cAMP Modulators before In Vitro Maturation Decrease DNA Damage and Boost Developmental Potential of Sheep Oocytes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oocyte Collection and Pre-Maturation Culture
2.2. Measurement of cAMP Levels in Denuded Oocytes
2.3. In Vitro Maturation
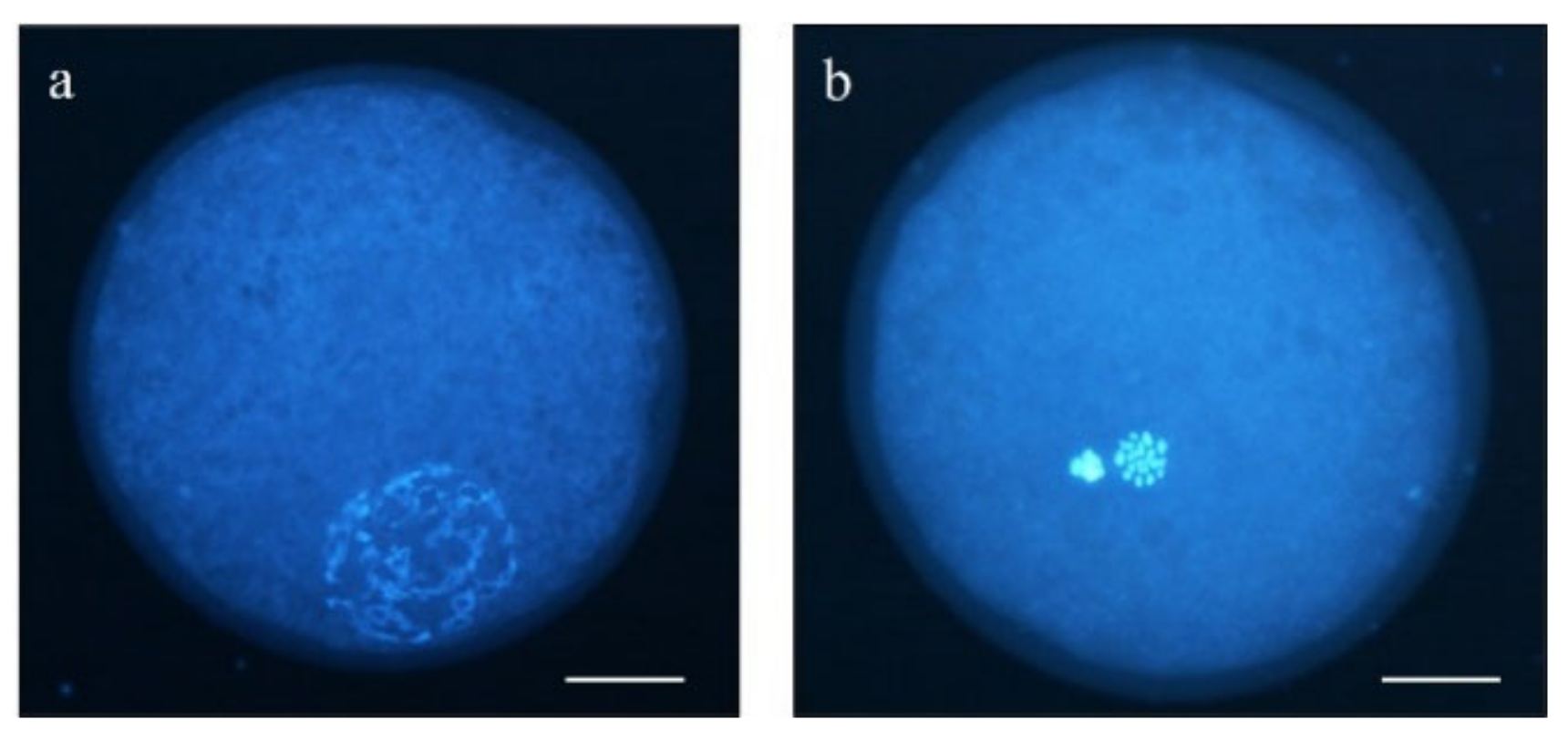
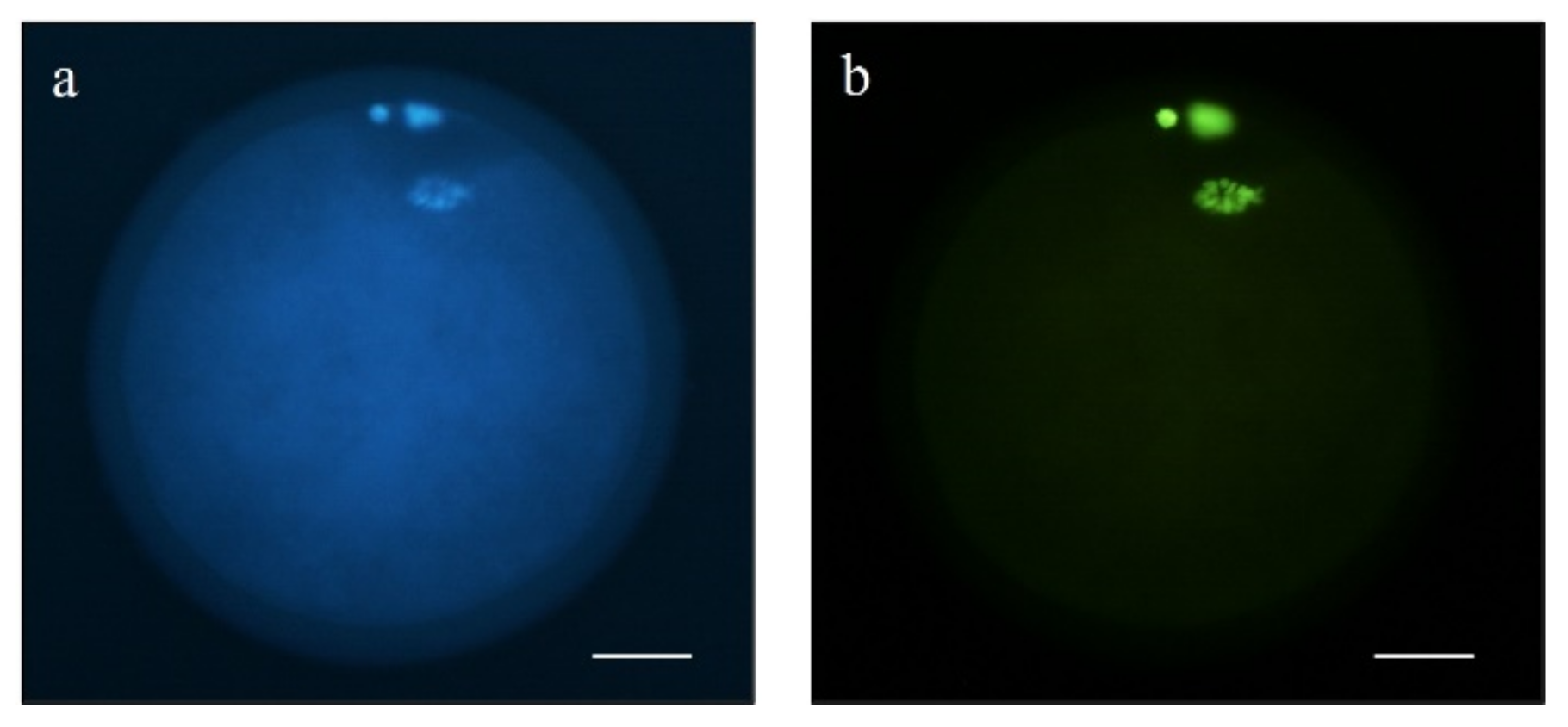
2.4. Determination of Nuclear Maturation Stage
2.5. Evaluation of Quality Parameters in Oocytes and Cumulus Cells
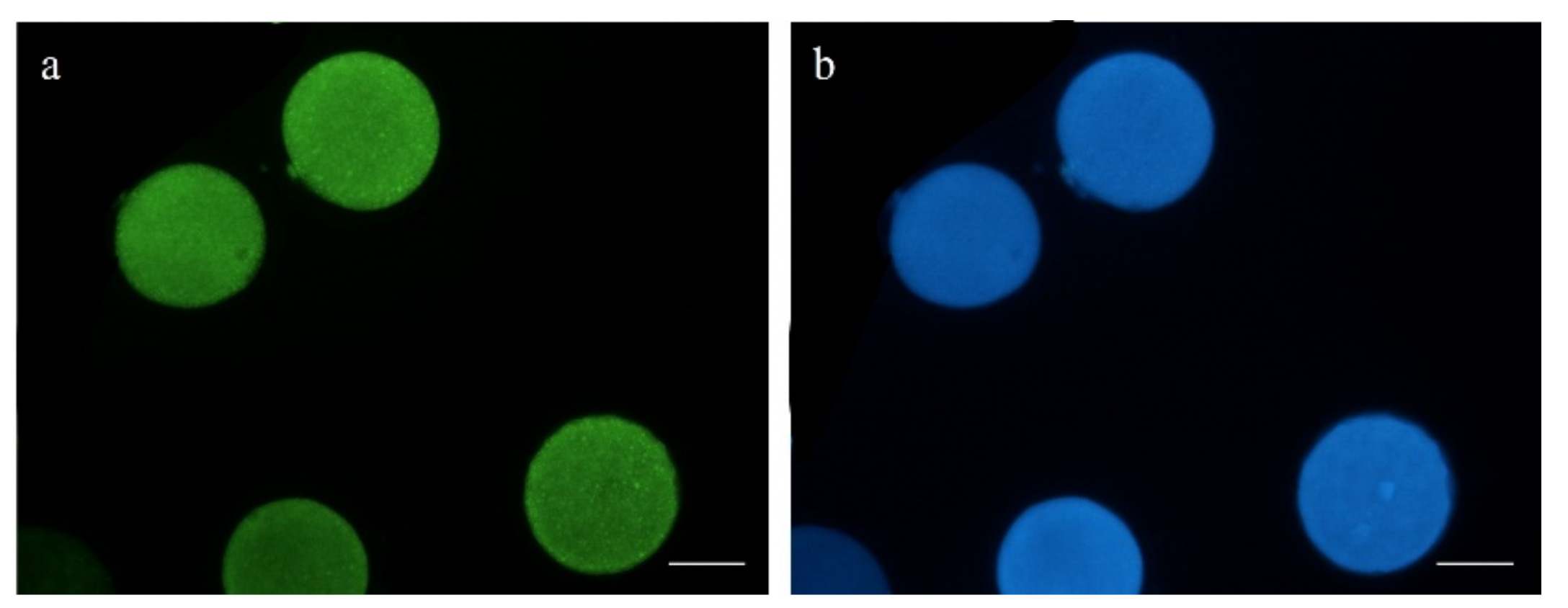
2.5.1. Early Apoptosis Assessment
2.5.2. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Reduced Glutathione (GSH)
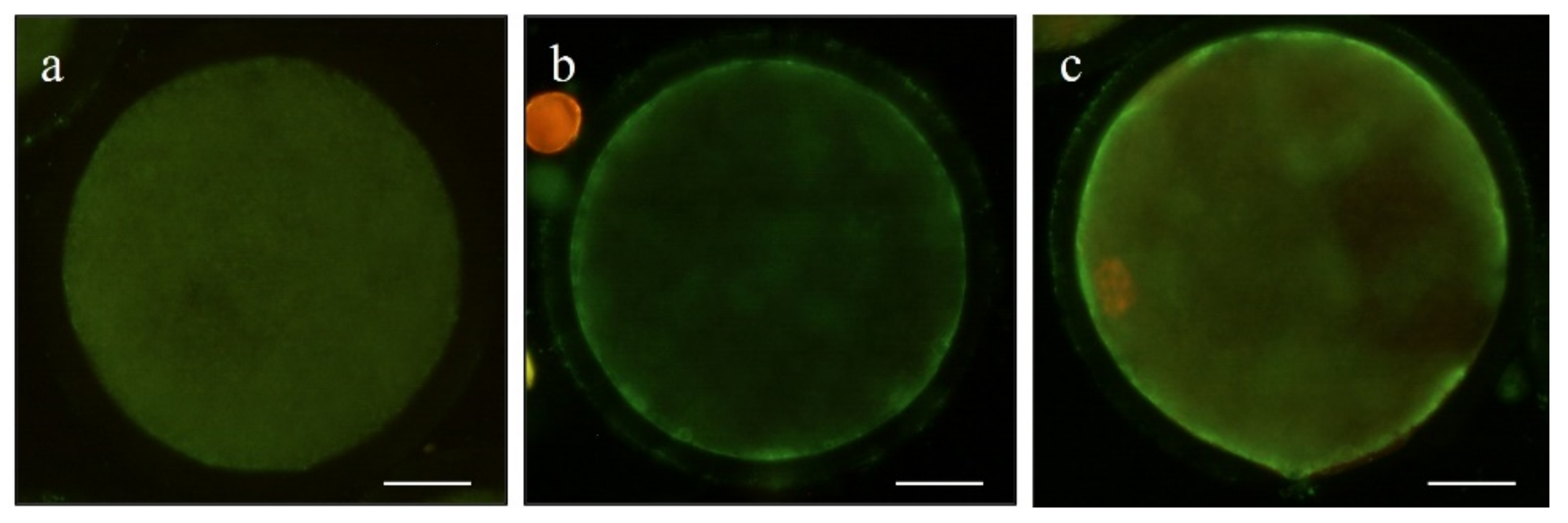
2.5.3. Evaluation of Mitochondrial and Cortical Granule Distribution
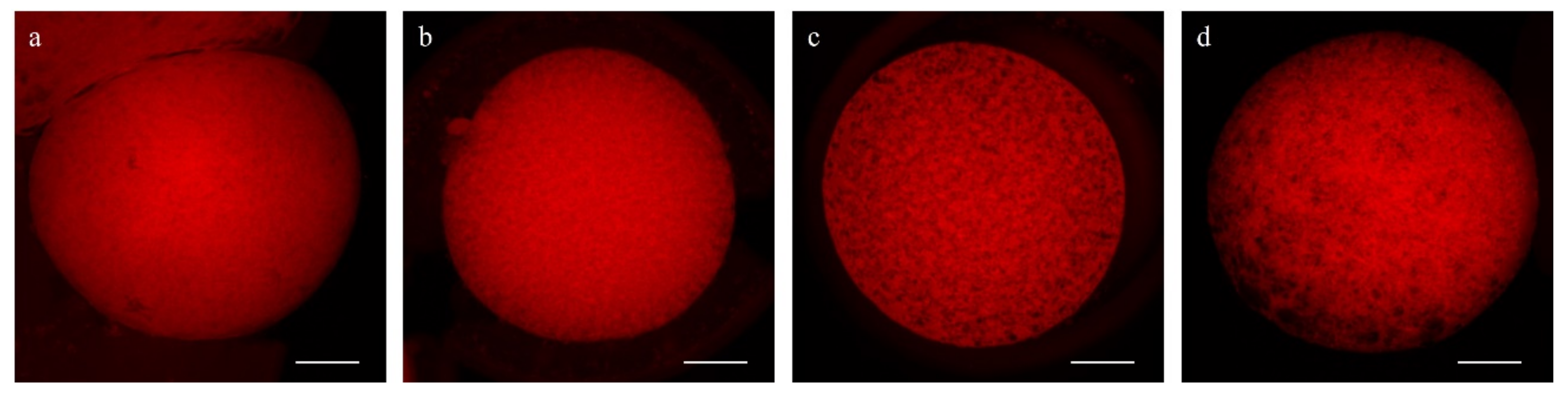
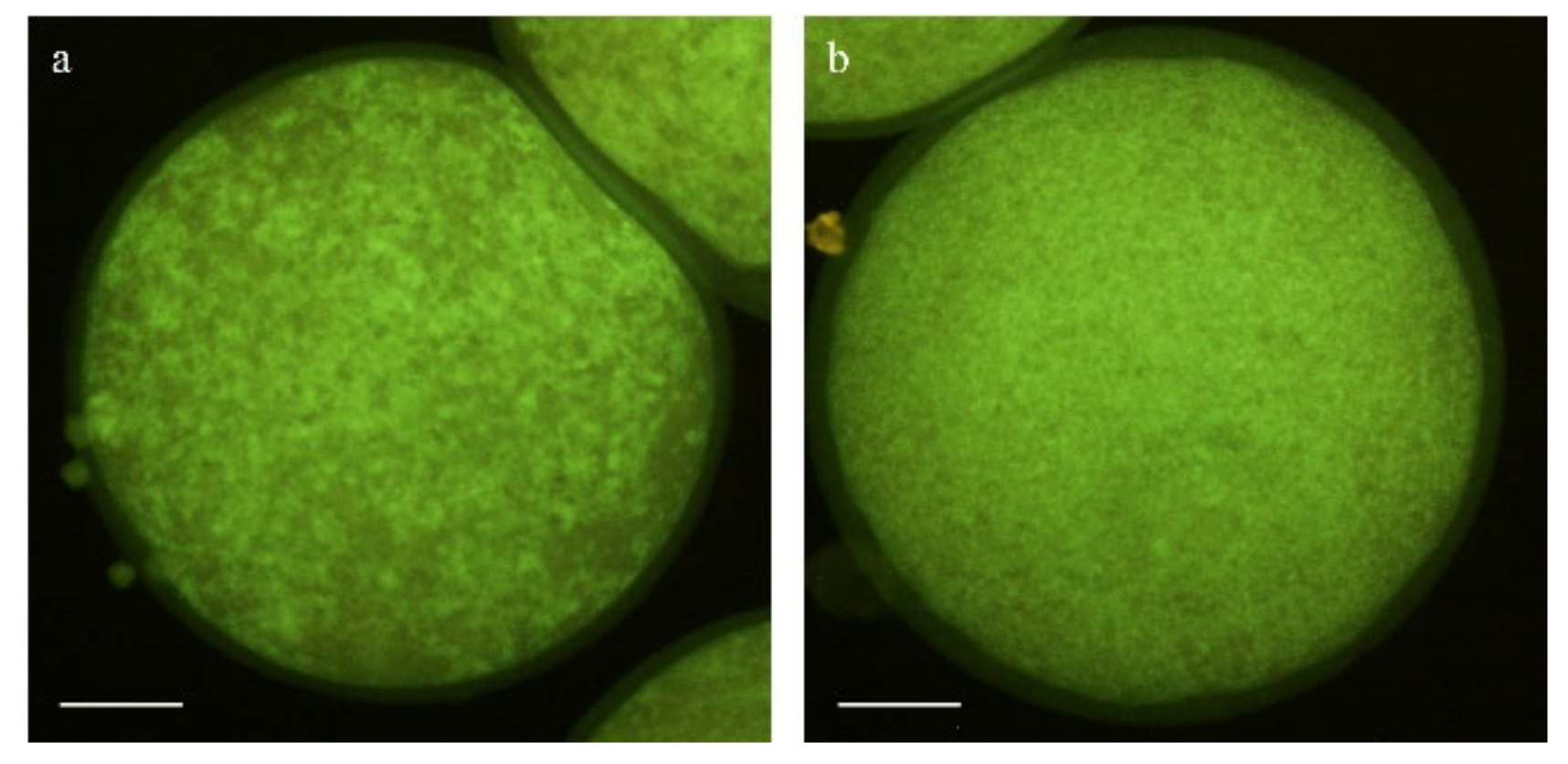
2.5.4. DNA Fragmentation Assay
2.5.5. mRNA Transcript Analysis
2.5.6. Cumulus Cells’ Analysis
2.6. In Vitro Embryo Production
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
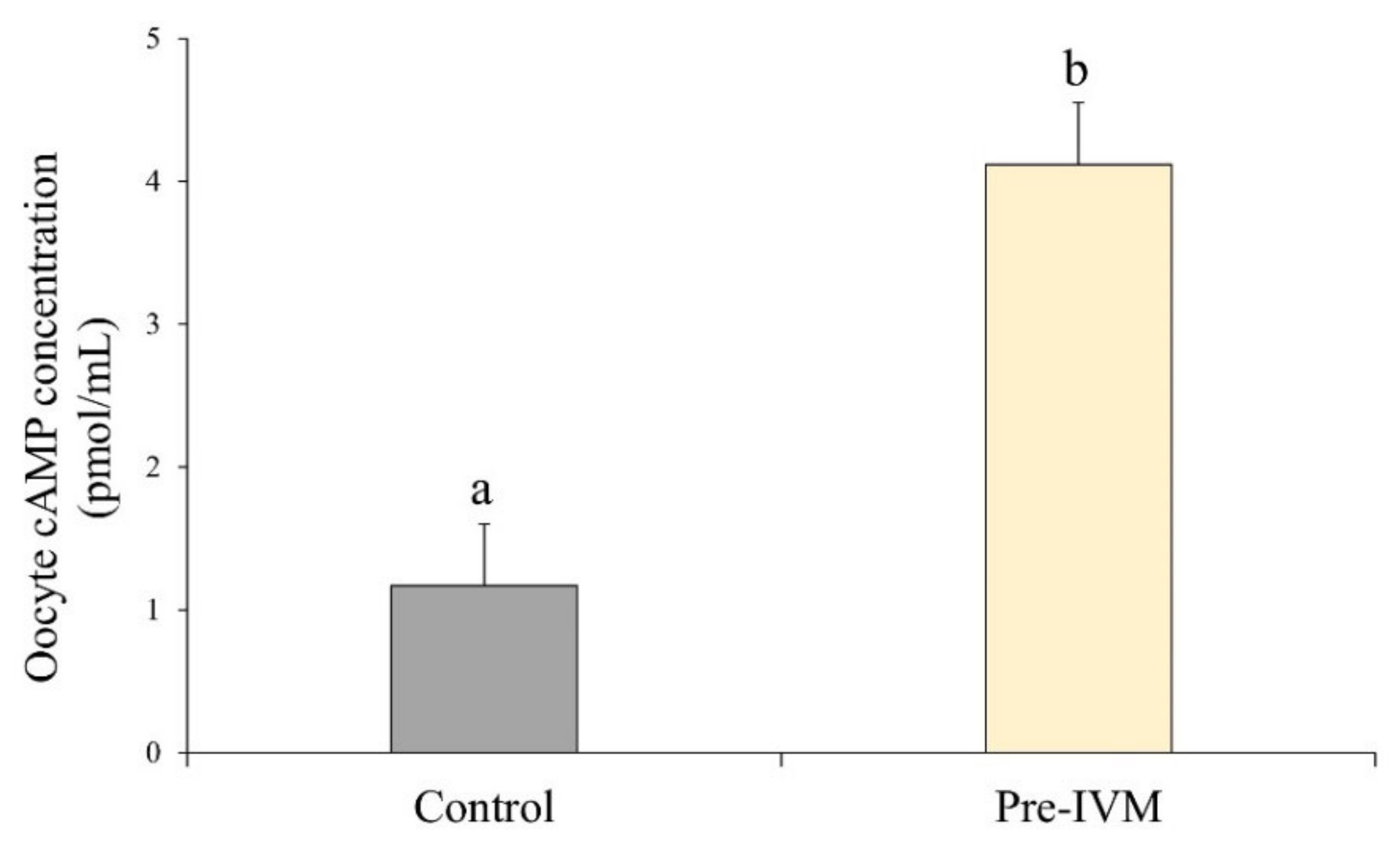
3.1. Changes in Intra-Oocyte cAMP Levels after Incubation with Forskolin and IBMX during Pre-IVM
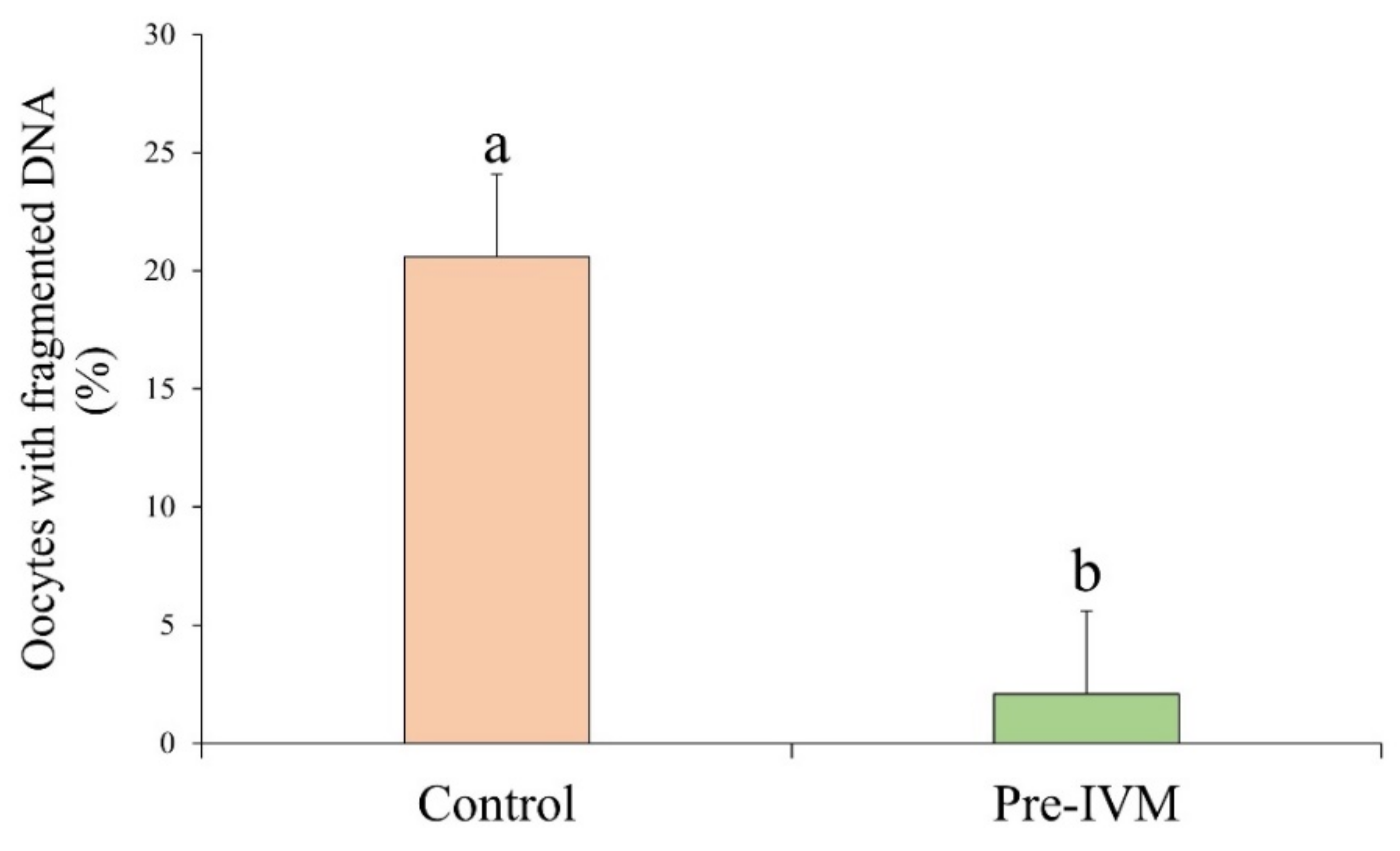
3.2. Oocyte DNA Fragmentation Levels Are Affected by cAMP Modulators
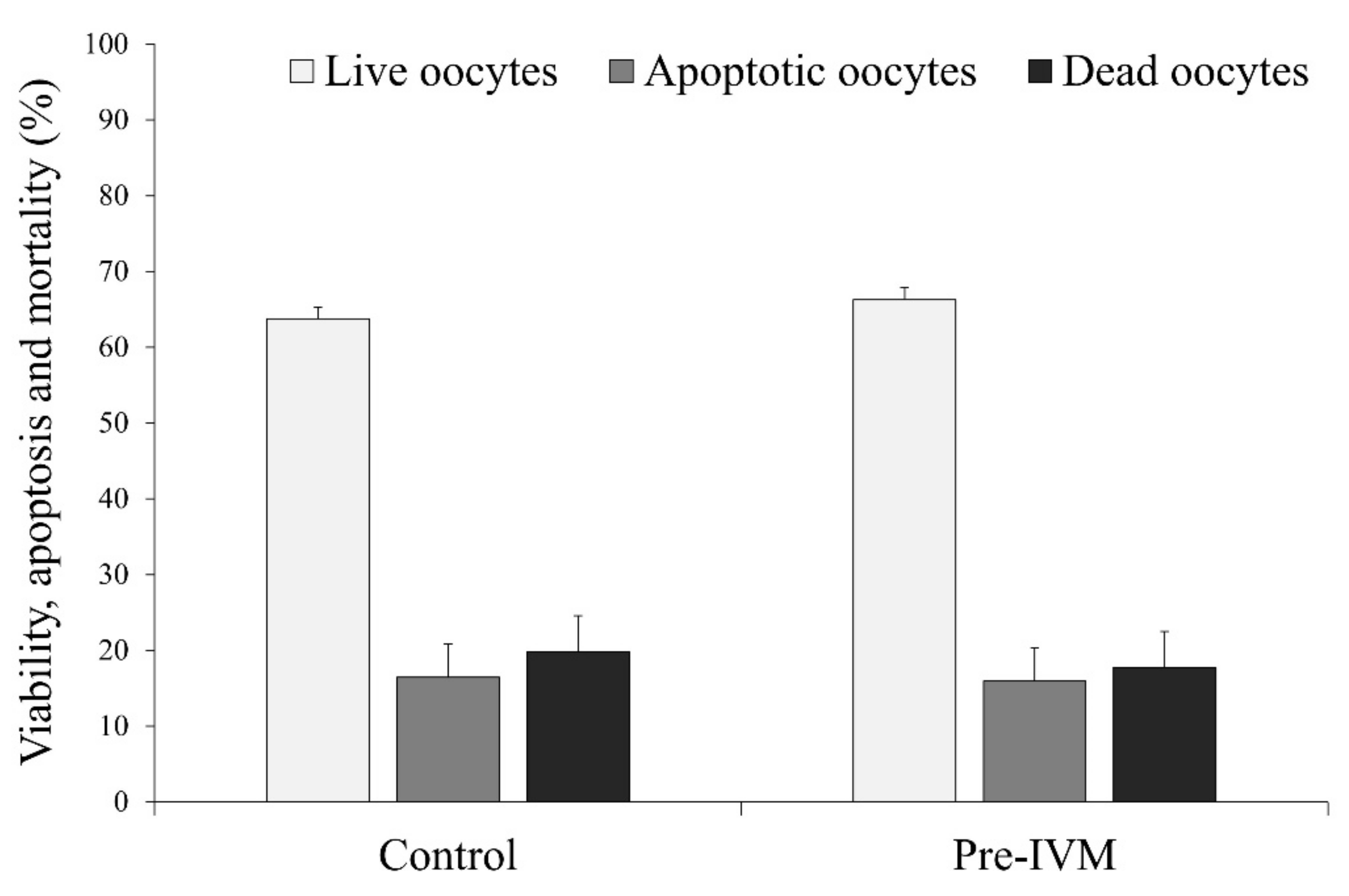
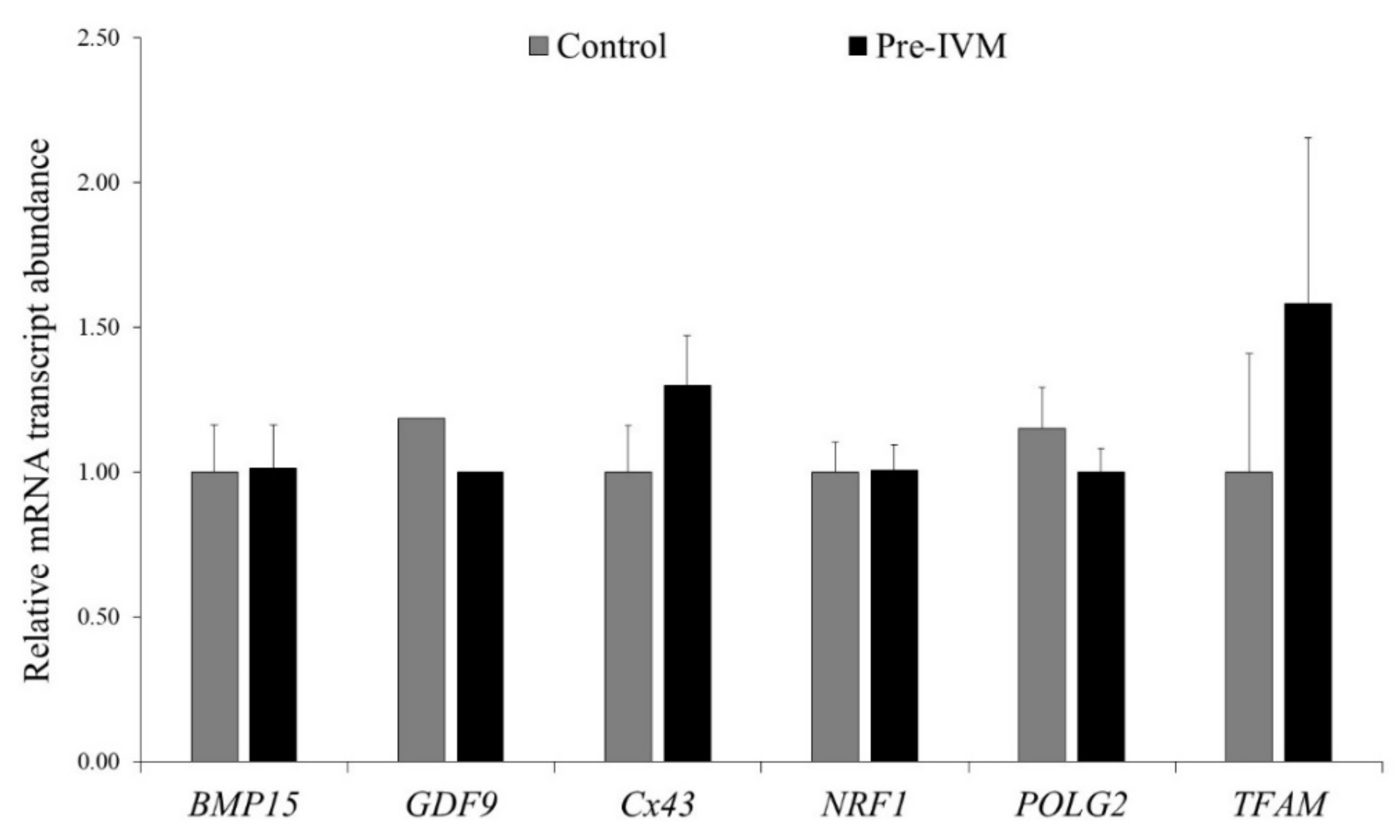
3.3. Effect of Pre-IVM on Oocyte Live/Death, Apoptosis and Oxidative Status, and Relative Abundance of mRNA Transcripts after IVM
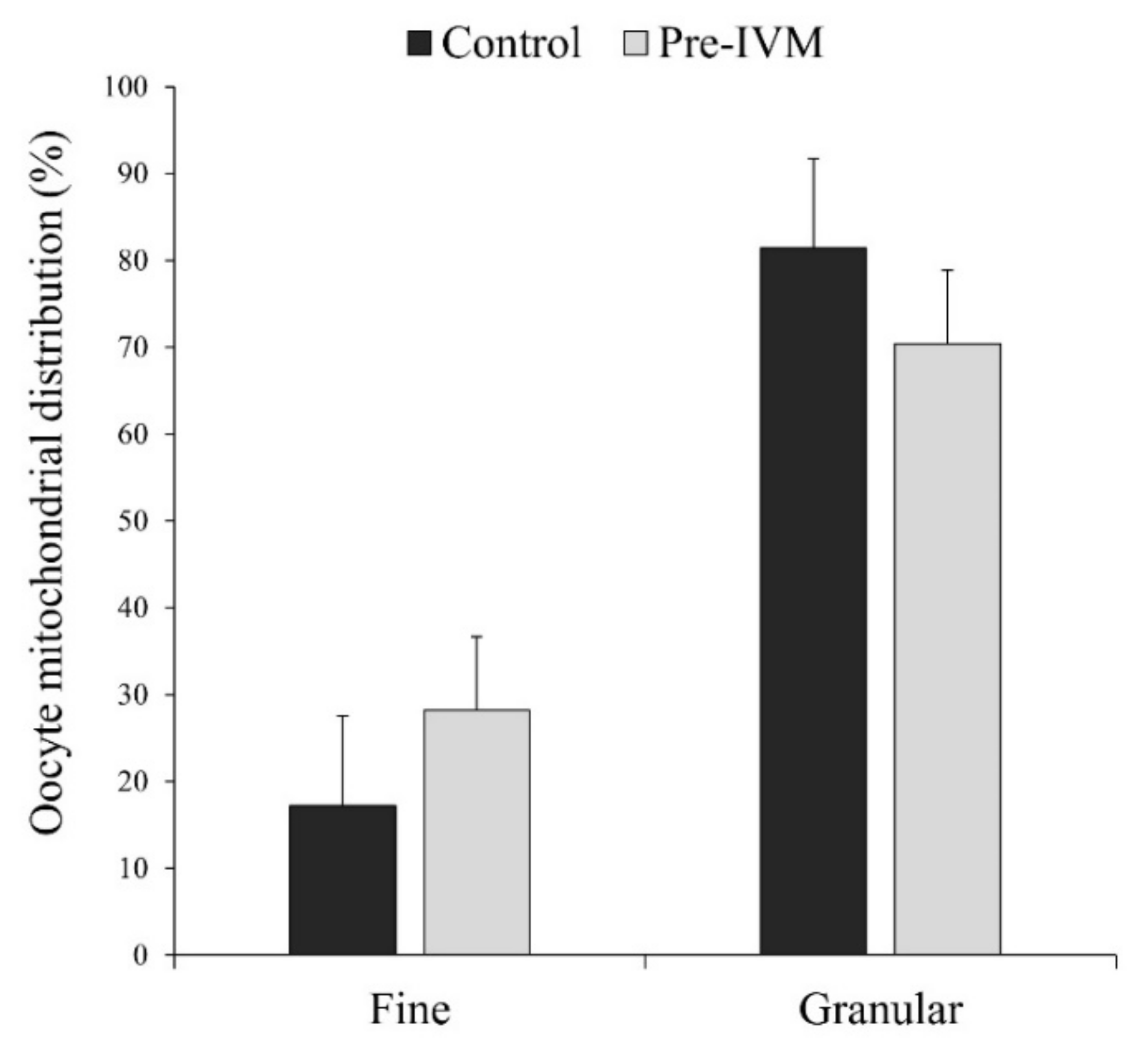
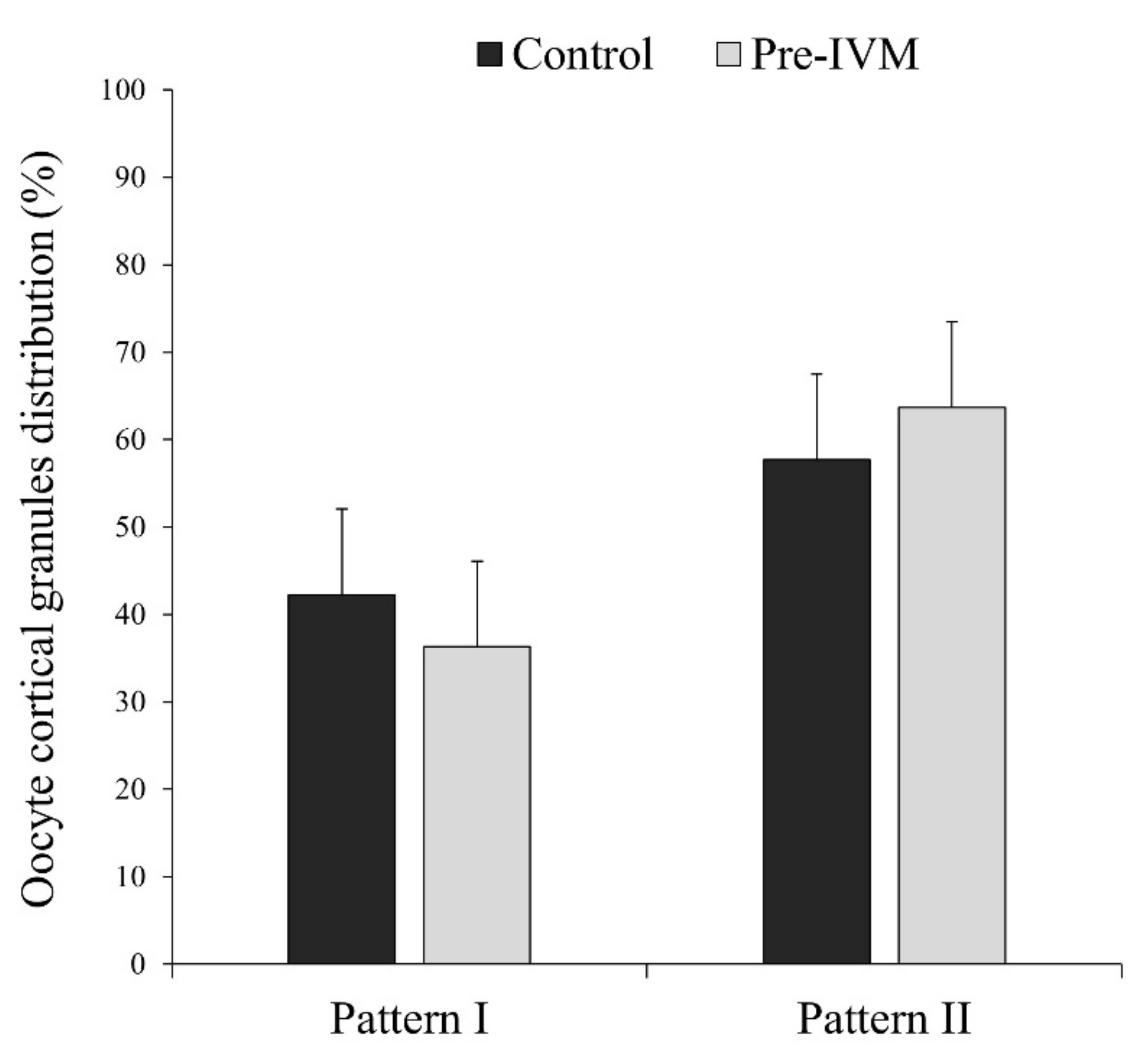
3.4. Effect of Pre-IVM on Cytoplasmic Maturation Features: Distribution of Organelles
3.5. Effect of Pre-IVM on Subsequent Maturation and Developmental Competence of Sheep Oocytes
3.6. Cumulus Cells’ Quality Parameters from In Vitro Matured COCs with and without Pre-IVM Culture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramos-Ibeas, P.; Gimeno, I.; Cañón-Beltrán, K.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A.; Rizos, D.; Gómez, E. Senescence and apoptosis during in vitro embryo development in a bovine model. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 619902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, G.Z.; Cui, W.; Yang, R.; Lin, J.; Gong, S.; Lian, H.Y.; Sun, M.J.; Tan, J.H. Optimized protocols for in vitro maturation of rat oocytes dramatically improve their developmental competence to a level similar to that of ovulated oocytes. Cell. Reprogram. 2016, 18, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatırnaz, Ş.; Ata, B.; Hatırnaz, E.S.; Dahan, M.H.; Tannus, S.; Tan, J.; Tan, S.L. Oocyte in vitro maturation: A sytematic review. Turk Jinekoloji ve Obstet. Dern. Derg. 2018, 15, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyttel, P.; Fair, T.; Callesen, H.; Greve, T. Oocyte growth, capacitation and final maturation in cattle. Science 1997, 47, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Kiyosu, C.; Akiyama, K.; Kunieda, T. CNP/NPR2 signaling maintains oocyte meiotic arrest in early antral follicles and is suppressed by EGFR-mediated signaling in preovulatory follicles. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2012, 79, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Su, Y.-Q.; Sugiura, K.; Xia, G.; Eppig, J.J. Granulosa cell ligand NPPC and its receptor NPR2 maintain meiotic arrest in mouse oocytes. Science 2010, 15, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaccari, S.; Weeks, J.L.; Hsieh, M.; Menniti, F.S.; Conti, M. Cyclic GMP signaling is involved in the luteinizing hormone-dependent meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasseville, M.; Côté, N.; Guillemette, C.; Richard, F.J. New insight into the role of phosphodiesterase 3A in porcine oocyte maturation. BMC Dev. Biol. 2006, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norris, R.P.; Ratzan, W.J.; Freudzon, M.; Mehlmann, L.M.; Krall, J.; Movsesian, M.A.; Wang, H.; Ke, H.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Jaffe, L.A. Cyclic GMP from the surrounding somatic cells regulates cyclic AMP and meiosis in the mouse oocyte. Development 2009, 136, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, F.J.; Tsafriri, A.; Conti, M. Role of phosphodiesterase type 3A in rat oocyte maturation. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieleman, S.J.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; Viuff, D.; Thomsen, P.D.; Hyttel, P.; Knijn, H.M.; Wrenzycki, C.; Kruip, T.A.M.; Niemann, H.; Gadella, B.M.; et al. Effects of in vivo prematuration and in vivo final maturation on developmental capacity and quality of pre-implantation embryos. Theriogenology 2002, 57, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, G.; Enzmann, E.V. The comparative behavior of mammalian eggs in vivo and in vitro: I. the activation of ovarian eggs. J. Exp. Med. 1935, 62, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte maturation: Emerging concepts and technologies to improve developmental potential in vitro. Theriogenology 2007, 67, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Li, J. The art of oocyte meiotic arrest regulation. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Luciano, A.M.; Richani, D.; Zeng, H.T.; Wang, X.; De Vos, M.; Sugimura, S.; Smitz, J.; Richard, F.J.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte maturation and quality: Role of cyclic nucleotides. Reproduction 2016, 152, R143–R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albuz, F.K.; Sasseville, M.; Lane, M.; Armstrong, D.T.; Thompson, J.G.; Gilchrist, R.B. Simulated physiological oocyte maturation (SPOM): A novel in vitro maturation system that substantially improves embryo yield and pregnancy outcomes. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2999–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rose, R.D.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Kelly, J.M.; Thompson, J.G.; Sutton-McDowall, M.L. Regulation of sheep oocyte maturation using cAMP modulators. Theriogenology 2013, 79, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buell, M.; Chitwood, J.L.; Ross, P.J. cAMP modulation during sheep in vitro oocyte maturation delays progression of meiosis without affecting oocyte parthenogenetic developmental competence. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 154, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razza, E.M.; Sudano, M.J.; Fontes, P.K.; Franchi, F.F.; Belaz, K.R.A.; Santos, P.H.; Castilho, A.C.S.; Rocha, D.F.O.; Eberlin, M.N.; Machado, M.F.; et al. Treatment with cyclic adenosine monophosphate modulators prior to in vitro maturation alters the lipid composition and transcript profile of bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes and blastocysts. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2018, 30, 1314–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Sutton-Mcdowall, M.L.; Wang, X.; Sugimura, S.; Thompson, J.G.; Gilchrist, R.B. Extending prematuration with cAMP modulators enhances the cumulus contribution to oocyte antioxidant defence and oocyte quality via gap junctions. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernal-Ulloa, S.M.; Heinzmann, J.; Herrmann, D.; Hadeler, K.G.; Aldag, P.; Winkler, S.; Pache, D.; Baulain, U.; Lucas-Hahn, A.; Niemann, H. Cyclic AMP affects oocyte maturation and embryo development in prepubertal and adult cattle. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.T.; Richani, D.; Sutton-McDowall, M.L.; Ren, Z.; Smitz, J.E.J.; Stokes, Y.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Thompson, J.G. Prematuration with cyclic adenosine monophosphate modulators alters cumulus cell and oocyte metabolism and enhances developmental competence of in vitro-matured mouse oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Zeng, H.T.; Wang, X.; Richani, D.; Smitz, J.; Thompson, J.G. Reevaluation and evolution of the simulated physiological oocyte maturation system. Theriogenology 2015, 84, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, G.G.; Palmerini, M.G.; Satta, V.; Succu, S.; Pasciu, V.; Zinellu, A.; Carru, C.; Macchiarelli, G.; Nottola, S.A.; Naitana, S.; et al. Differences in the kinetic of the first meiotic division and in active mitochondrial distribution between prepubertal and adult oocytes mirror differences in their developmental competence in a sheep model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilha, L.C.; Saraiva, N.Z.; Dell Collado, M.; Teixeira, P.P.M.; Pires-Buttler, E.A.; Apparicio, M.; Vicente, W.R.R. Description of cortical granule distribution in ovine matured oocytes: Preliminary results. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2013, 25, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ajofrín, I.; Iniesta-Cuerda, M.; Sánchez-Calabuig, M.J.; Peris-Frau, P.; Martín-Maestro, A.; Ortiz, J.A.; Fernández-Santos, M.R.; Garde, J.J.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A.; Soler, A.J. Oxygen tension during in vitro oocyte maturation and fertilization affects embryo quality in sheep and deer. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 213, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Álvarez, P.; Rizos, D.; Rath, D.; Lonergan, P.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A. Can bovine in vitro-matured oocytes selectively process X- or Y-sorted sperm differentially? Biol. Reprod. 2008, 79, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-Maestro, A.; Sánchez-Ajofrín, I.; Maside, C.; Peris-Frau, P.; Medina-Chávez, D.A.; Cardoso, B.; Navarro, J.C.; Fernández-Santos, M.R.; Garde, J.J.; Soler, A.J. Cellular and molecular events that occur in the oocyte during prolonged ovarian storage in sheep. Animals 2020, 10, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; First, N.L. In vitro development of bovine ane-cell embryos: Influence of glucose, lactate, pyruvate, amino acids and vitamins. Theriogelology 1992, 37, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Leal, G.; Santos Monteiro, C.A.; Souza-Fabjan, J.M.G.; de Paula Vasconcelos, C.O.; Garcia Nogueira, L.A.; Reis Ferreira, A.M.; Varella Serapião, R. Role of cAMP modulator supplementations during oocyte in vitro maturation in domestic animals. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 199, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Teng, M.; Zhao, G.; Lei, A. Coping with DNA double-strand breaks via ATM signaling pathway in bovine oocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Schramm, R.D.; Latham, K.E. Developmental regulation and in vitro culture effects on expression of DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoint control genes in rhesus monkey oocytes and embryos. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horta, F.; Catt, S.; Ramachandran, P.; Vollenhoven, B.; Temple-Smith, P. Female ageing affects the DNA repair capacity of oocytes in IVF using a controlled model of sperm DNA damage in mice. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 35, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Heras, S.; Paramio, M.T.; Thompson, J.G. Effect of pre-maturation with C-type natriuretic peptide and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine on cumulus-oocyte communication and oocyte developmental competence in cattle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 202, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tscharke, M.; Kind, K.; Kelly, J.; Kleemann, D.; Len, J. The phosphodiesterase inhibitor, isobutyl-1-methylxanthine prevents the sudden drop in cyclic adenosine monophosphate concentration and modulates glucose metabolism of equine cumulus-oocyte complexes matured in vitro. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 91, 103112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangos, P.; Carroll, J. Oocytes progress beyond prophase in the presence of DNA damage. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Böhm, M.; Wolff, I.; Scholzen, T.E.; Robinson, S.J.; Healy, E.; Luger, T.; Schwarz, A.; Schwarz, A. α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone protects from ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis and DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Malek, Z.A.; Knittel, J.; Kadekaro, A.L.; Swope, V.B.; Starner, R. The melanocortin 1 receptor and the UV response of human melanocytes -A shift in paradigm. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, J.E.; Kadekaro, A.L.; Kavanagh, R.J.; Wakamatsu, K.; Terzieva, S.; Schwemberger, S.; Babcock, G.; Rao, M.B.; Ito, S.; Abdel-Malek, Z.A. Melanin content and MC1R function independently affect UVR-induced DNA damage in cultured human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passeron, T.; Namiki, T.; Passeron, H.; Le Pape, E.; Hearing, V.J. Forskolin protects keratinocytes