Bias and Misrepresentation of Science Undermines Productive Discourse on Animal Welfare Policy: A Case Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodological Issues
2.1. Problematic Referencing
2.1.1. Unsupported Claims
2.1.2. Misleading Referencing
2.1.3. Selective Referencing
2.2. Overinterpretation
2.2.1. Self-Awareness
2.2.2. Von Economo Neurons
2.3. Misleading Word Choice
2.4. Fallacious Argumentation
2.4.1. Neuroanatomy
2.4.2. Survivorship and Life Expectancy
2.4.3. Causes of Illness and Death
2.4.4. Space
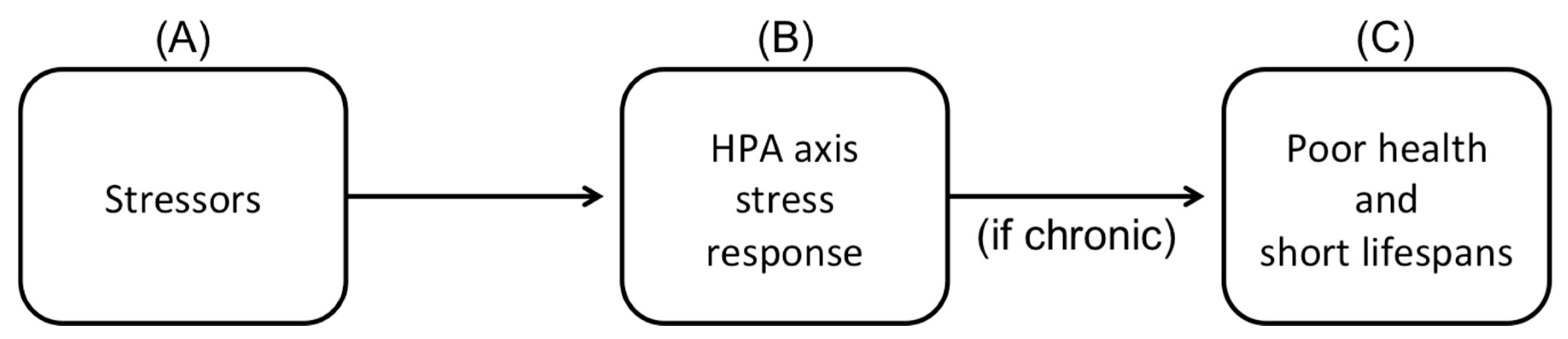
2.4.5. Stress
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hemsworth, P.; Mellor, D.; Cronin, G.; Tilbrook, A.; Hemsworth, P.H.; Tilbrook, A. Scientific assessment of animal welfare. N. Z. Vet. J. 2014, 63, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, H.M.; Jaakkola, K.; Walker, R.T.; Dudzinki, K.M. Special Issue on Animal Welfare: Introduction. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, D.J.; Hunt, S.; Gusset, M. (Eds.) Caring for Wildlife: The World Zoo and Aquarium Animal Welfare Strategy; WAZA Executive Office: Gland, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, D.M.; Watters, J.V. The Evolution of the Animal Welfare Movement in U.S. Zoos and Aquariums. Der Zool. Gart. 2017, 86, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, D.; Patterson-Kane, E.; Stafford, K.J. The Sciences of Animal Welfare; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-4443-0769-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, D.J.; Bayvel, A.C.D. The application of legislation, scientific guidelines and codified standards to advancing animal welfare. In Proceedings of the Global Conference on Animal Welfare: An OIE initiative (World Organisation for Animal Health), Paris, France, 23–25 February 2004; pp. 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, J.; Fraser, D. Zoo Animal Welfare: The Human Dimension. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2018, 21, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.M. Animal Welfare: An Aspect of Care, Sustainability, and Food Quality Required by the Public. J. Vet. Med Educ. 2010, 37, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Meer, L.; Kasdan, I.; Galvin, J. The Importance of Evidence, Animal-Based Measures, and the Rule of Law to Ensure Good Animal Welfare. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliance of Marine Mammal Parks and Aquariums. AMMPA Accreditation Standards & Guidelines. Available online: https://www.ammpa.org/membership/standards-guidelines (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Association of Zoos and Aquariums. The Accreditation Standards & Related Policies. Available online: https://www.speakcdn.com/assets/2332/aza-accreditation-standards.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- European Association for Aquatic Mammals. Standards and Guidelines for the Management of Aquatic Mammals under Human Care. Available online: https://eaam.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/EAAM-Standards-and-guidelines-2019.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- European Association of Zoos and Aquaria. EAZA Standards for the Accommodation and Care of Animals in Zoos and Aquaria. Available online: https://www.eaza.net/assets/Uploads/Standards-and-policies/2019-04-EAZA-Standards-for-Accomodation-and-Care.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Shepherdson, D.; Lewis, K.D.; Carlstead, K.; Bauman, J.; Perrin, N. Individual and environmental factors associated with stereotypic behavior and fecal glucocorticoid metabolite levels in zoo housed polar bears. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 147, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, B.J.; Meehan, C.L.; Hogan, J.N.; Leighty, K.A.; Mellen, J.; Mason, G.J.; Mench, J.A. The Days and Nights of Zoo Elephants: Using Epidemiology to Better Understand Stereotypic Behavior of African Elephants (Loxodonta africana) and Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus) in North American Zoos. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0144276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.A.; Boyd, I.; Campbell, P.; Craig, C.; Vallance, P.; Walport, M.; Whitty, C.J.M.; Woods, E.; Wormald, C. Four principles to make evidence synthesis more useful for policy. Nature 2018, 558, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, W.J.; Burgman, M. Policy advice: Use experts wisely. Nature 2015, 526, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, N.; Donald, A. Evidence based policy: Proceed with care Commentary: Research must be taken seriously. BMJ 2001, 323, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal Society. Academy of Medical Sciences Evidence Synthesis for Policy: A Statement of Principles. Available online: https://royalsociety.org/-/media/policy/projects/evidence-synthesis/principles-for-good-evidence-synthesis-for-policy.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- UK Government. Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE). Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/groups/scientific-advisory-group-for-emergencies-sage (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Whitty, C.J.M. What makes an academic paper useful for health policy? BMC Med. 2015, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heywood, V.H.; Watson, R.T. (Eds.) Global Biodiversity Assessment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; ISBN 978-0-521-56403-8. [Google Scholar]
