Spirulina platensis Reduced Oxidative Damage Induced by Chlorpyrifos Toxicity in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish, Diet, Chlorpyrifos (CPF), and Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Biochemical Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Biochemical Markers
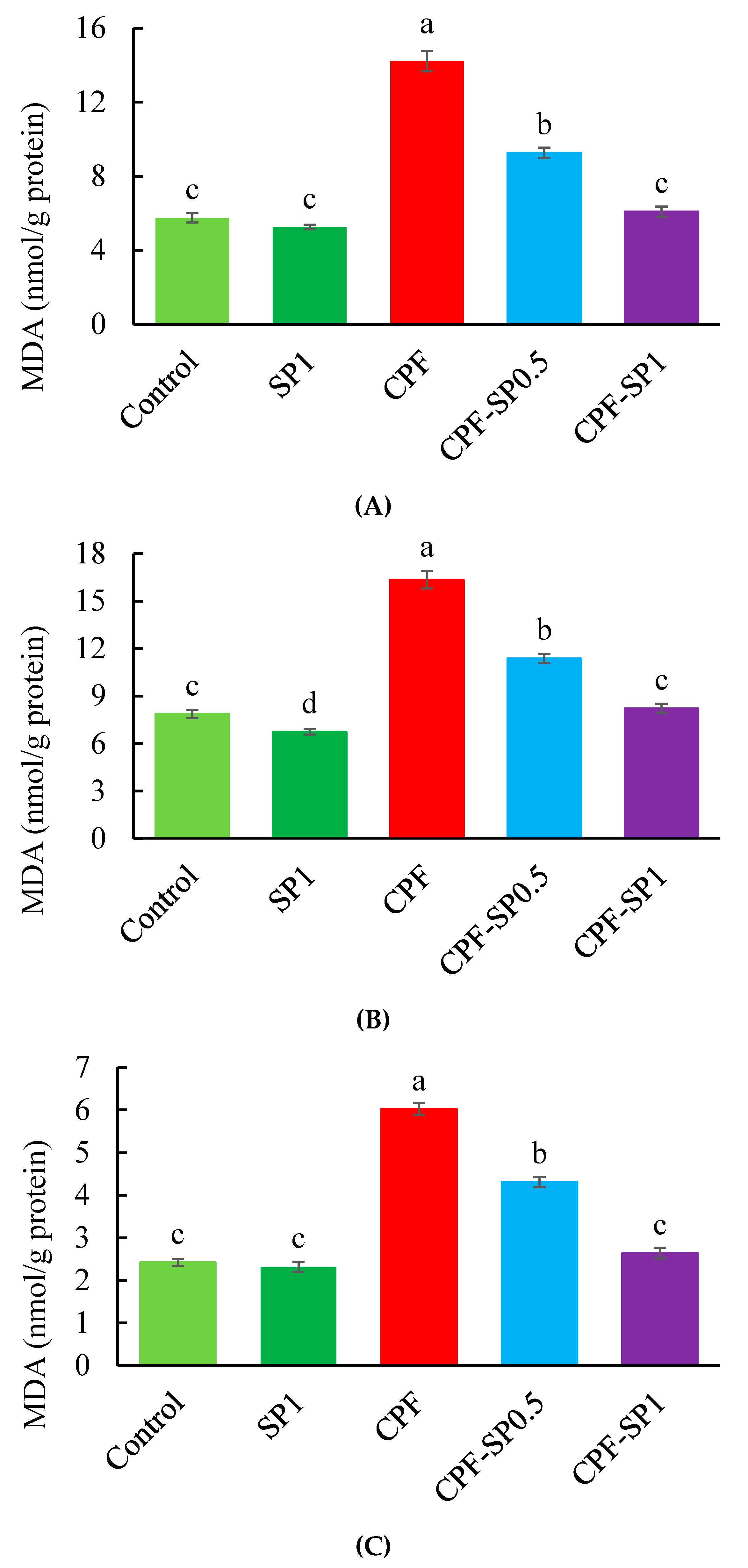
3.2. Tissue Lipid Peroxidation
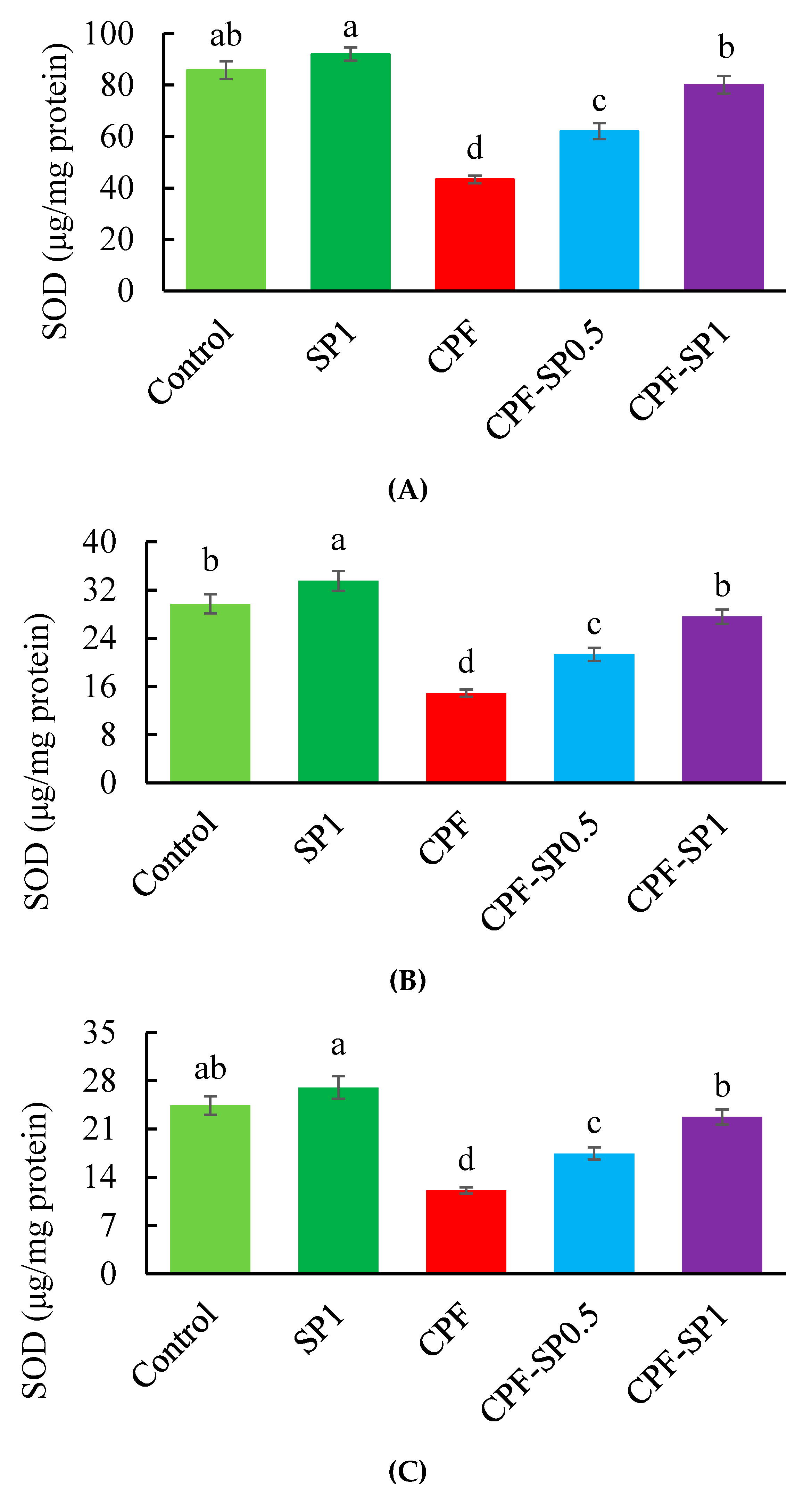
3.3. Tissues Enzymatic Antioxidant Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmadifar, E.; Dawood, M.A.; Moghadam, M.S.; Sheikhzadeh, N.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Musthafa, M.S. Modulation of immune parameters and antioxidant defense in zebrafish (Danio rerio) using dietary apple cider vinegar. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Dani, V.; Dhawan, D.K. Protective effects of zinc on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzymes and hepatic histoarchitecture in chlorpyrifos-induced toxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2005, 156, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandahl, J.F.; Baldwin, D.H.; Jenkins, J.J.; Scholz, N.L. Comparative thresholds for acetylcholinesterase inhibition and behavioral impairment in coho salmon exposed to chlorpyrifos. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, E.; Risha, E.; Awadin, W.; Palić, D. Acute exposure to chlorpyrifos induces reversible changes in health parameters of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 197, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Megid, A.A.; Abd Al Fatah, M.; El Asely, A.; El Senosi, Y.; Moustafa, M.M.A.; Dawood, A.O. Impact of pyrethroids and organochlorine pesticides residue on IGF-1 and CYP1A genes expression and muscle protein patterns of cultured Mugil capito. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.F.; Yacout, D.M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Status, constraints and potentials. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 1201–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjeibi, I.; Ben Saad, A.; Hfaiedh, N. Oxidative damage and hepatotoxicity associated with deltamethrin in rats: The protective effects of Amaranthus spinosus seed extract. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Moustafa, E.M.; Gewaily, M.S.; Abdo, S.E.; AbdEl-kader, M.F.; SaadAllah, M.S.; Hamouda, A.H. Ameliorative effects of Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to deltamethrin toxicity in rearing water. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 219, 734571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Abdo, S.E.; Gewaily, M.S.; Moustafa, E.M.; SaadAllah, M.S.; AbdEl-Kader, M.F.; Hamouda, A.H.; Omar, A.A.; Alwakeel, R.A. The influence of dietary β-glucan on immune, transcriptomic, inflammatory and histopathology disorders caused by deltamethrin toxicity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.; Dadar, M.; Khajavi, S.H.; Pourgholam, R.; Karimí, B.; Velisek, J. Hematological, biochemical and histopathological changes in Caspian brown trout (Salmo trutta caspius Kessler, 1877) following exposure to sublethal concentrations of chlorpyrifos. