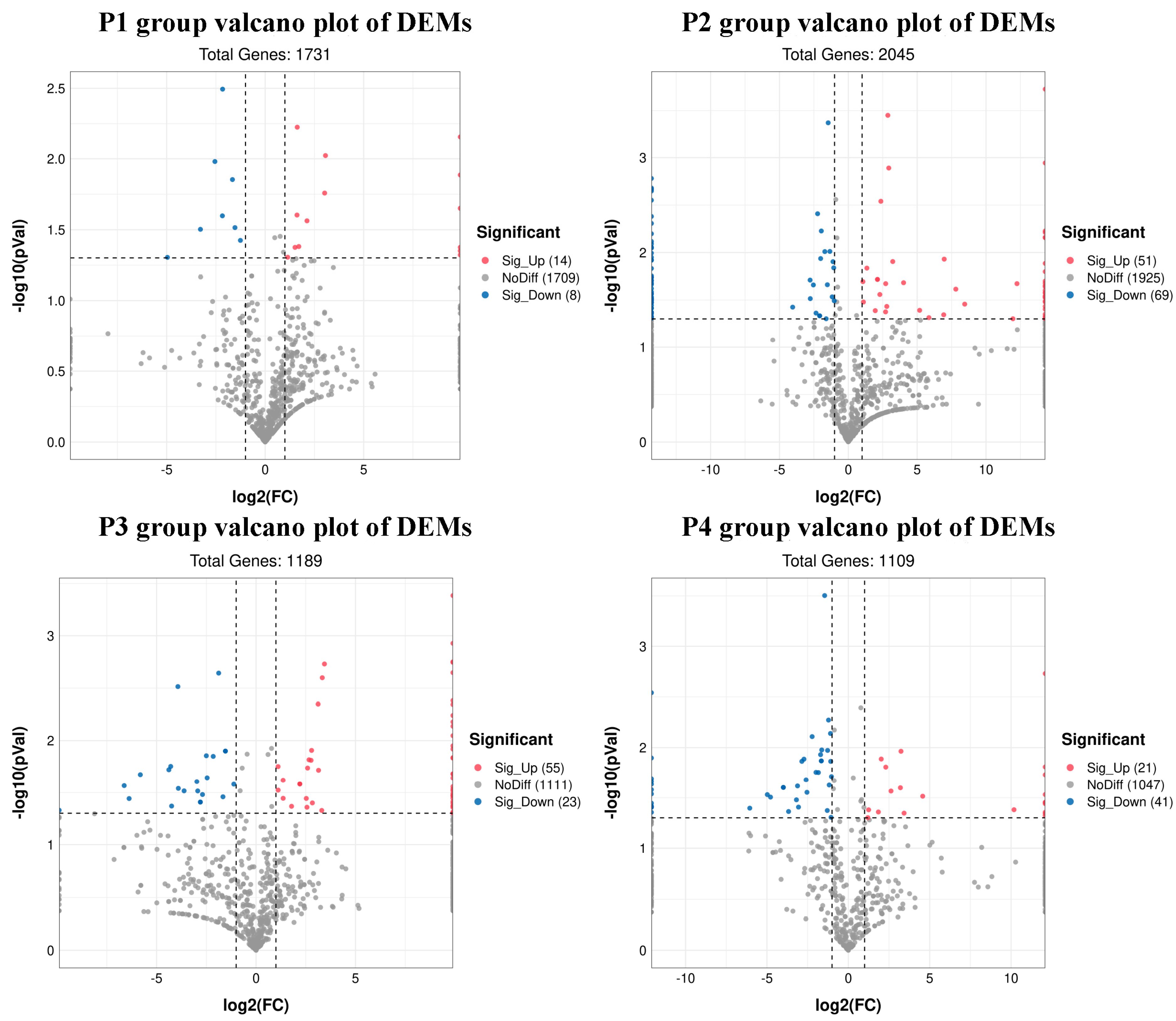
3.4. Analysis of Differential miRNAs
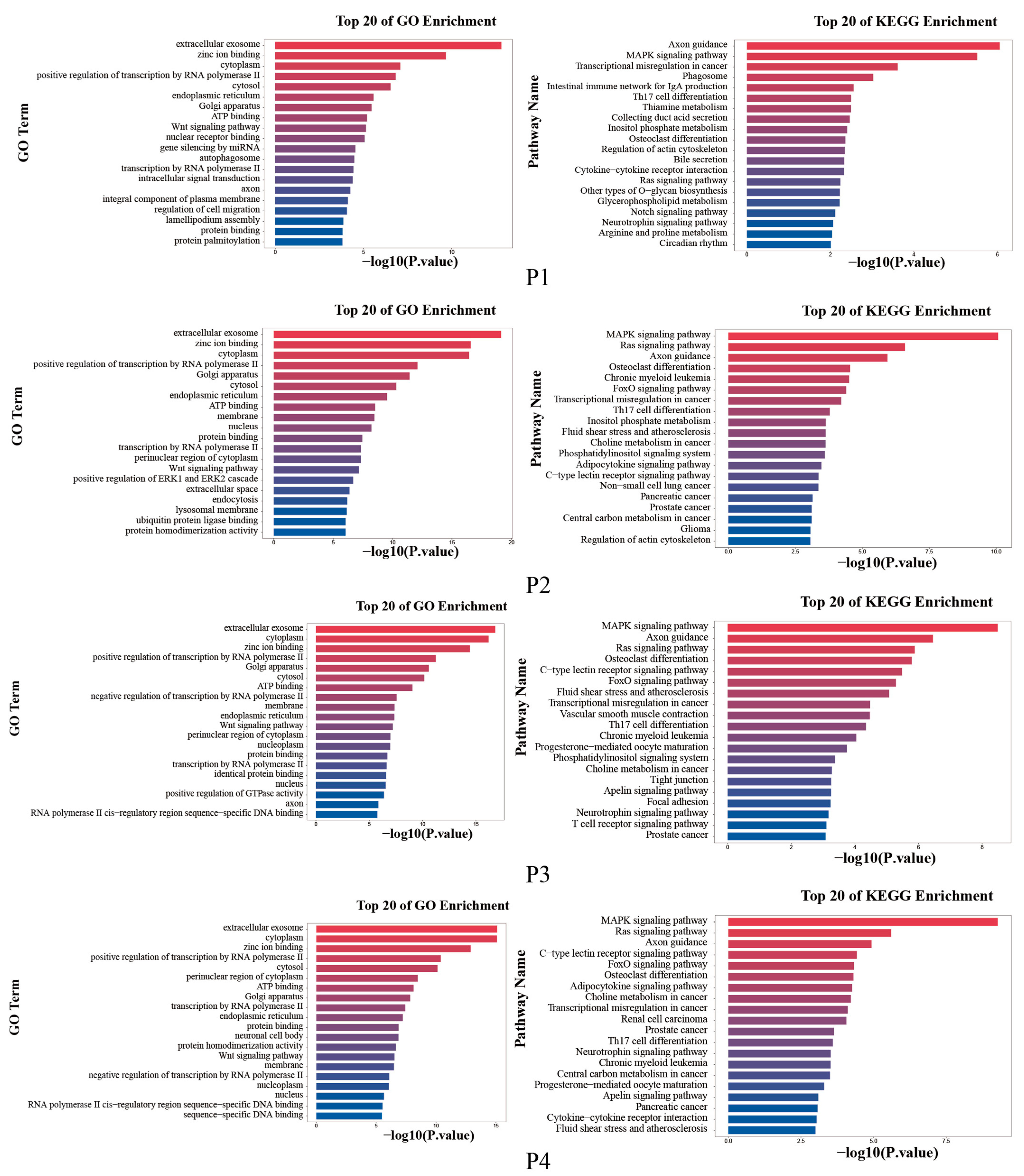
3.5. Enrichment Analysis of Target Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EV | extracellular vesicles |
| DEMs | differentially expressed miRNAs |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| Pol II | RNA polymerase II |
| UTR | untranslated regions |
References
- Jin, Y.C.; Yan, Z.X.; Li, S.S.; Liu, L.J. Research progress on male sterility of cattle-Yak in China. Chin. Qinghai J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2017, 47, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, F. Investigation and analysis report on Yak market and industry in China. Agric. Prod. Mark. 2021, 23, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Roveglia, C.; Niero, G.; Penasa, M.; Finocchiaro, R.; Marusi, M.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Cassandro, M. Phenotypic analysis of milk composition, milk urea nitrogen and somatic cell score of Italian Jersey cattle breed. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; Hao, H.S.; Zhu, H.B.; Du, W.H.; Wang, D. Jersey Cattle—An important breed genetic resource for dairy production in China. China Dairy Cattle 2008, 01, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.L.; Guo, S.Z.; Li, B.M.; Bao, Z.X.; Fan, J.F.; Wang, L.B.; Nan, J.J.; Wang, W.B.; Zhao, W.Y.; Gou, Q.; et al. Effect of Jersey Cattle frozen semen to crossbred and improve Gannan Yaks. China Cattle Sci. 2018, 44, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Du, L.N. Application of exosomes in brain-targeted delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2022, 57, 658–669. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintio, M.; Polacchini, G.; Scarsella, E.; Montanari, T.; Stefanon, B.; Colitti, M. MicroRNA Milk Exosomes: From Cellular Regulator to Genomic Marker. Animals 2020, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G. Exosomal miRNA Profiling during Gestation and Its Regulatory Mechanism on the Uterine Immune Microenvironment in the First Trimester of Dairy Cows. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Admyre, C.; Johansson, S.M.; Qazi, K.R.; Filén, J.J.; Lahesmaa, R.; Norman, M.; Neve, E.P.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C.; Schmitz, G. MicroRNAs: Milk’s epigenetic regulators. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 31, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Sato, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Namba, K.; Takeda, Y. Bovine milk exosomes contain microRNA and mRNA and are taken up by human macrophages. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2920–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, S.; Upadhyaya, B.; Mutai, E.; Desaulniers, A.T.; Cederberg, R.A.; White, B.R.; Zempleni, J. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Tsukasaki, Y.; Dasgupta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, N.; Ikebe, M.; Sauter, E.R. Exosomes in Human Breast Milk Promote EMT. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4517–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.B.; Mumford, P.W.; McCarthy, J.J.; Miller, M.E.; Young, K.C.; Martin, J.S.; Beck, D.T.; Lockwood, C.M.; Roberts, M.D. Whey protein-derived exosomes increase protein synthesis and hypertrophy in C(2-)C(12) myotubes. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiferman, A.; Shu, J.; Grove, R.; Cui, J.; Adamec, J.; Zempleni, J. A diet defined by its content of bovine milk exosomes and their RNA cargos has moderate effects on gene expression, amino acid profiles and grip strength in skeletal muscle in C57BL/6 mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 59, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Patel, M.; Williams, S.; Arora, H.; Brawner, K.; Sims, B. Human breast milk-derived exosomes attenuate cell death in intestinal epithelial cells. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.Y.; Tong, S.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M.; Zhao, X. Identification and characterization of differentially expressed exosomal microRNAs in bovine milk infected with Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkraus, B.R.; Toegel, M.; Fulga, T.A. Tiny giants of gene regulation: Experimental strategies for microRNA functional studies. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2016, 5, 311–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.P.; Glasner, M.E.; Yekta, S.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Vertebrate microRNA genes. Science 2003, 299, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.Y.; Jin, X.L.; Lo, L.J.; Liu, J.X. Expression profiles of microRNAs from lactating and non-lactating bovine mammary glands and identification of miRNA related to lactation. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.J.; Lan, X.Y.; Guo, W.J.; Sun, J.J.; Huang, Y.Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, T.H.; Lei, C.Z.; Fang, X.T.; Chen, H. Comparative transcriptome profiling of dairy goat microRNAs from dry period and peak lactation mammary gland tissues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Pan, H.P. Development and utilization of Yak dairy. China Dairy 2004, 07, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Agyare, A.N.; Liang, Q. Nutrition of Yak milk fat–Focusing on milk fat globule membrane and fatty acids. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 83, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.P.; Xu, J.T.; Tong, Z.B.; Chen, S.M.; Luo, X.L. Determination to the milk yields and milk contents of Pianniu in the Alpine Pasture Area. China Cattle Sci. 2008, 05, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xi, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Li, W.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of change in quality indices and volatile flavor components in raw milk during refrigerated storage. LWT 2022, 165, 113674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q. Isolation of Milk-Derived Exosomes and Identification of Mirnas Associated with Mastitis. M.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Inoshima, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Ishiguro, N. Comparison of methods for isolating exosomes from bovine milk. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 1523–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.N. Study of the Mechanism for Yak Milk Exosomal miRNAs in Alleviating Hypoxia Injury of Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Do, D.N.; Li, R.; Dudemaine, P.L.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M. MicroRNA roles in signalling during lactation: An insight from differential expression, time course and pathway analyses of deep sequence data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.N.; Dudemaine, P.L.; Li, R.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M. Co-Expression Network and Pathway Analyses Reveal Important Modules of miRNAs Regulating Milk Yield and Component Traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammah, A.A.; Do, D.N.; Bissonnette, N.; Gévry, N.