The Role of Mustelids in the Transmission of Sarcocystis spp. Using Cattle as Intermediate Hosts
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
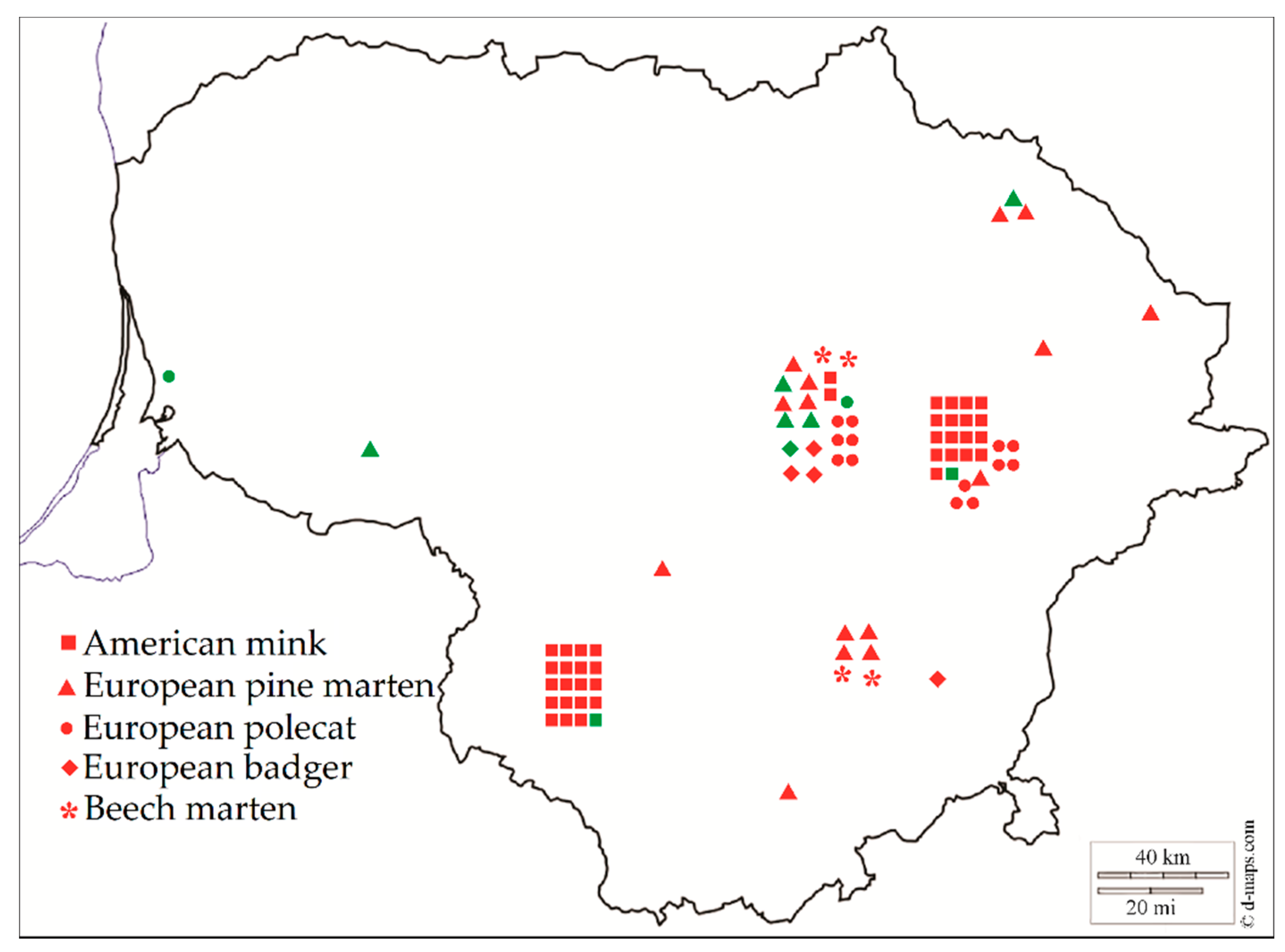
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Examination of Intestines
2.3. Molecular Analysis
