Global Studies of the Host-Parasite Relationships between Ectoparasitic Mites of the Family Syringophilidae and Birds of the Order Columbiformes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
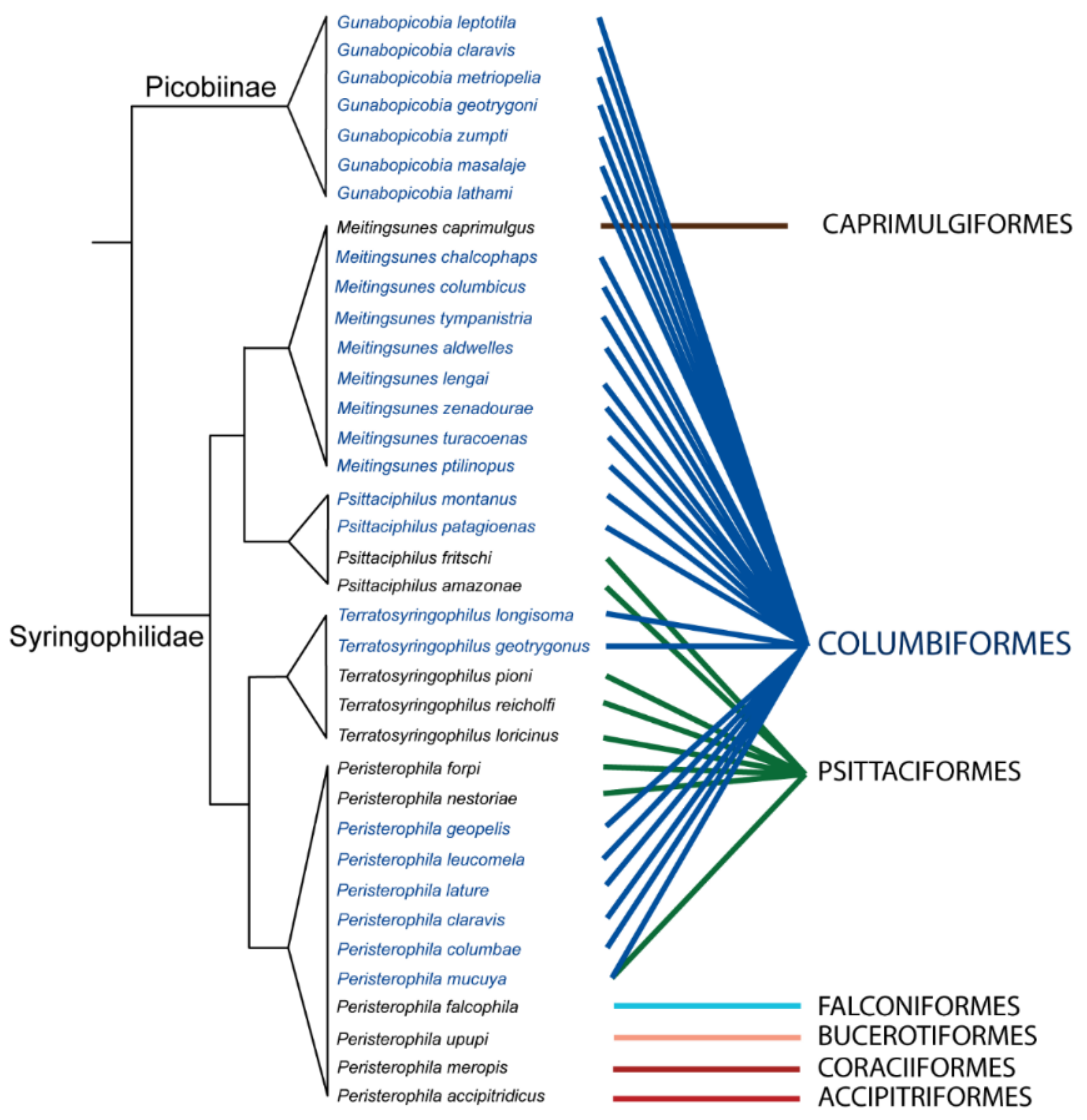
Historical Review of Quill Mite Genera Associated with Doves and Pigeons
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bipartite Networks and Statistics
2.2. Prevalence
2.3. Mite Phylogeny
2.4. Visualization of Host Phylogeny
2.5. Host Specificity
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence Index Birds from Order Columbiformes
- (1)
- IP 1–10% Chalcophaps indica (8.7%), Columba livia (8.7%), Columba palumbus (5%), Columbina squammata (6.7%), Leptotila verreauxi (4.2%), Patagioenas picazuro (6.2%), Streptopelia orientalis (9.1%), Streptopelia semitorquata (4.8%), Turtur chalcospilos (7%).
- (2)
- IP 11–20% Claravis pretiosa (20%), Columba delegorguei (14.3%), Columba oenas (11.1%), Columbina raucana (13.3%), Geotrygon linearis (12.5%), Geotrygon montana (12.5%), Leptotila rufaxilla (20%), Macropygia amboinensis (16.7%), Metriopelia melanoptera (12.5%), Patagioenas picazuro (12.5%), Patagioenas speciosa (12.5%), Patagioenas speciosa (12.5%), Ptilinopus magnificus (11.8%), Streptopelia semitorquata (14.3%), Streptopelia turtur (13.3%), Turacoena modesta (20), Turtur tympanistria (16.7%).
- (3)
- IP 21–30% Columbina talpacoti (25%), Geotrygon montana (25%), Macropygia phasianella (21.4%), Oena capensis (29.4%), Turacoena manadensis (25%).
- (4)
- IP 31–40% Geotrygon frenata (33%), Geopelia striata (38.5%).
- (5)
- IP 41–50% Caloenas nicobarica (50%), Columba arquatrix (50%), Columba delegorguei (42%), Columba guinea (50%), Columbina minuta (50%), Gallicolumba luzonica (50%), Geopelia cuneata (50%), Geopelia placida (50%), Metriopelia ceciliae (50%).
- (6)
- IP 61–70 Macropygia unchall (66.7%), Ptilinopus melanospilus (66.7%).
- (7)
- IP 100% Ducula bicolor, Geotrygon chrysie, Geotrygon chiriquensis, Leucosarcia melanoleuca, Ocyphaps lophotes, Ptilonopus rauca, Zenaida macroura.
3.2. Host Specificity of the Quill Mites
- (1)
- Monoxenous parasites, including 8 species: Gunabopicobia claravis, G. leptotila, G. metriopelia, Meitingsunes adewlles, M. chalcophas, Peristerophila leucomela, Psittaciphilus montanus, Terratosyringophilus geotrygonus.
- (2)
- Oligoxenous parasites, including 5 species: Gunabopicobia geotrygoni, Meitingsunes ptilinopus, M. tympanistria, Psittaciphilus patagioenas, Terratosyringophilus longisoma.
- (3)
- Mesostenoxenous parasites, including 8 species: Gunabopicobia lathami, G. masalaje, G. zumpti, Meitingsunes lengai, M. zenadourae, Peristerophila columbae, P. geopelis, P. lature.
- (4)
- Metastenoxenous parasites, including 3 species: Meitingsunes turacoenas, Peristerophila claravis, Meitingsunes columbicus.
- (5)
- Polyxenous parasites, including only one species: Peristerophila mucuya.
3.3. Co-Infestation of the Quill Mites
- (1)
- “Syr-Pic” (quill mite species belonging to the differential subfamily Syringophilinae or Picobiinae and inhabiting the same host species but different habitats.
- (i)
- Inhabiting niches: contour feathers (representatives of Picobiinae) and covert (representatives of Syringophilidae): Guanabopicobia claravis + Peristerophila claravis from Claravis pretiosa; G. masalaje + P. lature from Ducula luctuosa and D. spilorrhoa; G. metriopelia + P. mucuya from Metriopelia melanoptera, G. zumpti + P. columbae from Streptopelia semitorquata and Patagioenas speciosa.
- (ii)
- Inhabiting niche: contour feathers (Picobiinae) and under wing coverts (Syringophilidae): G. geotrygoni + M. zenadourae from Geotrygon frenata, G. zumpti + M. zenadourae from Patagioenas picazuro.
- (iii)
- Inhabiting niches: contour feathers (Picobiinae) and under tail coverts (Syringophilidae): G. geotrygoni + Psittaciphilus montanus from Geotrygon, montana, G. leptotila + M. zenadourae from Leptotila verreauxi.
- (iv)
- Inhabiting niches: contour feathers (Picobiinae) and rectrictres (Syringophilidae): G. zumpti + M. lengai.
- (2)
- “Syr-Syr” (different quill mites species belonging to the same subfamily-Syringophilinae and occupying the same host species.
- (i)
- Inhabiting niches: secondaries and covert: Meitingsunes columbicus + Peristerophila columbae from Columba palumbus.
