Bioconversion of Digestate, Pig Manure and Vegetal Residue-Based Waste Operated by Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Global Food Losses and Food Waste—Extent, Causes and Prevention; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- zu Ermgassen, E.K.H.J.; Phalan, B.; Green, R.E.; Balmford, A. Reducing the land use of EU pork production: Where there’s swill, there’s a way. Food Policy 2016, 58, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastor, B.; Velasquez, Y.; Gobbi, P.; Rojo, S. Conversion of organic wastes into fly larval biomass: Bottlenecks and challenges. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortmans, B.M.A.; Diener, S.; Verstappen, B.M.; Zurbrügg, C. Black Soldier Fly Biowaste Processing—A Step-by-Step Guide; Eawag—Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shumo, M.; Osuga, I.M.; Khamis, F.M.; Tanga, C.M.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Subramanian, S.; Ekesi, S.; van Huis, A.; Borgemeister, C. The nutritive value of black soldier fly larvae reared on common organic waste streams in Kenya. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.; Pineda-Mejia, J.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Performance of the Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) on Vegetable Residue-Based Diets Formulated Based on Protein and Carbohydrate Contents. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2676–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.B.; Gort, G.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Effects of dietary protein and carbohydrate on life-history traits and body protein and fat contents of the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens. Physiol. Entomol. 