Impacts of Rumen Degradable or Undegradable Protein Supplementation with or without Salt on Nutrient Digestion, and VFA Concentrations
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Intake and Digestibility
3.2. Rumen Dynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DelCurto, T.; Hess, B.; Huston, J.; Olson, K. Optimum supplementation strategies for beef cattle consuming low-quality roughages. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 77, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisemann, J.; Galyean, M.; Beauchemin, K.; Krehbiel, C.; Tedeschi, L. 1024 The eighth revised edition of the Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle: Protein and metabolic modifiers. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, H.; Cochran, R.; Titgemeyer, E.; Vanzant, E.; Abdelgadir, I.; St-Jean, G. Effect of increasing degradable intake protein on intake and digestion of low-quality, tallgrass-prairie forage by beef cows. J. Anim. Sci. 1996, 74, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickersham, T.; Titgemeyer, E.; Cochran, R.; Wickersham, E.; Gnad, D. Effect of rumen-degradable intake protein supplementation on urea kinetics and microbial use of recycled urea in steers consuming low-quality forage. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.; Hibberd, C. Incremental levels of supplemental ruminal degradable protein for beef cows fed low quality native grass hay. Anim. Sci. Res. Rep. 1990, 57–63. Available online: http://beefextension.okstate.edu/research_reports/1990rr/90_11.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Van Soest, P.J. Nutritional Ecology of the Ruminant; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Millen, D.D.; Arrigoni, M.D.B.; Pacheco, R.D.L. Rumenology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, L.; Paterson, J.; Ansotegui, R.; Cecava, M.; Schmutz, W. The effects of degradable and undegradable intake protein on the performance of lactating first-calf heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pina, D.; Valadares Filho, S.; Tedeschi, L.; Barbosa, A.; Valadares, R. Influence of different levels of concentrate and ruminally undegraded protein on digestive variables in beef heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sletmoen-Olson, K.; Caton, J.; Olson, K.; Reynolds, L. Undegraded intake protein supplementation: I. Effects on forage utilization and performance of periparturient beef cows fed low-quality hay. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 78, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schauer, C.; Lardy, G.; Slanger, W.; Bauer, M.; Sedivec, K. Self-limiting supplements fed to cattle grazing native mixed-grass prairie in the northern Great Plains. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohnert, D.; Schauer, C.; DelCurto, T. Influence of rumen protein degradability and supplementation frequency on performance and nitrogen use in ruminants consuming low-quality forage: Cow performance and efficiency of nitrogen use in wethers. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udén, P.; Colucci, P.E.; Van Soest, P.J. Agriculture. Investigation of chromium, cerium and cobalt as markers in digesta. Rate of passage studies. J. Sci. Food. 1980, 31, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raun, N.S.; Burroughs, W. Suction strainer technique in obtaining rumen fluid samples from intact lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 1962, 21, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Colorimetric Determination of Urea Nitrogen; Sigma Technical Bulletin #640; Sigma Chemical Co.: St. Louis, MO, USA.
