Effect of Dietary Clostridium butyricum Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier Function, Immune Function, and Microbiota Diversity of Pekin Ducks
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
2.2. Dietary Treatments and Feeding
2.3. Serum Measurements
2.4. Morphological Observation and Analyses
2.5. Measurement of Intestinal SCFAs
2.6. Gene Expression Measurement
2.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of C. butyricum and Aureomycin on Growth Performance of Pekin Duck
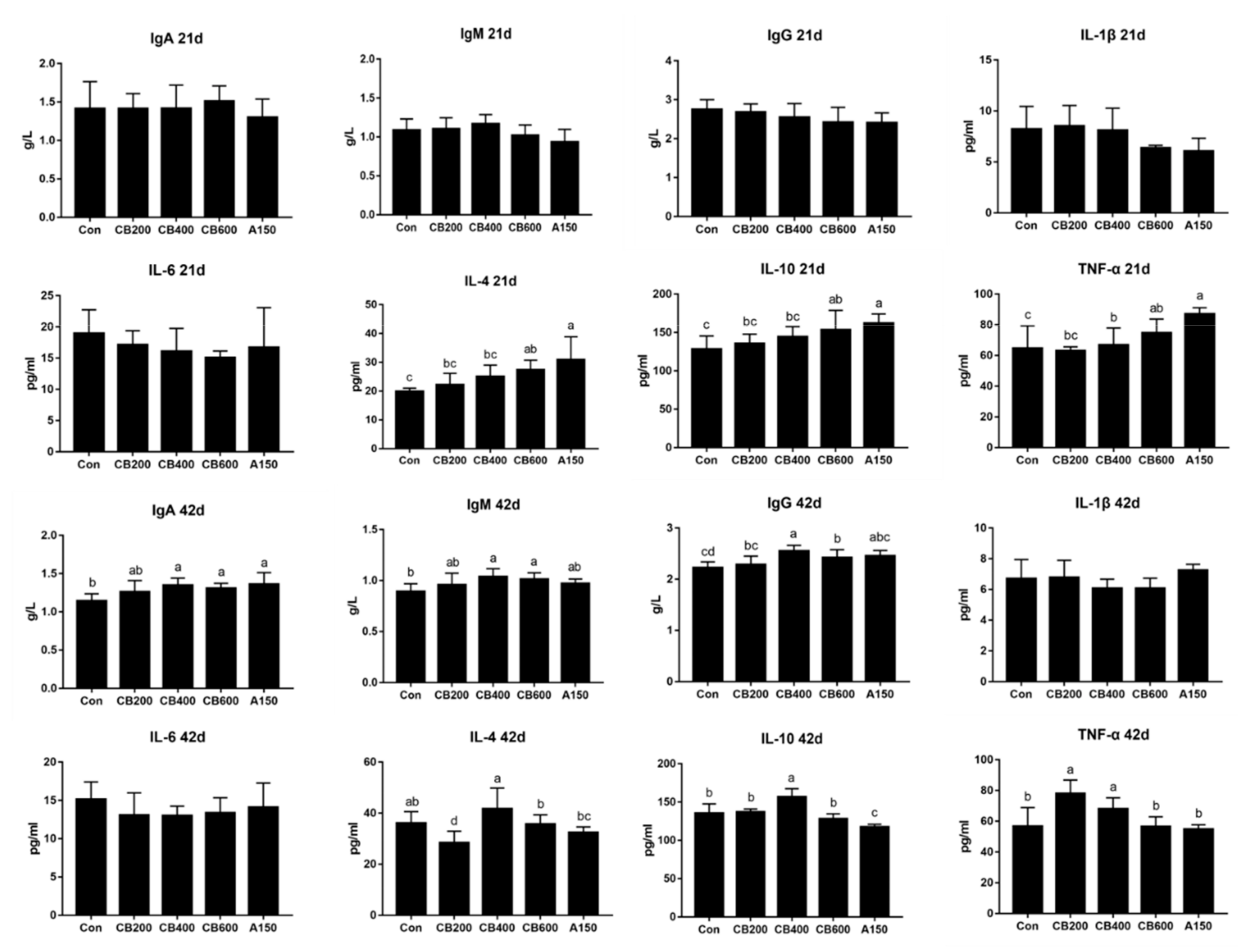
3.2. Effect of C. butyricum and Aureomycin on Immunologic Function of Pekin Duck
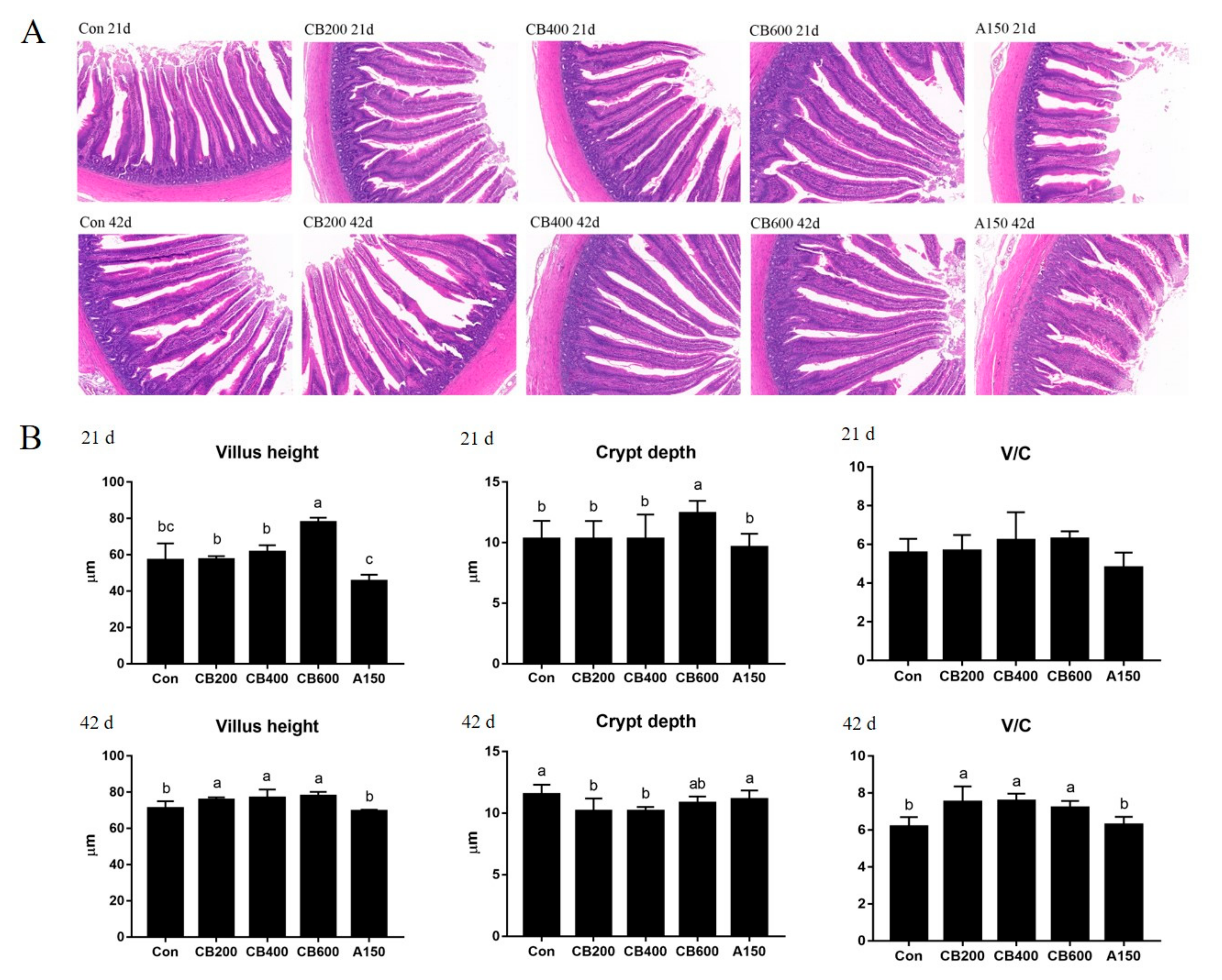
3.3. Effects of C. butyricum and Aureomycin on Intestinal Morphology of Pekin Duck
3.4. Effect of C. butyricum and Aureomycin on Fecal SCFAs
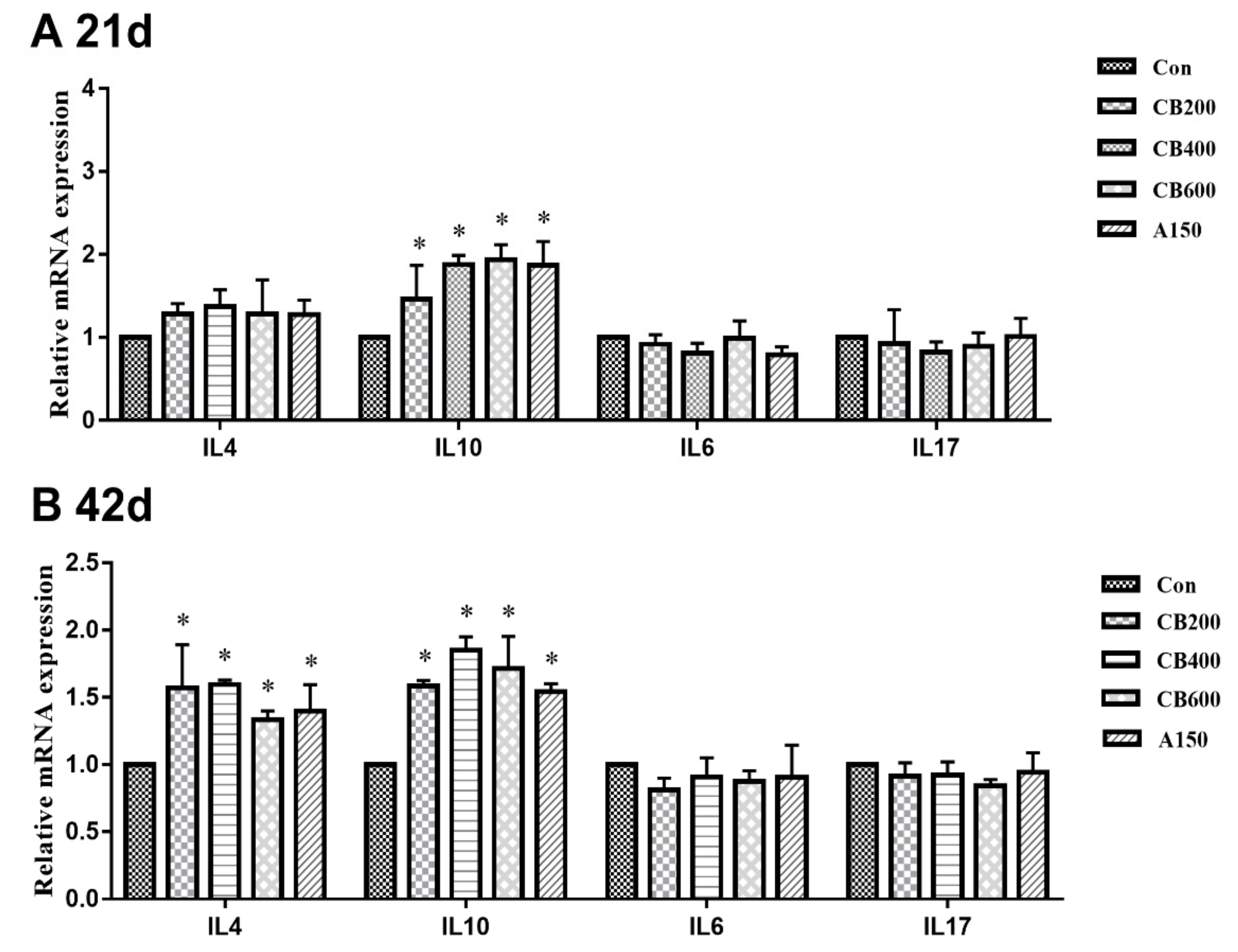
3.5. Expression of Tight Junction and Immune Related-Genes in Gut
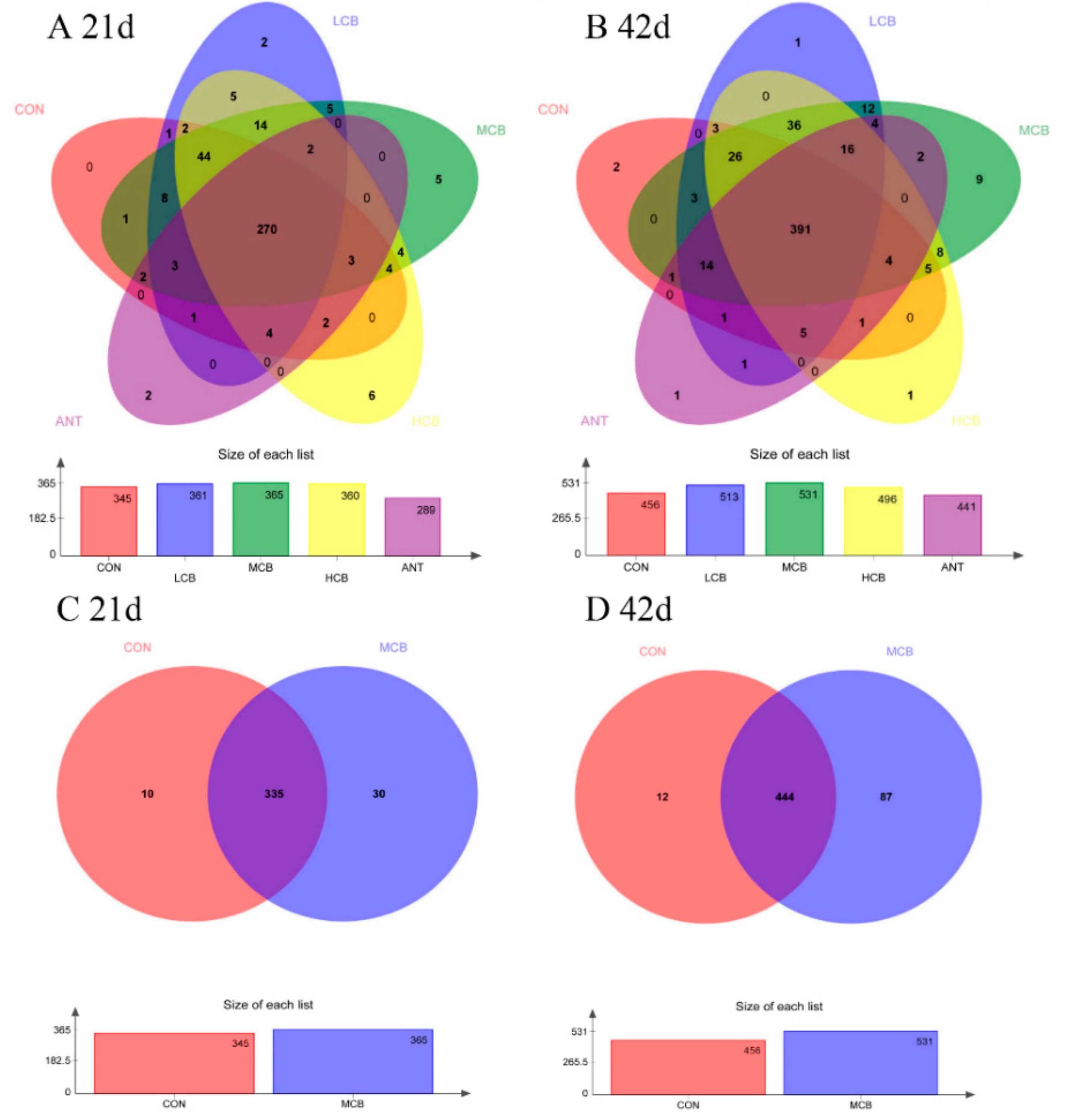
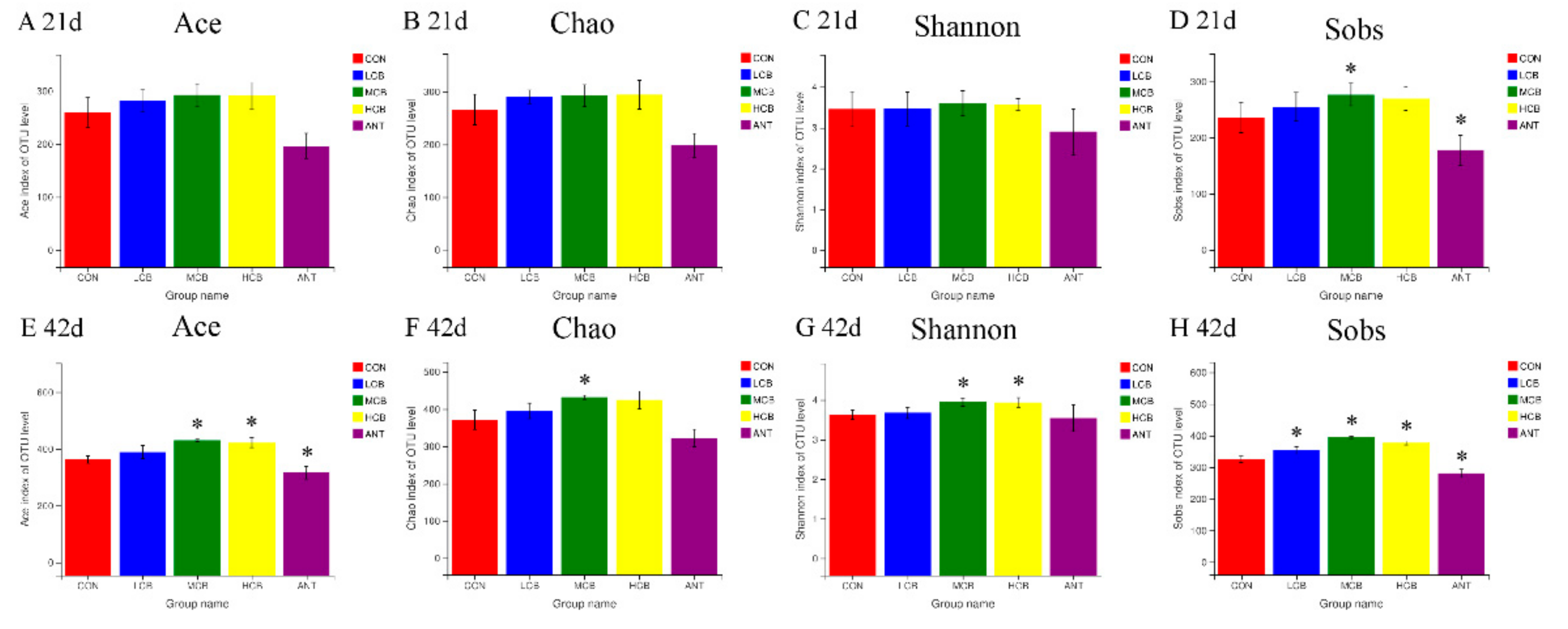
3.6. Quality of Sequencing Data
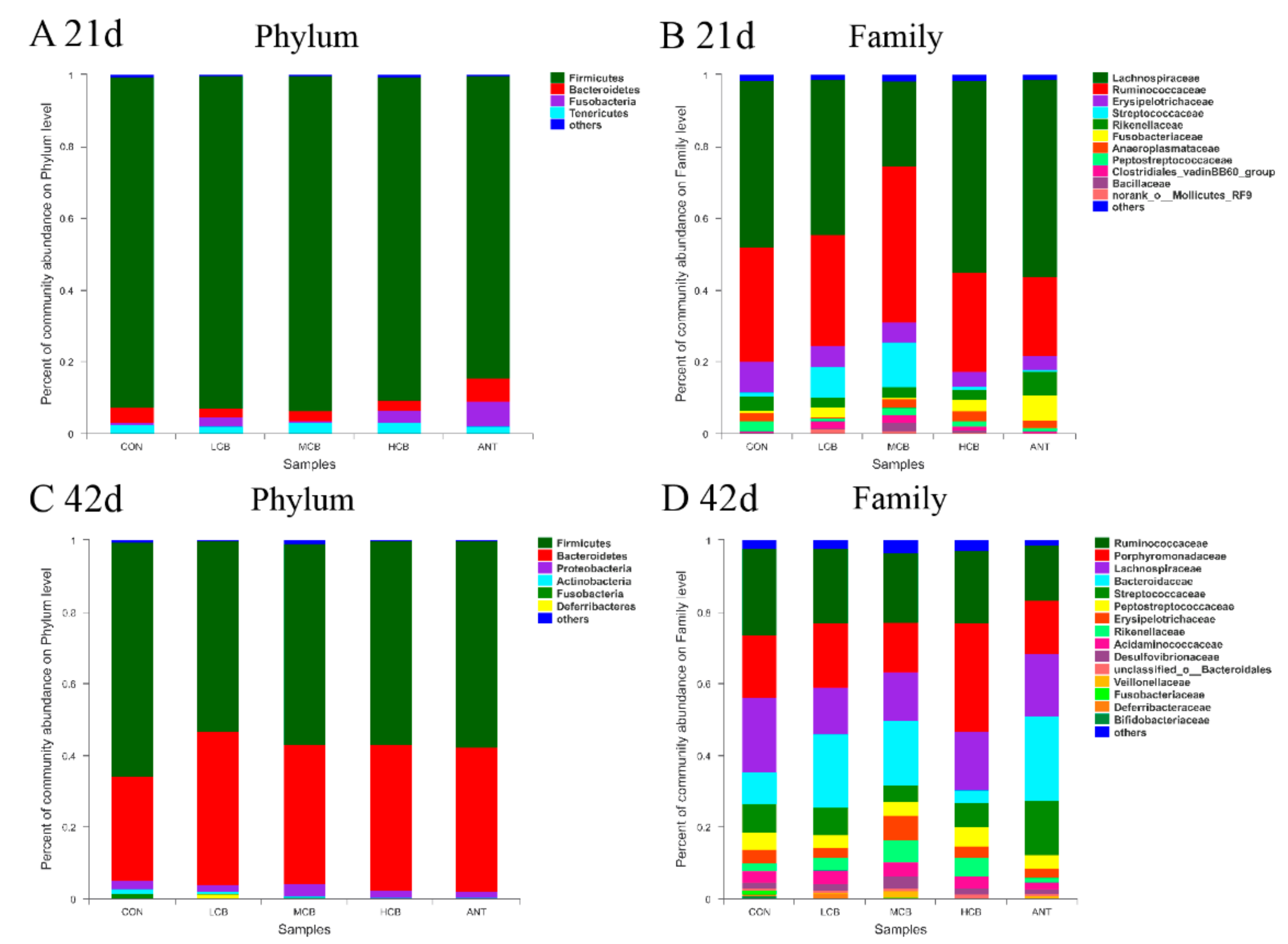
3.7. Effect of C. butyricum and Aureomycin on Relative Abundances of Species Structure and Community Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, J.; Kou, S.; Chen, C.; Raza, S.H.A.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.J.; Nie, C. Effects of Clostridium butyricum on growth performance, metabonomics and intestinal microbial differences of weaned piglets. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ding, X.; Yang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, S. Effects of Clostridium butyricum on breast muscle lipid metabolism of broilers. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 17, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagihara, M.; Yamashita, R.; Matsumoto, A.; Mori, T.; Kuroki, Y.; Kudo, H.; Oka, K.; Takahashi, M.; Nonogaki, T.; Yamagishi, Y.; et al. The impact of Clostridium butyricum MIYAIRI 588 on the murine gut microbiome and colonic tissue. Anaerobe 2018, 54, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Wu, R.; Ma, G.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, R. Effects of Clostridium butyricum on antioxidant properties, meat quality and fatty acid composition of broiler birds. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, H.; Ding, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, D. Changes in the Intestine Microbial, Digestive, and Immune-Related Genes of Litopenaeus vannamei in Response to Dietary Probiotic Clostridium butyricum Supplementation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z. Dietary supplementation with Clostridium butyricum modulates serum lipid metabolism, meat quality, and the amino acid and fatty acid composition of Peking ducks. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3218–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y.; Zong, X. Clostridium Butyricum ZJU-F1 Benefits the Intestinal Barrier Function and Immune Response Associated with Its Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Weaned Piglets. Cells 2021, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, B.R.; Siliciano, J.D.; Mooseker, M.S.; Goodenough, D.A. Identification of ZO-1: A high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J. Cell. Biol. 1986, 103, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, J.; Chang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B. Effects of alcohol on intestinal epithelial barrier permeability and expression of tight junction-associated proteins. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Deng, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Yang, X. Vitamin A Inhibits the Action of LPS on Intestinal Epithelial Barrie Function and Tight Junction Proteins. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Gui, W.; Sun, D.; Dai, H.; Xiao, L.; Chu, H.; Du, F.; Zhu, Q.; Schnabl, B. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid inhibits intestinal inflammation and barrier disruption in NAFLD mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Sadi, R.M.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1beta causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4641–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tossetta, G.; Paolinelli, F.; Avellini, C.; Salvolini, E.; Ciarmela, P.; Lorenzi, T.; Emanuelli, M.; Toti, P.; Giuliante, R.; Gesuita, R. IL-1β and TGF-β weaken the placental barrier through destruction of tight junctions: An in vivo and in vitro study. Placenta 2014, 35, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Niioka, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, T. Butyrate-producing probiotics reduce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in rats: New insight into the probiotics for the gut-liver axis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, Y.; Yu, Y.; Bai, F.