Association between THRSP Gene Polymorphism and Fatty Acid Composition in Milk of Dairy Cows
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
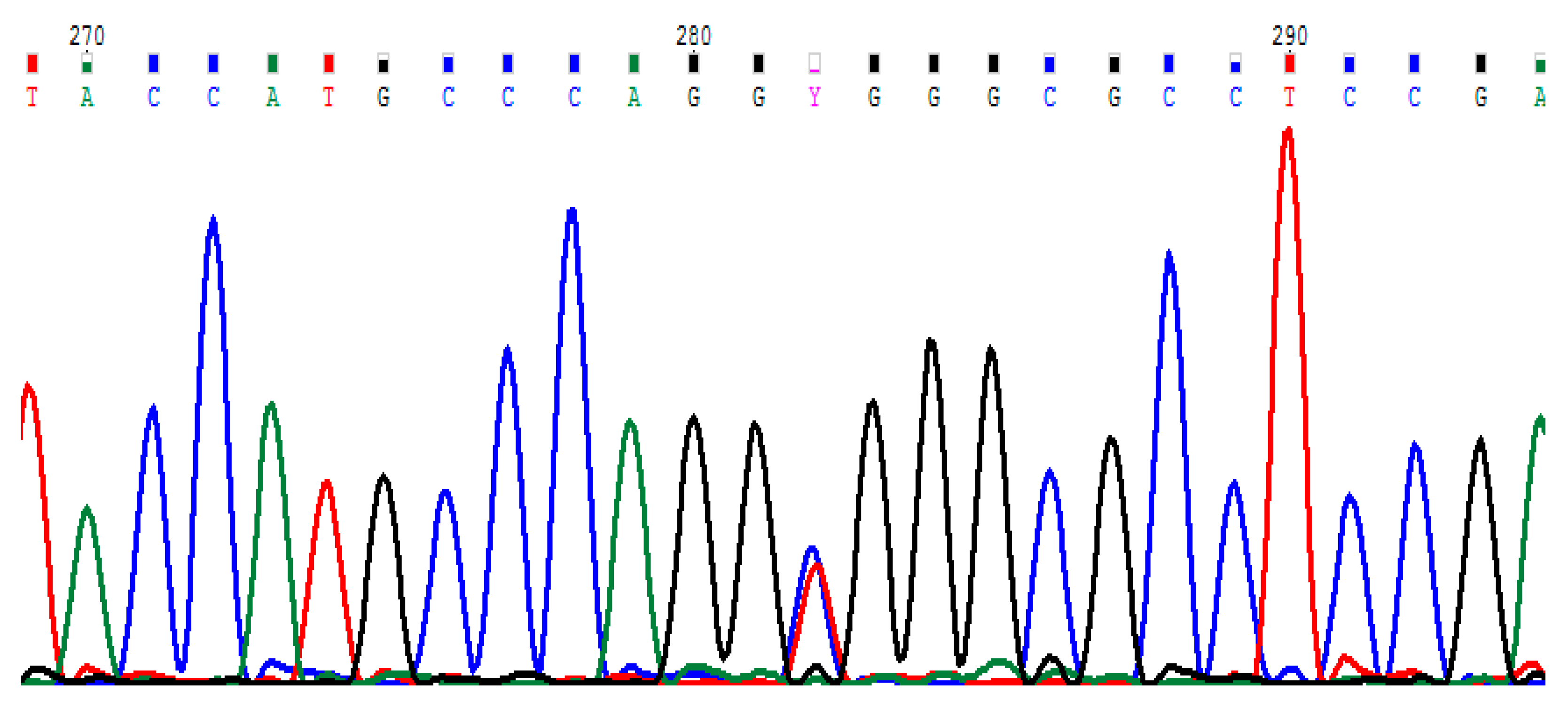
2.2. Polymorphism Analysis
2.3. Milk Composition Analysis
- saturated: C6:0 (caproic), C8:0 (caprylic), C10:0 (capric), C12:0 (lauric), C14:0 (myristic), C16:0 (palmitic), C18:0 (stearic);
- unsaturated: C14:1 (myristoleic), C16:1 (palmitoleic), C18:1n-9c (oleic), C18:1n-9t (elaidic), C18:2n-6c (linoleic), C18:3n3 (α-linoleic).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kęsek-Woźniak, M.M.; Wojtas, E.; Zielak-Steciwko, A.E. Impact of SNPs in ACACA, SCD1, and DGAT1 Genes on Fatty Acid Profile in Bovine Milk with Regard to Lactation Phases. Animals 2020, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellberg, E.A.; Rudolph, M.C.; Lewis, A.S.; Padilla-Just, N.; Jedlicka, P.; Anderson, S.M. Modulation of tumor fatty acids, through overexpression or loss of thyroid hormone responsive protein spot 14 is associated with altered growth and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Hou, X.; Qu, B.; Zhao, F.; Gao, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, Q. Thyroid hormone responsive protein spot 14 enhances lipogenesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2015, 51, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Carre, W.; Zhou, H.; Lamont, S.J.; Cogburn, L.A. Duplicated Spot 14 genes in the chicken: Characterization and identification of polymorphisms associated with abdominal fat traits. Gene 2004, 12, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.P.; Wang, S.Z.; Wang, Q.G.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, H. Association of Spot14α Gene Polymorphisms with Body Weight in the Chicken. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Zhao, H.; Bai, L.; Hou, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Cao, B. Polymorphism identification in the goat THRSP gene and association analysis with growth traits. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2012, 55, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, J.; Qin, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, G.; Shang, X.; Zhang, M.; Balsai, N.; Chen, H. Polymorphisms in 5′ proximal regulating region of THRSP gene are associated with fat production in pigs. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Zan, L.S.; Wang, H.B.; Hao, R.J.; Yang, Y.J. Correlation of C184T Mutation in THRSP Gene with Meat Traits in the Qinchuan Cattle. Sci. Agric. Sin. Zhongguo Nong Ye Ke Xue 2009, 42, 4058–4063. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, D.-Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; La, B.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Ha, J.-J.; Yi, J.-K.; Kim, B.-K.; Yeo, J.-S. Identification of Exonic Nucleotide Variants of the Thyroid Hormone Responsive Protein Gene Associated with Carcass Traits and Fatty Acid Composition in Korean Cattle. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanesi, L.; Calò, D.G.; Galimberti, G.; Negrini, R.; Marino, R.; Nardone, A.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Russo, V. A candidate gene association study for nine economically important traits in Italian Holstein cattle. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensembl. Ensembl Genome Browser. ENSBTAG00000011666. Available online: http://www.ensembl.org (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- UniprotKB. A0A4W2BRK0. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/A0A4W2BRK0 (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GenBank. rs42714482, AC_000186.1, AY656814. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Lock, A.; Garnsworthy, P. Seasonal variation in milk conjugated linoleic acid and Δ9—Desaturase activity in dairy cows. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2003, 79, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary heart disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Kinghorn, B.P. An algorithm for efficient constrained mate selection. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2011, 43, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therneau, T.; Atkinson, E.; Sinnwell, J.; Schaid, D.; Mcdonnell, S. Kinship2: Pedigree Functions. R Package Version 1.8.5. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=kinship2 (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Therneau, T.M. Coxme: Mixed Effects Cox Models, R Package Version 2.2-16. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=coxme (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Harvatine, K.J.; Bauman, D.E. SREBP1 and Thyroid Hormone Responsive Spot 14 (S14) Are Involved in the Regulation of Bovine Mammary Lipid Synthesis during Diet-Induced Milk Fat Depression and Treatment with CLA. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcedo-Tacuma, D.; Parales-Giron, J.; Prom, C.; Chirivi, M.; Laguna, J.; Lock, A.L.; Contreras, G.A. Transcriptomic profiling of adipose tissue inflammation, remodeling, and lipid metabolism in periparturient dairy cows (Bos taurus). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.H.; Christie, W.W. Lipid metabolism in the mammary gland or ruminant animals. Prog. Lipid Res. 1979, 17, 347–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Luo, J.; He, Q.; Wu, M.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, H.; Loor, J. Thyroid hormone responsive (THRSP) promotes the synthesis of medium-chain fatty acids in goat mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3124–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Cho, M.; Hong, W.-Y.; Lim, D.; Kim, H.-C.; Cho, Y.-M.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Choi, B.-H.; Ko, Y.; Kim, A.J. Evolutionary Analyses of Hanwoo (Korean Cattle)-Specific Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Genes Using Whole-Genome Resequencing Data of a Hanwoo Population. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobotka, W.; Stanek, M.; Fiedorowicz, E. Health-promoting properties of milk fat depending on cattle breed (Prozdrowotne właściwości tłuszczu mlekowego w zależności od rasy krów). Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2015, 96, 808–811. [Google Scholar]