- Chaney, A.L.; Marbach, E.P. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin. Chem. 1962, 8, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, D.; Squire, C.R. An improved method for the estimation of ammonia in blood plasma. J. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1967, 17, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, T.E.; Hagerty, J.C.; Mark, H.B. Reaction rate method for ammonia and blood urea nitrogen utilizing a pentacyanonitrosylferrate catalyzed Berthelot reaction. Anal. Chem. 1969, 41, 848–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgardt, B.R. Practical Observations on the Quantitative Analysis of Free Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA) in Aqueous Solutions by Gas-Liquid Chromatography; Department of Dairy Science, University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Supleco Inc. GC Separation of VFA C2-C5; Bulletin 749E; Supleco Inc.: Bellefonte, PA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, F. Measurement of Protein and Fat Accretion in Growing Beef Cattle through Isotope Dilution Procedures. Prog. Rep. Ohio Agr. Anim. Sci. Ser. 1979, 79, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, J.S.; Schenk, G.H. Quantitative Analytical Chemistry; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, A.; Stacy, B. The fate of water in the rumen: 1. A critical appraisal of the use of soluble markers. Brit. J. Nutr. 1968, 22, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- White, H.C.; Van Emon, M.L.; DelCurto-Wyffels, H.M.; Wyffels, S.A.; DelCurto, T. Impacts of form of salt-limited supplement on supplement intake behavior and performance with yearling heifers grazing dryland pastures. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2019, 3, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyffels, S.A. Dormant Season Grazing of Northern Mixed Grass Prairies: Effect of Supplementation and Winter Environmental Conditions on Beef Cattle Grazing Behavior, Residual Vegetation Conditions and Variation in Supplement