Effects of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Productive Performance, Pectoral Myopathies, and Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Treatments and Husbandry of Birds
2.2. Diets
2.3. Growth Performance
2.4. Carcass, Cutting Yield, and Muscle Sampling
2.5. Pectoral Myopathies
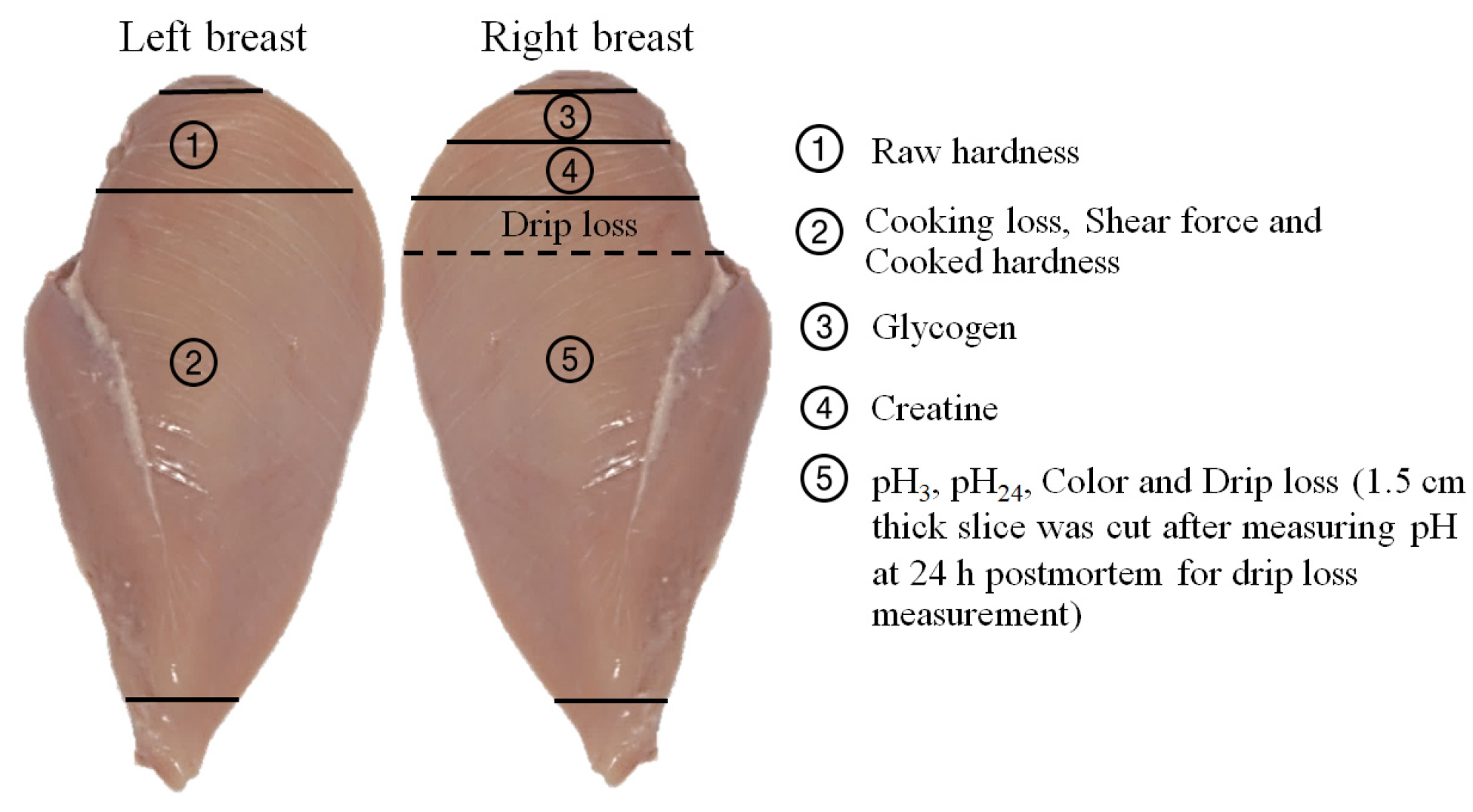
2.6. Creatine and Glycogen Evaluation
2.7. Meat Quality Evaluation
2.7.1. pH Measurement
2.7.2. Color Measurement
2.7.3. Drip Loss Measurement
2.7.4. Cooking Loss, Shear Force and Hardness Measurement
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diets
3.2. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Growth Performance
3.3. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Carcass Composition and Carcass Cuts
3.4. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Pectoral Myopathies
3.5. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Meat Quality
3.6. Effect of Myopathies on Carcass Composition
3.7. Effect of Myopathies on Creatine Content, Glycogen Content, and Meat Quality
3.8. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Growth Performance
4.2. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Carcass Composition and Carcass Cuts
4.3. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Pectoral Myopathies
4.4. Effect of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Meat Quality
4.5. Effect of Myopathies on Carcass Composition
4.6. Effect of Myopathies on Creatine, Glycogen Concentrations and Meat Quality
4.7. Principal Component Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.; Ahn, D.U. The Incidence of Muscle Abnormalities in Broiler Breast Meat—A Review. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.A.; Tedesco, D.C.; Schneider, T.; Teixeira, S.T.F.; Daroit, L.; Pilotto, F.; Dickel, E.L.; Santos, S.P.; dos Santos, L.R. Economic losses associated with Wooden Breast and White Striping in broilers. SCA 2018, 39, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kijowski, J.; Kupińska, E.; Stangierski, J.; Tomaszewska-Gras, J.; Szablewski, T. Paradigm of deep pectoral myopathy in broiler chickens. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2014, 70, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velleman, S.G. Recent Developments in Breast Muscle Myopathies Associated with Growth in Poultry. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuttappan, V.A.; Owens, C.M.; Coon, C.; Hargis, B.M.; Vazquez-Añon, M. Incidence of broiler breast myopathies at 2 different ages and its impact on selected raw meat quality parameters. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3005–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malila, Y.; U-Chupaj, J.; Srimarut, Y.; Chaiwiwattrakul, P.; Uengwetwanit, T.; Arayamethakorn, S.; Punyapornwithaya, V.; Sansamur, C.; Kirschke, C.P.; Huang, L.; et al. Monitoring of white striping and wooden breast cases and impacts on quality of breast meat collected from commercial broilers (Gallus gallus). Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuttappan, V.A.; Manangi, M.; Bekker, M.; Chen, J.; Vazquez-Anon, M. Nutritional Intervention Strategies Using Dietary Antioxidants and Organic Trace Minerals to Reduce the Incidence of Wooden Breast and Other Carcass Quality Defects in Broiler Birds. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 663409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudalal, S.; Lorenzi, M.; Soglia, F.; Cavani, C.; Petracci, M. Implications of white striping and wooden breast abnormalities on quality traits of raw and marinated chicken meat. Animal 2015, 9, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petracci, M.; Soglia, F.; Madruga, M.; Carvalho, L.; Ida, E.; Estévez, M. Wooden-Breast, White Striping, and Spaghetti Meat: Causes, Consequences and Consumer Perception of Emerging Broiler Meat Abnormalities. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Campo, M.M.; Mur, L.; Guerrero, A.; Barahona, M.; Resconi, V.C.; Magalhaes, D.R.; Lisbinski, E.; Boito, B.; Oliveira, I.M.; de Olleta, J.L. Differentiating Breast Myopathies through Color and Texture Analyses in Broiler. Foods 2020, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velleman, S.G.; Petracci, M. Editorial: Avian Muscle Development and Growth Mechanisms: Association With Muscle Myopathies and Meat Quality. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 601184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oviedo-Rondón, E.O.; Córdova-Noboa, H.A. The Potential of Guanidino Acetic Acid to Reduce the Occurrence and Severity of Broiler Muscle Myopathies. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; Al-Sagan, A.A.; Abdellatif, H.A.; Prince, A.; El-Banna, R. Effects of guanidinoacetic acid supplementation on zootechnical performance and some biometric indices in broilers challenged with T 3 -Hormone. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portocarero, N.; Braun, U. The physiological role of guanidinoacetic acid and its relationship with arginine in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarska-Schlattner, M.; Epand, R.F.; Meiler, F.; Zandomeneghi, G.; Neumann, D.; Widmer, H.R.; Meier, B.H.; Epand, R.M.; Saks, V.; Wallimann, T.; et al. Phosphocreatine interacts with phospholipids, affects membrane properties and exerts membrane-protective effects. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keshavarz, K.; Fuller, H.L. Relationship of arginine and methionine to creatine formation in chicks. J. Nutr. 1971, 101, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boney, J.W.; Patterson, P.H.; Solis, F. The effect of dietary inclusions of guanidinoacetic acid on D1-42 broiler performance and processing yields. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajali, F.; Lemme, A.; Rademacher-Heilshorn, M. Guanidinoacetic acid as a feed supplement for poultry. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2020, 76, 270–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Poel, A.F.B.; Braun, U.; Hendriks, W.H.; Bosch, G. Stability of creatine monohydrate and guanidinoacetic acid during manufacture (retorting and extrusion) and storage of dog foods. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeGroot, A.A.; Braun, U.; Dilger, R.N. Guanidinoacetic acid is efficacious in improving growth performance and muscle energy homeostasis in broiler chicks fed arginine-deficient or arginine-adequate diets. J. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2896–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviagen 2019. Ross 308: Broiler Nutrition Specifications. Available online: http://en.aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/RossBroilerNutritionSpecs2019-EN.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Community Reference Laboratory Feed Additives. CRL Evaluation Report on Guanidinoacetic Acid (CreAminoTM). FAD-2007-0003. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The European Commission’s Science an Knowledge Service, EU SCIENCE HUB. EFSA-Q-2007-050; European Comission: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kuttappan, V.A.; Hargis, B.M.; Owens, C.M. White striping and woody breast myopathies in the modern poultry industry: A review. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2724–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijare, V.V.; Yang, F.L.; Kuttappan, V.A.; Alvarado, C.Z.; Coon, C.N.; Owens, C.M. Meat quality of broiler breast fillets with white striping and woody breast muscle myopathies. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreiling, C.E.; Brown, D.E.; Casale, L.; Kelly, L. Muscle glycogen: Comparison of iodine binding and enzyme digestion assays and application to meat samples. Meat Sci. 1987, 20, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaosap, C.; Sitthigripong, R.; Sivapirunthep, P.; Pungsuk, A.; Adeyemi, K.D.; Sazili, A.Q. Myosin heavy chain isoforms expression, calpain system and quality characteristics of different muscles in goats. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviagen 2019. ROSS 308: Performance Objectives. Available online: https://en.aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Ross308-308FF-BroilerPO2019-EN.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Córdova-Noboa, H.A.; Oviedo-Rondón, E.O.; Sarsour, A.H.; Barnes, J.; Ferzola, P.; Rademacher-Heilshorn, M.; Braun, U. Performance, meat quality, and pectoral myopathies of broilers fed either corn or sorghum based diets supplemented with guanidinoacetic acid. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2479–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, M.; Ghasemi, H.A.; Hajkhodadadi, I.; Khaltabadi Farahani, A.H. Efficacy of guanidinoacetic acid at different dietary crude protein levels on growth performance, stress indicators, antioxidant status, and intestinal morphology in broiler chickens subjected to cyclic heat stress. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 254, 114208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çenesiz, A.A.; Yavaş, İ.; Çiftci, İ.; Ceylan, N.; Taşkesen, H.O. Guanidinoacetic acid supplementation is favourable to broiler diets even containing poultry by-product meal. Br. Poult. Sci. 2020, 61, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdova-Noboa, H.A.; Oviedo-Rondón, E.O.; Sarsour, A.H.; Barnes, J.; Sapcota, D.; López, D.; Gross, L.; Rademacher-Heilshorn, M.; Braun, U. Effect of guanidinoacetic acid supplementation on live performance, meat quality, pectoral myopathies and blood parameters of male broilers fed corn-based diets with or without poultry by-products. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2494–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGroot, A.A.; Braun, U.; Dilger, R.N. Efficacy of guanidinoacetic acid on growth and muscle energy metabolism in broiler chicks receiving arginine-deficient diets. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, N.; He, Z.; Song, P.; Hao, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Sun, Z. Guanidino-Acetic Acid: A Scarce Substance in Biomass That Can Regulate Postmortem Meat Glycolysis of Broilers Subjected to Pre-slaughter Transportation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 631194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, J.; Maertens, L.; Buyse, J.; Lemme, A.; Rademacher, M.; Dierick, N.A.; de Smet, S. Supplementation of guanidinoacetic acid to broiler diets: Effects on performance, carcass characteristics, meat quality, and energy metabolism. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David Brock East. Biochemical Pathways of Creatine and Creatine Phosphate. 2002. Available online: https://trace.tennessee.