Evidence of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in Dogs and Cats from Households and Animal Shelters in Korea
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Virus and Cells
2.3. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Reverse-Transcription Real-Time qPCR
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test (PRNT)
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Oropharyngeal and Nasal Samples of Dogs and Cats
3.2. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody in Serum Samples of Dogs and Cats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ORF3a | N | IPC | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | + | + | +/− | COVID-19 |
| + | − | +/− | COVID-19 | |
| − | + | +/− | Invalid or Potential COVID-19 | |
| − | − | + | Negative | |
| Positive Control | + | + | + | Valid |
| Negative Control | − | − | + | Valid |
| Risk Factor | Dogs | Cats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. + (Total) | % | p | No. + (Total) | % | p | |
| Household | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||||
| COVID+ | 2 (2) | 100% | 5 (5) | 100% | ||
| COVID− | 11 (538) | 2.05% | 11 (318) | 3.46% | ||
| Animal Shelter | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||||
| COVID+ | 0 (0) | 0% | 0 (0) | 0% | ||
| COVID− | 3 (132) | 2.27% | 2 (23) | 8.70% | ||
| Sex | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||||
| Male | 10 (317) | 3.16% | 9 (162) | 5.56% | ||
| Female | 6 (355) | 1.69% | 9 (184) | 4.89% | ||
| Age (years) | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||||
| <1 | 0 (40) | 0.00% | 1 (16) | 6.25% | ||
| 1–3 | 7 (233) | 3.00% | 11 (147) | 7.48% | ||
| 4–7 | 4 (246) | 1.63% | 3 (98) | 3.06% | ||
| 8+ | 3 (102) | 2.94% | 2 (67) | 2.99% | ||
| Unknown | 2 (51) | 3.92% | 1 (18) | 5.56% | ||
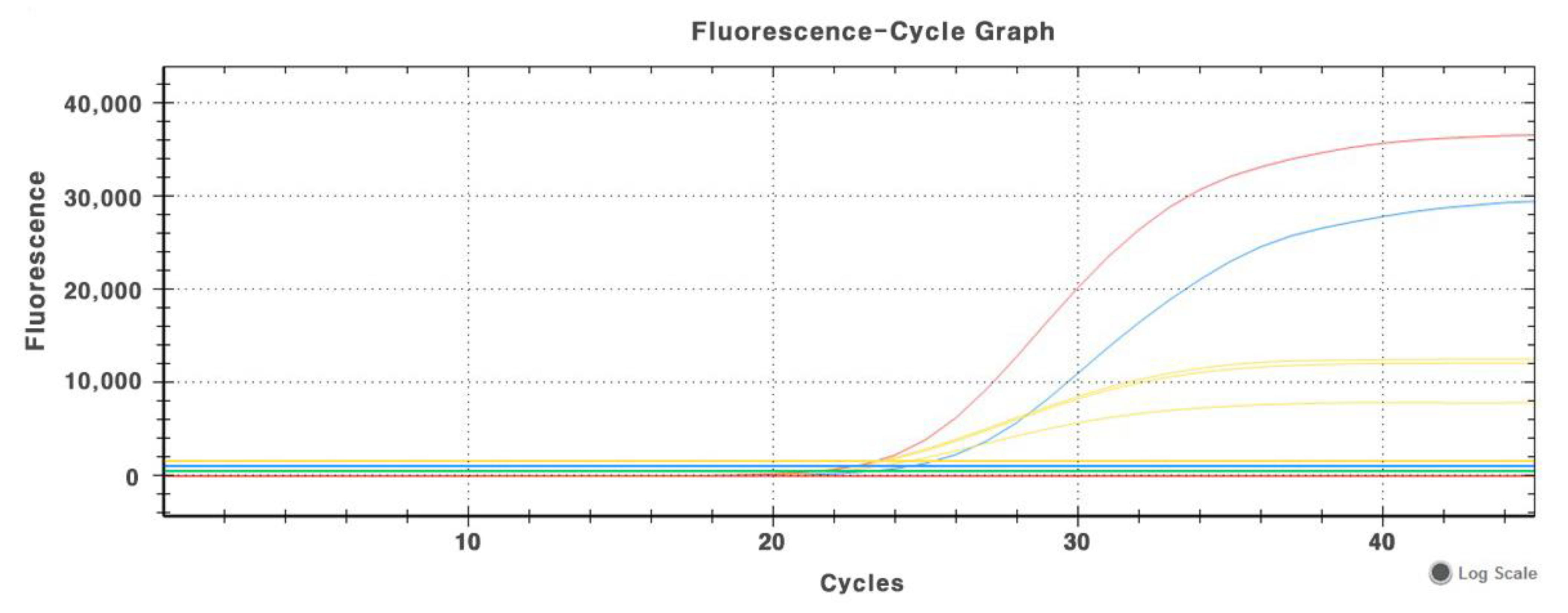
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 31 June 2022).