from ultraviolet (UV) B-induced apoptosis and increases DNA repair independent of its effects on melanogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 129, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, M.H.; Zheng, J.; Xie, F.Y.; Shen, W.; Yin, S.; Ma, J.Y. Cumulus cells block oocyte meiotic resumption via gap junctions in cumulus oocyte complexes subjected to DNA double-strand breaks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlova, E.V.; Fesenko, Z.S.; Sopova, J.V.; Leonova, E.I. Features of dna repair in the early stages of mammalian embryonic development. Genes 2020, 11, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kou, Z.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Dong, M.; Wilmut, I.; Gao, S. Proteome of mouse oocytes at different developmental stages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17639–17644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.T.; Ren, Z.; Guzman, L.; Wang, X.; Sutton-Mcdowall, M.L.; Ritter, L.J.; De Vos, M.; Smitz, J.; Thompson, J.G.; Gilchrist, R.B. Heparin and cAMP modulators interact during pre-in vitro maturation to affect mouse and human oocyte meiosis and developmental competence. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguila, L.; Treulen, F.; Therrien, J.; Felmer, R.; Valdivia, M.; Smith, L.C. Oocyte selection for in vitro embryo production in bovine species: Noninvasive approaches for new challenges of oocyte competence. Animals 2020, 10, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, L.; Cino, I.; Rabellotti, E.; Calzi, F.; Persico, P.; Borini, A.; Coticchio, G. Polar body morphology and spindle imaging as predictors of oocyte quality. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2005, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejera, A.; Herrero, J.; De Los Santos, M.J.; Garrido, N.; Ramsing, N.; Meseguer, M. Oxygen consumption is a quality marker for human oocyte competence conditioned by ovarian stimulation regimens. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Germinal Vesicle (%) | Maturation MII (%) | Cleaved Embryo at 48 hpi (%) | Expanded Blastocyst (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Cleaved | ||||
