Evaluation of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus Probiotics as Alternative Therapy for Salmonella typhimurium Infection in Broiler Chickens
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. S. typhimurium Culture and Determination of Colony Forming Unit (CFU)
2.2. Probiotics Culture
2.3. Adhesion of Probiotic Strains to Caco-2 Cells
2.4. Birds and Housing
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Determination of Serum IFN-γ and TNF-α
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LAB-Epithelial Adherence
3.2. Clinical Signs and Postmortem (PM) Lesions
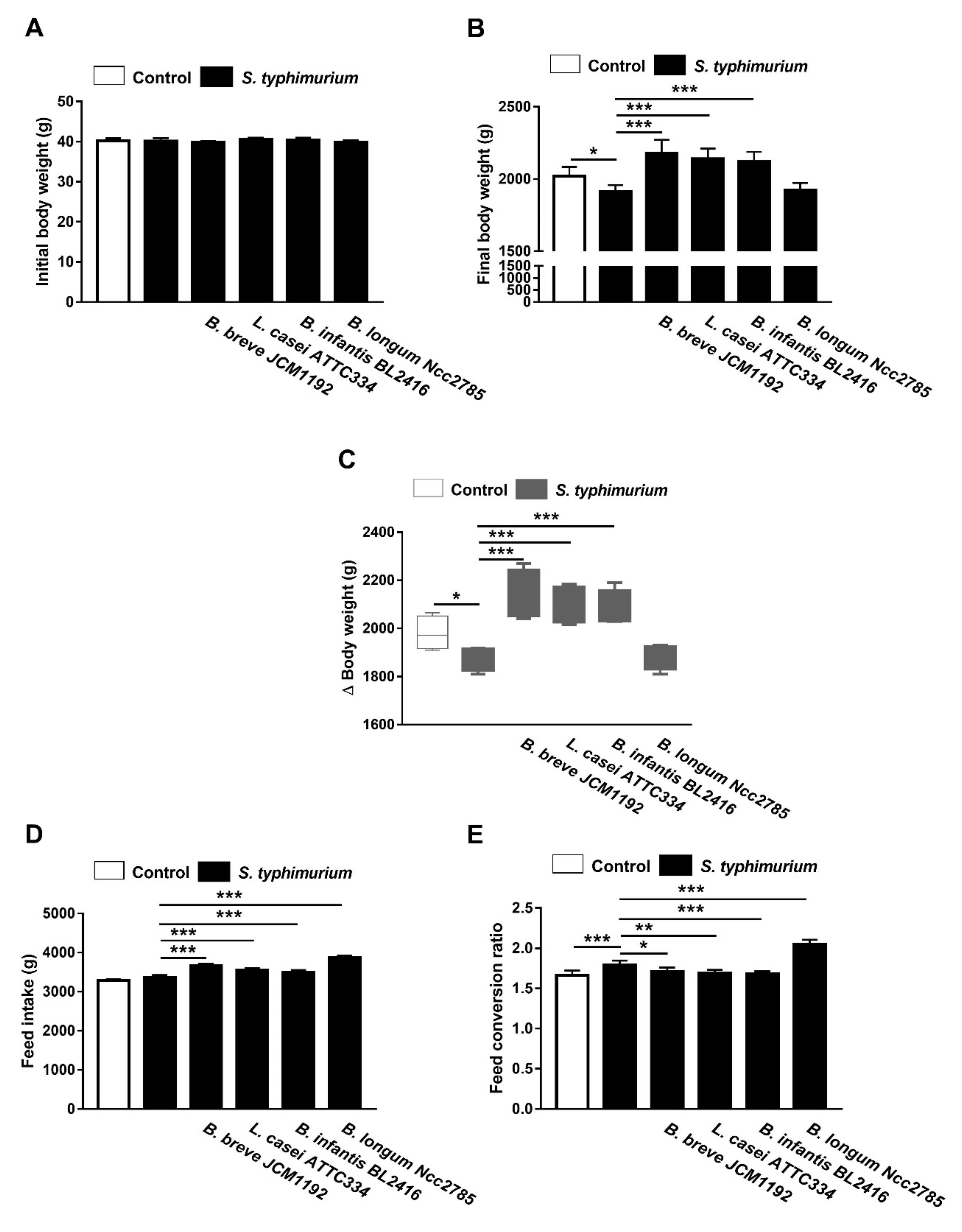
3.3. Probiotics Improve Growth Performance in S. typhimurium-Infected Broiler Chickens
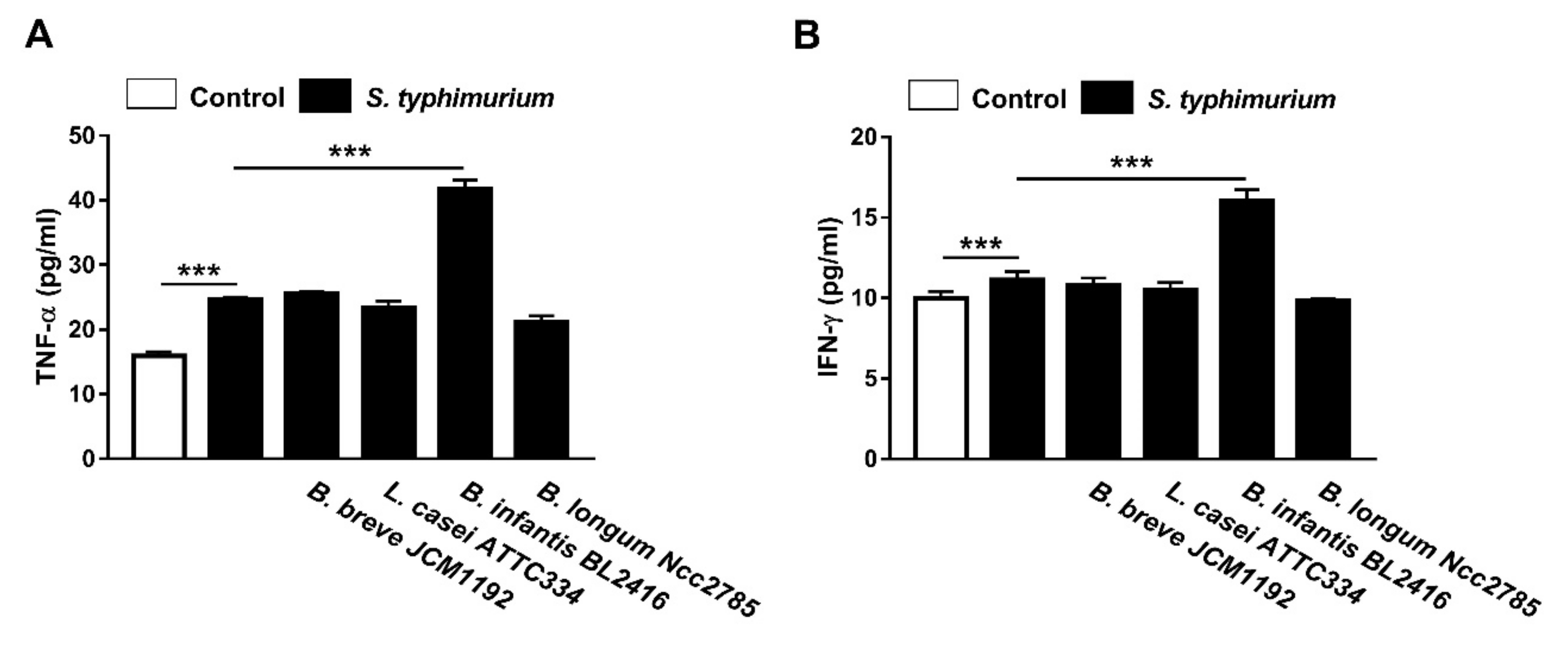
3.4. Effect of Probiotics on Serum TNF-α and IFN-γ Levels in and S. typhimurium-Infected Broiler Chickens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fantasia, M.; Filetici, E. Salmonella enteritidis in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1994, 21, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omwandho, C.O.A.; Kubota, T. Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis: A mini-review of contamination routes and limitations to effective control. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. JARQ 2010, 44, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padron, M. Salmonella typhimurium outbreak in broiler chicken flocks in Mexico. Avian Dis. 1990, 34, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, H.; Tahoun, A.; El-Gohary, A.E.-G.A.; El-Abasy, M.; El-Khayat, F.; Gillespie, T.; Kitade, Y.; Hafez, H.M.; Neubauer, H.; El-Adawy, H. Epidemiological, molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from chicken farms in Egypt. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sean, F.A.; Nathan, B.; Amy, C.; Robert, D.; Alecia, N.; Wayne, S.; Robert, U.; Patricia, W. Salmonella enteritidis in broiler chickens, United States, 2000–2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 12, 1848. [Google Scholar]
- Coble, D.J.; Sandford, E.E.; Ji, T.; Abernathy, J.; Fleming, D.; Zhao, H.; Lamont, S.J. Impacts of Salmonella enteritidis infection on liver transcriptome in broilers. Genesis 2013, 51, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, I.A.; Dobrogosz, W.J. Validation of the probiotic concept: Lactobacillus reuteri confers broad-spectrum protection against disease in humans and animals. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2000, 12, 247–285. [Google Scholar]
- Spinler, J.K.; Taweechotipatr, M.; Rognerud, C.L.; Ou, C.N.; Tumwasorn, S.; Versalovic, J. Human-derived probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri demonstrate antimicrobial activities targeting diverse enteric bacterial pathogens. Anaerobe 2008, 14, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, T.L.; Dobrogosz, W.J. Chemical characterization of an antimicrobial substance produced by Lactobacillus reuteri. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989, 33, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.R.; Sperandio, V. Enteric pathogens exploit the microbiota-generated nutritional environment of the gut. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 279–296. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, F.M.; Mousavi, H.; Mousavi, M.R.N.; Shahsafi, M. Efficacy of probiotics in prevention and treatment of infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2018, 40, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeer, S.; Bron, P.A.; Marco, M.L.; Van Pijkeren, J.-P.; O’Connell Motherway, M.; Hill, C.; Pot, B.; Roos, S.; Klaenhammer, T. Identification of probiotic effector molecules: Present state and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X. Using in vitro immunomodulatory properties of lactic acid bacteria for selection of probiotics against Salmonella infection in broiler chicks. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shall, N.A.; Awad, A.M.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Othman, S.I.; Allam, A.A.; Sedeik, M.E. The simultaneous administration of a probiotic or prebiotic with live Salmonella vaccine improves growth performance and reduces fecal shedding of the bacterium in Salmonella-challenged broilers. Animals 2019, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Hao, H.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Dai, M.; Huang, L.; Yuan, Z. Antibiotic alternatives: The substitution of antibiotics in animal husbandry? Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazorla, S.I.; Maldonado-Galdeano, C.; Weill, R.; De Paula, J.; Perdigón, G.D.V. Oral administration of probiotics increases paneth cells and intestinal antimicrobial activity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, G.; Beckloff, N.; Weinberg, A.; Kisich, K.O. The roles of antimicrobial peptides in innate host defense. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2377–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.R.; Haghighi, H.R.; Chambers, J.R.; Brisbin, J.; Read, L.R.; Sharif, S. Expression of antimicrobial peptides in cecal tonsils of chickens treated with probiotics and infected with salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2008, 15, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S. Detection of antimicrobial resistance genes of pathogenic Salmonella from swine with DNA microarray. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2007, 19, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Higgins, S.E.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Henderson, S.N.; Torres-Rodriguez, A.; Vicente, J.L.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez, G. Effect of lactic acid bacteria probiotic culture treatment timing on Salmonella enteritidis in neonatal broilers. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahoun, A.; Masutani, H.; El-Sharkawy, H.; Gillespie, T.; Honda, R.P.; Kuwata, K.; Inagaki, M.; Yabe, T.; Nomura, I.; Suzuki, T. Capsular polysaccharide inhibits adhesion of Bifidobacterium longum 105-a to enterocyte-like caco-2 cells and phagocytosis by macrophages. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry: Ninth Revised Edition; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Salminen, S.; Laine, M.; Vonwright, A.; Vuopio-Varkila, J.; Korhonen, T.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Development of selection criteria for probiotic strains to assess their potential in functional foods: A Nordic and European approach. Biosci. Microflora 1996, 15, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.N.; Rosenfeldt Nielsen, V.; Hayford, A.E.; Møller, P.L.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Paerregaard, A.; Sandström, B.; Tvede, M.; Jakobsen, M. Screening of probiotic activities of forty-seven strains of Lactobacillus spp. by in vitro techniques and evaluation of the colonization ability of five selected strains in humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4949–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crociani, J.; Grill, J.P.; Huppert, M.; Ballongue, J. Adhesion of different Bifidobacteria strains to human enterocyte-like caco-2 cells and comparison with in vivo study. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1995, 21, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alander, M.; Korpela, R.; Saxelin, M.; Vilpponen-Salmela, T.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; Von Wright, A. Recovery of Lactobacillus rhamnosus gg from human colonic biopsies. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Fata, G.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. Probiotics and the gut immune system: Indirect regulation. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Beagley, K.W.; France, M.P.; Shen, J.; Husband, A.J. Interferon-gamma plays a critical role in intestinal immunity against Salmonella typhimurium infection. Immunology 2000, 99, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, B.; Kaufmann, S.H. Bacterial virulence, proinflammatory cytokines and host immunity: How to choose the appropriate salmonella vaccine strain? Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, T.K.; Weihua, X.; Yuan, L.; Kalvakolanu, D.V.; Cross, A.S. Gamma interferon augments macrophage activation by lipopolysaccharide by two distinct mechanisms, at the signal transduction level and via an autocrine mechanism involving tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibuki, M.; Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Fukui, K.; Kanatani, H.; Mine, Y. Β 1-4 mannobiose enhances Salmonella-killing activity and activates innate immune responses in chicken macrophages. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 139, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasina, Y.O.; Holt, P.S.; Moran, E.T.; Moore, R.W.; Conner, D.E.; McKee, S.R. Intestinal cytokine response of commercial source broiler chicks to Salmonella typhimurium infection. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, N.; Hulme, S.D.; Barrow, P.A. Induction of antimicrobial pathways during early-phase immune response to Salmonella spp. In murine macrophages: Gamma interferon (ifn-gamma) and upregulation of ifn-gamma receptor alpha expression are required for nadph phagocytic oxidase gp91-stimulated oxidative burst and control of virulent salmonella spp. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4733–4741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rantala, M.; Nurmi, E. Prevention of the growth of Salmonella infantis in chicks by the flora of the alimentary tract of chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 1973, 14, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenship, L.C.; Bailey, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Stern, N.J.; Brewer, R.; Williams, O. Two-step mucosal competitive exclusion flora treatment to diminish salmonellae in commercial broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 1993, 72, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrier, D.E.; Hinton, A., Jr.; Ziprin, R.L.; Beier, R.C.; DeLoach, J.R. Effect of dietary lactose on cecal ph, bacteriostatic volatile fatty acids, and Salmonella typhimurium colonization of broiler chicks. Avian Dis. 1990, 34, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneitz, C. Competitive exclusion in poultry––30 years of research. Food Control 2005, 16, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, L.; Kagnoff, M.F. Cytokines in host defense against Salmonella. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderpool, C.; Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Mechanisms of probiotic action: Implications for therapeutic applications in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Yuan, K.T.; Yu, L.; Meng, Q.H.; Chung, P.C.; Yang, D.H. Bifidobacterium infantis attenuates colitis by regulating t cell subset responses. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18316–18329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revolledo, L.; Ferreira, C.S.; Ferreira, A.J. Prevention of Salmonella typhimurium colonization and organ invasion by combination treatment in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, A.W.; El-Shafii, S.A.S.; Hatem, M.E.; Dawood, E. A trial to prevent Salmonella enteritidis infection in broiler chickens using autogenous bacterin compared with probiotic preparation. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients (%) | Starter | Grower | Finisher |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn grains | 56.9 | 61.6 | 66.4 |
| Soybean meal 48% | 34.31 | 29.71 | 24.6 |
| Corn gluten meal 60% | 3.5 | 3 | 3 |
| Soybean oil | 1.5 | 2 | 2.71 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.6 | 1.37 | 1.27 |
| Limestone | 1.05 | 1.11 | 1 |
| Salt | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.24 |
| Lysine hydrochloride | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.15 |
| D.L Methionine | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 |
| Premix | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Nutrients content | |||
| Metabolizable energy (K Cal/kg) | 3050 | 3120 | 3150 |