- World Organisation for Animal Health. COVID-19 Portal. Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2022/08/sars-cov-2-situation-report-15.pdf (accessed on 31 June 2022).
- Hobbs, E.C.; Reid, T.J. Animals and SARS-CoV-2: Species susceptibility and viral transmission in experimental and natural conditions, and the potential implications for community transmission. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1850–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, T.; Sunghan, J.; Laochareonsuk, W.; Surasombatpattana, S.; Kongkamol, C.; Ingviya, T.; Siripaitoon, P.; Kositpantawong, N.; Kanchanasuwan, S.; Hortiwakul, T.; et al. Suspected Cat-to-Human Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Thailand, July-September 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Munnink, B.B.; Sikkema, R.S.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Molenaar, R.J.; Munger, E.; Molenkamp, R.; van der Spek, A.; Tolsma, P.; Rietveld, A.; Brouwer, M.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans. Science 2021, 371, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, S.A.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Zecca, I.B.; Davila, E.; Auckland, L.D.; Roundy, C.M.; Tang, W.; Torchetti, M.K.; Killian, M.L.; Jenkins-Moore, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Viral Isolations among Serially Tested Cats and Dogs in Households with Infected Owners in Texas, USA. Viruses 2021, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, E.I.; Elia, G.; Grassi, A.; Giordano, A.; Desario, C.; Medardo, M.; Smith, S.L.; Anderson, E.R.; Prince, T.; Patterson, G.T.; et al. Evidence of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs from households in Italy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y.; Hui, X.; He, X.; Li, C.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A serological survey of SARS-CoV-2 in cat in Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, K.; Hu, C.; Hui, X.; He, X.; Li, C.; Gong, W.; Lv, C.; et al. A serological survey of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in dogs in Wuhan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Vale, B.; Lopes, A.P.; Fontes, M.D.C.; Silvestre, M.; Cardoso, L.; Coelho, A.C. Bats, pangolins, minks and other animals—Villains or victims of SARS-CoV-2. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E-Index. E-Indicators in South Korea. Available online: http://www.index.go.kr/main.do (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Sereme, Y.; Medkour, H.; Watier-Grillot, S.; Scandola, P.; Ginesta, J.; Andréo, V.; Labarde, C.; Comtet, L.; Pourquier, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibodies seroprevalence in dogs from France using ELISA and an automated western blotting assay. One Health 2021, 13, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.A.; Mok, C.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Lv, H.; Ko, R.L.; Wu, N.C.; Yuan, M.; Leung, W.S.; Chan, J.M.; Chik, T.S.; et al. Serological assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), March 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Chakraborti, S.; He, Y.; Roberts, A.; Sheahan, T.; Xiao, X.; Hensley, L.E.; Prabakaran, P.; Rockx, B.; Sidorov, I.A.; et al. Potent cross-reactive neutralization of SARS coronavirus isolates by human monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12123–12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, K.R.; Coombes, N.S.; Gagnon, L.; McInroy, L.; Baker, N.; Shaik, I.; St-Jean, J.R.; St-Amant, N.; Buttigieg, K.R.; Humphries, H.E.; et al. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody by wild-type plaque reduction neutralization, microneutralization and pseudotyped virus neutralization assays. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3114–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprent, P. Fisher Exact Test. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Lovric, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.F.; Morales, V.; Dunn, S.L.; Godde, K.; Weaver, P.F. Pearson’s and Spearman’s Correlation. In An Introduction to Statistical Analysis in Research: With Applications in the Biological and Life Sciences; Weaver, K.F., Morales, V., Dunn, S.L., Godde, K., Weaver, P.F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H.; Ly, H. What are the risk levels of humans contracting SARS-CoV-2 from pets and vice versa? J. Med. Virol. 2022. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienzle, D.; Rousseau, J.; Marom, D.; MacNicol, J.; Jacobson, L.; Sparling, S.; Prystajecky, N.; Fraser, E.; Weese, J.S. Risk Factors for SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Illness in Cats and Dogs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.I.P.; de Brito, R.N.; Gontijo, C.C.; Romero, G.A.S.; Ramalho, W.M.; Haddad, R.; Noronha, E.F.; de Araújo, W.N. The role of pets in SARS-CoV-2 transmission: An exploratory analysis. Infection 2022, 1–4, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, R.; Vieira-Pires, A.; Antunes, A.; Fidalgo-Carvalho, I. Susceptibility of Pets to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Lessons from a Seroepidemiologic Survey of Cats and Dogs in Portugal. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Arévalo, S.; Barneto, A.; Ramos, Á.M.; Rivera, B.; Sánchez, R.; Sánchez-Morales, L.; Pérez-Sancho, M.; Buendía, A.; Ferreras, E.; Ortiz-Menéndez, J.C.; et al. Large-scale study on virological and serological prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs in Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e759–e774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessière, P.; Vergne, T.; Battini, M.; Brun, J.; Averso, J.; Joly, E.; Guérin, J.L.; Cadiergues, M.C. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Companion Animals: Prospective Serological Survey and Risk Factor Analysis in France. Viruses 2022, 14, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, L.; de Martinis, C.; Brandi, S.; Levante, M.; Cozzolino, L.; Spadari, L.; Boccia, F.; Carbone, C.; Pompameo, M.; Fusco, G. SARS-CoV-2 Serological and Biomolecular Analyses among Companion Animals in Campania Region (2020–2021). Microorganisms 2022, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannekens-Jager, M.M.; de Rooij, M.M.T.; de Groot, Y.; Biesbroeck, E.; de Jong, M.K.; Pijnacker, T.; Smit, L.A.M.; Schuurman, N.; Broekhuizen-Stins, M.J.; Zhao, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in dogs and cats is associated with contact to COVID-19-positive household members. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczorek-Łukowska, E.; Wernike, K.; Beer, M.; Wróbel, M.; Małaczewska, J.; Mikulska-Skupień, E.; Malewska, K.; Mielczarska, I.; Siwicki, A.K. High Seroprevalence against SARS-CoV-2 among Dogs and Cats, Poland, 2021/2022. Animals 2022, 12, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAloose, D.; Laverack, M.; Wang, L.; Killian, M.L.; Caserta, L.C.; Yuan, F.; Mitchell, P.K.; Queen, K.; Mauldin, M.R.; Cronk, B.D.; et al. From People to Panthera: Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Tigers and Lions at the Bronx Zoo. Mbio 2020, 11, e02220-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Hartwig, A.E.; Porter, S.M.; Gordy, P.W.; Nehring, M.; Byas, A.D.; VandeWoude, S.; Ragan, I.K.; Maison, R.M.; Bowen, R.A. Experimental infection of domestic dogs and cats with SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenesis, transmission, and response to reexposure in cats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26382–26388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Liu, R.; He, X.; Shuai, L.; Sun, Z.; et al. Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS-coronavirus 2. Science 2020, 368, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.; Smith, D.; Ghai, R.R.; Wallace, R.M.; Torchetti, M.K.; Loiacono, C.; Murrell, L.S.; Carpenter, A.; Moroff, S.; Rooney, J.A.; et al. First Reported Cases of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Companion Animals—New York, March–April 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sit, T.H.C.; Brackman, C.J.; Ip, S.M.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; To, E.M.W.; Yu, V.Y.T.; Sims, L.D.; Tsang, D.N.C.; Chu, D.K.W.; et al. Infection of dogs with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 586, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmam, S.; Barbarino, A.; Maso, D.; Behillil, S.; Enouf, V.; Huon, C.; Jaraud, A.; Chevallier, L.; Backovic, M.; Pérot, P.; et al. Absence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in cats and dogs in close contact with a cluster of COVID-19 patients in a veterinary campus. One Health 2020, 10, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, A.E.; André, N.M.; Jaimes, J.A.; Millet, J.K.; Whittaker, G.R. Coronaviruses in cats and other companion animals: Where does SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 fit? Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 247, 108777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N.; Grassi, A.; Lorusso, E.; Patterson, E.I.; Lorusso, A.; Desario, C.; Anderson, E.R.; Vasinioti, V.; Wastika, C.E.; Hughes, G.L.; et al. Long-term persistence of neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in pets. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3073–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.J.; Albery, G.F.; Merow, C.; Trisos, C.H.; Zipfel, C.M.; Eskew, E.A.; Olival, K.J.; Ross, N.; Bansal, S. Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk. Nature 2022, 607, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggel, C.; Bouwer, L.M.; Juhola, S.; Mechler, R.; Muccione, V.; Orlove, B.; Wallimann-Helmer, I. The existential risk space of climate change. Clim. Change 2022, 174, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
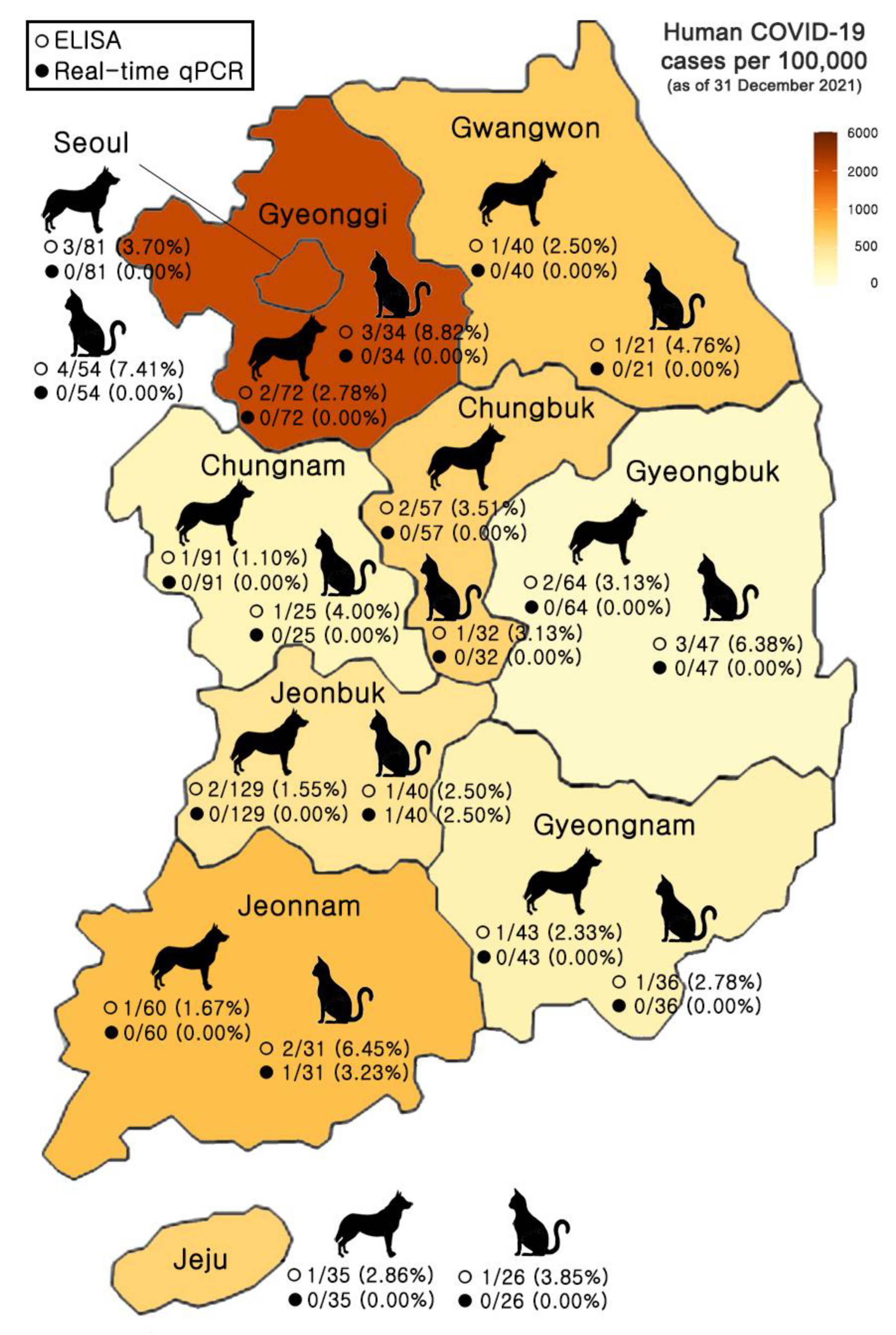