- Eijndhoven, M.M.-V.; Bovenhuis, H.; Soyeurt, H.; Calus, M. Differences in milk fat composition predicted by mid-infrared spectrometry among dairy cattle breeds in the Netherlands. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2570–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loften, J.R.; Linn, J.G.; Drackley, J.K.; Jenkins, T.C.; Soderholm, C.G.; Kertz, A.F. Invited review: Palmitic and stearic acid metabolism in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 4661–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, J.; Ledina, T.; Baltic, M.Z.; Trbovic, D.; Babic, M.; Bulajic, S. Fatty Acid Profile of Milk. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 60th International Meat Industry Conference MEATCON2019, Kopaonik, Serbia, 22–25 September 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 333, p. 012057. [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz-Kęszycka, M.; Czyżak-Runowska, G.; Lipińska, P.; Wójtowski, J. Fatty Acid Profile of Milk—A Review. Bull. Veter. Inst. Pulawy 2013, 57, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, O.-M.; Tan, C.-P.; Akoh, C.C. Palm Oil: Production, Processing, Characterisation, and Uses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780981893693. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Breed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Holstein-Friesian | Jersey | ||
| Dry weight | % | 45.0 | 40.7 |
| Protein | g/kg dw | 149.9 | 157.4 |
| Fat | g/kg dw | 32.6 | 29.8 |
| Carbohydrates | g/kg dw | 763.3 | 727.7 |
| Calcium | mg/kg dw | 6.0 | 9.0 |
| Magnesium | mg/kg dw | 2.9 | 3.4 |
| Phosphorus | mg/kg dw | 2.8 | 4.7 |
| Natrium | mg/kg dw | 2.6 | 2.7 |
| Breed | n | Genotypes | Alleles | HWE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | CT | TT | C | T | χ2 | p | ||
| Jersey | 80 | 0.16 (n = 13) | 0.51 (n = 41) | 0.33 (n = 26) | 0.42 | 0.58 | 0.223 | 0.637 |
| Polish Holstein-Friesian | 144 | 0.46 (n = 66) | 0.45 (n = 65) | 0.09 (n = 13) | 0.68 | 0.32 | 0.282 | 0.596 |
| Trait | Genotype | Mean | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC (n = 13) | CT (n = 41) | TT (n = 26) | |||
| MY | 22.646 ± 4.653 | 20.917 ± 3.749 | 22.323 ± 4.142 | 21.655 ± 4.053 | n.s. |
| FY | 1.193 ± 0.232 | 1.049 ± 0.191 | 1.114 ± 0.245 | 1.093 ± 0.220 | n.s. |
| FC | 5.306 ± 0.544 | 5.045 ± 0.624 | 4.995 ± 0.702 | 5.072 ± 0.640 | n.s. |
| C6:0 | 2.913 ± 0.433 | 2.626 ± 0.377 | 2.694 ± 0.370 | 2.695 ± 0.392 | n.s. |
| C8:0 | 1.877 ± 0.331 | 1.637 ± 0.238 | 1.653 ± 0.296 | 1.681 ± 0.284 | n.s. |
| C10:0 | 3.553 ± 0.292 | 3.407 ± 0.431 | 3.425 ± 0.453 | 3.437 ± 0.418 | n.s. |
