A Food-Safety Risk Assessment of Mercury, Lead and Cadmium in Fish Recreationally Caught from Three Lakes in Poland
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
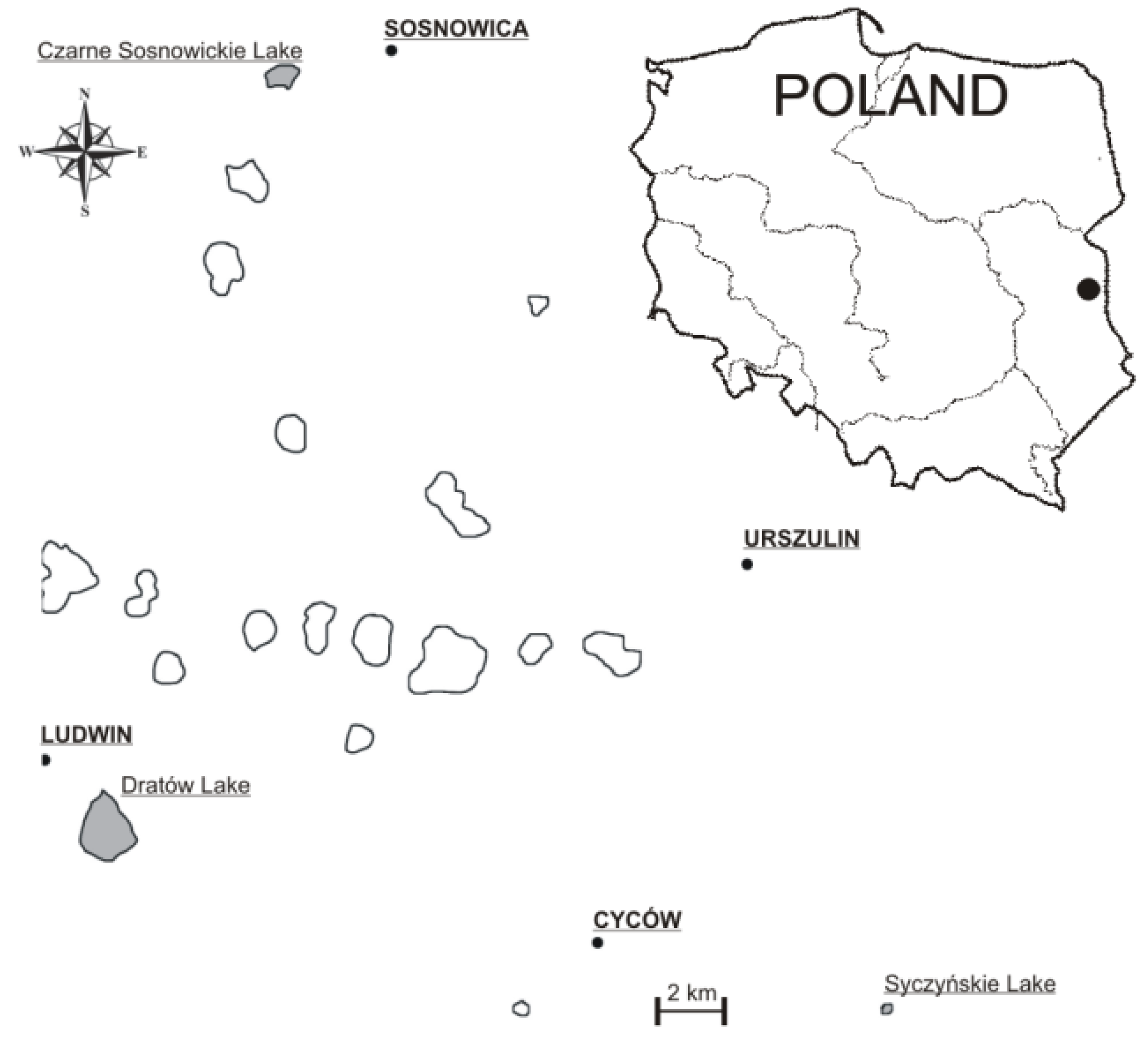
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Collection of Water, Sediment, and Fish Samples
2.3. Metal Analysis
2.4. Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fish and Angling Use of Studied Lakes
3.2. Heavy Metals in Water and Sediments
3.3. Heavy Metals in Fish Muscles and Health Risk for Humans
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebrahimpour, M.; Pourkhabbaz, A.; Baramak, R.; Babaei, H.; Rezaei, M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in freshwater fish species, Anzali, Iran. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 87, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esinulo, A.C.; Kelle, I.A.; Ogbuagu, D.H. Bioaccumulation of Zn in Muscle and Brain Tissues of the African Catfish—Clarias gariepinus. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, L.L.; Snyder, B.D.; Olsen, A.R.; Pitt, J.L. Contaminants in fish tissue from US lakes and reservoirs: A national probabilistic study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 150, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klavins, M.; Potapovics, O.; Rodinov, V. Heavy metals in fish from lakes in Latvia: Concentrations and trends of changes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roop, H.J.; Poudyal, N.C.; Jennings, C.A. Fishing preferences, angling behavior, and attitudes toward management: A comparison between White and Nonwhite anglers. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2020, 26, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, D.A.; Marković, R.V.; Teodorović, V.B.; Šefer, D.S.; Krstić, M.P.; Radulović, S.B.; Ivanović Ćirić, J.S.; Janjić, J.M.; Baltić, M. Determination of heavy metals in muscle tissue of six fish species with different feeding habits from the Danube River, Belgrade—Public health and environmental risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11383–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, D.; Skorić, S.; Lenhardt, M.; Hegediš, A.; Krpo-Ćetković, J. Risk assessment of using fish from different types of reservoirs as human food—A study on European perch (Perca fluviatilis). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, B.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, S. Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, and fish from Dongting Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34076–34090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivokapić, M. Risk assessment of toxic elements (Pb, Cd, Hg, As) in water, sediment and in thinlip grey mullet (Bojana river). Agric. For. Bull. 2020, 66, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseenko, T.I.; Gashkina, N.A. Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Hg, Cd and Pb) in fish: Influence of the aquatic environment and climate. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 115013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankwaa, G.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, N.; Luan, Y.; Cao, Y.; Huang, W.; Ni, X.; Gyimah, E. Heavy metals concentration profile of an aquatic environment and health implications of human exposure to fish and prawn species from an urban river (Densu). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2021, 20, 529–546. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Q.Y.; Yu, M.X.