| Region (Province) | Type | qPCR | Total (%) | ELISA | Total (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dogs (%) | Cats (%) | Dogs (%) | Cats (%) | ||||
| Seoul | Households | 0/81 (0.00) | 0/54 (0.00) | 0/135 (0.00) | 3/81 (3.70) | 4/54 (7.41) | 7/135 (5.19) |
| Animal Shelters | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gyeonggi | Households | 0/58 (0.00) | 0/31 (0.00) | 0/89 (0.00) | 1/58 (1.72) | 3/31 (9.68) | 4/89 (4.49) |
| Animal Shelters | 0/14 (0.00) | 0/3 (0.00) | 0/17 (0.00) | 1/14 (7.14) | 0/3 (0.00) | 1/17 (5.88) | |
| Gangwon | Households | 0/40 (0.00) | 0/21 (0.00) | 0/61 (0.00) | 1/40 (2.50) | 1/21 (4.76) | 2/61 (3.28) |
| Animal Shelters | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chungbuk | Households | 0/57 (0.00) | 0/32 (0.00) | 0/89 (0.00) | 2/57 (3.51) | 1/32 (3.13) | 3/89 (3.37) |
| Animal Shelters | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chungnam | Households | 0/91 (0.00) | 0/25 (0.00) | 0/116 (0.00) | 1/91 (1.10) | 1/25 (4.00) | 2/116 (1.72) |
| Animal Shelters | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gyeonbuk | Households | 0/40 (0.00) | 0/37 (0.00) | 0/77 (0.00) | 1/40 (2.50) | 1/37 (2.70) | 2/77 (2.60) |
| Animal Shelters | 0/24 (0.00) | 0/10 (0.00) | 0/34 (0.00) | 1/24 (4.17) | 2/10 (20.00) | 3/34 (8.82) | |
| Gyeongnam | Households | 0/43 (0.00) | 0/36 (0.00) | 0/79 (0.00) | 1/43 (2.33) | 1/36 (2.78) | 2/79 (2.53) |
| Animal Shelters | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Jeonbuk | Households | 0/56 (0.00) | 1/35 (2.86) | 1/91 (1.10) | 1/56 (1.79) | 1/35 (2.86) | 2/91 (2.20) |
| Animal Shelters | 0/73 (0.00) | 0/5 (0.00) | 0/78 (0.00) | 1/73 (1.37) | 0/5 (0.00) | 1/78 (1.28) | |
| Jeonnam | Households | 0/39 (0.00) | 1/26 (6.25) | 1/65 (1.82) | 1/39 (2.56) | 2/26 (7.69) | 3/65 (4.62) |
| Animal Shelters | 0/21 (0.00) | 0/5 (0.00) | 0/26 (0.00) | 0/21 (0.00) | 0/5 (0.00) | 0/26 (0.00) | |
| Jeju | Households | 0/35 (0.00) | 0/26 (0.00) | 0/61 (0.00) | 1/35 (2.86) | 1/26 (3.85) | 2/61 (3.28) |
| Animal Shelters | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Subtotal | Households | 0/540 (0.00) | 2/323 (0.62) | 2/863 (0.23) | 13/540 (2.41) | 16/323 (4.95) | 29/863 (3.36) |
| Animal Shelters | 0/132 (0.00) | 0/23 (0.00) | 0/155 (0.00) | 3/132 (2.27) | 2/23 (8.70) | 5/155 (3.23) | |
| Total | 0/672 (0.00) | 2/346 (0.61) | 2/1018 (0.20) | 16/672 (2.38) | 18/346 (5.20) | 34/1018 (3.34) | |
| No. | qPCR (Ct) | ELISA | PRNT | Background of Animal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORF3a | N Gene | (OD450) | Neutralization Titer | Species | Sex | Age (year) | Province | Source | COVID-19 Patient Owner | |
| 1 | >40 | >40 | 0.7340 | 1/33 | Cat | F | 3 | Seoul | Household | No |
| 2 | >40 | >40 | 0.6376 | 1/24 | Dog | M | 8 | Seoul | Household | No |
| 3 | >40 | >40 | 0.9325 | 1/24 | Cat | M | 9 | Seoul | Household | Yes |
| 4 | >40 | >40 | 1.4351 | 1/45 | Dog | M | 5 | Seoul | Household | No |
| 5 | >40 | >40 | 1.2310 | 1/45 | Cat | M | 1 | Seoul | Household | No |
| 6 | >40 | >40 | 0.6832 | 1/33 | Cat | F | 4 | Seoul | Household | No |
| 7 | >40 | >40 | 0.7138 | 1/24 | Dog | F | 2 | Seoul | Household | No |
| 8 | >40 | >40 | 0.6241 | 1/33 | Cat | M | 1 | Gyeonggi | Household | No |
| 9 | >40 | >40 | 0.6968 | 1/24 | Dog | F | 3 | Gyeonggi | Household | No |
| 10 | >40 | >40 | 0.7120 | 1/33 | Cat | F | 3 | Gyeonggi | Household | Yes |