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelock, C.E.; Eder, K.J.; Werner, I.; Huang, H.; Jones, P.D.; Brammell, B.F.; Elskus, A.A.; Hammock, B.D. Individual variability in esterase activity and CYP1A levels in Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) exposed to esfenvalerate and chlorpyrifos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilak, K.S.; Veeraiah, K.; Rao, D.K. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of chlorpyrifos in Indian carp Catla catla (Hamilton), Labeo rohita (Hamilton), and Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 73, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xing, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, H.; Sun, G.; Xu, Q.; Xu, S. Accumulation, histopathological effects and response of biochemical markers in the spleens and head kidneys of common carp exposed to atrazine and chlorpyrifos. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.V.; Begum, G.; Pallela, R.; Usman, P.K.; Rao, R.N. Changes in behavior and brain acetylcholinesterase activity in mosquito fish, Gambusia affinis in response to the sub-lethal exposure to chlorpyrifos. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharbidre, A.A.; Metkari, V.; Patode, P. Effect of methyl parathion and chlorpyrifos on certain biomarkers in various tissues of guppy fish, Poecilia reticulata. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 101, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.; Yeganeh, S.; Dadar, M.; Sakai, M.; Dawood, M.A. Effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on growth performance, humoral and mucosal immune responses and disease resistance in juvenile great sturgeon (Huso huso Linnaeus, 1754). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Kato, T.; Ota, Y. Spirulina (Arthrospira): Potential application as an animal feed supplement. J. Appl. Phycol. 1996, 8, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiklahan, R.; Chirasuwan, N.; Triratana, P.; Loha, V.; Tia, S.; Bunnag, B. Polysaccharide extraction from Spirulina sp. and its antioxidant capacity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Esteban, M.Á. Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 950–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, V.T.; Poersch, L.H.; Romano, L.A.; Tesser, M.B. Feasibility of the use of Spirulina in aquaculture diets. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 11, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkhalek, N.K.; Ghazy, E.W.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Pharmacodynamic interaction of Spirulina platensis and deltamethrin in freshwater fish Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus: Impact on lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Dawood, M.A.; Aleya, L.; Alkahtani, S. Effects of fucoidan on the hematic indicators and antioxidative responses of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed diets contaminated with aflatoxin B1. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oruc, E. Oxidative stress responses and recovery patterns in the liver of Oreochromis niloticus exposed to chlorpyrifos-ethyl. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fırat, Ö.; Cogun, H.Y.; Yüzereroğlu, T.A.; Gök, G.; Fırat, Ö.; Kargin, F.; Kötemen, Y. A comparative study on the effects of a pesticide (cypermethrin) and two metals (copper, lead) to serum biochemistry of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishikimi, M.; Appaji, N.; Yagi, K. The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1972, 46, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. [13] Catalase in Vitro, in Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Mihara, M.; Uchiyama, M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Mitkovska, V.; Chassovnikarova, T. Chlorpyrifos levels within permitted limits induce nuclear abnormalities and DNA damage in the erythrocytes of the common carp. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7166–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Abo-Al-Ela, H.G.; Hasan, M.T. Modulation of transcriptomic profile in aquatic animals: Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics scenarios. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; AbdEl-Kader, M.F.; Moustafa, E.M.; Gewaily, M.S.; Abdo, S.E. Growth performance and hemato-immunological responses of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to deltamethrin and fed immunobiotics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hakim, Y.A.; Neamat-Allah, A.N.; Baeshen, M.; Ali, H.A. Immune-protective, antioxidant and relative gene expression impacts of β-glucan against fipronil toxicity in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Upasani, C.D.; Balaraman, R. Protective effect of Spirulina on lead induced deleterious changes in the lipid peroxidation and endogenous antioxidants in rats. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffer, N.S.; Rabee, A.M.; Al-Chalabi, S.M. Biochemical and hematological parameters and histological alterations in fish Cyprinus carpio L. as biomarkers for water pollution with chlorpyrifos. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. 2017, 23, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akturk, O.; Demirin, H.; Sutcu, R.; Yilmaz, N.; Koylu, H.; Altuntas, I. The effects of diazinon on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in rat heart and ameliorating role of vitamin E and vitamin C. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, B.; Narayan, G. Certain pesticide-induced carbohydrate metabolic disorders in the serum of freshwater fish Clarias batrachus (Linn.). Food Chem. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkhalek, N.K.; Eissa, I.A.; Ahmed, E.; Kilany, O.E.; El-Adl, M.; Dawood, M.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Protective role of dietary Spirulina platensis against diazinon-induced Oxidative damage in Nile tilapia; Oreochromis niloticus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 54, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üner, N.; Oruç, E.