| C12:0 | 4.173 ± 0.389 | 3.928 ± 0.539 | 3.901 ± 0.609 | 3.959 ± 0.545 | n.s. |
| C14:0 | 12.716 ± 0.873 | 12.351 ± 1.211 | 12.241 ± 1.320 | 12.375 ± 1.198 | n.s. |
| C16:0 | 37.197 ± 2.523 a | 37.346 ± 3.207 | 38.462 ± 3.028 b | 37.684 ± 3.062 | p < 0.05 |
| C18:0 | 12.516 ± 1.461 | 12.883 ± 1.599 b | 12.242 ± 1.726 a | 12.615 ± 1.627 | p < 0.05 |
| C14:1 | 1.517 ± 0.396 | 1.299 ± 0.351 | 1.323 ± 0.423 | 1.342 ± 0.386 | n.s. |
| C16:1 | 1.588 ± 0.235 | 1.543 ± 0.282 | 1.710 ± 0.444 | 1.605 ± 0.342 | n.s. |
| C18:1n-9c | 15.703 ± 1.959 | 17.001 ± 3.496 | 16.569 ± 3.716 | 16.650 ± 3.370 | n.s. |
| C18:1n-9t | 1.092 ± 0.168 | 1.021 ± 0.204 | 1.039 ± 0.220 | 1.038 ± 0.203 | n.s. |
| C18:2n-6c | 2.119 ± 0.321 | 2.018 ± 0.334 | 1.900 ± 0.389 | 1.996 ± 0.355 | n.s. |
| C18:3n-3 | 0.114 ± 0.042 | 0.118 ± 0.050 | 0.103 ± 0.045 | 0.113 ± 0.047 | n.s. |
| ΣC14 | 14.233 ± 1.093 b | 13.650 ± 1.439 | 13.564 ± 1.583 a | 13.717 ± 1.441 | p < 0.05 |
| ΣC16 | 38.786 ± 2.466 a | 38.889 ± 3.152 | 40.172 ± 3.057 b | 39.289 ± 3.048 | p < 0.05 |
| ΣC6–16 | 62.622 ± 3.452 | 61.511 ± 4.809 a | 62.717 ± 4.770 b | 62.083 ± 4.590 | p < 0.05 |
| ΣC18 | 31.557 ± 3.396 | 33.055 ± 5.002 | 31.865 ± 5.106 | 32.424 ± 4.807 | n.s. |
| Δ9IC14 | 9.458 ± 3.342 | 9.065 ± 2.775 | 10.052 ± 3.308 | 9.450 ± 3.042 | n.s. |
| Δ9IC16 | 5.734 ± 2.214 | 4.847 ± 1.417 | 4.839 ± 1.569 | 4.988 ± 1.628 | n.s. |
| Δ9IC18 | 65.067 ± 7.090 | 63.796 ± 5.739 | 65.410 ± 3.995 | 64.527 ± 5.472 | n.s. |
| Δ9MUFA | 23.154 ± 2.379 | 24.049 ± 3.908 | 23.703 ± 4.181 | 23.791 ± 3.772 | n.s. |
| SFA | 77.304 ± 2.314 | 76.467 ± 3.776 | 76.839 ± 4.176 | 76.724 ± 3.694 | n.s. |
| UFA | 22.696 ± 2.314 | 23.533 ± 3.776 | 23.161 ± 4.176 | 23.276 ± 3.694 | n.s. |
| MUFA | 20.160 ± 2.120 | 21.135 ± 3.560 | 20.913 ± 3.928 | 20.904 ± 3.479 | n.s. |
| PUFA | 2.536 ± 0.394 | 2.398 ± 0.416 | 2.248 ± 0.438 | 2.372 ± 0.426 | n.s. |
| UFA/SFA | 0.295 ± 0.039 | 0.311 ± 0.069 | 0.305 ± 0.077 | 0.307 ± 0.067 | n.s. |
| AI | 4.125 ± 0.661 | 3.986 ± 0.878 | 4.095 ± 0.907 | 4.044 ± 0.849 | n.s. |
| TI | 5.250 ± 0.739 | 5.183 ± 0.987 | 5.324 ± 0.978 | 5.240 ± 0.940 | n.s. |
| Trait | Genotype | Mean | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC (n = 66) | CT (n = 65) | TT (n = 13) | |||
| MY | 31.344 ± 8.441 | 30.434 ± 8.711 | 30.877 ± 7.975 | 30.891 ± 8.478 | n.s. |
| FY | 1.267 ± 0.369 | 1.266 ± 0.350 | 1.264 ± 0.383 | 1.266 ± 0.359 | n.s. |
| FC | 4.067 ± 0.598 | 4.221 ± 0.663 | 4.098 ± 0.678 | 4.140 ± 0.635 | n.s. |
| C6:0 | 2.296 ± 0.442 | 2.173 ± 0.420 a | 2.458 ± 0.470 b | 2.255 ± 0.440 | p < 0.05 |
| C8:0 | 1.333 ± 0.241 | 1.278 ± 0.247 | 1.372 ± 0.288 | 1.312 ± 0.248 | n.s. |
| C10:0 | 3.097 ± 0.510 | 2.988 ± 0.581 | 3.169 ± 0.730 | 3.054 ± 0.564 | n.s. |
| C12:0 | 3.712 ± 0.554 | 3.656 ± 0.708 | 3.756 ± 0.774 | 3.691 ± 0.644 | n.s. |
| C14:0 | 12.478 ± 1.342 | 12.170 ± 1.592 | 12.379 ± 1.381 | 12.330 ± 1.461 | n.s. |
