Spotted Wolffish Broodstock Management and Egg Production: Retrospective, Current Status, and Research Priorities
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Spotted Wolffish Farming
2. Spotted Wolffish Reproduction
2.1. Reproductive Strategy
2.2. Sexual Dimorphism
2.3. Internal Fertilization/Insemination
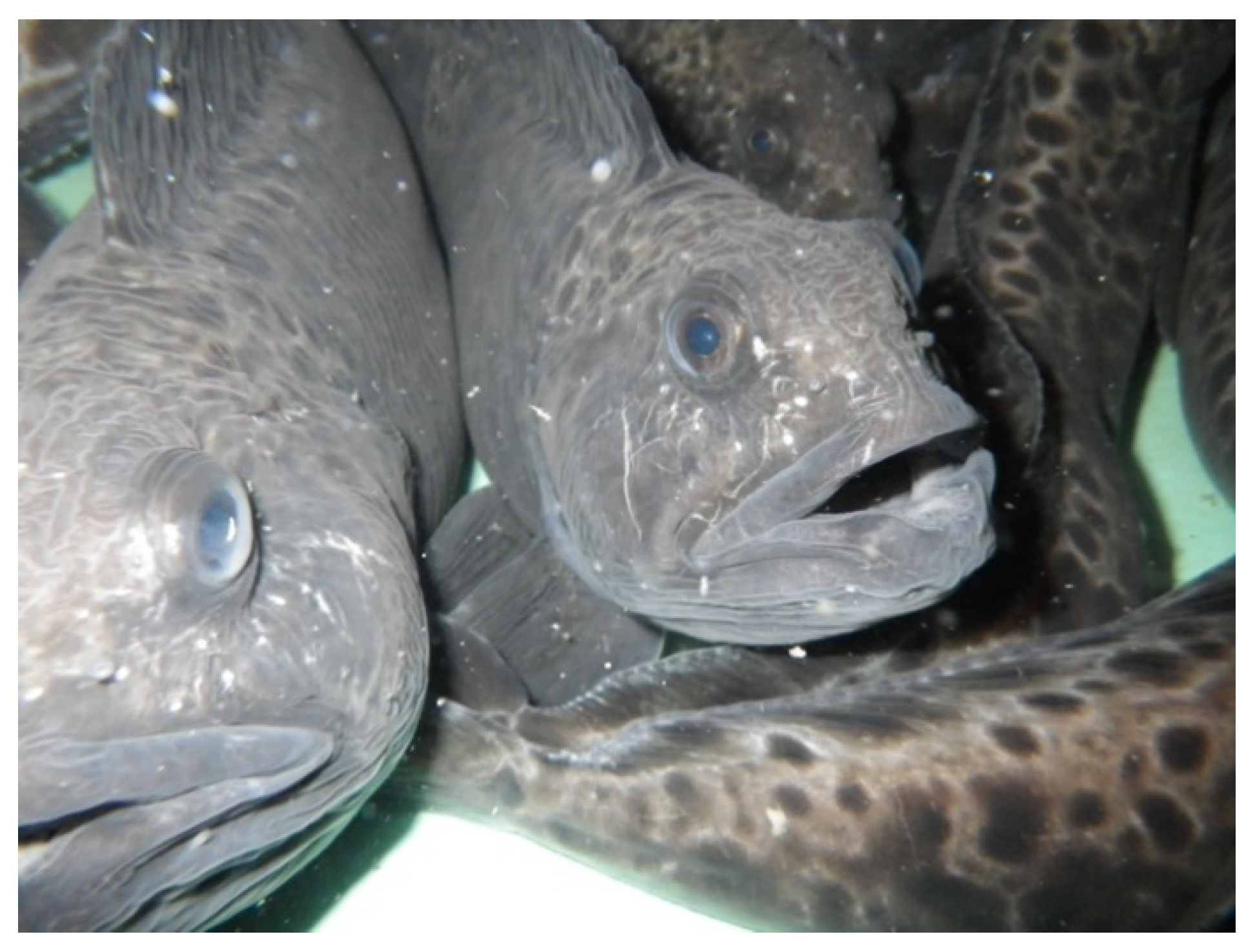
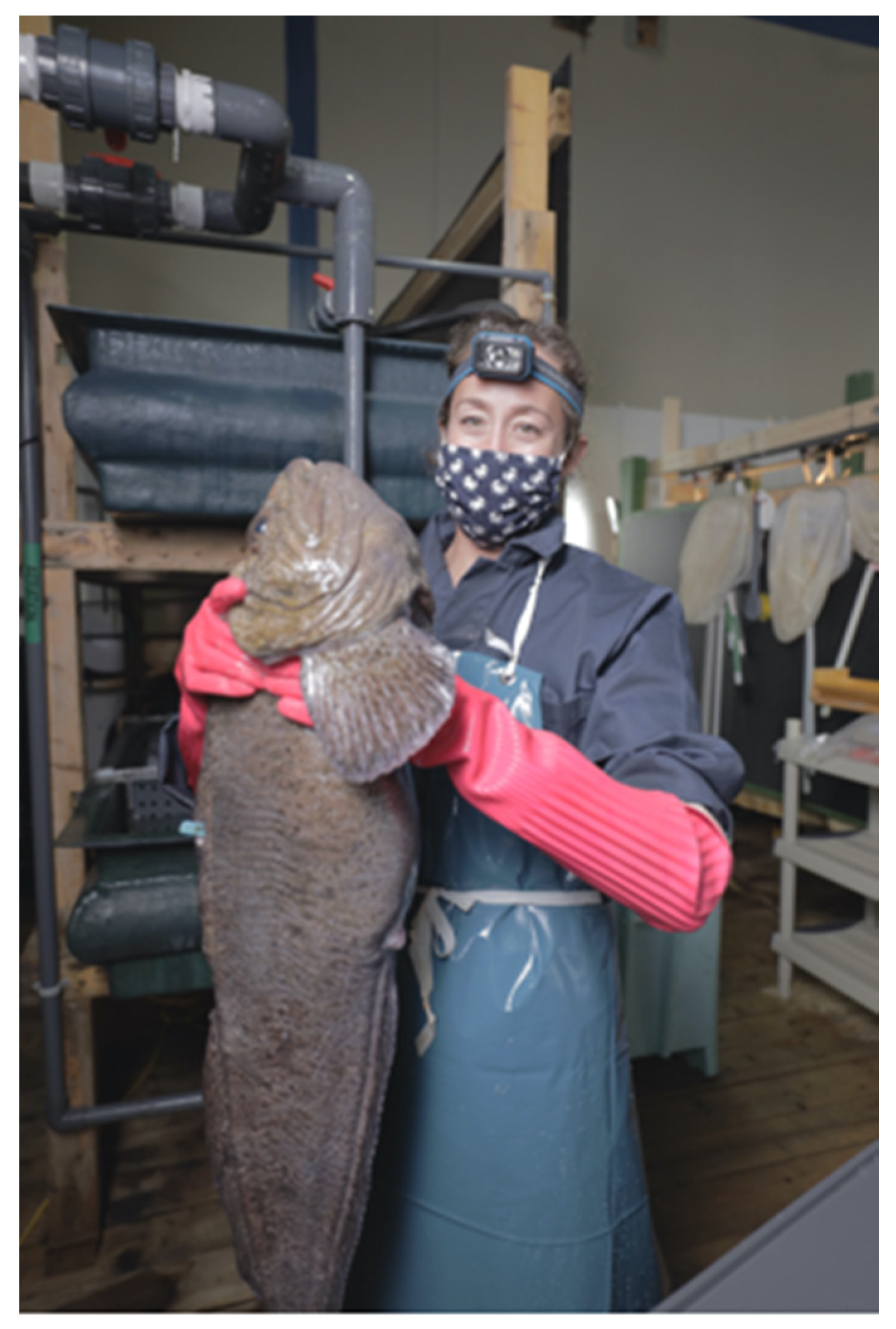
3. Broodstock Capture and Adaptation
3.1. Capture and Transport
3.2. Adaptation
4. Culture Environment and Welfare
4.1. Water Quality
4.1.1. Temperature
4.1.2. Salinity
4.1.3. Dissolved Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, and Ammonia
4.2. Stocking Density, Handling, and Rearing Environment
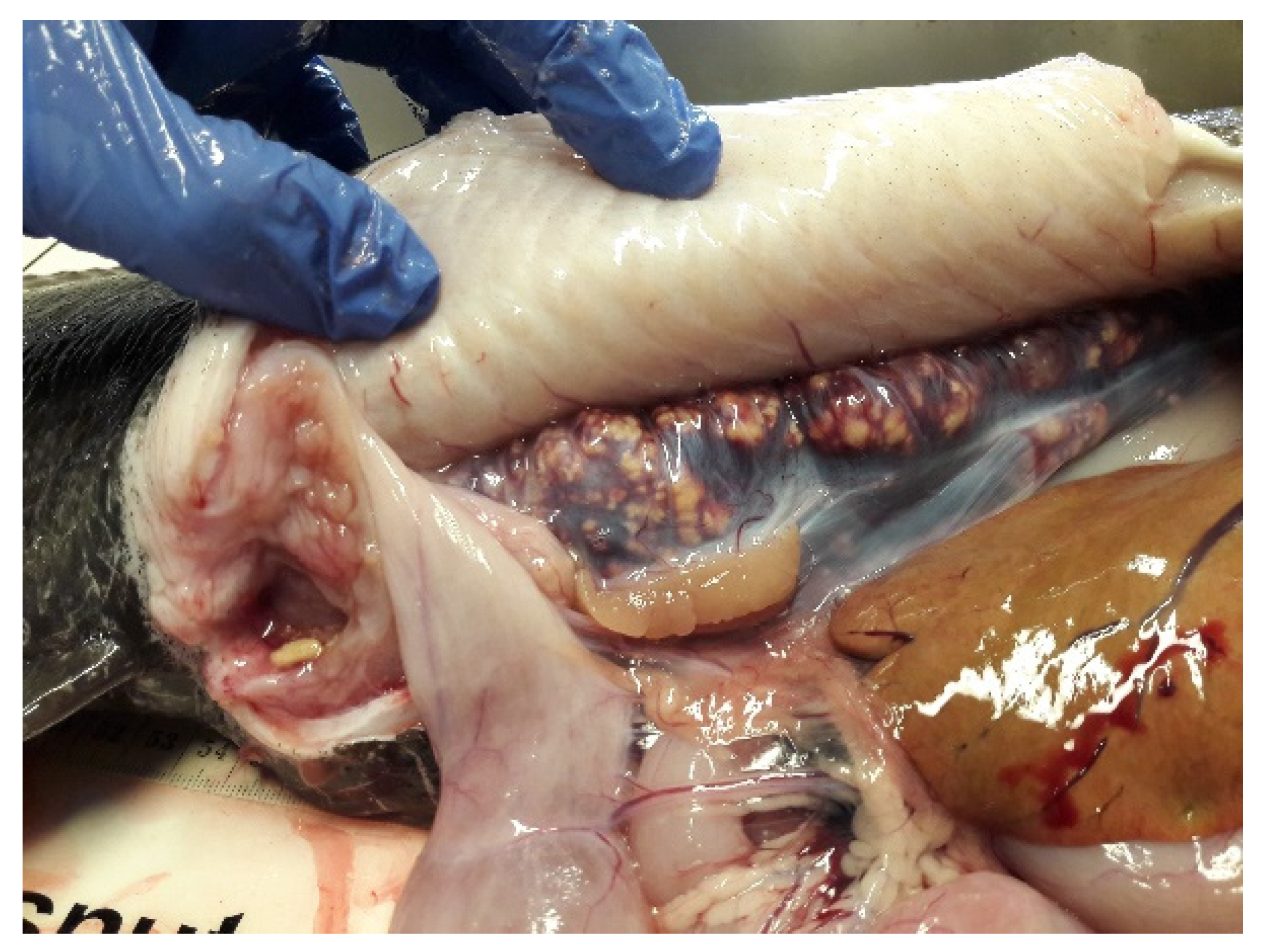
4.3. Health and Diseases
5. Nutrition
5.1. Protein Requirement
5.2. Lipid Requirements
5.3. Carbohydrates
6. Control of Reproduction
6.1. Environmental Manipulation
6.1.1. Thermal Control of Spawning
6.1.2. Photoperiodic Control of Spawning
6.2. Endocrinology and Hormonal Therapies
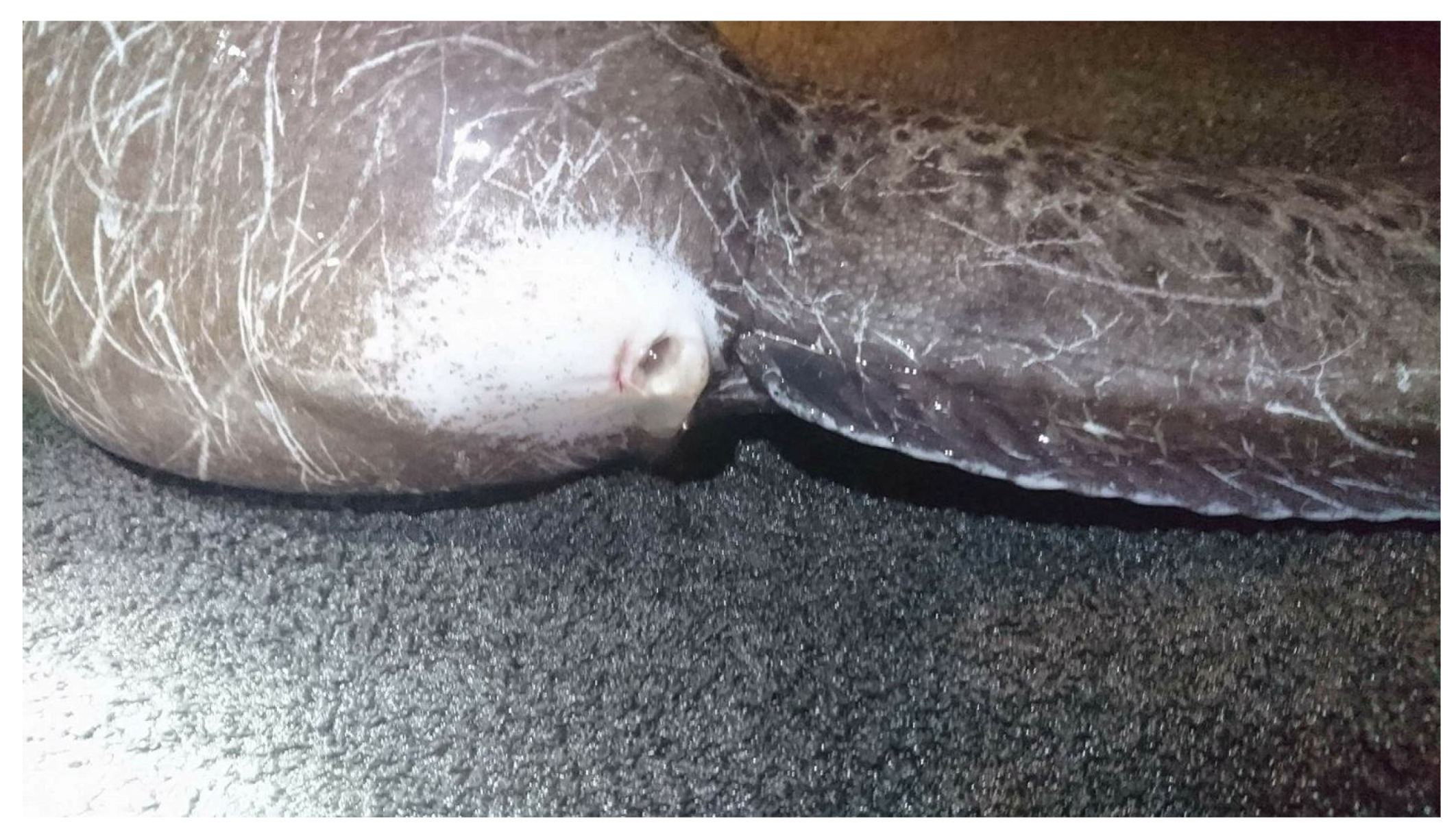
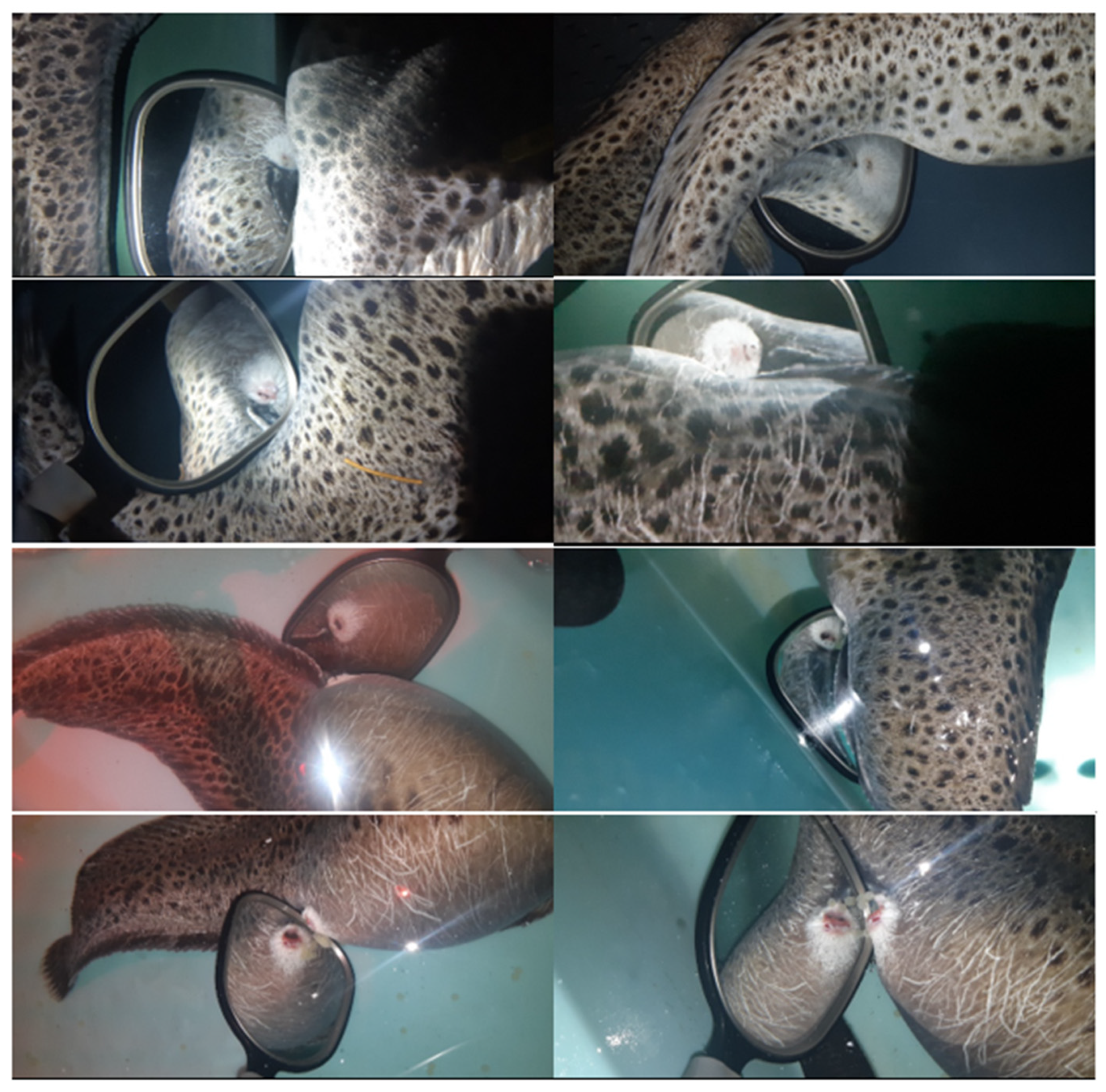
7. Gamete Collection, Quality, and Handling
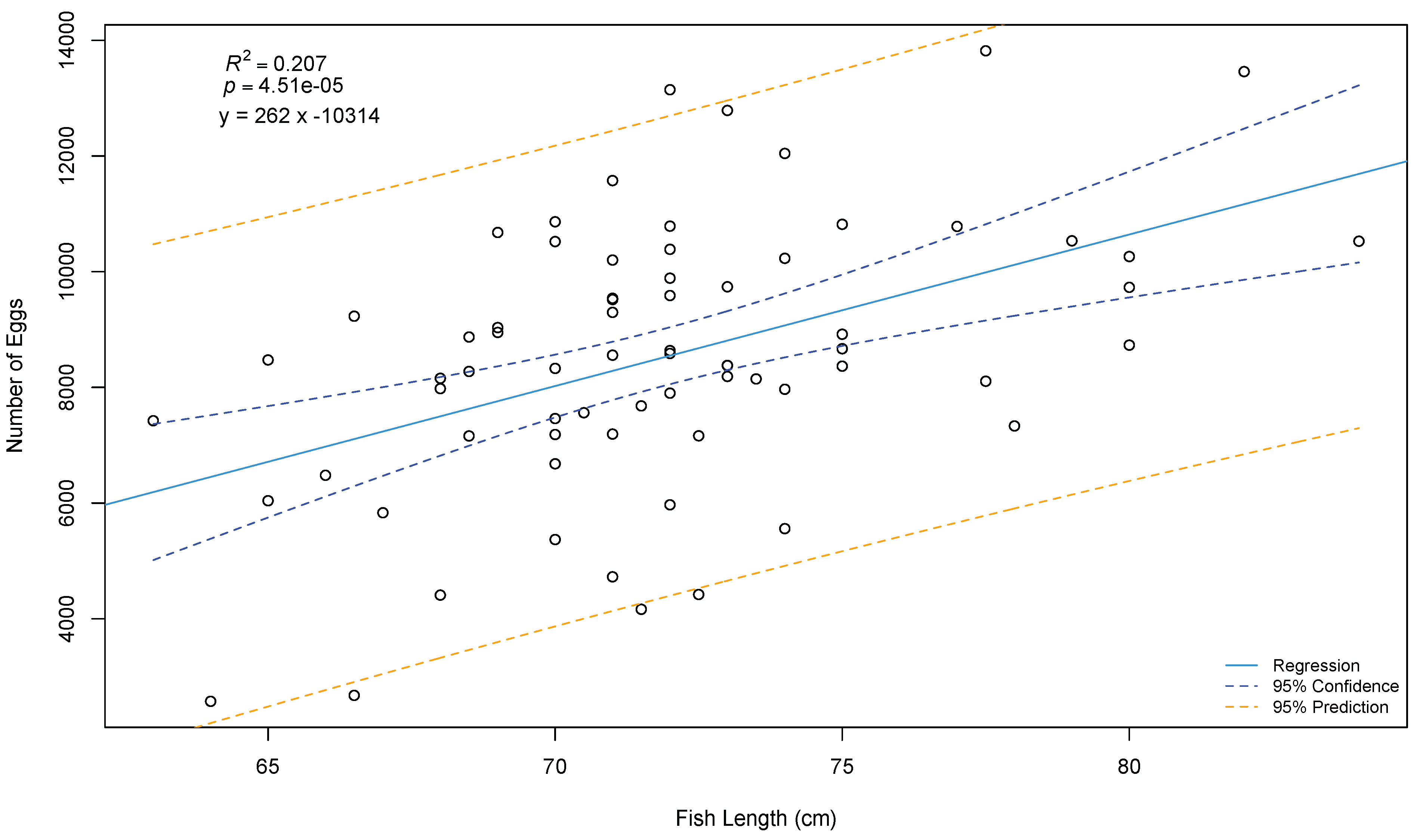
7.1. Oocytes
7.1.1. Collection and Handling
7.1.2. Quality Evaluation
7.1.3. Storage
7.2. Sperm
7.2.1. Collection and Handling
7.2.2. Quality Evaluation
7.2.3. Storage
8. Fertilization
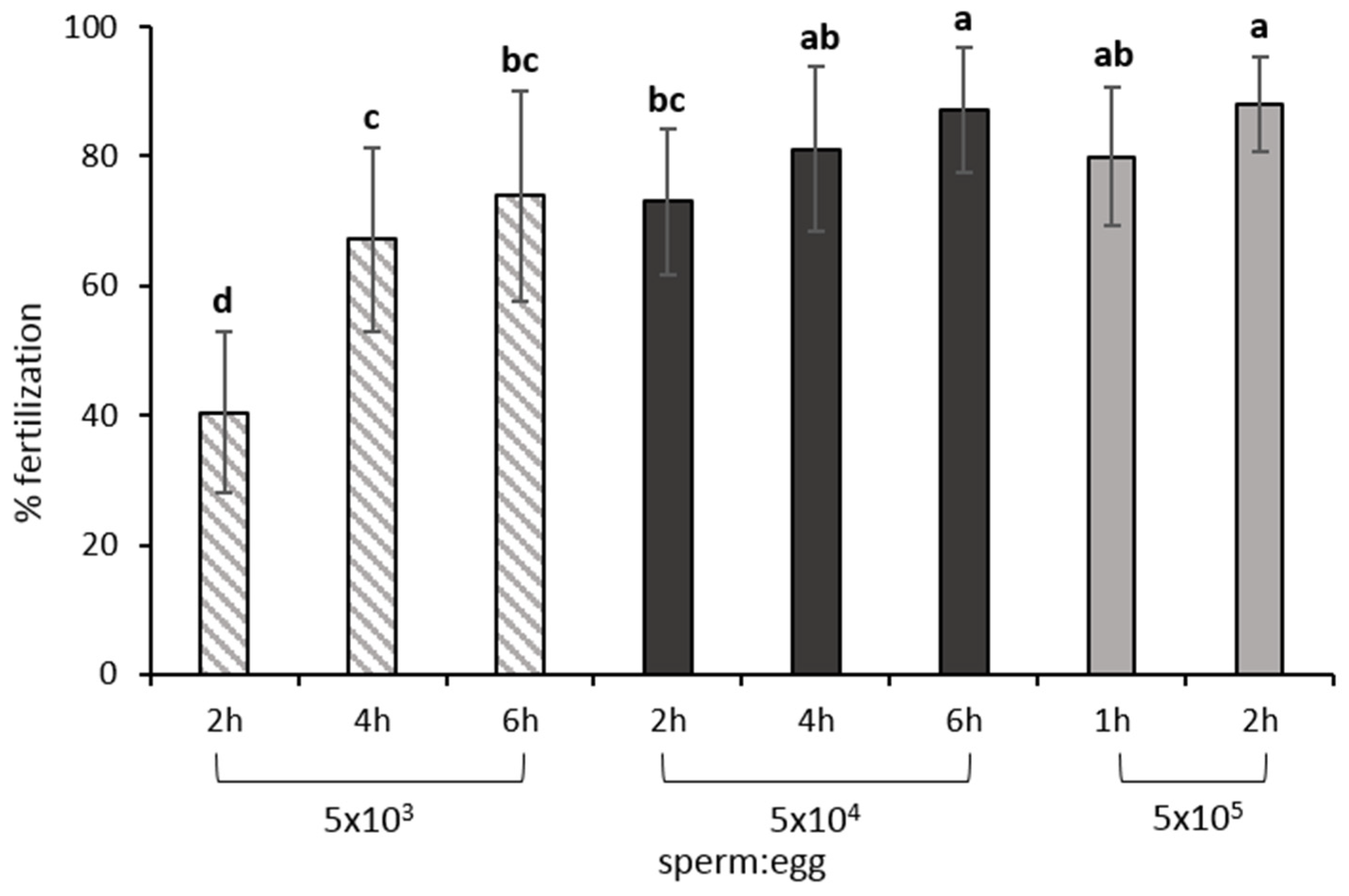
8.1. Gamete Mixture, Sperm: Egg Ratio and Contact Time
8.2. Egg Stickiness
9. Egg Incubation
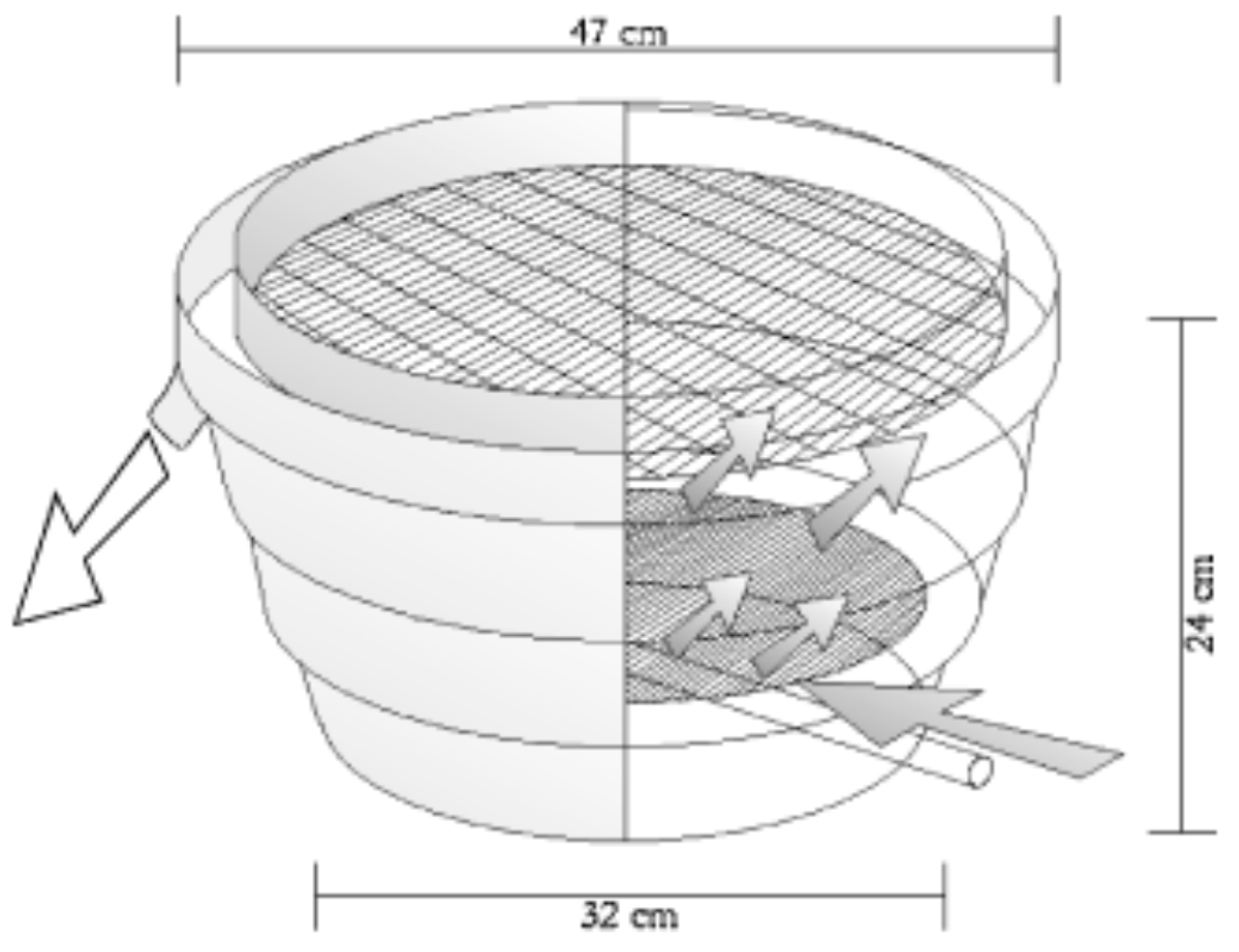
9.1. Incubation Environment
9.2. Disinfection
9.3. Incubation Technology and Egg Transportation
9.4. Hatching and Newly Hatched
10. Future Research and Conclusions
- (1)
- Development of Specific Diets
- (2)
- Health and Welfare
- (3)
- Establishment of Breeding Programs
- (4)
- Improvement of Egg Incubation and Early-Stage Cultivation Techniques
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falk-Petersen, I.; Hansen, T.; Fieler, R.; Sunde, L. Cultivation of the spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor (Olafsen)–a new candidate for cold-water fish farming. Aquac. Res. 1999, 30, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, A.; Imsland, A.K.; Falk-Petersen, I.-B.; Øiestad, V. A review of the culture potential of spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor Olafsen. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2004, 14, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le François, N.; Lemieux, H.; Blier, P. Biological and technical evaluation of the potential of marine and anadromous fish species for cold-water mariculture. Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le François, N.R.; Savoie, A.; Blier, P.U. Quantitative Approaches for Identifying Finfish Species Suited for Sustainable and Productive Aquaculture. In Finfish Aquaculture Diversification; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010; Volume Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Le François, N.R.; Tveiten, H.; Halfyard, L.C.; Foss, A. Finfish Aquaculture Diversification; The Wolffishes (Family: Anarhichadidae); CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010; Volume Chapter 19. [Google Scholar]
- Chabot, D.; Savoie, A.; Dufresne, F.; Le François, N.R. Détermination du taux de croissance du loup tacheté (Anarhichas minor) de souche québécoise. In Rapport Technique Canadien des Sciences Halieutique et Aquatiques; Pêches et Océans: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012; Volume 3016, p. Viii +. 68p. [Google Scholar]
- O’Dea, N.; Haedrich, R. COSEWIC Status Report on the Spotted Wolffish Anarhichas Minor in Canada; Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2001; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Le François, N.R.; Fairchild, E.A.; Nardi, G.; Dupont-Cyr, B. The status of spotted wolffish, Anarhichas minor: A commercially ready species for US marine aquaculture? J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D.; Novikov, G. Life history and peculiarities of common wolffish (Anarhichas lupus) in the White Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1993, 50, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, E.A.; Tallack, S.; Elzey, S.P.; Armstrong, M.P. Spring feeding of Atlantic wolffish (Anarhichas lupus) on Stellwagen Bank, Massachusetts. Fish. Bull. 2015, 113, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeman, W. Contribution to the Biology of the Spotted Wolffish (Anarhichas minor) in the Northwest Atlantic. J. Northw. Atl. Fish. Sci. 1986, 7, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keats, D.; South, G.; Steele, D. Reproduction and egg guarding by Atlantic wolffish (Anarhichas lupus: Anarhichidae) and ocean pout (Macrozoarces americanus: Zoarcidae) in Newfoundland waters. Can. J. Zool. 1985, 63, 2565–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont Cyr, B.