2.4. Statistical Tests
3. Results
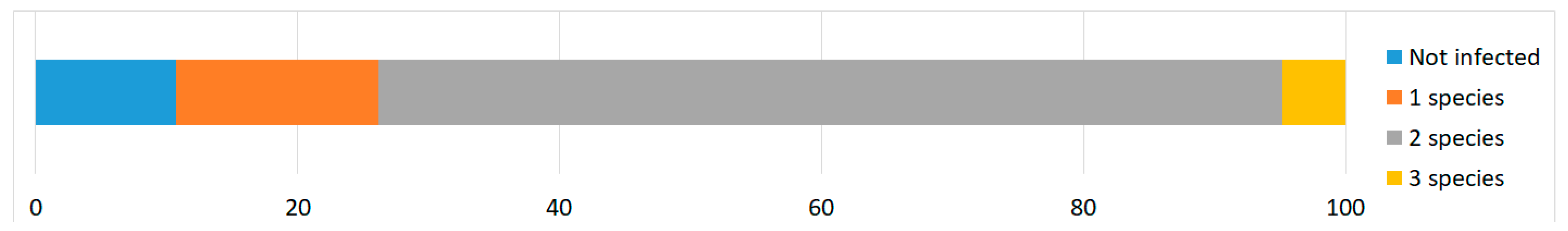
3.1. Differences in Prevalence of Sarcocystis spp. Using Microscopic and Molecular Methods
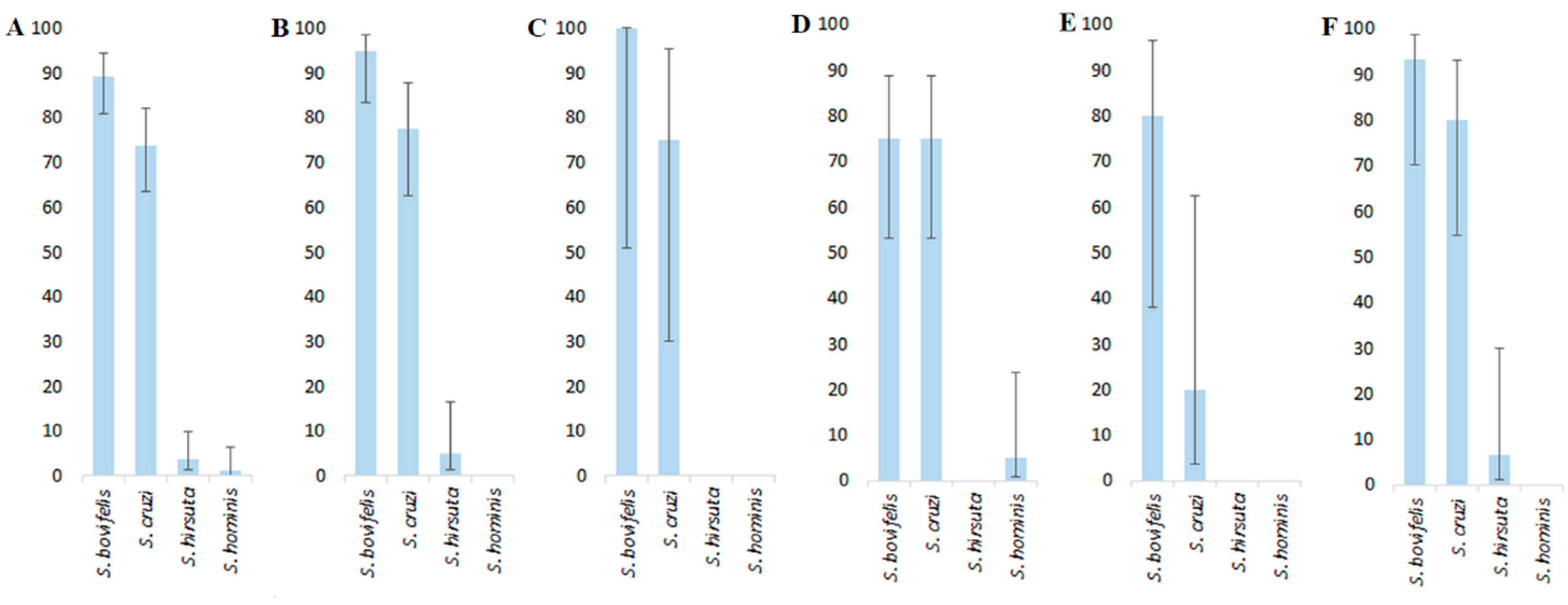
3.2. Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis spp.
