The World of Organoids: Gastrointestinal Disease Modelling in the Age of 3R and One Health with Specific Relevance to Dogs and Cats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
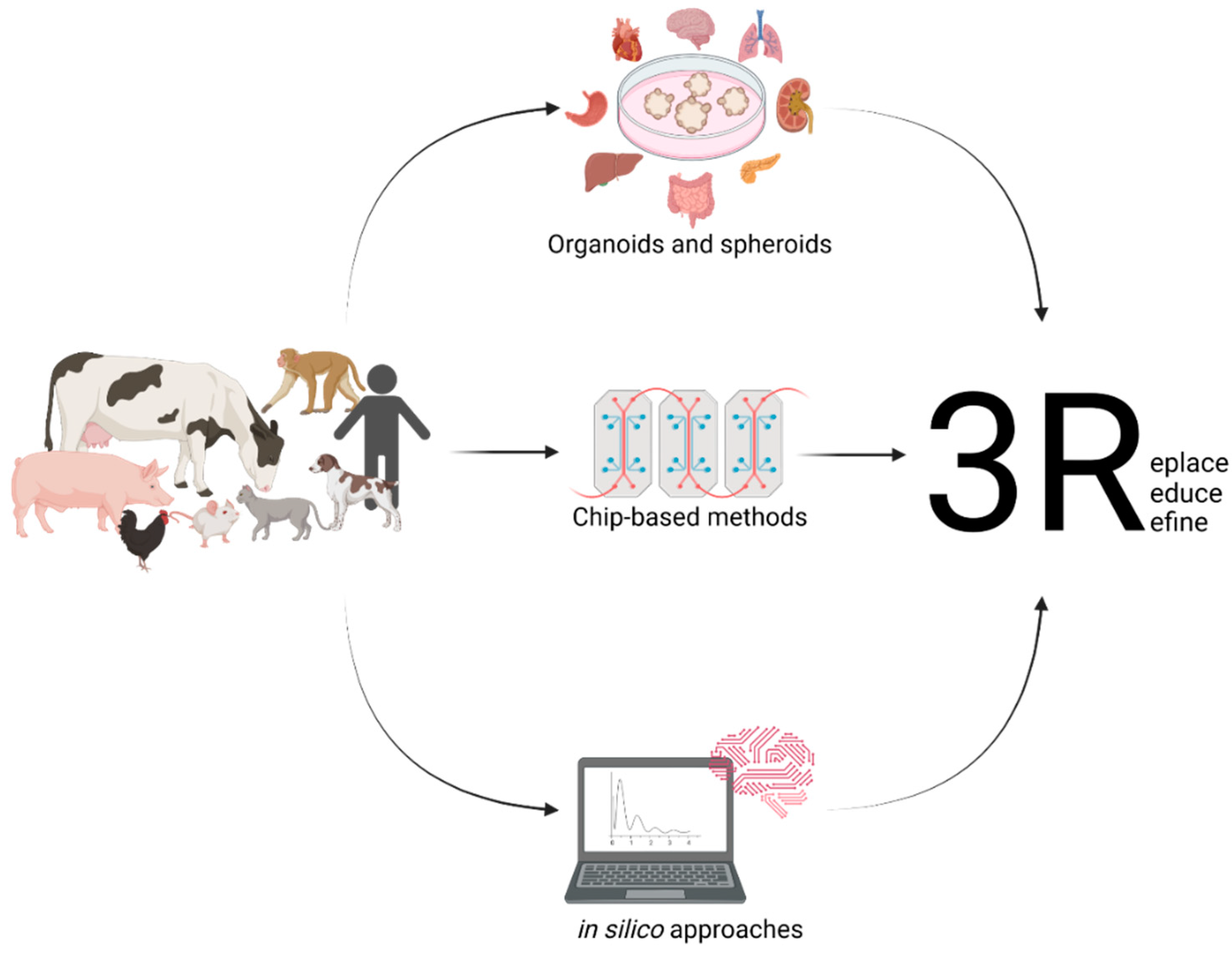
1. Introduction
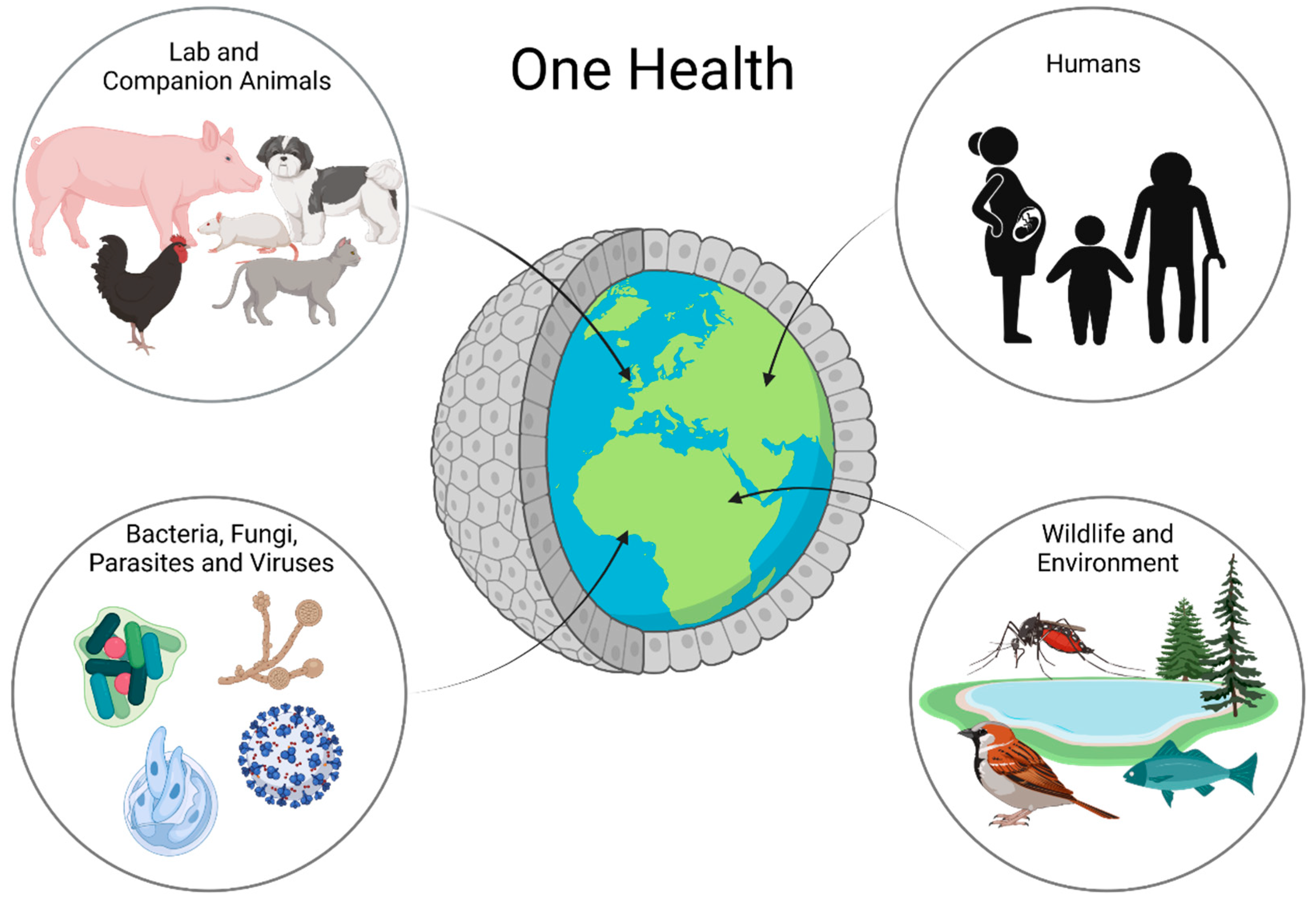
2. The Importance of Organoids for One Health
3. Organoids Modelling the Intestinal Epithelium
3.1. Microinjection
3.2. Apical-Out Organoids
3.3. Organoid-Derived Monolayers
4. Limitations
5. Outlook
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anholt, M.; Barkema, H. What Is One Health? Can Vet. J. 2021, 62, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nerpel, A.; Yang, L.; Sorger, J.; Käsbohrer, A.; Walzer, C.; Desvars-Larrive, A. SARS-ANI: A Global Open Access Dataset of Reported SARS-CoV-2 Events in Animals. Sci Data 2022, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amman, F.; Markt, R.; Endler, L.; Hupfauf, S.; Agerer, B.; Schedl, A.; Richter, L.; Zechmeister, M.; Bicher, M.; Heiler, G.; et al. Viral Variant-Resolved Wastewater Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 at National Scale. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.; Burch, R. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique. In John Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health; 1959; Available online: https://caat.jhsph.edu/principles/the-principles-of-humane-experimental-technique (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Office of the Law Revision Counsel. Title 7 of the Code of Laws of the United States of America, Chapter 54: Transportation, Sale, and Handling of Certain Animals; US Congress. Available online: http://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title7/chapter54&edition=prelim (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- European Parliament; European Council. Directive 2010/63/EU; European Union, 2010. Available online: https://norecopa.no/legislation/eu-directive-201063 (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science, e.V. Reduce, Refine, Replace–Responsibility. Available online: https://www.mpg.de/10973438/4rs (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- European Commission. Summary Report on the Statistics on the Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes in the Member States of the European Union and Norway in 2018; Brussels, 2021. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwj2nInjn536AhVCumMGHXqaCcEQFnoECA0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fec.europa.eu%2Fenvironment%2Fchemicals%2Flab_animals%2Fpdf%2FSWD_%2520part_A_and_B.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0opxqbviYJ0WzPyGdJUFKo (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- United States Department of Agriculture. Annual Report Animal Usage by Fiscal Year. Available online: https://Www.Aphis.Usda.Gov/Animal_welfare/Downloads/Reports/Fy19-Summary-Report-Column-F.Pdf (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Ellahham, S. Artificial Intelligence: The Future for Diabetes Care. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Faizal, A.S.; Thevarajah, T.M.; Khor, S.M.; Chang, S.W. A Review of Risk Prediction Models in Cardiovascular Disease: Conventional Approach vs. Artificial Intelligent Approach. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2021, 207, 106190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peetluk, L.S.; Ridolfi, F.M.; Rebeiro, P.F.; Liu, D.; Rolla, V.C.; Sterling, T.R. Systematic Review of Prediction Models for Pulmonary Tuberculosis Treatment Outcomes in Adults. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Luna, J.; Grisoni, F.; Weskamp, N.; Schneider, G. Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-Dimensional Culture Systems in Cancer Research: Focus on Tumor Spheroid Model. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Organogenesis in a Dish: Modeling Development and Disease Using Organoid Technologies. Science 2014, 345, 1247125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willyard, C. Rise of the Organoids. Nature 2015, 523, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Renner, M.; Martin, C.A.; Wenzel, D.; Bicknell, L.S.; Hurles, M.E.; Homfray, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Jackson, A.P.; Knoblich, J.A. Cerebral Organoids Model Human Brain Development and Microcephaly. Nature 2013, 501, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, C.S.; Renner, M.; de Gennaro, M.; Gross-Scherf, B.; Goldblum, D.; Hou, Y.; Munz, M.; Rodrigues, T.M.; Krol, J.; Szikra, T.; et al. Cell Types of the Human Retina and Its Organoids at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell 2020, 182, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Choi, W.H.; Jeon, S.G.; Lee, S.; Park, J.M.; Park, M.; Lee, H.; Lew, H.; Yoo, J. Establishment of Functional Epithelial Organoids from Human Lacrimal Glands. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundipe, V.M.L.; Groen, A.H.; Hosper, N.; Nagle, P.W.K.; Hess, J.; Faber, H.; Jellema, A.L.; Baanstra, M.; Links, T.P.; Unger, K.; et al. Generation and Differentiation of Adult Tissue-Derived Human Thyroid Organoids. Stem Cell Rep. 2021, 16, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, N.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Zomer-van Ommen, D.D.; Heo, I.; Böttinger, L.; Klay, D.; Weeber, F.; Huelsz-Prince, G.; Iakobachvili, N.; Amatngalim, G.D.; et al. Long-term Expanding Human Airway Organoids for Disease Modeling. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, R.A.; Leopoldi, A.; Aichinger, M.; Wick, N.; Hantusch, B.; Novatchkova, M.; Taubenschmid, J.; Hämmerle, M.; Esk, C.; Bagley, J.A.; et al. Human Blood Vessel Organoids as a Model of Diabetic Vasculopathy. Nature 2019, 565, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis-Israeli, Y.R.; Wasserman, A.H.; Gabalski, M.A.; Volmert, B.D.; Ming, Y.; Ball, K.A.; Yang, W.; Zou, J.; Ni, G.; Pajares, N.; et al. Self-Assembling Human Heart Organoids for the Modeling of Cardiac Development and Congenital Heart Disease. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.F.; van Vliet, E.J.; Sachs, N.; Rosenbluth, J.M.; Kopper, O.; Rebel, H.G.; Wehrens, E.J.; Piani, C.; Visvader, J.E.; Verissimo, C.S.; et al. Long-Term Culture, Genetic Manipulation and Xenotransplantation of Human Normal and Breast Cancer Organoids. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 1936–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartfeld, S.; Bayram, T.; van de Wetering, M.; Huch, M.; Begthel, H.; Kujala, P.; Vries, R.; Peters, P.J.; Clevers, H. In Vitro Expansion of Human Gastric Epithelial Stem Cells and Their Responses to Bacterial Infection. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 126–136.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huch, M.; Gehart, H.; van Boxtel, R.; Hamer, K.; Blokzijl, F.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Ellis, E.; van Wenum, M.; Fuchs, S.A.; de Ligt, J.; et al. Long-Term Culture of Genome-Stable Bipotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Liver. Cell 2015, 160, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasato, M.; Er, P.X.; Chiu, H.S.; Maier, B.; Baillie, G.J.; Ferguson, C.; Parton, R.G.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Roost, M.S.; de Sousa Lopes, S.M.C.; et al. Kidney Organoids from Human IPS Cells Contain Multiple Lineages and Model Human Nephrogenesis. Nature 2015, 526, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broutier, L.; Andersson-Rolf, A.; Hindley, C.J.; Boj, S.F.; Clevers, H.; Koo, B.K.; Huch, M. Culture and Establishment of Self-Renewing Human and Mouse Adult Liver and Pancreas 3D Organoids and Their Genetic Manipulation. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Stange, D.E.; Ferrante, M.; Vries, R.G.J.; van Es, J.H.; van den Brink, S.; van Houdt, W.J.; Pronk, A.; van Gorp, J.; Siersema, P.D.; et al. Long-Term Expansion of Epithelial Organoids from Human Colon, Adenoma, Adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s Epithelium. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 Stem Cells Build Crypt-Villus Structures in Vitro without a Mesenchymal Niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Chu, T.Y.; Ding, D.C. Human Fallopian Tube Epithelial Cells Exhibit Stemness Features, Self-Renewal Capacity, and Wnt-Related Organoid Formation. J Biomed Sci 2020, 27, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boretto, M.; Cox, B.; Noben, M.; Hendriks, N.; Fassbender, A.; Roose, H.; Amant, F.; Timmerman, D.; Tomassetti, C.; Vanhie, A.; et al. Development of Organoids from Mouse and Human Endometrium Showing Endometrial Epithelium Physiology and Long-Term Expandability. Development (Cambridge) 2017, 144, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Choi, S.; Kang, B.; Kong, J.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, W.H.; Lee, H.