| Control | 6.50 ± 2.26 | 87.85 ± 1.52 | 55.28 ± 4.00 | 18.22 ± 1.47 a | 32.88 ± 1.73 a |
| Pre-IVM | 3.43 ± 2.26 | 91.75 ± 1.52 | 55.01 ± 4.00 | 23.89 ± 1.47 b | 45.16 ± 1.73 b |
| Treatment | Viable Cells (%) | Apoptotic Cells (%) | Dead Cells (%) | Active Mitochondria (%) | ROS Levels (Fluorescence Intensity) | GSH Levels (Fluorescence Intensity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 77.7 ± 2.4 | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 16.1 ± 1.7 | 61.2 ± 1.2 | 6906.5 ± 339.1 | 8915.7 ± 738.7 |
| Pre-IVM | 80.6 ± 2.4 | 7.60 ± 1.0 | 11.2 ± 1.7 | 64.2 ± 1.2 | 6950.0 ± 339.1 | 9022.1 ± 738.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina-Chávez, D.-A.; Sánchez-Ajofrín, I.; Peris-Frau, P.; Maside, C.; Montoro, V.; Fernández-Santos, R.; Garde, J.J.; Soler, A.J. cAMP Modulators before In Vitro Maturation Decrease DNA Damage and Boost Developmental Potential of Sheep Oocytes. Animals 2021, 11, 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092512
Medina-Chávez D-A, Sánchez-Ajofrín I, Peris-Frau P, Maside C, Montoro V, Fernández-Santos R, Garde JJ, Soler AJ. cAMP Modulators before In Vitro Maturation Decrease DNA Damage and Boost Developmental Potential of Sheep Oocytes. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092512
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina-Chávez, Daniela-Alejandra, Irene Sánchez-Ajofrín, Patricia Peris-Frau, Carolina Maside, Vidal Montoro, Rocío Fernández-Santos, José Julián Garde, and Ana Josefa Soler. 2021. "cAMP Modulators before In Vitro Maturation Decrease DNA Damage and Boost Developmental Potential of Sheep Oocytes" Animals 11, no. 9: 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092512
APA StyleMedina-Chávez, D.-A., Sánchez-Ajofrín, I., Peris-Frau, P., Maside, C., Montoro, V., Fernández-Santos, R., Garde, J. J., & Soler, A. J. (2021). cAMP Modulators before In Vitro Maturation Decrease DNA Damage and Boost Developmental Potential of Sheep Oocytes. Animals, 11(9), 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092512