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1536&context=utk_chanhonoproj (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Kuttappan, V.A.; Huff, G.R.; Huff, W.E.; Hargis, B.M.; Apple, J.K.; Coon, C.; Owens, C.M. Comparison of hematologic and serologic profiles of broiler birds with normal and severe degrees of white striping in breast fillets. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnahhas, N.; Berri, C.; Chabault, M.; Chartrin, P.; Boulay, M.; Bourin, M.C.; Le Bihan-Duval, E. Genetic parameters of white striping in relation to body weight, carcass composition, and meat quality traits in two broiler lines divergently selected for the ultimate pH of the pectoralis major muscle. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brambila, G.S.; Bowker, B.C.; Zhuang, H. Comparison of sensory texture attributes of broiler breast fillets with different degrees of white striping. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2472–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, B.; Zhuang, H. Impact of white striping on functionality attributes of broiler breast meat. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasoniero, G.; Cullere, M.; Cecchinato, M.; Puolanne, E.; Dalle Zotte, A. Technological quality, mineral profile, and sensory attributes of broiler chicken breasts affected by White Striping and Wooden Breast myopathies. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2707–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, T.; Zhao, X.; Cai, L.; Guanghong, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of salt content on gelation of normal and wooden breast myopathy chicken pectoralis major meat batters. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgaard, L.B.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Bertram, H.C.; Jensen, J.A.; Møller, H.S.; Aaslyng, M.D.; Hejbøl, E.K.; Pedersen, J.R.; Elsser-Gravesen, D.; Young, J.F. Classification of wooden breast myopathy in chicken pectoralis major by a standardised method and association with conventional quality assessments. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, J.P.; Veiseth-Kent, E.; Høst, V.; Løvland, A. Rapid on-line detection and grading of wooden breast myopathy in chicken fillets by near-infrared spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Shao, W.; Chen, X.; Campbell, Y.L.; Nair, M.N.; Suman, S.P.; Beach, C.M.; Guyton, M.C.; Schilling, M.W. Meat quality traits and proteome profile of woody broiler breast (pectoralis major) meat. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petracci, M.; Mudalal, S.; Bonfiglio, A.; Cavani, C. Occurrence of white striping under commercial conditions and its impact on breast meat quality in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soglia, F.; Baldi, G.; Laghi, L.; Mudalal, S.; Cavani, C.; Petracci, M. Effect of white striping on turkey breast meat quality. Animal 2018, 12, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttappan, V.A.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Shaw, D.P.; Valentine, B.A.; Hargis, B.M.; Clark, F.D.; McKee, S.R.; Owens, C.M. Pathological changes associated with white striping in broiler breast muscles. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soglia, F.; Mudalal, S.; Babini, E.; Di Nunzio, M.; Mazzoni, M.; Sirri, F.; Cavani, C.; Petracci, M. Histology, composition, and quality traits of chicken Pectoralis major muscle affected by wooden breast abnormality. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudalal, S.; Babini, E.; Cavani, C.; Petracci, M. Quantity and functionality of protein fractions in chicken breast fillets affected by white striping. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey, A.; Smith, A.E.; Garner, L.J.; Cox, M.K. Application of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis to Detect Broiler Breast Filets Affected With Woody Breast Myopathy. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madruga, M.S.; Da Rocha, T.C.; Carvalho, L.M.; de Sousa, A.M.B.L.; de Sousa Neto, A.C.; Coutinho, D.G.; Carvalho Ferreira, A.S.; de Soares, A.J.; Sousa Galvão, M.; de Ida, E.I.; et al. The impaired quality of chicken affected by the wooden breast myopathy is counteracted in emulsion-type sausages. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Xia, T.; Li, Z.; Zhao, T. Effect of wooden breast myopathy on water-holding capacity and rheological and gelling properties of chicken broiler breast batters. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3742–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, G.; Yen, C.-N.; Daughtry, M.R.; Bodmer, J.; Bowker, B.C.; Zhuang, H.; Petracci, M.; Gerrard, D.E. Exploring the Factors Contributing to the High Ultimate pH of Broiler Pectoralis Major Muscles Affected by Wooden Breast Condition. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampiga, M.; Soglia, F.; Petracci, M.; Meluzzi, A.; Sirri, F. Effect of different arginine-to-lysine ratios in broiler chicken diets on the occurrence of breast myopathies and meat quality attributes. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadipour, B.; Sharifi, M.; Khajali, F. Pulmonary hypertensive response of broiler chickens to arginine and guanidinoacetic acid under high-altitude hypoxia. Acta Vet. Hung. 2018, 66, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, M.; Karimi Dehkordi, S.; Zamiani Moghadam, A.K.; Ahmadipour, B.; Khajali, F. Combined effects of guanidinoacetic acid, coenzyme Q10 and taurine on growth performance, gene expression and ascites mortality in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Ingredient | Starter (0–10 Day) | Grower (10–28 Day) | Finisher (28–42 Day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 54.08 | 58.83 | 63.09 |
| Soybean meal (48% crude protein) | 35.00 | 30.64 | 25.61 |
| Corn gluten meal (60% crude protein) | 3.88 | 3.01 | 3.50 |
| Soya oil | 2.16 | 3.00 | 3.65 |
| Limestone | 1.70 | 1.57 | 1.45 |
| Monodicalcium phosphate (21.8%) | 1.07 | 0.91 | 0.75 |
| DL-Methionine (99%) | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.25 |
| Pellet binder | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Salt (NaCl) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| L-Lysine HCL (78%) | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.25 |
| Premix 1,2 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Mold inhibitor | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| L-Threonine (98.5%) | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.07 |
| Choline chloride (60%) | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Coccidiostat 3 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Phytase 4 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Calculated and (analyzed 5) nutrient content (%) | |||
| Dry mater | 89.29 (90.00) | 89.27 (90.03) | 89.25 (88.73) |
| Metabolizable energy (kcal/kg) | 2950 | 3050 | 3150 |
| Crude protein | 23.81 (24.73) | 21.50 (22.57) | 19.64 (20.23) |
| Calcium | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.78 |
| Available phosphorous | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.39 |