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M. Co-Expression Network Analysis Identifies miRNA–mRNA Networks Potentially Regulating Milk Traits and Blood Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billa, P.A.; Faulconnier, Y.; Ye, T.; Chervet, M.; Le Provost, F.; Pires, J.A.A.; Leroux, C. Deep RNA-Seq reveals miRNome differences in mammary tissue of lactating Holstein and Montbéliarde cows. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M. The Internal Self-Regulatory Rules Inside the Mammary Gland of Chinese Holstein Cow during Lactation Cycle. M.D. Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.C.; Guo, W.L.; Zan, L.S.; Wang, Y.N.; Tang, K.Q. Bta-miR-130a regulates the biosynthesis of bovine milk fat by targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 2898–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Beaudoin, F.; Ammah, A.A.; Bissonnette, N.; Benchaar, C.; Zhao, X.; Lei, C.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M. Deep sequencing shows microRNA involvement in bovine mammary gland adaptation to diets supplemented with linseed oil or safflower oil. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markkandan, K.; Ahn, K.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, T.I.; Dang, C.; Hong, S.E.; Yoon, H.B.; Lim, H.J.; Hong, C.P. Profiling and identification of pregnancy-associated circulating microRNAs in dairy cattle. Genes Genom. 2018, 40, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.S.N.; Coutinho, L.L.; Cesar, A.S.M.; Diniz, W.; de Souza, M.M.; Andrade, B.G.; Koltes, J.E.; Mourão, G.B.; Zerlotini, A.; Reecy, J.M.; et al. Co-Expression Networks Reveal Potential Regulatory Roles of miRNAs in Fatty Acid Composition of Nelore Cattle. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Y.; Li, F.X.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, B.; Gao, Y.; Ma, T.H.; Dai, L.S.; Xu, J.B.; Sun, G.J.; Xu, C.; et al. Identification of EphA2 as a novel target of bta-miR-26b in bovine. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 32, 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. The Regulating Function of MiR-26 Family on Fatty Acid Metabolism in Mammary Gland of Dairy Goats. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A & F University, Xianyang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wicik, Z.; Gajewska, M.; Majewska, A.; Walkiewicz, D.; Osińska, E.; Motyl, T. Characterization of microRNA profile in mammary tissue of dairy and beef breed heifers. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2016, 133, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, R.; Sengar, G.S. Comparative miRNA signatures among Sahiwal and Frieswal cattle breeds during summer stress. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, G.S.; Deb, R.; Singh, U.; Junghare, V.; Hazra, S.; Raja, T.V.; Alex, R.; Kumar, A.; Alyethodi, R.R.; Kant, R.; et al. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in Sahiwal (Bos indicus) breed of cattle during thermal stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, R.M. Major advances associated with hormone and growth factor regulation of mammary growth and lactation in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osińska, E.; Wicik, Z.; Godlewski, M.M.; Pawłowski, K.; Majewska, A.; Mucha, J.; Gajewska, M.; Motyl, T. Comparison of stem/progenitor cell number and transcriptomic profile in the mammary tissue of dairy and beef breed heifers. J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 55, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
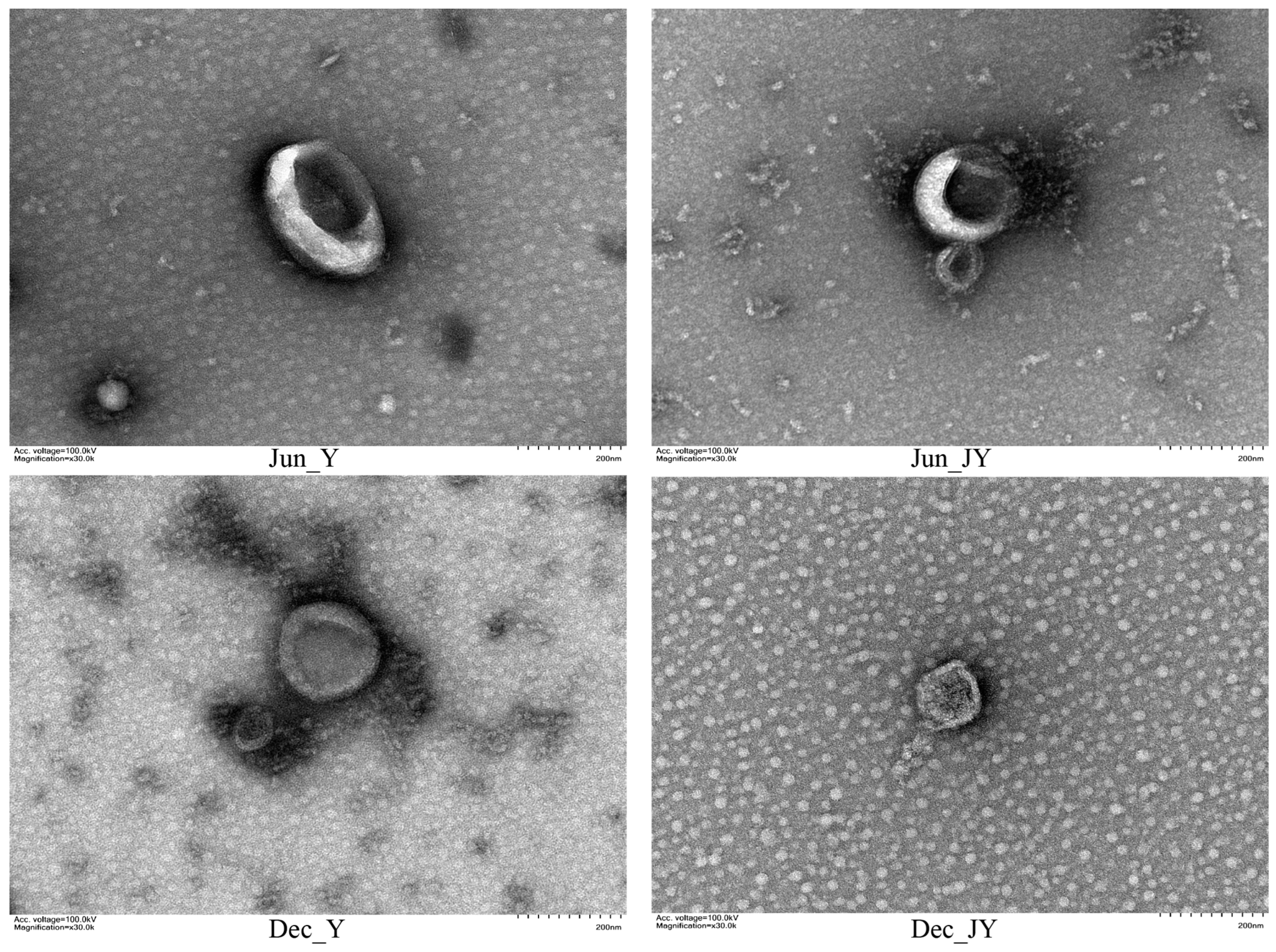
| June (P1) | December (P3) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk Quality | Yak | Jeryak | Significance | p-Value | Yak | Jeryak | Significance | p-Value |
| Casein | 3.739 ± 0.211 | 3.189 ± 0.209 | ** | <0.01 | 4.049 ± 0.692 | 3.754 ± 0.348 | 0.284 | |
| Protein | 4.056 ± 0.206 | 3.831 ± 0.322 | 0.071 | 5.011 ± 0.927 | 4.746 ± 0.691 | 0.476 | ||
| Fat | 8.137 ± 2.095 | 4.670 ± 0.930 | ** | <0.001 | 7.399 ± 2.726 | 6.164 ± 1.471 | 0.241 | |
| TS | 18.550 ± 1.950 | 14.367 ± 0.877 | ** | <0.001 | 18.195 ± 3.364 | 16.296 ± 1.782 | 0.146 | |
| SNF | 10.402 ± 0.280 | 9.834 ± 0.338 | ** | <0.001 | 10.779 ± 0.630 | 10.094 ± 0.521 | * | 0.012 |
| Lactose | 5.275 ± 0.092 | 4.829 ± 0.180 | ** | <0.001 | 4.600 ± 0.340 | 4.333 ± 0.234 | 0.054 | |
| Freezing point | 0.700 ± 0.000 | 0.600 ± 0.000 | ** | <0.001 | 0.737 ± 0.060 | 0.663 ± 0.052 | ** | 0.005 |
| Acidity | 8.886 ± 0.788 | 8.953 ± 1.020 | 0.866 | 13.110 ± 2.523 | 11.625 ± 1.877 | 0.148 | ||
| Citric acid | 0.209 ± 0.221 | 0.208 ± 0.256 | 0.921 | 0.214 ± 0.437 | 0.166 ± 0.303 | ** | 0.009 | |
| Jeryak (P2) | Yak (P4) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk Quality | June | December | Significance | p-Value | June | December | Significance | p-Value |
