Social and Seasonal Factors Contribute to Shifts in Male African Elephant (Loxodonta africana) Foraging and Activity Patterns in Kruger National Park, South Africa
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Clearance
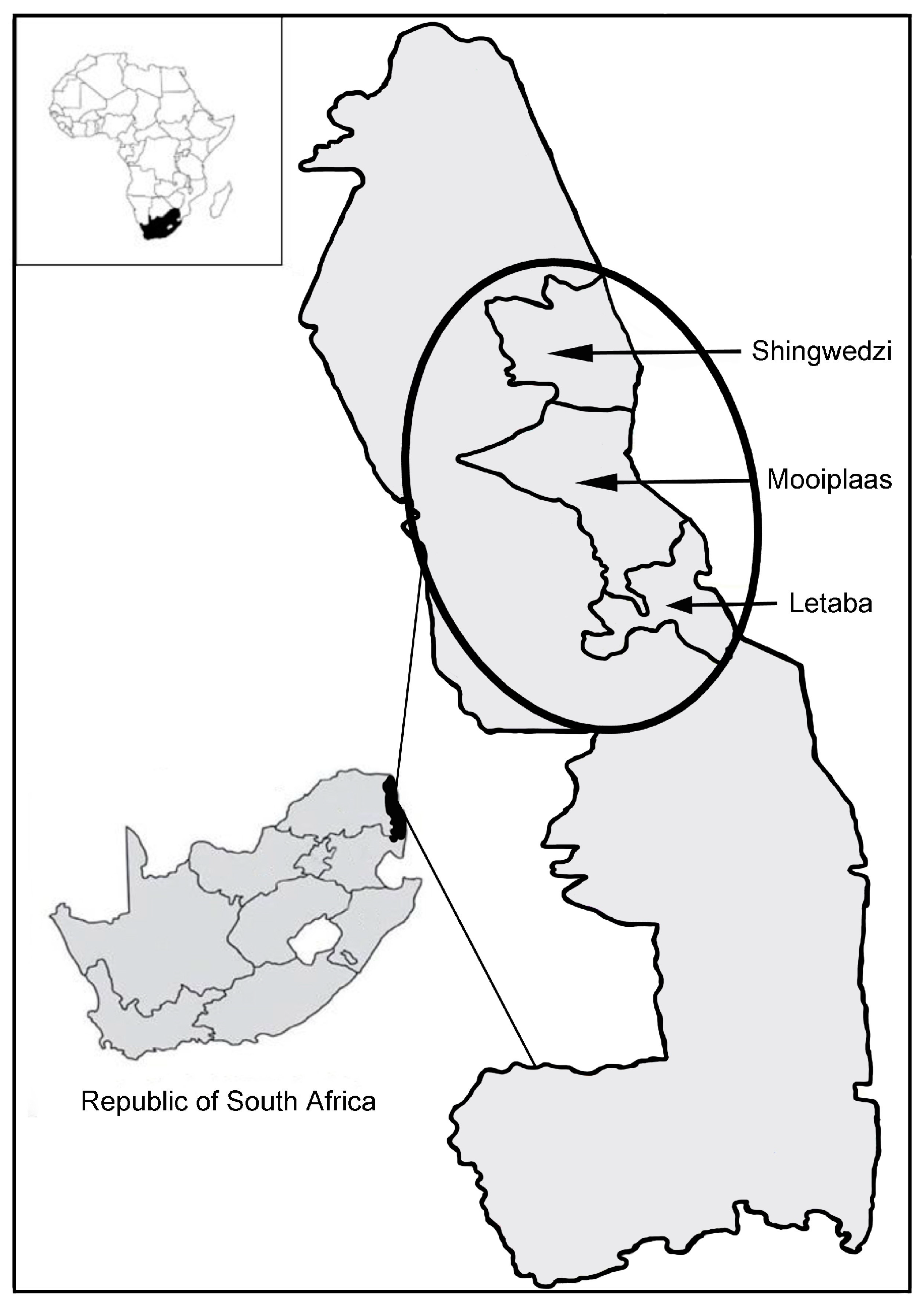
2.2. Study Area
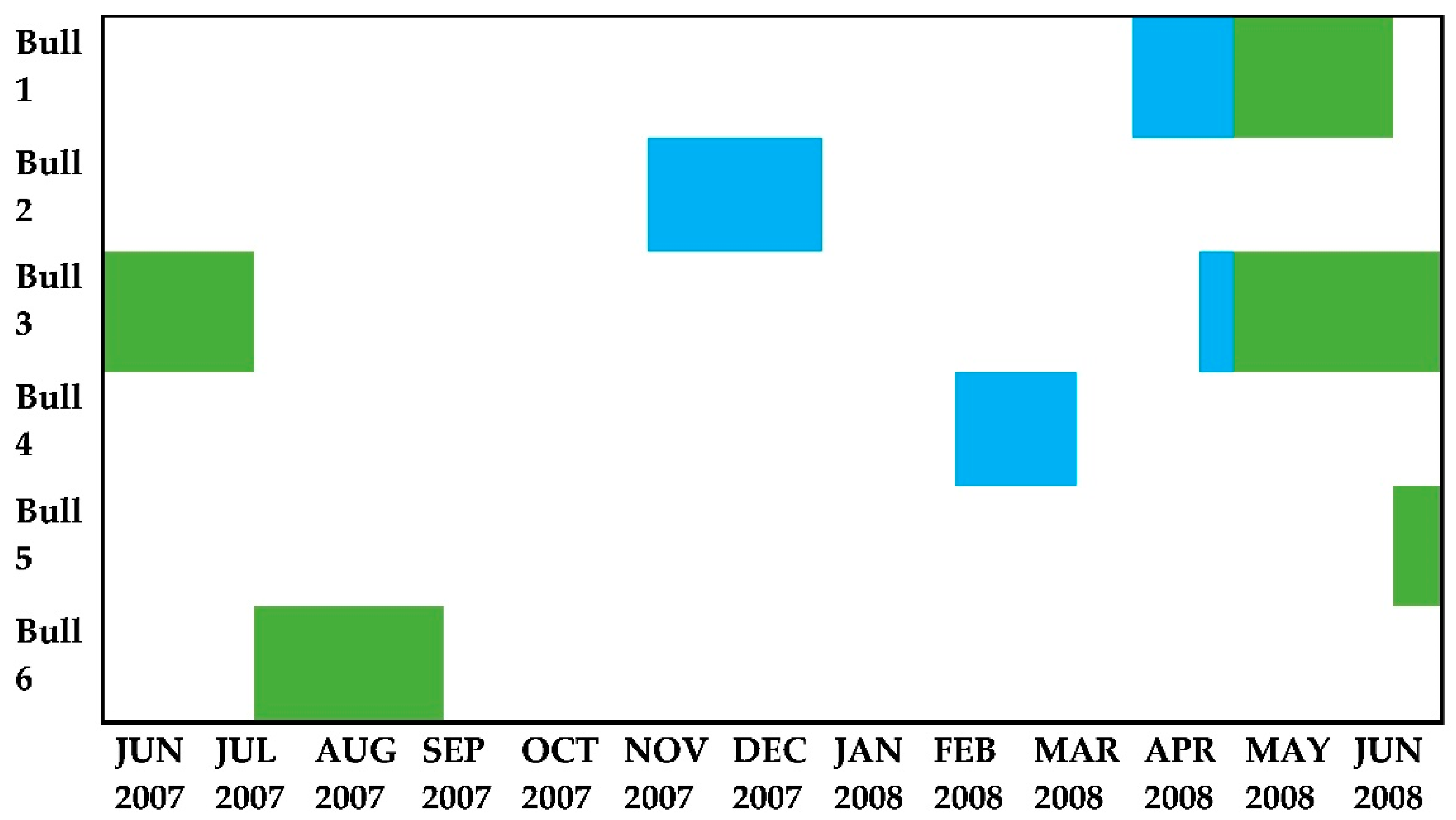
2.3. Study Animals and Behavioural Observations
2.4. Time of Day and Season
2.5. Association and Injury
2.6. Presence or Absence of Musth
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
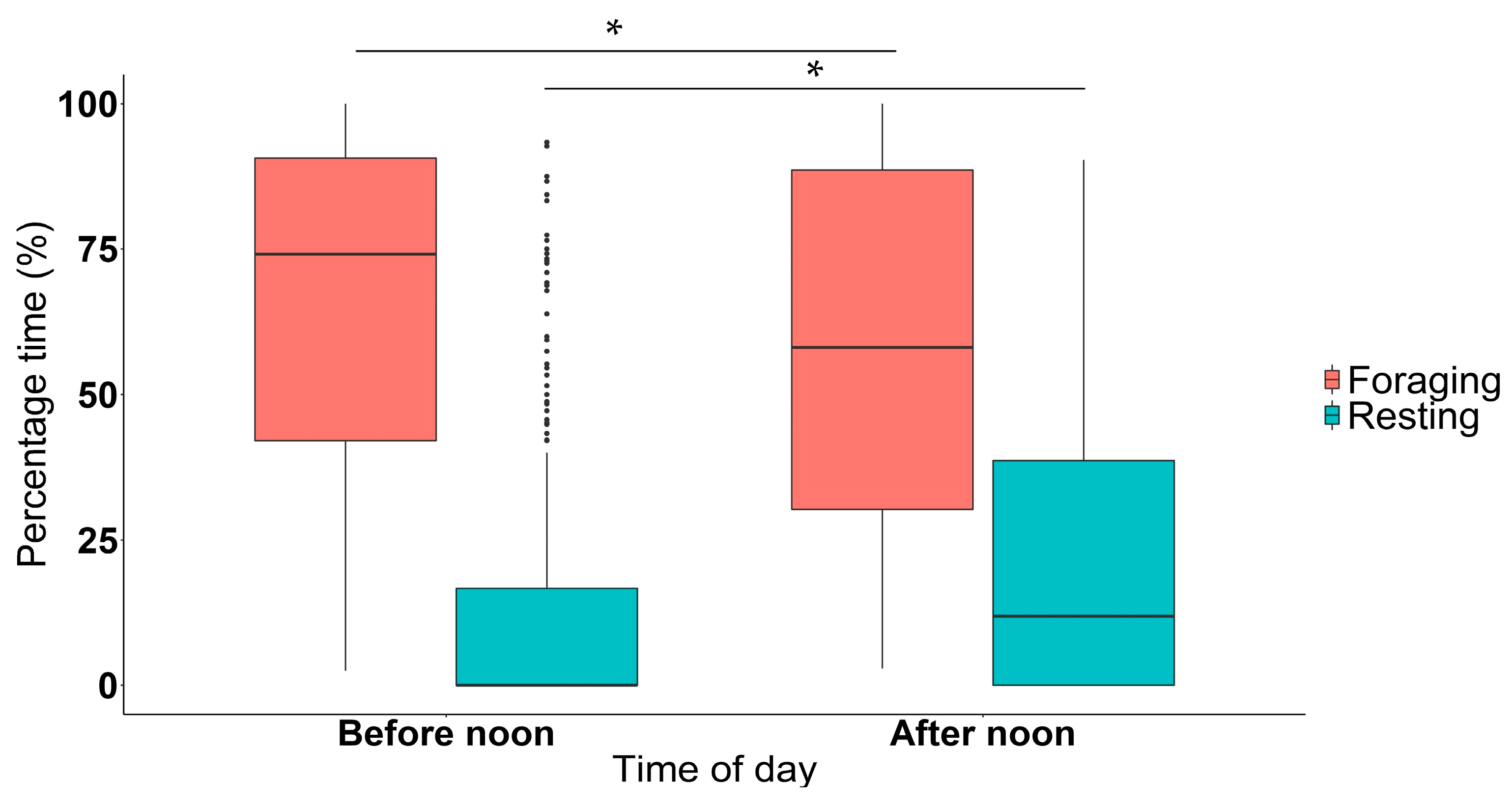
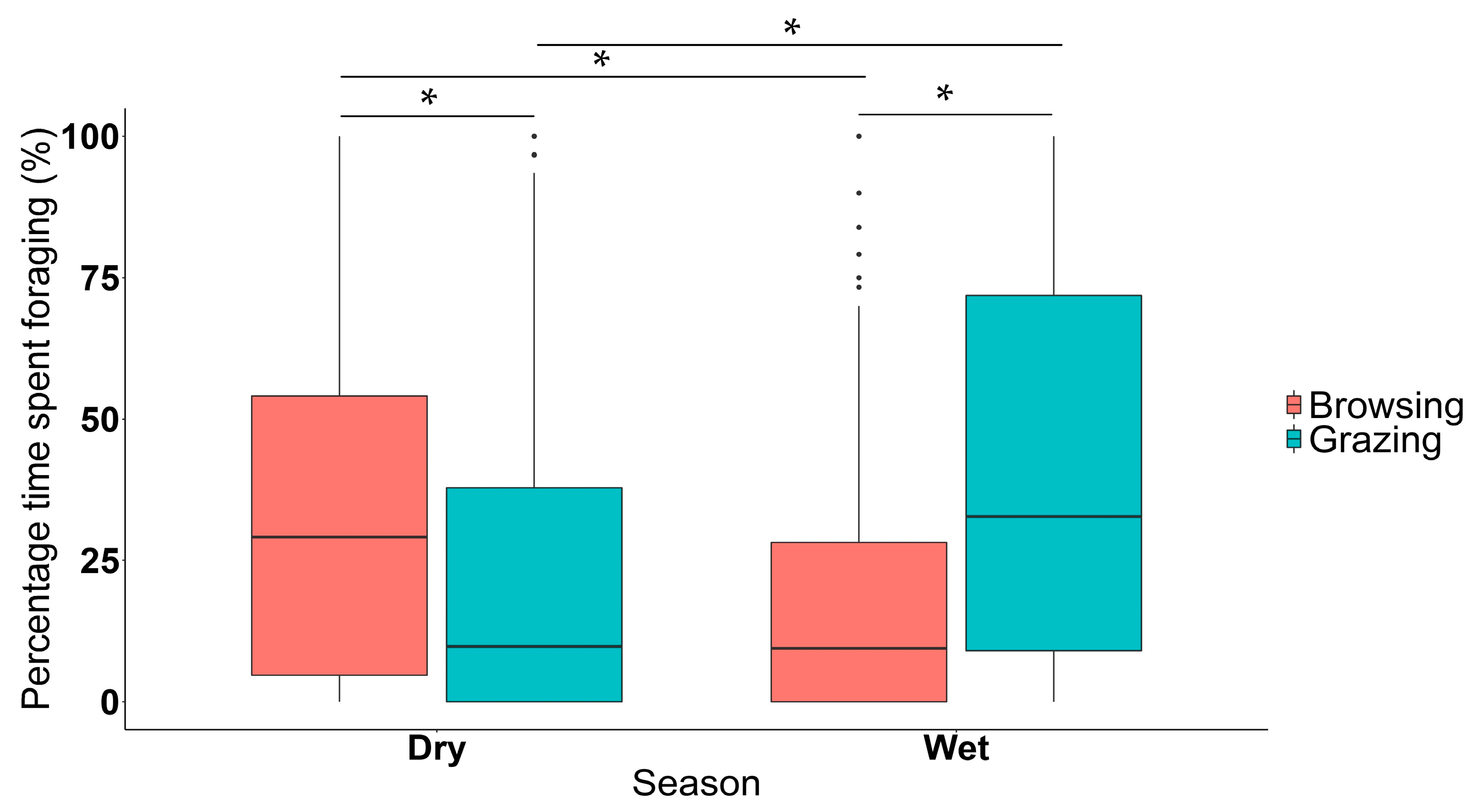
3.1. Time of Day and Season
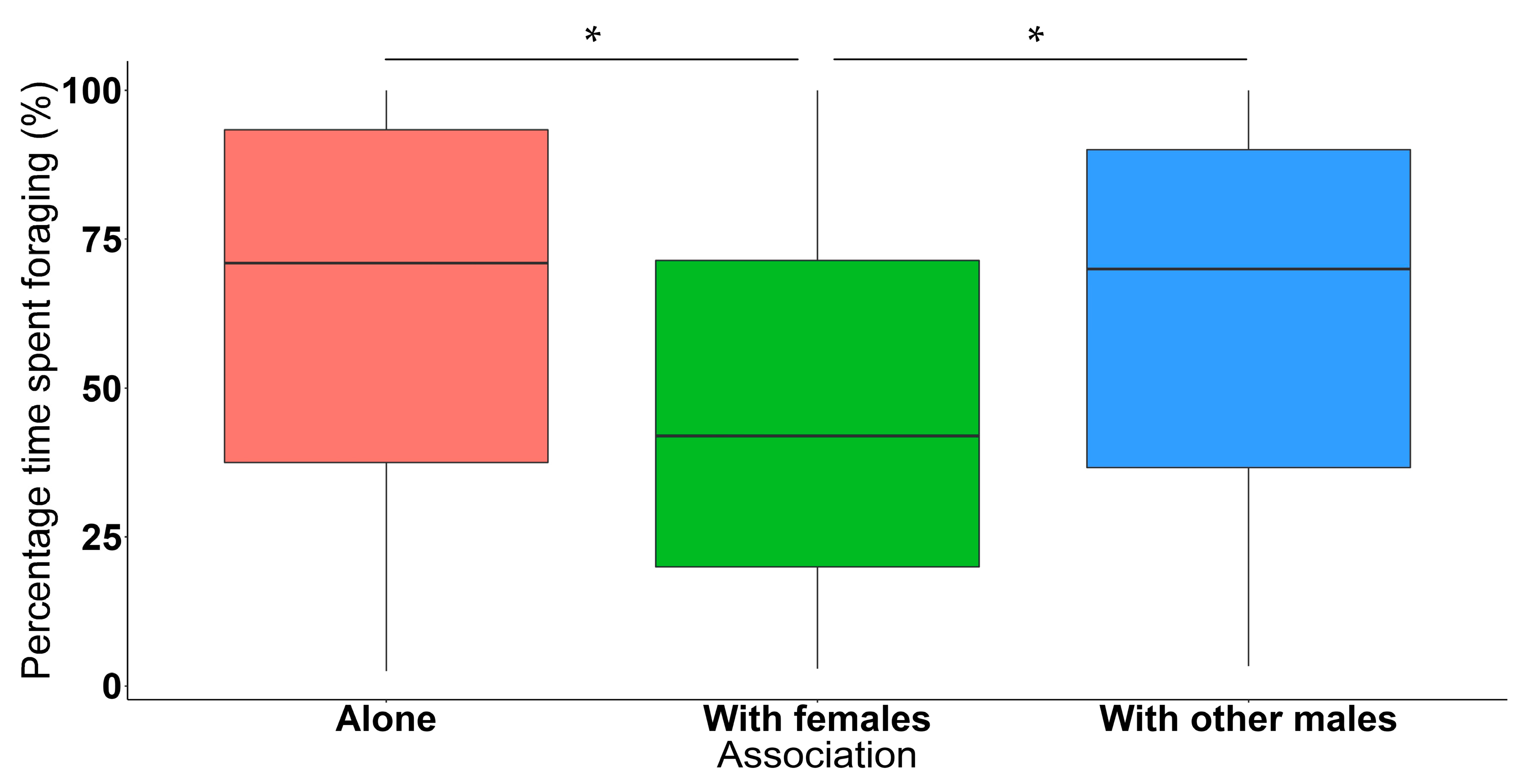
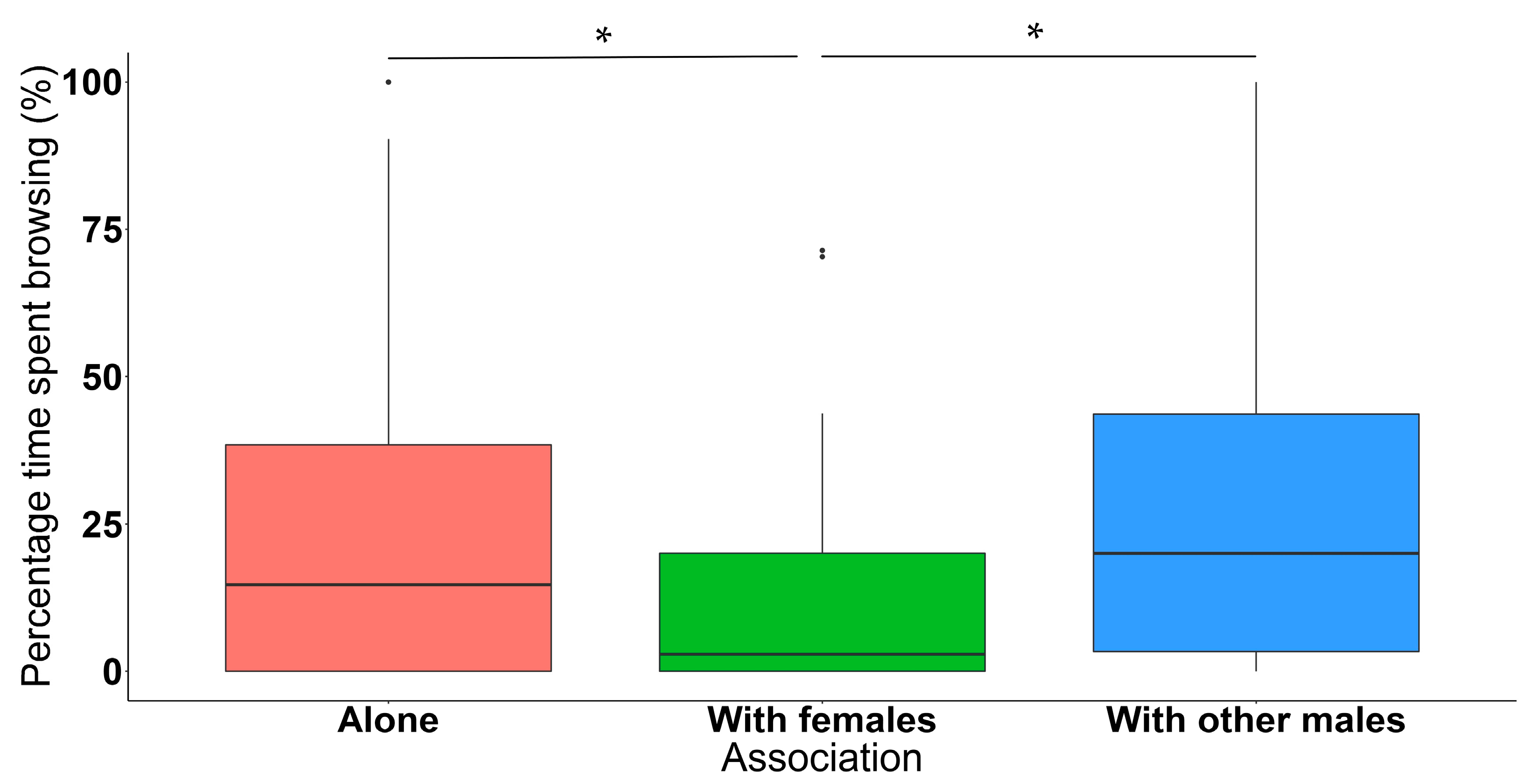
3.2. Association
3.3. Presence or Absence of Musth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pyke, G.H.; Pulliam, H.R.; Charnov, E.L. Optimal foraging: A selective review of theory and tests. Q. Rev. Biol. 1977, 52, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olff, H.; Ritchie, M.E. Effects of herbivores on grassland plant diversity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustine, D.J.; McNaughton, S.J. Ungulate effects on the functional species composition of plant communities: Herbivore selectivity and plant tolerance. J. Wildl. Manag. 1998, 62, 1165–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntly, N. Herbivores and the dynamics of communities and ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1991, 22, 477–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.S.; Ritchie, M.E.; Olff, H.; Milchunas, D.G.; Knops, J.M. Herbivore impact on grassland plant diversity depends on habitat productivity and herbivore size. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howe, H.; Brown, J.; Zorn-Arnold, B. A rodent plague on prairie diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, K.A.; O’Hare, M.T.; McDonald, C.; Searle, K.R.; Daunt, F.; Stillman, R.A. Herbivore regulation of plant abundance in aquatic ecosystems. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haynes, G. Elephants (and extinct relatives) as earth-movers and ecosystem engineers. Geomorphology 2012, 157, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laws, R.M. Elephants as agents of habitat and landscape change in East Africa. Oikos 1970, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, N.A.; McBrayer, L.D.; Schulte, B.A. The impact of tree modification by