3.3. Distribution of Sarcocystis spp. in the Intestine Samples of Mustelids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Speer, C.A.; Fayer, R. Sarcocystosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moré, G.; Maksimov, A.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis spp. in Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) from Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 220, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, A.P.; Dubey, J.P.; Rosenthal, B.M. Rhinitis and Disseminated Disease in a Ferret (Mustela putorius furo) Naturally Infected with Sarcocystis neurona. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Strazdaitė-Žielienė, Ž.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Servienė, E.; Butkauskas, D. Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis lutrae (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) in Muscles of Five Species of the Family Mustelidae. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B.; Josefsen, T.D. Molecular Characterisation of Sarcocystis lutrae n. sp. and Toxoplasma gondii from the Musculature of Two Eurasian Otters (Lutra lutra) in Norway. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, V.; Prakas, P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Gavarāne, I.; Fernández-García, J.L.; Martínez-González, M.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Martinez-Estellez, M.A.H.; Butkauskas, D.; Kirjušina, M. Identification and Genetic Characterization of Sarcocystis arctica and Sarcocystis lutrae in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Baltic States and Spain. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Máca, O. Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis lutrae (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) from the Raccoon Dog, Nyctereutes procyonoides, and the Common Raccoon, Procyon lotor, in the Czech Republic. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odening, K. The Present State of Species-Systematics in Sarcocystis Lankester, 1882 (Protista, Sporozoa, Coccidia). Syst. Parasitol. 1998, 41, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas of Lithuanian Mammals. Available online: https://gamtostyrimai.lt/lt/users/viewGroup/id.24/pageId.26 (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Kontrimavičius, V.; Januškis, V.; Virbickas, J.; Augustauskas, J.; Eitminavičiūtė, I.; Kazlauskas, R.; Logminas, V.; Pileckis, S.; Prūsaitė, J.; Valenta, V.; et al. Lietuvos Fauna. Žinduoliai; Mokslas: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Balčiauskas, L.; Trakimas, G.; Juškaitis, R.; Ulevičius, A.; Balčiauskienė, L. Atlas of Lithuanian Mammals, Amphibians and Reptiles, 2nd ed.; Akstis: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Baghli, A.; Engel, E.; Verhagen, R. Feeding Habits and Trophic Niche Overlap of Two Sympatric Mustelidae, the Polecat Mustela putorius and the Beech Marten Martes foina. Z. Jagdwiss. 2002, 48, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanszki, J.; Heltai, M. Feeding Habits of Sympatric Mustelids in an Agricultural Area of Hungary. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 2011, 57, 291–304. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, C.; Zhou, Y.B.; Buesching, C.D.; Kaneko, Y.; Macdonald, D.W. Contrasting Sociality in Two Widespread, Generalist, Mustelid Genera, Meles and Martes. Mammal Study 2011, 36, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecha, A.W.; Antczak, M. Diet of the European Polecat Mustela putorius in an Agricultural Area in Poland. J. Vertebr. Biol. 2013, 62, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, L.; Vohralík, V. Diet of Martes foina in Bohemia, Czech Republic (Carnivora: Mustelidae). Lynx New Ser. 2017, 48, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrūnaitė, L. Diet Composition of the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes L.), Pine Marten (Martes martes L.) and Raccoon Dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides Gray) in Clay Plain Landscape, Lithuania. Acta Zool. Litu. 2002, 12, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januškevičius, V.; Januškevičienė, G.; Prakas, P.; Butkauskas, D.; Petkevičius, S. Prevalence and Intensity of Sarcocystis spp. Infection in Animals Slaughtered for Food in Lithuania. Vet. Med. Czech 2019, 64, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Strazdaitė-Žielienė, Ž.; Januškevičius, V.; Chiesa, F.; Baranauskaitė, A.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Servienė, E.; Petkevičius, S.; Butkauskas, D. Molecular Identification of Four Sarcocystis Species in Cattle from Lithuania, Including S. hominis, and Development of a rapid Molecular Detection Method. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balčiauskas, L.; Balčiauskienė, L.; Litvaitis, J.A.; Tijušas, E. Citizen Scientists Showed a Four-fold Increase of Lynx Numbers in Lithuania. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Lindsay, D.S.; Grigg, M.E.; Dubey, J.P. Isolation, Culture and Cryopreservation of Sarcocystis species. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2017, 45, 11–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakas, P.; Butkauskas, D.; Rudaitytė, E.; Kutkienė, L.; Sruoga, A.; Pūraitė, I. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Sarcocystis taeniata and Sarcocystis pilosa n. sp. from the Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) in Lithuania. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3021–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B. Phylogenetic Relationships among Sarcocystis Species in Cervids, Cattle and Sheep Inferred from the Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I Gene. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.G.; Sullivan, K.M.; Soe, M.M. OpenEpi: Open Source Epidemiologic Statistics for Public Health. Available online: www.OpenEpi.com (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Brown, L.D.; Cat, T.T.; DasGupta, A. Interval Estimation for a Proportion. Stat. Sci. 2001, 16, 101–133. [Google Scholar]
- Abramson, J.H. WINPEPI Updated: Computer Programs for Epidemiologists, and their Teaching Potential. Epidemiol. Perspect. Innov. 2011, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.R.; Salazar, W.; Landers, D.M. What is Missing in p < 05? Effect Size. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1991, 62, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakas, P.; Liaugaudaitė, S.; Kutkienė, L.; Sruoga, A.; Švažas, S. Molecular Identification of Sarcocystis rileyi Sporocysts in red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Lithuania. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, W.; Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Buob, D.; Ruetten, M.; Deplazes, P. Sarcocystis Infection in Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) With Eosinophilic Myositis/Fasciitis in Switzerland and Involvement of Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and Hunting Dogs in the Transmission. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 13, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, T.; Uraguchi, K.; Ito, T.; Yamazaki, A.; Takai, S.; Yagi, K. First Report of Sarcocystis pilosa Sporocysts in Feces from red fox, Vulpes vulpes schrencki, in Hokkaido, Japan. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 11, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, B. Molecular Characterisation of Sarcocystis bovifelis, Sarcocystis bovini n. sp., Sarcocystis hirsuta and Sarcocystis cruzi from Cattle (Bos taurus) and Sarcocystis sinensis from Water Buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, B.; Hilali, M.; Abbas, I.E. Molecular Differentiation of Sarcocystis buffalonis and Sarcocystis levinei in Water Buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) from Sarcocystis hirsuta and Sarcocystis cruzi in Cattle (Bos taurus). Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2459–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odening, K.; Wesemeier, H.H.; Walter, G.; Bockhardt, I. The Wisent (Bison bonasus, Bovidae) as an Intermediate Host of Three Sarcocystis species (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) of Cattle. Folia Parasitol. 1994, 41, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pyziel, A.M.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W. Sarcocystis cruzi (Protozoa: Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) Infection in European Bison (Bison bonasus) from Białowieza Forest, Poland. Wiad. Parazytol. 2009, 55, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Calero-Bernal, R.; Verma, S.K.; Seaton, C.T.; Sinnett, D.; Ball, E.; Dunams, D.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Dubey, J.P. Sarcocystis cruzi Infection in Wood Bison (Bison bison athabascae). Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 210, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, P.W. Lessons from Lean Beasts: Conservation Biology of the Mustelids. Mamm. Rev. 2000, 30, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschille, J.; Stier, N.; Roth, M.; Mayer, R. Feeding Habits of Invasive American mink (Neovison vison) in Northern Germany—Potential Implications for Fishery and Waterfowl. Acta Theriol. 2013, 59, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Opo, R.; Margalida, A. Human-Mediated Carrion: Effects on Ecological Processes. In Carrion Ecology and Management. Wildlife Research Monographs; Olea, P., Mateo-Tomás, P., Sánchez-Zapata, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 183–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, S.S.; Gjerde, B. The red fox (Vulpes vulpes) and the Arctic fox (Vulpes lagopus) are Definitive Hosts of Sarcocystis alces and Sarcocystis hjorti from Moose (Alces alces). Parasitology 2010, 137, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Evans, L. Prevalence of Sarcocystis spp. in Two Subspecies of Caribou (Rangifer tarandus) in Newfoundland and Labrador, and Foxes (Vulpes vulpes), Wolves (Canis lupus), and Husky Dogs (Canis familiaris) as Potential Definitive hosts. J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 662–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, B.; Hilali, M. Domestic cats (Felis catus) are Definitive Hosts for Sarcocystis sinensis from Water Buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, S.M.; Perminova, V.V.; Yeshtokina, N.V. Sarcocystis citellivulpes sp. n. from the Yellow Suslik Citellus fulvus Lichtenstain, 1923. In Toksoplazmidy, Protozoologiya; Beyer, T.V., Bezukladnikova, N.A., Galuzo, I.G., Konovalova, S.I., Pak, S.M., Eds.; Akademii Nauk Sovetskoi Sotsialisticheskoi Respubliki: Moscow, Russia, 1979; pp. 