Ö.; Sevgiler, Y.; Şahin, N.; Durmaz, H.; Usta, D. Effects of diazinon on acetylcholinesterase activity and lipid peroxidation in the brain of Oreochromis niloticus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 21, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachankar, R.S.; Juvekar, A.R.; Sonawane, A. Prevention of cold stress induced adrenal hypertrophy by Spirulina platensis. Acta Hortic. 2005, 680, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Sahu, N.P.; Pal, A.K.; Akhtar, M.S. Haemato-immunological and stress responses of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings: Effect of rearing temperature and dietary gelatinized carbohydrate. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 95, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.E.; Hastings, T.S.; Munro, A.L.S. The role of Aeromonas salmonicida extracellular products in the pathology of furunculosis. J. Fish Dis. 1981, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori-Siakpere, O. Some alterations in haematological parameters in Clarias, isheriensis (Sydenham) exposed to sublethal concentration of water-born lead. BioSci. Res. Commun. 1995, 8, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, M.; Cedeño, R.; Rodríguez, J.; van der Knaap, W.P.; Mialhe, E.; Bachère, E. Measurement of reactive oxygen intermediate production in haemocytes of the penaeid shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2000, 191, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.Y.; Fu, L.L.; Li, W.F.; Zhu, Y.R. Effect of dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis on the growth, performance, immune response and antioxidant activities of the shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Marafioti, S.; Filiciotto, F.; Buscaino, G.; Panzera, M.; Faggio, C. Blood hemogram profiles of farmed onshore and offshore gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) from Sicily, Italy. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 13, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.X.; Xun, A.Y.; Zeng, W.S.; Jia, C.H.; Wei, X.X.; Feng, J.L.; Zhao, L.; et al. Anti-oxidant Effects of Resveratrol on Mice with DSS-induced Ulcerative Colitis. Arch. Med. Res. 2010, 41, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Eweedah, N.M.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Abdelhamid, A.I. Dietary sodium butyrate ameliorated the blood stress biomarkers, heat shock proteins, and immune response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to heat stress. J. Ther. Biol. 2020, 88, 102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Eweedah, N.M.; Moustafa, E.M.; El-Sharawy, M.E.; Soliman, A.A.; Amer, A.A.; Atia, M.H. Copper Nanoparticles mitigate the growth, immunity, and oxidation resistance in Common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romay, C.H.; Gonzalez, R.; Ledon, N.; Remirez, D.; Rimbau, V. C-phycocyanin: A biliprotein with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2003, 4, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhadi, I.; Alizadeh, E.; Ahmadifar, E.; Adineh, H.; Dawood, M.A. Skin mucosal, serum immunity and antioxidant capacity of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fed artemisia (Artemisia annua). Ann. Anim. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S. Vitamin C supplementation to optimize growth, health and stress resistance in aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Fish meal | 26 |
| Yellow corn | 29 |
| Soybean meal | 20.5 |
| Corn gluten meal | 2 |
| Wheat bran | 9 |
| Egyptian clover meal | 7.2 |
| Cod liver oil | 3 |
| Gelatin | 2 |
| Vitamin mixture | 0.5 |
| Mineral mixture | 0.5 |
| Salt | 0.3 |
| Chemical analysis | |
| Crude protein % | 31.78 |
| Ether extract % | 7.15 |
| Ash % | 8.14 |
| Parameters | Experimental Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | SP1 | CPF | CPF-SP0.5 | CPF-SP1 | |
| AST (U/L) | 40.7 ± 2.16cd | 39.2 ± 2.21d | 99.4 ± 1.45a | 71.3 ± 2.08b | 47.4 ± 2.1c |
| ALT (U/L) | 15.4 ± 0.56c | 15.3 ± 0.58c | 35.4 ± 1.41a | 24.8 ± 0.57b | 16.9 ± 0.76c |
| ALP (U/L) | 9.81 ± 0.55cd | 8.36 ± 0.40d | 20.9 ± 0.89a | 14.3 ± 0.40b | 10.1 ± 0.36c |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 5.24 ± 0.35b | 5.99 ± 0.18a | 3.59 ± 0.17d | 4.42 ± 0.25c | 4.99 ± 0.28bc |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.26 ± 0.20b | 3.77 ± 0.11a | 2.04 ± 0.090d | 2.64 ± 0.20c | 3.21 ± 0.20b |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 226.7 ± 9.15c | 220.6 ± 6.26c | 344.2 ± 14.7a | 279.7 ± 3.04b | 238.5 ± 6.92c |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 7.02 ± 0.44c | 6.74 ± 0.23c | 17.7 ± 0.86a | 11.5 ± 0.23b | 7.63 ± 0.41c |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.51 ± 0.03c | 0.46 ± 0.020c | 2.57 ± 0.21a | 1.28 ± 0.05b | 0.67 ± 0.04c |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Elbadawy, M.; Aleya, L.; Alkahtani, S. Spirulina platensis Reduced Oxidative Damage Induced by Chlorpyrifos Toxicity in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals 2020, 10, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030473
Abdel-Daim MM, Dawood MAO, Elbadawy M, Aleya L, Alkahtani S. Spirulina platensis Reduced Oxidative Damage Induced by Chlorpyrifos Toxicity in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals. 2020; 10(3):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030473
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel-Daim, Mohamed M., Mahmoud A.O. Dawood, Mohamed Elbadawy, Lotfi Aleya, and Saad Alkahtani. 2020. "Spirulina platensis Reduced Oxidative Damage Induced by Chlorpyrifos Toxicity in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)" Animals 10, no. 3: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030473
APA StyleAbdel-Daim, M. M., Dawood, M. A. O., Elbadawy, M., Aleya, L., & Alkahtani, S. (2020). Spirulina platensis Reduced Oxidative Damage Induced by Chlorpyrifos Toxicity in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals, 10(3), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030473








