Recommendations for Standardizing Thorax PET–CT in Non-Human Primates by Recent Experience from Macaque Studies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animal Use and Ethics
2.2. PET–CT Scanner
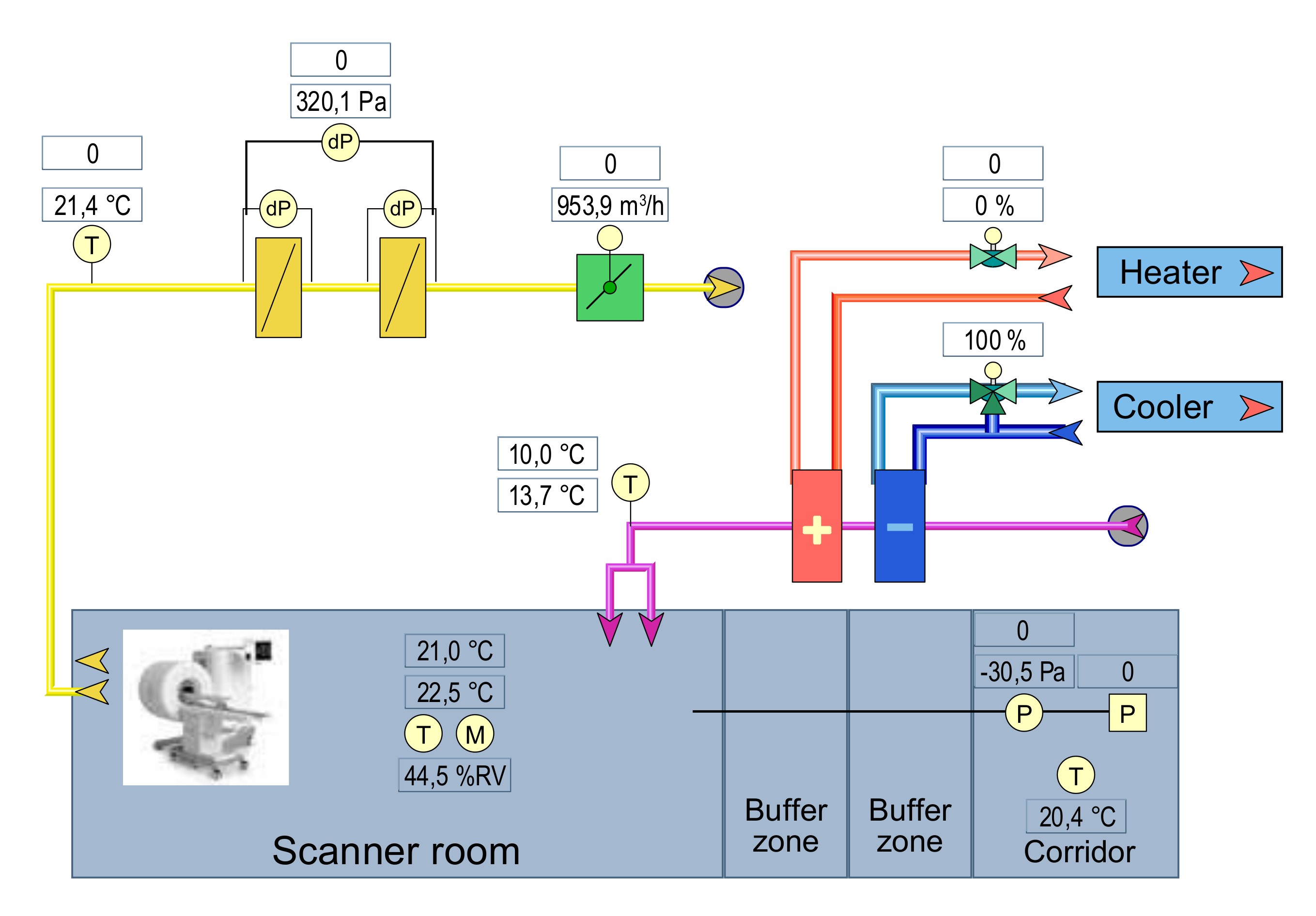
2.3. Scanner Room
2.4. Animal Housing and Care
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Animal Characteristics & Preparation
3.1.1. Body Composition
3.1.2. Blood Glucose Level
