Comparative Analyses of the Gut Microbiota in Growing Ragdoll Cats and Felinae Cats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Fecal DNA Extraction
2.4. PCR Amplification and Next-Generation Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
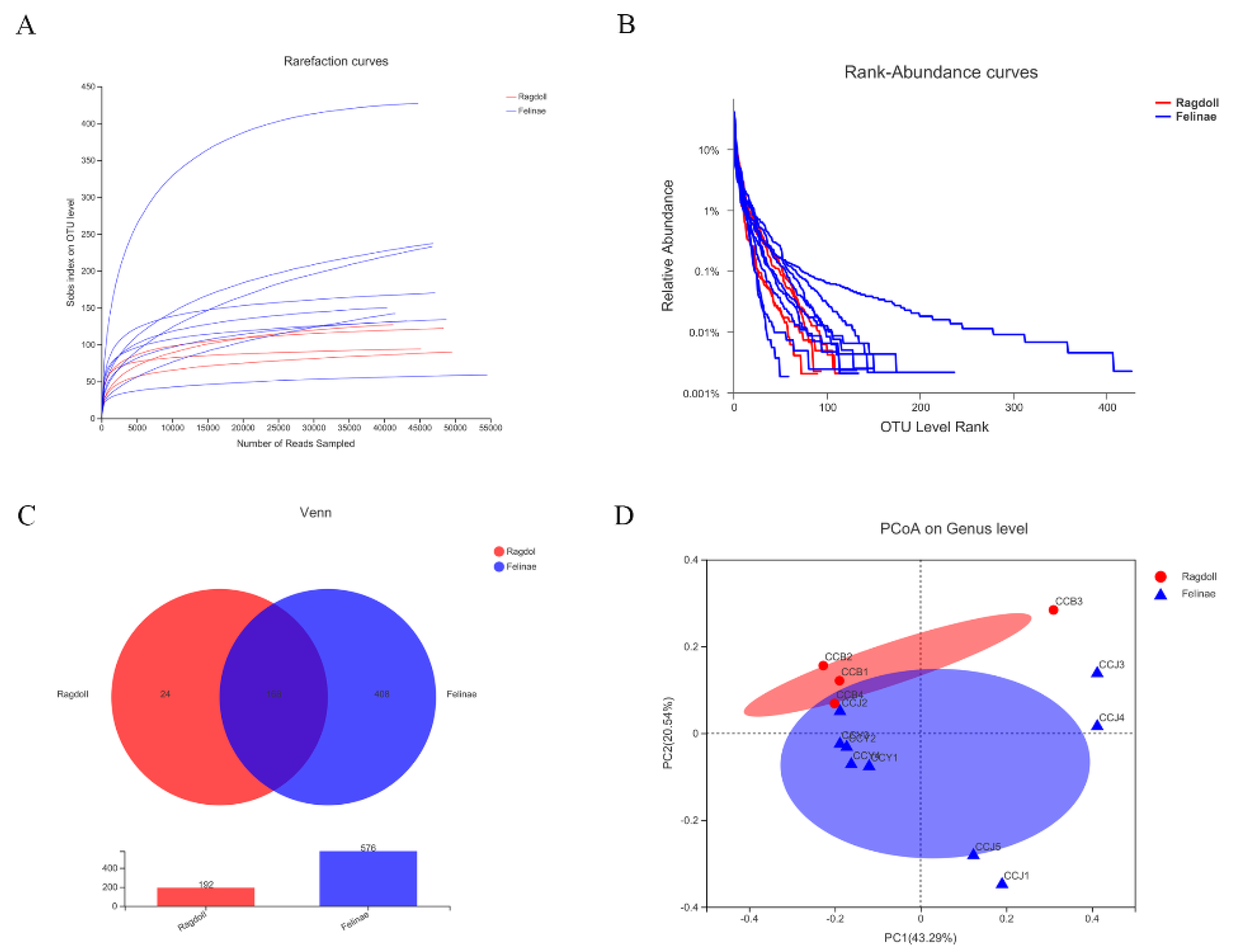
3.1. OTUs Clustering
3.2. Microbial Diversity Analysis of the Feline Gut Microbiota
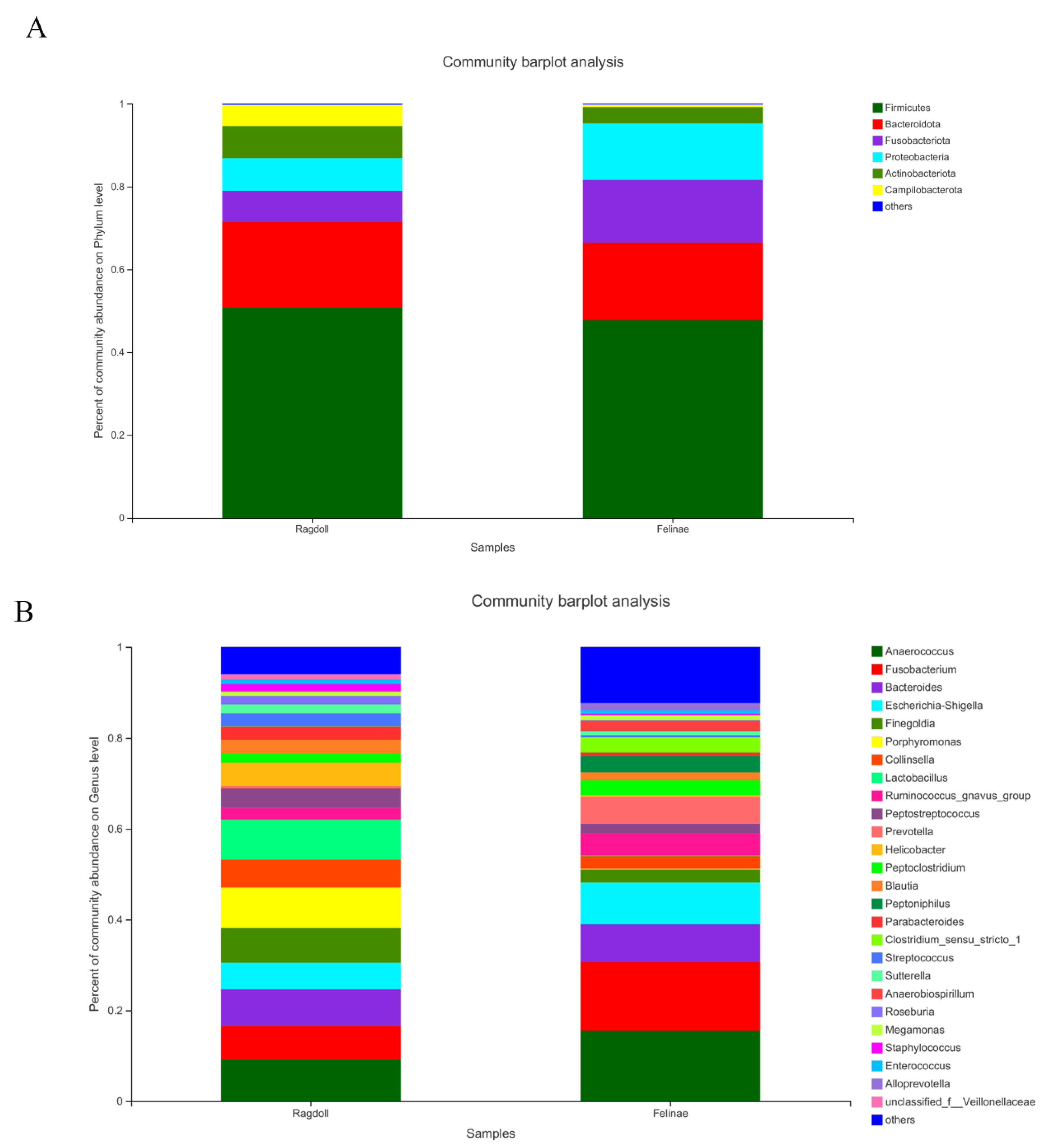
3.3. Microbial Compositions of the Feline Gut Microbiota
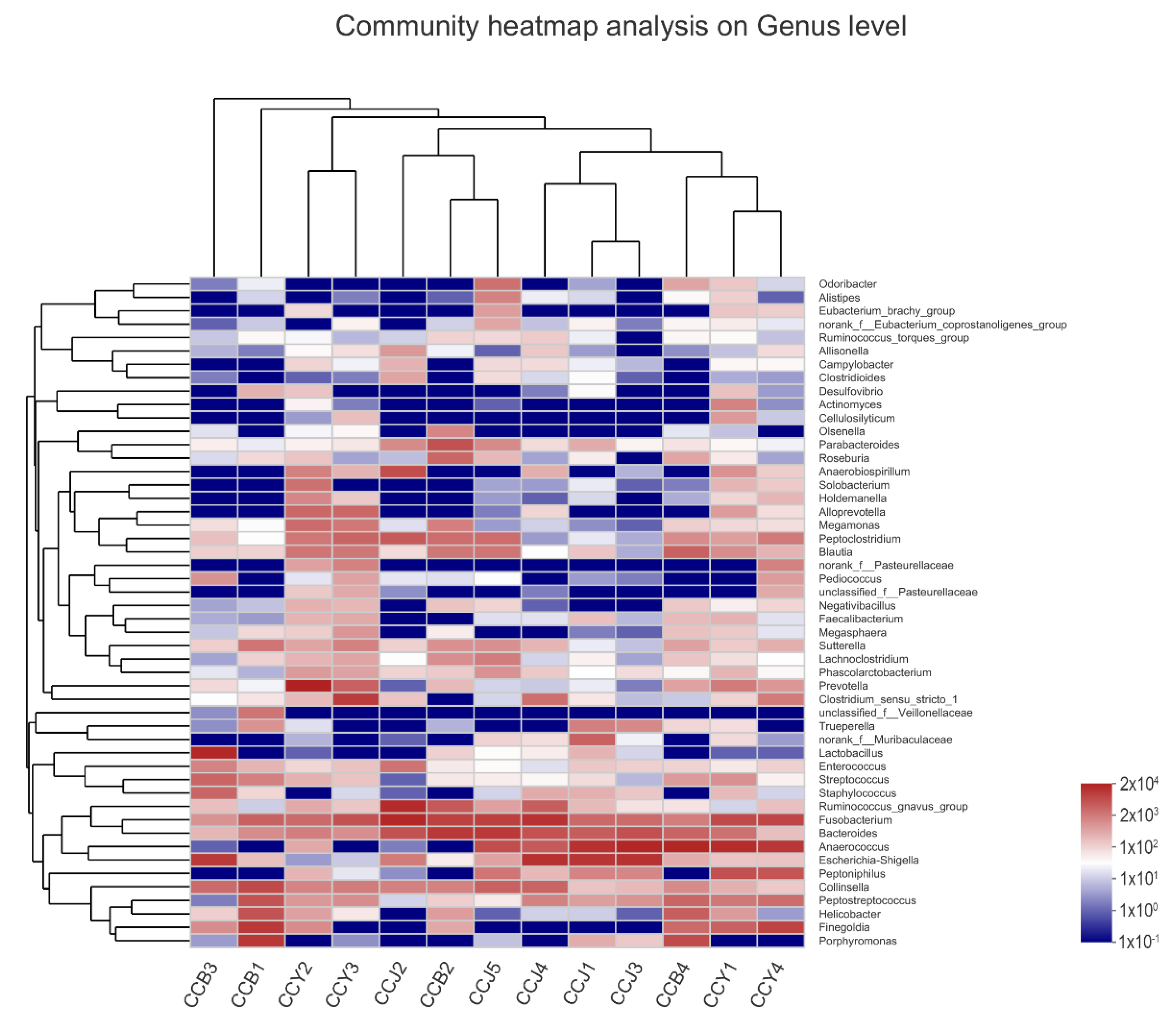
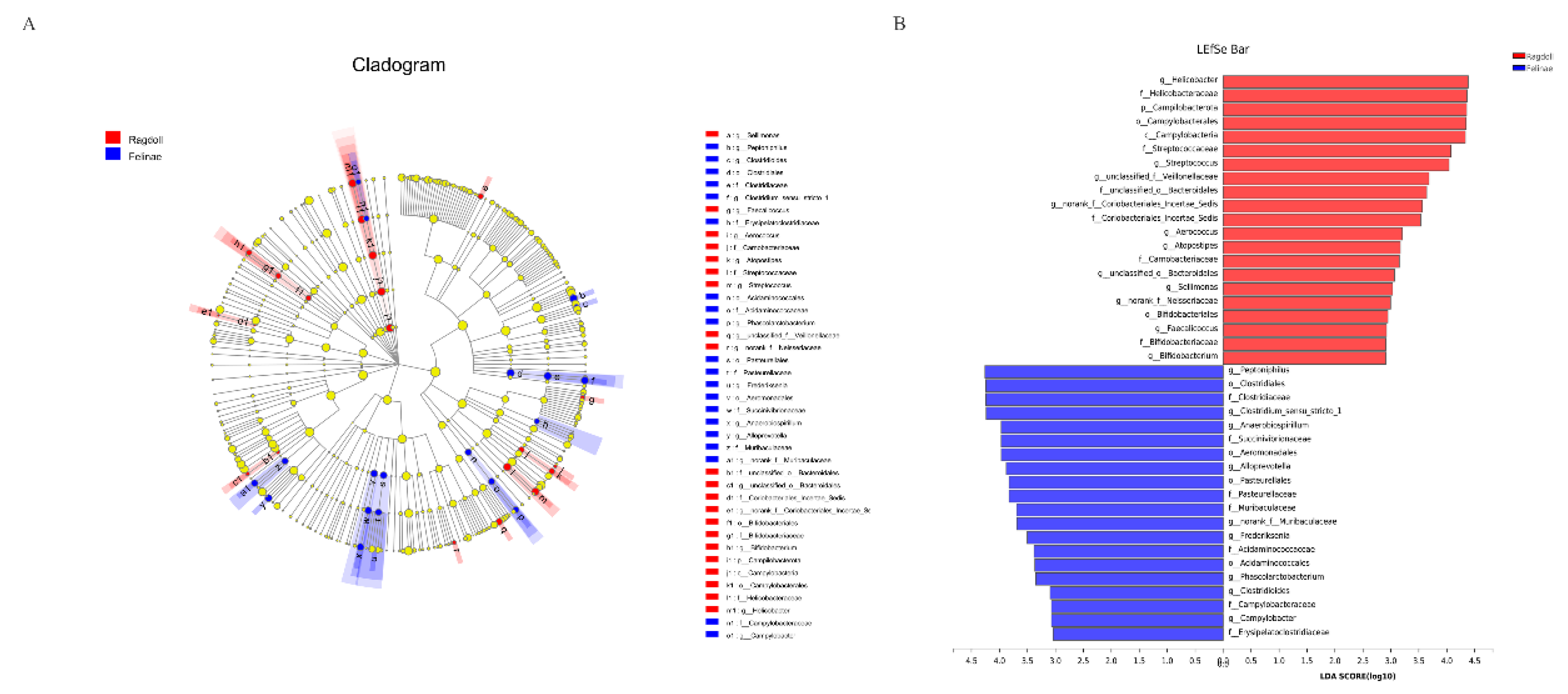
3.4. Comparison of Feline Gut Microbial Communities
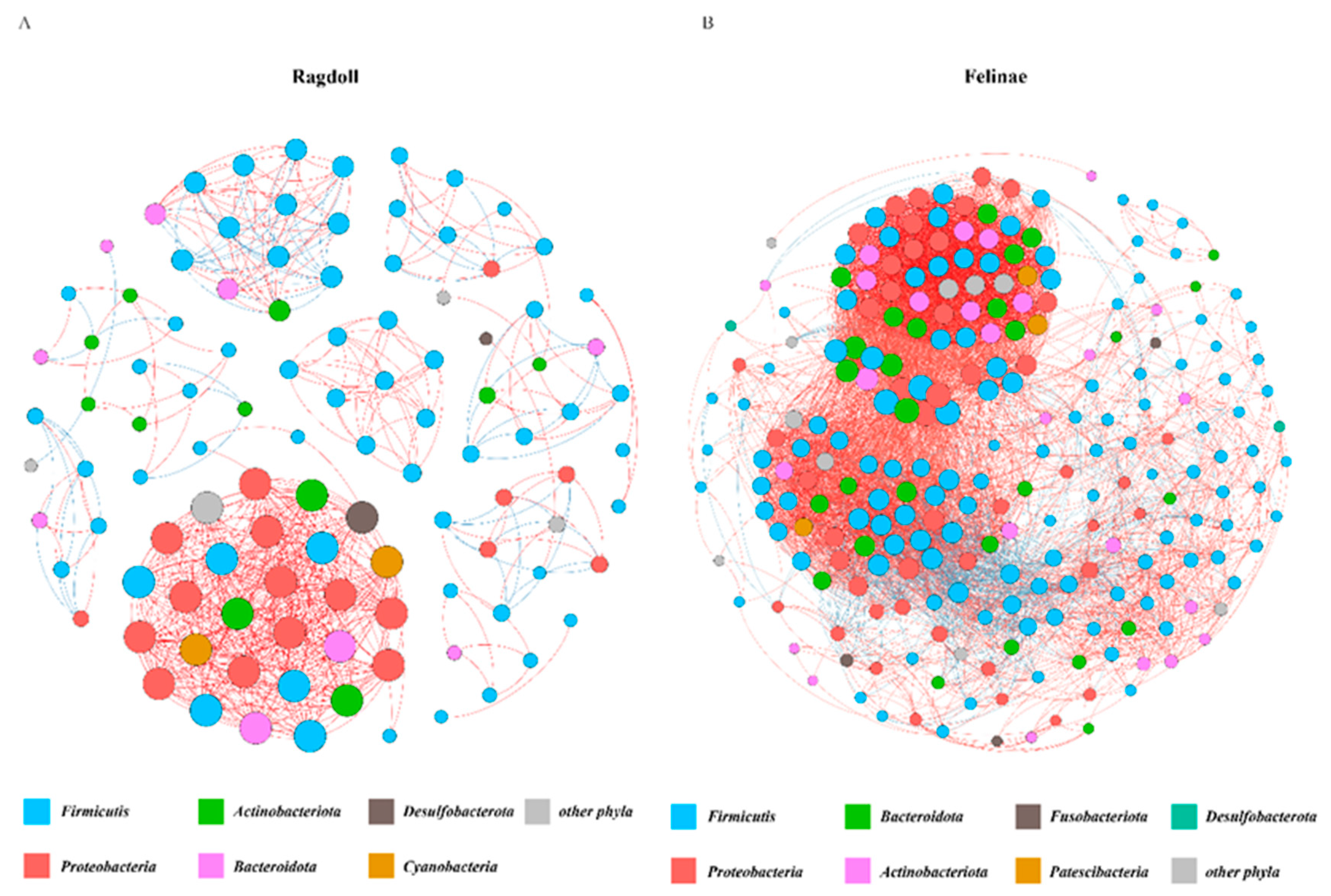
3.5. Co-Occurrence Network of the Feline Gut Microbiota
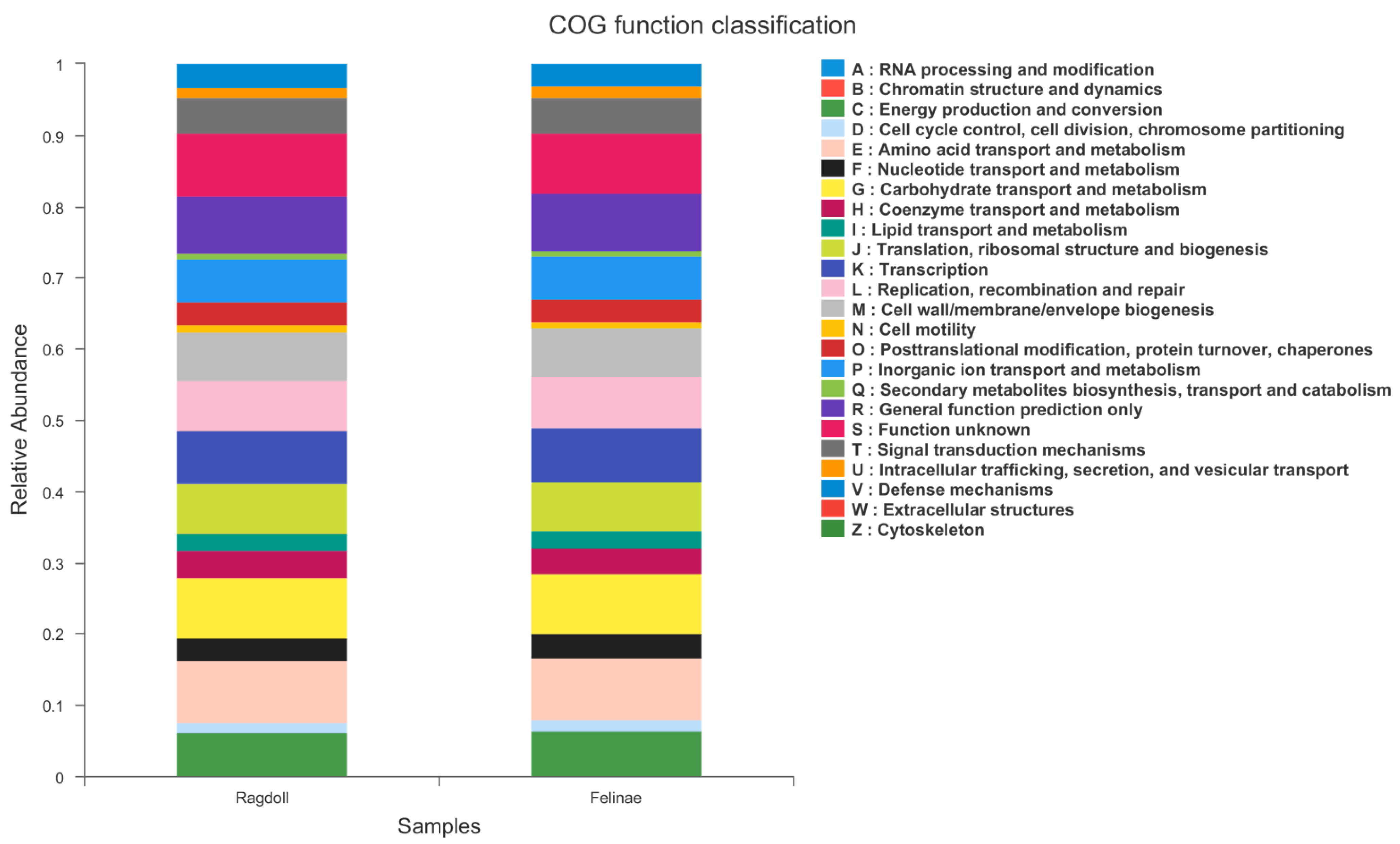
3.6. PICRUSt Functional Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forrest, R.; Awawdeh, L.; Esam, F.; Pearson, M.; Waran, N. The diets of companion cats in aotearoa new zealand: Identification of obesity risk factors. Animals 2021, 11, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesch, R.; Kitchener, A.; Hantke, G.; Kotrschal, K.; Fitch, W.T. Cranial volume and palate length of cats, Felis spp., under domestication, hybridization and in wild populations. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 210477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkola, S.; Salonen, M.; Hakanen, E.; Sulkama, S.; Lohi, H. Reliability and Validity of Seven Feline Behavior and Personality Traits. Animals 2021, 11, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tun, H.M.; Konya, T.; Takaro, T.K.; Brook, J.R.; Chari, R.; Field, C.J.; Guttman, D.S.