Intake. Ph.D. Thesis, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- McClain, T.P.; Wyffels, S.A.; Larsen, S.R.; Müller, A.L.; Davis, N.G.; Carter, B.H.; Bowman, J.G.; Boss, D.L.; DelCurto, T. Supplement intake variation, weight, and body condition change in yearling heifers grazing late-summer dryland pastures with Rumax BoviBox vs. Rumax BoviBox HM protein supplements. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2020, 4, S155–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Toone, C.; Ludden, P. Effects of supplemental ruminally degradable protein versus increasing amounts of supplemental ruminally undegradable protein on site and extent of digestion and ruminal characteristics in lambs fed low-quality forage. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 3322–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.C.; Davis, N.G.; Van Emon, M.L.; Wyffels, S.A.; DelCurto, T. Impacts of increasing levels of salt on intake, digestion, and rumen fermentation with beef cattle consuming low-quality forages. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2019, 3, 1818–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croom, W.J., Jr.; Harvey, R.; Froetschel, M.; Linnerud, A. High levels of sodium chloride in beef cattle diets. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1982, 62, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.; Croom, W.J.; Pond, K.; Hogarth, B.W.; Leonard, E. High levels of sodium chloride in supplements for growing cattle. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1986, 66, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbach, J.R.; Kristensen, N.B.; Donkin, S.S.; Hammon, H.M.; Penner, G.B. Gluconeogenesis in dairy cows: The secret of making sweet milk from sour dough. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, E.; Davidovich, A.; Barr, G.; Griffel, G.; Dayton, A.; Deyoe, C.; Bechtle, R. Ammonia toxicity in cattle. I. Rumen and blood changes associated with toxicity and treatment methods. J. Anim. Sci. 1976, 43, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Sato, S.; Kato, T.; Ikuta, K.; Yamagishi, N.; Okada, K.; Mizuguchi, H.; Ito, K. Relationship between pH and temperature in the ruminal fluid of cows, based on a radio-transmission pH-measurement system. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Item Analyzed | RDP-HF 1 | RDP-SF 1 | RUP-HF 1 | RUP-SF 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter, % | 87.7 | 86.6 | 77.4 | 77.3 |
| Analyzed nutrient composition, % DM basis | ||||
| Crude protein | 37.7 | 37.0 | 27.6 | 27.8 |
| ADICP 2 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 2.5 |
| Soluble protein, % CP | 27 | 15 | 16 | 13 |
| Degradable protein, % CP | 54 | 63 | 35 | 30 |
| Acid detergent fiber | 18.7 | 5.5 | 8.1 | 6.4 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | 30.1 | 8.8 | 11.7 | 8.8 |
| Lignin | 7.6 | 1.1 | 3.4 | 2.6 |
| Non-fiber carbohydrates | 21.4 | 22.1 | 16.4 | 16.6 |
| Starch | 3.0 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 2.5 |
| Crude fat | 3.64 | 1.17 | 7.42 | 7.20 |
| Ash | 14.91 | 28.0 | 35.0 | 35.3 |
| Total digestible nutrients | 68.0 | 60.0 | 57.0 | 57.0 |
| Macrominerals composition, % DM basis | ||||
| Calcium | 2.68 | 2.77 | 2.07 | 1.98 |
| Phosphorus | 1.52 | 1.91 | 2.25 | 2.04 |
| Magnesium | 0.62 | 0.80 | 3.10 | 2.96 |
| Potassium | 1.34 | 2.5 | 2.10 | 1.84 |
| Sodium | 0.26 | 4.30 | 5.84 | 6.15 |
| Sulfur | 0.85 | 0.73 | 1.49 | 1.23 |
| Microminerals composition, mg kg−1 | ||||
| Iron | 485 | 1060 | 1000 | 852 |
| Zinc | 680 | 1300 | 1460 | 1530 |
| Copper | 216 | 222 | 788 | 848 |
| Manganese | 303 | 726 | 1000 | 1060 |
| Molybdenum | 1.3 | 8.1 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Item Analyzed | |
|---|---|
| Dry matter, % | 85.16 |
| Analyzed nutrient composition, % DM basis | |
| Crude protein | 7.21 |
| Total digestible nutrients | 57.58 |
| Acid detergent insoluble crude protein | 1.07 |
| Soluble protein | 39.94 |
| Acid detergent fiber | 31.23 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | 61.01 |
| Lignin | 7.13 |
| Fat | 1.99 |