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.G.; Yu, Z.Q. Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Res. 2016, 92, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, G. Technical Raport: Trace Metals/Heavy Metals and Its Impact on Environment, Biodiversity and Human Health—A Short Review. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266618621_Traceheavy_Metals_and_Its_Impact_on_the_Environment_Biodiversity_and_Human_Health-_A_Short_Review (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Kibria, G.; Yousuf Haroon, A.K.; Nugegoda, D.; Rose, G. Climate Change and Chemicals: Environmental and Biological Aspects; New India Publishing Agency (NIPA): New Delhi, India, 2010; pp. 1–475. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadede, H.; Ünlü, E. Concentrations of some heavy metals in water, sediment and fish species from the Ataturk Dam Lake (Euphrates), Turkey. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Feng, C.; Quan, W.; Chen, X.; Niu, J.; Shen, Z. Role of living environments in the accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in fishes and crabs in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, G. Biomonitoring: An appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 606, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naigaga, I.; Kaiser, H.; Muller, W.J.; Ojok, L.; Mbabazi, D.; Magezi, G.; Muhumuza, E. Fish as bioindicators in aquatic environmental pollution assessment: A case study in Lake Victoria wetlands, Uganda. Phys. Chem. Earth A B C 2011, 36, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessl, C.; Otachi, E.O.; Körner, W.; Avenant-Oldewage, A.; Jirsa, F. Fish as bioindicators for trace element pollution from two contrasting lakes in the Eastern Rift Valley, Kenya: Spatial and temporal aspects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19767–19776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nussey, G.; van Vuren, J.H.J.; du Preez, H.H. Bioaccumulation of chromium, manganese, nickel and lead in the tissues of the moggel, Labeo umbratus (Cyprinidae), from Witbank Dam, Mpumalanga. Water 2000, 26, 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Hyder, M.; Zafer, M.N.; Gilani, S.R.; Shaheer, M.; Ahmed, N. Concentration trends of Pb, Cr, Cd and Hg in fish from different habitats in Pakistan. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosn, M.; Mahfouz, C.; Chekri, R.; Khalaf, G.; Guérin, T.; Jitaru, P.; Amara, R. Seasonal and Spatial Variability of Trace Elements in Livers and Muscles of Three Fish Species from the Eastern Mediterranean. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12428–12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diop, M.; Net, S.; Howsam, M.; Lencel, P.; Watier, D.; Grard, T.; Duflos, G.; Diouf, A.; Amara, R. Concentrations and Potential Human Health Risks of Trace Metals (Cd, Pb, Hg) and Selected Organic Pollutants (PAHs, PCBs) in Fish and Seafood from the Senegalese Coast. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, I.; Migdał, W.; Topolska, K.; Gambuś, F.; Szczurowska, K.; Cieślik, E. Changes in the content of heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Hg, As, Ni, Cr) in freshwater fish after processing—The consumer’s exposure. J. Elem. 2018, 23, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isangedighi, I.A.; David, G.S. Heavy Metals Contamination in Fish: Effects on Human Health. J. Aquat. Sci. Mar. Biol. 2019, 2, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Djedjibegovic, J.; Marjanovic, A.; Tahirovic, D.; Caklovica, K.; Turalic, A.; Lugusic, A.; Omeragic, E.; Sober, M.; Caklovica, F. Heavy metals in commercial fish and seafood products and risk assessment in adult population in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, P.L.; Bistoni, M.d.l.A.; Monferran, M.V. Trace element concentrations in six fish species from freshwater lentic environments and evaluation of possible health risks according to international standards of consumption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27598–27608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, A.; Barone, G.; Dambrosio, A.; Garofalo, R.; Busco, A.; Storelli, M.M. Occurrence of trace metals in fish from South Italy: Assessment risk to consumer’s health. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2020, 90, 103487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, X. Metal concentrations in fish from nine lakes of Anhui Province and the health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 20117–20124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, J.; Wiedner, C.; Zippel, P. Factors controlling the dominance of Planktothrix agardhii and Limnothrix redekei in eutrophic shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 1997, 342, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, M.; Krupa, D.; Pawlik-Skoworońska, B.; Kornijów, R. Development of toxic Planktothrix agardhii (Gom.) Anagn. et Kom. and potentially toxic algae in the hypertrophic Lake Syczyńskie (Eastern Poland). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2007, 35, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Konieczka, P.; Misztal-Szkudlińska, M.; Namieśnik, J.; Szefer, P. Determination of total mercury in fish and cormorant using cold vapour atomic absorption spectrometry. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 19, 931–936. [Google Scholar]
- Szkoda, J.; Żmudzki, J. Determination of lead and cadmium in biological material by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry method. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2005, 49, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Heshmati, A.; Karami-Momtaz, J.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, A.; Ghadimi, S. Dietary exposure to toxic and essential trace elements by consumption of wild and farmed carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Caspian kutum (Rutilus frisii kutum) in Iran. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukowska, J.; Biziuk, M. Methodological evaluation of method for dietary heavy metal intake. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, R21–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E. Trophic transfer, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification of non-essential hazardous heavy metals and metalloids in food chains/webs—Concepts and implications for wildlife and human health. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 1353–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Buchmeier, G.; Claus, E.; Duester, L.; Heininger, P.; Körner, A.; Mayer, P.; Paschke, A.; Rauert, C.; Reifferscheid, G.; et al. Bioaccumulation in aquatic systems: Methodological approaches, monitoring and assessment. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrektywa Parlamentu Europejskiego i Rady 2000/60/WE z dnia 23 października 2000 r. Ustanawiająca Ramy Wspólnotowego Działania w Dziedzinie Polityki Wodnej (Dz.U. UE L z dnia 22 Grudnia 2000 r.). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/PL/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:02000L0060-20141120&from=En (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Gospodarki Morskiej i Żeglugi Śródlądowej z dnia 11 Października 2019 r. w Sprawie Klasyfikacji Stanu Ekologicznego, Potencjału Ekologicznego i Stanu Chemicznego Oraz Sposobu Klasyfikacji Stanu Jednolitych Części wód Powierzchniowych, a Także Środowiskowych norm Jakości dla Substancji Priorytetowych (Dz. U. z 2018 r. poz. 2268 oraz z 2019 r. poz. 125, 534 i 1495). Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20190002148/O/D20192148.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Główny Inspektorat Ochrony Środowiska. 2019. Available online: https://www.gios.gov.pl/pl/stan-srodowiska/monitoring-wod (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Gwoździński, K.; Mazur, J.; Pieniążek, A. Concentrations of Metals in Water of Unmonitored Lakes Near a Landscape Park. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Daniszewski, P. Heavy metals in the waters of Dąbie Lake (North-West Poland) in the years 2008–2012. World Sci. News 2017, 69, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Daniszewski, P.; Konieczny, R. Heavy Metal Content in Water of Miedwie Lake (North-West Poland). Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2013, 15, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yi, L.; Yin, X.; Wang, A.; Li, Y.; Chen, J. The source of natural and anthropogenic heavy metals in the sediments of the Minjiang River estuary (SE China): Implications for historical pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, G.T.; Kara, M.; Bayram, A.; Gündüz, O. Assessment of seasonal and spatial variations of physicochemical parameters and trace elements along a heavily polluted effluent-dominated stream. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—A tributary of the Ganges. India J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojakowska, I.; Sokołowska, G. Geochemiczne klasy czystości osadów wodnych. Przegl. Geol. 1998, 46, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bojakowska, I. The criteria for the assessment of water sediments conatmination. Przegl. Geol. 2001, 49, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Szafran, K. Heavy metals in bottom sediments of three shallow lakes in the Łęczna-Włodawa lakeland. Acta Agrophys. 2003, 1, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Tylmann, W.; Lysek, K.; Kinder, M.; Pempkowiak, J. Regional Pattern of Heavy Metal Content in Lake Sediments in Northeastern Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staszowska, A.; Skałecki, P.; Florek, M.; Litwińczuk, A. Impact of fish species and their living environment on concentration of lead and estimated intake thereof from muscle tissue. Żywnosci Nauk. Technol. Jakosc. 2013, 6, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Markiewicz, K.; Jaworski, J. Interspecific differences in the concentrates of macro- and microelements in the muscle of six fish species from lakes of the Olsztyn lake district (north-east of Poland). Pol. J. Food Nutr. 2006, 15, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Xu, X.; Shi, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Q.; Shou, L. Heavy metal concentrations in tissues of marine fish and crab collected from the middle coast of Zhejiang Province, China. Environ. Monit Assess 2020, 192, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Brucka-Jastrzębska, E. Heavy metal analysis in muscles of fish from lakes of North-Eastern Poland. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci 2006, 56, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kostecki, M. Heavy metals in flesh and liver of some fish species in Dzierżno Duże Dam-Reservoir (upper Silesia). Arch. Ochr. Środ 2000, 26, 109–125. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Novotna Kruzikova, K.; Siroka, Z.; Jurajda, P.; Harustiakova, D.; Smolikova, Z.; Kubicek, M.; Svobodova, Z. Mercury content in fish from drinking-water reservoirs in the Morava River Basin (Czech Republic). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, Z.; Dušek, L.; Hejtmánek, M.; Vykusová, B.; Šmid, R. Bioaccumulation of mercury in various fish species from Orlik and Kamýk water reservoirs in the Czech Republic. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 43, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Parsa, Y. Bioaccumulation of trace mercury in trophic levels of benthic, benthopelagic, pelagic fish species, and sea birds from Arvand River, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 156, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polak-Juszczak, L. Distribution of organic and inorganic mercury in the tissues and organs of fish from the southern Baltic Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 34181–34189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łuczyńska, J.; Paszczyk, B.; Łuczyński, M.J. Fish as a bioindicator of heavy metals pollution in aquatic ecosystem of Pluszne Lake, Poland, and risk assessment for consumer’s health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Xu, X.R.; Ding, Z.H.; Peng, J.X.; Jin, M.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Hong, Y.G.; Yue, W.Z. Heavy metals in wild marine fish from South China Sea: Levels, tissue- and species-specific accumulation and potential risk to humans. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kh, M.; El-Moselhy, A.I.; Othman, H.; Abd El-Azem, M.E.; El-Metwally, A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some tissues of fish in the Red Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32006R1881&from=EN (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Leung, H.M.; Leung, A.O.W.; Wang, H.S.; Ma, K.K.; Liang, Y.; Ho, K.C.; Cheung, K.C.; Tohidi, F.; Yung, K.K.L. Assessment of heavy metals/metalloid (As, Pb, Cd, Ni, Zn, Cr, Cu, Mn) concentrations in edible fish species tissue in the Pearl River Delta (PRD). China Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiful Islam, M.; Kawser Ahmed, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M. Heavy metals in sediment and their accumulation in commonly consumed fish species in Bangladesh. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2017, 72, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawuro, A.A.; Voegborlo, R.B.; Adimado, A.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some tissues of fish in Lake Geriyo, Adamawa State, Nigeria. J. Environ. Public Health 2018, 2018, 1854892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, A.S.S.; Sultana, S.; Habib, A.; Ullah, H.; Musa, N.; Hossain, M.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Sarker, M.S.I. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some commercially important fishes from a tropical river estuary suggests higher potential health risk in children than adults. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehouel, F.; Bouayad, L.; Hammoudi, A.H.; Ayadi, O.; Regad, F. Evaluation of the heavy metals (mercury, lead, and cadmium) contamination of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) and swordfish (Xiphias gladius) fished in three Algerian coasts. Vet. World 2019, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahjoub, M.; Fadlaoui, S.; El Maadoudi, M.; Smiri, Y. Mercury Lead, and Cadmium in the Muscles of Five Fish Species from the Mechraa-Hammadi Dam in Morocco and Health Risks for Their Consumers. J. Toxicol. 2021, 2021, 8865869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Lake | Dratów | Syczyńskie | Czarne Sosnowickie |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| Surface area (ha) | 167.9 | 5.7 | 39.0 |
| Max. depth (m) | 3.3 | 4.0 | 15.6 |
| pH * | 8.32 ± 0.31 | 7.94 ± 0.61 | 7.44 ± 0.25 |
| Oxygen (mg O2 dm−3) * | 10.65 ± 0.56 | 11.69 ± 3.28 | 7.20 ± 2.37 |
| N-NH4 (mg NH4 dm−3) * | 0.085 ± 0.069 | 0.548 ± 0.283 | 0.835 ± 0.095 |
| N-NO3 (mg NO3 dm−3) * | 0.096 ± 0.112 | 0.185 ± 0.238 | 0.636 ± 0.202 |
| P-PO43− (mg PO43−dm−3) * | 0.024 ± 0.020 | 0.232 ± 0.185 | 0.037 ± 0.031 |
| Ptot (mg P dm−3) * | 0.191 ± 0.010 | 0.499 ± 0.098 | 0.146 ± 0.057 |
| Chlorophyll a (mg dm−3) * | 79.06 ± 41.64 | 73.84 ± 39.24 | 14.52 ± 10.01 |
| TOC (mg C dm−3) * | 6.7 ± 0.7 | 7.1 ± 1.4 | 24.5 ± 4.9 |
| Trophic status | eutrophic | hypertrophic | eutrophic |
| Water mixing type | polimyctic | polimyctic | polimyctic |
| Fishery lake type | tench-pike | tench-pike | tench-pike |
| Used by | PAA Lublin | PAA Lublin | PAA Chełm |
| Lake | Fish Species | N | Total Length | Body Mass | Participation in Results of Angling (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Min–Max | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | In Abundance | In Biomass | |||
| Dratów | R. rutilus | 11 | 16.38 ± 2.41 | 13.00–20.50 | 51.30 ± 27.23 | 18.85–110.68 | ||
| E. lucius | 4 | 35.75 ± 0.87 | 35.00–36.50 | 361.63 ± 38.83 | 328.00–395.25 | 7.39 ± 8.47 | 7.16 ± 5.43 | |
| P. fluviatilis | 6 | 16.83 ± 4.48 | 12.00–22.00 | 45.56 ± 40.30 | 10.11–96.27 | |||
| Syczyńskie | R. rutilus | 22 | 16.40 ± 1.99 | 13.80–23.50 | 53.88 ± 26.89 | 26.44–160.61 | ||
| E. lucius | 4 | 32.25 ± 2.60 | 30.00–34.50 | 257.79 ± 83.38 | 185.58–330.00 | 79.70 ± 26.25 | 73.23 ± 14.91 | |
| P. fluviatilis | 10 | 13.48 ± 1.66 | 11.00–17.60 | 27.39 ± 13.92 | 12.85–63.87 | |||
| Czarne Sosnowickie | R. rutilus | 24 | 16.60 ± 2.79 | 13.00–26.00 | 47.23 ± 38.08 | 16.10–195.04 | ||
| E. lucius | 4 | 35.50 ± 0.71 | 35.00–36.00 | 397.00 ± 4.24 | 394.00–400.00 | 22.39 ± 11.35 | 30.94 ± 9.62 | |
| P. fluviatilis | 5 | 23.10 ± 4.98 | 15.00–28.50 | 180.57 ± 110.54 | 41.11–346.58 | |||
| Lake | Dratów | Syczyńskie | Czarne Sosnowickie |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| Total number of fish caught by anglers (ind. year−1) | 3807.80 ± 566.73 | 245.52 ± 165.94 | 468.80 ± 279.58 |
| Total biomass of caught fish by anglers (kg year−1) | 1663.54 ± 832.25 | 147.80 ± 217.14 | 189.36 ± 124.23 |
| Participation of predatory fish in abundance (%) | 5.76 ± 6.87 | 48.72 ± 42.75 | 13.29 ± 4.32 |
| Participation of non-predatory fish in abundance (%) | 94.24 ± 6.87 | 51.28 ± 42.75 | 86.71 ± 4.32 |
| Participation of predatory fish in biomass (%) | 18.12 ± 11.93 | 47.17 ± 29.44 | 45.02 ± 6.86 |
| Participation of non-predatory fish in biomass (%) | 81.88 ± 11.93 | 52.83 ± 29.44 | 54.98 ± 6.86 |
| Number of fish on ha of the lake (ind. year−1) | 22.68 ± 3.38 b | 43.07 ± 29.11 a | 12.02 ± 7.17 b |
