Changes in Blood Metabolites, Intestinal Microbiota Composition and Gene Expression of 95 Weeks Old Laying Hens Differing in Egg Production and Egg Breaking Strength
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
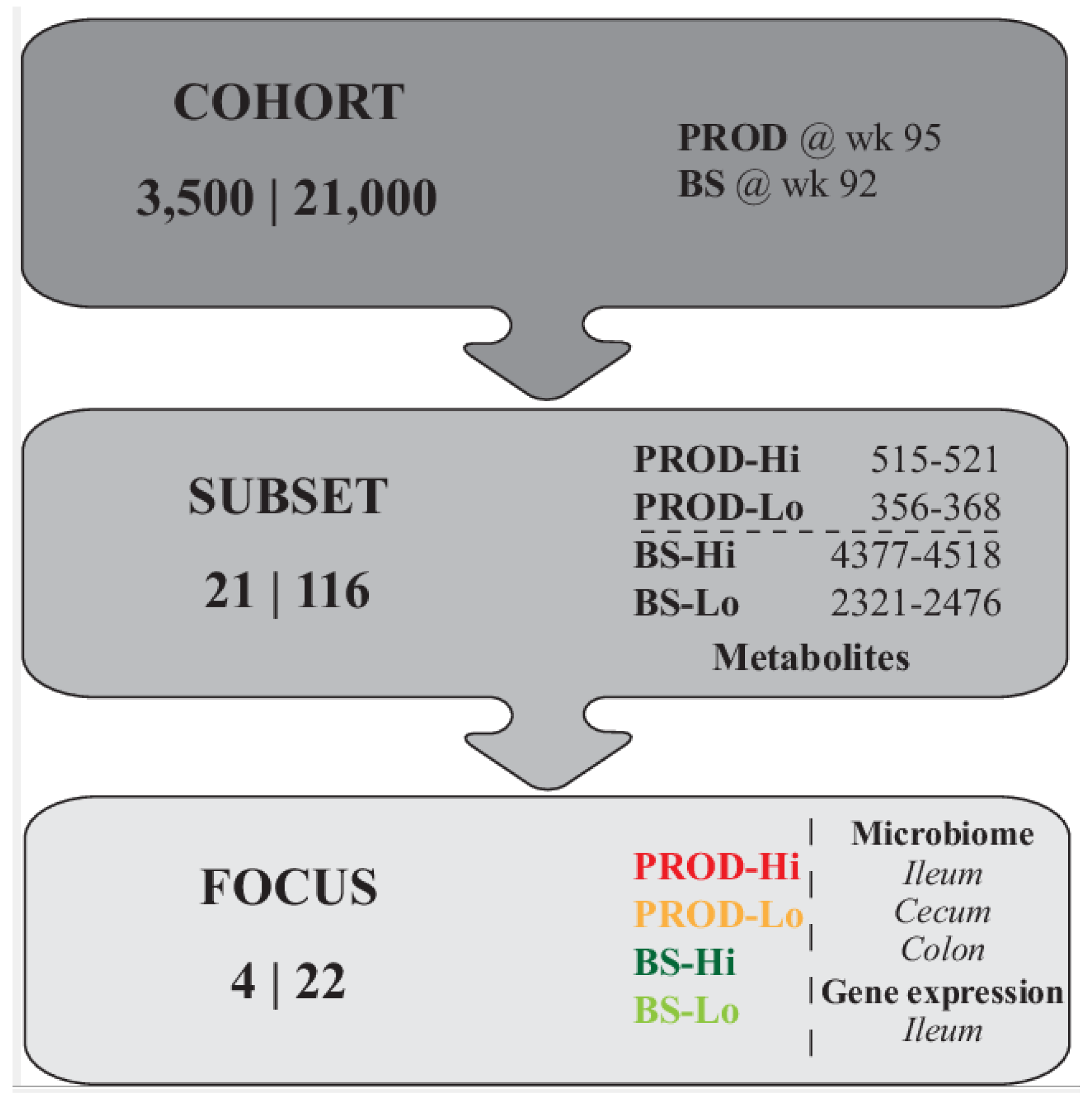
2.2. General Experimental Design
2.3. Hen Housing
2.4. Autopsy
2.5. Blood Samples
2.6. Microbiota: Intestinal Luminal Content Samples
2.7. Ileal Gene Expression
3. Results
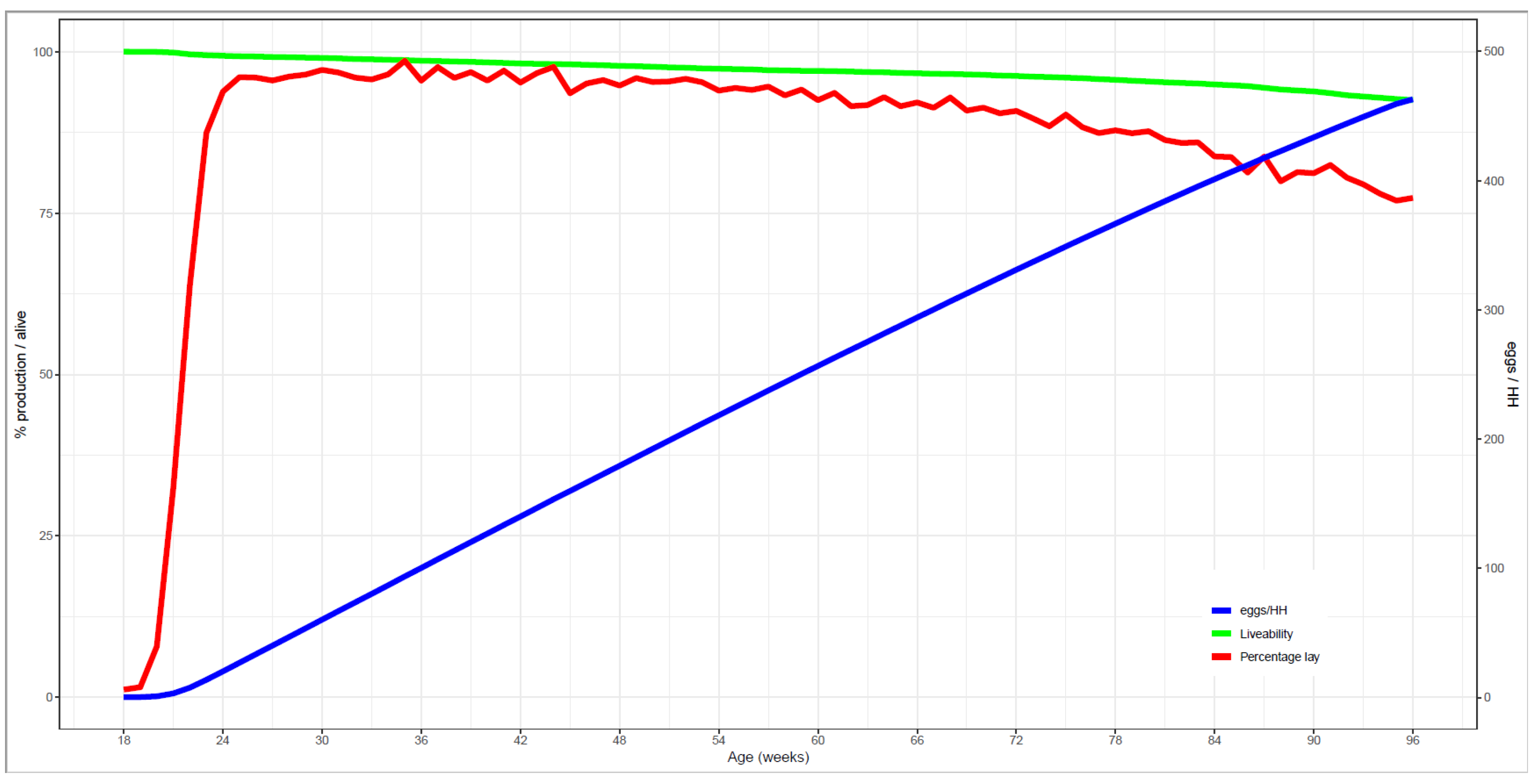
3.1. Flock Performance
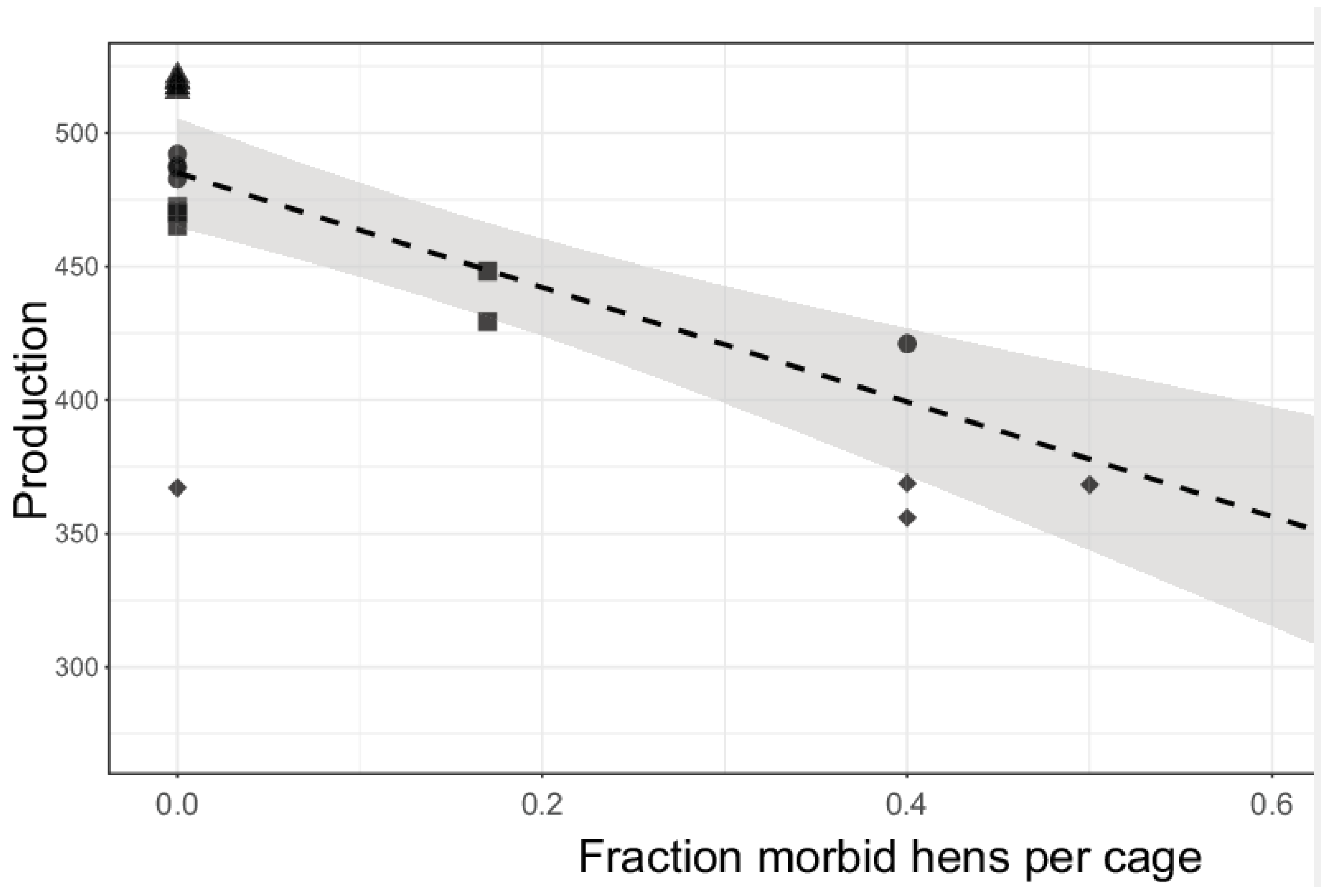
3.2. Pathology, Blood Metabolites, and Intestinal Characteristics (in Subsets of Cages)
3.3. Systemic Level: Blood Metabolites
3.4. Molecular Phenotyping at the Local Intestinal Level
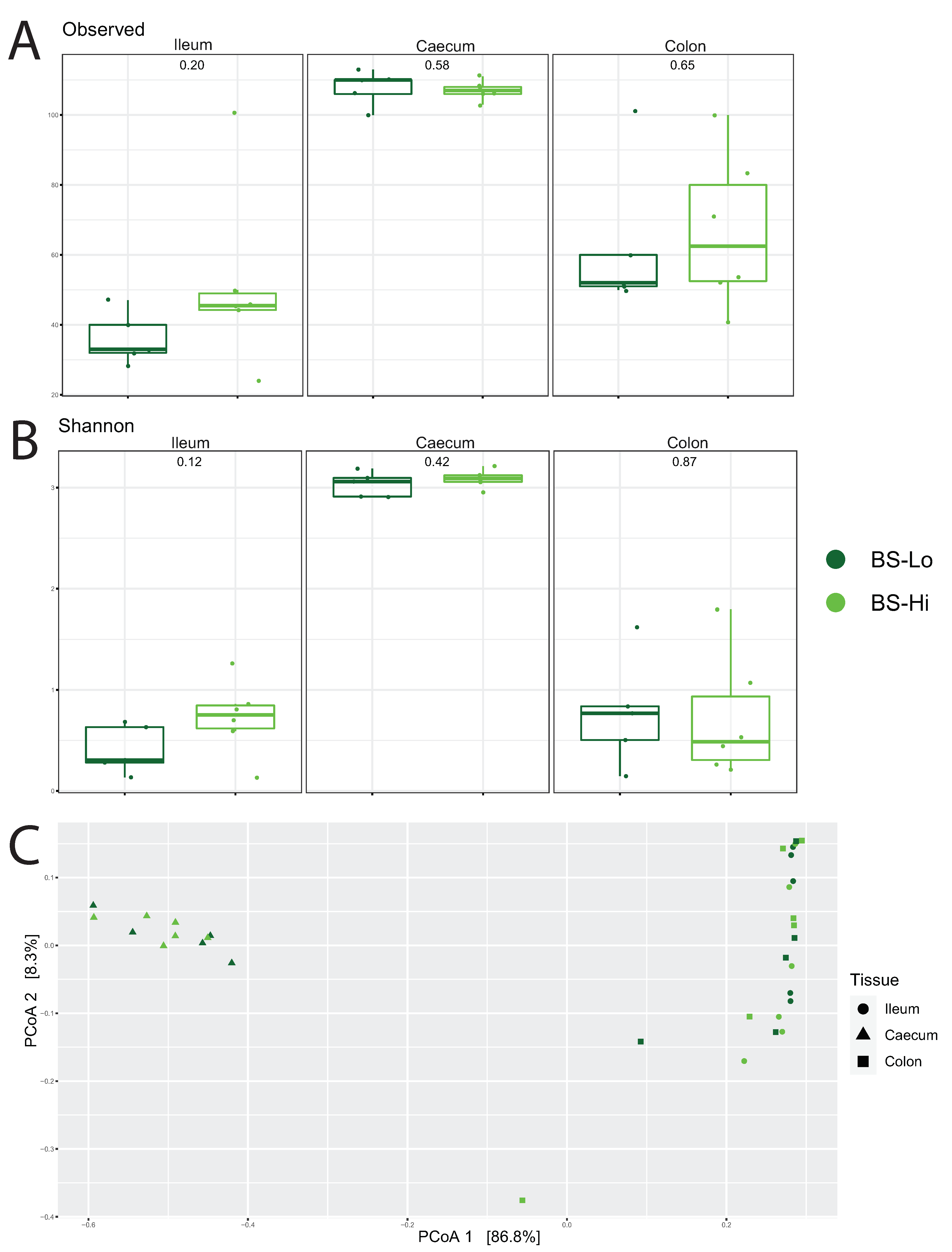
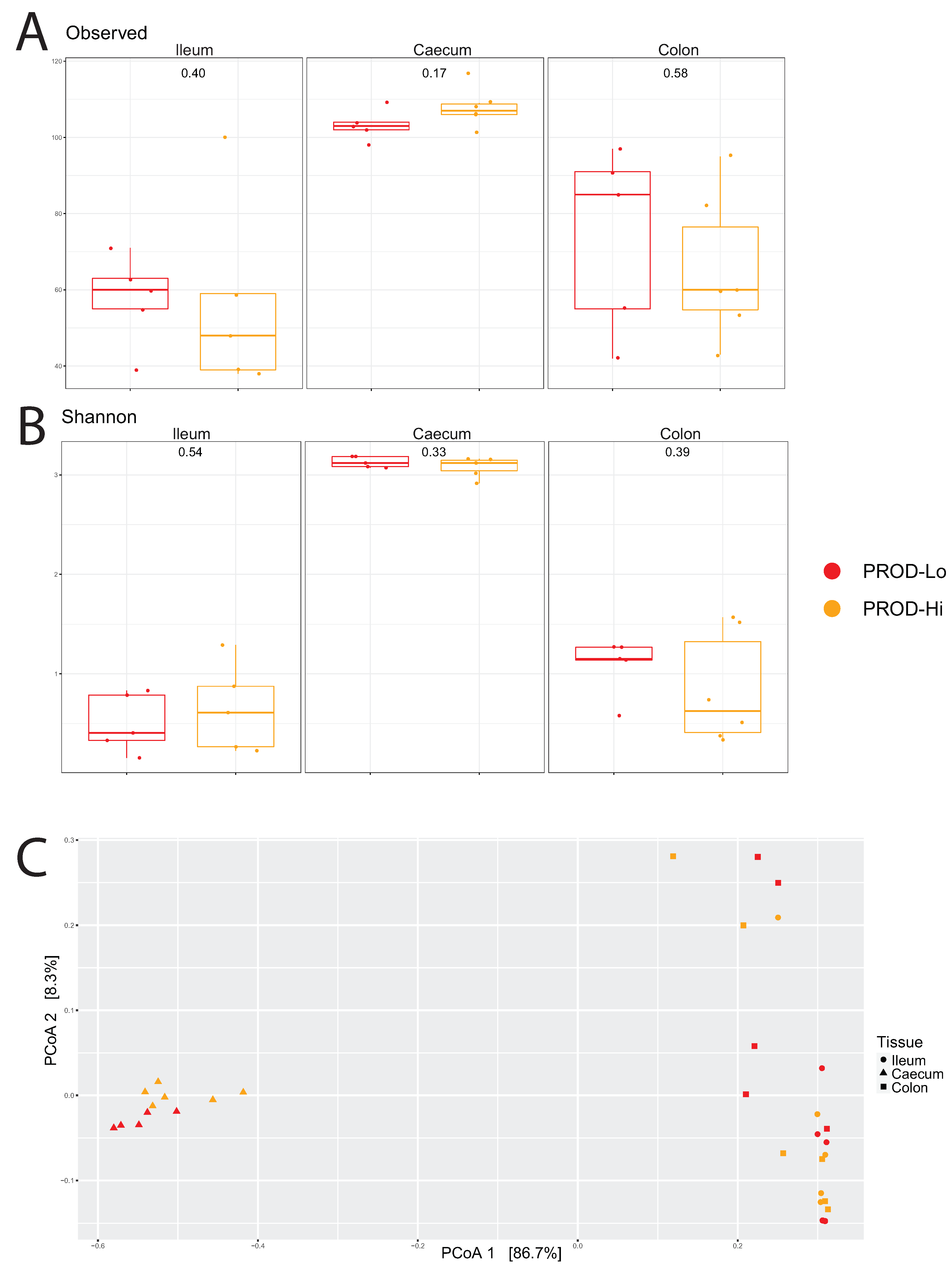
3.4.1. Profiling Microbiota in Different Intestinal Segments
3.4.2. Comparing the Gene Expression in the Ileum between High and Low Production and Breaking Strength Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Systemic Blood Metabolites in Hens with Differing Performance Parameters and Organ Morbidity
4.2. Intestinal Functionality in Hens with Differing Performance Parameters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broom, L.J.; Kogut, M.H. The role of the gut microbiome in shaping the immune system of chickens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 204, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shira, E.; Friedman, A. Development and adaptations of innate immunity in the gastrointestinal tract of the newly hatched chick. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shira, E.; Sklan, D.; Friedman, A. Establishment of immune competence in the avian GALT during the immediate post-hatch period. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schokker, D.; Hoekman, A.J.; Smits, M.A.; Rebel, J.M. Gene expression patterns associated with chicken jejunal development. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videnska, P.; Sedlar, K.; Lukac, M.; Faldynova, M.; Gerzova, L.; Cejkova, D.; Sisak, F.; Rychlik, I. Succession and Replacement of Bacterial Populations in the Caecum of Egg Laying Hens over Their Whole Life. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurburg, S.D.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Ceccarelli, D.; Van Der Goot, J.; Jansman, A.J.M.; Bossers, A. Patterns of community assembly in the developing chicken microbiome reveal rapid primary succession. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Babaei, P.; Ji, B.; Nielsen, J. Human gut microbiota and healthy aging: Recent developments and future prospective. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 4, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saraswati, S.; Sitaraman, R. Aging and the human gut microbiota-from correlation to causality. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’Connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’Sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, R.; Wang, C.; Wen, C.; Zhou, Y. A comparison of intestinal integrity, digestive function, and egg quality in laying hens with different ages. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelqader, A.; Al-Fataftah, A.-R.; Daş, G. Effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis and inulin supplementation on performance, eggshell quality, intestinal morphology and microflora composition of laying hens in the late phase of production. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2013, 179, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkaiaty, A.M.; Badran, A.M.; Bayoumi, A.A.; Eshera, A.A.; El-Sayed, O.A. Effect of dietary yeast supplementation on productive performance, eggshell quality and lipid profile of laying hens. Egypt. Poult. Sci. J. 2019, 39, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Świątkiewicz, S.; Arczewska-Włosek, A.; Krawczyk, J.; Szczurek, W.; Puchała, M.; Józefiak, D. Effect of selected feed additives on egg performance and eggshell quality in laying hens fed a diet with standard or decreased calcium content. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2018, 18, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalaei, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Zergani, E. Effect of different supplements on eggshell quality, some characteristics of gastroin-testinal tract and performance of laying hens. Vet. Res. Forum Int. Q. J. 2014, 5, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlik, A.; Pokludová, M.; Zapletal, D.; Jelinek, P. Effects of Housing Systems on Biochemical Indicators of Blood Plasma in Laying Hens. Acta Vet. Brno 2007, 76, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harr, K.E. Clinical Chemistry of Companion Avian Species: A Review. Veter. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 31, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabčáková, P.; Voslářová, E.; Bedáňová, I.; Pistĕková, V.; Chloupek, J.; Večerek, V. Haematological and Biochemical Parameters during the Laying Period in Common Pheasant Hens Housed in Enhanced Cages. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 364602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ladirat, S.E.; Schols, H.A.; Nauta, A.; Schoterman, M.H.C.; Keijser, B.J.F.; Montijn, R.C.; Gruppen, H.; Schuren, F.H.J. High-throughput analysis of the impact of antibiotics on the human intestinal microbiota composition. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 92, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glendinning, L.; Watson, K.A.; Watson, M. Development of the duodenal, ileal, jejunal and caecal microbiota in chickens. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauffmann, A.; Gentleman, R.; Huber, W. arrayQualityMetrics—A bioconductor package for quality assessment of microarray data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 415–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz, C.E.B.; Freitas, E.R.; Braz, N.D.M.; Salles, R.P.R.; Da Silva, I.N.G. Blood parameters and enzymatic and oxidative activity in the liver of chickens fed with calcium anacardate. Rev. Ciênc. Agron. 