- Janetos, A.C.; Watson, R.T.; Zinyowera, M.C.; Moss, R.-H. Climate Change 1995: Impacts, Adaptations and Mitigation of Climate Change: Scientific-Technical Analyses; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lubchenco, J. Entering the Century of the Environment: A New Social Contract for Science. Science 1998, 279, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Animal Welfare Institute. 63rd Annual Report. Available online: https://awionline.org/sites/default/files/uploads/ar/14AnnualReport/AWI-AnnualReport-2014.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Animal Welfare Institute. 65th Annual Report. Available online: https://awionline.org/sites/default/files/uploads/ar/16AnnualReport/AWI-AnnualReport-2016.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Center for Responsive Politics. Bills Lobbied By People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals, 2016. Available online: https://www.opensecrets.org/federal-lobbying/clients/bills?cycle=2016&id=D000070071 (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Center for Responsive Politics. Bills Lobbied By Animal Defenders International, 2017. Available online: https://www.opensecrets.org/federal-lobbying/clients/bills?cycle=2017&id=D000064519 (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- California Legislature. AB-2140, Marine mammals: Protection of orcas: Unlawful Activities (United States). Available online: http://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billNavClient.xhtml?bill_id=201320140AB2140. (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- United States H.R. H.R.1584—Orca Responsibility and Care Advancement Act of 2017. Available online: https://www.congress.gov/bill/115th-congress/house-bill/1584 (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Marino, L.; Rose, N.A.; Visser, I.N.; Rally, H.; Ferdowsian, H.; Slootsky, V. The harmful effects of captivity and chronic stress on the well-being of orcas (Orcinus orca). J. Vet. Behav. 2020, 35, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülpınar, Ö.; Guclu, A.G. How to write a review article? Turk. J. Urol. 2013, 39, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmatier, R.W.; Houston, M.B.; Hulland, J. Review articles: Purpose, process, and structure. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2017, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, M. Critical Issues in the Teaching of Responsible Writing. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 2014, 15, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crance, J.L.; Bowles, A.E.; Garver, A. Evidence for vocal learning in juvenile male killer whales, Orcinus orca, from an adventitious cross-socializing experiment. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremers, D.; Lemasson, A.; Almunia, J.; Wanker, R. Vocal sharing and individual acoustic distinctiveness within a group of captive orcas (Orcinus orca). J. Comp. Psychol. 2012, 126, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, W.B.; Bowles, A.E.; Grebner, D.M.; Crance, J.L. Differences in acoustic features of vocalizations produced by killer whales cross-socialized with bottlenose dolphins. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 1990–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, R.J.; DeMaster, D.P. Survival of five species of captive marine mammals. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 1995, 11, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodley, T.H.; Hannah, J.L.; Lavigne, D.M. A Comparison of Survival Rates for Captive and Free-Ranging Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus), Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) and Beluga Whales (Delphinapterus leucas); IMMA Technical Report 97-02; International Marine Mammal Association: Guelph, Canada, 1997; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jett, J.; Ventre, J. Captive killer whale (Orcinus orca) survival. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 2015, 31, 1362–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeck, T.; Willis, K.; Scarpuzzi, M.R.; O’Brien, J. Comparisons of life-history parameters between free-ranging and captive killer whale (Orcinus orca) populations for application toward species management. J. Mammal. 2015, 96, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissy, A.; Manteuffel, G.; Jensen, M.B.; Moe, R.O.; Spruijt, B.; Keeling, L.J.; Winckler, C.; Forkman, B.; Dimitrov, I.; Langbein, J.; et al. Assessment of positive emotions in animals to improve their welfare. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawkins, M.S. Evolution and Animal Welfare. Q. Rev. Biol. 1998, 73, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, I.; Van Elk, C.; Delfour, F. Applying welfare science to bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Anim. Welf. 2017, 26, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitham, J.C.; Wielebnowski, N. New directions for zoo animal welfare science. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 147, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E. The Evolution of Tag-Based Cooperation in Humans: The case for accent. Curr. Anthropol 2012, 53, 588–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marler, P. A comparative approach to vocal learning: Song development in white-crowned sparrows. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1970, 71, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.K.B. Vocal traditions among resident killer whales (Orcinus orca) in coastal waters of British Columbia. Can. J. Zool. 1991, 69, 1454–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesiuk, P.F.; Bigg, M.A.; Ellis, G.M. Life history and population dynamics of resident killer whales (Orcinus orca) in the coastal waters of British Columbia and Washington State. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Issue 1990, 12, 209–243. [Google Scholar]
- Olesiuk, P.F.; Ellis, G.M.; Ford, J.K. Life History and Population Dynamics of Northern Resident Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) in British Columbia; Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hofman, M.A. Size and Shape of the Cerebral Cortex in Mammals: I. The cortical surface. Brain Behav. Evol. 1985, 27, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manger, P.R.; Prowse, M.; Haagensen, M.; Hemingway, J. Quantitative analysis of neocortical gyrencephaly in African elephants (Loxodonta africana) and six species of cetaceans: Comparison with other mammals. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 2430–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, B.; Herculano-Houzel, S. Cortical folding scales universally with surface area and thickness, not number of neurons. Science 2015, 349, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, P.; Manger, P.R. Order-specific quantitative patterns of cortical gyrification. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Brownson, R.H. Relative brain sizes and cortical surface areas in odontocetes. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1984, 172, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, L. Cetacean brains: How aquatic are they? Anat. Rec. 2007, 290, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.R. How to write an effective discussion. Respir. Care 2004, 49, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Ochodo, E.A.; De Haan, M.C.; Reitsma, J.B.; Hooft, L.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Leeflang, M. Overinterpretation and Misreporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies: Evidence of “Spin. ” Radiology 2013, 267, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, F. Cognitive enrichment and welfare: Current approaches and future directions. Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2017, 4, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, C.L.; Mench, J. The challenge of challenge: Can problem solving opportunities enhance animal welfare? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 102, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.; Sherwen, S.; Clark, F.E. Advances in Applied Zoo Animal Welfare Science. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2018, 21, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor, K.W.; Haag, R.; O’Reilly, J. The creative porpoise: Training for novel behavior. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 1969, 12, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.P.; Brignac, S.E.; Keaton, L. Dolphins demonstrate the understanding of an abstract idea. Soundings 2013, 38.2, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, F.E. Marine mammal cognition and captive care: A proposal for cognitive enrichment in zoos and aquariums. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.R. How cognitive studies help shape our obligations for the ethical care of chimpanzees. In The Mind of the Chimpanzee: Ecological and Experimental Perspectives; Lonsdorf, E.V., Ross, S.R., Matsuzawa, T., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010; pp. 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, K. Understanding reflections of self and other objects. In Drawing and the Non-Verbal Mind: A Life-Span Perspective; Lange-Küttner, C., Vinter, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 23–41. ISBN 978-0-511-48973-0. [Google Scholar]