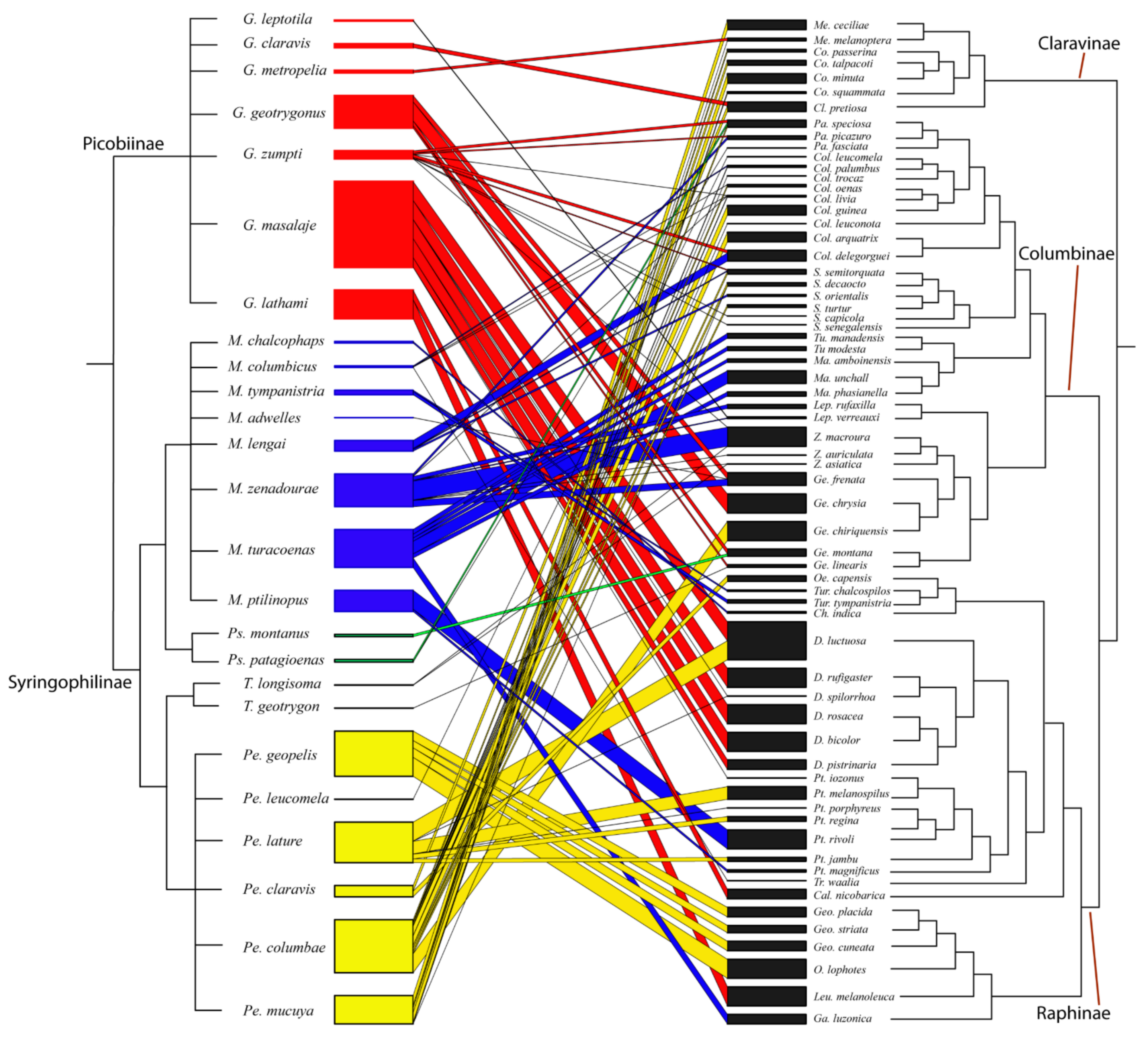
3.4. Bipartite Network Analysis
- (1)
- d’ 0.1–0.59: M. adwelles (0.2), T. longisoma (0.46), T. geotrygonus (0.5).
- (2)
- d’ 0.6–0.99: G. zumpti (0.66), P. montanus (0.75), P. patagioenas (0.77), M. columbicus (0.78), G. claravis (0.78), G. leptotila (0.85), P. lature (0.86), M. lengai (0.9), G. masalaje (0.9), M. zenadourae (0.92), G. geotrygoni (0.92), P. claravis (0.92), P. columbae (0.95), G. metriopelia (0.98), P. mucuya (0.98).
- (3)
- d’ = 1: G. lathami, M. chalophaps, M. tympanistria, M. turacoenas, M. ptilinopus, P. geopelis, P. leucomela.
- Single-host module: (1) Gunabopicobia leptotila—Leptotila verrauxi, (2) Gunabopicobia metriopelia—Metriopelia melanoptera, (6) Peristerophila leucomela—Columba leucomela, (14) Terratosyringophilus longisoma—Zenaida asiatica, (16) Meitingsunes chalcophas—Chalcophaps indica.
- Multi-host module: (4) Gunabopicobia masalaje—(Ducula bicolor, Ducula rufigaster, Ducula rosacea, Ducula pistrinaria, Ptilinopus iozonus); (5) Gunabopicobia lathami—(Leucosarcia melanoleuca, Caloenas nicobarica); (7) Meitingunes columbicus—(Columba palumbus, Treron waalia); (8) Meitingsunes tympanistria—(Turtur chalcospilos, Turtur tympanistria); (10) Meitingsunes zenadourae—(Leptotila rufaxilla, Patagioenas picazuro, Zenaida auriculata, Zenaida macroura); (11) Meitingsunes turacoenas (Gallicolumba luzonica, Macropygia amboinensis, Macropygia phasianella, Macropygia unchall, Turacoena manadensis, Turacoena modesta); (12) Meitingsunes psittaciphilus (Ptilinopus magnificus, Ptilinopus rivoli); (13) Psittaciphilus patagioenas—(Patagioenas fasciata, Patagioenas speciosa); (15) Peristerophila geopelis (Geopelia cuneata, Geopelia placida, Geopelia striata, Ocyphaps lophotes); (17) Peristerophila lature (Ducula luctuosa, Ducula spilorrhoa, Ptilinopus jambu, Ptilinopus melanospilus, Ptilinopus porphyreus, Ptilinopus regina); (19) Peristerophila columbicus (Columba arguatrix, Columba guinea, Columba livia, Columba oenas, Columba trocaz, Columba leuconota, Geotrygon chiriquensis, Streptopelia decaocto, Streptopelia semitorquata, Streptopelia turtur); (20) Peristerophila mucuya (Columbina minuta, Columbina passerina, Columbina squammata, Columbina talpacoti, Metriopelia ceciliae).
- Multi-parasite module: (18) Peristerophila claravis—Gunabopicobia claravis Gunabopicobia geotrygoni—Meitingsunes zenadourae—Psittaciphilus montanus—Meitingsunes columbicus; (9) Gunabopicobia zumpti—Meitingsunes lenagi.
3.5. Zoogeographical Distribution of Quill Mite Species Associated with Pigeons and Doves
- Neotropical: Gunabopicobia (5), Meitingsunes (2), Peristerophila (3), Psittaciphilus (2), Terratosyringophilus (1);
- Nearctic: Meitingsunes (1), Peristerophila (2), Terratosyringophilus (1), Gunabopicobia (1);
- Panamanian: Psittaciphilus (1), Peristerophila (2), Gunabopicobia (1);
- Palaearctic: Meitingsunes (8), Peristerophila (2), Gunabopicobia (1);
- Saharo-Arabian: Peristerophila (1);
- Afrotropical: Meitingsunes (4), Peristerophila (2), Gunabopicobia (1);
- Oriental: Meitingsunes (2), Peristerophila (4), Gunabopicobia (2);
- Oceanian: Meitingsunes (2), Peristerophila (1), Gunabopicobia (2);
- Australasian: Meitingsunes (2), Peristerophila (4).
- Neotropical + Nearctic + Palaearctic + Afrotropical: Gunabopicobia zumpti; Meitingsunes zenadourae; Peristerophila claravis;
- Neotropical + Nearctic: Psittaciphilus patagioenas;
- Palaearctic + Afrotropical: Meitingsunes columbicus, Meitingsunes lengai;
- Oriental + Oceanian: Meitingsunes turacones;
- Oriental + Australasian: Meitingsunes chalcophas;
- Oceanian + Oriental + Australasian: Peristerophila lature;
- Neotropical + Nearctic + Palaearctic + Afrotropical + Saharo-Arabian + Oriental: Peristerophila columbae.