| Casein | 3.189 ± 0.209 | 3.754 ± 0.348 | ** | 0.002 | 3.739 ± 0.211 | 4.0489 ± 0.692 | 0.181 | |
| Protein | 3.831 ± 0.322 | 4.746 ± 0.691 | ** | 0.001 | 4.056 ± 0.206 | 5.0105 ± 0.927 | ** | 0.004 |
| Fat | 4.670 ± 0.930 | 6.164 ± 1.471 | * | 0.012 | 8.137 ± 2.095 | 7.3989 ± 2.726 | 0.462 | |
| TS | 14.367 ± 0.877 | 16.296 ± 1.782 | ** | 0.005 | 18.550 ± 1.950 | 18.1953 ± 3.364 | 0.762 | |
| SNF | 9.834 ± 0.338 | 10.094 ± 0.521 | 0.191 | 10.402 ± 0.280 | 10.7789 ± 0.630 | 0.085 | ||
| Lactose | 4.829 ± 0.180 | 4.333 ± 0.234 | ** | <0.001 | 5.275 ± 0.092 | 4.5995 ± 0.340 | ** | <0.001 |
| Freezing point | 0.600 ± 0.000 | 0.663 ± 0.052 | ** | <0.001 | 0.700 ± 0.000 | 0.7368 ± 0.060 | 0.064 | |
| Acidity | 8.953 ± 1.012 | 11.625 ± 1.877 | ** | 0.001 | 8.886 ± 0.788 | 13.1095 ± 2.523 | ** | <0.001 |
| Citric acid | 0.208 ± 0.256 | 0.166 ± 0.303 | ** | 0.004 | 0.209 ± 0.221 | 0.2140 ± 0.437 | 0.723 | |
| Sample Name | Mean Particle Size (nm) | Concentration (Particles/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Jun_ Y | 81.95 | 3.85 × 1010 |
| Jun_ JY | 77.80 | 2.05 × 1010 |
| Dec_ Y | 82.61 | 2.59 × 1010 |
| Dec_ JY | 80.82 | 6.89 × 109 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dingkao, R.; Huang, C.; Ma, X.; Wu, X.; La, Y.; Chu, M.; Bao, P.; Guo, X.; et al. Comparative Study of the Expression Profiles of miRNAs of Milk-Derived Exosomes of Yak and Jeryak. Animals 2022, 12, 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223189
Ren W, Zhang Y, Dingkao R, Huang C, Ma X, Wu X, La Y, Chu M, Bao P, Guo X, et al. Comparative Study of the Expression Profiles of miRNAs of Milk-Derived Exosomes of Yak and Jeryak. Animals. 2022; 12(22):3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223189
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Wenwen, Yongfeng Zhang, Renqing Dingkao, Chun Huang, Xiaoming Ma, Xiaoyun Wu, Yongfu La, Min Chu, Pengjia Bao, Xian Guo, and et al. 2022. "Comparative Study of the Expression Profiles of miRNAs of Milk-Derived Exosomes of Yak and Jeryak" Animals 12, no. 22: 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223189
APA StyleRen, W., Zhang, Y., Dingkao, R., Huang, C., Ma, X., Wu, X., La, Y., Chu, M., Bao, P., Guo, X., Pei, J., Yan, P., & Liang, C. (2022). Comparative Study of the Expression Profiles of miRNAs of Milk-Derived Exosomes of Yak and Jeryak. Animals, 12(22), 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223189