| Biomass of fish on ha of the lake (kg year−1) | 9.91 ± 4.96 | 25.93 ± 38.10 | 4.86 ± 3.19 |
| Number of anglers on ha of the lake (pers. year−1) | 1.37 ± 0.57 b | 2.63 ± 0.28 a | 0.93 ± 0.19 b |
| Number of fish per capita (ind. angler−1 year−1) | 19.55 ± 9.87 | 16.31 ± 10.28 | 12.37 ± 5.87 |
| Biomass of fish per capita (kg angler−1 year−1) | 7.11 ± 1.19 | 9.88 ± 14.45 | 4.92 ± 2.06 |
| Lake | Fish Species | Dratów | Syczyńskie | Czarne Sosnowickie |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metal | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |
| Pb | R. rutilus | 0.0399 ± 0.0200 | 0.0672 ± 0.1472 | 0.1595 ± 0.1215 |
| E. lucius | 0.0360 ± 0.0010 | 0.0305 ± 0.0064 | 0.0920 ± 0.0014 | |
| P. fluviatilis | 0.0533 ± 0.0325 | 0.1057 ± 0.0787 | 0.0296 ± 0.0050 | |
| Water | 0.0046 ± 0.0007 | 0.0189 ± 0.0079 b | 0.0220 ± 0.0400 b | |
| Sediment | 2.5852 ± 0.9636 C | 38.2960 ± 1.2839 aB | 45.8234 ± 10.5580 aA | |
| Cd | R. rutilus | 0.0020 ± 0.0011 B | 0.0014 ± 0.0018 B | 0.0095 ± 0.0098 A |
| E. lucius | 0.0010 ± 0.0010 | 0.0010 ± 0.0001 | 0.0015 ± 0.0007 | |
| P. fluviatilis | 0.0020 ± 0.0015 | 0.0020 ± 0.0008 | 0.0020 ± 0.0014 | |
| Water | 0.0012 ± 0.0002 b | 0.0020 ± 0.0006 b | 0.0030 ± 0.0008 b | |
| Sediment | 0.2940 ± 0.0463 aB | 0.4337 ± 0.0878 aA | 0.4769 ± 0.1563 aA | |
| Hg | R. rutilus | 0.0123 ± 0.0040 bB | 0.0243 ± 0.0063 B | 0.0499 ± 0.0130 aA |
| E. lucius | 0.0185 ± 0.0000 b | 0.0255 ± 0.0081 | 0.0215 ± 0.0007 b | |
| P. fluviatilis | 0.0216 ± 0.0037 aB | 0.0319 ± 0.0168 B | 0.0583 ± 0.0171 aA | |
| Water | 0.0016 ± 0.0004 bB | 0.0010 ± 0.0002 B | 0.0050 ± 0.0008 bA | |
| Sediment | 0.0062 ± 0.0001 aB | 0.0012 ± 0.0002 C | 0.0211 ± 0.0001 aA |
| Fish Species | Metal | Range of Concentration (µg g−1 ww) | RfD (µg kg−1 per day) | EDI (µg kg−1 per day) | THQ/TTHQ * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R. rutilus E. lucius P. fluviatilis | Pb | 0.0399–0.1595 0.0305–0.0920 0.0296–0.1057 | 4 | 0.0031–0.0125 0.0024–0.0072 0.0023–0.0083 | 0.0008–0.0031 0.0006–0.0018 0.0006–0.0021 |
| R. rutilus E. lucius P. fluviatilis | Cd | 0.0014–0.0095 0.0010–0.0015 0.0020 | 1 | 0.0001–0.0007 0.0001–0.0001 0.0002 | 0.0001–0.0007 0.0001–0.0001 0.0002 |
| R. rutilus E. lucius P. fluviatilis | Hg | 0.0123–0.0499 0.0185–0.0255 0.0216–0.0583 | 0.1 | 0.0010–0.0039 0.0014–0.0020 0.0017–0.0046 | 0.0100–0.0390 0.0140–0.0200 0.0170–0.0460 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chałabis-Mazurek, A.; Rechulicz, J.; Pyz-Łukasik, R. A Food-Safety Risk Assessment of Mercury, Lead and Cadmium in Fish Recreationally Caught from Three Lakes in Poland. Animals 2021, 11, 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123507
Chałabis-Mazurek A, Rechulicz J, Pyz-Łukasik R. A Food-Safety Risk Assessment of Mercury, Lead and Cadmium in Fish Recreationally Caught from Three Lakes in Poland. Animals. 2021; 11(12):3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123507
Chicago/Turabian StyleChałabis-Mazurek, Agnieszka, Jacek Rechulicz, and Renata Pyz-Łukasik. 2021. "A Food-Safety Risk Assessment of Mercury, Lead and Cadmium in Fish Recreationally Caught from Three Lakes in Poland" Animals 11, no. 12: 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123507
APA StyleChałabis-Mazurek, A., Rechulicz, J., & Pyz-Łukasik, R. (2021). A Food-Safety Risk Assessment of Mercury, Lead and Cadmium in Fish Recreationally Caught from Three Lakes in Poland. Animals, 11(12), 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123507