| Ash | 7.22 |
| NDFD 1, % NDF | 40.8 |
| uNDF240h 2, % NDF | 38.1 |
| Macromineral composition, % DM basis | |
| Calcium | 0.26 |
| Phosphorus | 0.14 |
| Magnesium | 0.16 |
| Potassium | 1.62 |
| Sodium | 0.03 |
| Chloride | 0.44 |
| Sulfur | 0.12 |
| Item | RDP 1 | RUP 1 | SEM 3 | p-Value 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF 2 | SF 2 | HF | SF | D | P | D × P | ||
| Dry matter intake, kg d−1 | 11.61 | 13.25 | 12.11 | 12.91 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 0.56 | 0.49 |
| Dry matter intake, g kg BW−1 d−1 | 21.53 | 24.75 | 22.54 | 24.54 | 1.82 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 0.74 |
| Supplement intake, kg d−1 | 0.83 | 2.34 | 0.76 | 1.40 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 0.24 |
| Supplement intake, g kg BW−1 d−1 | 1.54 | 3.91 | 1.41 | 2.20 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.82 |
| Forage intake, kg d−1 | 10.78 | 10.91 | 11.35 | 11.52 | 0.60 | 0.89 | 0.52 | 0.97 |
| Forage intake, g kg BW−1 d−1 | 19.98 | 20.24 | 21.11 | 21.72 | 1.27 | 0.89 | 0.54 | 0.89 |
| NDF intake, kg d−1 | 6.63 | 7.81 | 6.89 | 7.32 | 0.37 | 0.04 | 0.63 | 0.33 |
| Dry matter digestibility, % | 49.10 | 51.17 | 51.37 | 48.05 | 1.44 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.08 |
| NDF digestibility, % | 42.03 a | 50.27 b | 46.86 ab | 43.11 ab | 2.61 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.04 |
| Water intake, L d−1 | 48.38 a | 72.60 b | 52.61 ab | 52.81 ab | 4.87 | <0.01 | 0.55 | 0.03 |
| uNDF Fill, kg | 4.47 | 5.11 | 4.89 | 4.12 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.54 | 0.15 |
| uNDF Fill, g kg BW−1 | 8.22 | 9.29 | 9.28 | 7.7 | 0.90 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.15 |
| uNDF Retention, h | 62.98 | 73.7 | 68.34 | 56.52 | 6.82 | 0.29 | 0.59 | 0.12 |
| uNDF Passage, % h−1 | 1.64 | 1.42 | 1.49 | 1.84 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.55 | 0.12 |
| Item | RDP 1 | RUP 1 | SEM 3 | p-Value 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF 2 | SF 2 | HF | SF | D | P | D × P | ||