2018, 49, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, H.H.; Chen, G.H.; Cheng, J.H.; Yousif, G.M. Relation between abdominal fat and serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and lipoprotein concentrations in chicken breeds. Turk. J. Vet. Sci. 2007, 31, 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Clench, H.M.; Mathias, J.R. The Avian Cecum—A Review. Wilson Bull. 1995, 107, 93–121. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeputte, D.; Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Tito, R.Y.; Joossens, M.; Raes, J. Stool consistency is strongly associated with gut microbiota richness and composition, enterotypes and bacterial growth rates. Gut 2016, 65, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.R.; Dong, X.F.; Liu, S.; Tong, J.M. Effects of long-term Bacillus subtilis CGMCC 1.921 supplementation on performance, egg quality, and fecal and cecal microbiota of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.S.; Li, D.F.; Xing, J.J.; Ma, Y.X.; Li, Z.J.; Lv, S.Q. Effects of Feed Particle Size and Feed Form on Survival of Salmonella typhimurium in the Alimentary Tract and Cecal S. typhimurium Reduction in Growing Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Ravindran, V.; Wester, T.; Molan, A.L. Influence of feeding coarse corn on performance, nutrient utilization, digestive tract measurements, carcass characteristics, and cecal microflora counts of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Moreno, E.; Frikha, M.; de Coca-Sinova, A.; Lázaro, R.; Mateos, G. Oat hulls and sugar beet pulp in diets for broilers. Effects on the development of the gastrointestinal tract and on the structure of the jejunal mucosa. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2013, 182, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.R.; Ravindran, V.; Svihus, B. Pelleting of broiler diets: An overview with emphasis on pellet quality and nutri-tional value. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 179, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.K.; Mahapatra, C.M.; Verma, S.S.; Johari, D.C. Effect of strain on physical egg quality characteristics in White Leghorn chickens. Indian J. Poult. Sci. 1986, 21, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, I. 11—Poultry Breeding for Egg Quality: Traditional and Modern Genetic Approaches. In Improving the Safety and Quality of Eggs and Egg Products; Nys, Y., Bain, M., van Immerseel, F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, W.A.; Heiman, V.; Wilhelm, L.A. The Relationship between Egg Shell Thickness and Strength. Poult. Sci. 1938, XVII, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, S.; Xu, G.; Liu, X.; Yang, N. Global variation and uniformity of eggshell thickness for chicken eggs. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2718–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.-S.; Mi, J.-D.; Mei, L.; Liang, J.; Feng, K.-X.; Wu, Y.-B.; Liao, X.-D.; Wang, Y. Microbial Diversity and Community Variation in the Intestines of Layer Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metabolite | # 1 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | Cage | Organ Morbidity | ||
| Globulins (g/L) | 113 | <0.001 | 0.225 | 0.371 |
| γGT (U/L) | 100 | <0.001 | 0.319 | 0.024 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 12 | 0.53 | 0.499 | 0.053 |
| GLDH (U/L) | 100 | <0.001 | 0.096 | 0.577 |
| Triglycerids (mmol/L) | 113 | <0.001 | 0.866 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 116 | <0.001 | 0.624 | 0.518 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 109 | <0.001 | 0.997 | 0.343 |
| AST (U/L) | 81 | <0.001 | 0.017 | 0.265 |
| ALT (U/L) | 81 | <0.001 | 0.169 | 0.817 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 43 | 0.143 | 0.544 | 0.008 |
| Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 72 | <0.001 | 0.722 | 0.299 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 113 | <0.001 | 0.882 | 0.002 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 111 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.448 |
| AP (U/L) | 114 | <0.001 | 0.226 | 0.068 |
| Total Protein (g/L) | 113 | <0.001 | 0.223 | 0.733 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 113 | <0.001 | 0.878 | 0.014 |
| LDH (U/L) | 115 | <0.001 | 0.554 | 0.611 |
| n 1 | Cage | Morbid | BW 2 (g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST (U/L) | Urea (mmol/L) | Cholesterol (mmol/L) | Glucose (mmol/L) | Triglycerides (mmol/L) | |||
| All hens | |||||||
| All groups | 116 | 43.0 | 0.45 | 4.43 | 11.4 | 12.6 | 1717 |
| BS-hi | 30 | 47.6 | 0.47 | 4.39 | 11.5 | 13.0 | 1615 |
| BS-lo | 27 | 47.9 | 0.51 | 4.46 | 11.1 | 12.3 | 1686 |
| PROD-hi | 34 | 26.8 | 0.40 | 4.36 | 11.5 | 13.4 | 1761 |
| PROD-lo | 25 | 53.7 | 0.44 | 4.55 | 11.2 | 11.3 | 1814 |
| Healthy | |||||||
| All groups | 102 | 41.6 | 0.44 | 4.31 | 11.5 | 13.1 | 1692 |
| BS-hi | 28 | 48.1 | 0.47 | 4.41 | 11.6 | 13.2 | 1605 |
| BS-lo | 25 | 47.9 | 0.49 | 4.32 | 11.1 | 12.9 | 1660 |
| PROD-hi | 34 | 26.8 | 0.40 | 4.36 | 11.5 | 13.4 | 1761 |
| PROD-lo | 15 | 48.9 | 0.41 | 3.99 | 11.7 | 12.2 | 1749 |
| Morbid | |||||||
| All groups | 14 | 58.1 | 0.54 | 5.42 | 10.3 | 9.0 | 1901 |
| BS-hi | 2 | 42.5 | 0.45 | 4.10 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 1754 |
| BS-lo | 2 | - | 0.80 | 6.20 | 10.8 | 5.0 | 2002 |
| PROD-hi | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PROD-lo | 10 | 64.3 | 0.50 | 5.55 | 10.3 | 9.8 | 1910 |
| Subset | Cage | PROD 1 | BS 2 | Sample | BW (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROD-hi | 24.036 | 521 | 2610 (5) | 55 | 1641 |
| 56 | 1659 | ||||
| 57 | 1777.5 | ||||
| 58 | 1847 | ||||
| 59 | 1726 | ||||
| 60 | 1789 | ||||
| PROD-lo | 22.011 | 367 | 3311 (1) | 50 | 1772.5 |
| 51 | 1620 | ||||
| 52 | 1611.5 | ||||
| 53 | 1693 | ||||