| Sodium | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| Potassium | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.79 |
| Chloride | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| Dietary electrolyte balance (mEq/kg) | 261 | 240 | 215 |
| Total lysine | 1.41 (1.50) | 1.27 (1.28) | 1.12 (1.07) |
| Total methionine | 0.67 (0.69) | 0.61 (0.57) | 0.56 (0.49) |
| Total methionine + cysteine | 1.05 (1.08) | 0.96 (0.93) | 0.88 (0.82) |
| Total threonine | 1.00 (1.08) | 0.89 (0.92) | 0.79 (0.79) |
| Total arginine | 1.50 (1.64) | 1.35 (1.41) | 1.19 (1.23) |
| Parameters | Starter | Grower | Finisher | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Calculated | |||||||||
| Creamino®, mg/kg | 0 | 600 | 1200 | 0 | 600 | 1200 | 0 | 600 | 1200 |
| Analyzed 2 | |||||||||
| Creamino®, mg/kg | <21 | 613 | 1222 | <21 | 572 | 1235 | <21 | 560 | 1110 |
| GAA, mg/kg | <20 | 588 | 1173 | <20 | 549 | 1186 | <20 | 538 | 1066 |
| Parameters 2 | Days | Treatment 1 | RMSE 3 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | ||||
| BW (g) | 10 | 314.67 | 315.45 | 320.42 | 8.13 | 0.141 |
| 28 | 1949.15 | 1933.03 | 1902.16 | 51.13 | 0.058 | |
| 42 | 3145.26 | 3146.93 | 3194.32 | 151.34 | 0.637 | |
| WG (g) | 0–10 | 272.43 | 273.21 | 278.18 | 8.21 | 0.146 |
| 0–28 | 1906.91 | 1890.79 | 1859.92 | 51.2 | 0.059 | |
| 0–42 | 3103.02 | 3104.69 | 3152.07 | 154.34 | 0.637 | |
| FI (g) | 0–10 | 285.60 | 280.33 | 282.32 | 8.25 | 0.245 |
| 0–28 | 2501.37 a | 2468.97 b | 2390.64 b | 93.75 | 0.010 | |
| 0–42 | 4938.02 | 4790.41 | 4851.61 | 197.85 | 0.153 | |
| FCR (g:g) | 0–10 | 1.048 a | 1.026 b | 1.015 b | 0.018 | <0.0001 |
| 0–28 | 1.312 | 1.306 | 1.286 | 0.039 | 0.198 | |
| 0–42 | 1.594 a | 1.544 b | 1.540 b | 0.043 | 0.003 | |
| Parameters | T1 | T2 | T3 | RMSE 2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 56 | 56 | 56 | ||
| Live weight (kg) | 3.12 | 3.12 | 3.13 | 0.23 | 0.972 |
| Carcass weight (kg) | 2.58 | 2.57 | 2.57 | 0.18 | 0.956 |
| Carcass (%) | 82.63 | 82.28 | 82.08 | 1.87 | 0.295 |
| Breast (%) | 30.14 | 30.07 | 30.51 | 2.14 | 0.504 |
| Fillet (%) | 12.80 | 12.65 | 12.88 | 0.99 | 0.462 |
| Wing (%) | 9.96 | 9.85 | 9.86 | 1.46 | 0.263 |
| Leg (%) | 31.12 | 31.55 | 31.19 | 0.53 | 0.485 |
| Treatments | Wooden Breast Scores | White Striping Scores | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| T1 | 37.5% (21) | 26.8% (15) | 7.1% (4) a,b | 28.6% (16) a | 30.4% (17) | 44.6% (25) | 23.2% (13) | 1.8% (1) |
| T2 | 46.4% (26) | 30.4% (17) | 5.4% (3) b | 17.9% (10) a,b | 39.3% (22) | 42.9% (24) | 17.9% (10) | 0.0% (0) |
| T3 | 44.6% (25) | 26.8% (15) | 19.6% (11) a | 8.9% (5) b | 37.5% (21) | 50.0% (28) | 12.5% (7) | 0.0% (0) |
| Parameters | T1 | T2 | T3 | RMSE 4 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n 2,3 | 56 (21) | 56 (21) | 56 (23) | ||
| Creatine (mg/kg) | 4315.24 | 4570.95 | 4770.87 | 863.16 | 0.224 |
| Glycogen (mg/g) | 6.44 b | 27.19 a | 31.04 a | 13.88 | <0.0001 |
| pH3 | 6.32 a | 6.26 b | 6.25 b | 0.12 | 0.006 |
| pH24 | 6.16 a | 6.07 b | 6.05 b | 0.15 | 0.0002 |
| L* (lightness) | 52.88 | 52.88 | 53.19 | 3.94 | 0.893 |
| a* (redness) | 1.20 | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.02 | 0.753 |
| b* (yellowness) | 12.25 | 11.60 | 12.27 | 2.61 | 0.312 |
| Drip loss (%) | 1.55 | 1.39 | 1.53 | 0.55 | 0.321 |
| Cooking Loss (%) | 14.37 | 14.76 | 14.97 | 3.80 | 0.709 |
| Shear force (kg) | 4.27 | 4.15 | 4.31 | 1.15 | 0.754 |
| Traits | Wooden Breast Score (WB) | White Striping Score (WS) | RMSE 2 | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | WB | WS | ||
| n 1 | 72 | 47 | 18 | 30 | 60 | 77 | 30 | |||