2019, 44, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gligorescu, A.; Toft, S.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Axelsen, J.A.; Nielsen, S.A. Development, metabolism and nutrient composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in relation to temperature and diet. J. Insects Food Feed 2018, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorescu, A.; Toft, S.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Axelsen, J.A.; Nielsen, S.A. Development, growth and metabolic rate of Hermetia illucens larvae. J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 143, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Y.K.; Chiu, S.L.H.; Lo, I.M.C. Effects of moisture content of food waste on residue separation, larval growth and larval survival in black soldier fly bioconversion. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Gutiérrez, F.R.; Nguyen, D.H.; Morel, A.; Koottatep, T.; Tockner, K. Black soldier fly larvae for organic waste treatment—prospects and constraints. Proc. WasteSafe 2011, 2, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Oonincx, D.; van Broekhoven, S.; van Huis, A.; van Loon, J.J.A. Feed Conversion, Survival and Development, and Composition of Four Insect Species on Diets Composed of Food By-Products. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzepe, D.; Nana, P.; Kuietche, H.M.; Kimpara, J.M.; Magatsing, O.; Tchuinkam, T.; Djouaka, R. Feeding strategies for small-scale rearing black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) as organic waste recycler. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Conversion of organic material by black soldier fly larvae: Establishing optimal feeding rates. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VSN-International. Genstat for Windows; VSN International: Hemel Hempstead, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.B.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Influence of larval density and dietary nutrient concentration on performance, body protein, and fat contents of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2018, 166, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paz, A.S.P.; Carrejo, N.S.; Rodriguez, C.H.G. Effects of Larval Density and Feeding Rates on the Bioconversion of Vegetable Waste Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae Hermetia illucens (L.), (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Waste Biomass Valorization 2015, 6, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.X.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vanlaerhoven, S. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmawati, R.; Buchori, D.; Hidayat, P.; Hem, S.; Fahmi, M. Perkembangan dan Kandungan Nutrisi Larva Hermetia illucens (Linnaeus) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) pada Bungkil Kelapa Sawit. J. Entomol. Indones. 2015, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meneguz, M.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F.; Dama, A.; Lussiana, C.; Renna, M.; Gasco, L. Effect of rearing substrate on growth performance, waste reduction efficiency and chemical composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5776–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Zurbrugg, C.; Vinneras, B. Effects of feedstock on larval development and process efficiency in waste treatment with black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). J. Clean Prod. 2019, 208, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bava, L.; Jucker, C.; Gislon, G.; Lupi, D.; Savoldelli, S.; Zucali, M.; Colombini, S. Rearing of Hermetia illucens on Different Organic By-Products: Influence on Growth, Waste Reduction, and Environmental Impact. Animals 2019, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Diener, S.; Zurbrugg, C.; Mathys, A. Decomposition of biowaste macronutrients, microbes, and chemicals in black soldier fly larval treatment: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; De Boer, I.J.M.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Van Loon, J.J.A.; Heetkamp, M.J.W.; Van Schelt, J.; Bolhuis, J.E.; Van Zanten, H.H. Bioconversion efficiencies, greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions during black soldier fly rearing—A mass balance approach. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 271, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Huang, H.; Awasthi, S.K.; Lahori, A.H.; Li, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z. Role of biochar amendment in mitigation of nitrogen loss and greenhouse gas emission during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perednia, D.A.; Anderson, J.; Rice, A. A comparison of the greenhouse gas production of black soldier fly larvae versus aerobic microbial decomposition of an organic feed material. Res. Rev. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ermolaev, E.; Lalander, C.; Vinneras, B. Greenhouse gas emissions from small-scale fly larvae composting with Hermetia illucens. Waste Manag. 2019, 96, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