| 54 | 1733.5 | ||||
| BS-hi | 2.053 | 470 | 4518 (3) | 1 | 1351 |
| 2 | 1593 | ||||
| 3 | 1558 | ||||
| 4 | 1559.5 | ||||
| 5 | 1447 | ||||
| 6 | 1668 | ||||
| BS-lo | 32.074 | 482 | 2321 (3) | 101 | 1758 |
| 102 | 1731 | ||||
| 103 | 1593.5 | ||||
| 104 | 1557.5 | ||||
| 105 | 1722.5 |
| Comparison | Contrast | Probes | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| BS-hi vs. BS-lo | Up | 96 | 38 |
| Down | 50 | 15 | |
| PROD-hi vs. PROD-lo | Up | 1157 | 334 |
| Down | 179 | 89 |
| Score | SuperPath Name | SuperPath Total Genes | SuperPath Matched Genes | Matched Genes (Symbols) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.13 | SMAD Signaling Network | 131 | 3 | HDAC1, ACTA1, FLNC |
| 7.84 | ICos-ICosL Pathway in T-Helper Cell | 141 | 3 | HDAC1, ITPR1, ACTA1 |
| 5.73 | Proteoglycans in Cancer | 242 | 3 | ITPR1, FLNC, WNT5B |
| 5.45 | Pancreatic Secretion | 100 | 2 | ITPR1, CPA1 |
| 5.13 | Immune Response Function of MEF2 in T Lymphocytes | 113 | 2 | HDAC1, ITPR1 |
| 4.74 | Phospholipase-C Pathway | 544 | 4 | HDAC1, ITPR1, PLCH2, ACTA1 |
| 4.60 | VEGF Pathway | 138 | 2 | ITPR1, ACTA1 |
| 4.51 | NFAT and Cardiac Hypertrophy | 338 | 3 | HDAC1, ITPR1, ACTA1 |
| 4.38 | FMLP Pathway | 350 | 3 | HDAC1, ITPR1, ACTA1 |
| 4.34 | Adipogenesis | 153 | 2 | WNT5B, CISD1 |
| Score | SuperPath Name | SuperPath Total Genes | SuperPath Matched Genes | Matched Genes (Symbols) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.23 | Cyclins and Cell Cycle Regulation | 92 | 9 | HDAC1, RAF1, PPP2R2A, PPP2R2B, SKP1, E2F4, TP53, UBB, UBC |
| 13.02 | ADP Signalling Through P2Y Purinoceptor 12 | 237 | 14 | GRK6, GNAT2, ITPR1, GNAT3, RAF1, WNT10A, CRHR2, SRC, WNT3, AKT2, UBB, UBC, ADRA2A, CLTA |
| 13.00 | ECM Proteoglycans | 60 | 7 | LUM, MATN3, NCAN, COL9A2, NCAM1, COL9A1, COMP |
| 12.65 | Peptide Ligand-binding Receptors | 692 | 27 | NMU, TRH, GNAT2, GPR6, NPY, LHCGR, GPR15, GNAT3, CCR2, PPY, PTGER2, TSPO, S1PR4, RGS14, GABRG1, PROK1, PRSS3, TACR2, WNT10A, PCDHA6, SSTR2, CRHR2, GABRB3, WNT3, SSTR4, TAS2R7, ADRA2A |