-R.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-M.; Lee, H.; et al. Creation of Bladder Assembloids Mimicking Tissue Regeneration and Cancer. Nature 2020, 588, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, J.; Karthaus, W.R.; Gao, D.; Driehuis, E.; Sawyers, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Clevers, H. Organoid Culture Systems for Prostate Epithelial and Cancer Tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.T.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Giangarra, V.; Grzeskowiak, C.L.; Ju, J.; Liu, I.H.; Chiou, S.H.; Salahudeen, A.A.; Smith, A.R.; et al. Organoid Modeling of the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cell 2018, 175, 1972–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, L.; Borcherding, D.C.; Kingsbury, D.; Atherly, T.; Ambrosini, Y.M.; Bourgois-Mochel, A.; Yuan, W.; Kimber, M.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Derivation of Adult Canine Intestinal Organoids for Translational Research in Gastroenterology. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, N.; Pratscher, B.; Meneses, A.M.C.; Tschulenk, W.; Walter, I.; Swoboda, A.; Kruitwagen, H.S.; Schneeberger, K.; Penning, L.C.; Spee, B.; et al. Generation of Differentiating and Long-Living Intestinal Organoids Reflecting the Cellular Diversity of Canine Intestine. Cells 2020, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, V.; Zdyrski, C.; Sahoo, D.K.; Dao, K.; Bourgois-Mochel, A.; Kopper, J.; Zeng, X.L.; Estes, M.K.; Mochel, J.P.; Allenspach, K. Standardization and Maintenance of 3D Canine Hepatic and Intestinal Organoid Cultures for Use in Biomedical Research. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekes, G.; Ehmann, R.; Boulant, S.; Stanifer, M.L. Development of Feline Ileum- and Colon-Derived Organoids and Their Potential Use to Support Feline Coronavirus Infection. Cells 2020, 9, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruitwagen, H.S.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; Vernooij, I.G.W.H.; Schrall, I.M.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Bannink, F.; Roesch, C.; van Uden, L.; Molenaar, M.R.; Helms, J.B.; et al. Long-Term Adult Feline Liver Organoid Cultures for Disease Modeling of Hepatic Steatosis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruitwagen, H.S.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Chen, C.; Nantasanti Assawarachan, S.; Schneeberger, K.; Kummeling, A.; van Straten, G.; Akkerdaas, I.C.; Vinke, C.R.; et al. Long-Term Survival of Transplanted Autologous Canine Liver Organoids in a COMMD1-Deficient Dog Model of Metabolic Liver Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Neupane, M.; Chien, S.J.; Chuang, F.R.; Crawford, R.B.; Kaminski, N.E.; Chang, C.C. Characterization of Adult Canine Kidney Epithelial Stem Cells That Give Rise to Dome-Forming Tubular Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawy, M.; Usui, T.; Mori, T.; Tsunedomi, R.; Hazama, S.; Nabeta, R.; Uchide, T.; Fukushima, R.; Yoshida, T.; Shibutani, M.; et al. Establishment of a Novel Experimental Model for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Using a Dog Bladder Cancer Organoid Culture. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2806–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, T.; Sakurai, M.; Nishikawa, S.; Umata, K.; Nemoto, Y.; Haraguchi, T.; Itamoto, K.; Mizuno, T.; Noguchi, S.; Mori, T.; et al. Establishment of a Dog Primary Prostate Cancer Organoid Using the Urine Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, D.J.; Basak, O.; Asra, P.; Boonekamp, K.E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Clevers, H. Establishment and Characterization of a Canine Keratinocyte Organoid Culture System. Vet. Dermatol. 2018, 29, 375-e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Dettwiler, M.; Fernández, M.G.; Tièche, E.; Hahn, K.; April-Monn, S.; Dettmer, M.S.; Kessler, M.; Rottenberg, S.; Campos, M. Validation of Immunohistochemistry for Canine Proteins Involved in Thyroid Iodine Uptake and Their Expression in Canine Follicular Cell Thyroid Carcinomas (FTCs) and FTC-Derived Organoids. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.H.; Behnke, M.S. WRN Conditioned Media Is Sufficient for in Vitro Propagation of Intestinal Organoids from Large Farm and Small Companion Animals. Biol. Open 2017, 6, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, M.; Goyama, T.; Tachibana, Y.; Nagao, I.; Ambrosini, Y.M. Farm and Companion Animal Organoid Models in Translational Research: A Powerful Tool to Bridge the Gap Between Mice and Humans. Front. Med. Technol. 