African elephant (Loxodonta africana) on herpetofaunal species richness in northern Tanzania. Afr. J. Ecol. 2011, 49, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabar, H.; Hattas, D.; Du Toit, J.T. Differential effects of defoliation by mopane caterpillars and pruning by African elephants on the regrowth of Colophospermum mopane foliage. J. Trop. Ecol. 2009, 25, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’connor, T.G.; Puttick, J.R.; Hoffman, M.T. Bush encroachment in southern Africa: Changes and causes. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2014, 31, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beer, Y.; Kilian, W.; Versfeld, W.; Van Aarde, R.J. Elephants and low rainfall alter woody vegetation in Etosha National Park, Namibia. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 64, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunney, K.; Bond, W.J.; Henley, M. Seed dispersal kernel of the largest surviving megaherbivore—The African savanna elephant. Biotropica 2017, 49, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, D.H.; Fenton, M.B.; Rautenbach, I.L.; Taylor, R.D.; Cumming, G.S.; Cumming, M.S.; Dunlop, J.M.; Ford, A.G.; Hovorka, M.D.; Johnston, D.S. Elephants, woodlands and biodiversity in southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1997, 93, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, H.; Duncan, P.; Gordon, I.J.; Illius, A.W. Megaherbivores influence trophic guilds structure in African ungulate communities. Oecologia 2002, 131, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen-Smith, R.N. Megaherbivores: The Influence of Very Large Body Size on Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Belovsky, G.E.; Schmitz, O.J. Plant defenses and optimal foraging by mammalian herbivores. J. Mammal. 1994, 75, 816–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaille-James, S.; Fritz, H.; Murindagomo, F. Climate-driven fluctuations in surface-water availability and the buffering role of artificial pumping in an African savanna: Potential implication for herbivore dynamics. Austral. Ecol. 2007, 32, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beest, F.M.; Rivrud, I.M.; Loe, L.E.; Milner, J.M.; Mysterud, A. What determines variation in home range size across spatiotemporal scales in a large browsing herbivore? J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, W.C.; Jolles, A.E.; Owen-Smith, N. Alternating