| 11 | >40 | >40 | 0.9221 | 1/45 | Cat | M | 4 | Gyeonggi | Household | No |
| 12 | >40 | >40 | 0.6793 | 1/24 | Dog | M | Unknown | Gyeonggi | Animal shelter | No |
| 13 | >40 | >40 | 0.7418 | 1/24 | Dog | M | 4 | Gangwon | Household | No |
| 14 | >40 | >40 | 0.6274 | >1/5 | Cat | F | 2 | Gangwon | Household | No |
| 15 | >40 | >40 | 1.2123 | 1/33 | Cat | F | 3 | Chungbuk | Household | No |
| 16 | >40 | >40 | 1.8163 | 1/45 | Dog | M | 8 | Chungbuk | Household | Yes |
| 17 | >40 | >40 | 1.4465 | 1/33 | Dog | M | 9 | Chungbuk | Household | No |
| 18 | >40 | >40 | 0.6275 | >1/5 | Dog | M | 5 | Chungnam | Household | No |
| 19 | >40 | >40 | 0.9278 | 1/33 | Cat | M | 4 | Chungnam | Household | No |
| 20 | >40 | >40 | 0.6431 | 1/24 | Cat | M | 1 | Gyeongbuk | Household | Yes |
| 21 | >40 | >40 | 0.8537 | 1/33 | Dog | F | 2 | Gyeongbuk | Household | No |
| 22 | >40 | >40 | 1.1062 | 1/33 | Dog | M | Unknown | Gyeongbuk | Animal shelter | No |
| 23 | >40 | >40 | 1.2013 | 1/33 | Cat | F | 1 | Gyeongbuk | Animal shelter | No |
| 24 | >40 | >40 | 1.0152 | 1/24 | Cat | F | Unknown | Gyeongbuk | Animal shelter | No |
| 25 | >40 | >40 | 0.9312 | 1/24 | Dog | F | 1 | Gyeongnam | Household | No |
| 26 | >40 | >40 | 1.1136 | 1/33 | Cat | M | 8 | Gyeongnam | Household | No |
| 27 | >40 | >40 | 0.8532 | 1/33 | Dog | M | 2 | Jeonbuk | Household | Yes |
| 28 | 24.241 | 24.316 | 1.5630 | 1/24 | Cat | M | 2 | Jeonbuk | Household | Yes |
| 29 | >40 | >40 | 0.7381 | 1/33 | Dog | F | 1 | Jeonbuk | Animal shelter | No |
| 30 | 29.853 | 29.472 | 1.5422 | 1/24 | Cat | F | 3 | Jeonnam | Household | Yes |
| 31 | >40 | >40 | 0.8922 | >1/5 | Dog | F | 1 | Jeonnam | Household | No |
| 32 | >40 | >40 | 0.9273 | 1/33 | Cat | M | 3 | Jeonnam | Household | No |
| 33 | >40 | >40 | 1.4685 | 1/24 | Dog | M | 4 | Jeju | Household | No |
| 34 | >40 | >40 | 0.9014 | 1/33 | Cat | F | 2 | Jeju | Household | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, D.-Y.; Tark, D.; Moon, S.-H.; Oem, J.-K.; Kim, W.-I.; Park, C.; Na, K.-J.; Park, C.-K.; Oh, Y.; Cho, H.-S. Evidence of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in Dogs and Cats from Households and Animal Shelters in Korea. Animals 2022, 12, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202786
Bae D-Y, Tark D, Moon S-H, Oem J-K, Kim W-I, Park C, Na K-J, Park C-K, Oh Y, Cho H-S. Evidence of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in Dogs and Cats from Households and Animal Shelters in Korea. Animals. 2022; 12(20):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202786
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Da-Yun, Dongseob Tark, Sung-Hyun Moon, Jae-Ku Oem, Won-Il Kim, Chul Park, Ki-Jeong Na, Choi-Kyu Park, Yeonsu Oh, and Ho-Seong Cho. 2022. "Evidence of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in Dogs and Cats from Households and Animal Shelters in Korea" Animals 12, no. 20: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202786
APA StyleBae, D.-Y., Tark, D., Moon, S.-H., Oem, J.-K., Kim, W.-I., Park, C., Na, K.-J., Park, C.-K., Oh, Y., & Cho, H.-S. (2022). Evidence of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in Dogs and Cats from Households and Animal Shelters in Korea. Animals, 12(20), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202786