| Live weight (kg) | 3.14 | 3.10 | 3.18 | 3.17 | 3.10 | 3.12 | 3.23 | 0.23 | 0.534 | 0.059 |
| Carcass weight (kg) | 2.58 | 2.55 | 2.64 | 2.62 | 2.56 | 2.58 | 2.65 | 0.17 | 0.194 | 0.079 |
| Breast (g) | 768.24 b | 773.86 b | 826.81 a | 800.52 a,b | 773.20 | 790.40 | 814.97 | 80.99 | 0.035 | 0.122 |
| Fillet (g) | 324.61 b | 324.96 b | 352.97 a | 343.75 a | 327.93 | 334.26 | 347.52 | 36.58 | 0.007 | 0.108 |
| Carcass (%) | 82.07 | 82.12 | 83.20 | 82.45 | 82.62 | 82.57 | 82.20 | 1.86 | 0.126 | 0.641 |
| Breast (%) | 29.78 b | 30.36 b | 31.23 a | 30.60 a,b | 30.19 | 30.63 | 30.70 | 2.09 | 0.048 | 0.464 |
| Fillet (%) | 12.58 c | 12.73 b,c | 13.33 a | 13.13 a,b | 12.79 | 12.94 | 13.09 | 0.95 | 0.009 | 0.431 |
| Traits | Wooden Breast Score | White Striping Score | RMSE 3 | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | WB | WS | ||
| n 1,2 | 72 (18) | 47 (18) | 18 (12) | 30 (17) | 60 (21) | 77 (29) | 30 (14) | |||
| Creatine (mg/kg) | 5206.11 a | 4682.22 a,b | 4345.00 b,c | 3894.71 c | 4712.90 | 4581.38 | 4422.86 | 725.19 | <0.0001 | 0.615 |
| Glycogen (mg/g) | 28.50 | 20.72 | 17.92 | 19.86 | 27.02 | 19.43 | 21.24 | 19.95 | 0.460 | 0.430 |
| pH3 | 6.26 | 6.26 | 6.29 | 6.32 | 6.26 | 6.30 | 6.29 | 0.12 | 0.262 | 0.111 |
| pH24 | 6.06 b | 6.08 b | 6.12 a,b | 6.18 a | 6.09 | 6.12 | 6.12 | 0.15 | 0.005 | 0.543 |
| L* | 50.84 c | 53.44 b | 55.32 a | 55.07 a,b | 53.31 | 54.54 | 53.15 | 3.47 | <0.0001 | 0.063 |
| a* | 1.23 | 1.08 | 1.36 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 1.02 | 1.44 | 1.02 | 0.718 | 0.209 |
| b* | 10.99 b | 12.57 a | 13.09 a | 13.12 a | 12.52 | 12.39 | 12.42 | 2.47 | 0.0002 | 0.957 |
| Drip loss (%) | 1.46 | 1.43 | 1.54 | 1.74 | 1.32 b | 1.68 a | 1.24 b | 0.43 | 0.183 | <0.0001 |
| Cooking Loss (%) | 13.64 b | 15.86 a | 16.29 a | 15.72 a | 15.24 | 14.67 | 16.22 | 3.59 | 0.003 | 0.162 |
| Shear force (kg) | 4.52 a,b | 4.55 a | 4.09 a,b | 3.54 b | 4.06 | 4.03 | 4.45 | 1.11 | 0.001 | 0.251 |
| rHard (N/cm2) | 29.95 b,c | 27.12 c | 37.30 a,b | 48.62 a | 31.58 | 32.86 | 38.31 | 18.18 | 0.0002 | 0.325 |
| cHard (N/cm2) | 46.20 | 47.17 | 38.67 | 41.52 | 39.31 b | 41.56 b | 49.30 a | 13.57 | 0.079 | 0.014 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalil, S.; Saenbungkhor, N.; Kesnava, K.; Sivapirunthep, P.; Sitthigripong, R.; Jumanee, S.; Chaosap, C. Effects of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Productive Performance, Pectoral Myopathies, and Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113180
Khalil S, Saenbungkhor N, Kesnava K, Sivapirunthep P, Sitthigripong R, Jumanee S, Chaosap C. Effects of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Productive Performance, Pectoral Myopathies, and Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113180
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalil, Shady, Nualprae Saenbungkhor, Kajorn Kesnava, Panneepa Sivapirunthep, Ronachai Sitthigripong, Sukanya Jumanee, and Chanporn Chaosap. 2021. "Effects of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Productive Performance, Pectoral Myopathies, and Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens" Animals 11, no. 11: 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113180
APA StyleKhalil, S., Saenbungkhor, N., Kesnava, K., Sivapirunthep, P., Sitthigripong, R., Jumanee, S., & Chaosap, C. (2021). Effects of Guanidinoacetic Acid Supplementation on Productive Performance, Pectoral Myopathies, and Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens. Animals, 11(11), 3180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113180







