Chorion Alterations in Eyed-Stage Salmonid Eggs Farmed in La Araucanía, Chile: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
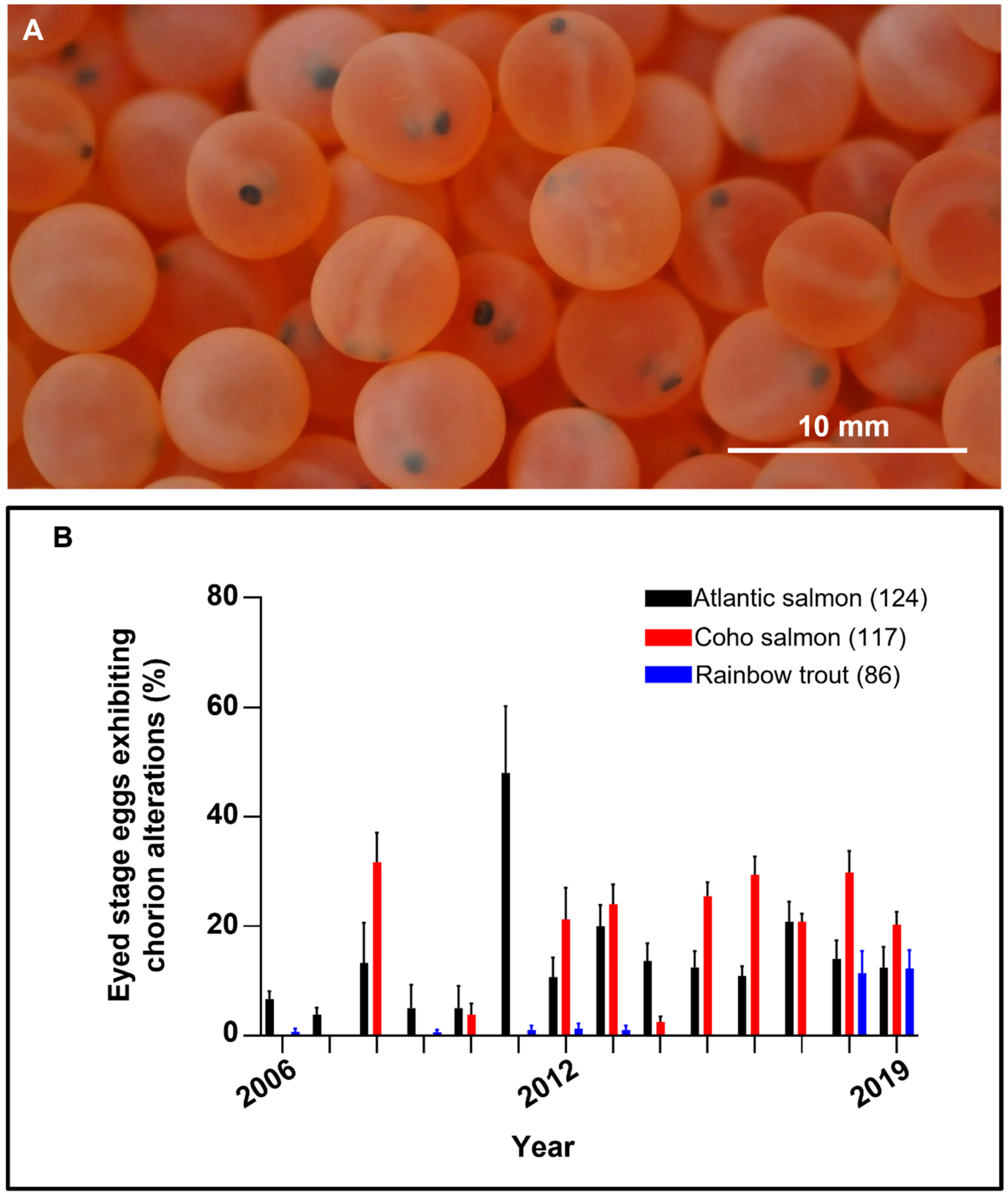
3. Results
3.1. Chorion Alterations
3.2. Occurrence of Chorion Alterations
3.2.1. Atlantic Salmon
3.2.2. Coho Salmon
3.2.3. Rainbow Trout
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arukwe, A.; Goksoyr, A. Eggshell and egg yolk proteins in fish: Hepatic proteins for the next generation: Oogenetic, population, and evolutionary implications of endocrine disruption. Comp. Hepatol. 2003, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubzens, E.; Young, G.; Bobe, J.; Cerda, J. Oogenesis in teleosts: How eggs are formed. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modig, C.; Westerlund, L.; Olsson, P. Oocyte zona pellucida proteins. In The Fish Oocyte: From Basic Studies to Biotechnological Applications; Babin, P.J., Cerdà, J., Lubzens, E., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, Germany, 2007; pp. 113–139. [Google Scholar]
- Brivio, M.F.; Bassi, R.; Cotelli, F. Identification and characterization of the major components of the Oncorhynchus mykiss egg chorion. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1991, 28, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, R.; Goicoechea, O.; Garrido, O.; Molinari, E. Caracterización electroforética de las proteínas del corion normal y del corion duro de Salmo salar. Arch. Med. Vet. 2012, 44, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grier, H.J. Development of the follicle complex and oocyte staging in red drum, Sciaenops ocellatus Linnaeus, 1776 (Perciformes, Sciaenidae). J. Morphol. 2012, 273, 801–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, E.P.; Alderdice, D.F. Fine structure of the external egg membrane of five species of Pacific salmon and steelhead trout. Can. J. Zool. 1985, 63, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, Y. 6 The Functional Morphology of Teleost Gonads. In Fish Physiology; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Donaldson, E.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 9, pp. 223–275. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, S.; Teshima, C. Enzyme activities and antifungal action of fertilization envelope extract from fish eggs. J. Exp. Zool. 1991, 259, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Tyler, C.R.; Sumpter, J.P. Egg quality in fish: What makes a good egg? Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1997, 7, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjørsvik, E.; Mangor-Jensen, A.; Holmefjord, I. Egg Quality in Fishes. In Advances in Marine Biology; Blaxter, J.H.S., Southward, A.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 26, pp. 71–113. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, D.; Adams, C.; McDade, K.; Solomon, S.; Bain, M. Effect of broodstock holding environment on egg quality in farmed brown trout (Salmo trutta). Anim. Reprod. 2016, 13, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.E.; Cordes, R.J.; Sayler, W.A.; Hanten, R.P. Soft-Egg Disease in Landlocked Fall Chinook Salmon Eggs: Possible Causes and Therapeutic Treatments. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2003, 65, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, M.; Kishihara, T.; Watanabe, T.; Inaba, T.; Kato, T.; Ikushima, S.; Khomvilai, C.; Yoshioka, M. Alleviation of rainbow trout egg softening caused by sodium hypochlorite as an antifungal agent. Fish. Sci. 2007, 73, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.; Cárcamo, J.; Yañez, A.; Olavarria, V.; Ruiz, P.; Manríquez, R.; Muñoz, C.; Romero, A.; Avendaño-Herrera, R. Addressing viral and bacterial threats to salmon farming in Chile: Historical contexts and perspectives for management and control. Rev. Aquacult. 2019, 11, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobe, J.; Labbe, C. Egg and sperm quality in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, K.L.; Jensen, J.O.T. The effects of temperature on external egg membranes in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and the occurrence of soft-shell disease. Can. J. Zool. 1994, 72, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, K.; Hamazaki, T.S.; Yasumasut, S.; Masuda, K.; Iuchi, I. Molecular and Cellular Basis of Formation, Hardening, and Breakdown of the Egg Envelope in Fish. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 136, 51–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderman, D.J. The toxicity of iodophors to salmonid eggs. Aquaculture 1984, 40, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, D.F. Comparative Toxicity of Two Iodophors to Rainbow Trout Eggs. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1974, 103, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songe, M.M.; Willems, A.; Sarowar, M.N.; Rajan, K.; Evensen, O.; Drynan, K.; Skaar, I.; van West, P. A thicker chorion gives ova of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) the upper hand against Saprolegnia infections. J. Fish. Dis. 2016, 39, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahnsteiner, F. Morphological, physiological and biochemical parameters characterizing the over-ripening of rainbow trout eggs. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 23, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, R.; Goicoechea, O.; Garrido, O.; Molinari, E. Salmo salar: Morfología ultraestructural de la pared del corion en ovas normales y con problemas de eclosión. Arch. Med. Vet. 2009, 41, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.M.; Hatai, K.; Nomura, T. Saprolegniosis in salmonids and their eggs in Japan. J. Wildl. Dis. 2001, 37, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fregeneda-Grandes, J.M.; Rodríguez-Cadenas, F.; Aller-Gancedo, J.M. Fungi isolated from cultured eggs, alevins and broodfish of brown trout in a hatchery affected by saprolegniosis. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, K. Mechanisms of Hatching in Fish: Secretion of Hatching Enzyme and Enzymatic Choriolysis. Am. Zool. 1981, 21, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppen-Berntsen, D.O.; Bogsnes, A.; Walther, B.T. The effects of hypoxia, alkalinity and neurochemicals on hatching of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) eggs. Aquaculture 1990, 86, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.H.; Daye, P.G.; Metcalfe, J.L. Inhibition of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Hatching at Low pH. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, R.A.; Fuentes, M.; Montes, R.M.; Soto, D.; León-Muñoz, J. Environmental issues in Chilean salmon farming: A review. Rev. Aquacult. 2019, 11, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamjunke, N.; Nimptsch, J.; Harir, M.; Herzsprung, P.