Immunosuppressant-Responsive Enteropathy and Non-Responsive Enteropathy in Dogs: Prognostic Factors, Short- and Long-Term Follow Up
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
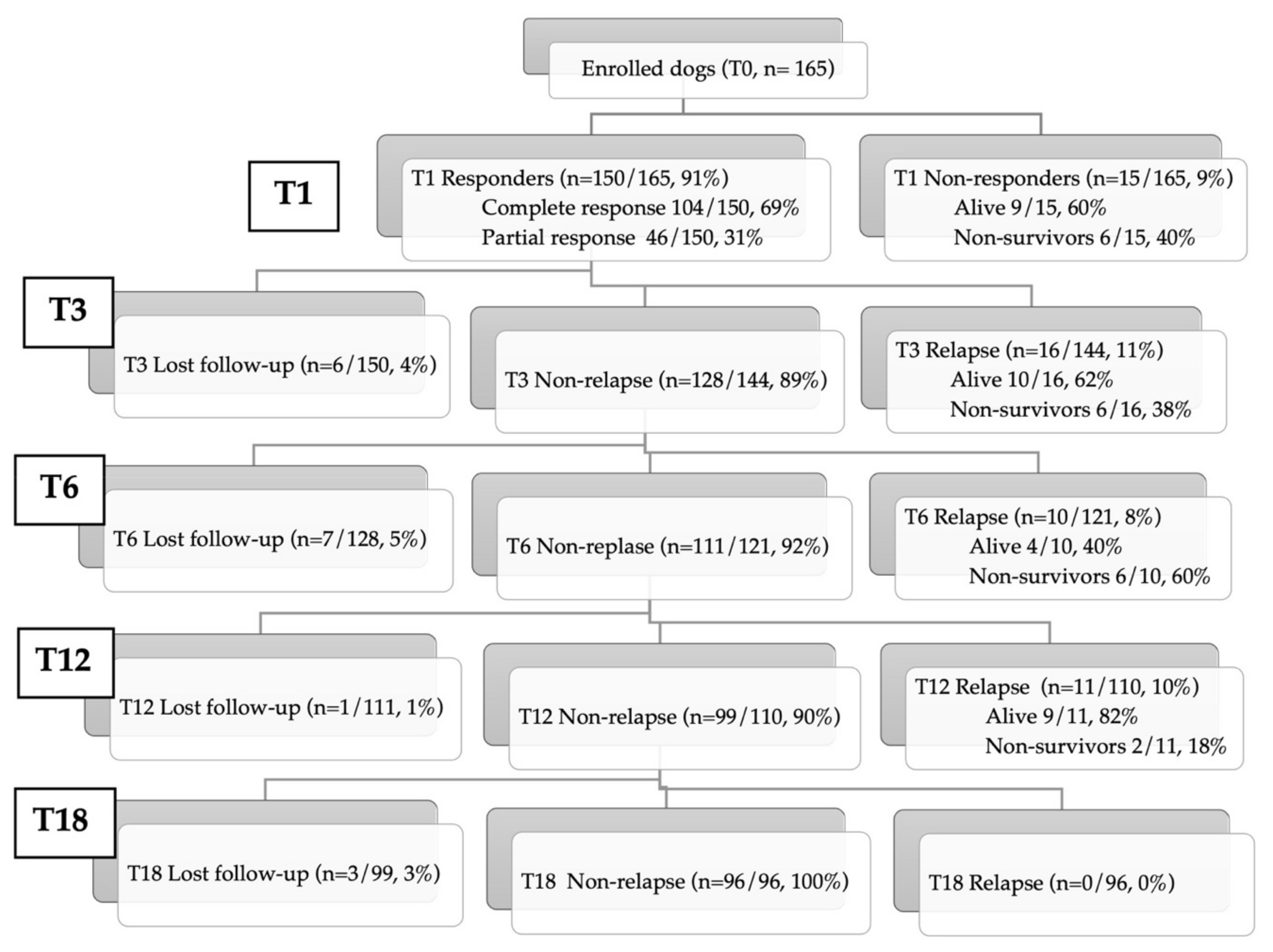
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makielski, K.; Cullen, J.; O’Connor, A.; Jergens, A.E. Narrative Review of Therapies for Chronic Enteropathies in Dogs and Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerquetella, M.; Rossi, G.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Schmitz, S.S.; Allenspach, K.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Furlanello, T.; Gavazza, A.; Marchegiani, A.; Unterer, S.; et al. Proposal for Rational Antibacterial Use in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Dogs with Chronic Diarrhoea. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 61, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandrieux, J.R.S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease versus Chronic Enteropathy in Dogs: Are They One and the Same? J. Small Anim. 2016, 57, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandrieux, J.R.S.; Mansfield, C.S. Chronic Enteropathy in Canines: Prevalence, Impact And Management Strategies. Vet. Med. Med. 2019, 10, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craven, M.D.; Washabau, R.J. Comparative Pathophysiology and Management of Protein-Losing Enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennogle, S.A.; Stockman, J.; Webb, C.B. Prospective Evaluation of a Change in Dietary Therapy in Dogs with Steroid-resistant Protein-losing Enteropathy. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenspach, K.; Wieland, B.; Gröne, A.; Gaschen, F. Chronic Enteropathies in Dogs: Evaluation of Risk Factors for Negative Outcome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, M.; Steiner, J.M.; Fosgate, G.T.; Zentek, J.; Hartmann, S.; Kohn, B. Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs—Retrospective Study in 136 Cases. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianella, P.; Lotti, U.; Bellino, C.; Bresciani, F.; Cagnasso, A.; Fracassi, F.; D’angelo, A.; Pietra, M. Clinicopathologic and Prognostic Factors in Short- and Long-Term Surviving Dogs with Protein-Losing Enteropathy. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd 2017, 159, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakashima, K.; Hiyoshi, S.; Ohno, K.; Uchida, K.; Goto-Koshino, Y.; Maeda, S.; Mizutani, N.; Takeuchi, A.; Tsujimoto, H. Prognostic Factors in Dogs with Protein-Losing Enteropathy. Vet. J. 2015, 205, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathrani, A.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, F.; Hall, E.J. Association of Chronic Enteropathy Activity Index, Blood Urea Concentration, and Risk of Death in Dogs with Protein-losing Enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equilino, M.; Théodoloz, V.; Gorgas, D.; Doherr, M.G.; Heilmann, R.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Burgener, I.A. Evaluation of Serum Biochemical Marker Concentrations and Survival Time in Dogs with Protein-Losing Enteropathy. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoni, C.C.; Heilmann, R.M.; García-Sancho, M.; Sainz, A.; Ackermann, M.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E. Serologic and Fecal Markers to Predict Response to Induction Therapy in Dogs with Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Berghoff, N.; Mansell, J.; Grützner, N.; Parnell, N.K.; Gurtner, C.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Association of Fecal Calprotectin Concentrations with Disease Severity, Response to Treatment, and Other Biomarkers in Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathies. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpinen, S.; Spillmann, T.; Westermarck, E. Efficacy of Two Low-Dose Oral Tylosin Regimens in Controlling the Relapse of Diarrhea in Dogs with Tylosin-Responsive Diarrhea: A Prospective, Single-Blinded, Two-Arm Parallel, Clinical Field Trial. Acta Vet. Scand. 2014, 56, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagata, N.; Ohta, H.; Yokoyama, N.; Teoh, Y.B.; Nisa, K.; Sasaki, N.; Osuga, T.; Morishita, K.; Takiguchi, M. Clinical Characteristics of Dogs with Food-responsive Protein-losing Enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laflamme, D. Nutritional management. Vet. Clin. 1997, 27, 1561–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WSAVA International Gastrointestinal Standardization Group; Washabau, R.J.; Day, M.J.; Willard, M.D.; Hall, E.J.; Jergens, A.E.; Mansell, J.; Minami, T.; Bilzer, T.W. Endoscopic, Biopsy, and Histopathologic Guidelines for the Evaluation of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Companion Animals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.J.; Bilzer, T.; Mansell, J.; Wilcock, B.; Hall, E.J.; Jergens, A.; Minami, T.; Willard, M.; Washabau, R. Histopathological Standards for the Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Endoscopic Biopsy Samples from the Dog and Cat: A Report from the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Gastrointestinal Standardization Group. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138, S1–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, E.; Pierini, A.; Benali, S.L.; Gori, E.; Abramo, F.; Bottero, E.; Pietra, M.; Ruggiero, P.; Marchetti, V. Evaluation of Duodenal Endoscopic and Histologic Findings, Including Counts of Forkhead Box P3-Positive Regulatory T Cells, in Dogs with Immunosuppressant-Responsive Enteropathy. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 82, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, M.; Simpson, J.W.; Ridyard, A.E.; Chandler, M.L. Canine Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Retrospective Analysis of Diagnosis and Outcome in 80 Cases (1995–2002). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenspach, K.; Culverwell, C.; Chan, D. Long-Term Outcome in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies: 203 Cases. Vet. Rec. 2016, 178, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jergens, A.E.; Schreiner, C.A.; Frank, D.E.; Niyo, Y.; Ahrens, F.E.; Eckersall, P.D.; Benson, T.J.; Evans, R. A Scoring Index for Disease Activity in Canine Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmerson, S.M.; Armstrong, P.J.; Wünschmann, A.; Jessen, C.R.; Crews, L.J.; Washabau, R.J. Clinical Features, Intestinal Histopathology, and Outcome in Protein-Losing Enteropathy in Yorkshire Terrier Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, M.; O’Morain, C. Nutritional Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Diseas. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2004, 7, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.C.; Munsell, M.; Harris, M.L. Nationwide Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Clinically Diagnosable Protein-Calorie Malnutrition in Hospitalized Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2008, 14, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirlich, M.; Schütz, T.; Kemps, M.; Luhman, N.; Burmester, G.-R.; Baumann, G.; Plauth, M.; Lübke, H.J.; Lochs, H. Prevalence of Malnutrition in Hospitalized Medical Patients: Impact of Underlying Disease. Digest. Dis. 2003, 21, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassull, M.A. Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Its Relation to Pathophysiology, Outcome and Therapy. Digest. Dis. 2003, 21, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenspach, K.; Rizzo, J.; Jergens, A.E.; Chang, Y.M. Hypovitaminosis D Is Associated with Negative Outcome in Dogs with Protein Losing Enteropathy: A Retrospective Study of 43 Cases. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allenspach, K.A.; Mochel, J.P.; Du, Y.; Priestnall, S.L.; Moore, F.; Slayter, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Ackermann, M.; Krockenberger, M.; Mansell, J.; et al. Correlating Gastrointestinal Histopathologic Changes to Clinical Disease Activity in Dogs with Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennogle, S.A.; Priestnall, S.L.; Webb, C.B. Histopathologic Characteristics of Intestinal Biopsy Samples from Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy With and Without Hypoalbuminemia. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moser, K.; Mitze, S.; Teske, E.; von Bomhard, W.; Stockhaus, C. Correlation of Clinical, Diagnostic and Histopathological Parameters in Dogs with Chronic Lymphocytic-Plasmacytic Enteropathy. Tierärztliche Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere/Heimtiere 2018, 46, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.S.; Gow, A.; Bommer, N.; Morrison, L.; Mellanby, R. Diagnostic Features, Treatment, and Outcome of Dogs with Inflammatory Protein-losing Enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Couto, K.M.; Moore, P.F.; Zwingenberger, A.L.; Willcox, J.L.; Skorupski, K.A. Clinical Characteristics and Outcome in Dogs with Small Cell T-cell Intestinal Lymphoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol 2018, 16, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.; Price, J.; Moore, A.; Dandrieux, J.R.S.; Clifford, C.; Curran, K.; Choy, K.; Cannon, C. Low-grade Gastrointestinal Lymphoma in Dogs: 20 Cases (2010 to 2016). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Abbreviation | Time | Variable Type | Variable Classes | Outcome or Potential Predictor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | T0 | Continuous | Potential predictor | ||