3.1.3. Anesthesia
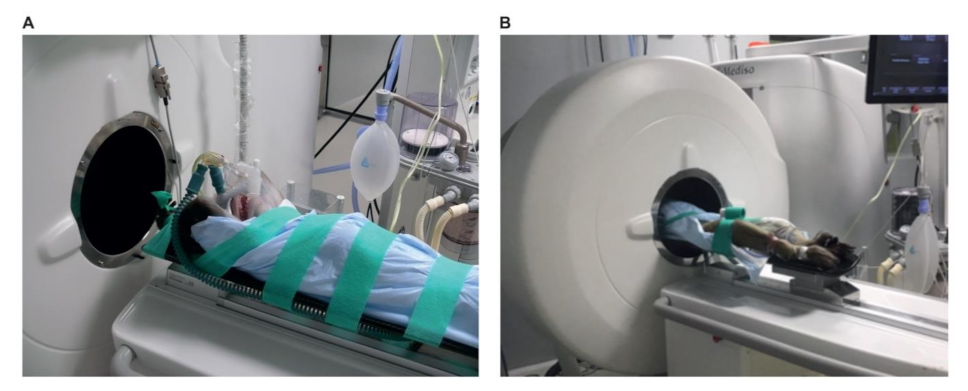
3.1.4. Animal Positioning
3.2. Scan Acquisition
3.2.1. CT
3.2.2. PET Circulation Time
3.2.3. PET Scanning Time & Activity
3.3. Reconstruction
3.3.1. Reconstruction Settings
3.3.2. Attenuation Correction
3.4. Data Analysis
3.4.1. ROI Definition
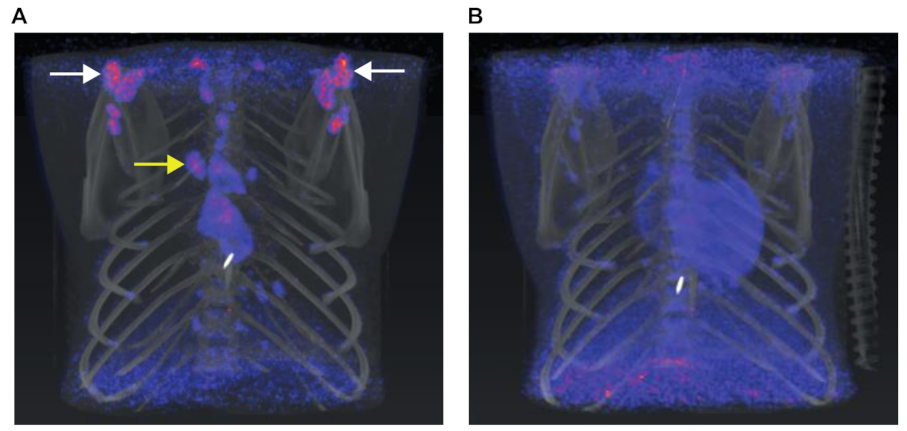
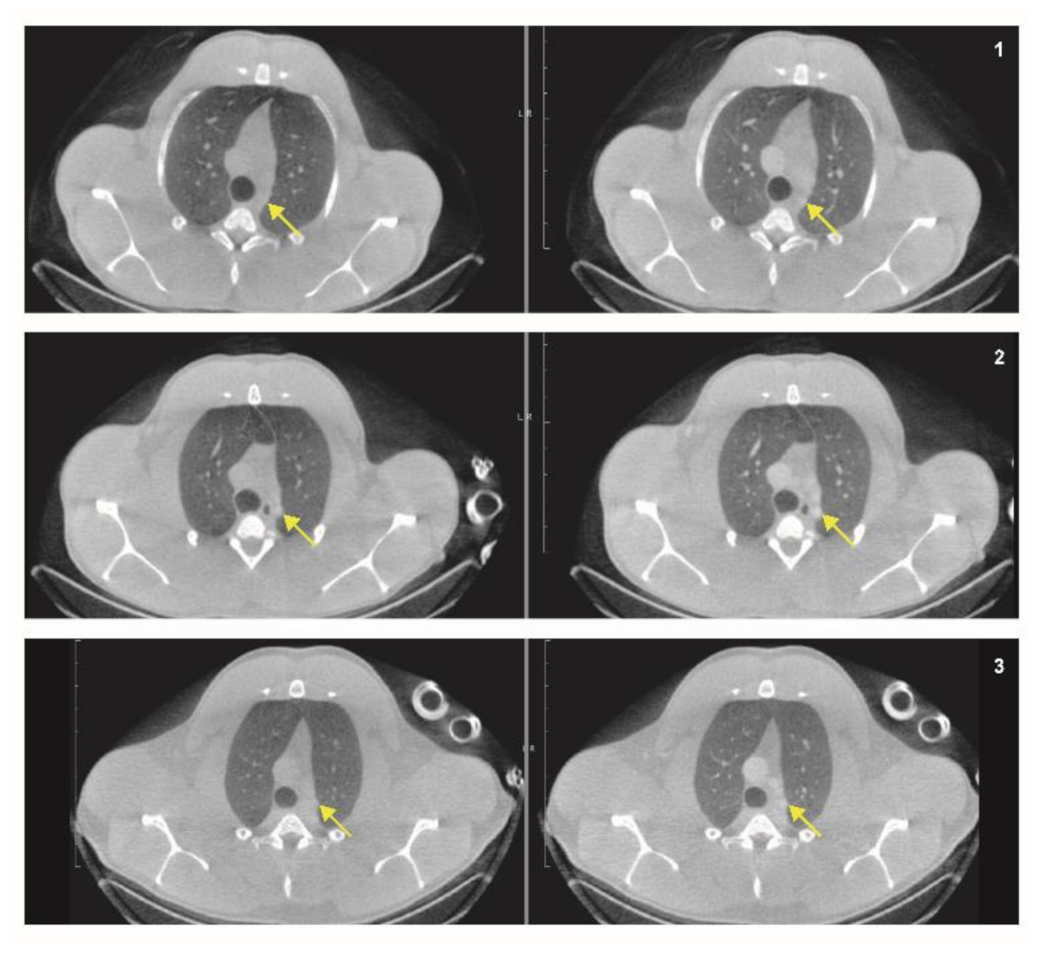
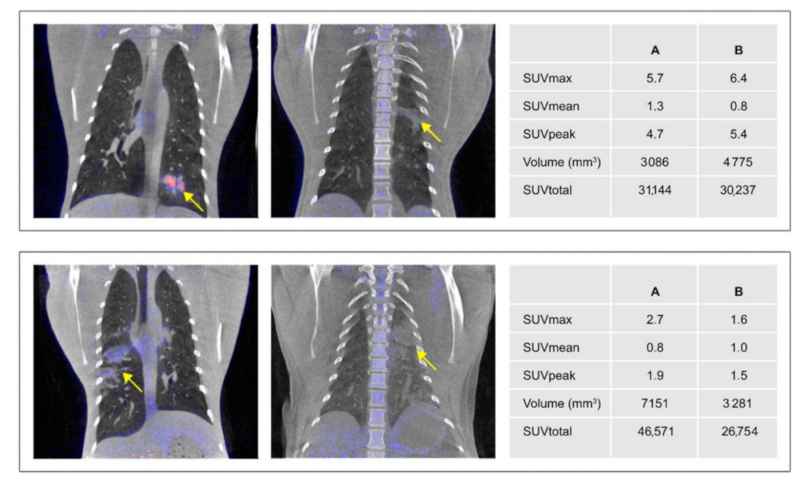
3.4.2. Anatomical and Functional Results
4. Conclusions
4.1. Animal Characteristics and Preparation
4.2. Scan Acquisition
4.3. Reconstruction
4.4. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Global Impact of Respiratory Disease, 2nd ed. In Proceedings of the Forum of International Respiratory Societies, Geneva, Switzerland, 25 May 2017; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2017.