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Neu, T.R.; Graeber, D.; Osorio, S.; Valenzuela, J.; Reyes, J.C.; et al. Land-based salmon aquacultures change the quality and bacterial degradation of riverine dissolved organic matter. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, D.; Aguayo, C.; Lara, G.; Encina, F.; Nimptsch, J.; Esse, C.; Aguayo, M.F.; Hodgges, C. Evaluación y Análisis de los Posibles Parámetros Ambientales a ser Incorporados en las Normas de Emisión y/o de Calidad de Aguas Fluviales y Lacustres, Destinados a Centros de Cultivo Ubicados en Tierra. Reporte Final.; FIP N°2015-05; Subsecretaría de Pesca y Acuicultura: Temuco, Chile, 2017; p. 264. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J.; Shepherd, C.J. Handbook of Trout and Salmon Diseases; Fishing News (Books) Ltd.: West Byfleet, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]

| Species | Chorion Alteration | Year | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| S. salar | Soft | 3.3 ± 1.7 | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 13.3 ± 7.3 | 5.0 ± 5.0 | 5.0 ± 5.0 | 35.0 ± 11.0 | 10.7 ± 3.8 | 15.0 ± 3.1 | 10.0 ± 3.6 | 5.0 ± 1.7 | 0.5 ± 0.5 | 10.0 ± 1.7 | 6.0 ± 2.1 | 4.3 ± 1.7 |
| Perforated | 5.0 ± 1.9 | 7.5 ± 3.0 | 10.0 ± 3.2 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 4.8 ± 2.6 | ||||||||||
| White-Spotted | 13.0 ± 4.9 | 3.6 ± 2.8 | 10.5 ± 1.7 | 0.8 ± 0.8 | 6.0 ± 2.8 | 3.3 ± 2.0 | |||||||||
| Dark | 3.3 ± 1.7 | ||||||||||||||
| n | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 21 | |
| O. kisutch | Soft | 10.0 ± 3.5 | 20.0 ± 3.5 | 11.7 ± 1.7 | 10.6 ± 0.6 | 13.1 ± 0.9 | 10.0 ± 1.8 | 7.4 ± 1.2 | |||||||
| Perforated | 11.3 ± 3.1 | 4.0 ± 1.0 | 7.5 ± 1.6 | 6.2 ± 1.2 | 10.7 ± 2.3 | 5.2 ± 1.4 | |||||||||
| White-Spotted | 31.7 ± 6.7 | 3.8 ± 2.4 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 15.0 ± 2.2 | 11.3 ± 2.1 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 9.1 ± 1.8 | 7.6 ± 1.3 | |||||||
| Dark | |||||||||||||||
| n | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 13 | 16 | 21 | |
| O. mykiss | Soft | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 0.6 ± 0.6 | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 1.3 ± 1.3 | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 5.7 ± 2.5 | 5.0 ± 2.2 | |||||||
| Perforated | 5.7 ± 2.8 | 7.3 ± 2.1 | |||||||||||||
| White-Spotted | |||||||||||||||
| Dark | |||||||||||||||
| n | 7 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 13 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdebenito, I.; Figueroa, E.; Valdebenito, M.; Paiva, L. Chorion Alterations in Eyed-Stage Salmonid Eggs Farmed in La Araucanía, Chile: A Retrospective Study. Animals 2021, 11, 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082427
Valdebenito I, Figueroa E, Valdebenito M, Paiva L. Chorion Alterations in Eyed-Stage Salmonid Eggs Farmed in La Araucanía, Chile: A Retrospective Study. Animals. 2021; 11(8):2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082427
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdebenito, Iván, Elías Figueroa, Matías Valdebenito, and Luis Paiva. 2021. "Chorion Alterations in Eyed-Stage Salmonid Eggs Farmed in La Araucanía, Chile: A Retrospective Study" Animals 11, no. 8: 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082427
APA StyleValdebenito, I., Figueroa, E., Valdebenito, M., & Paiva, L. (2021). Chorion Alterations in Eyed-Stage Salmonid Eggs Farmed in La Araucanía, Chile: A Retrospective Study. Animals, 11(8), 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082427