- De Veer, M.W.; Bos, R.V.D. A critical review of methodology and interpretation of mirror self-recognition research in nonhuman primates. Anim. Behav. 1999, 58, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povinelli, D.J.; Rulf, A.B.; Landau, K.R.; Bierschwale, D.T. Self-recognition in chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes): Distribution, ontogeny, and patterns of emergence. J. Comp. Psychol. 1993, 107, 347–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, H.E. Consciousness in dolphins? A review of recent evidence. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2013, 199, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfour, F.; Marten, K. Mirror image processing in three marine mammal species: Killer whales (Orcinus orca), false killer whales (Pseudorca crassidens) and California sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Behav. Process. 2001, 53, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnik, J.M.; De Waal, F.B.M.; Reiss, D. Self-recognition in an Asian elephant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17053–17057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, D.; Marino, L. Mirror self-recognition in the bottlenose dolphin: A case of cognitive convergence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5937–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallup, G.G. Chimpanzees: Self-Recognition. Science 1970, 167, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, S.D.; Gallup, G.G. Self-recognition in chimpanzees and orangutans, but not gorillas. J. Hum. Evol. 1981, 10, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westergaard, G.C.; Hyatt, C.W. The responses of bonobos (Pan paniscus) to their mirror images: Evidence of selfrecognition. Hum. Evol. 1994, 9, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, H.; Schwarz, A.; Güntürkün, O. Mirror-induced behavior in the magpie (Pica pica): Evidence of self-recognition. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohda, M.; Hotta, T.; Takeyama, T.; Awata, S.; Tanaka, H.; Asai, J.-Y.; Jordan, A. If a fish can pass the mark test, what are the implications for consciousness and self-awareness testing in animals? PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allman, J.M.; Watson, K.; Tetreault, N.A.; Hakeem, A.Y. Intuition and autism: A possible role for Von Economo neurons. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghanti, M.A.; Munger, E.L.; Wicinski, B.; Butti, C.; Hof, P.R. Comparative structure of the cerebral cortex in large mammals. In Evolution of Nervous Systems; Kaas, J.H., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 267–289. ISBN 978-0-12-804096-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hof, P.R.; Van Der Gucht, E. Structure of the cerebral cortex of the humpback whale, Megaptera novaeangliae (Cetacea, Mysticeti, Balaenopteridae). Anat. Rec. 2007, 290, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butti, C.; Sherwood, C.C.; Hakeem, A.Y.; Allman, J.M.; Hof, P.R. Total number and volume of Von Economo neurons in the cerebral cortex of cetaceans. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 515, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, A.Y.; Sherwood, C.C.; Bonar, C.J.; Butti, C.; Hof, P.R.; Allman, J.M. Von Economo Neurons in the Elephant Brain. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernfeind, A.; De Sousa, A.A.; Avasthi, T.; Dobson, S.D.; Raghanti, M.A.; Lewandowski, A.H.; Zilles, K.; Semendeferi, K.; Allman, J.M.; Craig, A.D.; et al. A volumetric comparison of the insular cortex and its subregions in primates. J. Hum. Evol. 2013, 64, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butti, C.; Hof, P.R. The insular cortex: A comparative perspective. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butti, C.; Raghanti, M.A.; Sherwood, C.C.; Hof, P.R. The neocortex of cetaceans: Cytoarchitecture and comparison with other aquatic and terrestrial species. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1225, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butti, C.; Fordyce, E.; Raghanti, M.A.; Gu, X.; Bonar, C.J.; Wicinski, B.A.; Wong, E.W.; Roman, J.; Brake, A.; Eaves, E.; et al. The Cerebral Cortex of the Pygmy Hippopotamus, Hexaprotodon liberiensis (Cetartiodactyla, Hippopotamidae): MRI, Cytoarchitecture, and Neuronal Morphology. Anat. Rec. 2014, 297, 670–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrard, H.C.; Forro, T.; Logothetis, N.K. Von Economo Neurons in the Anterior Insula of the Macaque Monkey. Neuron 2012, 74, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghanti, M.A.; Spurlock, L.B.; Treichler, F.R.; Weigel, S.E.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Butti, C.; Thewissen, J.G.M.; Hof, P.R. An analysis of von Economo neurons in the cerebral cortex of cetaceans, artiodactyls, and perissodactyls. Brain Struct. Funct. 2014, 220, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Acosta, C.A.; Escobar, M.I.; Casanova, M.F.; Pimienta, H.J.; Buriticá, E. Von Economo Neurons in the Human Medial Frontopolar Cortex. Front. Neuroanat. 2018, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaxco, K.W. The art of writing science. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 2261–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerison, H.J. Evolution of the Brain and Intelligence; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973; ISBN 978-0-12-385250-2. [Google Scholar]