2022, 4, 895379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.R.; Proctor, L.M.; Surette, M.G.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Microbiome: The Trillions of Microorganisms That Maintain Health and Cause Disease in Humans and Companion Animals. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honneffer, J.B.; Minamoto, Y.; Suchodolski, J.S. Microbiota Alterations in Acute and Chronic Gastrointestinal Inflammation of Cats and Dogs. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16489–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondo, E.; Marliani, G.; Accorsi, P.A.; Cocchi, M.; di Leone, A. Role of Gut Microbiota in Dog and Cat’s Health and Diseases. Open Vet. J. 2019, 9, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, A.; Palanisamy, G.; Manuel, M.; Paulsamy, C.; Rose, A.; Kaliappan, S.P.; Ward, H.; Walson, J.L.; Halliday, K.E.; Rao Ajjampur, S.S. A One Health Approach to Defining Animal and Human Helminth Exposure Risks in a Tribal Village in Southern India. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 105, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Trelis, M.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Cifre, S.; Gosálvez, C.; Sanxis-Furió, J.; Pascual, J.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Franco, S.; Peracho, V.; et al. One Health Approach to Zoonotic Parasites: Molecular Detection of Intestinal Protozoans in an Urban Population of Norway Rats, Rattus Norvegicus, in Barcelona, Spain. Pathogens 2021, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, M. Prevalence of Clostridioides Difficile in Animals and Its Relationship with Human Infections. Jpn. J. Chemother. 2020, 68, 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Usui, M. One Health Approach to Clostridioides Difficile in Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterwalder, S.K.; Loncaric, I.; Cabal, A.; Szostak, M.P.; Barf, L.M.; Marz, M.; Allerberger, F.; Burgener, I.A.; Tichy, A.; Feßler, A.T.; et al. Dogs as Carriers of Virulent and Resistant Genotypes of Clostridioides Difficile. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Lereclus, D.; Koehler, T.M. The Bacillus Cereus Group: Bacillus Species with Pathogenic Potential. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.P.; Humphrey, T.J.; Maskell, D.J. Molecular Insights into Farm Animal and Zoonotic Salmonella Infections. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Diaz, C.; Seyboldt, C.; Rupnik, M. Non-Human C. Difficile Reservoirs and Sources: Animals, Food, Environment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1050, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McLure, A.; Clements, A.C.A.; Kirk, M.; Glass, K. Modelling Diverse Sources of Clostridium Difficile in the Community: Importance of Animals, Infants and Asymptomatic Carriers. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, E152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, A.M.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Fazil, A.; Weese, J.S. Disease Transmission Model for Community-Associated Clostridium Difficile Infection. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redding, L.E.; Tu, V.; Abbas, A.; Alvarez, M.; Zackular, J.P.; Gu, C.; Bushman, F.D.; Kelly, D.J.; Barnhart, D.; Lee, J.J.; et al. Genetic and Phenotypic Characteristics of Clostridium (Clostridioides) Difficile from Canine, Bovine, and Pediatric Populations. Anaerobe 2022, 74, 102539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, V.; Ferrão, J.; Pimentel, L.; Pintado, M.; Fernandes, T. One Health, Fermented Foods, and Gut Microbiota. Foods 2018, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, L.; Hohwieler, M.; Müller, M.; Klaus, J. Intestinal Organoids as a Novel Complementary Model to Dissect Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopper, J.J.; Iennarella-Servantez, C.; Jergens, A.E.; Sahoo, D.K.; Guillot, E.; Bourgois-Mochel, A.; Martinez, M.N.; Allenspach, K.; Mochel, J.P. Harnessing the Biology of Canine Intestinal Organoids to Heighten Understanding of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis and Accelerate Drug Discovery: A One Health Approach. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.; Zahedi, A.; O’dea, M.; King, B.; Monis, P.; Thierry, B.; Carr, J.M.; Ryan, U. Organoids and Bioengineered Intestinal Models: Potential Solutions to the Cryptosporidium Culturing Dilemma. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowcutt, R.; Forman, R.; Glymenaki, M.; Carding, S.R.; Else, K.J.; Cruickshank, S.M. Heterogeneity across the Murine Small and Large Intestine. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, J.M.; Thompson, T.; Geskin, A.; Laframboise, W.; Lagasse, E. Distinct Human Stem Cell Populations in Small and Large Intestine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Takahashi, D.; Takano, S.; Kimura, S.; Hase, K. The Roles of Peyer’s Patches and Microfold Cells in the Gut Immune System: Relevance to Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burclaff, J.; Bliton, R.J.; Breau, K.A.; Ok, M.T.; Gomez-Martinez, I.; Ranek, J.S.; Bhatt, A.P.; Purvis, J.E.; Woosley, J.T.; Magness, S.T. A Proximal-to-Distal Survey of Healthy Adult Human Small Intestine and Colon Epithelium by Single-Cell Transcriptomics. CMGH 2022, 13, 1554–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoos, Y.; Vantrappen, G. The Cytochemical Localization of Lysozyme in Paneth Cell Granules. Histochem. J. 1971, 3, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, D.G.; Jervis, H.R. Comparative Histochemistry of Gastrointestinal Mucosubstances. Am. J. Anat. 1976, 146, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, J.Y.; Margalef-Català, M.; Li, X.; Mah, A.T.; Kuo, C.J.; Monack, D.M.; Amieva, M.R. Controlling Epithelial Polarity: A Human Enteroid Model for Host-Pathogen Interactions. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2509–2520.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Cui, A.; Zhao, J.; Ji, W.; Chen, Y.G. Establishment of Porcine and Monkey Colonic Organoids for Drug Toxicity Study. Cell Regen. 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselot, A.E.; Park, M.; Kim, M.; Matsu-Ura, T.; Wu, G.; Flores, D.E.; Subramanian, K.R.; Lee, S.; Sundaram, N.; Broda, T.R.; et al. Ontogeny and Function of the Circadian Clock in Intestinal Organoids. EMBO.J 2022, 41, e106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.R.; Huang, S.; Nagy, M.S.; Yadagiri, V.K.; Fields, C.; Mukherjee, D.; Bons, B.; Dedhia, P.H.; Chin, A.M.; Tsai, Y.H.; et al. Bacterial Colonization Stimulates a Complex Physiological Response in the Immature Human Intestinal Epithelium. Elife 2017, 6, e29132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuaita, B.H.; Lawrence, A.L.E.; Berger, R.P.; Hill, D.R.; Huang, S.; Yadagiri, V.K.; Bons, B.; Fields, C.; Wobus, C.E.; Spence, J.R.; et al. Comparative Transcriptional Profiling of the Early Host Response to Infection by Typhoidal and Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Serovars in Human Intestinal Organoids. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Heo, I.; O’connor, R. Studying Cryptosporidium Infection in 3D Tissue-Derived Human Organoid Culture Systems by Microinjection. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 2019, e59610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.S.; Ki, S.J.; Thanavel, R.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, M.O.; Kim, J.; Jung, C.R.; Han, T.S.; Cho, H.S.; Ryu, C.M.; et al. Maturation of Human Intestinal Organoids in Vitro Facilitates Colonization by Commensal Lactobacilli by Reinforcing the Mucus Layer. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9899–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroulios, G.; Stahl, M.; Elstone, F.; Chang, W.; Louis, S.; Eaves, A.; Simmini, S.; Conder, R.K. Culture Methods to Study Apical-Specific Interactions Using Intestinal Organoid Models. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 2021, e62330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojakian, G.K.; Schwimmer, R. Regulation of Epithelial Cell Surface Polarity Reversal by Β1 Integrins. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107 Pt 3, 561–576.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.S.; Gu, B.H.; Park, Y.J.; Rim, C.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, M. Porcine Intestinal Apical-Out Organoid Model for Gut Function Study. Animals 2022, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, N.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, N.; Yang, S.; Liu, G.; Liu, G. Next-Generation Porcine Intestinal Organoids: An Apical-Out Organoid Model for Swine Enteric Virus Infection and Immune Response Investigations. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01006–e01020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Price, D.R.G.; Burrells, A.; Faber, M.N.; Hildersley, K.A.; Chintoan-Uta, C.; Chapuis, A.F.; Stevens, M.; Stevenson, K.; Burgess, S.T.G.; et al. The Development of Ovine Gastric and Intestinal Organoids for Studying Ruminant Host-Pathogen Interactions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, T.J.; Morris, K.M.; Mabbott, N.A.; Vervelde, L. Inside-out Chicken Enteroids with Leukocyte Component as a Model to Study Host–Pathogen Interactions. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullman, S.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Sicinska, E.; Clancy, T.E.; Zhang, X.; Cai, D.; Neuberg, D.; Huang, K.; Guevara, F.; Nelson, T.; et al. Analysis of Fusobacterium Persistence and Antibiotic Response in Colorectal Cancer. Science 2017, 358, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterer, S.; Busch, K. Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome in Dogs. Vet. Clin. N. Am. -Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlShawaqfeh, M.K.; Wajid, B.; Minamoto, Y.; Markel, M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Serpedin, E.; Suchodolski, J.S. A Dysbiosis Index to Assess Microbial Changes in Fecal Samples of Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Hyde, E.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Knight, R. Dog and Human Inflammatory Bowel Disease Rely on Overlapping yet Distinct Dysbiosis Networks. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, H.; Rajca, S.; Rainteau, D.; Benarous, D.; Maubert, M.A.; Quervain, E.; Thomas, G.; Barbu, V.; Humbert, L.; Despras, G.; et al. Connecting Dysbiosis, Bile-Acid Dysmetabolism and Gut Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gut 2013, 62, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, A.C.C.; Cross, G.; Taylor, D.R.; Sherwood, R.A.; Watson, P.J. Measurement of Serum 7α-Hydroxy-4-Cholesten-3-One as a Marker of Bile Acid Malabsorption in Dogs with Chronic Diarrhoea: A Pilot Study. Vet. Rec. Open 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guard, B.C.; Suchodolski, J.S. Horse Species Symposium: Canine Intestinal Microbiology and Metagenomics: From Phylogeny to Function. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 2247–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, F.; Holthaus, D.; Kraft, M.; Klotz, C.; Schneemann, M.; Schulzke, J.D.; Krug, S.M. Human Duodenal Organoid-Derived Monolayers Serve as a Suitable Barrier Model for Duodenal Tissue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chow, E.C.Y.; Liu, S.; Du, Y.; Pang, K.S. The Caco-2 Cell Monolayer: Usefulness and Limitations. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Inui, T.; Yokota, J.; Kawakami, K.; Morinaga, G.; Takatani, M.; Hirayama, D.; Nomoto, R.; Ito, K.; Cui, Y.; et al. Monolayer Platform Using Human Biopsy-Derived Duodenal Organoids for Pharmaceutical Research. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 22, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Inoue, Y.; Sato, S.; Shimizu, M.; Kojima, H.; Okabe, T.; Kiyono, H.; Yamauchi, Y.; Sato, R. Organoid-Derived Intestinal Epithelial Cells Are a Suitable Model for Preclinical Toxicology and Pharmacokinetic Studies. iScience 2022, 25, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuka, K.; He, Y.; Koo-McCoy, S.; Kumaraswamy, P.; Nie, B.; Shaw, K.; Chan, P.; Leadbetter, M.; He, L.; Lewis, J.G.; et al. Development and Characterization of a Human and Mouse Intestinal Epithelial Cell Monolayer Platform. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 1976–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, P.; Schnepel, N.; Langeheine, M.; Künnemann, K.; Grassl, G.A.; Brehm, R.; Seeger, B.; Mazzuoli-Weber, G.; Breves, G. Intestinal Organoid-Based 2D Monolayers Mimic Physiological and Pathophysiological Properties of the Pig Intestine. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, Y.M.; Park, Y.; Jergens, A.E.; Shin, W.; Min, S.; Atherly, T.; Borcherding, D.C.; Jang, J.; Allenspach, K.; Mochel, J.P.; et al. Recapitulation of the Accessible Interface of Biopsy-Derived Canine Intestinal Organoids to Study Epithelial-Luminal Interactions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorgas, A.; Dotti, I.; Martínez-Picola, M.; Esteller, M.; Bonet-Rossinyol, Q.; Ricart, E.; Salas, A.; Martínez-Medina, M. A Novel Strategy to Study the Invasive Capability of Adherent-Invasive Escherichia Coli by Using Human Primary Organoid-Derived Epithelial Monolayers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, N.; Miyamoto, K.; Maslowski, K.M.; Ohno, H.; Kanai, T.; Sato, T. Development of a Scalable Coculture System for Gut Anaerobes and Human Colon Epithelium. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayguinov, P.O.; Oakley, D.M.; Shih, C.C.; Geanon, D.J.; Joens, M.S.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.J. Modern Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2018, 85, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Silva, P.N.; Syed, A.M.; Sindhwani, S.; Rocheleau, J.V.; Chan, W.C.W. Clarifying Intact 3D Tissues on a Microfluidic Chip for High-Throughput Structural Analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14915–14920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ineveld, R.L.; Ariese, H.C.R.; Wehrens, E.J.; Dekkers, J.F.; Rios, A.C. Single-Cell Resolution Three-Dimensional Imaging of Intact Organoids. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanDussen, K.L.; Sonnek, N.M.; Stappenbeck, T.S. L-WRN Conditioned Medium for Gastrointestinal Epithelial Stem Cell Culture Shows Replicable Batch-to-Batch Activity Levels across Multiple Research Teams. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, C.Y.; Dang, L.T.; You, C.; Chang, J.; de Lau, W.; Zhong, Z.A.; Yan, K.S.; Marecic, O.; Siepe, D.; Li, X.; et al. Surrogate Wnt Agonists That Phenocopy Canonical Wnt and β-Catenin Signalling. Nature 2017, 545, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Ha, A.; de Lau, W.; Yuki, K.; Santos, A.J.M.; You, C.; Geurts, M.H.; Puschhof, J.; Pleguezuelos-Manzano, C.; Peng, W.C.; et al. Next-Generation Surrogate Wnts Support Organoid Growth and Deconvolute Frizzled Pleiotropy In Vivo. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 840–851.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, V.C.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; Hollander, M.J.; Kuo, C.J.; Christopher Garcia, K. Surrogate R-Spondins for Tissue-Specific Potentiation of Wnt Signaling. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M.; Matano, M.; Toshimitsu, K.; Takano, A.; Mikami, Y.; Nishikori, S.; Sugimoto, S.; Sato, T. Human Intestinal Organoids Maintain Self-Renewal Capacity and Cellular Diversity in Niche-Inspired Culture Condition. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 787–793.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantasanti, S.; Spee, B.; Kruitwagen, H.S.; Chen, C.; Geijsen, N.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Pelaez, N.; Fieten, H.; Wubbolts, R.W.; et al. Disease Modeling and Gene Therapy of Copper Storage Disease in Canine Hepatic Organoids. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisenbrey, E.A.; Murphy, W.L. Synthetic Alternatives to Matrigel. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, B.; Khalil, T.; Workman, V.L.; Smith, A.; Brown, C.P.; Streuli, C.; Saiani, A.; Domingos, M. 3D Cell Bioprinting of Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Hydrogels. Mater. Lett. 2017, 190, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherne, M.D.; Sidar, B.; Sebrell, T.A.; Sanchez, H.S.; Heaton, K.; Kassama, F.J.; Roe, M.M.; Gentry, A.B.; Chang, C.B.; Walk, S.T.; et al. A Synthetic Hydrogel, VitroGel® ORGANOID-3, Improves Immune Cell-Epithelial Interactions in a Tissue Chip Co-Culture Model of Human Gastric Organoids and Dendritic Cells. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Malinen, M.M.; Lauren, P.; Lou, Y.R.; Kuisma, S.W.; Kanninen, L.; Lille, M.; Corlu, A.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Ikkala, O.; et al. Nanofibrillar Cellulose Hydrogel Promotes Three-Dimensional Liver Cell Culture. Proc. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, M.; Oosterhoff, L.A.; van Wolferen, M.E.; Schiele, S.A.; Walther, A.; Geijsen, N.; de Laporte, L.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Kock, L.M.; Spee, B. Cellulose Nanofibril Hydrogel Promotes Hepatic Differentiation of Human Liver Organoids. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaig, I.; Radenković, M.; Najman, S.; Pröhl, A.; Jung, O.; Barbeck, M. In Vivo Analysis of the Biocompatibility and Immune Response of Jellyfish Collagen Scaffolds and Its Suitability for Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Mun, H.; Sung, C.O.; Cho, E.