Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation on Milk Yield and Quality in Italian Mediterranean Lactating Buffaloes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Feeding
2.2. Milk Yield and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
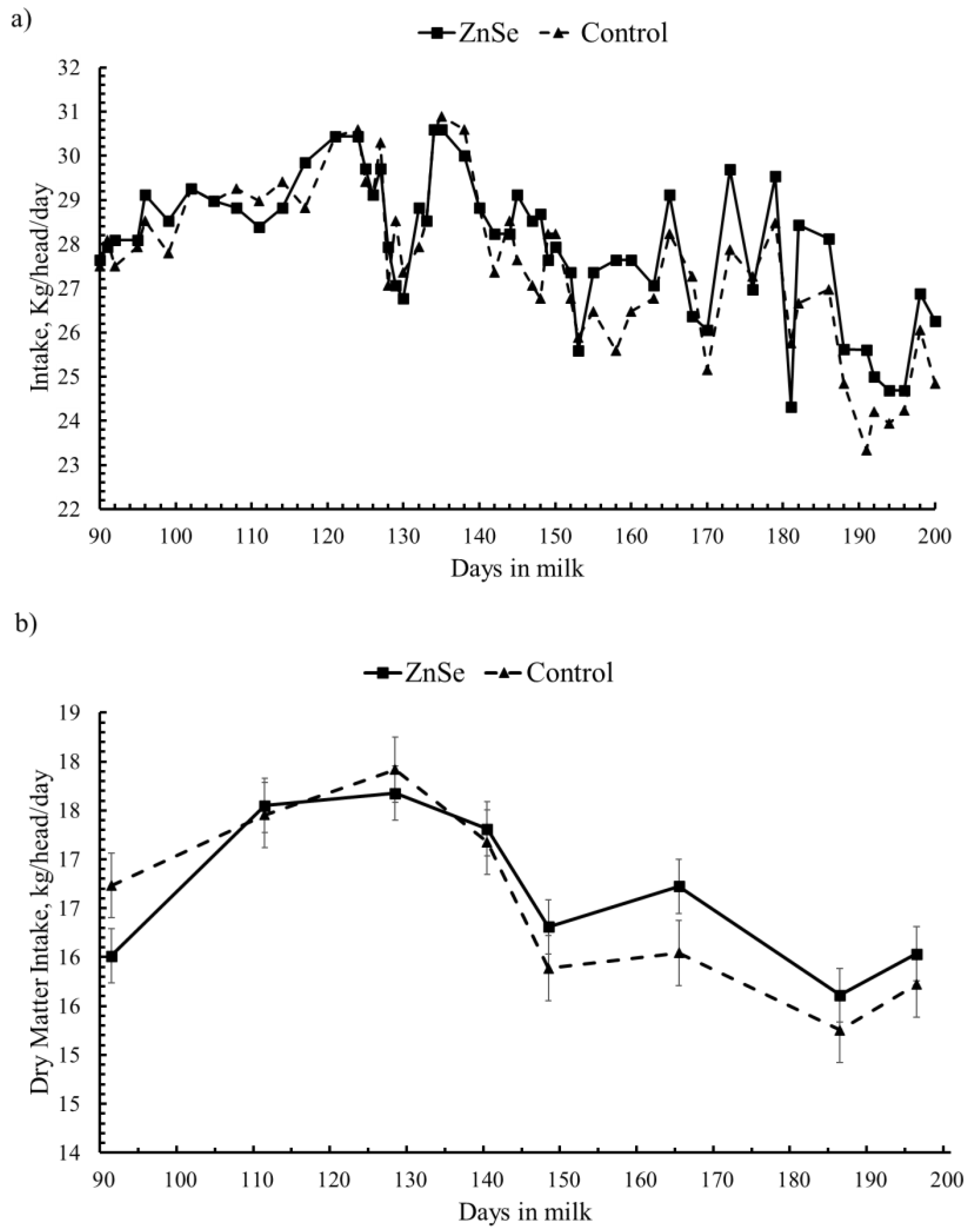
3.1. Feed Intake and Diet Characteristics
3.2. Milk Yield and Milk Quality Traits
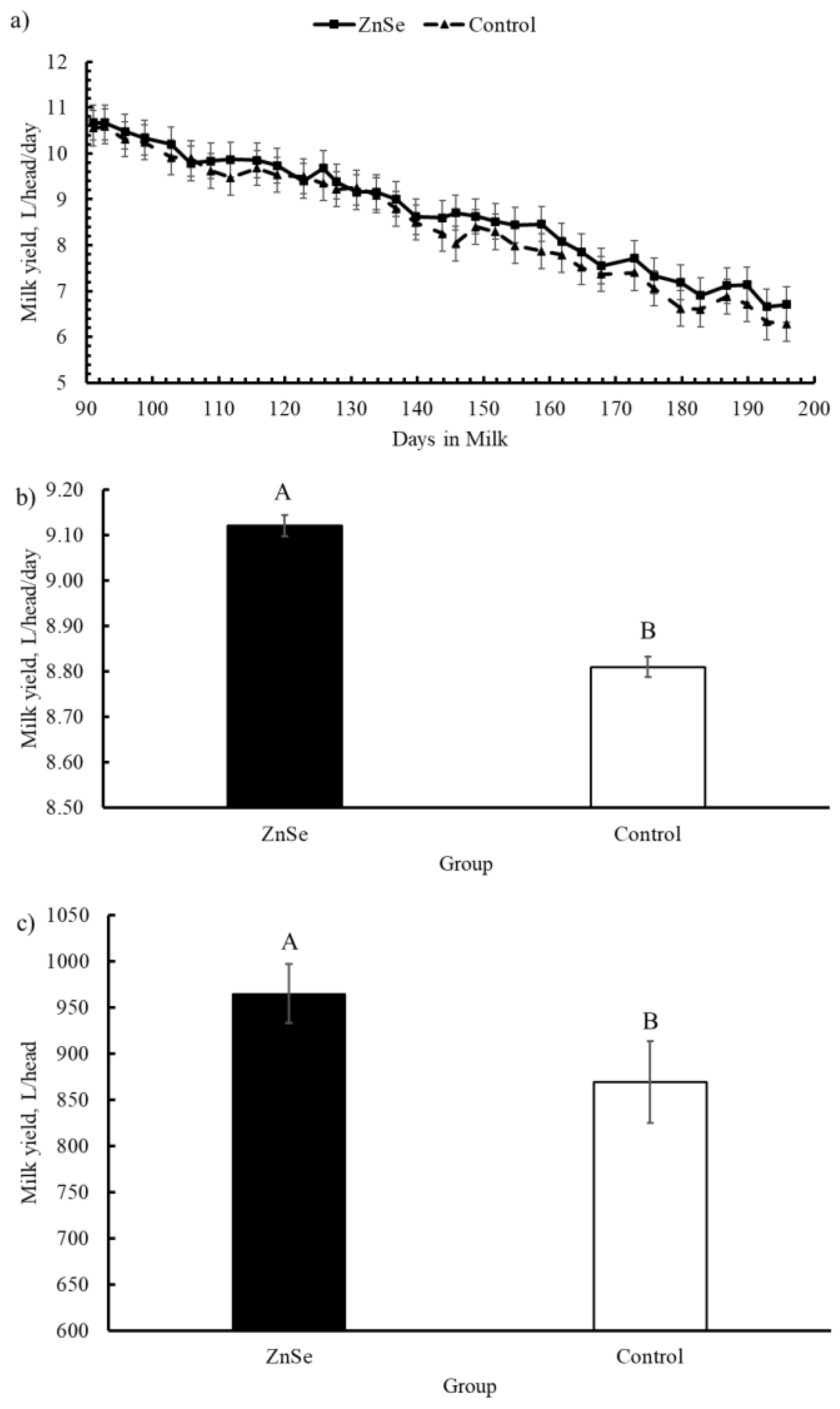
3.2.1. Milk Yield
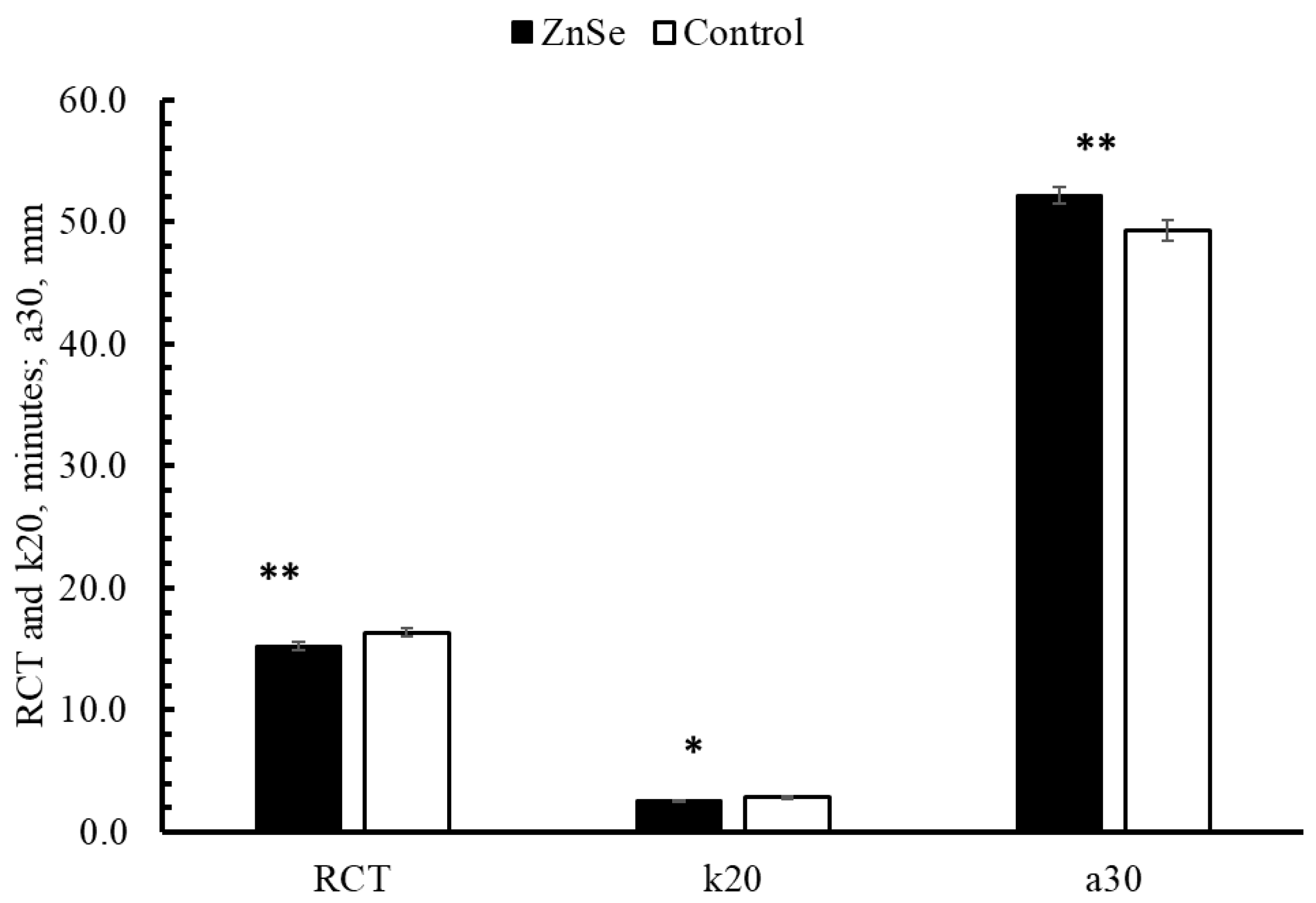
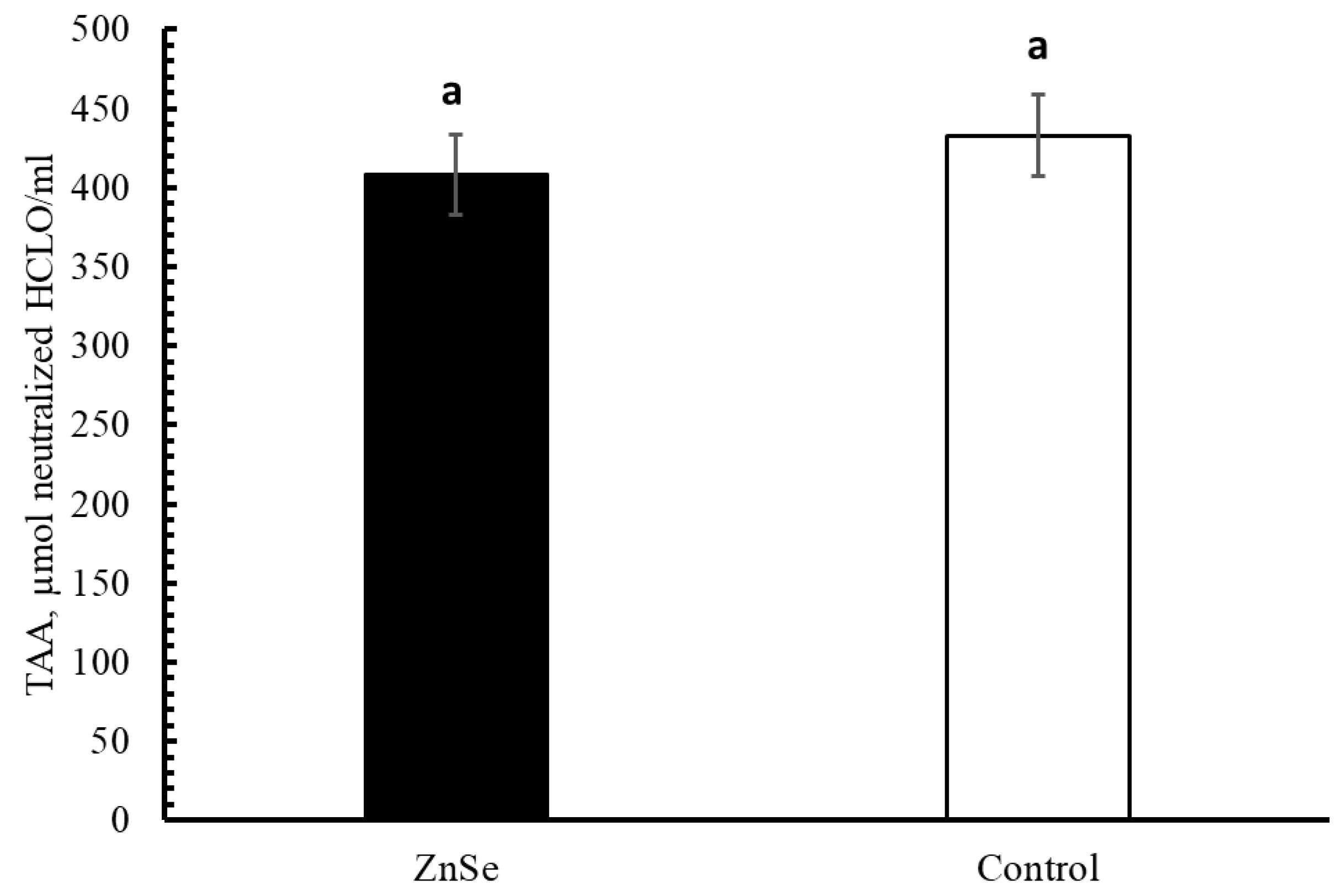
3.2.2. Milk Quality Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zicarelli, L. Buffalo milk: Its properties, dairy yield and mozzarella production. Vet. Res. Commun. 2004, 28, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzano, A.; Neglia, G.; D’Onofrio, N.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Limone, A.; Cotticelli, A.; Marrone, R.; Anastasio, A.; D’Occhio, M.J.; Campanile, G. Green feed increases antioxidant and antineoplastic activity of buffalo milk: A globally significant livestock. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Hendricks, G. Improving Buffalo Milk; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781845698065. [Google Scholar]
- Pegolo, S.; Stocco, G.; Mele, M.; Schiavon, S.; Bittante, G.; Cecchinato, A. Factors affecting variations in the detailed fatty acid profile of Mediterranean buffalo milk determined by 2-dimensional gas chromatography. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2564–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfatti, V.; Giantin, M.; Gervaso, M.; Coletta, A.; Dacasto, M.; Carnier, P. Effect of CSN1S1-CSN3 (αS1-κ-casein) composite genotype on milk production traits and milk coagulation properties in Mediterranean water buffalo. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 3435–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.I.; Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Ullah, R.; Ajmal, M.; Jaspal, M.H. Antioxidant properties of milk and dairy products: A comprehensive review of the current knowledge. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.T.; Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Ayaz, M.; Ajmal, M.; Ellahi, M.Y.; Khalique, A. Antioxidant capacity and fatty acids characterization of heat-treated cow and buffalo milk. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykkesfeldt, J.; Svendsen, O. Oxidants and antioxidants in disease: Oxidative stress in farm animals. Vet. J. 2007, 173, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Anjum, F.M.; Huma, N.; Sameen, A.; Zahoor, T. Composition and physico-chemical characteristics of buffalo milk with particular emphasis on lipids, proteins, minerals, enzymes and vitamins. JAPS J. Anim. Plant. Sci. 2013, 23, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Cortinhas, C.S.; Botaro, B.G.; Sucupira, M.C.A.; Renno, F.P.; Santos, M.V. Antioxidant enzymes and somatic cell count in dairy cows fed with organic source of zinc, copper and selenium. Livest. Sci. 2010, 127, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychen, G.; Aquilina, G.; Azimonti, G.; Bampidis, V.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Bories, G.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Flachowsky, G.; Gropp, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of Zinc-L-Selenomethionine as feed additive for all animal species. EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmead, H.D.; Samford, R.A. Effects of metal amino acid chelates or inorganic minerals on three successive lactations in dairy cows. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2004, 2, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Meglia, G.E.; Holtenius, K.; Petersson, L.; Öhagen, P.; Persson Waller, K. Prediction of vitamin A, vitamin E, selenium and zinc status of periparturient dairy cows using blood sampling during the mid dry period. Acta Vet. Scand. 2004, 45, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, L.M.; Loeffler, S.H.; Socha, M.T.; Tomlinson, D.J.; Johnson, A.B. Effects of supplementing complexed zinc, manganese, copper and cobalt on lactation and reproductive performance of intensively grazed lactating dairy cattle on the South Island of New Zealand. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, W.P.; Hogan, J.S. Effect of selenium source on selenium status, neutrophil function, and response to intramammary endotoxin challenge of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinhas, C.; Esler de Freitas Junior, J.; de Rezende Naves, J.; de Felicio Porcionato, M.A.; Prada e Silva, L.F.; Palma Rennó, F.; Veiga dos Santos, M. Organic and inorganic sources of zinc, copper and selenium in diets for dairy cows: Intake, blood metabolic profile, milk yield and composition. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2012, 41, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kononoff, P.J.; Heinrichs, A.J.; Buckmaster, D.R. Modification of the Penn State Forage and total mixed ration particle separator and the effects of moisture content on its measurements. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC: Official Method of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- AOAC: Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- AOAC: Official Method of Analysis, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggans, G.R.; Shook, G.E. A Lactation Measure of Somatic Cell Count. J. Dairy Sci. 1987, 70, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanile, G.; De Filippo, C.; Di Palo, R.; Taccone, W.; Zicarelli, L. Influence of dietary protein on urea levels in blood and milk of buffalo cows. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1998, 55, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannoni, M.; Annibaldi, S. Standardization of the renneting ability of milk by Formagraph. Sci. Tecn. Latt. Cas. 1981, 32, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, L.; Nunzi, C.; Pauselli, M.; Moscati, L.; Cestola, E.; Duranti, E.; Casoli, C. Evaluating the antioxidant capacity in different fractions of sheep milk. Milchwissenschaft 2011, 66, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Beghelli, D.; Lupidi, G.; Damiano, S.; Cavallucci, C.; Bistoni, O.; De Cosmo, A.; Polidori, P. Rapid assay to evaluate the total antioxidant capacity in donkey milk and in more common animal milk for human consumption. Austin Food Sci. 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D. R Core Team 2020. nlme: Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R Package Version 3.1-151. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.orgpackage=nlme.pdf (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Patil, I. Multiple Pairwise Comparison Tests. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.orgpackage=pairwiseComparisons.pdf (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- R Core Team, A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2021, Volume 2. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Singh, H.P.; Jain, R.K.; Tiwari, D.; Mehta, M.K.; Mudgal, V. Strategic supplementation of antioxidant micronutrients in peri-parturient Murrah buffaloes helps augment the udder health and milk production. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufarelli, V.; Dario, M.; Laudadio, V. Diet composition and milk characteristics of Mediterranean water buffaloes reared in Southeastern Italy during spring season. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2008, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, A.; Negrini, R.; De Marchi, M.; Campanile, G.; Neglia, G. Phenotypic characterization of milk yield and quality traits in a large population of water buffaloes. Animals 2020, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.I.A. (Associazione Italiana Allevatori). Bollettino On-line. Available online: http://bollettino.aia.it/Contenuti.aspx?CD_GruppoStampe=TB&CD_Specie=C4#Pcd7d7bb756a24202947362bd23a6160a_5_oHit0 (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Singh, M.; Ludri, R.S. Somatic cell counts in Murrah buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) during different stages of lactation, parity and season. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, F.; Altomonte, I.; Martini, M. Il latte di bufala: Studio di alcuni parametri produttivi. Large Anim. Rev. 2013, 19, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kantwa, S.C.; Shekhawat, S.S.; Pratap, R.; Meena, Y.K.; Samota, S.D. Effect of chelated mineral supplementation on productive and reproductive performance of lactating buffalo. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 91, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Tanwar, P.S.; Verma, H.K.; Jadoun, Y.S. Effect of mineral supplementation on production and reproduction performance of buffaloes under farmer management practices. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 7707–7709. [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg, D.W.; Tomlinson, D.J.; Socha, M.T.; Johnson, A.B. Effects of zinc methionine complex on milk production and somatic cell count of dairy cows: Twelve-Trial Summary. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2004, 20, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, W.A.; El-esawy, G.S.; Mohy el-dein, A.; Ali, M.F.; Gaafar, H.M. Effect of supplementary chelated Zinc and Manganese methionine on productive and reproductive performance of Friesian cows. Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 96, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Rana, D.S.; Kumari, R.; Gupta, R. Effect of area specific mineral mixture feeding on productive and reproductive performance of dairy animals. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 2407–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Singh, K.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, M. Effect of supplementation of minerals on the productive and reproductive performance of crossbred cattle. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, S.G.; Wang, Y.J.; Purdie, N.G.; Osborne, V.R.; Coomber, B.L.; Cant, J.P. Selenomethionine stimulates expression of glutathione peroxidase 1 and 3 and growth of bovine mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2670–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jia, D.; He, R.; Lian, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, R. Association between serum Selenium level and subclinical mastitis in dairy cattle. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade, K.D.; Do Nascimento Rangel, A.H.; De Lima Júnior, D.M.; Galvão Júnior, J.G.B.; Urbano, S.A.; Novaes, L.P. Quality of buffalo milk supplemented with selenium. Acta Vet. Bras. 2016, 10, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripaldi, C.; Palocci, G.; Miarelli, M.; Catta, M.; Orlandini, S.; Amatiste, S.; Di Bernardini, R.; Catillo, G. Effects of mastitis on buffalo milk quality. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niero, G.; Currò, S.; Costa, A.; Penasa, M.; Cassandro, M.; Boselli, C.; Giangolini, G.; De Marchi, M. Short communication: Phenotypic characterization of total antioxidant activity of buffalo, goat, and sheep milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4864–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzotto, E.F.; Stivanin, S.C.B.; de Paris, M.; Passos, L.T.; Werncke, D.; Klein, C.P.; Stone, V.; Matté, C.; Zanela, M.B.; Fischer, V. Supplementation with green tea and oregano extracts on productive characteristics, blood metabolites, and antioxidant status of Jersey cows during the transition period. Animal 2021, 15, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, M.; Osimani, A.; Tavoletti, S.; Moreno, I.; Clementi, F.; Trombetta, M.F. Trends in the quality and hygiene parameters of bulk Italian Mediterranean buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) milk: A three-year study. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; De Marchi, M.; Battisti, S.; Guarducci, M.; Amatiste, S.; Bitonti, G.; Borghese, A.; Boselli, C. On the Effect of the Temperature-Humidity Index on Buffalo Bulk Milk Composition and Coagulation Traits. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 577758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombade, K.; Kamboj, A.; Alhussien, M.N.; Mohanty, A.K.; Dang, A.K. Diurnal variation of milk somatic and differential leukocyte counts of murrah buffaloes as influenced by different milk fractions, seasons and parities. Biol. Rhythm Res. 2018, 49, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.P.; Nagvekar, A.S.; Ingole, S.D.; Bharucha, S.V.; Palve, V.T. Somatic cell count and alkaline phosphatase activity in milk for evaluation of mastitis in buffalo. Vet. World 2015, 8, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, H.M.; Abo El-Nor, S.A.H.; Kholif, S.M.; El-Sayed, H.M.; Abd El-Shaffy, O.H.; Saada, M. Effect of different additive sources on milk yield and composition of lactating buffaloes. Livest. Sci. 2010, 131, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariota, B.; Campanile, G.; Potena, A.; Napolano, R.; Gasparrini, B.; Neglia, G.L.; Di Palo, R. Ca and P in buffalo milk: Curd yield and milk clotting parameters. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 6, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, I.; Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.F. Effects of Somatic Cell Counts and Milk Composition on the Coagulating Properties of Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potena, A.; Napolano, R.; Galiero, G.; Coletta, A.; Palo, D.; Neglia, G.; Zicarelli, L. Relationship between lactodinamographic and characteristics of buffalo milk. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 6, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cecchinato, A.; Penasa, M.; Cipolat Gotet, C.; De Marchi, M.; Bittante, G. Short communication: Factors affecting coagulation properties of Mediterranean buffalo milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1709–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbo, T.; Cipolat-Gotet, C.; Bittante, G.; Cecchinato, A. The nonlinear effect of somatic cell count on milk composition, coagulation properties, curd firmness modeling, cheese yield, and curd nutrient recovery. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5104–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedholm, A.; Larsen, L.B.; Lindmark-Månsson, H.; Karlsson, A.H.; Andrén, A. Effect of protein composition on the cheese-making properties of milk from individual dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3296–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfatti, V.; Gervaso, M.; Rostellato, R.; Coletta, A.; Carnier, P. Protein composition affects variation in coagulation properties of buffalo milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4182–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, H.B.; Poulsen, N.A.; Andersen, K.K.; Hammershøj, M.; Poulsen, H.D.; Larsen, L.B. Distinct composition of bovine milk from Jersey and Holstein-Friesian cows with good, poor, or noncoagulation properties as reflected in protein genetic variants and isoforms. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6905–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfatti, V.; Cecchinato, A.; Gallo, L.; Blasco, A.; Carnier, P. Genetic analysis of detailed milk protein composition and coagulation properties in Simmental cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5183–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabucci, U.; Basiricò, L.; Morera, P.; Dipasquale, D.; Vitali, A.; Piccioli Cappelli, F.; Calamari, L. Effect of summer season on milk protein fractions in Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, M.; Fieni, S.; Tosi, F.; Franceschi, P.; Formaggioni, P.; Summer, A. Seasonal variations of the rennet-coagulation properties of herd milks in Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese manufacture: Comparison between Italian Friesian and Italian Brown cattle breeds. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 4, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, T.; Nedelkov, K.; Yordanova, D.; Karabashev, V.; Krastanov, J. Effects of liquid organic mineral complex (MultiMix®) on milk yield, composition and cheesemaking capacity of milk in dairy cows. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 13, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, M.J.; Weiss, W.P. Effect of source of trace minerals in either forage- or by-product–based diets fed to dairy cows: 1. Production and macronutrient digestibility. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 5358–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, F.; Heinrichs, A.J. Effect of trace minerals and starch on digestibility and rumen fermentation in diets for dairy heifers. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2797–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloetens, L.; Panee, J.; Åkesson, B. The antioxidant capacity of milk-The application of different methods in vitro and in vivo. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2013, 59, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | ZnSe | Control |
|---|---|---|
| Parity (n) | 5.2 ± 3.2 a | 5.0 ± 3.2 a |
| Days in milk | 91.5 ± 26.7 a | 91.2 ± 25.6 a |
| Daily milk yield (L/head/d) | 10.67 ± 2.37 a | 10.55 ± 2.16 a |
| Feed | Kg/Head (w.b. 1) |
|---|---|
| Corn silage | 10.0 |
| Grass silage | 10.0 |
| Commercial mixed feed 2 | 5.0 |