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; et al. Exposure to household furry pets influences the gut microbiota of infant at 3–4 months following various birth scenarios. Microbiome 2017, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, P.L.; Commodore, S.; Neelon, B.; Cobbs, J.; Sciscione, A.C.; Grobman, W.A.; Newman, R.B.; Tita, A.T.; Nageotte, M.P.; Palomares, K.; et al. Early Exposure to Animals and Childhood Body Mass Index Percentile and Percentage Fat Mass. Child Adolesc. Obes. 2022, 5, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Sitarik, A.R.; Woodcroft, K.; Johnson, C.C.; Zoratti, E. Birth Mode, Breastfeeding, Pet Exposure, and Antibiotic Use: Associations with the Gut Microbiome and Sensitization in Children. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiainen, T.; Paalanne, N.; Tejesvi, M.V.; Koivusaari, P.; Korpela, K.; Pokka, T.; Salo, J.; Kaukola, T.; Pirttilä, A.M.; Uhari, M.; et al. Maternal influence on the fetal microbiome in a population-based study of the first-pass meconium. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kates, A.E.; Jarrett, O.; Skarlupka, J.H.; Sethi, A.; Duster, M.; Watson, L.; Suen, G.; Poulsen, K.; Safdar, N. Household Pet Ownership and the Microbial Diversity of the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. Microbiome: Puppy power. Nature 2017, 543, S48–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Ying, L. Effects of cat ownership on the gut microbiota of owners. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Hooda, S.; Swanson, K.S.; Suchodolski, J.S. Feline gastrointestinal microbiota. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2012, 13, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, J.S. Analysis of the gut microbiome in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 50, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vientós-Plotts, A.I.; Ericsson, A.C.; Rindt, H.; Grobman, M.E.; Graham, A.; Bishop, K.; Cohn, L.A.; Reinero, C.R. Dynamic changes of the respiratory microbiota and its relationship to fecal and blood microbiota in healthy young cats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Gut Microbiome of Dogs and Cats, and the Influence of Diet. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermingham, E.N.; Young, W.; Butowski, C.F.; Moon, C.D.; Maclean, P.H.; Rosendale, D.; Cave, N.J.; Thomas, D.G. The fecal microbiota in the domestic cat (Felis catus) is influenced by interactions between age and diet; a five year Longitudinal Study. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butowski, C.F.; Moon, C.D.; Thomas, D.G.; Young, W.; Bermingham, E.N. The effects of raw-meat diets on the gastrointestinal microbiota of the cat and dog: A review. N. Z. Vet. J. 2022, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badri, D.V.; Jackson, M.I.; Jewell, D.E. Dietary Protein and carbohydrate levels affect the gut microbiota and clinical assessment in healthy adult cats. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3637–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, P.M.; Vidal, S.; Wyss, R.; Miao, Y.; Adesokan, Y.; Swanson, K.S. Effect of a novel animal milk oligosaccharide biosimilar on the gut microbial communities and metabolites of in vitro incubations using feline and canine fecal inocula. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.S. Value of probiotics in canine and feline gastroenterology. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 171–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vientós-Plotts, A.I.; Ericsson, A.C.; Rindt, H.; Reinero, C.R. Oral probiotics alter healthy feline respiratory microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grześkowiak, Ł.; Endo, A.; Beasley, S.; Salminen, S. Microbiota and probiotics in canine and feline welfare. Anaerobe 2015, 34, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavroulaki, E.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Pilla, R.; Fosgate, G.T.; Sung, C.H.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Xenoulis, P.G. Short- and long-term effects of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid or doxycycline on the gastrointestinal microbiome of growing cats. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.M.; Kessler, A.M.; Kieffer, D.A.; Knotts, T.A.; Kim, K.; Wei, A.; Ramsey, J.J.; Fascetti, A.J. Effects of obesity, energy restriction and neutering on the faecal microbiota of cats. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butowski, C.F.; Thomas, D.G.; Young, W.; Cave, N.J.; McKenzie, C.M.; Rosendale, D.I.; Bermingham, E.N. Addition of plant dietary fibre to a raw red meat high protein, high fat diet, alters the faecal bacteriome and organic acid profiles of the domestic cat (Felis catus). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgeon, A.; Pinder, S.L.; Costa, M.C.; Weese, J.S. Characterization of the oral microbiota of healthy cats using next-generation sequencing. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, E.S.; Tress, B.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Nisar, T.; Ravindran, P.; Weber, K.; Hartmann, K.; Schulz, B.S. Bacterial microbiome in the nose of healthy cats and in cats with nasal disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Guan, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, B.; Liu, K.; Shao, D.; Mi, R.; Liu, H.; et al. Analysis and comparison of gut microbiome in young detection dogs. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 872230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Jin, C.; Xie, T.; Cheng, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, N. Alterations in the fecal microbiota of patients with HIV-1 Infection: An observational study in a chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Brinker, E.; Graff, E.C.; Cao, W.; Gross, A.L.; Johnson, A.K.; Zhang, C.; Martin, D.R.; Wang, X. Whole-genome shotgun metagenomic sequencing reveals distinct gut microbiome signatures of obese cats. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 202, e00837-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuchun, Y.; Lixue, Y. Seasonal variations in soil fungal communities and co-occurrence networks along an altitudinal gradient in the cold temperate zone of China: A case study on Oakley Mountain. Catena 2021, 204, 105448. [Google Scholar]
- Tatlock, S.; Gober, M.; Williamson, N.; Arbuckle, R. Development and preliminary psychometric evaluation of an owner-completed measure of feline quality of life. Vet. J. 2017, 228, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legatzki, A.; Rösler, B.; Mutius, E. Microbiome diversity and asthma and allergy risk. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, M.; Vapalahti, K.; Tiira, K.; Mäki-Tanila, A.; Lohi, H. Breed differences of heritable behaviour traits in cats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, E.R. Elucidating the role of the host genome in shaping microbiome composition. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.D. The human microbiome. Early life determinant of health outcomes. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11 (Suppl. S1), S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.M.; Worthing, K.A.; Kulkarni, N.; Li, F.; Nakatsuji, T.; McGrosso, D.; Mills, R.H.; Kalla, G.; Cheng, J.Y.; Norris, J.M.; et al. Antimicrobials from a feline commensal bacterium inhibit skin infection by drug-resistant S. pseudintermedius. eLife 2021, 10, e66793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, G.; Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Longhi, G.; Anzalone, R.; Lugli, G.A.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; Sinderen, D.; et al. Deciphering the Bifidobacterial Populations within the Canine and Feline Gut Microbiota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02875-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Swanson, K.S. Gut microbiota of humans, dogs and cats: Current knowledge and future opportunities and challenges. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, S6–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmis, K.; Jebok, F.; Rigat, F.; De Vos, W.M.; Timmis, J.K. Microbiome yarns: Microbiomology of curly and straight hair. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Ingredients | Nutrient Composition |