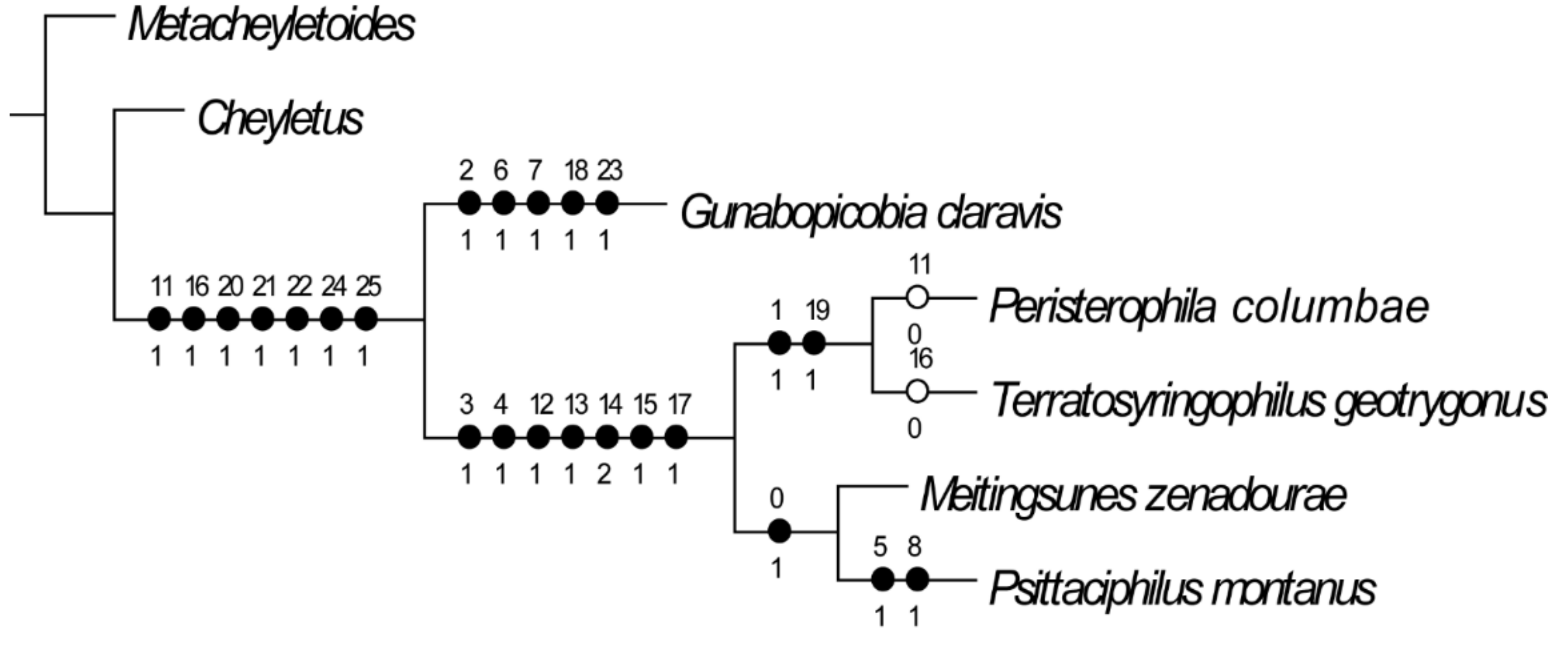
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Species Richness and Phylogenetic Relationship of Quill Mites Associated with Columbiform Birds
4.2. Columbiform Hosts and Quill Mite Fauna
4.3. Prevalence
4.4. Habitat Specificity and Multi-Infestation of Syringophilid Mites
4.5. Bipartite Network of the Quill Mites–Doves Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mora, C.; Tittensor, D.P.; Adl, S.; Simpson, A.G.B.; Worm, B. How many species are there on Earth and in the ocean? PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, B.; Hartigan, A.; Naldoni, J. Extensive uncharted biodiversity: The parasite dimension. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2018, 58, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M.; Hechinger, R.F.; Jetz, W. Homage to Linneaus: How many parasites? How many hosts? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11482–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Bonsall, M.B.; Dobson, A.P. Parasitism, biodiversity, and conservation. In Parasitism and Ecosystems; Thomas, F., Renaud, F., Guegan, J.F., Eds.; Oxford Scholarship: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 124–139. [Google Scholar]
- Poulin, R. Parasite biodiversity revisited: Frontiers and constraints. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J. Parasite rates of discovery, global species richness and host specificity. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissling, W.D.; Schleuning, M. Multispecies interactions across trophic levels at macroscales: Retrospective and future directions. Ecography 2015, 38, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R. Network analysis shining light on parasite ecology and diversity. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, W.S.; Kollár, J. First characterization of a highly specialized ecological network composed by gall-inducing mites and their host plants. Int. J. Acarol. 2019, 45, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.F.; Schulenberg, T.S.; Iliff, M.J.; Roberson, D.; Fredericks, T.A.; Sullivan, B.L.; Wood, C.L. The eBird/Clements Checklist of Birds of the World. 2019. Available online: http://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/v2019 (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Gibbs, D.; Barnes, E.; Cox, J. Pigeons and Doves: A Guide to the Pigeons and Doves of the World; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2001; p. 615. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.L.; Johnson, K.P.; Clayton, D.H.; Baker, A.J. Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences support a Cretaceous origin of Columbiformes and a dispersal-driven radiation in the Paleocene. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachos, J.; Pagani, M.; Sloan, L.; Thomas, E.; Billups, K. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science 2001, 292, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohaty, S.M.; Zachos, J.C.; Delaney, M.L. Foraminiferal Mg/Ca evidence for southern ocean cooling across the eocene–oligocene transition. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2012, 317, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Novak, B.; James, H.; Heupink, T.; Fjeldså, J.; Gilbert, T.; Poinar, H.; Church, G.; Shapiro, B. Complete mitochondrial genomes of living and extinct pigeons revise the timing of the columbiform radiation. Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kethley, J.B. A revision of the family Syringophilidae (Prostigmata: Acarina). Contrib. Am. Entomol. Inst. 1970, 5, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kethley, J.B. Population regulation in quill mites (Acari: Syringophilidae). Ecology 1971, 52, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casto, S.D. Quill wall thickness and feeding of Syringophiloidus minor (Berlese) (Acarina: Syringophilidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1974, 67, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonova, S.A.; Mironov, S.V. Functional morphology of the gnathosoma in the quill mite Syringophilopsis fringilla Fritsch (Acari: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae). Zoologischer Anzeiger—A J. Comp. Zool. 2010, 249, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmudzinski, M.; Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B. An Updated Checklist of Quill Mites of the Family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata). 2020. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/syringophilidae/v2020 (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Johnston, D.E.; Kethley, J.B. A numerical phenetic study of the quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari). J. Parasitol. 1973, 59, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M. Quill mites (Acari: Syringophilidae) of the Palaearctic region. Zootaxa 2011, 2840, 1–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Unsoeld, M.; Marciniak, N.; Sikora, B. Diversity of quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Prostigmata) parasitizing owls (Aves: Strigiformes) with remarks on the host–parasite relationships. J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Zmudzinski, M.; Unsoeld, M.; Sikora, B. Parasitic quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) associated with Sub Saharan Sunbirds (Passeriformes: Nectariniidae): Species composition and host-parasite relationships. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Prevuznakova, P.; Wamiti, W. Mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Cheyletoidea) parasitizing waxbills of the genus Estrilda (Passeriformes: Estrildidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 24, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Kaszewska, K.; Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M. A review of the quill mites of the genus Gunabopicobia Skoracki and Hromada (Acariformes: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae) associated with birds of the order Columbiformes. Int. J. Acarol. 2018, 44, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, S. Notes on Acari parasitic on birds with descriptions of two new species. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1920, 6, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.M. The acarine genus Syringophilus in North American birds. Acarologia 1964, 6, 76–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, R.F. New mite parasites of African birds. Parasitology 1959, 49, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casto, S.D. A new quill mite (Acarina: Syringophilidae) from the ground dove. Southwest. Entomol. 1980, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Casto, S.D. A new syringophilid mite from the white-winged dove. Tex. J. Sci. 1979, 31, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Mironov, S.V. Quill mites of the family Syringophilidae Lavoipierre, 1953 (Acariformes: Prostigmata) parasitic on birds (Aves) of the fauna of the former USSR. Acarina 1998, 6, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fain, A.; Bochkov, A.V.; Mironov, S.V. New genera and species of quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Prostigmata). Bulletin de l’Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique 2000, 70, 33–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Perez, T.M. New quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Cheyletoidea) parasitizing Mexican parrots. Belg. J. Entomol. 2002, 4, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Fain, A. New and little known species of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Cheyletoidea) from parrots (Aves: Psittaciformes). Acarina 2003, 11, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Williams, G.; Proctor, H. First record of Picobia zumpti (Acari: Syringophilidae) from quills of the rock pigeon in North America and description of the male. Belg. J. Entomol. 2005, 7, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Glowska, E. Quill mites (Acari: Syringophilidae) associated with columbiform birds. Genus 2008, 19, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Nattress, B.; Skoracki, M. A new species and further records of quill mites (Acari: Cheyletoidea: Syringophilidae) parasitic on birds (Aves) in England. Zootaxa 2009, 2133, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowska, E.; Skoracki, M. Meitingsunes, a new genus of the ectoparasitic quill mites (Acari: Cheyletoidea: Syringophilidae). Zootaxa 2010, 2514, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Dabert, J. A review of parasitic mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari, Prostigmata) from African birds, with descriptions of four new species. Acta Parasitol. 