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell-Jones, A.J.; Amori, G.; Bogdanowicz, W.; Krystufek, B.; Reijnders, P.J.H.; Spitzenberger, F.; Stubbe, M.; Thissen, J.B.M.; Vohralik, V.; Zima, J. The Atlas of European Mammals, 1st ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Primer Name | Primer Sequence | Orientation | The Run of Nested PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. bovifelis | SF1 1 | ATGGCGTACAACAATCATAAAGAA | Forward | First |
| SkatR | CAGGCTGAACAGHABTACGA | Reverse | First | |
| V2bo3 | ATATTTACCGGTGCCGTACTTATGTT | Forward | Second | |
| V2bo4 | GCCACATCATTGGTGCTTAGTCT | Reverse | Second | |
| S. cruzi | SF1 1 | ATGGCGTACAACAATCATAAAGAA | Forward | First |
| SsunR2 | GTGCCTCCCAGGCTGAAYAG | Reverse | First | |
| GsScruF | TGTATCTACTTACGGCAGGTATCTTT | Forward | Second | |
| GsScruR | CGTAGTTAGATCCATATCACTCGGTA | Reverse | Second | |
| S. hirsuta | SF1 1 | ATGGCGTACAACAATCATAAAGAA | Forward | First |
| SkatR | CAGGCTGAACAGHABTACGA | Reverse | First | |
| GaHiEF 2 | GTTGTGCGGTATGAATTATCAACCT | Forward | Second | |
| GaHiER 2 | GGTAAGAACTGGAATGGTTAATATCAG | Reverse | Second | |
| S. hominis | VohoF | GTGCGGTATGAACTGTCTACTGCT | Forward | First |
| VohoR | AATACCTGCCCGGCCTTAAC | Reverse | First | |
| GaHoEF 2 | TCTCTGGTTTTGGTAACTACTTCGT | Forward | Second | |
| GaHoER 2 | CAGACACTGGGATATAATACCGAAC | Reverse | Second |
| Host Species | N | Sarcocystis spp. Positive Animals | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopic Analysis | Molecular Analysis | ||||||
| n | % | 95% CI | N | % | 95% CI | ||
| American mink | 40 | 15 | 37.5 | 24.2–53.0 | 38 | 95.0 *** | 83.5–98.6 |
| Beech marten | 4 | 3 | 75.0 | 30.1–95.4 | 4 | 100 NS | 51.0–100.0 |
| European pine marten | 20 | 12 | 60.0 | 38.7–78.1 | 15 | 75.0 NS | 53.1–88.8 |
| European badger | 5 | 1 | 20.0 | 36.2–62.5 | 4 | 80.0 * | 37.6–96.4 |
| European polecat | 15 | 9 | 60.0 | 35.8–80.2 | 14 | 93.3 ** | 70.2–98.8 |
| Total | 84 | 40 | 47.6 | 37.3–58.2 | 75 | 89.3 *** | 80.9–94.34 |
| Sarcocystis spp. | GenBank Accession No. (Length in bp) | Sequence Similarity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparing Obtained sequences | Comparing Isolates of the Same Species | Comparing Isolates with Other Closely Related Species | ||
| S. bovifelis | MW595468–MW595542 (361) | 98.4–100 | 97.2–100% S. bovifelis (KT900961–KT900998, KC209690–KC209696, MK962347–MK962348, MT796903–MT796925) | 92.5–94.5% S. bovini (KT900999–KT901022, LC171858) |
| S. cruzi | MW595543–MW595604 (556) | 98.2–100 | 96.0–100% S. cruzi (KC209597–KC209600, KT901078–KT901095, LC171859–LC171862, MG787071–MG787076, MT796926–MT796945) | 90.8–93.4% S. pilosa (KU753903–KU753910, LC349942, LC349966–LC349967, LC466196–LC466201, LC481077–LC481081, LC496070, MT070670– MT070677) |
| S. hirsuta | MW595605–MW595607 (461) | 98.9–99.8 | 98.9–99.8% S. hirsuta (KC209634, KT901023–KT901077, LC171863, MT796946–MT796951, MT796958–MT7969) | 95.6–96.3% S. buffalonis (KU247868–KU247873, MG792800–MG792802) |
| S. hominis | MW595608 (501) | - | 97.6–99.0% S. hominis (MH021119, MK497840–MK497843, MT796961–MT796964) | 87.1–87.8% S. bovifelis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prakas, P.; Balčiauskas, L.; Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Butkauskas, D. The Role of Mustelids in the Transmission of Sarcocystis spp. Using Cattle as Intermediate Hosts. Animals 2021, 11, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030822
Prakas P, Balčiauskas L, Juozaitytė-Ngugu E, Butkauskas D. The Role of Mustelids in the Transmission of Sarcocystis spp. Using Cattle as Intermediate Hosts. Animals. 2021; 11(3):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030822
Chicago/Turabian StylePrakas, Petras, Linas Balčiauskas, Evelina Juozaitytė-Ngugu, and Dalius Butkauskas. 2021. "The Role of Mustelids in the Transmission of Sarcocystis spp. Using Cattle as Intermediate Hosts" Animals 11, no. 3: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030822
APA StylePrakas, P., Balčiauskas, L., Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E., & Butkauskas, D. (2021). The Role of Mustelids in the Transmission of Sarcocystis spp. Using Cattle as Intermediate Hosts. Animals, 11(3), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030822