- Radinsky, L.; Jerison, H. Evolution of the Brain and Intelligence. Curr. Anthropol. 1975, 29, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairό, O. External Measures of Cognition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.; Avin, S.; Boogert, N.; Buskell, A.; Cross, F.R.; Currie, A.; Jelbert, S.; Lukas, D.; Mares, R.; Navarrete, A.F.; et al. Beyond brain size: Uncovering the neural correlates of behavioral and cognitive specialization. Comp. Cogn. Behav. Rev. 2018, 13, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.D.; Harvey, P.H. Brain size allometry ontogeny and phylogeny. In Size and Scaling in Primate Biology; Jungers, W.L., Ed.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 147–173. ISBN 978-1-4899-3649-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pagel, M.; Harvey, P. Taxonomic differences in the scaling of brain on body weight among mammals. Science 1989, 244, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddy, A.M.; McGowen, M.R.; Sherwood, C.C.; Grossman, L.I.; Goodman, M.; Wildman, D.E. Comparative analysis of encephalization in mammals reveals relaxed constraints on anthropoid primate and cetacean brain scaling. J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 25, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, R.C.; Smolker, R.A.; Richards, A.F. Dolphin alliances and coalitions. In Coalitions and Alliances in Humans and Other Animals; Harcourt, A.H., de Waal, F.B.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 415–443. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, R.; Mann, J. Social cognition in the wild: Machiavellian dolphins? In Rational Animals? Hurley, S., Nudds, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 329–368. ISBN 978-0-19-852827-2. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, R.C. Dolphin social intelligence: Complex alliance relationships in bottlenose dolphins and a consideration of selective environments for extreme brain size evolution in mammals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herculano-Houzel, S.; Catania, K.; Manger, P.R.; Kaas, J.H. Mammalian Brains Are Made of These: A Dataset of the Numbers and Densities of Neuronal and Nonneuronal Cells in the Brain of Glires, Primates, Scandentia, Eulipotyphlans, Afrotherians and Artiodactyls, and Their Relationship with Body Mass. Brain, Behav. Evol. 2015, 86, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güntürkün, O.; Bugnyar, T. Cognition without Cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2016, 20, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, J.W.; Ghazanfar, A.A.; Gomez-Marin, A.; Maciver, M.A.; Poeppel, D. Neuroscience Needs Behavior: Correcting a Reductionist Bias. Neuron 2017, 93, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, P.R.; Chanis, R.; Marino, L. Cortical complexity in cetacean brains. Anat. Rec. Part. A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2005, 287, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola, K.; Willis, K. How long do dolphins live? Survival rates and life expectancies for bottlenose dolphins in zoological facilities vs. Wild populations. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 2019, 35, 1418–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, D. Examining the validity of inferences drawn from photo-identification data, with special reference to studies of the killer whales (Orcinus orca) in British Columbia. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Issue 1990, 12, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Health Statistics: Pneumonia. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/pneumonia.htm (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Van Bressem, M.; Van Waerebeek, K.; Raga, J.A. A review of virus infections of cetaceans and the potential impact of morbilliviruses, poxviruses and papillomaviruses on host population dynamics. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 38, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaydos, J.K.; Balcomb, K.C.; Osborne, R.W.; Dierauf, L. Evaluating potential infectious disease threats for southern resident killer whales, Orcinus orca: A model for endangered species. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 117, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegrove, K.M.; Leger, J.S.; Raverty, S.; Jang, S.; Berman-Kowalewski, M.; Gaydos, J.K. Salmonella Newport Omphaloarteritis in a Stranded Killer Whale (Orcinus orca) Neonate. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reckendorf, A.; Ludes-Wehrmeister, E.; Wohlsein, P.; Tiedemann, R.; Siebert, U.; Lehnert, K. First record of Halocercus sp. (Pseudaliidae) lungworm infections in two stranded neonatal orcas (Orcinus orca). Parasitology 2018, 145, 1553–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vere, A.J.; Lilley, M.K.; Frick, E.E. Anthropogenic Impacts on the Welfare of Wild Marine Mammals. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 150–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J. Welfare of whales by-caught in fishing gear or struck by vessels. Anim. Welf. 2013, 22, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, M.E.; Carlstead, K. The importance of maintaining natural behaviors in captive mammals. In Wild Mammals in Captivity: Principles and Techniques for Zoo Management, 2nd ed.; Kleiman, D.G., Thompson, K.V., Baer, C.K., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010; pp. 303–313. ISBN 978-0-226-44011-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, G. Species differences in responses to captivity: Stress, welfare and the comparative method. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clubb, R.; Mason, G. Captivity effects on wide-ranging carnivores. Nature 2003, 425, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clubb, R.; Mason, G.J. Natural behavioural biology as a risk factor in carnivore welfare: How analysing species differences could help zoos improve enclosures. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 102, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, D. Across the Boundaries: Extrapolation in Biology and Social Science; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-19-533144-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, K.; Ramirez, K. Modern animal training: A transformative technology. In The Wiley Blackwell Handbook of Operant and Classical Conditioning; McSweeney, F.K., Murphy, E.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 453–482. ISBN 978-1-118-46813-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, K. Marine Mammal Training. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2012, 15, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maple, T.L. Toward a Science of Welfare for Animals in the Zoo. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2007, 10, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.J. Chapter 11. Stress. In An Introduction to Behavioral Endocrinology; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 669–720. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, J.P. Neural control of chronic stress adaptation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, S.; Dierauf, L. Stress and Marine Mammals. In CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 141–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos, G.P. Stress and disorders of the stress system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.L.; Butler, L.K. Endocrinology of stress. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Selye, H. Stress without Distress; New American Library: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Toates, F. Stress: Conceptual and Biological Aspects; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, S.; Crocker, D.; Houser, D.S.; Mashburn, K. Stress physiology in marine mammals: How well do they fit the terrestrial model? J. Comp. Physiol. B 2015, 185, 463–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupien, S.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Gunnar, M.R.; Heim, C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B. Neurobiological and Systemic Effects of Chronic Stress. Chronic Stress 2017, 1, 247054701769232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monreal-Pawlowsky, T.; Carbajal, A.; Tallo-Parra, O.; Sabés-Alsina, M.; Monclús, L.; Almunia, J.; Bellon, H.F.; López-Béjar, M. Daily salivary cortisol levels in response to stress factors in captive common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus): A potential welfare indicator. Vet. Rec. 2017, 180, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proie, S. A Systematic Review of Cortisol Levels in Wild and Captive Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus), Killer Whale (Orcinus orca), and Beluga Whale (Delphinapterus leucas). Master’s Thesis, Evergreen State College, Olympia, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aubin, D.J.S.; Ridgway, S.H.; Wells, R.S.; Rhinehart, H. Dolphin thyroid and adrenal hormones: Circulating levels in wild and semidomesticated tursiops truncatus, and influence of sex, age, and season. Mar. Mammal. Sci. 1996, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, C.A.; Geraci, J.R. Cortisol, Aldosterone, and Leucocytes in the Stress Response of Bottlenose Dolphins, Tursiops truncatus. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1986, 43, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, M.C.; Mench, J.A.; Olsson, I.A.; Hughes, B.O. (Eds.) Animal Welfare, 2nd ed.; CABI: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-84593-659-4. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaakkola, K.; Bruck, J.N.; Connor, R.C.; Montgomery, S.H.; King, S.L. Bias and Misrepresentation of Science Undermines Productive Discourse on Animal Welfare Policy: A Case Study. Animals 2020, 10, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071118
Jaakkola K, Bruck JN, Connor RC, Montgomery SH, King SL. Bias and Misrepresentation of Science Undermines Productive Discourse on Animal Welfare Policy: A Case Study. Animals. 2020; 10(7):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071118
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaakkola, Kelly, Jason N. Bruck, Richard C. Connor, Stephen H. Montgomery, and Stephanie L. King. 2020. "Bias and Misrepresentation of Science Undermines Productive Discourse on Animal Welfare Policy: A Case Study" Animals 10, no. 7: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071118
APA StyleJaakkola, K., Bruck, J. N., Connor, R. C., Montgomery, S. H., & King, S. L. (2020). Bias and Misrepresentation of Science Undermines Productive Discourse on Animal Welfare Policy: A Case Study. Animals, 10(7), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071118