2002, 47, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M. A review of picobiine mites (Acari: Syringophilidae: Picobiinae) parasitising African birds. Folia Parasitol. 2013, 60, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszewska, K.; Skoracki, M. Two new quill mite species of the genus Psittaciphilus Fain, Bochkov & Mironov, 2000 (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) associated with pigeons and doves (Columbiformes: Columbidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2018, 95, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaszewska, K.; Kavetska, K.; Skoracki, M. Two new species of quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Cheyletoidea) associated with treronine doves (Columbiformes: Columbidae: Treroninae). Zootaxa 2014, 3846, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszewska, K.; Skoracki, M.; Kavetska, K. Two new Meitingsunes species (Acari: Syringophilidae) from Indonesian doves (Columbiformes: Columbidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4109, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszewska, K.; Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M. The mites of the genus Meitingsunes Glowska and Skoracki (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) associated with pigeons and doves (Aves: Columbiformes): Taxonomic studies with description of two new species. Int. J. Acarol. 2020, 46, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszewska, K.; Skoracki, M.; Kosicki, Z.J.; Hromada, M. New species and records of the quill mites of the genus Peristerophila Kethley, 1970 (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) associated with pigeons and doves (Aves: Columbiformes). Zootaxa 2020, 4878, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B.; Spicer, G.S. A review of the subfamily Picobiinae Johnston and Kethley, 1973 (Acariformes: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4113, 1–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoracki, M.; Lontkowski, J.; Stawarczyk, T. New taxa of the parasitic quill mites associated with accipitrid birds indicating close relationship of falconid birds to Psittaci-Columbi clade. J. Nat. Hist. 2010, 44, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Kaszewska, K.; Sikora, B. Females of the quill mite genera Peristerophila and Castosyringophilus (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) are two morphological forms: Ontogenetic and population evidences. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 25, 1803–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Kaszewska, K.; Unsoeld, M.; Skorupski, M. First record of parasitic quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Prostigmata: Cheyletoidea) on an avian representative of the order Caprimulgiformes. Int. J. Acarol. 2015, 41, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, F.; Gruber, B.; Fründ, J. Introducing the bipartite package: Analysing ecological networks. R News 2008, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Blüthgen, N.; Menzel, F.; Bliithgen, N. Measuring specialization in species interaction networks. BMC Ecol. 2006, 9, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Blüthgen, N. Why network analysis is often disconnected from community ecology: A critique and an ecologist’s guide. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Fründ, J.; Vázquez, D.P.; Menzel, F. What do interaction network metrics tell us about specialization and biological traits. Ecology 2008, 89, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmar, W.; Patterson, B.D. The measure of order and disorder in the distribution of species in fragmented habitat. Oecologia 1993, 96, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bascompte, J.; Jordano, P.; Melia, C.J.; Olesen, J.M. The nested assembly of plant–animal mutualistic networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9383–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Kontou, P.I.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Bouyioukos, C.; Markou, E.; Bagos, P.G. Bipartite graphs in systems biology and medicine: A survey of methods and applications. GigaScience 2018, 7, giy014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, M.A.; Stouffer, D.B.; Olesen, J.M.; Jordano, P.; Mouillot, D.; Krasnov, B.R.; Poulin, R.; Bascompte, J. Nestedness versus modularity in ecological networks: Two sides of the same coin? J. Anim. Ecol. 2010, 79, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Barabási, A.L.; Watts, D.J. The Structure and Dynamics of Networks; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Guimera, R.; Amaral, L.A.N. Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormann, C.F.; Strauss, R. A method for detecting modules in quantitative bipartite networks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, D.W.; Sabatino, M.; Morellato, L.P.C. Modularity, pollination systems, and interaction turnover in plant-pollinator networks across space. Ecology 2016, 97, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiczigel, J.; Marozzi, M.; Fábián, I.; Rózsa, L. Biostatistics for parasitologists—A primer to Quantitative Parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.D.M. NDE, NEXUS Data Editor 0.5.0; University of Glasgow: Glasgow, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nixon, K.C. Program and documentation. In WINCLADA; Version 0.9.9b; Ithaca: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Available online: https://cladistics.com (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Strong, E.E.; Lipscomb, D. Character coding and inapplicable data. Cladistics 1999, 15, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazeau, M.D. Problematic character coding methods in morphology and their effects. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 104, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP* Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods), Version 4; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, K. PRAP—Computation of Bremer support for large data sets. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 2004, 31, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.D.M. TreeView: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar]
- Jetz, W.; Thomas, G.H.; Joy, J.B.; Hartmann, K.; Mooersm, O.A. The global diversity of birds in space and time. Nature 2012, 491, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caira, J.N.; Jensen, K.; Holsinger, K.I. On a new index of host specificity. In Taxonomie, Écologie et Évolution des Metazoaires Parasites; Combes, C., Jourdane, J., Eds.; Presses Universitaires de Perpignan: Perpignan, France, 2003; pp. 161–201. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, B.G.; Lessardb, J.P.; Borregaard, M.K.; Fritz, S.A.; Araújo, M.B.; Dimitrov, D.; Fabre, P.H.; Graham, C.H.; Graves, G.R.; Jønsson, K.A.; et al. An update of Wallace’s zoogeographic regions of the world. Science 2013, 339, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casto, S.D. Host records and observations of quill mites (Acarina: Syringophilidae) from Texas birds. Southwest. Entomol. 1976, 1, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B. New ectoparasitic mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Prostigmata: Cheyletoidea) associated with birds from Argentina. Zootaxa 2002, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimovičová, M.; Skoracki, M.; Wamiti, W.; Hromada, M. Quill mites of the subfamily Picobiinae (Acari: Syringophilidae) parasitising African birds, with description of two new species. Folia Parasitol. 2014, 61, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Hendricks, S.A.; Spicer, G.S. Systematics of the genus Syringophilopsis Kethley, 1970 (Acari: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae) with description of three new species from North American passerines. Zootaxa 2011, 2793, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromada, M.; Klimovičová, M.; Unsöld, M.; Skoracki, M. Host-parasite relationships in the system composed by cuckoos and quill mites. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 21, 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Glowska, E.; Bochkov, A.V. Phylogeny of quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Prostigmata) based on their external morphology. Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B. Tinamiphilopsis elegans gen. nov. et sp. nov., a first record of the quill mites (Acari, Syringophilidae) from tinamou birds (Tinamiformes, Tinamidae). Acta Parasitol. 2004, 49, 348–352. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, E.D.; Mirarab, S.; Aberer, A.J.; Li, B.; Houde, P.; Li, C.