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Chun, S.M.; Jung, D.J.; Shin, T.H.; Jeong, G.S.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Patient-Derived Lung Cancer Organoids as in Vitro Cancer Models for Therapeutic Screening. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driehuis, E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Clevers, H. Establishment of Patient-Derived Cancer Organoids for Drug-Screening Applications. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3380–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HUB Organoids A Patient in the Lab®. Available online: https://www.huborganoids.nl (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Sampaziotis, F.; Muraro, D.; Tysoe, O.C.; Sawiak, S.; Beach, T.E.; Godfrey, E.M.; Upponi, S.S.; Brevini, T.; Wesley, B.T.; Garcia-Bernardo, J.; et al. Cholangiocyte Organoids Can Repair Bile Ducts after Transplantation in the Human Liver. Science 2021, 371, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, E.; O’Connor, C.; Gasser, E.; Wei, Z.; Oh, T.G.; Tseng, T.W.; Wang, D.; Cayabyab, F.; Dai, Y.; Yu, R.T.; et al. Immune-Evasive Human Islet-like Organoids Ameliorate Diabetes. Nature 2020, 586, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meran, L.; Massie, I.; Campinoti, S.; Weston, A.E.; Gaifulina, R.; Tullie, L.; Faull, P.; Orford, M.; Kucharska, A.; Baulies, A.; et al. Engineering Transplantable Jejunal Mucosal Grafts Using Patient-Derived Organoids from Children with Intestinal Failure. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, S.; Kobayashi, E.; Fujii, M.; Ohta, Y.; Arai, K.; Matano, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Toshimitsu, K.; Takahashi, S.; et al. An Organoid-Based Organ-Repurposing Approach to Treat Short Bowel Syndrome. Nature 2021, 592, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, H.; Iwasawa, K.; Ouchi, R.; Maezawa, M.; Giesbrecht, K.; Saiki, N.; Ferguson, A.; Kimura, M.; Thompson, W.L.; Wells, J.M.; et al. Modelling Human Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Organogenesis from the Foregut–Midgut Boundary. Nature 2019, 574, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattanayak, P.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Vishwas, S.; Kapoor, B.; Chellappan, D.K.; Anand, K.; Gupta, G.; Jha, N.K.; Gupta, P.K.; et al. Microfluidic Chips: Recent Advances, Critical Strategies in Design, Applications and Future Perspectives. Microfluid Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapp, N.; Amour, A.; Rowan, W.C.; Candarlioglu, P.L. Organ-on-Chip Applications in Drug Discovery: An End User Perspective. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picollet-D’hahan, N.; Zuchowska, A.; Lemeunier, I.; le Gac, S. Multiorgan-on-a-Chip: A Systemic Approach To Model and Decipher Inter-Organ Communication. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 788–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson-Bouchard, K.; Teles, D.; Yeager, K.; Tavakol, D.N.; Zhao, Y.; Chramiec, A.; Tagore, S.; Summers, M.; Stylianos, S.; Tamargo, M.; et al. A Multi-Organ Chip with Matured Tissue Niches Linked by Vascular Flow. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Csukovich, G.; Pratscher, B.; Burgener, I.A. The World of Organoids: Gastrointestinal Disease Modelling in the Age of 3R and One Health with Specific Relevance to Dogs and Cats. Animals 2022, 12, 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182461
Csukovich G, Pratscher B, Burgener IA. The World of Organoids: Gastrointestinal Disease Modelling in the Age of 3R and One Health with Specific Relevance to Dogs and Cats. Animals. 2022; 12(18):2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182461
Chicago/Turabian StyleCsukovich, Georg, Barbara Pratscher, and Iwan Anton Burgener. 2022. "The World of Organoids: Gastrointestinal Disease Modelling in the Age of 3R and One Health with Specific Relevance to Dogs and Cats" Animals 12, no. 18: 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182461
APA StyleCsukovich, G., Pratscher, B., & Burgener, I. A. (2022). The World of Organoids: Gastrointestinal Disease Modelling in the Age of 3R and One Health with Specific Relevance to Dogs and Cats. Animals, 12(18), 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12182461