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Qin, C.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on neurological restoration in a spinal cord injury mouse model: Involvement of brain-gut axis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, T.F.; Casarotti, S.N.; de Oliveira, G.L.V.; Penna, A.L.B. The impact of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on the biochemical, clinical, and immunological markers, as well as on the gut microbiota of obese hosts. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Kuroki, Y.; Oka, K.; Takahashi, M.; Rao, S.; Sukegawa, S.; Fujimura, T. Effects of Dietary Supplementation With Enterococcus faecium and Clostridium butyricum, Either Alone or in Combination, on Growth and Fecal Microbiota Composition of Post-weaning Pigs at a Commercial Farm. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molnár, A.; Such, N.; Farkas, V.; Pál, L.; Menyhárt, L.; Wágner, L.; Husvéth, F.; Dublecz, K. Effects of Wheat Bran and Clostridium butyricum Supplementation on Cecal Microbiota, Short-Chain Fatty Acid Concentration, pH and Histomorphometry in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2020, 10, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinolo, M.A.R.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Nachbar, R.T.; Curi, R. Modulation of inflammatory and immune responses by short-chain fatty acids. Diet Immun. Inflamm. 2013, 17, 435–458. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Yan, X.; Su, L. Anti-inflammation effects of fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from Acaudina molpadioides by altering gut microbiota in obese mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, M.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Shewita, R.S.; Ba-Awadh, H.A.; Alowaimer, A.N.; Abd El-Hamid, H.S. Single and Combined Effects of Clostridium butyricum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on Growth Indices, Intestinal Health, and Immunity of Broilers. Animals 2018, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zeng, D.; Yang, M.; Wen, B.; Lai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, H.; Xiong, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; et al. Probiotic Clostridium butyricum Improves the Growth Performance, Immune Function, and Gut Microbiota of Weaning Rex Rabbits. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 11, 1278–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Dai, R.; Yang, L.; He, C.; Xu, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, L.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Inheritance and Establishment of Gut Microbiota in Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Miao, Z.; Song, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tian, W.; Guo, Y. Effect of Dietary Nutrient Density on Small Intestinal Phosphate Transport and Bone Mineralization of Broilers during the Growing Period. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus on the growth performance and intestinal health of broilers challenged with Clostridium perfringens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, X.A.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, L.; Cao, G.; Chen, A.G.; Yang, C. Effects of dietary supplementation of probiotic, Clostridium butyricum, on growth performance, immune response, intestinal barrier function, and digestive enzyme activity in broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli K88. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, G.; Tao, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, B.; Zhan, X. Positive effects of a Clostridium butyricum-based compound probiotic on growth performance, immune responses, intestinal morphology, hypothalamic neurotransmitters, and colonic microbiota in weaned piglets. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, F.D.; Cummings, T.S.; Barbosa, T.M.; Williams, C.J.; Gerard, P.D.; Peebles, E.D. Comparison of two methods for determination of intestinal villus to crypt ratios and documentation of early age-associated ratio changes in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.; Freitas, V.D.; Almeida, L.M.; Laranjinha, J. Red wine extract preserves tight junctions in intestinal epithelial cells under inflammatory conditions: Implications for intestinal inflammation. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, G.U.; Liu, J.B.; Huo, W.Z. BBI blocks LPS-mediated inhibitory effect on tight junction protein of intestinal epithelial cells. Chin. J. Infect. Control. 