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Faircloth, B.C.; Nabholz, B.; Howard, J.T.; et al. Whole-genome analyses resolve early branches in the tree of life of modern birds. Science 2014, 346, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, R.O.; Jacob, S.B.; Dornburg, A.; Field, D.J.; Townsend, J.P.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R. A comprehensive phylogeny of birds (Aves) using targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. Nat. Lett. 2015, 15697, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, R.T.; Oliveros, C.H.; Wang, N.; White, N.D.; Barker, F.K.; Field, D.J.; Ksepka, D.T.; Chesser, R.T.; Moyle, R.G.; Braun, M.J.; et al. A phylogenomic super tree of birds. Diversity 2019, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Sikora, B. Castosyringophilus meropis sp. n. (Acariformes: Syringophilidae)—A new quill mite species parasitising the world population of Merops apiaster Linnaeus (Coraciiformes: Meropidae). Folia Parasitol. 2017, 64, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marciniak, N.; Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M. Peristerophila nestoriae, a new species of quill mite of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) parasitizing New Zealand Kaka Nestor meridionalis (Gmelin) (Psittaciformes: Strigopidae). N. Z. J. Zool. 2019, 46, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebrassier, R.E.; Martin, E.D. Syringophilus bipectinatus a quill mite of poultry. Science 1932, 76, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casto, S.D. The effect of the postjuvenal molt in the House Sparrow on infestations of the quill mite, Syringophiloidus minor (Berlese) (Acarina: Syringophilidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1975, 12, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Tryjanowski, P. Description of a new species of quill mite Syringophiloidus weiszii sp. n. (Acari, Prostigmata, Syringophilidae) from Great Grey Shrike Lanius excubitor. Acta Parasitol. 2001, 46, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Møller, A.P.; Tryjanowski, P. A new species of parasitic mites of the genus Syringophiloidus Kethley, 1970 (Acari: Syringophilidae) from the Barn Swallow Hirundo rustica Linnaeus, 1758. Parasite 2003, 10, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skoracki, M.; Michalik, J.; Sikora, B. Prevalence and habitat preference of quill mites (Acari, Syringophilidae) parasitizing forest passerine birds in Poland. Acta Parasitol. 2010, 55, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hache, S.; Bayne, E.M.; Villard, M.A.; Proctor, H.C.; Davis, C.S.; Stralberg, D.; Janes, J.K.; Hallworth, M.T.; Foster, K.R.; Chidambara-Vasi, E.; et al. Phylogeography of a migratory songbird across its Canadian breeding range: Implications for conservation units. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6078–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, A.; Proctor, H. The distribution of quill mites (Betasyringophiloidus seiuri) among flight feathers of the ovenbird (Seiurus aurocapilla). J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, E.O.; Daemon, E. Biological and ecological aspects of quill mites, parasites of domestic hen Gallus gallus domesticus (Aves, Phasianidae) from rusting breeding locations in the municipality of Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Zoociencias 2007, 9, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Skirnisson, K.; Nielsen, Ó.K. Quill mite infestation of rock ptarmigan Lagopus muta (Aves: Phasianidae) in relation to year and host age, sex, body condition, and density. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skirnisson, K.; Palsdottir, G.R. Past and present status of poultry parasites in Iceland. Icel. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim, C.C.; Cunha, L.M.; Do Carmo Rezende, L.; Teixeira, C.M.; Silva Martins, N.R.; Oliveira, P.R.; Leite, R.C.; Faccini, J.L.H.; Leite, R.C. Quill mites in Brazilian psittacine birds (Aves: Psittaciformes). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2012, 43, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doster, G.L.; Wilson, N.; Kellogg, F.E. Ectoparasites collected from bobwhite quail in the south-eastern United States. J. Wildl. Dis. 1980, 5, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Órdenes, J.S.M.; Ibáñez, C.B.; Contreras, L.R.; Schmäschke, R.; Daugschies, A.; González-Acuña, D. Ectoparasitism in the common chimango caracara Milvago chimango chimango (Vieillot, 1816) (Aves, Falconidae) in the Ñuble Area, Chile. Lundiana 2005, 6, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Goulart, T.M.; Moraes, D.L.; Prado, A.P. Mites associated with the eared dove, Zenaida auriculata (Des Murs, 1847), in São Paulo State, Brazil. Zoosymposia 2011, 6, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, D.L.; Goulart, T.M.; Prado, A.P. Mites associated with the ruddy ground dove, Columbina talpacoti (Temminck, 1810), in São Paulo State, Brazil. Zoosymposia 2011, 6, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsenko, E.F. The biology and ecology of the quill mite Syringophilus bipectinatus Heller, 1880. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress of Acarology, Prague, Czechoslovakia, 31 August–6 September 1971; Milan, D., Rosicky, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1973; pp. 515–516. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Kwieciński, Z. Distribution of the parasitic mite Bubophilus aegolius sp. n. (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) on the Boreal Owl Aegolius funereus (L) (Strigiformes: Strigidae) and the low effectiveness of infestation. Eur. Zool. J. 2021, 88, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmäschke, R.; Sachse, M.; Eulenberger, K.; Schöne, R. Quill Mites—Little Known Parasites of Birds; Internationalen Symposiums über die Erkrankungen der Zoo und Wildtiere: Berlin, Germany, 2003; Volume 41, pp. 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur, R.H.; Levins, R. The limiting similarity, convergence and divergence of coexisting species. Am. Nat. 1967, 101, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasekare, P. Competitive coexistence in spatially structure environments: A synthesis. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Acuna, D.; Venzal, J.M.; Keirans, J.E.; Robbins, R.G.; Ippi, S.; Guglielmone, A.A. New host and locality records for the Ixodes auritulus (Acari: Ixodidae) species group, with a review of host relationships and distribution in the Neatropical Zoogeographic Region. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2005, 37, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Q.; Guo, X.-G.; Wu, D.; Zhou, D.H. Distribution and ecological niches of gamasid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) on small mammals in Southwest China. Psyche 2010, 934508, 934508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Labrzycka, A.; Skoracki, M.; Saveljev, A.P. Fur mites of the genus Schizocarpus Trouessart (Acari: Chirodiscidae) parasitizing the Eurasian beaver Castor fiber belorussicus Lavrov (Rodentia: Castoridae) in NE Poland (Suwałki). Zootaxa 2012, 3162, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, L.M.; Gómez-Díaz, E.; Elguero, E.; Proctor, H.C.; McCoy, K.D.; González-Solís, J. Niche partitioning of feather mites within a seabird host, Calonectris borealis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowska, E.; Dragun-Damian, A.; Dabert, J. DNA-barcoding contradicts morphology in quill mite species Torotrogla merulae and T. rubeculi (Prostigmata: Syringophilidae). Folia Parasitol. 2013, 60, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, P.; Minoarivelo, H.O.; Brännström, A.; Hui, C.; Dieckmann, U. Complexity and stability of ecological networks: A review of the theory. Popul. Ecol. 2018, 60, 319–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, A.; Saldaña-Vázquez, R.; Graciolli, G.; Peinado, L. Specialization and Modularity of a Bat Fly Antagonistic Ecological Network in a Dry Tropical Forest in Northern Colombia. Acta Chiropterologica 2019, 20, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, O.T.; Memmott, J.; Lasalle, J.; Lyal, C.; Whitefoord, C.; Godfray, C.J. Blackwell Science, Ltd. Structure of a diverse tropical forest insect—Parasitoid community. J. Anim. Ecol. 2002, 71, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C.F.; Fründ, J.; Blüthgen, N.; Gruber, B. Indices, graphs and null models: Analysing bipartite ecological networks. Open Ecol. J. 2009, 2, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thebault, E.; Fontaine, C. Stability of ecological communities and the architecture of mutualistic and trophic networks. Science 2010, 329, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, E.; Besson, M.; Brice, M.H.; Burkle, L.A.; Dalla Riva, G.V.; Fortin, M.J.; Gravel, D.; Guimarães, P.R., Jr.; Hembry, D.H.; Newman, E.A.; et al. Analysing ecological networks of species interactions. Biol. Rev. 2018, 94, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, F. Environmental control of food web structure. Ecology 1983, 64, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmott, J.; Waser, N.M. Integration of alien plants into a native flower pollinator visitation web. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B—Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 2395–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, R.H.; Lacerda, I.; Ramos, J.A.; Memmott, J. Evaluation of restoration effectiveness: Community response to the removal of alien plants. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devictor, V.; Julliard, R.; Jig, F. Distribution of specialist and generalist species along spatial gradients of habitat disturbance and fragmentation. Oikos 2008, 117, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, R.; Devoto, M.; Pocock, M. Connectance of species interaction networks and conservation value: Is it any good to be well connected? Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, A.V. The classification and phylogeny of the mite superfamily Cheyletoidea (Acari, Prostigmata). Entomol. Rev. 2002, 82, 643–664. [Google Scholar]