-A.; Tveiten, H.; Maltais, D.; Vandenberg, G.W.; Le François, N.R. Photoperiod manipulation for the reproductive management of captive wolffish populations: Anarhichas minor and A. lupus. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson, Á.; Sólmundsson, J.; Björnsson, H.; Sigurðsson, G.; Pampoulie, C. Migration pattern and evidence of homing in Atlantic wolffish (Anarhichas lupus). Fish. Res. 2019, 215, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le François, N.; Archer, B. L’élevage du Loup Tacheté: Reproduction et Incubation; Ministère de l’Agriculture des Pêcheries et de l’Alimentation (Ministère de l’Agriculture, des Pêcheries et de l’Alimentation du Québec (MAPAQ)): Quebec, QC, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Cyr, B.-A.; Tveiten, H.; Vandenberg, G.W.; Blier, P.U.; Roy, R.L.; Le François, N.R. Characterization of the growth rate of adult wolffishes Anarhichas minor and A. lupus: Is avoidance of paternal care at the origin of the expression of a sexual size dimorphism? Aquaculture 2018, 497, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D.A.; Moksness, E. Production and quality of eggs obtained from wolffish (Anarhichas lupus L.) reared in captivity. Aquaculture 1994, 122, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveiten, H.; Solevag, S.E.; Johnsen, H.K. Holding temperature during the breeding season influences final maturation and egg quality in common wolffish. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 58, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østvedt, O.J. On the Life History of the Spotted Catfish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen). Fisk. Skrifter Ser. Hav. 1963, 16, 54–72. [Google Scholar]
- Shevelev, M. Regularities of spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor olafsen) growth. ICES CM 1995, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Marliave, J.B. The life history and captive reproduction of the Wolf-eel Anarrhichthys ocellatus at the Vancouver Public Aquarium. Int. Zoo Yearb. 1987, 26, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Thoney, D.; Balfry, S. Comparative efficacy of formalin, freshwater and hydrogen peroxide against Gyrodactylus corti infestations on captive wolf-eels (Anarrhichthys ocellatus). Bulletion Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2015, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ringø, E.; Lorentsen, H. Brood protection of wolf fish (Anarhichas lupus L.) eggs. Aquac. Neth. 1987, 65, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, D.; Dupont-Cyr, B.-A.; Roy, R.L.; Le François, N.R. Purification and partial characterization of vitellogenin from spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor) and development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of gender and sexual maturity. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kime, D.; Tveiten, H. Unusual motility characteristics of sperm of the spotted wolffish. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 61, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão, J.; Ottesen, O.H. Optimization of a fertilization protocol for spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor). Aquaculture 2018, 484, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D. Fertilization in the wolffish, Anarhichas lupus: External or internal? J. Ichthyol. 