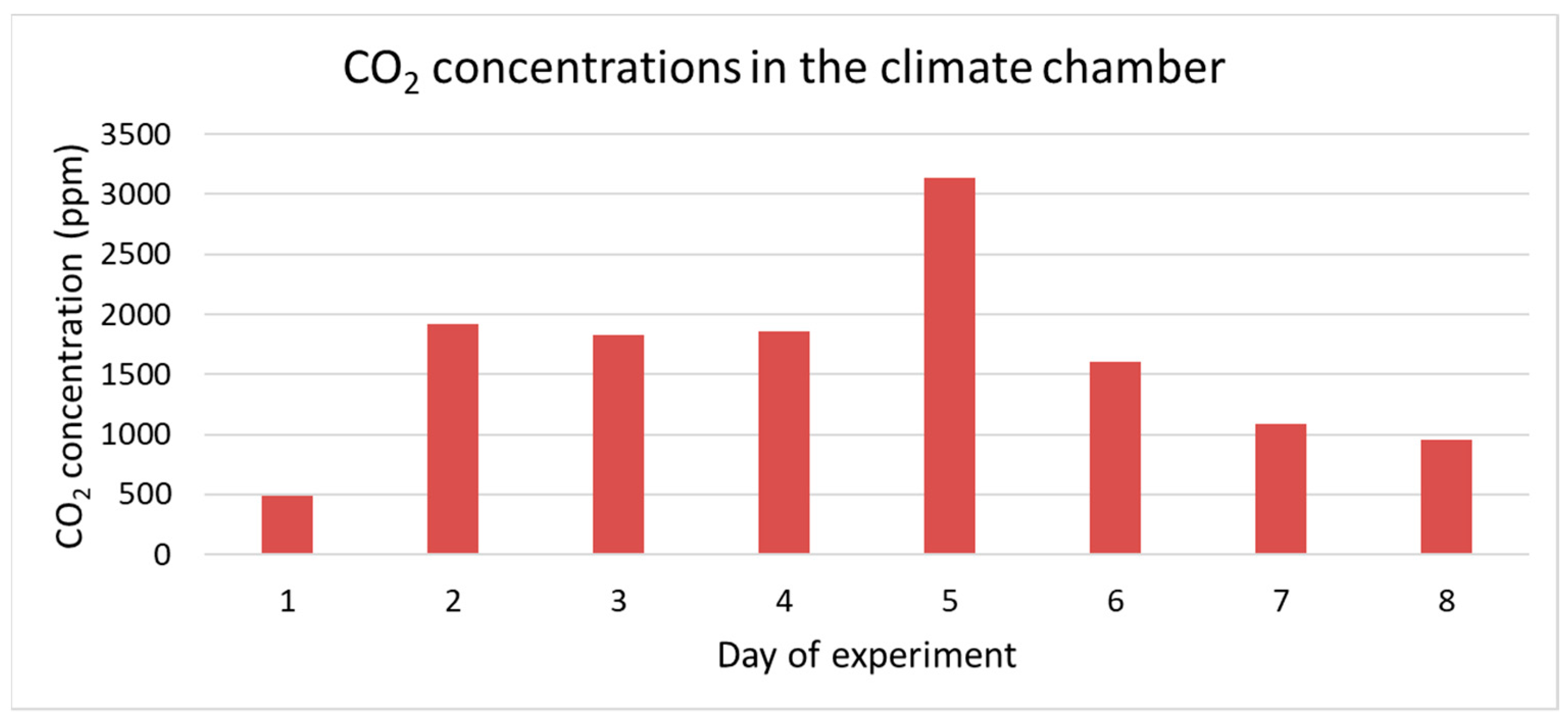
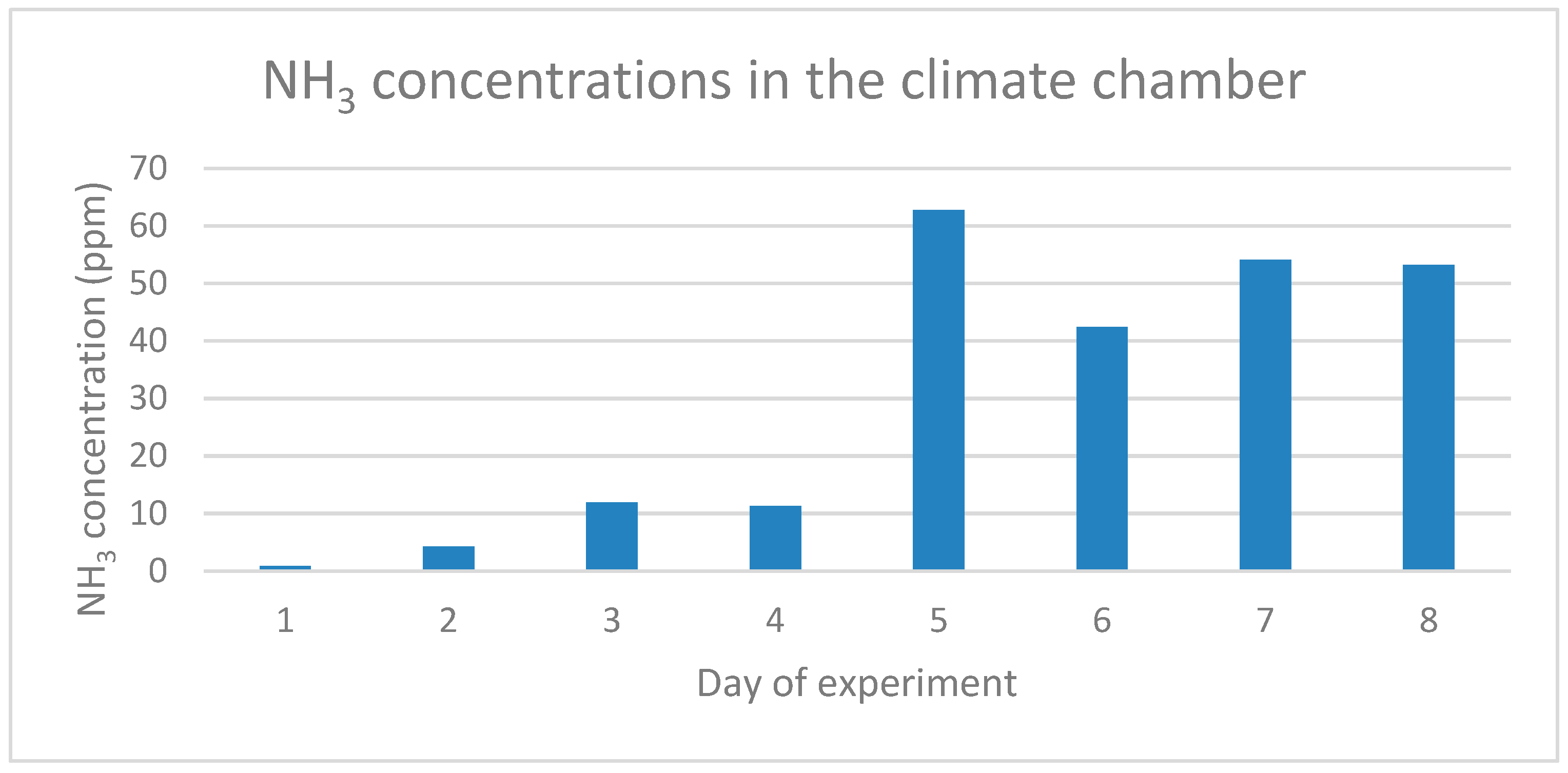
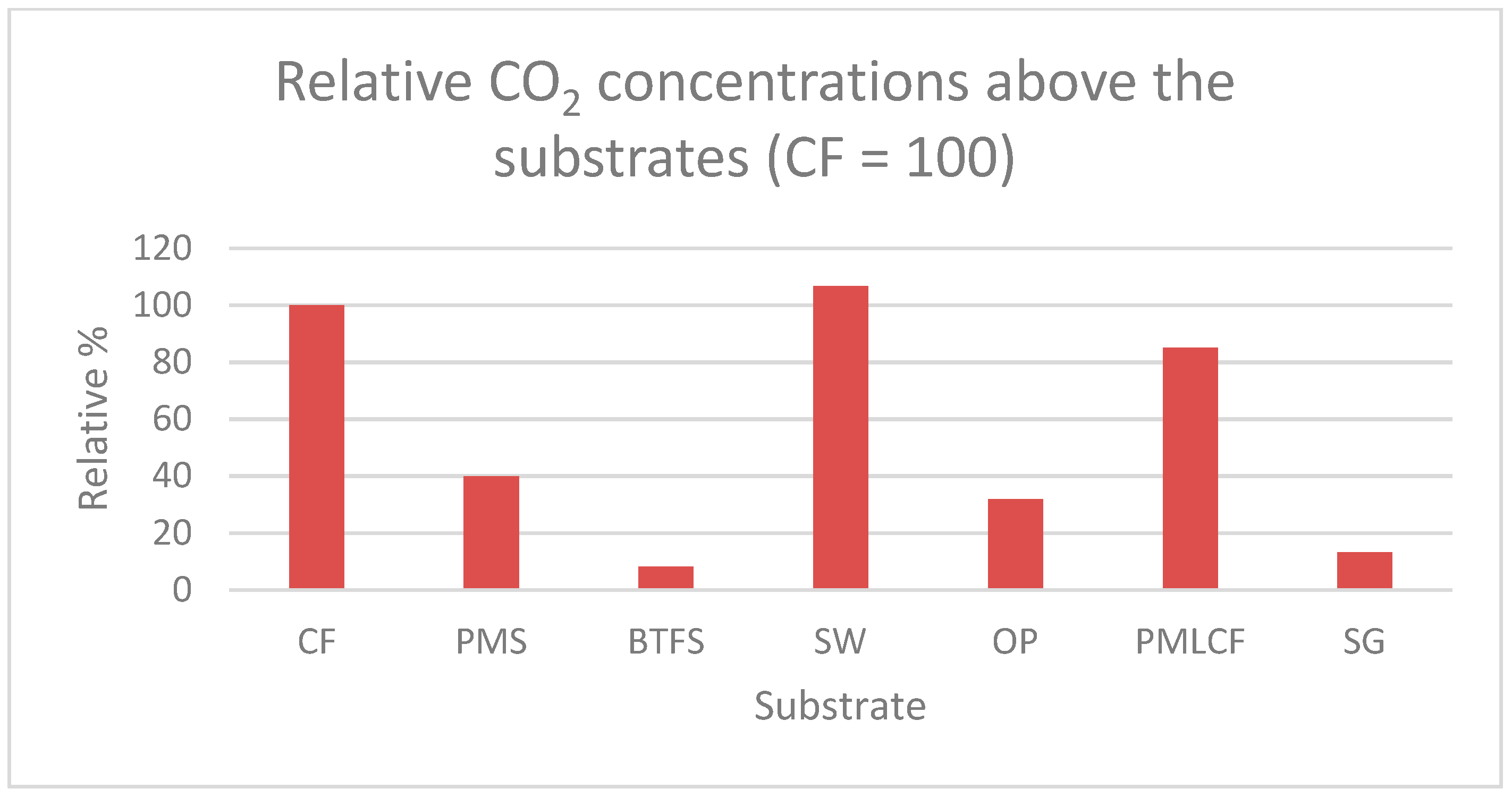
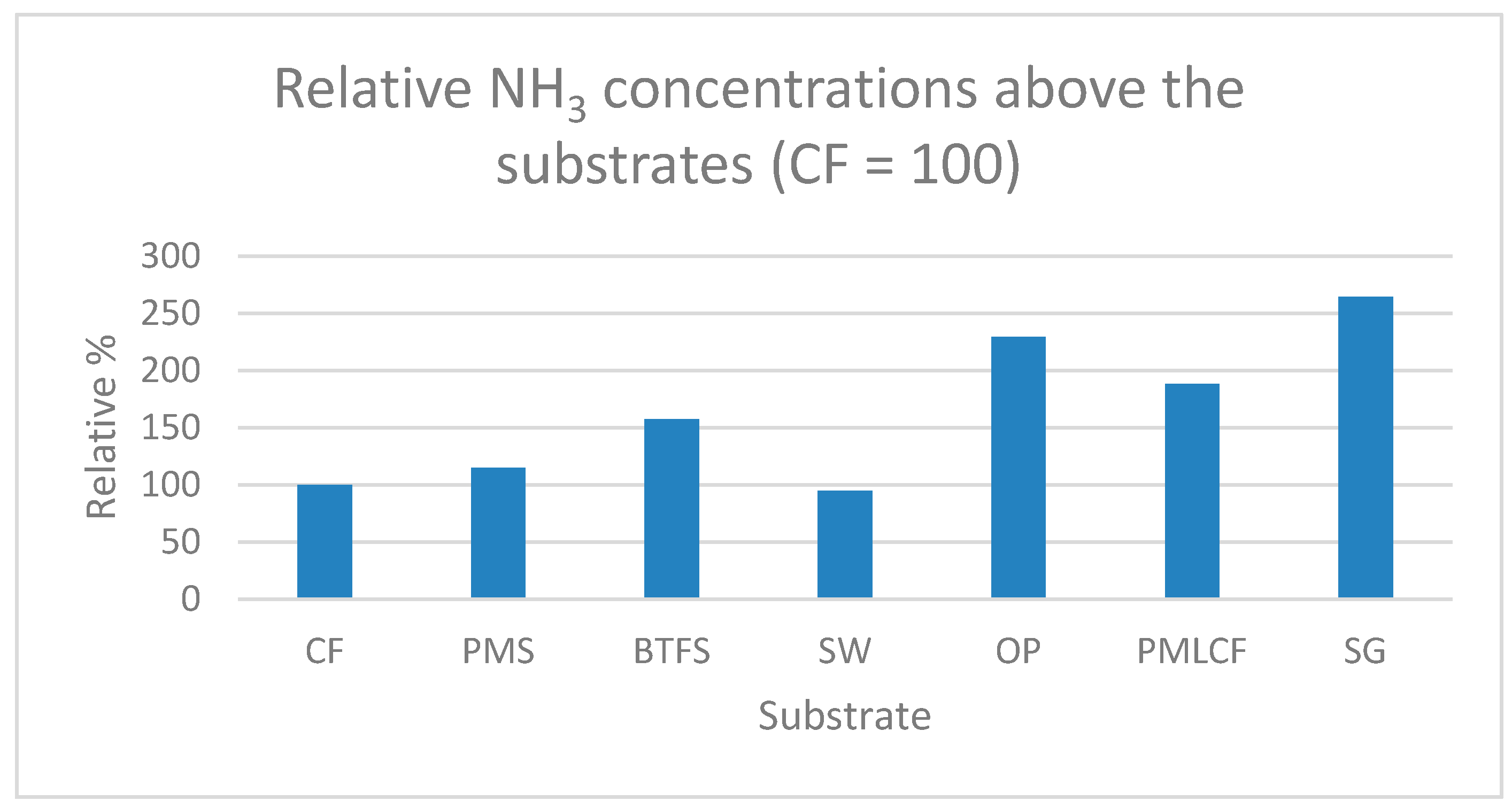
| Substrate | Quantity of Wet Substrate (kg) | Number of BSF Larvae | Substrate per BSF Larva (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken feed (CF; reference diet) | 10.0 | 24,995 | 0.4 |
| Pig manure solid (PMS) | 6.8 | 16,910 | 0.4 |
| Betafert® solid (BTFS) | 10.0 | 24,892 | 0.4 |
| Swill (SW) | 9.9 | 24,805 | 0.4 |
| Olive pulp (OP) | 10.0 | 25,021 | 0.4 |
| Pig manure liquid mixed with CF (PMLCF) | 9.7 | 24,289 | 0.4 |
| Silage grass (SG) | 4.9 | 12,374 | 0.4 |
| Dry Matter (%) | CF | PMS | BTFS | SW | OP | PMLCF | SG | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate start | 40 b | 32 d | 30 e | 28 f | 57 a | 38 c | 30 e | 0.1 | <0.001 |
| Substrate end | 81 a | 62 b | 38 d | 47 c | 66 b | 83 a | 43 cd | 1.6 | <0.001 |
| BSF larvae end | 33 b | 21 d | 17 e | 38 a | 27 c | 32 b | 14 e | 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Parameter | CF | PMS | BTFS | SW | OP | PMLCF | SG | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day of harvest (d) | 8 | 8 | 11 | 8 | 11 | 8 | 11 | - | - |
| BSF larvae weight start (mg) | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | - | - |
| BSF larvae weight end (mg) | 69 b | 37 c | 18 d | 119 a | 13 d | 70 b | 19 d | 1.6 | <0.001 |
