Investigating Unused Tools for the Animal Behavioral Diversity Toolkit
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Behavioral Diversity: Literature Review and Categories
3. Summary of Behavioral Diversity Literature
4. Tools to Measure Behavioral Diversity
4.1. Behavioral Richness
4.2. Shannon–Wiener Index
4.3. Simpson’s Index
4.4. Menhinick’s Index
4.5. Margalef Index
4.6. Chao
4.7. Behavioral Variety Index
5. Comparison of Indices
Taxonomic Differences
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Behavioral diversity | Any index used to assess the quantify the evenness and diversity of behaviors that an animal expresses. |
| Behavioural evenness | The variance in quantity of behavior between behavior types. For example, an observation where all behaviors are seen equally frequently has a higher evenness score than an observation when only one behavior is seen frequently, and all others are seen rarely. |
| Behavioral richness | The number of behaviors an animal shows during a study. For example, an animal that engages in eating, resting and climbing has a behavioral richness of 3. |
| Behavior category | A behavior that can be defined in an ethogram (for example, foraging). For the purpose of this paper, the term ‚behavior type‘ used in other research is synonymous. The number of behavior categories identified in a behavioral diversity study is referred to as behavioral richness. |
| Observation | A block of time during which animals are observed (e.g., 1 h observation). A study is made up of a series of observations. |
References
- Miller, L.J.; Vicino, G.A.; Sheftel, J.; Lauderdale, L.K. Behavioral Diversity as a Potential Indicator of Positive Animal Welfare. Animals 2020, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltz, D.; Berger-Tal, O.; Motro, U.; Shkedy, Y.; Raanan, N. Conservation Implications of Habituation in Nubian Ibex in Response to Ecotourism. Anim. Conserv. 2019, 22, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, N.L.; LaDue, C.A. The Behavioral Effects of Exhibit Size versus Complexity in African Elephants: A Potential Solution for Smaller Spaces. Zoo Biol. 2019, 38, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchetti, L.; Righi, C.; Guelfi, G.; Enas, C.; Moscati, L.; Mancini, S.; Diverio, S. Multi-Operator Qualitative Behavioural Assessment for Dogs Entering the Shelter. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2019, 213, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuser, V.; Weinhold, L.; Hillemacher, S.; Tiemann, I. Welfare-Related Behaviors in Chickens: Characterization of Fear and Exploration in Local and Commercial Chicken Strains. Animals 2021, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, G.J. Age and Context Affect the Stereotypies of Caged Mink. Behaviour 1993, 127, 191–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.J.; Latham, N. Can’t stop, won’t stop: Is stereotypy a reliable animal welfare indicator? Anim. Welf. 2004, 102, 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, L.J.; Ivy, J.A.; Vicino, G.A.; Schork, I.G. Impacts of Natural History and Exhibit Factors on Carnivore Welfare. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2019, 22, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.J.; Lauderdale, L.K.; Bryant, J.L.; Mellen, J.D.; Walsh, M.T.; Granger, D.A. Behavioral Diversity as a Potential Positive Indicator of Animal Welfare in Bottlenose Dolphins. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, J.E. Directions in Animal Enclosure Use Studies. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2020, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Pisacane, C.; Vicino, G. Relationship between Behavioural Diversity and Faecal Glucocorticoid Metabolites: A Case Study with Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus). Anim. Welf. 2016, 25, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, K.; Ross, S. Technical Contribution: A Cautionary Note on the Use of Behavioural Diversity (H-Index) in Animal Welfare Science. Anim. Welf. 2019, 28, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, J.; Fernandez, E. Which Index Should I Use? A Comparison of Indices for Enclosure Use Studies. Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2022, 9, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Harvey, E. Enclosure Use as a Measure of Behavioral Welfare in Zoo-Housed African Wild Dogs (Lycaon pictus). J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2021, 9, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, J.E.; Tuke, J.; Fernandez, E.J. A Simulated Comparison of Behavioural Observation Sampling Methods. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, F.E.; Melfi, V.A. Environmental Enrichment for a Mixed-Species Nocturnal Mammal Exhibit: Nocturnal Mammal Enrichment. Zoo Biol. 2012, 31, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; Corkery, I.; Haigh, A.; McKeown, S.; Quirke, T.; O’Riordan, R. The Effects of Environmental and Visitor Variables on the Behavior of Free-Ranging Ring-Tailed Lemurs (Lemur catta) in Captivity. Zoo Biol. 2017, 36, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.K.; Quirke, T.; Overy, L.; Flannery, K.; O’Riordan, R. The Effect of the Zoo Setting on the Behavioural Diversity of Captive Gentoo Penguins and the Implications for Their Educational Potential. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2016, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.J.; Timberlake, W. Selecting and Testing Environmental Enrichment in Lemurs. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiezio, C.; Altamura, M.; Weerman, J.; Regaiolli, B. Behaviour of Zoo-Housed Red Pandas (Ailurus fulgens): A Case-Study Testing the Behavioural Variety Index. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2022, 3, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiezio, C.; Valsecchi, V.; Sandri, C.; Regaiolli, B. Investigating Individual and Social Behaviour of the Northern Bald Ibis (Geronticus eremita): Behavioural Variety and Welfare. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. The Mathematical Theory of Communication, by CE Shannon (and Recent Contributions to the Mathematical Theory of Communication), W. Weaver; University of Illinois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Cairo, P.L.G.; Nogueira, S.S.C.; Altino, V.S.; Vandenheede, M.; Schroyen, M.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; Gross, E.; Bindelle, J.; Nogueira-Filho, S.L.G. Individual Differences in Behaviour and Gut Bacteria Are Associated in Collared Peccary (Mammalia, Tayassuidae). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2748–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, M.J.; Lussier, J.P. Environmental Enrichment for the Captive Spectacled Bear (Tremarctos ornatus). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, R.S. A New Sampling Formula for Neutral Biodiversity: A New Sampling Formula. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.; Gartland, K.N.; Jones, M.; Fuller, G. Behavioral Assessment of Six Reptile Species during a Temporary Zoo Closure and Reopening. Animals 2022, 12, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kistler, C.; Hegglin, D.; Würbel, H.; König, B. Preference for structured environment in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and checker barbs (Puntius oligolepis). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 135, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.M.; Bullock, E.V.W. Evaluation of Factors Affecting Emotional Responses in Zoo Visitors and the Impact of Emotion on Conservation Mindedness. Anthrozoös 2014, 27, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJong, T.M. A Comparison of Three Diversity Indices Based on Their Components of Richness and Evenness. Oikos 1975, 26, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, C.; Miller, L.; Schulte, B. Examination of Enrichment Using Space and Food for African Elephants (Loxodonta africana) at the San Diego Zoo Safari Park. Anim. Welf. 2018, 27, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Metter, J.E.; Harriger, M.D.; Bolen, R.H. Environmental enrichment utilizing stimulus objects for African lions (Panthera leo leo) and Sumatran tigers (Panthera tigris sumatrae). Bios 2008, 79, 7–16. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/25433813 (accessed on 23 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.; Bryant, J.; Staley, M.; Whitham, J.; Miller, L. Behavioural Diversity as a Potential Welfare Indicator for Professionally Managed Chimpanzees (Pan Troglodytes): Exploring Variations in Calculating Diversity Using Species-Specific Behaviours. Anim. Welf. 2021, 30, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.; Madsen, R.V.E.; Sørensen, S.B.F.; Hansen, T.B.; Gottschalk, A.; Linder, A.C.; Alstrup, A.K.O.; Pagh, S.; Jensen, T.H.; Pertoldi, C. Enrichment Study in Three Captive Polar Bears (Ursus maritimus) at Aalborg Zoo. Genet. Biodivers. J. 2021, 5, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.J.; Kinley, R.C.; Timberlake, W. Training penguins to interact with enrichment devices for lasting effects. Zoo Biol. 2019, 38, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubac, C.M.; Miller, J.M.; Coltman, D.W. The Genetic Basis of Animal Behavioural Diversity in Natural Populations. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 1957–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, S.; Mason, G. Stereotypic Behavior in Asiatic Black and Malayan Sun Bears. Zoo Biol. 2004, 23, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamito, S. Caution Is Needed When Applying Margalef Diversity Index. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 550–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-R.; Shin, J.; Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Seol, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.B.; Isaacson, R.E. Deciphering Diversity Indices for a Better Understanding of Microbial Communities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardo, L.; Correia, J.; Oliveira, R. The Effect of Substrate Availability on Behavioural and Physiological Indicators of Welfare in the African Cichlid (Oreochromis mossambicus). Anim. Welf. 2008, 17, 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, S.; Tyagi, P.C.; Malik, P.K.; Pandit, S.J.; Kadivar, R.F.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Mondol, S. Effects of Personality and Rearing-History on the Welfare of Captive Asiatic Lions (Panthera leo persica). PeerJ 2020, 8, e8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaDue, C.A.; Schulte, B.A. Pheromonal Enrichment in the Zoo: An Empirical Approach with Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 235, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano Jimenez, A.I.; Drago, M.; Vinyoles, D.; Maté, C. Play Behavior in Two Captive Bottlenose Dolphin Calves (Tursiops Truncatus): Ethogram, Ontogeny, and Individual Differences. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2021, 24, 292–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, D.; Morton, D.B. Inventory of the Behaviour of New Zealand White Rabbits in Laboratory Cages. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1995, 45, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyvia, A.; Faggioli, A.B.; Cipreste, C.F. Effects of Environmental Enrichment in a Captive Pair of Golden Parakeet (Guaruba guarouba, Psittacidae) with Abnormal Behaviors. Rev. Bras. Ornitol. 