sexual segregation during the mating season by male African buffalo (Syncerus caffer). J. Zool. 2005, 267, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codron, J.; Codron, D.; Lee-Thorp, J.A.; Sponheimer, M.; Kirkman, K.; Duffy, K.J.; Sealy, J. Landscape-scale feeding patterns of African elephant inferred from carbon isotope analysis of feces. Oecologia 2011, 165, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codron, J.; Lee-Thorp, J.A.; Sponheimer, M.; Codron, D.; Grant, R.C.; de Ruiter, D.J. Elephant (Loxodonta africana) diets in Kruger National Park, South Africa: Spatial and landscape differences. J. Mammal. 2006, 87, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, M.; Hoetmer, A.J.; Pretorius, Y.; de Boer, W.F.; de Knegt, H.; Grant, C.; Kohi, E.; Page, B.; Peel, M.; Slotow, R. Seasonal diet changes in elephant and impala in mopane woodland. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2012, 58, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baskaran, N.; Balasubramanian, M.; Swaminathan, S.; Desai, A.A. Feeding ecology of the Asian elephant Elephas maximus Linnaeus in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, southern India. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 2010, 107, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, P. Diurnal activity patterns of elephant in the Sengwa area, Rhodesia. Afr. J. Ecol. 1976, 14, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemera, M. Dry season diurnal activity of elephants in Lake Manyara National Park, Tanzania. Afr. J. Ecol. 1987, 25, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, G.; Page, B.R.; Duffy, K.J.; Slotow, R. The role of foraging behaviour in the sexual segregation of the African elephant. Oecologia 2006, 150, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, C.; Poole, J. Relationships and social structure of African elephants. Primate Soc. Relatsh. Integr. Approach 1983, 315, 325. [Google Scholar]
- Wittemyer, G.; Okello, J.B.; Rasmussen, H.B.; Arctander, P.; Nyakaana, S.; Douglas-Hamilton, I.; Siegismund, H.R. Where sociality and relatedness diverge: The genetic basis for hierarchical social organization in African elephants. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiyo, P.I.; Archie, E.A.; Hollister-Smith, J.A.; Lee, P.C.; Poole, J.H.; Moss, C.J.; Alberts, S.C. Association patterns of African elephants in all-male groups: The role of age and genetic relatedness. Anim. Behav. 