- Volgin, V.I. Kleschi Semeistva Cheyletidae Mirovoi Fauny; Akademiia NAUK SSSR Zoologicheskii Institut: Leningrad, Russia, 1969; Volume 101, p. 432. [Google Scholar]

| Quill Mite Species | Host Species | Host Subfamily | Distribution | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subfamily Syringophilinae Lavoipierre, 1953 | ||||
| Genus Meitingsunes Glowska & Skoracki, 2010 | ||||
| M. aldwelles Glowska & Skoracki, 2010 | Geotrygon frenata * (Tschudi) | Columbinae | Neot. (Colombia) | [39] |
| M. columbicus Skoracki, 2011 | Columba oenas * Linnaeus | Columbinae | Pala. (Kazakhstan) | [22] |
| “ | Columba livia Gmelin | Columbinae | Pala. (Poland, Slovakia) | [22,45] |
| “ | Columba palumbus Linnaeus | Columbinae | Pala. (Germany, Russia) | [22,45] |
| “ | Treron waalia (Meyer) | Raphinae | Afro. (Cameroon) | [43] |
| M. chalcophas Kaszewska, Skoracki & Kavetska, 2016 | Chalcophas indica * (Linnaeus) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Timor) Aust. (Australia) | [44,45] |
| M. ptilinopus Kaszewska, Skoracki & Hromada, 2020 | Ptilinopus magnificus * Temminck | Raphinae | Aust. (Australia) | [45] |
| “ | Ptilinopus rivoli (Prevost) | Raphinae | Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [45] |
| M. lengai Kaszewska, Skoracki & Hromada, 2020 | Columba delegorguei * Delegorgue | Columbinae | Afro. (Tanzania) | [45] |
| “ | Streptopelia orientalis (Latham) | Columbinae | Afro. (Tanzania) | [45] |
| “ | Streptopelia semitorquata Ruppell | Columbinae | Pala. (Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan) | [45] |
| M. turacoenas Kaszewska, Skoracki & Kavetska, 2016 | Gallicolumba luzonica Scopoli | Raphinae | Orie. (Philippines) | [45] |
| “ | Macropygia amboinensis (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [45] |
| “ | Macropygia phasianella (Temminck) | Columbinae | Orie. (Philippines, Indonesia: Java) | [45] |
| “ | Macropygia unchall (Wagler) | Columbinae | Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [45] |
| “ | Turacoena manadensis * (Quoy &Gaimard) | Columbinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Sulavesi, Nepal) | [44] |
| “ | Turacoena modesta (Temminck) | Columbinae | Orie. (Indonesia) | [44] |
| M. tympanistria (Skoracki & Dabert, 2012) | Turtur chalcospilos (Wagler) | Raphinae | Afro. (Tanzania) | [40] |
| “ | Turtur tympanistria * (Temminck) | Raphinae | Afro. (Togo, Tanzania) | [40,45] |
| M. zenadourae (Clark, 1964) | Columba livia Gmelin | Columbinae | Near. (USA: Texas); Afro. (N. Africa, Djibouti) | [30,39,45] |
| “ | Geotrygon frenata (Tschudi) | Columbinae | Neot. (Colombia) | [45] |
| “ | Leptotila rufaxilla (Richard, Bernard) | Columbinae | Neot. (Surinam, Argentina) | [45] |
| “ | Leptotila verreauxi (Bonaparte) | Columbinae | Neot. (Colombia) | [45] |
| “ | Patagioenas picazuro Temminck | Columbinae | Neot. (Paraguay) | [45] |
| “ | Zenaida asiatica (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Near. (USA: Texas) | [75] |
| “ | Zenaida auriculata (Murs) | Columbinae | Neot. (Argentina) | [76] |
| “ | Zenaida macroura * (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Near. (USA: Maryland, Arizona, San Francisco) | [28,39,45] |
| Genus Peristerophila Kethley, 1970 | ||||
| P. columbae (Hirst, 1920) | Columba arguatrix (Temminck) | Columbinae | Afro. (Kenya) | [46] |
| “ | Columba guinea Linnaeus | Columbinae | Afro. (S Africa, Tanzania) | [46] |
| “ | Columba leuconota (Vigors) | Columbinae | Orie. (Nepal) | [46] |
| “ | Columba livia * Gmelin | Columbinae | Pala. (England, Macedonia, Poland, Turkey); Near. (Canada, USA); Orie. (India); Sa-Arab. (Iran) | [22,27,32,38,46] |
| “ | Columba oenas Linnaeus | Columbinae | Pala. (Germany) | [46] |
| “ | Columba palumbus Linnaeus | Columbinae | Pala. (Germany, England) | [46] |
| “ | Columba trocaz Heineken | Columbinae | Pala. (Portugal) | [46] |
| “ | Geotrygon chiriquensis Sclater | Columbinae | Pana. (Panama) | [46] |
| “ | Patagioenas speciosa (Gmelin) | Columbinae | Neot. (Surinam) | [46] |
| “ | Streptopelia capicola (Sundevall) | Columbinae | Afro. (Angola) | [46] |
| “ | Streptopelia decaocto (Frivaldszky) | Columbinae | Sa-Arab. (Jordan) | [22] |
| “ | Streptopelia decipiens (Hartlaub & Finsch.) | Columbinae | Pala. (Macedonia), Afro. (Tanzania) | [46] |
| “ | Streptopelia orientalis (Latham) | Columbinae | Orie. (Japan) | [46] |
| “ | Streptopelia semitorquata (Ruppell) | Columbinae | Afro. (Angola, Tanzania, D. R. Congo) | [46] |
| “ | Streptopelia tranquebarica (Hermann) | Columbinae | Orie. (China) | [46] |
| “ | Streptopelia turtur (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Pala. (Germany, Greece, Hungary, Macedonia) | [46] |
| P. claravis (Skoracki & Glowska, 2008) | Claravis pretiosa * Ferrari-Pérez | Claravinae | Neot. (Bolivia, Colombia, Paraguay), Pana. (Panama) | [37,46] |
| “ | Oena capensis (Linnaeus) | Raphinae | Afro. (Ethiopia, Sudan, Tanzania) | [46] |
| P. geopelis Kaszewska, Skoracki, Kosicki & Hromada, 2020 | Geopelia cuneata (Latham) | Raphinae | Austr. (Australia) | [46] |
| “ | Geopelia placida Gould | Raphinae | Austr. (Australia) | [46] |
| “ | Geopelia striata * (Linnaeus) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Celebes, Java, Sumatra) | [46] |
| “ | Ocyphaps lophotes (Temminck) | Raphinae | Austr. (Australia) | [46] |
| P. lature Kaszewska, Kavetska & Skoracki, 2014 | Ducula luctuosa * (Temminck) | Raphinae | Austr. (Australia) | [43] |
| “ | Ducula spilorrhoa (Gray) | Raphinae | Austr. (Papua New Guinea) | [43] |
| “ | Ptilinopus jambu (Gmelin) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Sumatra) | [43] |
| “ | Ptilinopus melanospilus (Salvadori) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Mount Gade) | [43] |
| “ | Ptilinopus porphyreus (Temminck) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Java) | [43] |
| “ | Ptilinopus regina (Swainson) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Marina Isl.) | [43] |
| P. leucomela Kaszewska, Skoracki, Kosicki & Hromada, 2020 | Columba leucomela * Temminck | Columbinae | Austr. (Australia) | [46] |
| P. mucuya Casto, 1980 | Columbina minuta Linnaeus | Claravinae | Neot. (Paraguay) | [46] |
| “ | Columbina passerina * (Linnaeus) | Claravinae | Neot. (Colombia, Surinam); Near. (USA) | [30,46] |
| “ | Columbina squammata (Lesson) | Claravinae | Neot. (Brazil, Paraguay) | [35,46] |
| “ | Columbina talpacoti (Temminck) | Claravinae | Neot. (Brazil, Surinam, Trinidad and Tobago); Pala. (Monaco) | [37,46] |
| “ | Geophaps plumifera Gould | Columbinae | Aust. (Australia) | [35] |
| “ | Metriopelia ceciliae (Lesson) | Claravinae | Neot. (Peru) | [46] |
| “ | Metriopelia melanoptera (Molina) | Claravinae | Neot. (Argentina) | [37] |
| “ | Brotogeris versicolurus ** Muller | Psittacidae | Neot. (Brazil) | [35] |
| “ | Psilopsiagon aymara ** d’Orbigny | Psittacidae | Neot. (S. America) | [35] |
| “ | Trichoglossus haematodus ** (Linnaeus) | Psittaculidae | Ori. (Indonesia) | [35] |
| Genus Psittaciphilus, Bochkov & Mironov, 2000 | ||||
| P. montanus Kaszewska & Skoracki, 2018 | Geotrygon montana * (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Neot. (Brazil, Trinidad and Tobago); Pana. (Panama) | [42] |
| P. patagioenas Kaszewska & Skoracki, 2018 | Patagioenas fasciata * (Say) | Columbinae | Neot. (Colombia) | [42] |
| “ | Patagioenas speciosa (Gmelin) | Columbinae | Neot. (Surinam) | [42] |
| Genus Terratosyringophilus Bochkov and Perez, 2002 | ||||