2015, 23, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfour, F.; Vaicekauskaite, R.; García-Párraga, D.; Pilenga, C.; Serres, A.; Brasseur, I.; Pascaud, A.; Perlado-Campos, E.; Sánchez-Contreras, G.J.; Baumgartner, K.; et al. Behavioural Diversity Study in Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) Groups and Its Implications for Welfare Assessments. Animals 2021, 11, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J. Social Ontogeny and Behavioural Diversity: Consequences for Bighorn Sheep Oris Canadensis Inhabiting Desert and Mountain Environments. J. Zool. 1979, 188, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Non-parametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A.J.; Waran, N.K.; Young, R.J. Environmental enrichment for Australian mammals. Anim. Welf. 1998, 7, 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Swaisgood, R.R.; White, A.M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, G.; Lindburg, D.G. How Do Giant Pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) Respond to Varying Properties of Enrichments? A Comparison of Behavioral Profiles among Five Enrichment Items. J. Comp. Psychol. 2005, 119, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frézard, A.; Pape, G.L. Contribution to the Welfare of Captive Wolves (Canis lupus lupus): A Behavioral Comparison of Six Wolf Packs: Comparison of Six Wolf Packs. Zoo Biol. 2003, 22, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Swarts, H.M.; Crooks, K.R.; Willits, N.; Woodroffe, R. Possible Contemporary Evolution in an Endangered Species, the Santa Cruz Island Fox. Anim. Conserv. 2009, 12, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, J.V.; Miller, J.T.; Sullivan, T.J. Note on optimizing environmental enrichment: A study of fennec fox and zoo guests. Zoo Biol. 2011, 30, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myles, S.; Montrose, V.T. The Effects of Olfactory Stimulation on the Behaviour of Captive Meerkats (Suricata suricatta). J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2015, 3, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiddie, J.; Bodymore, A.; Dittrich, A. Environmental Enrichment in Kennelled Pit Bull Terriers (Canis lupus familiaris). Animals 2017, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acaralp-Rehnberg, L.K.; Coleman, G.J.; Magrath, M.J.L.; Melfi, V.; Fanson, K.V.; Bland, I.M. The Effect of Behind-The-Scenes Encounters and Interactive Presentations on the Welfare of Captive Servals (Leptailurus serval). Animals 2020, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddon, A.R.; Aubin-Horth, N.; Reader, S.M. Wild Guppies from Populations Exposed to Higher Predation Risk Exhibit Greater Vasotocin Brain Gene Expression. J. Zool. 2022, 316, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, L.P.; Newton-Fisher, N.E. How Abnormal Is the Behaviour of Captive, Zoo-Living Chimpanzees? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.J.N.; Hau, J.; Schapiro, S.J. Relationships between captive chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) welfare and voluntary participation in behavioural studies. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2019, 214, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalan, A.K.; Kulik, L.; Arandjelovic, M.; Boesch, C.; Haas, F.; Dieguez, P.; Barratt, C.D.; Abwe, E.E.; Agbor, A.; Angedakin, S. Environmental Variability Supports Chimpanzee Behavioural Diversity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, H.S.; Boesch, C.; Kulik, L.; Haas, F.; Arandjelovic, M.; Dieguez, P.; Bocksberger, G.; McElreath, M.B.; Agbor, A.; Angedakin, S.; et al. Human Impact Erodes Chimpanzee Behavioral Diversity. Science 2019, 363, 1453–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashaw, M.J.; Gibson, M.D.; Schowe, D.M.; Kucher, A.S. Does Enrichment Improve Reptile Welfare? Leopard Geckos (Eublepharis macularius) Respond to Five Types of Environmental Enrichment. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 184, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, M.; Fuller, G.; Allard, S. Effects of Habitat Modifications on Behavioral Indicators of Welfare for Madagascar Giant Hognose Snakes (Leioheterodon madagascariensis). Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2020, 7, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monreal-Pawlowsky, T.; Vaicekauskaitė, R.; Palencia Membrive, G.; Delfour, F.; Manteca, X. Goal-Oriented Behavioural and Environmental Enrichment in Aquarium Species. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2021, 9, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, S.R.; Brereton, J.E. Sixty Years of Collection Planning: What Species Do Zoos and Aquariums Keep? Int. Zoo Yearb. 2020, 54, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler-Finn, K.; Boyer, S.L.; Ikagawa, R.; Jeffries, T.; Kahn, P.C.; Larsen, E.M.; Lee, D.; Sasson, D.; Smeester, M. Qualitative and Quantitative Comparisons of Mating Behaviour across Multiple Populations and Six Species of Leiobunine Harvestmen (Arachnida: Opiliones). Behaviour 2019, 156, 363–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Torres, A.; Sánchez-Guillén, R.A.; Cordero-Rivera, A. Alternative Reproductive Strategies in Black-Winged Territorial Males of Paraphlebia zoe (Odonata, Thaumatoneuridae). PeerJ 2019, 7, e6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melfi, V.A. There Are Big Gaps in Our Knowledge, and Thus Approach, to Zoo Animal Welfare: A Case for Evidence-Based Zoo Animal Management. Zoo Biol. 2009, 28, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, P.E.; Brereton, J.E.; Rowden, L.J.; de Figueiredo, R.L.; Riley, L.M. What’s New from the Zoo? An Analysis of Ten Years of Zoo-Themed Research Output. Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemelsfelder, F.; Haskell, M.; Mendl, M.T.; Calvert, S.; Lawrence, A.B. Diversity of Behaviour during Novel Object Tests Is Reduced in Pigs Housed in Substrate-Impoverished Conditions. Anim. Behav. 2000, 60, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, L.A.; Lay, D.C.; Eicher, S.D.; Johnson, A.K.; Richert, B.T.; Pajor, E.A. Group Space Allowance Has Little Effect on Sow Health, Productivity, or Welfare in a Free-Access Stall System1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 2554–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

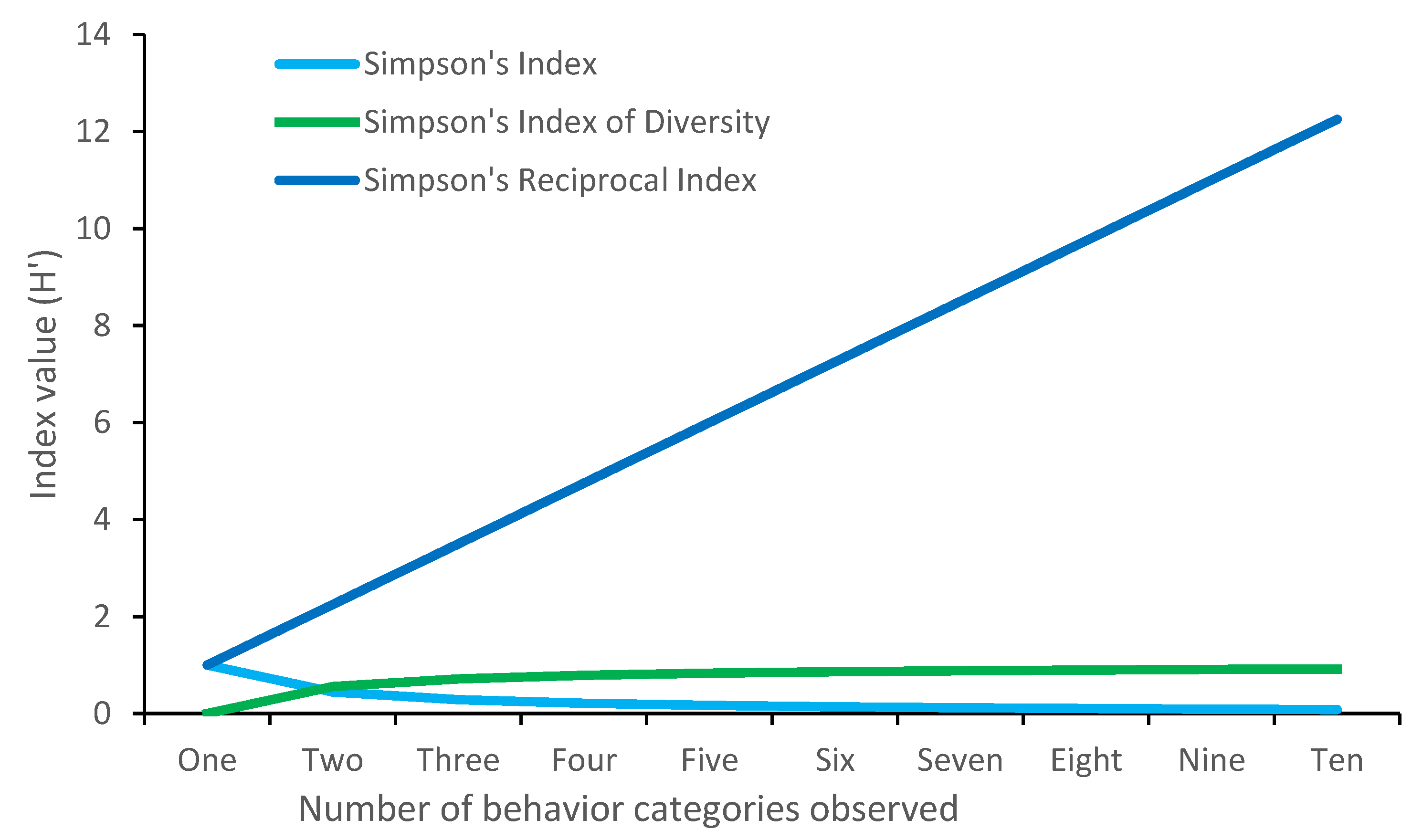


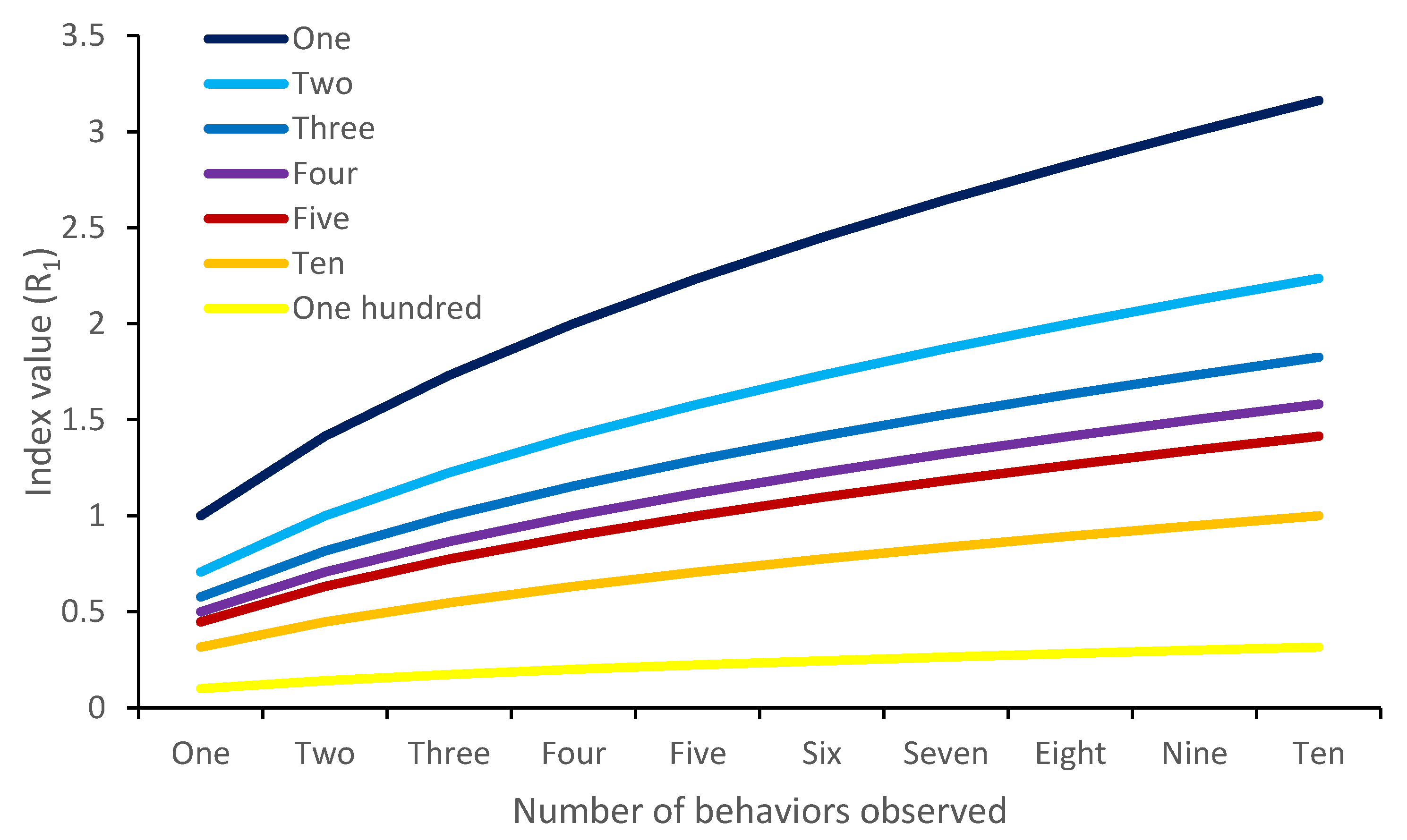
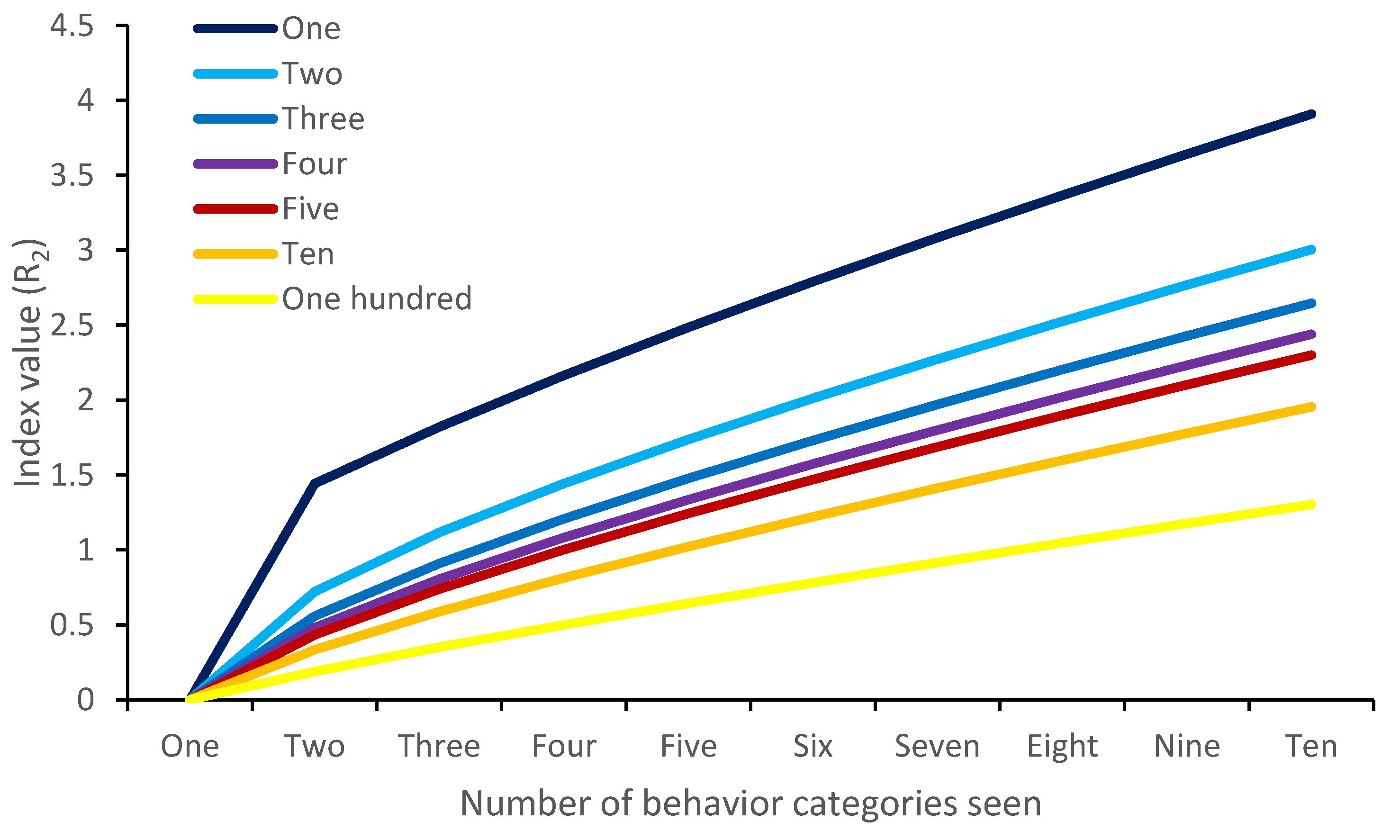

| Taxon | Shannon–Wiener | Richness | Behavioral Variety | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphibians | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Birds | 1 | 11 | 1 | 13 |
| Fish | 3 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| Invertebrates | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Mammals | 67 | 16 | 1 | 84 |
| Reptiles | 8 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Total | 79 | 31 | 2 | 112 |
| Does the Index Take Into Account: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Behaviors | Evenness of Behaviors | Number of Observations | Notes | |
| Shannon–Wiener | Yes | Yes | No | Based on proportion data. |
| Simpson’s | Yes | Yes | Yes | Not based on proportions, considers evenness. |
| Menhinick’s | Yes | No | Yes | Evenness not considered by this index. |
| Margalef | Yes | No | Yes | Evenness not considered by the index. |
| Chao | Yes | No | Yes | Used for estimating the number of missing behavior categories. |
| Behavioral Variety Index | Yes | No | No | Developed for comparing captive animal behavior against wild-type behavior. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brereton, J.E.; Fernandez, E.J. Investigating Unused Tools for the Animal Behavioral Diversity Toolkit. Animals 2022, 12, 2984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12212984
Brereton JE, Fernandez EJ. Investigating Unused Tools for the Animal Behavioral Diversity Toolkit. Animals. 2022; 12(21):2984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12212984
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrereton, James Edward, and Eduardo J. Fernandez. 2022. "Investigating Unused Tools for the Animal Behavioral Diversity Toolkit" Animals 12, no. 21: 2984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12212984
APA StyleBrereton, J. E., & Fernandez, E. J. (2022). Investigating Unused Tools for the Animal Behavioral Diversity Toolkit. Animals, 12(21), 2984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12212984