2018, 17, 185–190. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lucke, A.; Böhm, J.; Zebeli, Q.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U. Dietary Deoxynivalenol Contamination and Oral Lipopolysaccharide Challenge Alters the Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berni, C.; Canani, M.; Costanzo, L.; Leone, M.; Pedata, R. Potential beneficial effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Q.F.; Gao, F.; Dai, S.F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, G.H. Sodium butyrate maintains growth performance by regulating the immune response in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2011, 52, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Packialakshmi, B.; Makkar, S.K.; Dridi, S.; Rath, N.C. Effect of butyrate on immune response of a chicken macrophage cell line. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 162, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herron, L.R.; Pridans, C.; Turnbull, M.L.; Smith, N.; Lillico, S.; Sherman, A.; Gilhooley, H.J.; Wear, M.; Kurian, D.; Papadakos, G. A chicken bioreactor for efficient production of functional cytokines. BMC Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fata, G.L.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. Probiotics and the Gut Immune System: Indirect Regulation. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, E.; Williams, B.A.; Smidt, H.; Verstegen, M.W.; Mosenthin, R. Influence of the gastrointestinal microbiota on development of the immune system in young animals. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2006, 7, 35–51. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, R.X.; Zhu, X.X.; Wan, C.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.Y. Effect of Clostridium butyricum supplementation on the development of intestinal flora and the immune system of neonatal mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Cresci, G.A.; Thangaraju, M.; Mellinger, J.D.; Liu, K.; Ganapathy, V. Colonic Gene Expression in Conventional and Germ-Free Mice with a Focus on the Butyrate Receptor GPR109A and the Butyrate Transporter SLC5A8. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2010, 14, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Tauro, S.; Das, I.; Tong, H.; Chen, A.C.H.; Jeffery, P.L.; Mcdonald, V.; Florin, T.H.; Mcguckin, M.A. IL-10 Promotes Production of Intestinal Mucus by Suppressing Protein Misfolding and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Goblet Cells. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimiaeitalab, M.V.; Goudarzi, S.M.; Jiménez-Moreno, E.; Cámara, L.; Mateos, G.G. A comparative study on the effects of dietary sunflower hulls on growth performance and digestive tract traits of broilers and pullets fed a pullet diet from 0 to 21 days of age. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 236, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, B.; Lv, H.; Guo, Y. Effects of Kluyveromyces marxianus supplementation on immune responses, intestinal structure and microbiota in broiler chickens. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Derrien, M.; Rocher, E.; van-Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.; Strissel, K.; Zhao, L.; Obin, M.; et al. Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Iji, P.A.; Choct, M. Dietary modulation of gut microflora in broiler chickens: A review of the role of six kinds of alternatives to in-feed antibiotics. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2009, 65, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhong, H.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y. Effect of probiotics on the meat flavour and gut microbiota of chicken. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanca, A.; Manghina, V.; Fraumene, C.; Palomba, A.; Abbondio, M.; Deligios, M.; Silverman, M.; Uzzau, S. Metaproteogenomics Reveals Taxonomic and Functional Changes between Cecal and Fecal Microbiota in Mouse. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; He, M.; Shen, J.; Li, G.; Tao, Z.; Wu, R.; Lu, L. Different rearing conditions alter gut microbiota composition and host physiology in Shaoxing ducks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, K.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tso, P.; Wu, Z. Interactions between Intestinal Microbiota and Host Immune Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Guo, P.; Lu, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Johnston, L.J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Dietary Corn Bran Altered the Diversity of Microbial Communities and Cytokine Production in Weaned Pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, R.J.; Hinsu, A.T.; Patel, N.V.; Koringa, P.G.; Jakhesara, S.J.; Thakkar, J.R.; Shah, T.M.; Limon, G.; Psifidi, A.; Guitian, J.; et al. Microbial diversity and community composition of caecal microbiota in commercial and indigenous Indian chickens determined using 16s rDNA amplicon sequencing. Microbiome 2018, 6, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | 1–21 d | 22–42 d |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients (%) | ||
| Corn | 56.00 | 60.24 |
| Soybean meal | 32.69 | 24.67 |
| Wheat middling | 5.00 | 9.00 |
| Soybean oil | 2.10 | 1.80 |
| Phytases | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.00 | 1.60 |
| Limestone | 1.50 | 1.20 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| L-Lysine | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| Vitamin premix 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Trace mineral premix 2 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| NaCl | 0.35 | 0.30 |
| Choline chloride (50%) | 0.24 | 0.20 |
| Ethoxyquin (33%) | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Bentonite | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| Nutrient levels 3 (%) | ||
| AME (MJ/kg) | 12.31 | 12.53 |
| Crude protein (%) | 19.52 | 16.83 |
| Lysine (%) | 1.12 | 0.87 |
| Methionine (%) | 0.46 | 0.39 |
| Calcium (%) | 0.88 | 0.89 |
| Available phosphorus (%) | 0.29 | 0.39 |
| Total phosphorus (%) | 0.54 | 0.62 |
| Methionine + Cysteine (%) | 0.79 | 0.69 |
| Items 2 | Group Con | Group CB200 | Group CB400 | Group CB600 | Group A150 | SEM3 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–21 d | |||||||
| ABW (kg) | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.26 | 1.17 | 1.07 | 0.02 | 0.062 |
| ADG (g/d) | 55.98 | 54.04 | 56.21 | 53.95 | 53.42 | 0.58 | 0.439 |
| ADFI (g/d) | 90.62 | 86.36 | 85.46 | 89.24 | 86.16 | 1.23 | 0.651 |
| FCR | 1.62 | 1.61 | 1.52 | 1.66 | 1.62 | 0.03 | 0.753 |
| 22–42 d | |||||||
| ABW (kg) | 2.88 b | 2.98 b | 3.18 a | 3.15 a | 2.94 b | 0.03 | 0.009 |
| ADG (g/d) | 155.09 b | 157.19 b | 162.75 a | 155.43 b | 155.31 b | 0.92 | 0.028 |
| ADFI (g/d) | 246.96 | 236.39 | 244.32 | 244.85 | 243.82 | 2.08 | 0.584 |
| FCR | 1.59 a | 1.50 b | 1.50 b | 1.58 a | 1.57 a | 0.01 | 0.029 |