| Larval growth rate (mg/d) | 7.2 b | 3.2 c | 0.6 d | 13.4 a | 0.2 d | 7.3 b | 0.7 d | 0.17 | <0.001 |
| Waste Reduction Index (DM g/d) | 4.5 c | 3.0 d | 1.2 ef | 10.6 a | 0.5 f | 5.4 b | 1.9 e | 0.15 | <0.001 |
| Efficiency of Conversion of Ingested substrate (g:g DM) | 0.34 abc | 0.31 abc | 0.20 cd | 0.46 a | 0.26 bcd | 0.37 ab | 0.14 d | 0.027 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veldkamp, T.; van Rozen, K.; Elissen, H.; van Wikselaar, P.; van der Weide, R. Bioconversion of Digestate, Pig Manure and Vegetal Residue-Based Waste Operated by Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Animals 2021, 11, 3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113082
Veldkamp T, van Rozen K, Elissen H, van Wikselaar P, van der Weide R. Bioconversion of Digestate, Pig Manure and Vegetal Residue-Based Waste Operated by Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Animals. 2021; 11(11):3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113082
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeldkamp, Teun, Klaas van Rozen, Hellen Elissen, Piet van Wikselaar, and Rommie van der Weide. 2021. "Bioconversion of Digestate, Pig Manure and Vegetal Residue-Based Waste Operated by Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae)" Animals 11, no. 11: 3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113082
APA StyleVeldkamp, T., van Rozen, K., Elissen, H., van Wikselaar, P., & van der Weide, R. (2021). Bioconversion of Digestate, Pig Manure and Vegetal Residue-Based Waste Operated by Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Animals, 11(11), 3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113082