| Fluid flow rate, L h−1 | 1.89 | 2.72 | 2.75 | 2.92 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.18 |
| DM volume, L | 12.09 | 13.53 | 13.69 | 12.23 | 1.19 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.25 |
| Fluid volume, L | 81.06 | 84.77 | 99.14 | 90.92 | 6.31 | 0.69 | 0.07 | 0.36 |
| Item | RDP 1 | RUP 1 | SEM 3 | p-Value 4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF 2 | SF 2 | HF | SF | D | P | H | D × P | D × H | P × H | D × P × H | ||
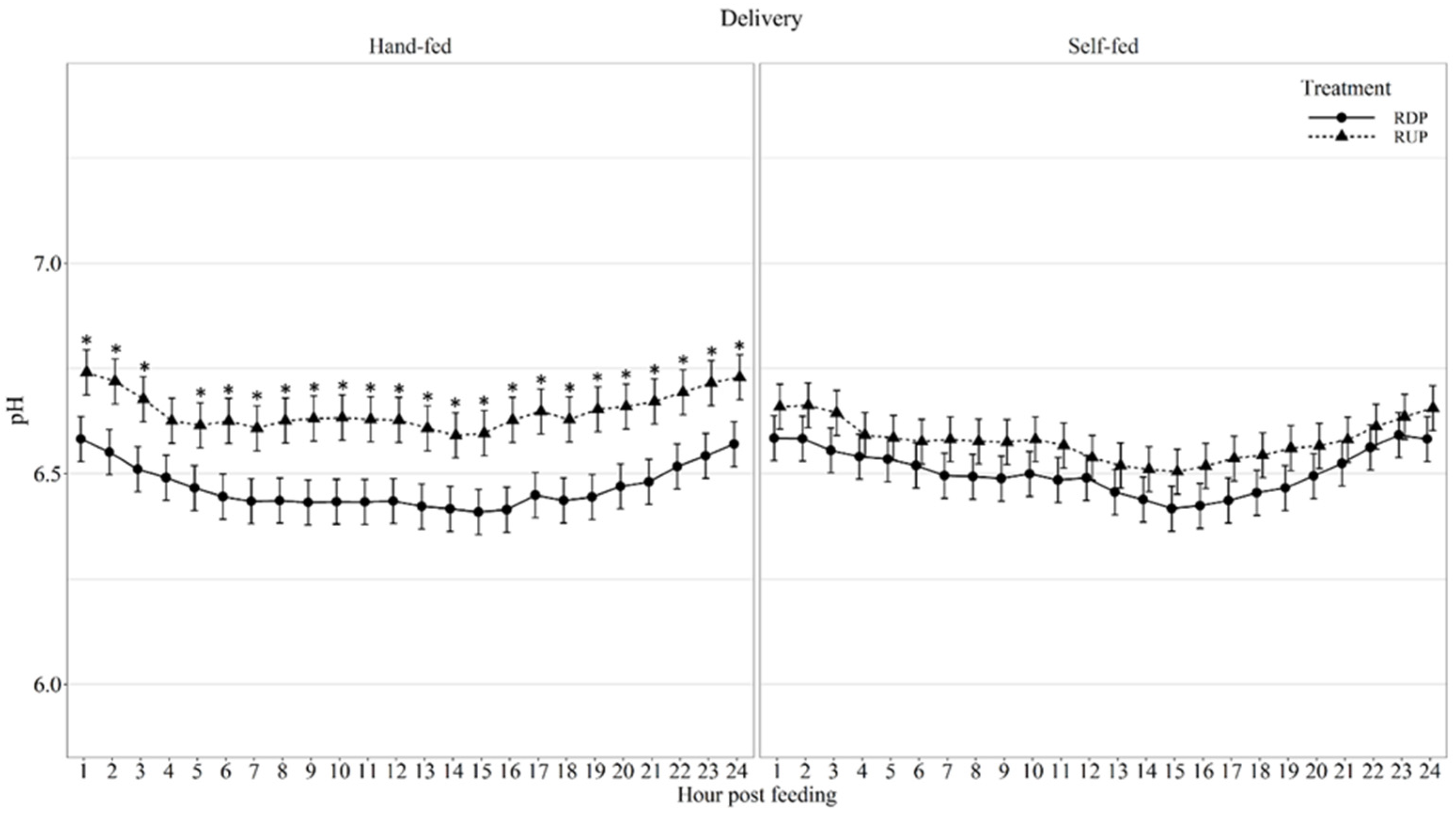
| Average daily ruminal pH | 6.47 | 6.51 | 6.65 | 6.58 | 0.053 | 0.62 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.31 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Average daily ruminal pH CV, % | 1.14 | 1.31 | 0.90 | 1.03 | 0.085 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.40 |
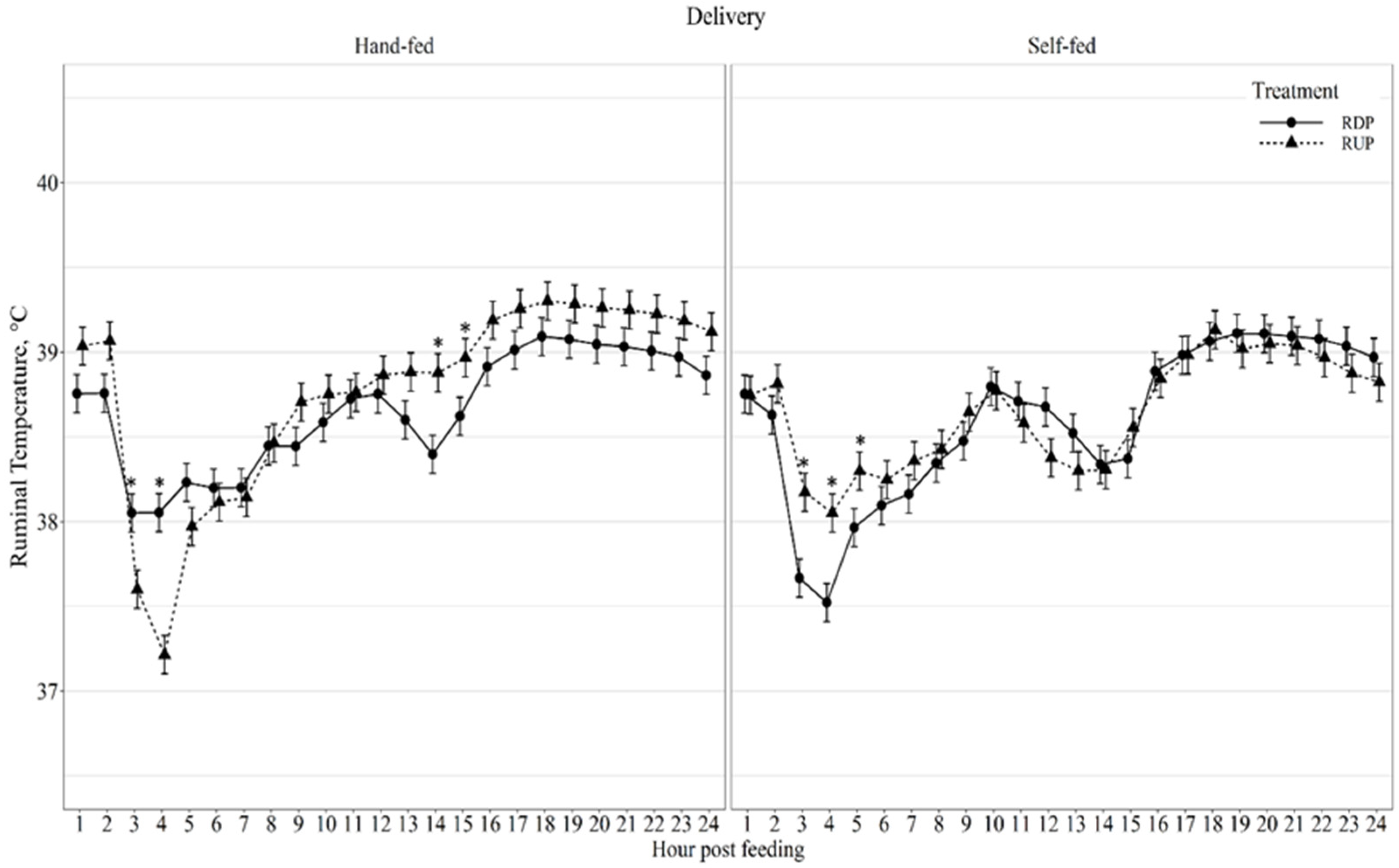
| Average daily ruminal temp., °C | 38.66 | 38.60 | 38.77 | 38.64 | 0.095 | 0.65 | 0.41 | <0.01 | 0.72 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Average daily ruminal temp. CV, % | 2.09 | 2.45 | 2.41 | 2.04 | 0.201 | 0.20 | 0.26 | <0.01 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 0.01 | <0.01 |
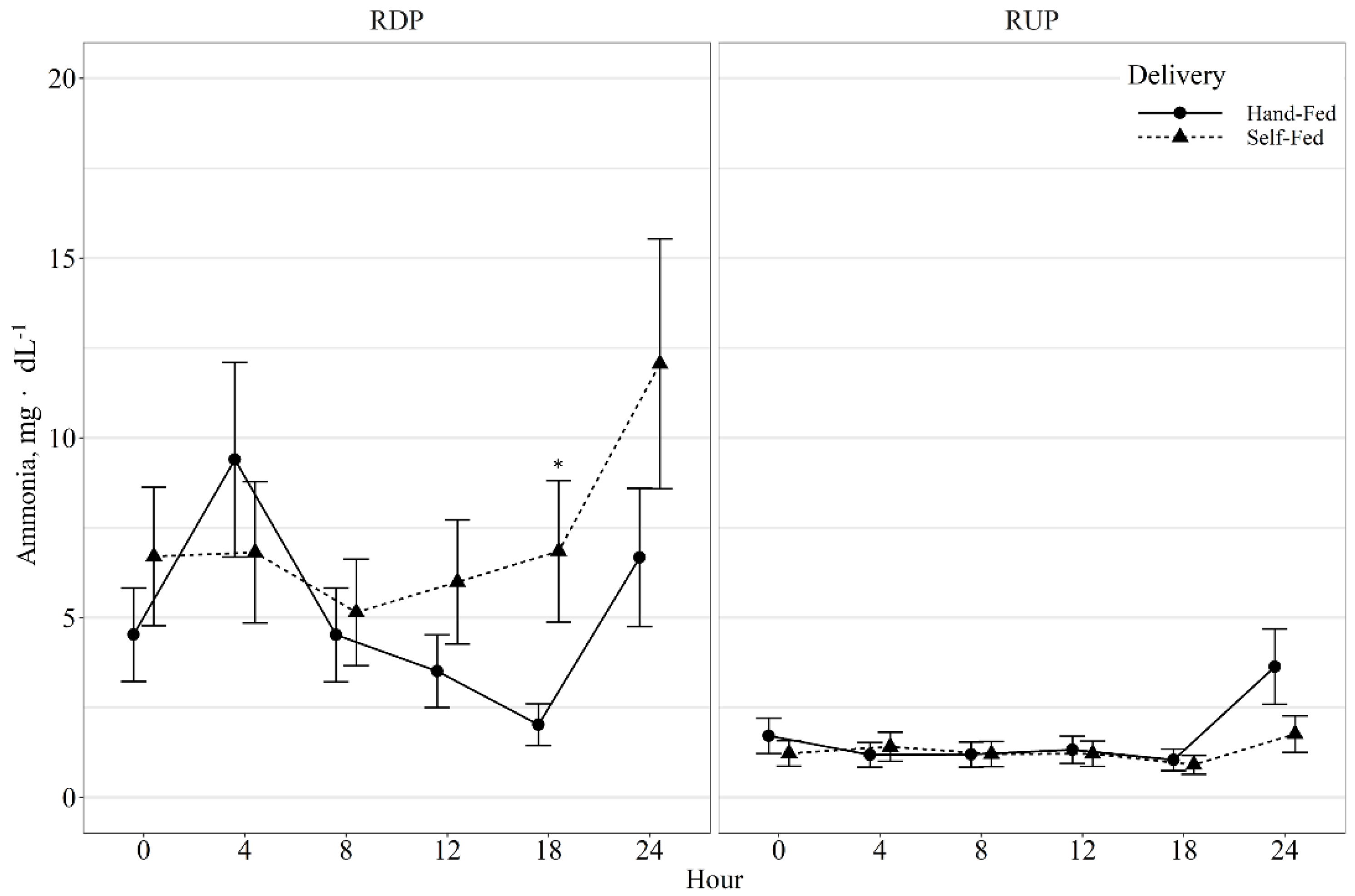
| Ammonia, mg dL−1 | 4.57 | 6.99 | 1.52 | 1.26 | 0.89 | 0.33 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.21 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Volatile fatty acids, mol 100 mol−1 | ||||||||||||
| Acetate | 66.06 | 65.73 | 67.40 | 66.13 | 0.68 | 0.87 | 0.22 | <0.01 | 0.85 | 0.57 | 0.93 | 0.41 |
| Propionate | 18.14 | 17.94 | 17.51 | 18.47 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.44 | <0.01 | 0.32 | 0.96 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
| Isobutyrate | 1.40 | 1.67 | 1.29 | 1.30 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.40 | <0.01 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.80 | 0.17 |
| Butyrate | 9.86 | 9.51 | 10.10 | 10.47 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.90 | <0.01 | 0.32 | 0.63 | 0.59 | 0.71 |