| T. geotrygonus Skoracki & Glowska, 2008 | Geotrygon linearis * (Prévost) | Columbinae | Neot. (Venezuela) | [37] |
| T. longisoma (Casto, 1979) | Zenaida asiatica * (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Near. (USA) | [31] |
| “ | Zenaida macroura (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Near. (USA) | [37] |
| Subfamily Picobiinae Johnson & Kethley, 1973 | ||||
| Genus Gunabopicobia Skoracki & Hromada, 2013 | ||||
| G. claravis Kaszewska, Skoracki & Hromada, 2018 | Claravis pretiosa * (Ferrari-Perez) | Claravinae | Neot. (Colombia) | [26] |
| G. geotrygoni Kaszewska, Skoracki & Hromada, 2018 | Geotrygon linearis * (Prevost) | Columbinae | Neot. (Venezuela) | [26] |
| “ | Geotrygon chrysia Bonaparte | Columbinae | Ocea. (Martinique) | [26] |
| “ | Geotrygon frenata (Tschudi) | Columbinae | Neot. (Colombia) | [26] |
| “ | Geotrygon montana (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Neot. (Paraguay) | [26] |
| G. masalaje Kaszewska, Kavetska & Skoracki, 2014 | Ducula bicolor (Scopoli) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia) | [43] |
| “ | Ducula rufigaster (Quoy and Gaimard) | Raphinae | Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [43] |
| “ | Ducula rosacea (Temminck) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Semau Isl.) | [43] |
| “ | Ducula pistrinaria Bonaparte | Raphinae | Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [43] |
| “ | Ducula spilorrhoa (Gray) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia: Semau Isl.) | [43] |
| “ | Ducula luctuosa (Temminck) | Raphinae | Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [43] |
| “ | Ptilinopus iozonus * Gray | Raphinae | Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [43] |
| G. metriopelia Kaszewska, Skoracki and Hromada, 2018 | Metriopelia melanoptera * (Molina) | Claravinae | Neot. (Argentina) | [26] |
| G. lathami Kaszewska, Skoracki and Hromada, 2018 | Leucosarcia melanoleuca * Gould | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia); Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [26] |
| “ | Caloenas nicobarica (Linnaeus) | Raphinae | Orie. (Indonesia); Ocea. (Papua New Guinea) | [26] |
| G. leptotila Kaszewska, Skoracki & Hromada, 2018 | Leptotila verreauxi * (Bonaparte) | Columbinae | Neot. (Argentina) | [26] |
| G. zumpti (Lawrence, 1959) | Columba livia Gmelin | Columbinae | Near. (USA); Pala. (Poland) | [36,47] |
| “ | Columba delegorquei Delegorgue | Columbinae | Afro. (Tanzania) | [26] |
| “ | Patagioenas picazuro (Temminck) | Columbinae | Neot. (West Brazil) | [26] |
| “ | Patagioenas speciosa Gmelin | Columbinae | Neot. (North Brazil) | [26] |
| “ | Streptopelia capicola * (Sundevall) | Columbinae | Afro. (South Africa) | [29] |
| “ | Streptopelia semitorquata (Ruppell) | Columbinae | Afro. (Ethiopia) | [26] |
| “ | Streptopelia senegalensis (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Afro.(South Africa) | [41] |
| “ | Zenaida macroura (Linnaeus) | Columbinae | Near. (USA) | [28] |
| Host Species | Exa. | Inf. | IP; CI | Mite Species | Habitat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caloenas nicobarica * | Nicobar pigeon | 4 | 2 | 50 (9.8–90.2) | G. lathami | contour |
| Chalcophaps indica | Grey-capped Emerald Dove | 23 | 2 | 8.7 (1.6–27.8) | M. chalcophas | coverts |
| Claravis pretiosa | Blue Ground-dove | 10 | 3 | 30 (8.7–61.9) | P. claravis | coverts |
| “ * | 2 | 20 (3.7–55.3) | G. claravis | contour | ||
| Columba arquatrix | African Olive-pigeon | 4 | 2 | 50 (9.8–90.2) | P. columbae | under-wings cov. |
| Columba delegorguei | Delegorgue’s Pigeon | 7 | 2 | 42 (14.9–77.5) | M. lengai | under-tail cov. |
| “ * | 1 | 14.3 (0.7–55.4) | G. zumpti | contour | ||
| Columba guinea | Speckled Pigeon | 4 | 2 | 50 (9.8–90.2) | P. columbae | under-wings cov. |
| Columba leucomela | White-headed Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | P. leucomela | - |
| Columba leuconota | Snow Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | P. columbae | - |
| Columba livia | Rock Pigeon | 20 | 1 | 5 (0.3–24.4) | P. columbae | contour |
| “ | NA | NA | - | G. zumpti | contour | |
| “ | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | M.zenadourae | covert | |
| “ | NA | NA | - | M. columbicus | secondaries | |
| Columba oenas | Stock Dove | NA | NA | - | M. columbicus | secondaries |
| “ | 9 | 1 | 11.1 (0.6–44.4) | P. columbae | under-wings cov. | |
| Columba palumbus | Common Wood-Pigeon | 20 | 1 | 5 (0.3–24.4) | M. columbicus | tail cov. |
| “ | 20 | 1 | 5 (0.3–24.4) | P. columbae | covert | |
| Columba trocaz | Madeira laurel Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | P. columbae | under wing cov. |
| Columbina minuta | Plain-breasted Ground-Dove | 4 | 2 | 50 (9.8–90.2) | P.mucuya | contour |
| Columbina passerina | Common Ground-Dove | 15 | 2 | 13.3 (2.4–39.7) | P.mucuya | secondaries |
| Columbina talpacoti | Ruddy Ground-Dove | 32 | 8 | 25 (12.2–42.3) | P.mucuya | under-wings cov |
| Columbina squammata | Scaled Dove | 11 | 1 | 9.1 (0.5–40.5) | P.mucuya | tertials |
| Ducula bicolor * | Pied Imperial-Pigeon | 2 | 2 | 100 (22.4–100) | G. masalaje | contour |
| Ducula luctuosa * | Silver-tipped Imperial-Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (22.4–100) | G. masalaje | contour |
| “ | 1 | 1 | 100 (22.4–100) | P.lature | covert | |
| Ducula pistrinaria * | Island Imperial-Pigeon | 2 | 1 | 50 (2.5–97.5) | G. masalaje | contour |
| Ducula rosacea * | Pink-headed Imperial-Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (22.4–100) | G. masalaje | contour |
| Ducula rufigaster * | Purple-tailed Imperial-Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (22.4–100) | G. masalaje | contour |
| Ducula spilorrhoa * | Torresian Imperial-Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | G. masalaje | contour |
| “ | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | P.lature | - | |
| Gallicolumba luzonica | Luzon Bleeding-heart | 2 | 1 | 50 (2.5–97.5) | M. turacoenas | contour |
| Geopelia cuneata | Diamond Dove | 2 | 1 | 50 (2.5–97.5) | P. geopelis | covert |
| Geopelia placida | Peaceful Dove | 2 | 1 | 50 (2.5–97.5) | P. geopelis | contour |
| Geopelia striata | Zebra Dove | 13 | 5 | 38.5 (16.6–65.8) | P. geopelis | covert |
| Geotrygon chrysie * | Key West Quail-Dove | 1 | 1 | 100 (22.4–100) | G. geotrygoni | contour |
| Geotrygon chiriquensis | Chiriqui Quail-Dove | 1 | 1 | 100 (5–100) | P. columbae | under-tail cov. |
| Geotrygon frenata | White-throated Quail-Dove | 3 | 1 | 33 (1.7–86.5) | M. zenadourae | - |
| “ * | 1 | 33 (1.7–86.5) | G. geotrygoni | contour | ||
| Geotrygon linearis * | Lined Quail-Dove | 8 | 1 | 12.5 (0.6–50) | G. geotrygoni | contour |
| 1 | 12.5 (0.6–50) | T. geotrygonus | primaries | |||
| Geotrygon montana * | Ruddy Quail-Dove | 8 | 2 | 25 (4.6–63.5) | G. geotrygoni | contour |
| “ | 1 | 12.5 (0.6–50) | P. montanus | under tail cov. | ||
| Leptotila verreauxi | White-tipped dove | 24 | 1 | 4.2 (0.2–20.4) | M. zenadourae | under-tail cov. |
| “ * | 1 | 4.2 (0.2–20.4) | G. leptotila | contour | ||
| Leptotila rufaxilla | Gray-fronted Dove | 10 | 2 | 20 (3.7–55.3) | M. zenadourae | under-tail cov. |
| Leucosarcia melanoleuca * | Wonga Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5–100) | G. lathami | contour |
| Macropygia amboinensis | Amboyna Cuckoo-Dove | 6 | 1 | 16.7 (0.9–58.9) | M. turacoenas | - |
| Macropygia phasianella | Brown Cuckoo-Dove | 14 | 3 | 21.4 (6.1–50) | M. turacoenas | under and upper-tail cov. |
| Macropygia unchall | Barred Cuckoo-Dove | 3 | 2 | 66.7 (13.5–98.3) | M. turacoenas | under-tail cov. |
| Metriopelia ceciliae | Bare-faced Ground-Dove | 2 | 1 | 50 (2.5–97.5) | P. mucuya | secondaries, covert |
| Metriopelia melanoptera * | Black-winged Ground-Dove | 8 | 1 | 12.5 (0.6–50) | G. metriopelia | contour |
| Ocyphaps lophotes | Crested Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5–100) | P. geopelis | small covert under-tail cov. |
| Oena capensis | Namaqua Dove | 17 | 5 | 29.4 (12.4–54.4) | P. claravis | under-tail cov. |
| Patagioenas fasciata | Band-tailed pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | P. patagioenas | upper-tail cov. |
| Patagioenas picazuro | Picazuro Pigeon | 16 | 2 | 12.5 (2.3–37.2) | M. zenadourae | under-wing cov. |
| “ * | 1 | 6.2 (0.3–30.5) | G. zumpti | contour | ||
| Patagioenas speciosa | Scaled Pigeon | 8 | 1 | 12.5 (0.6–50) | P. columbae | - |
| “ * | 1 | 12.5 (0.6–50) | G. zumpti | contour | ||
| “ | 1 | 12.5 (0.6–50) | P. patagioenas | coverts | ||
| Ptilinopus iozonus * | Orange-Bellied Fruit Dove | 4 | 1 | 25 (1.3–75.1) | G. masalaje | contour |
| Ptilinopus jambu | Jambu Fruit-Dove | 5 | 1 | 20 (1–65,7) | P. lature | coverts |
| Ptilinopus magnificus | Wompoo Fruit-Dove | 17 | 2 | 11.8 (2.1–35) | M. ptilinopus | under-tail cov. |