| 11.82 | Beta-catenin Independent WNT Signaling | 197 | 12 | GNAT2, ITPR1, PSMD11, PRKG2, WNT10A, SKP1, WNT5B, WNT3, CAMK2A, UBB, UBC, CLTA |
| 11.58 | Signaling By NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants in Cancer | 118 | 9 | HDAC1, KAT2A, FURIN, TLE3, SKP1, TP53, UBB, UBC, ATP2A1 |
| 10.83 | Thyroid Hormone Signaling Pathway | 127 | 9 | HDAC1, KAT2A, RAF1, TSC2, ATP1A3, DIO3, TP53, SRC, AKT2 |
| 10.44 | Ion Channel Transport | 160 | 10 | TRPV4, RAF1, TRPV6, ATP1A3, GABRB3, UBB, UBC, ATP2A1, ASIC5, BEST4 |
| 10.44 | Mitotic G1-G1/S Phases | 160 | 10 | HDAC1, PSMD11, PPP2R2A, PRIM2, SKP1, E2F4, TP53, ORC6, UBB, UBC |
| 10.33 | Apoptosis Signaling Pathways | 82 | 7 | PPIG, NGFR, TNFRSF10B, TNFRSF25, PIDD1, TP53, AXIN2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schokker, D.; Visscher, J.; Woelders, H. Changes in Blood Metabolites, Intestinal Microbiota Composition and Gene Expression of 95 Weeks Old Laying Hens Differing in Egg Production and Egg Breaking Strength. Animals 2021, 11, 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113012
Schokker D, Visscher J, Woelders H. Changes in Blood Metabolites, Intestinal Microbiota Composition and Gene Expression of 95 Weeks Old Laying Hens Differing in Egg Production and Egg Breaking Strength. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchokker, Dirkjan, Jeroen Visscher, and Henri Woelders. 2021. "Changes in Blood Metabolites, Intestinal Microbiota Composition and Gene Expression of 95 Weeks Old Laying Hens Differing in Egg Production and Egg Breaking Strength" Animals 11, no. 11: 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113012
APA StyleSchokker, D., Visscher, J., & Woelders, H. (2021). Changes in Blood Metabolites, Intestinal Microbiota Composition and Gene Expression of 95 Weeks Old Laying Hens Differing in Egg Production and Egg Breaking Strength. Animals, 11(11), 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113012