1994, 34, 140–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kugathaj, S. Effects of 11-Ketotestosterone on Sperm Production by Male Spotted Wolffish (Anarhichas Minor). Master’s Thesis, Norwegian College of Fishery Science, University of Tromso, Tromso, Norway, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Munehara, H.; Takano, K.; Koya, Y. Internal gametic association and external fertilization in the elkhorn sculpin, Alcichthys alcicornis. Copeia 1989, 3, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koya, Y.; Munehara, H.; Takano, K.; Takahashi, H. Effects of extracellular environments on the motility of spermatozoa in several marine sculpins with internal gametic association. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1993, 106, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, C.W.; Mazzoldi, C.; Zarrella, K.A.; Hale, R.E. Fertilization mode, sperm characteristics, mate choice and parental care patterns in Artedius spp. (Cottidae). J. Fish Biol. 2005, 67, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Munehara, H. Fertilization environment of the non-copulating marine sculpin, Hemilepidotus gilberti. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1998, 52, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, N.J.; Sonesson, A.K.; Chavanne, H. Principles of finfish broodstock management in aquaculture: Control of reproduction and genetic improvement. In Advances in Aquaculture Hatchery Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 23–75. ISBN 978-0-85709-119-2. [Google Scholar]
- Foss, A.; Evensen, T.H.; Imsland, A.K.; Oiestad, V. Effects of reduced salinities on growth, food conversion efficiency and osmoregulatory status in the spotted wolffish. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.K.; Falk-Petersen, I.B. The influence of rearing temperature on early development and growth of spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor (Olafsen): Development and growth of spotted wolffish. Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundamo, I. Growth and Survival in Spotted Wolffish (Anarhichas minor). Effects of temperature and photoperiod. Cand. Scient. Master's Thesis, Norwegian College of Fishery Science, University of Tromso, Tromso, Norway, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Huntingford, F.A.; Kadri, S. Defining, assessing and promoting the welfare of farmed fish: -EN- Defining, assessing and promoting the welfare of farmed fish -FR- Définir, évaluer et promouvoir le bien-être des poissons d’élevage -ES- Definición, evaluación y fomento del bienestar de los peces de cultivo. Rev. Sci. Tech. OIE 2014, 33, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Foss, A.; Vollen, T.; Øiestad, V. Growth and oxygen consumption in normal and O2 supersaturated water, and interactive effects of O2 saturation and ammonia on growth in spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen). Aquaculture 2003, 224, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsland, A.; Foss, A.; Sparboe, L.; Sigurdsson, S. The effect of temperature and fish size on growth and feed efficiency ratio of juvenile spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 68, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarre, S.G.; Le François, N.R.; Driedzic, W.R.; Blier, P.U. Protein synthesis is lowered while 20S proteasome activity is maintained following acclimation to low temperature in juvenile spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen). J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarre, S.; Blier, P.; Driedzic, W.; Le Francois, N. White muscle 20S proteasome activity is negatively correlated to growth rate at low temperature in the spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le François, N.R.; Lamarre, S.G.; Blier, P.U. Tolerance, growth and haloplasticity of the Atlantic wolffish (Anarhichas lupus) exposed to various salinities. Aquaculture 2004, 236, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, A.B.; Imsland, A.K.; Foss, A. Interactive Effects of Different Temperatures and Salinities on Growth, Feed Conversion Efficiency, and Blood Physiology in Juvenile Spotted Wolffish, Anarhichas minor Olafsen. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2008, 39, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, A.; Evensen, T.H.; Øiestad, V. Effects of hypoxia and hyperoxia on growth and food conversion efficiency in the spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor (Olafsen): Growth of spotted wolffish under hypoxia and hyperoxia. Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, F.; Chabot, D.; Le François, N.; Blier, P. Effect of chronic sublethal hypoxia on growth in the spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor) and its hybrid with Atlantic wolffish (A. lupus). In Aquaculture CanadaOM 2010 Cold HarvestTM 2010; Aquaculture Association of Canada: Torbay, NL, Canada, 2011; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Jetté, M.; Chabot, D.; Le François, N.; Garant, D. Determination of the lethal dissolved oxygen threshold in spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor) of Quebec origin according to two methods: The LC50 and PO2crit. Aquac. Assoc. Can. Spec. Publ. 2011, 17, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Foss, A.; Røsnes, B.A.; Øiestad, V. Graded environmental hypercapnia in juvenile spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen): Effects on growth, food conversion efficiency and nephrocalcinosis. Aquaculture 2003, 220, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T.; Wilton, G.; Roberts, D.; Rimmer, T.; Fonkalsrud, K. Developments in recirculating systems for Arctic char culture in North America. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 30, 31–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T.; Vinci, B.; Piedrahita, R. Oxygenation and carbon dioxide control in water reuse systems. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 22, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, S.; Forsberg, O.I. Modelling pH and carbon dioxide in single-pass sea-water aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 1996, 15, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, A.; Evensen, T.H.; Vollen, T.; Øiestad, V. Effects of chronic ammonia exposure on growth and food conversion efficiency in juvenile spotted wolffish. Aquaculture 2003, 228, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, M. Animal welfare in farmed fish. Bus. Benchmark Farm Anim. Welf. Invest. Brief. 2016, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay-Bourgeois, S.; Le François, N.R.; Roy, R.L.; Benfey, T.J.; Imsland, A.K. Effect of rearing density on the growth and welfare indices of juvenile spotted wolffish, Anarhichas minor (Olafsen). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachance, A.-A.; Dutil, J.-D.; Larocque, R.; Daigle, G. Shelter use and behaviour of juvenile Spotted Wolffish (Anarhichas minor) in an experimental context. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2010, 88, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lays, N.; Iversen, M.M.T.; Frantzen, M.; Jørgensen, E.H. Physiological stress responses in spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor) subjected to acute disturbance and progressive hypoxia. Aquaculture 2009, 295, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le François, N.R.; Tremblay-Bourgeois, S.; Dupont Cyr, B.-A.; Savoie, A.; Roy, R.L.; Imsland, A.K.; Benfey, T.J. Cortisol and Behavioral Response to Handling (Acute) and Confinement (Chronic) Stressors in Juvenile Spotted Wolffish, Anarhichas minor. J. Appl. Aquac. 2013, 25, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espelid, S. Susceptibility of spotted wolffish to infectious diseases and use of immunoprophylaxis. Bull.-Aquac. Assoc. Can. 2002, 102, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Grøntvedt, R.N.; Lund, V.; Espelid, S. Atypical furunculosis in spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor O.) juveniles: Bath vaccination and challenge. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristmundsson, A.; Bambir, S.; Helgason, S. Gyrodactylus anarhichatis Mo & Lile (Monogenea: Gyrodactylidae) infection of farmed spotted wolffish, Anarhichas minor Olafsen, in Iceland. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- Grøntvedt, R.N.; Espelid, S. Vaccination and immune responses against atypical Aeromonas salmonicida in spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen) juveniles. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2004, 16, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, R.; Amundsen, M.; Dannevig, B.; Sommer, A. Acute and persistent experimental nodavirus infection in spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 57, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Amundsen Strand, M.; Rasmussen, E.; Mennen, S. Susceptibility of spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor to experimental infection with nodavirus and infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 59, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béland, K.; Wong, E.; St-Cyr, J.