- Stammes, M.A.; Bugby, S.L.; Port, T.; Pierzchalski, K.; Devling, T.; Otto, C.; Dijkstra, J.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; de Geus-Oei, L.-F.; Mieog, J.S.D. Modalities for image- and molecular-guided cancer surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, e69–e83. [Google Scholar]
- Mankoff, D.A. A definition of molecular imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 18N–21N. [Google Scholar]
- Muijres, A. (Ed.) European Nuclear Medicine Guide; HGP Vullers: Neer, OR, USA, 2018; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Abrantes, A.M.; Pires, A.S.; Monteiro, L.; Teixo, R.; Neves, A.R.; Tavares, N.T.; Marques, I.A.; Botelho, M.F. Tumour functional imaging by PET. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis. Dis. 2020, 1866, 165717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, M.; Ewing, P.; Cselenyi, Z.; Fridén, M.; Takano, A.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L. Pulmonary PET imaging confirms preferential lung target occupancy of an inhaled bronchodilator. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Abadie, J.; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abernathy, M.; Accadia, T.; Acernese, F.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.; Ajith, P.; Allen, B.; et al. Directional limits on persistent gravitational waves using LIGO S5 science data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 271102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, H.; Ator, N.; Haigwood, N.; Newsome, W.; Allan, J.S.; Golos, T.G.; Kordower, J.H.; Shade, R.E.; Goldberg, M.E.; Bailey, M.R.; et al. The Critical Role of Nonhuman Primates in Medical Research. Pathog. Immun. 2017, 2, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnyai, Z.; Nagy, K.; Patay, G.; Molnar, M.; Rosenqvist, G.; Toth, M.; Takano, A.; Gulyas, B.; Major, P.; Halldin, C.; et al. Performance Evaluation of a High Resolution Non-Human Primate PET/CT System. J. Nucl. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Maniawski, P.; Knopp, M.V. Performance evaluation of the next generation solid-state digital photon counting PET/CT system. EJNMMI Res. 2018, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, P.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, H.; Liu, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Wei, L. NEMA NU-4 performance evaluation of a non-human primate animal PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solutions, M. MRS*PET/CT 220. Available online: https://www.mrsolutions.com/molecular-imaging-main/molecular-imaging/pet-ct/petct-220/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Conlee, K.M.; Hoffeld, E.H.; Stephens, M.L. A demographic analysis of primate research in the United States. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2004, 32 (Suppl. 1A), 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, M.K.; Maher, M.M.; Prasad, S.R.; Hayat, M.S.; Blake, M.A.; Varghese, J.; Halpern, E.F.; Saini, S. Correlation of patient weight and cross-sectional dimensions with subjective image quality at standard dose abdominal CT. Korean J. Radiol. 2003, 4, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterck, E.H.M.; Zijlmans, D.G.M.; de Vries, H.; van den Berg, L.M.; van Schaik, C.P.; Langermans, J.A.M. Determining overweight and underweight with a new weight-for-height index in captive group-housed macaques. Am. J. Primatol. 2019, 81, e22996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskian, M.; Alavi, A.; Khorasanizadeh, M.; Viglianti, B.L.; Jacobsson, H.; Barwick, T.D.; Meysamie, A.; Yi, S.K.; Iwano, S.; Bybel, B.; et al. Effect of blood glucose level on standardized uptake value (SUV) in (18)F- FDG PET-scan: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 20,807 individual SUV measurements. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boellaard, R.; O’Doherty, M.J.; Weber, W.A.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Lonsdale, M.N.; Stroobants, S.G.; Oyen, W.J.; Kotzerke, J.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Pruim, J.; et al. FDG PET and PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour PET imaging: Version 1.