2011, 81, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croze, H. The Seronera bull problem: The elephants. Afr. J. Ecol. 1974, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.E.; Harris, S. Adolescence in male African elephants, Loxodonta africana, and the importance of sociality. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaDue, C.A.; Schulte, B.A.; Kiso, W.K.; Freeman, E.W. Musth and sexual selection in elephants: A review of signalling properties and potential fitness consequences. Behaviour 2021, 1, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.H. Musth and Male-Male Competition in the African Elephant; University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Martin, A. Role of musth in the reproductive strategy of the African elephant (Loxodonta africana). S. Afr. J. Sci. 1987, 83, 616–620. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, J.H. Rutting behavior in African elephants: The phenomenon of musth. Behaviour 1987, 102, 283–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, H.B.; Okello, J.; Wittemyer, G.; Siegismund, H.R.; Arctander, P.; Vollrath, F.; Douglas-Hamilton, I. Age and tactic-related paternity success in male African elephants. Behav. Ecol. 2008, 19, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.H. Announcing intent: The aggressive state of musth in African elephants. Anim. Behav. 1989, 37, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganswindt, A.; Muenscher, S.; Henley, M.; Henley, S.; Heistermann, M.; Palme, R.; Thompson, P.; Bertschinger, H. Endocrine correlates of musth and the impact of ecological and social factors in free-ranging African elephants (Loxodonta africana). Horm. Behav. 2010, 57, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabunda, D.; Pienaar, D.J.; Verhoef, J. The Kruger National Park: A century of management and research. In The Kruger Experience: Ecology and Management of Savanna Heterogeneity; du Toit, J., Rogers, K., Biggs, H., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Smith, N.; Kerley, G.; Page, B.; Slotow, R.; Van Aarde, R. A scientific perspective on the management of elephants in the Kruger National Park and elsewhere: Elephant conservation. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2006, 102, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Van Aarde, R.; Whyte, I.; Pimm, S. Culling and the dynamics of the Kruger National Park African elephant population. In Animal Conservation Forum; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Kerley, G.I.H.; Landman, M.; Kruger, L.; Owen-Smith, N.; Balfour, D.; de Boer, W.F.; Gaylard, A.; Lindsay, K.; Slotow, R. Effects of elephants on ecosystems and biodiversity. In Elephant Management; A Scientific Assessment for South Africa; Scholes, R.J., Mennell, K.G., Eds.; Wits University Press: Pretoria, South Africa, 2008; pp. 146–205. [Google Scholar]
- Whyte, I. History of the KNP elephant culling policies. In Elephant Effects on Biodiversity: An Assessment of Current Knowledge and Understanding as a Basis for Elephant Management in SANParks. A Compilation of Contributions by the Scientific Community for SANParks Scientific Report; South African National Parks: Skukuza, South Africa, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Slotow, R.; Whyte, I.; Hofmeyr, M.; Kerley, G.H.I.; Conway, T.; Scholes, R.J. Lethal management of elephants. In Elephant management; A Scientific Assessment for South Africa; Scholes, R.J., Mennell, K.G., Eds.; Wits University Press: Pretoria, South Africa, 2008; pp. 370–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.M.; Greaver, C.; Simms, C. Elephant population growth in Kruger National Park, South Africa, under a landscape management approach. Koedoe Afr. Prot. Area Conserv. Sci. 2017, 59, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Aarde, R.; Jackson, T.; Ferreira, S. Conservation science and elephant management in southern Africa: Elephant conservation. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2006, 102, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Gertenbach, W.D. Landscapes of the Kruger national park. Koedoe 1983, 26, 9–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, F.; Scholes, R.; Eckhardt, H. The abiotic template and its associated vegetation pattern. Kruger Exp. Ecol. Manag. Savanna Heterogeneity 2003, 21, 83–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ganswindt, A.; Münscher, S.; Henley, M.; Palme, R.; Thompson, P.; Bertschinger, H. Concentrations of faecal glucocorticoid metabolites in physically injured free-ranging African elephants Loxodonta africana. Wildl. Biol. 2010, 16, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altmann, J. Observational study of behavior: Sampling methods. Behaviour 1974, 49, 227–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolker, B.M.; Brooks, M.E.; Clark, C.J.; Geange, S.W.; Poulsen, J.R.; Stevens, M.H.H.; White, J.