| Items | Group Con | Group CB200 | Group CB400 | Group CB600 | Group A150 | SEM2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 day | |||||||
| Acetate | 526.61 | 517.34 | 540.61 | 527.64 | 504.90 | 4.60 | 0.136 |
| Propionate | 283.37 a | 270.80 ac | 245.50 bc | 251.82 bc | 211.23 d | 7.54 | 0.004 |
| Iso-butyrate | 122.81 | 128.40 | 137.27 | 128.32 | 126.84 | 1.67 | 0.056 |
| Butyrate | 1360.59 d | 1513.37 c | 1560.94 a | 1556.94 ab | 1539.56 ab | 20.23 | <0.001 |
| Iso-valerate | 42.74 c | 51.38 a | 49.65 ab | 45.98 bc | 46.14 bc | 0.95 | 0.006 |
| Valerate | 62.60 | 60.18 | 61.08 | 57.48 | 58.97 | 1.01 | 0.619 |
| 42 day | |||||||
| Acetate | 647.54 b | 617.41 b | 780.75 a | 777.65 a | 681.57 b | 21.21 | 0.037 |
| Propionate | 283.38 ab | 297.46 ab | 352.17 a | 255.15 ab | 218.89 b | 4.72 | 0.022 |
| Iso-butyrate | 124.48 c | 145.06 ab | 157.50 ab | 165.00 a | 144.84 b | 4.40 | 0.011 |
| Butyrate | 1773.96 bc | 1909.93 ab | 2070.21 a | 2000.27 a | 1736.23 bc | 39.73 | 0.006 |
| Iso-valerate | 48.74 b | 74.71 a | 87.98 a | 89.31 a | 89.41 a | 5.21 | 0.024 |
| Valerate | 85.93 | 126.84 | 124.41 | 137.48 | 112.30 | 6.96 | 0.152 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; An, K.; Gong, X.; Xia, Z. Effect of Dietary Clostridium butyricum Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier Function, Immune Function, and Microbiota Diversity of Pekin Ducks. Animals 2021, 11, 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092514
Liu Y, Liu C, An K, Gong X, Xia Z. Effect of Dietary Clostridium butyricum Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier Function, Immune Function, and Microbiota Diversity of Pekin Ducks. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092514
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanhan, Cun Liu, Keying An, Xiaowei Gong, and Zhaofei Xia. 2021. "Effect of Dietary Clostridium butyricum Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier Function, Immune Function, and Microbiota Diversity of Pekin Ducks" Animals 11, no. 9: 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092514
APA StyleLiu, Y., Liu, C., An, K., Gong, X., & Xia, Z. (2021). Effect of Dietary Clostridium butyricum Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier Function, Immune Function, and Microbiota Diversity of Pekin Ducks. Animals, 11(9), 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092514