| Ptilinopus melanospilus | Black-naped Fruit-Dove | 3 | 2 | 66.7 (13.5–98.3) | P. lature | coverts |
| Ptilinopus regina | Rose-crowned Fruit-Dove | 4 | 1 | 25 (1.3–75.1) | P. lature | coverts |
| Ptilonopus rivoli | White-bibbed Fruit-Dove | 1 | 1 | 100 (5–100) | M. ptilinopus | under-tail cov. |
| Streptopelia decaocto | Eurasian Collared-Dove | 12 | 2 | 16.7 (3–45.7) | P. columbae | secondaries |
| Streptopelia capicola | Ring-Necked Dove | NA | NA | - | G. zumpti | contour |
| Streptopelia orientalis | Oriental Turtle-Dove | 22 | 2 | 9.1 (1.6–29.1) | M. lengai | under-tail cov. |
| Streptopelia semitorquata | Red-eyed Dove | 21 | 1 | 4.8 (0.2–23.3) | M. lengai | rectrices |
| “ * | 1 | 4.8 (0.2–23.3) | G. zumpti | contour | ||
| “ | 3 | 14.3 (4–35.4) | P. columbae | coverts | ||
| Streptopelia turtur | European Turtle-Dove | 30 | 4 | 13.3 (4.7–29.8) | P. columbae | contour under-tail cov. |
| Treron waalia | Bruce’s Green-Pigeon | 1 | 1 | 100 (5.0–100) | M. columbicus | covert |
| Turacoena manadensis | White-faced Cuckoo-Dove | 4 | 1 | 25 (1.3–75.1) | M. turacoenas | under tail cov |
| Turacoena modesta | Black Cuckoo-Dove | 5 | 1 | 20 (1–65.7) | M. turacoenas | under tail cov |
| Turtur chalcospilos | Emerald-spotted Wood-Dove | 13 | 1 | 7 (0.4–34.2) | M. tympanistria | coverts |
| Turtur tympanistria | Tambourine Dove | 12 | 2 | 16.7 (3–45.7) | M. tympanistria | rectrices |
| Zenaida asiatica | White-winged Dove | NA | NA | - | M. zenadourae | - |
| “ | NA | NA | - | T. longisoma | - | |
| Zenaida auriculata | Eared Dove | NA | NA | - | M. zenadourae | - |
| Zenaida macroura | Mourning Dove | 1 | 1 | 100 (5–100) | M. zenadourae | coverts |
| “ | NA | NA | - | T. longisoma | primaries | |
| Specificity | d’ | Quill Mites | Hosts Spectrum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monoxenous | 0.2 | Meitingsunes adwelles | Geotrygon frenata |
| 1 | Meitingsunes chalcophas | Chalcophaps indica | |
| 1 | Peristerophila leucomela | Columba leucomela | |
| 0.75 | Psittaciphilus montanus | Geotrygon montana | |
| 0.5 | Terratosyringophilus geotrygonus | Geotrygon linearis | |
| Oligoxenous | 1 | Meitingsunes tympanistria | Turtur chalcospilos |
| Turtur tympanistria | |||
| 0.77 | Psittaciphilus patagioenas | Patagioenas fasciata | |
| Patagioenas speciosa | |||
| 0.46 | Terratosyringophilus longisoma | Zenaida asiatica | |
| Zenaida macroura | |||
| 1 | Meitingsunes ptilinopus | Ptilinopus magnificus | |
| Ptilinopus rivoli | |||
| Mesostenoxenous | 0.9 | Meitingsunes lengai | Columba delegorguei |
| Streptopelia orientalis | |||
| Streptopelia semitorquata | |||
| 0.92 | Meitingsunes zenadourae | Columba livia | |
| Geotrygon frenata | |||
| Leptotila verreauxi | |||
| Leptotila rufaxilla | |||
| Patagioenas picazuro | |||
| Zenaida asiatica | |||
| Zenaida auriculata | |||
| Zenaida macroura | |||
| 0.95 | Peristerophila columbae | Columba arquatrix | |
| Columba guinea | |||
| Columba livia | |||
| Columba oenas | |||
| Columba palumbus | |||
| Columba leuconota | |||
| Columba trocaz | |||
| Geotrygon chiriquensis | |||
| Patagioenas speciosa | |||
| Streptopelia capicola | |||
| Streptopelia decaocto | |||
| Streptopelia orientalis | |||
| Streptopelia semitorquata | |||
| Streptopelia tranquebarica | |||
| Streptopelia turtur | |||
| 1 | Peristerophila geopelis | Geopelia cuneata | |
| Geopelia placida | |||
| Geopelia striata | |||
| Ocyphaps lophotes | |||
| 0.86 | Peristerophila lature | Ducula luctuosa | |
| Ducula spilorrhoa | |||
| Ptilinopus melanospilus | |||
| Ptilinopus porphyreus | |||
| Ptilinopus regina | |||
| Metastenoxenous | 1 | Meitingsunes turacoenas | Gallicolumba luzonica |
| Macropygia amboinensis | |||
| Macropygia phasianella | |||
| Macropygia unchall | |||
| Turacoena manadensis | |||
| Turacoena modesta | |||
| 0.92 | Peristerophila claravis | Claravis pretiosa | |
| Oena capensis | |||
| 0.78 | Meitingsunes columbicus | Columba livia | |
| Columba oenas | |||
| Columba palumbus | |||
| Treron waalia | |||
| Polixenous | 0.98 | Peristerophila mucuya | Columbina minuta |
| Columbina passerina | |||
| Columbina squammata | |||
| Columbina talpacoti | |||
| Metriopelia ceciliae | |||
| Metriopelia melanoptera | |||
| Streptopelia decaocto | |||
| Brotogeris versicolurus * | |||
| Psilopsiagon aymara * | |||
| Trichoglossus haematodus * |
| Specificity | d’ | Quill Mites | Hosts Spectrum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monoxenous | 0.78 | Gunabopicobia claravis | Claravis pretiosa |
| 0.85 | Gunabopicobia leptotila | Leptotila verreauxi | |
| 0.98 | Gunabopicobia metriopelia | Metriopelia melanoptera | |
| Oligoxenous | 0.92 | Gunabopicobia geotrygoni | Geotrygon chrysia |
| Geotrygon frenata | |||
| Geotrygon linearis | |||
| Geotrygon montana | |||
| Mesostenoxenous | 1 | Gunabopicobia lathami | Caloenas nicobarica |
| Leucosarcia melanoleuca | |||
| 0.9 | Gunabopicobia masalaje | Ducula bicolor | |
| Ducula luctuosa | |||
| Ducula pistrinaria | |||
| Ducula rosacea | |||
| Ducula rufigaster | |||
| Ducula spilorrhoa | |||
| Ptilinopus iozonus | |||
| 0.66 | Gunabopicobia zumpti | Columba delegorguei | |
| Columba livia | |||
| Patagioenas picazuro | |||
| Patagioenas speciosa | |||
| Streptopelia capicola | |||
| Streptopelia semitorquata | |||
| Streptopelia senegalensis | |||
| Zenaida macroura |
| Hosts | Quill Mites | Subfamily | Niche |
|---|---|---|---|
| Claravis pretiosa | Gunabopicobia claravis | P | contour |
| Peristerophila claravis | S | covert | |
| Columba palumbus | Meitingsunes columbicus | S | secondaries |
| Peristerophila columbae | S | covert | |
| Ducula spilorrhoa | Gunabopicobia masalaje | P | contour |
| Peristerophila lature | S | covert | |
| Ducula luctuosa | Gunabopiconia masalaje | P | contour |
| Peristerophila lature | S | covert | |
| Geotrygon frenata | Gunabopicobia geotrygoni | P | contour |
| Meitingsnes zenadourae | S | under-wing covert | |
| Geotrygon montana | Gunabopicobia geotrygoni | P | contour |
| Psittaciphilus montanus | S | under-tail covert | |
| Leptotila verreauxi | Gunabopicobia leptotila | P | contour |
| Meitingsunes zenadoure | S | under tail-covert | |
| Metriopelia melanoptera | Gunapopicobia metriopelia | P | contour |
| Peristerophila mucuya | S | covert | |
| Patagioenas picazuro | Gunabopicobia zumpti | P | contour |
| Meitingsunes zenadourae | S | under-wing covert | |
| Patagioenas speciosa | Gunabopicobia zumpti | P | contour |
| Peristerophila columbae | S | covert | |
| Psittaciphilus patagioenas | S | covert | |
| Streptopelia semitorquata | Gunabopicobia zumpti | P | contour |
| Meitingsunes lengai | S | rectrices | |
| Peristerophila columbae | S | covert |
| Zoogeographic Regions | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quill Mites Species | Neot. | Near. | Pana. | Pala. | Sa-Ara. | Afro. | Orie. | Ocean. | Austr. |
| M. aldwelles | |||||||||
| M. columbicus | |||||||||
| M. chalcophas | |||||||||
| M. ptilinopus | |||||||||
| M. lengai | |||||||||
| M. turacoenas | |||||||||
| M. tympanistria | |||||||||
| M. zenadourae | |||||||||
| P. columbae | |||||||||
| P. claravis | |||||||||
| P. geopelis | |||||||||
| P. lature | |||||||||
| P. leucomela | |||||||||
| P. mucuya | |||||||||
| P. montanus | |||||||||
| P. patagioenas | |||||||||
| T. geotrygonus | |||||||||
| T. longisoma | |||||||||
| G. claravis | |||||||||
| G. geotrygoni | |||||||||
| G. masalaje | |||||||||
| G. metriopelia | |||||||||
| G. lathami | |||||||||
| G. leptotila | |||||||||
| G. zumpti | |||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaszewska-Gilas, K.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Hromada, M.; Skoracki, M. Global Studies of the Host-Parasite Relationships between Ectoparasitic Mites of the Family Syringophilidae and Birds of the Order Columbiformes. Animals 2021, 11, 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123392
Kaszewska-Gilas K, Kosicki JZ, Hromada M, Skoracki M. Global Studies of the Host-Parasite Relationships between Ectoparasitic Mites of the Family Syringophilidae and Birds of the Order Columbiformes. Animals. 2021; 11(12):3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaszewska-Gilas, Katarzyna, Jakub Ziemowit Kosicki, Martin Hromada, and Maciej Skoracki. 2021. "Global Studies of the Host-Parasite Relationships between Ectoparasitic Mites of the Family Syringophilidae and Birds of the Order Columbiformes" Animals 11, no. 12: 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123392
APA StyleKaszewska-Gilas, K., Kosicki, J. Z., Hromada, M., & Skoracki, M. (2021). Global Studies of the Host-Parasite Relationships between Ectoparasitic Mites of the Family Syringophilidae and Birds of the Order Columbiformes. Animals, 11(12), 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123392