-S.S. Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawley, M. The R Book; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Ripley, B.; Venables, B.; Bates, D.M.; Hornik, K.; Gebhardt, A.; Firth, D.; Ripley, M.B. Package mass. Cran R 2013, 538, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. Rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. R Package Version 0.4.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rstatix/index(2020) (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S.; Adler, D.; Bates, D.; Baud-Bovy, G.; Ellison, S.; Firth, D.; Friendly, M.; Gorjanc, G.; Graves, S. Package ‘Car’; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Thaker, M.; Gupte, P.R.; Prins, H.H.; Slotow, R.; Vanak, A.T. Fine-scale tracking of ambient temperature and movement reveals shuttling behavior of elephants to water. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt-Nielsen, K.; Knut, S.-N. Scaling: Why Is Animal Size So Important? Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mole, M.A.; Rodrigues DÁraujo, S.; Van Aarde, R.J.; Mitchell, D.; Fuller, A. Coping with heat: Behavioural and physiological responses of savanna elephants in their natural habitat. Conserv. Physiol. 2016, 4, cow044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillip, P.; Heath, J. Heat exchange by the pinna of the African elephant. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1992, 101, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folland, C.K.; Karl, T.R.; Jim Salinger, M. Observed climate variability and change. Weather 2002, 57, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.H.; Brivio, F.; Stephens, P.A.; Apollonio, M.; Grignolio, S. The behavioral trade-off between thermoregulation and foraging in a heat-sensitive species. Behav. Ecol. 2017, 28, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, J.; Eltringham, S. The daily activity of the elephant in the Rwenzori National Park, Uganda. Afr. J. Ecol. 1974, 12, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E.; Wittemyer, G.; Rasmussen, H.B.; Vollrath, F.; Cerling, C.E.; Robinson, T.J.; Douglas-Hamilton, I. Stable isotopes in elephant hair document migration patterns and diet changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beekman, J.; Prins, H. Feeding