| Crude protein % | 23.12 | 21.02 | 19.01 |
| Crude fat % | 4.01 | 4.8 | 5.5 |
| Ash | 6.1 | 5.5 | 5.0 |
| Acid detergent fiber % | 4.51 | 4.34 | 4.3 |
| Calcium % | 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.86 |
| Available phosphorus % | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.38 |
| Groups | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Control | Inoculated orally with saline. |
| S. typhimurium | Inoculated orally with S. typhimurium. |
| B. breve JCM1192 + S. typhimurium | Inoculated orally with B. breve JCM1192 and S. typhimurium. |
| L. casei ATTC334 + S. typhimurium | Inoculated orally with L. casei ATTC334 and S. typhimurium. |
| B. longum Ncc2785 + S. typhimurium | Inoculated orally with B. longum Ncc2785 and S. typhimurium. |
| B infantis BL2416 + S. typhimurium | Inoculated orally with B infantis BL2416 and S. typhimurium. |
| Group | S. typhimurium-Positive Cecal Tonsils/Total Cecal Tonsils (%) | S. typhimurium-Cecal Recovery (×104) |
|---|---|---|
| S. typhimurium | 10/10 (100%) | 230.0 ± 4.14 |
| B. breve JCM1192 + S. typhimurium | 2/10 (20%) * | 26.4 ± 8.067 *** |
| L. casei ATTC334 + S. typhimurium | 1/10 (10%) * | 17.18 ± 3.45 *** |
| B. longum Ncc2785 + S. typhimurium | 9/10 (90%) | 179.03 ± 7.81 |
| B infantis BL2416 + S. typhimurium | 3/10 (30%) | 22.61 ± 6.65 *** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Sharkawy, H.; Tahoun, A.; Rizk, A.M.; Suzuki, T.; Elmonir, W.; Nassef, E.; Shukry, M.; Germoush, M.O.; Farrag, F.; Bin-Jumah, M.; et al. Evaluation of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus Probiotics as Alternative Therapy for Salmonella typhimurium Infection in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2020, 10, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061023
El-Sharkawy H, Tahoun A, Rizk AM, Suzuki T, Elmonir W, Nassef E, Shukry M, Germoush MO, Farrag F, Bin-Jumah M, et al. Evaluation of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus Probiotics as Alternative Therapy for Salmonella typhimurium Infection in Broiler Chickens. Animals. 2020; 10(6):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061023
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Sharkawy, Hanem, Amin Tahoun, Amira M. Rizk, Tohru Suzuki, Walid Elmonir, Eldsokey Nassef, Mustafa Shukry, Mousa O. Germoush, Foad Farrag, May Bin-Jumah, and et al. 2020. "Evaluation of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus Probiotics as Alternative Therapy for Salmonella typhimurium Infection in Broiler Chickens" Animals 10, no. 6: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061023
APA StyleEl-Sharkawy, H., Tahoun, A., Rizk, A. M., Suzuki, T., Elmonir, W., Nassef, E., Shukry, M., Germoush, M. O., Farrag, F., Bin-Jumah, M., & Mahmoud, A. M. (2020). Evaluation of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus Probiotics as Alternative Therapy for Salmonella typhimurium Infection in Broiler Chickens. Animals, 10(6), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061023