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinz, C.; Altmayer, S.; Zanon, M.; Watte, G.; Irion, K.; Marchiori, E.; Hochhegger, B. Effects of blood glucose level on 18F-FDG uptake for PET/CT in normal organs: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, C. Imaging in Research using Nonhuman Primates. In Nonhuman Primates in Biomedical Research; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 795–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, L.K. Medetomidine sedation in dogs and cats: A review of its pharmacology, antagonism and dose. Br. Vet. J. 1996, 152, 519–535. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, M.D. A review of the physiological effects of alpha2-agonists related to the clinical use of medetomidine in small animal practice. Can. Vet. J. 2003, 44, 885–897. [Google Scholar]
- Verstegen, J.; Fargetton, X.; Ectors, F. Medetomidine/ketamine anaesthesia in cats. Acta Vet. Scand. Suppl. 1989, 85, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, R.S.; Davis, B.R. Pressure-controlled versus volume-controlled ventilation: Does it matter? Respir. Care 2002, 47, 416–424. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, S.F.; Abdelmalik, A.G.; Nguyen, N.C.; Farghaly, H.R.; Osman, M.M. Whole-body 18F-FDG PET/CT: The need for a standardized field of view—A referring-physician aid. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2010, 38, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, R.T.; McCallister, A.; Yuan, H.; Aghajanian, A.; Faber, J.E.; Weimer, N.; Buchanan, R.; Floyd, C.S.; Antonacci, M.; Zhang, L.; et al. Accurate quantification of brown adipose tissue mass by xenon-enhanced computed tomography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, J.D.; Vogel, W.; Vegt, E. Factors influencing brown fat activation in FDG PET/CT: A retrospective analysis of 15,000+ cases. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20170093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Perspective: Does brown fat protect against diseases of aging? Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.C.; Tadi, P. Intravenous Contrast. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Layer, G. When are contrast agents really needed?: Cross-sectional imaging with computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Radiologe 2019, 59, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhull, V.S.; Rana, N.; Nazar, A.H. Contrast Media in PET/Computed Tomography Imaging. PET Clin. 2016, 11, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.G.; Maiello, P.; Coleman, M.T.; Tomko, J.A.; Frye, L.J.; Scanga, C.A.; Lin, P.L.; Flynn, J.L. Analysis of 18FDG PET/CT Imaging as a Tool for Studying Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection and Treatment in Non-human Primates. J. Vis. Exp. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boellaard, R. Standards for PET image acquisition and quantitative data analysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50 (Suppl. 1), 11S–20S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: Version 2.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiber, M. Body size and metabolism. Hilgardia 1932, 6, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, C. Basal metabolic rate, body weight and diet in primates: An evaluation of the evidence. Folia Primatol. 1992, 58, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrey, D.E. (Ed.) Energy. In Nutrient Requirements of Nonhuman Primates, 2nd ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, L.R.; Harrison, R.L.; Alessio, A.M.; Hunter, W.C.; Lewellen, T.K.; Kinahan, P.E. Effective count rates for PET scanners with reduced and extended axial field of view. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 3629–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vos, C.S.; Koopman, D.; Rijnsdorp, S.; Arends, A.J.; Boellaard, R.; van Dalen, J.A.; Lubberink, M.; Willemsen, A.T.M.; Visser, E.P. Quantification, improvement, and harmonization of small lesion detection with state-of-the-art PET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertzen, A.L.; Bao, Q.; Bergeron, M.; Blankemeyer, E.; Blinder, S.; Canadas, M.; Chatziioannou, A.F.; Dinelle, K.; Elhami, E.; Jans, H.S.; et al. NEMA NU 4-2008 comparison of preclinical PET imaging systems. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Chu-Shern, J.L.; Loi, H.Y.; Khor, L.K.; Sinha, A.K.; Quek, S.T.; Tham, I.W.; Townsend, D. Impact of Image Reconstruction Settings on Texture Features in 18F-FDG PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Velden, F.H.; Kramer, G.M.; Frings, V.; Nissen, I.A.; Mulder, E.R.; de Langen, A.J.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Smit, E.F.; Boellaard, R. Repeatability of Radiomic Features in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer [(18)F]FDG-PET/CT Studies: Impact of Reconstruction and Delineation. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbeke, D.; Coleman, R.E.; Guiberteau, M.J.; Brown, M.L.; Royal, H.D.; Siegel, B.A.; Townsend, D.W.; Berland, L.L.; Parker, J.A.; Hubner, K.; et al. Procedure guideline for tumor imaging with 18F-FDG PET/CT 1.0. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 885–895. [Google Scholar]
- Sureshbabu, W.; Mawlawi, O. PET/CT imaging artifacts. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2005, 33, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Seith, F.; Schmidt, H.; Gatidis, S.; Bezrukov, I.; Schraml, C.; Pfannenberg, C.; la Fougere, C.; Nikolaou, K.; Schwenzer, N. SUV-quantification of physiological lung tissue in an integrated PET/MR-system: Impact of lung density and bone tissue. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Via, L.; Chen, R.; Dodd, L.; Cai, Y.; Paripati, P.; Goldfeder, L.; Winter, J.; Arora, K.; Wang, J.; et al. 121. Improving Predictive Value of Phase 2a TB Drug Development Models Through PET/CT Imaging (NexGen EBA). In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Finch, C.L.; Crozier, I.; Lee, J.H.; Byrum, R.; Cooper, T.K.; Liang, J.; Sharer, K.; Solomon, J.; Sayre, P.J.; Kocher, G.; et al. Characteristic and quantifiable COVID-19-like abnormalities in CT- and PET/CT-imaged lungs of SARS-CoV-2-infected crab-eating macaques (Macaca fascicularis). bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkman, K.; Sombroek, C.C.; Vervenne, R.A.W.; Hofman, S.O.; Boot, C.; Remarque, E.J.; Kocken, C.H.M.; Ottenhoff, T.H.M.; Kondova, I.; Khayum, M.A.; et al. Prevention of tuberculosis infection and disease by local BCG in repeatedly exposed rhesus macaques. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabisch, P.A.; Xu, Z.; Boydston, J.A.; Solomon, J.; Bohannon, J.K.; Yeager, J.J.; Taylor, J.R.; Reeder, R.J.; Sayre, P.; Seidel, J.; et al. Quantification of regional aerosol deposition patterns as a function of aerodynamic particle size in rhesus macaques using PET/CT imaging. Inhal. Toxicol. 2017, 29, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| I:E ratio | 1:4 |
| PEEP | 4 cm H2O |
| Oxygen flow rate | 0.7 L/min |
| Air flow rate | 0.7 L/min |
| Pmax | 17 |
| Tidal volume | 10–15 mL/kg |
| Respiratory rate | 15/min |
| Weight (kg) | Activity (MBq) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 26 |
| 4 | 30 |
| 6 | 44 |
| 8 | 55 |
| 10 | 70 |
| 12 | 81 |
| 14 | 92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stammes, M.A.; Bakker, J.; Vervenne, R.A.W.; Zijlmans, D.G.M.; van Geest, L.; Vierboom, M.P.M.; Langermans, J.A.M.; Verreck, F.A.W. Recommendations for Standardizing Thorax PET–CT in Non-Human Primates by Recent Experience from Macaque Studies. Animals 2021, 11, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010204
Stammes MA, Bakker J, Vervenne RAW, Zijlmans DGM, van Geest L, Vierboom MPM, Langermans JAM, Verreck FAW. Recommendations for Standardizing Thorax PET–CT in Non-Human Primates by Recent Experience from Macaque Studies. Animals. 2021; 11(1):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010204
Chicago/Turabian StyleStammes, Marieke A., Jaco Bakker, Richard A. W. Vervenne, Dian G. M. Zijlmans, Leo van Geest, Michel P. M. Vierboom, Jan A. M. Langermans, and Frank A. W. Verreck. 2021. "Recommendations for Standardizing Thorax PET–CT in Non-Human Primates by Recent Experience from Macaque Studies" Animals 11, no. 1: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010204
APA StyleStammes, M. A., Bakker, J., Vervenne, R. A. W., Zijlmans, D. G. M., van Geest, L., Vierboom, M. P. M., Langermans, J. A. M., & Verreck, F. A. W. (2021). Recommendations for Standardizing Thorax PET–CT in Non-Human Primates by Recent Experience from Macaque Studies. Animals, 11(1), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010204