|---|---|
| Crude protein | 40% |
| Crude fat | 20% |
| Crude fiber | 9.0% |
| Crude ash | 10.0% |
| Calcium | 1.0% |
| Phosphorus | 0.8% |
| Taurine | 0.2% |
| Chloride | 0.3% |
| Moisture | 10% |
| Energy | 14,585 kJ/kg |
| Amplified Region | Samples | Sequences | Bases (bp) | Average Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 338F_806R | 13 | 658,037 | 271,867,357 | 413 |
| Taxonomic Level | Taxa | Felinae (%) | Ragdoll (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Firmicutes | 47.80 | 50.83 |
| Bacteroidota | 18.66 | 20.73 | |
| Fusobacteriota | 15.16 | 7.41 | |
| Proteobacteria | 13.63 | 7.91 | |
| Actinobacteriota | 4.00 | 7.74 | |
| Campilobacterota | 0.55 | 5.14 | |
| Genus | Anaerococcus | 15.55 | 9.19 |
| Fusobacterium | 15.15 | 7.41 | |
| Bacteroides | 8.26 | 8.04 | |
| Escherichia-Shigella | 9.21 | 5.86 | |
| Finegoldia | 2.86 | 7.66 | |
| Porphyromonas | 0.15 | 8.90 | |
| Collinsella | 2.82 | 6.17 | |
| Lactobacillus | 0.12 | 8.84 | |
| Ruminococcus_gnavus_group | 4.88 | 2.51 | |
| Peptostreptococcus | 2.14 | 4.33 | |
| Prevotella | 5.93 | 0.54 | |
| Helicobacter | 0.33 | 5.14 | |
| Peptoclostridium | 3.30 | 2.07 | |
| Blautia | 1.79 | 2.99 | |
| Peptoniphilus | 3.63 | 0.00 | |
| Parabacteroides | 0.72 | 2.87 | |
| Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 | 3.33 | 0.08 | |
| Streptococcus | 0.44 | 2.80 | |
| Sutterella | 0.95 | 1.94 | |
| Anaerobiospirillum | 2.16 | 0.00 | |
| Roseburia | 0.17 | 1.92 | |
| Megamonas | 1.09 | 0.95 | |