| Sex | T0 | Categorical nominal | Female Male | Potential predictor | |
| Sexual status | T0 | Categorical nominal | Entire De-sexed | Potential predictor | |
| Body condition score | BCS | T0 | Categorical ordinal | 1–3; 4–6. | Potential predictor |
| Total protein | TP | T0 | Continuous | N/A | Potential predictor |
| Albumin | ALB | T0 | Continuous | N/A | Potential predictor |
| Cholesterol | COL | T0 | Continuous | N/A | Potential predictor |
| C-reactive protein | CRP | T0 | Continuous | N/A | Potential predictor |
| Tissue appearance at endoscopy | T0 | Categorical ordinal | Normal, 0; Mild, 1; Moderate, 2; Severe, 3 | Potential predictor | |
| Tissue histopathology | T0 | Categorical ordinal | Normal, 0; Mild, 1; Moderate, 2; Severe, 3 | Potential predictor | |
| Crypt dilatation | CD | T0 | Categorical nominal | Yes/no | Potential predictor |
| Intraepithelial lymphocytes | IEL | T0 | Categorical nominal | Yes/no | Potential predictor |
| Mucosal fibrosis | MF | T0 | Categorical nominal | Yes/no | Potential predictor |
| Lacteal dilatation | LD | T0 | Categorical nominal | Yes/no | Potential predictor |
| Sum of histopathological lesions | SUM | T0 | Categorical ordinal | Sum of scores for presence/absence of crypt dilatation (CD), intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL), mucosal fibrosis (MF) and lacteal dilatation (LD) | Potential predictor |
| Canine chronic enteropathy clinical activity index at T0 | CCECAIT0 | T0 | Categorical ordinal | 0–9; >=10 | Potential predictor |
| Response to treatment | T1 vs. T0 | Categorical ordinal | Complete response: reduction in CCECAI >75% Partial response: reduction in CCECAI of 25–75% No response: reduction in CCECAI <=25% | Outcome | |
| Relapse | T3 > T18 | Categorical nominal | Yes/no, with yes defined as either an increase of >=2 in the CCECAI or death or euthanasia between any 2 time points from T3 to T18 | Outcome | |
| Mortality | T1–T18 | Categorical nominal | Yes/no with yes defined as either death or euthanasia | Outcome | |
| Long-term response | T1–T18 | Categorical nominal | Positive or negative where positive is defined as dogs responding at T0 and with no subsequent relapse, death or euthanasia | Outcome |
| Variable | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | 4 (7–15 Years) | |
| Sex and Sexual Status | 100 Males 65 Females | 100 Intact Males |
| 33 Spayed Females, 32 Intact Females | ||
| Breed | Mixed-breed | 36 dogs (22%) |
| German Shepherd | 26 dogs (16%) | |
| Boxer | 8 dogs (5%) | |
| English Setter | 7 dogs (4%) | |
| Yorkshire Terrier | 6 dogs (3%) | |
| Jack Russell Terrier | 6 dogs (3%) | |
| Dachshund | 5 dogs (3%) | |
| Maltese | 5 dogs (3%) | |
| Border Collie | 4 dogs (2%) | |
| Pinscher | 4 dogs (2%) | |
| Rottweiler | 4 dogs (2%) | |
| Golden Retriever | 3 dogs (2%) | |
| Siberian Husky | 3 dogs (2%) | |
| Bernese Mountain Dog, Italian Bracco, Cavalier King Charles Spaniel, Chihuahua, Dobermann, Irish Setter, Labrador Retriever, Poodle, Pug, Springer Spaniel, Weimaraner and West Highland White Terrier | 2 dogs each breed | |