| Alfalfa Hay | 4.0 |
| Mixed Hay | 3.0 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.02 |
| Parameters | ZnSe | Control |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Matter, % | 59.77 ± 1.7 a | 60.20 ± 1.6 a |
| Ash, % | 7.5 ± 0.36 a | 7.58 ± 0.48 a |
| Crude Protein, % | 11.24 ± 1.05 a | 11.23 ± 0.71 a |
| Ethereal Extract, % | 2.19 ± 0.3 a | 2.33 ± 0.52 a |
| aNDF, % | 41.98 ± 2.94 a | 42.37 ± 2.26 a |
| ADF, % | 29.48 ± 2.88 a | 29.94 ± 2.24 a |
| ADL, % | 3.81 ± 0.7 a | 4.10 ± 0.43 a |
| Starch, % | 20.23 ± 1.34 a | 20.13 ± 0.83 a |
| S1, % | 10.20 ± 4.23 a | 10.37 ± 3.72 a |
| S2, % | 29.95 ± 4.49 a | 29.55 ± 4.31 a |
| S3, % | 35.61 ± 1.38 a | 34.74 ± 1.68 a |
| Bottom, % | 24.24 ± 3.56 a | 25.33 ± 3.48 a |
| Parameters | ZnSe | Control |
|---|---|---|
| H.I. | 55.42 ± 4.30 a | 50.12 ± 7.03 a |
| S.I. | 38.17 ± 2.95 a | 39.78 ± 4.25 a |
| Parameters | ZnSe | Control |
|---|---|---|
| Fat, % | 8.20 ± 1.48 a | 8.33 ± 1.61 a |
| Protein, % | 4.64 ± 0.35 a | 4.64 ± 0.47 a |
| Lactose, % | 4.66 ± 0.20 a | 4.66 ± 0.19 a |
| Solid Not-fat, % | 10.00 ± 0.35 a | 10.03 ± 0.50 a |
| pH | 6.63 ± 0.14 a | 6.61 ± 0.17 a |
| SCC, thousand cells/mL | 118.78 ± 201.75 a | 131.62 ± 188.41 a |
| SCS | 2.76 ± 0.78 a | 2.73 ± 0.97 a |
| ECM, Kg/h/d | 14.34 ± 1.10 a | 13.64 ± 1.06 a |
| FEr | 0.57 ± 0.09 a | 0.56 ± 0.08 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evangelista, C.; Bernabucci, U.; Basiricò, L. Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation on Milk Yield and Quality in Italian Mediterranean Lactating Buffaloes. Animals 2022, 12, 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151903
Evangelista C, Bernabucci U, Basiricò L. Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation on Milk Yield and Quality in Italian Mediterranean Lactating Buffaloes. Animals. 2022; 12(15):1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151903
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvangelista, Chiara, Umberto Bernabucci, and Loredana Basiricò. 2022. "Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation on Milk Yield and Quality in Italian Mediterranean Lactating Buffaloes" Animals 12, no. 15: 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151903
APA StyleEvangelista, C., Bernabucci, U., & Basiricò, L. (2022). Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation on Milk Yield and Quality in Italian Mediterranean Lactating Buffaloes. Animals, 12(15), 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151903