-F.; Lair, S. High occurrence rate of xanthomatosis and nephrocalcinosis in aquarium-housed Atlantic wolffish Anarhichas lupus and spotted wolffish A. minor. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2020, 139, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desrosiers, V.; Le François, N.R.; Tveiten, H.; Andreassen, I.; Blier, P.U. Ontogenesis of catabolic and energy metabolism capacities during the embryonic development of spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 150, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.-Y.; Lucas, M.C. Diet of the common wolffish Anarhichas lupus in the North Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2000, 80, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.; Paz, X.; Román, E.; Alvárez, M. Feeding Habits of Wolffishes (Anarhichas Denticulatus, A. Lupus, A. Minor) in the North Atlantic. 2006. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download;jsessionid=EC8FD5E9DBA1A1F267605F5B2249E6C3?doi=10.1.1.538.3589&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Falk-Petersen, I.-B.; Kanapathippilai, P.; Primicerio, R.; Hansen, T.K. Size, locality and seasonally related feeding preferences of common wolffish (Anarhichas lupus L.) from north-Norwegian waters. Mar. Biol. Res. 2010, 6, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D.A.; Moksness, E. Repeat sexual maturation of wolffish (Anarhichas lupus L.) broodstock. Aquaculture 1996, 139, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glencross, B.D.; Baily, J.; Berntssen, M.H.; Hardy, R.; MacKenzie, S.; Tocher, D.R. Risk assessment of the use of alternative animal and plant raw material resources in aquaculture feeds. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 703–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moksness, E. Weaning of wild-caught common wolffish (Anarhichas lupus) larvae. Aquaculture 1990, 91, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, J. The Protein Requirement of the Atlantic Wolffish (Anarhichas lupus) and the Effects on Growth and Intestinal Function. Available online: https://studentportal.gu.se/digitalAssets/1702/1702366_bio725-josefin-roos-vt18.pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Kelly, J.R.; Scheibling, R.E.; Iverson, S.J.; Gagnon, P. Fatty acid profiles in the gonads of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis on natural algal diets. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 373, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Cervera, M.Á.; González-Barriga, V.; Romero, J.; Rojas, R.; López-Arana, S. Quantification and distribution of omega-3 fatty acids in South Pacific fish and shellfish species. Foods 2020, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonas, C.C.; Fostier, A.; Zanuy, S. Broodstock management and hormonal manipulations of fish reproduction. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 516–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohar, Y.; Mylonas, C.C. Endocrine manipulations of spawning in cultured fish: From hormones to genes. In Reproductive Biotechnology in Finfish Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 99–136. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, D.J.; Mylonas, C.C.; Zohar, Y.; Crim, L.W. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue (GnRH-A) induces multiple ovulations of high-quality eggs in a cold-water, batch-spawning teleost, the yellowtail flounder (Pleuronectes ferrugineus). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 54, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, C.C.; Scott, A.P.; Vermeirssen, E.L.M.; Zohar, Y. Changes in Plasma Gonadotropin II and Sex Steroid Hormones, and Sperm Production of Striped Bass after Treatment with Controlled-Release Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonist-Delivery Systems1. Biol. Reprod. 