| C16:0 | 41.211 ± 5.073 | 41.450 ± 4.590 b | 39.644 ± 5.248 a | 41.177 ± 4.867 | p < 0.05 |
| C18:0 | 9.377 ± 2.416 | 8.871 ± 2.541 | 10.269 ± 2.699 | 9.229 ± 2.514 | n.s. |
| C14:1 | 1.321 ± 0.462 | 1.443 ± 0.521 b | 1.107 ± 0.372 a | 1.357 ± 0.490 | p < 0.05 |
| C16:1 | 2.062 ± 0.633 | 2.352 ± 0.758 b | 1.849 ± 0.606 a | 2.174 ± 0.707 | p < 0.05 |
| C18:1n-9c | 16.275 ± 2.863 | 16.660 ± 3.609 | 17.012 ± 3.400 | 16.515 ± 3.253 | n.s. |
| C18:1n-9t | 0.962 ± 0.291 | 1.046 ± 0.327 | 0.896 ± 0.165 | 0.994 ± 0.302 | n.s. |
| C18:2n-6c | 2.865 ± 0.679 | 2.718 ± 0.618 | 3.180 ± 0.737 | 2.827 ± 0.666 | n.s. |
| C18:3n-3 | 0.280 ± 0.099 | 0.280 ± 0.087 | 0.310 ± 0.106 | 0.283 ± 0.094 | n.s. |
| ΣC14 | 13.799 ± 1.490 | 13.613 ± 1.798 | 13.486 ± 1.342 | 13.687 ± 1.619 | n.s. |
| ΣC16 | 43.274 ± 5.066 | 43.801 ± 4.705 | 41.493 ± 5.249 | 43.351 ± 4.929 | n.s. |
| ΣC6–16 | 67.511 ± 4.836 | 67.509 ± 5.456 | 65.733 ± 5.704 | 67.350 ± 5.190 | n.s. |
| ΣC18 | 29.772 ± 4.810 | 29.588 ± 5.701 | 31.680 ± 5.718 | 29.861 ± 5.305 | n.s. |
| Δ9IC14 | 9.515 ± 2.952 | 10.493 ± 3.352 | 8.263 ± 2.846 | 9.844 ± 3.184 | n.s. |
| Δ9IC16 | 4.824 ± 1.563 | 5.393 ± 1.647 | 4.511 ± 1.519 | 5.053 ± 1.619 | n.s. |
| Δ9IC18 | 63.698 ± 5.355 | 65.449 ± 5.205 | 62.483 ± 6.037 | 64.379 ± 5.411 | n.s. |
| Δ9MUFA | 23.766 ± 3.896 | 24.625 ± 3.980 | 24.245 ± 4.534 | 24.197 ± 3.986 | n.s. |
| SFA | 75.709 ± 3.746 | 74.937 ± 3.897 | 75.112 ± 4.524 | 75.306 ± 3.877 | n.s. |
| UFA | 24.291 ± 3.746 | 25.063 ± 3.897 | 24.888 ± 4.524 | 24.694 ± 3.877 | n.s. |
| MUFA | 20.901 ± 3.286 | 21.805 ± 3.702 | 21.135 ± 4.013 | 21.330 ± 3.547 | n.s. |
| PUFA | 3.391 ± 0.782 | 3.259 ± 0.715 | 3.753 ± 0.874 | 3.364 ± 0.768 | n.s. |
| UFA/SFA | 0.324 ± 0.069 | 0.338 ± 0.074 | 0.336 ± 0.082 | 0.332 ± 0.072 | n.s. |
| AI | 4.017 ± 0.785 | 3.860 ± 0.800 | 3.902 ± 1.052 | 3.936 ± 0.815 | n.s. |
| TI | 4.922 ± 0.953 | 4.725 ± 0.893 | 4.777 ± 1.185 | 4.820 ± 0.947 | n.s. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polasik, D.; Golińczak, J.; Proskura, W.; Terman, A.; Dybus, A. Association between THRSP Gene Polymorphism and Fatty Acid Composition in Milk of Dairy Cows. Animals 2021, 11, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041144
Polasik D, Golińczak J, Proskura W, Terman A, Dybus A. Association between THRSP Gene Polymorphism and Fatty Acid Composition in Milk of Dairy Cows. Animals. 2021; 11(4):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041144
Chicago/Turabian StylePolasik, Daniel, Jacek Golińczak, Witold Proskura, Arkadiusz Terman, and Andrzej Dybus. 2021. "Association between THRSP Gene Polymorphism and Fatty Acid Composition in Milk of Dairy Cows" Animals 11, no. 4: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041144
APA StylePolasik, D., Golińczak, J., Proskura, W., Terman, A., & Dybus, A. (2021). Association between THRSP Gene Polymorphism and Fatty Acid Composition in Milk of Dairy Cows. Animals, 11(4), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041144