strategies of sedentary large herbivores in East Africa, with emphasis on the African buffalo, Syncerus coffer. Afr. J. Ecol. 1989, 27, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.M.; Owen-Smith, N. Condensed tannins deter feeding by browsing ruminants in a South African savanna. Oecologia 1985, 67, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.J.; Jung, H.-J.G. Lignin and fiber digestion. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. J. Range Manag. Arch. 2001, 54, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D. Histological and physical factors affecting digestibility of forages. Agron. J. 1989, 81, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.H. Mate guarding, reproductive success and female choice in African elephants. Anim. Behav. 1989, 37, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiyo, P.I.; Wilson, J.W.; Archie, E.A.; Lee, P.C.; Moss, C.J.; Alberts, S.C. The influence of forage, protected areas, and mating prospects on grouping patterns of male elephants. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 25, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colaço, B.; Pinto, A.; Stelvig, M.; Costa, C.; Colaço, J. Influence of male presence on female Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) behaviour in captivity. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2020, 8, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hufenus, R.; Schiffmann, C.; Hatt, J.M.; Müller, D.W.; Lackey, L.B.; Clauss, M.; Zerbe, P. Seasonality of reproduction in Asian elephants Elephas maximus and African elephants Loxodonta africana: Underlying photoperiodic cueing? Mammal. Rev. 2018, 48, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittemyer, G.; Barner Rasmussen, H.; Douglas-Hamilton, I. Breeding phenology in relation to NDVI variability in free-ranging African elephant. Ecography 2007, 30, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, D. Musth in elephants. Zoos Print J. 2000, 15, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Individual | Total Observation Time per Individual (h) | Number of Sampling Sessions per Individual | Average Sampling Session per Individual (min) | Maximum Time Spent Observing Each Individual (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bull 1 | 27.8 | 45 | 37.1 | 173.0 |
| Bull 2 | 39.1 | 76 | 30.9 | 67.0 |
| Bull 3 | 40.0 | 78 | 30.7 | 66.0 |