1997, 57, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bromage, N.; Jones, J.; Randall, C.; Thrush, M.; Davies, B.; Springate, J.; Duston, J.; Barker, G. Broodstock management, fecundity, egg quality and the timing of egg production in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 1992, 100, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassin, S.; De Monbrison, D.; Hanin, Y.; Elizur, A.; Zohar, Y.; Popper, D. Domestication of the white grouper, Epinephelus aeneus 1. Growth and reproduction. Aquaculture 1997, 156, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migaud, H.; Davie, A.; Taylor, J. Current knowledge on the photoneuroendocrine regulation of reproduction in temperate fish species. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlinsky, D.L.; Kenter, L.W.; Reading, B.J.; Goetz, F.W. Aquaculture. Chapter 1, Regulating Reproductive Cycles for Captive Spawning. Fish Physiol. 2020, 38, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, Y.; Goren, A.; Tosky, M.; Pagelson, G.; Leibovitz, D.; Koch, Y. The bioactivity of gonadotropin releasing hormones and its regulation in the gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata: In vivo andin vitro studies. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1989, 7, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.D.; Scott, A.P.; Lam, T. Reproductive Seasonality in Teleosts: Environmental Influences; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; ISBN 0-8493-6875-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yaron, Z. Endocrine control of gametogenesis and spawning induction in the carp. Aquaculture 1995, 129, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Iwai Jr, T.; Zhao, B.; Lee, C.; Yang, J. Identification of microsatellite DNA markers for Pacific threadfin parentage assignment. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2010, 41, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Kraak, G.; Pankhurst, N.W. Temperature effects on the reproductive performance of fish. Glob. Warm. Implic. Freshw. Mar. Fish 1997, 61, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Tveiten, H.; Johnsen, H.K. Temperature experienced during vitellogenesis influences ovarian maturation and the timing of ovulation in common wolffish. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 55, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveiten, H.; Scott, A.P.; Johnsen, H.K. Plasma-Sulfated C21-Steroids Increase during the Periovulatory Period in Female Common Wolffish and Are Influenced by Temperature during Vitellogenesis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2000, 117, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveiten, H.; Johnsen, H.K. Thermal influences on temporal changes in plasma testosterone and oestradiol-17beta concentrations during gonadal recrudescence in female common wolffish. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarre, S.G.; Le François, N.R.; Falk-Petersen, I.; Blier, P.U. Can digestive and metabolic enzyme activity levels predict growth rate and survival of newly hatched Atlantic wolffish (Anarhichas lupus Olafsen)? Aquac. Res. 2004, 35, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk-Petersen, I.; Hansen, T.K. Early ontogeny of the spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen). Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzen, M.; Tveiten, H.; Jobling, M. Effects of cortisol and 11-ketotestosterone (11-KT) on testicular development and sperm quality in male spotted wolffish. CYBIUM 2008, 32, 247. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, D.; Moksness, E. Development of wolffish eggs at different temperature regimes. Aquac. Int. 1995, 3, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Beese, G.; Kändler, R. Beitrage zur Biologie der drei nordatlantischen Katfischarten Anarhichas lupus L. A. Minor 1969, 21–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson, Á.; Hjörleifsson, E.; Thórarinsson, K.; Marteinsdóttir, G. Growth, maturity and fecundity of female spotted wolffish Anarhichas minor in Icelandic waters. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveiten, H. Management of wolffish broodstock. Bull. Aquac. Assoc. Can. 2002, 102, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson, Á.; Björnsson, H.; Elvarsson, B.; Pampoulie, C. Spatio-temporal variation in the reproduction timing of Atlantic Wolffish (Anarhichas lupus L) in Icelandic waters and its relationship with size. Fish. Res. 2016, 183, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveiten, H.; Jobling, M.; Andreassen, I. Influence of egg lipids and fatty acids on egg viability, and their utilization during embryonic development of spotted wolf-fish, Anarhichas minor Olafsen. Aquac. Res. 2004, 35, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciereszko, A.; Wojtczak, M.; Dietrich, G.J.; Kuźmiński, H.; Dobosz, S. A lack of consistent relationship between distribution of lipid droplets and egg quality in hatchery-raised rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2009, 289, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdebenito, I.I.; Gallegos, P.C.; Effer, B.R. Gamete quality in fish: Evaluation parameters and determining factors. Zygote 2015, 23, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moksness, E.; Pavlov, D. Management by life cycle of wolffish, Anarhichas lupus L., a new species for cold-water aquaculture: A technical paper. Aquac. Res. 1996, 27, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, J.; Cabrita, E.; Eggen, B.; Beirão, J. Step by step optimization of a sperm cryopreservation protocol for spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen, 1772). Theriogenology 2020, 149, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, T.; Gjøsæter, J.; Moksness, E. Reproduction, spawning behaviour and captive breeding of the common wolffish Anarhichas lupus L. Aquaculture 1993, 115, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D.; Moksness, E. Bacterial destruction of the egg shell of common wolffish during incubation. Aquac. Int. 1993, 1, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le François, N.R.; Lamarre, S.G.; Tveiten, H.; Blier, P.U.; Bailey, J. Sperm cryoconservation in Anarhichas sp., endangered cold-water aquaculture species with internal fertilization. Aquac. Int. 2008, 16, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, W.A.; Patel, D.M.; Duncan, N.; Beirão, J. Is it possible to store spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor) sperm by refrigeration? Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 47, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakitin, A.; Ferguson, M.M.; Trippel, E.A. Spermatocrit and spermatozoa density in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua): Correlation and variation during the spawning season. Aquaculture 1999, 170, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvedt, H.B.; Benfey, T.J.; Martin-Robichaud, D.J.; Power, J. The relationship between sperm density, spermatocrit, sperm motility and fertilization success in Atlantic halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus. Aquaculture 2001, 194, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, S.; Sigurdsson, S.; Thorarensen, H.; Imsland, A.K. Cryopreservation of sperm from spotted wolffish. Aquac. Int. 2009, 17, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, C.; Suquet, M.; Cosson, J. Evaluation of fish sperm quality: Evaluation of fish sperm quality. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2010, 26, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão, J.; Flengstad, S.; Babiak, I. Spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor) sperm cryopreservation in 5-mL cryovials. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 47, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurangwa, E.; Kime, D.E.; Ollevier, F.; Nash, J.P. The measurement of sperm motility and factors affecting sperm quality in cultured fish. Aquaculture 2004, 234, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyuba, B.; Bondarenko, O.; Fedorov, P.; Gazo, I.; Prokopchuk, G.; Cosson, J. Energetics of fish spermatozoa: The proven and the possible. Aquaculture 2017, 472, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D.A.; Knudsen, P.; Natal’ya, G.; Moksness, E. Spermatozoon ultrastructure and sperm production in wolffish (Anarhichas lupus), a species with internal fertilization. Aquat. Living Resour. 1997, 10, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, M.; Le François, N.R.; Fletcher, G.L.; Blier, P.U. High antifreeze protein levels in wolffish (Anarhichas lupus) make them an ideal candidate for culture in cold, potentially ice laden waters. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, M.; Le François, N.R.; Fletcher, G.L.; Blier, P.U. Seasonal modulation of plasma antifreeze protein levels in Atlantic (Anarhichas lupus) and spotted wolffish (A. minor). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 335, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão, J.; Zilli, L.; Vilella, S.; Cabrita, E.; Schiavone, R.; Herráez, M.P. Improving Sperm Cryopreservation with Antifreeze Proteins: Effect on Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Plasma Membrane Lipids1. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beirão, J.; Boulais, M.; Gallego, V.; O’Brien, J.K.; Peixoto, S.; Robeck, T.R.; Cabrita, E. Sperm handling in aquatic animals for artificial reproduction. Theriogenology 2019, 133, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão, J.; Egeland, T.B.; Purchase, C.F.; Nordeide, J.T. Fish sperm competition in hatcheries and between wild and hatchery origin fish in nature. Theriogenology 2019, 133, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk-Petersen, I. Factors affecting survival and growth during early life stages of spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen). Bull. Aquac. Assoc. Can. 2002, 102, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sund, T.; Falk-Petersen, I. Effects of incubation temperature on development and yolk sac conversion efficiencies of spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen) embryos until hatch. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoie, A.; Le François, N.; Cahu, C.; Blier, P.; Andreassen, I. Do protein hydrolysates improve survival and growth of newly-hatched spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor), a non-metamorphic aquaculture fish species? Aquaculture 2006, 261, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hansen, T.; Falk-Petersen, I. Effects of egg disinfection and incubation temperature on early life stages of spotted wolffish. Aquac. Int. 2001, 9, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsen, T.; Strand, C.; Monsen, E.; Bøgwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A. The ontogeny of complement component C3 in the spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2005, 18, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoie, A.; Le François, N.R.; Cahu, C.; Blier, P.U. Metabolic and digestive enzyme activity profiles of newly hatched spotted wolffish (Anarhichas minor Olafsen): Effect of temperature. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, H.K.; Hansen, T.K.; Pedersen, A.; Falk-Petersen, I.B. First feeding of common wolffish on formulated dry feed diets in a low water-level raceway system. Aquac. Int. 1995, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T. The view from here-Broodstock genetics: A warning to the wise. Bull. Aquac. Assoc. Can. 2002, 102, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.R.; Martin-Robichaud, D.; Reith, M.E. Application of DNA markers to the management of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) broodstock. Aquaculture 2003, 220, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le François, N.R.; Beirão, J.; Superio, J.; Dupont Cyr, B.-A.; Foss, A.; Bolla, S. Spotted Wolffish Broodstock Management and Egg Production: Retrospective, Current Status, and Research Priorities. Animals 2021, 11, 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11102849
Le François NR, Beirão J, Superio J, Dupont Cyr B-A, Foss A, Bolla S. Spotted Wolffish Broodstock Management and Egg Production: Retrospective, Current Status, and Research Priorities. Animals. 2021; 11(10):2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11102849
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe François, Nathalie Rose, José Beirão, Joshua Superio, Bernard-Antonin Dupont Cyr, Atle Foss, and Sylvie Bolla. 2021. "Spotted Wolffish Broodstock Management and Egg Production: Retrospective, Current Status, and Research Priorities" Animals 11, no. 10: 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11102849
APA StyleLe François, N. R., Beirão, J., Superio, J., Dupont Cyr, B.-A., Foss, A., & Bolla, S. (2021). Spotted Wolffish Broodstock Management and Egg Production: Retrospective, Current Status, and Research Priorities. Animals, 11(10), 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11102849