| Isovalerate | 1.69 | 2.38 | 1.40 | 1.27 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.31 | <0.01 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.13 |
| Valerate | 2.03 | 2.12 | 1.84 | 2.02 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.04 | <0.01 | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.73 | 0.17 |
| Acetate:propionate | 3.59 | 3.67 | 3.87 | 3.59 | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.35 | <0.01 | 0.44 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.45 |
| Total VFA, mM | 89.51 | 91.21 | 89.67 | 88.77 | 3.03 | 0.21 | 0.75 | <0.01 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 0.99 | 0.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manoukian, M.; DelCurto, T.; Kluth, J.; Carlisle, T.; Davis, N.; Nack, M.; Wyffels, S.; Scheaffer, A.; Van Emon, M. Impacts of Rumen Degradable or Undegradable Protein Supplementation with or without Salt on Nutrient Digestion, and VFA Concentrations. Animals 2021, 11, 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113011
Manoukian M, DelCurto T, Kluth J, Carlisle T, Davis N, Nack M, Wyffels S, Scheaffer A, Van Emon M. Impacts of Rumen Degradable or Undegradable Protein Supplementation with or without Salt on Nutrient Digestion, and VFA Concentrations. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113011
Chicago/Turabian StyleManoukian, Marley, Timothy DelCurto, Janessa Kluth, Tanner Carlisle, Noah Davis, Makae Nack, Samuel Wyffels, Abe Scheaffer, and Megan Van Emon. 2021. "Impacts of Rumen Degradable or Undegradable Protein Supplementation with or without Salt on Nutrient Digestion, and VFA Concentrations" Animals 11, no. 11: 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113011
APA StyleManoukian, M., DelCurto, T., Kluth, J., Carlisle, T., Davis, N., Nack, M., Wyffels, S., Scheaffer, A., & Van Emon, M. (2021). Impacts of Rumen Degradable or Undegradable Protein Supplementation with or without Salt on Nutrient Digestion, and VFA Concentrations. Animals, 11(11), 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113011