| Bull 4 | 36.9 | 68 | 32.5 | 54.0 |
| Bull 5 | 36.8 | 62 | 35.6 | 91.0 |
| Bull 6 | 52.9 | 99 | 32.0 | 104.0 |
| Category Recorded | Number of Observations |
|---|---|
| Time of day—before noon (05h00–12h00) | 297 |
| Time of day—after noon (12h01–18h00) | 131 |
| Wet season | 224 |
| Dry season | 204 |
| Association—alone | 233 |
| Association—with other males only | 170 |
| Association—with females | 25 |
| In musth | 101 |
| Non musth | 327 |
| Model | Estimated Autocorrelation Value (ACF) |
|---|---|
| Foraging ~ Time of day + Season + Association + Musth * | 0.087 |
| Resting ~ Time of day + Season + Association + Musth * | 0.107 |
| Grazing ~ Time of day + Season + Association + Musth * | 0.304 |
| Browsing ~ Time of day + Season + Association + Musth * | 0.178 |
| 1 Foraging ~ Time spent grazing versus browsing (wet season) * | 0.344 |
| 1 Foraging ~ Time spent grazing versus browsing (dry season) * | 0.137 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
du Plessis, K.; Ganswindt, S.B.; Bertschinger, H.; Crossey, B.; Henley, M.D.; Ramahlo, M.; Ganswindt, A. Social and Seasonal Factors Contribute to Shifts in Male African Elephant (Loxodonta africana) Foraging and Activity Patterns in Kruger National Park, South Africa. Animals 2021, 11, 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113070
du Plessis K, Ganswindt SB, Bertschinger H, Crossey B, Henley MD, Ramahlo M, Ganswindt A. Social and Seasonal Factors Contribute to Shifts in Male African Elephant (Loxodonta africana) Foraging and Activity Patterns in Kruger National Park, South Africa. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113070
Chicago/Turabian Styledu Plessis, Kara, Stefanie Birgit Ganswindt, Henk Bertschinger, Bruce Crossey, Michelle Deborah Henley, Mmatsawela Ramahlo, and André Ganswindt. 2021. "Social and Seasonal Factors Contribute to Shifts in Male African Elephant (Loxodonta africana) Foraging and Activity Patterns in Kruger National Park, South Africa" Animals 11, no. 11: 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113070
APA Styledu Plessis, K., Ganswindt, S. B., Bertschinger, H., Crossey, B., Henley, M. D., Ramahlo, M., & Ganswindt, A. (2021). Social and Seasonal Factors Contribute to Shifts in Male African Elephant (Loxodonta africana) Foraging and Activity Patterns in Kruger National Park, South Africa. Animals, 11(11), 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113070