| Staphylococcus | 0.33 | 1.68 | |
| Enterococcus | 0.74 | 1.00 | |
| Alloprevotella | 1.57 | 0.00 |
| Network Features | Ragdoll | Felinae |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Nodes | 107 | 240 |
| Number of Edges | 579 | 4932 |
| Average Degree | 10.822 | 41.1 |
| Average Path Length | 1 | 2.455 |
| Density | 0.102 | 0.172 |
| Modularity | 0.605 | 0.393 |
| Average Clustering Coefficient | 1 | 0.648 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Di, D.; Sun, Q.; Yao, X.; Wei, J.; Li, B.; Liu, K.; Shao, D.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Comparative Analyses of the Gut Microbiota in Growing Ragdoll Cats and Felinae Cats. Animals 2022, 12, 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182467
Li Z, Di D, Sun Q, Yao X, Wei J, Li B, Liu K, Shao D, Qiu Y, Liu H, et al. Comparative Analyses of the Gut Microbiota in Growing Ragdoll Cats and Felinae Cats. Animals. 2022; 12(18):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182467
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zongjie, Di Di, Qing Sun, Xiaohui Yao, Jianchao Wei, Beibei Li, Ke Liu, Donghua Shao, Yafeng Qiu, Haixia Liu, and et al. 2022. "Comparative Analyses of the Gut Microbiota in Growing Ragdoll Cats and Felinae Cats" Animals 12, no. 18: 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182467
APA StyleLi, Z., Di, D., Sun, Q., Yao, X., Wei, J., Li, B., Liu, K., Shao, D., Qiu, Y., Liu, H., Cheng, Z., & Ma, Z. (2022). Comparative Analyses of the Gut Microbiota in Growing Ragdoll Cats and Felinae Cats. Animals, 12(18), 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182467