| Akita Inu, Great Dane, Australian Shepherd, Basenji, Beagle, Belgian Shepherd, Bichon Frise, Bolognese, Central Asian Shepherd, Cocker Spaniel, Cane Corso, Dogue de Bordeaux, English Bulldog, Lagotto Romagnolo, Parson Russell Terrier, Russian Toy, St. Bernard, Shih Tzu, Pitbull, Levriero Italiano, Spanish Galgo, Swiss Shepherd Dog, Vizsla and Italian Volpino | 1 dog each breed | |
| Body condition score | 4 (range 1–6) | BCS 1/9 → 1 dog (0.6%) |
| BCS 2/9 → 9 dogs (5.5%) | ||
| BCS 3/9 → 54 dogs (32.7%) | ||
| BCS 4/9 → 65 dogs (39.4%) | ||
| BCS 5/9 → 34 dogs (20.6%) | ||
| BCS 6/9 → 2 dogs (1.2%) | ||
| Total protein | 5.5 ± 1.3 g/dL | Hypoproteinaemia → 92 dogs (56%) |
| Albumin | 2.6 g/dL (range 0.7–4.4 g/dL) | Hypoalbuminaemia (PLE) → 84 dogs (51%) |
| Cholesterol | 152 mg/dL (range 54–428 mg/dL) | Hypocholesterolaemia → 42 dogs (25%) |
| C-reactive protein | 0.3 mg/dL (range 0–2.8 mg/dL) | ↑ CRP (>0.3 mg/dL) → 81 dogs (49%) |
| Endoscopic score | Endoscopic score 0–1 → 0 dogs | |
| Endoscopic score 2 → 66 dogs (40%) | ||
| Endoscopic score 3 → 99 dogs (60%) | ||
| Histopathological score | Histopathological score 1 → 11 dogs (7%) | |
| Histopathological score 2 → 108 dogs (65%) | ||
| Histopathological score 3 → 46 dogs (28%) | ||
| Histopathological lesions | Crypt distension | 115 dogs (70%) |
| Intraepithelial lymphocytes | 64 dogs (39%) | |
| Mucosal fibrosis | 45 dogs (27%) | |
| Lacteal dilatation | 62 dogs (39%) | |
| Parameter | BCS | TP | ALB | COL | CRP | SUM | CCECAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCS | 1 | p = 0.0001 ρ = 0.317 | p = 0.0001 ρ = 0.362 | p = 0.005 ρ = 0.218 | NS | p = 0.0001 ρ = −0.240 | p = 0.012 ρ = −0.199 |
| TP | 1 | p = 0.0001 ρ = 0.867 | p = 0.0001 ρ = 0.649 | NS | p = 0.0001 ρ = −0.258 | NS | |
| ALB | 1 | p = 0.0001 ρ = 0.582 | NS | p = 0.002 ρ = −0.240 | NS | ||
| COL | 1 | p = 0.014 ρ = 0.193 | p = 0.047 ρ = −0.156 | NS | |||
| CRP | 1 | NS | NS | ||||
| SUM | 1 | NS | |||||
| CCECAI | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benvenuti, E.; Pierini, A.; Bottero, E.; Pietra, M.; Gori, E.; Salvadori, S.; Marchetti, V. Immunosuppressant-Responsive Enteropathy and Non-Responsive Enteropathy in Dogs: Prognostic Factors, Short- and Long-Term Follow Up. Animals 2021, 11, 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092637
Benvenuti E, Pierini A, Bottero E, Pietra M, Gori E, Salvadori S, Marchetti V. Immunosuppressant-Responsive Enteropathy and Non-Responsive Enteropathy in Dogs: Prognostic Factors, Short- and Long-Term Follow Up. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092637
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenvenuti, Elena, Alessio Pierini, Enrico Bottero, Marco Pietra, Eleonora Gori, Stefano Salvadori, and Veronica Marchetti. 2021. "Immunosuppressant-Responsive Enteropathy and Non-Responsive Enteropathy in Dogs: Prognostic Factors, Short- and Long-Term Follow Up" Animals 11, no. 9: 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092637
APA StyleBenvenuti, E., Pierini, A., Bottero, E., Pietra, M., Gori, E., Salvadori, S., & Marchetti, V. (2021). Immunosuppressant-Responsive Enteropathy and Non-Responsive Enteropathy in Dogs: Prognostic Factors, Short- and Long-Term Follow Up. Animals, 11(9), 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092637









