Oregano Feed Supplementation Affects Glycoconjugates Production in Swine Gut
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Morphological and Histochemical Analyses
2.3. Statistics
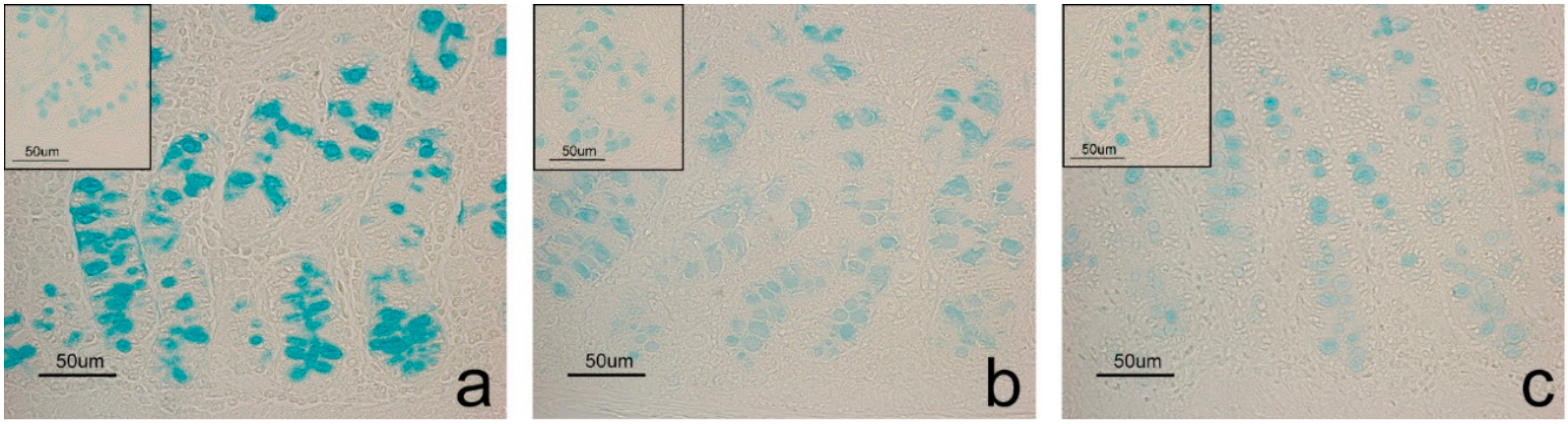
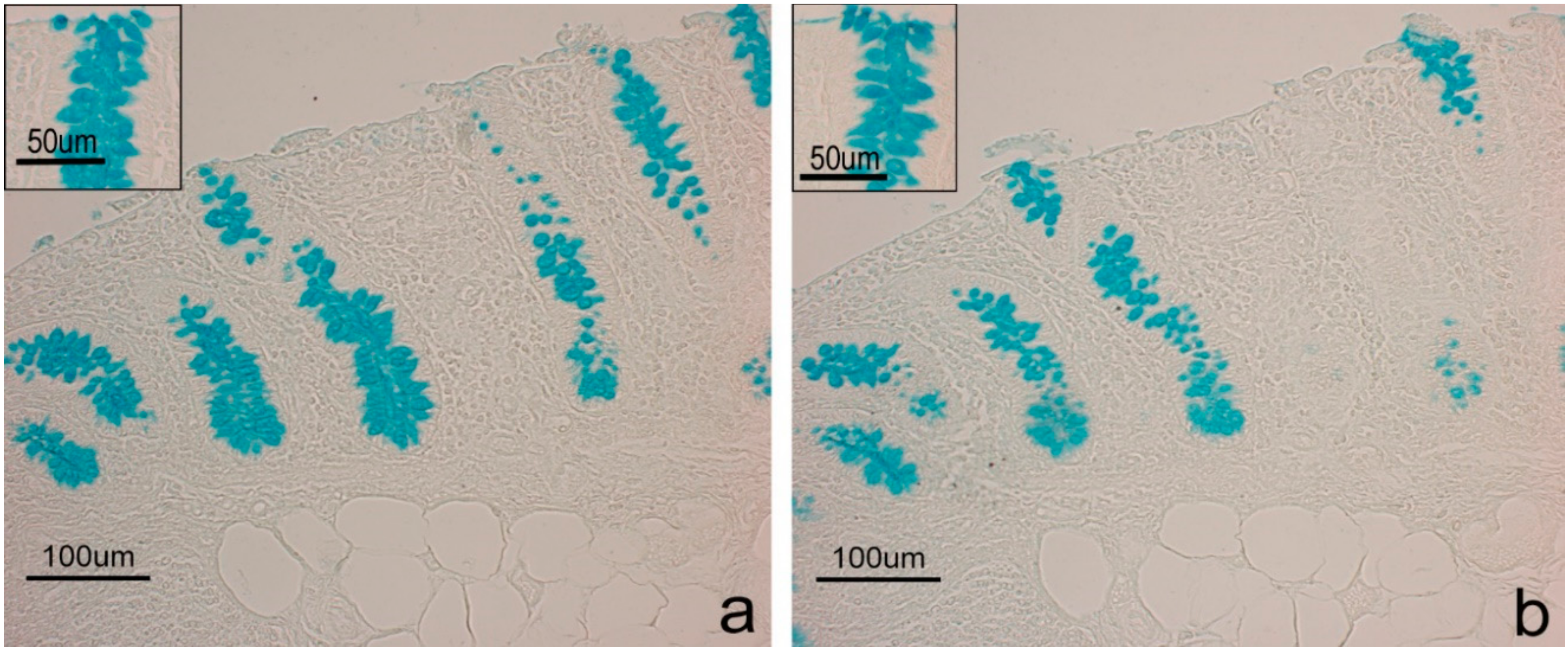
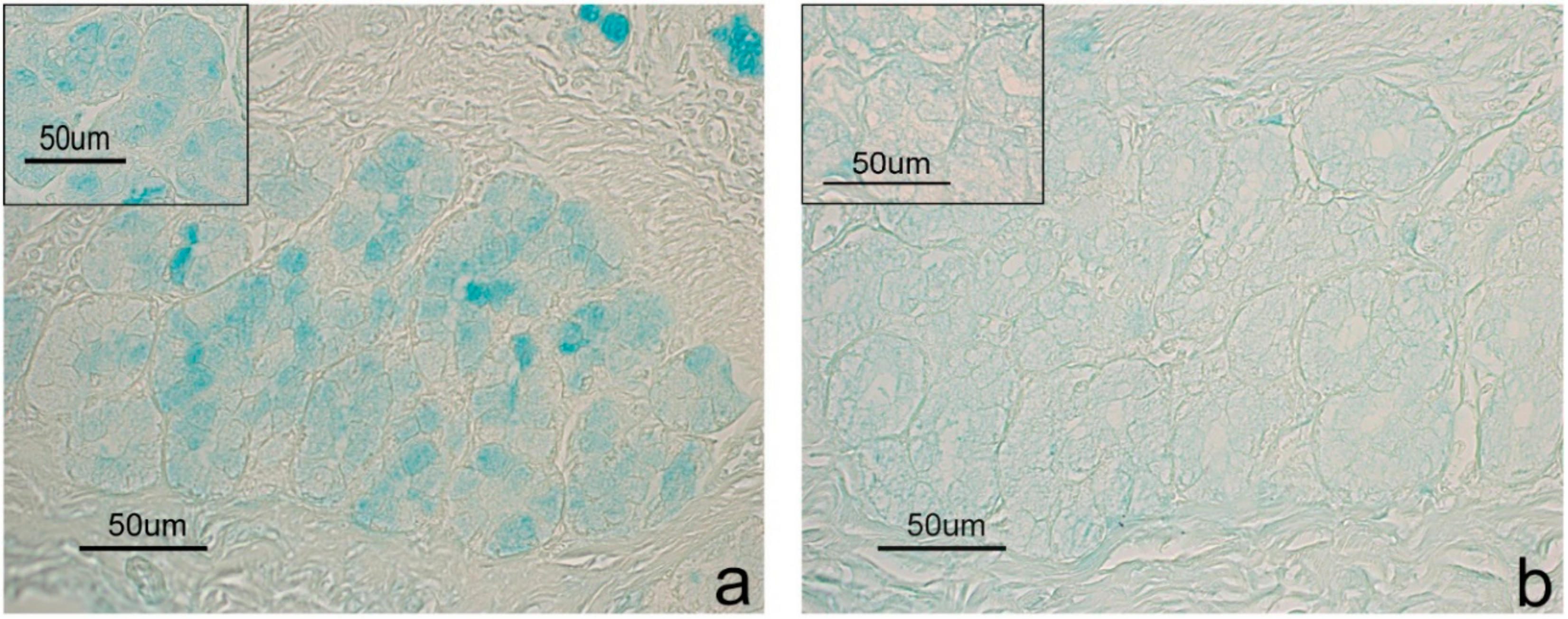
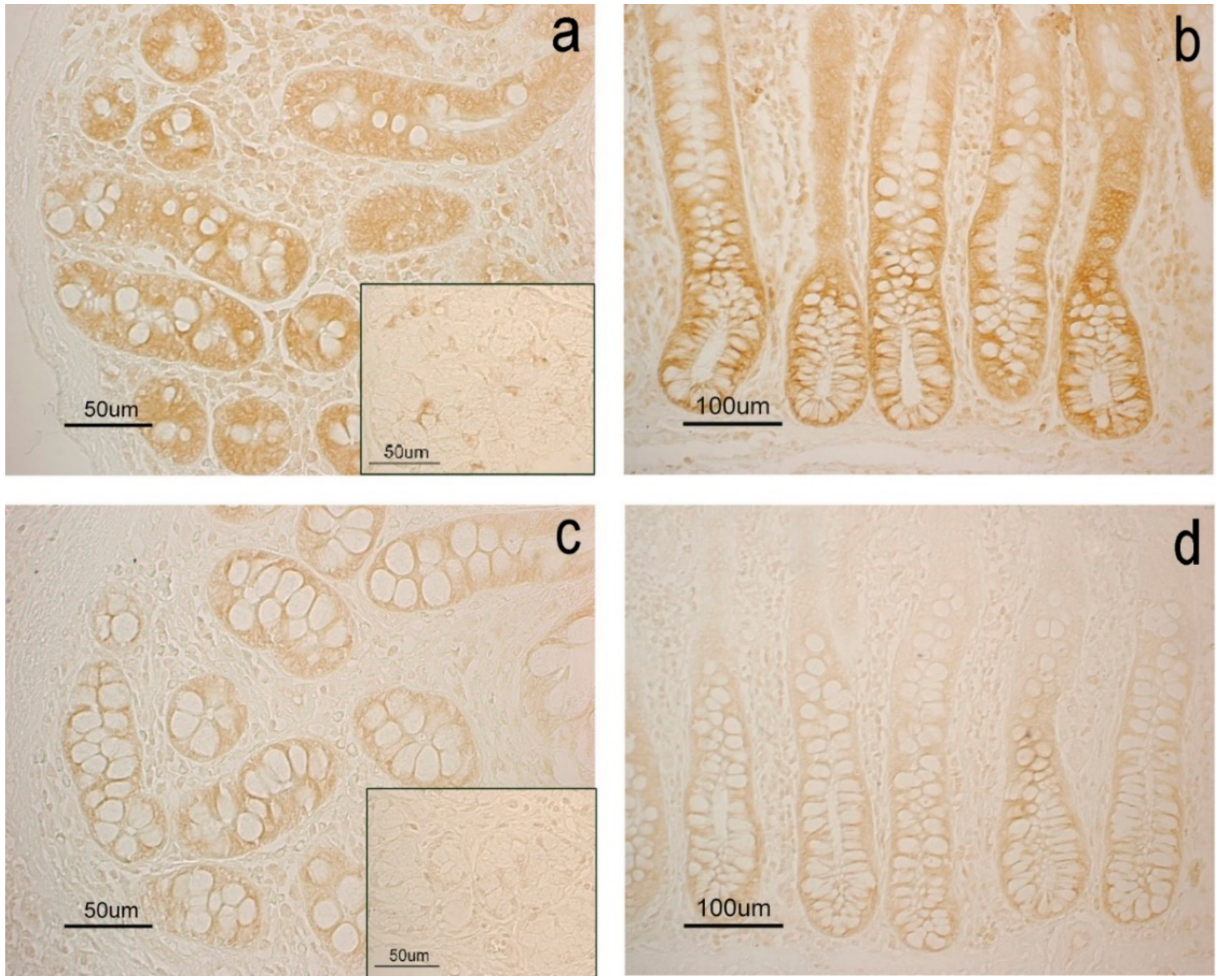
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ranucci, D.; Beghelli, D.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; Branciari, R.; Forte, C.; Olivieri, O.; Badillo Pazmay, G.V.; Cavallucci, C.; Acuti, G. Dietary effects of a mix derived from oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) essential oil and sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) wood extract on pig performance, oxidative status and pork quality traits. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, C.; Ranucci, D.; Beghelli, D.; Branciari, R.; Acuti, G.; Todini, L.; Cavallucci, C.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M. Dietary integration with oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) essential oil improves growth rate and oxidative status in outdoor-reared, but not indoor-reared, pigs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, e352–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.M.; Opapeju, F.O.; Pluske, J.R.; Kim, J.C.; Hampson, D.J.; Nyachoti, C.M. Gastrointestinal health and function in weaned pigs: A review of feeding strategies to control post-weaning diarrhoea without using in-feed antimicrobial compounds. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 97, 207–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suiryanrayna, M.V.; Ramana, J.V. A review of the effects of dietary organic acids fed to swine. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Vidal, E.; Martín-Orúe, S.M.; Castillejos, L. Are we using probiotics correctly in post-weaning piglets? Animal 2018, 12, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhaya, S.D.; Kim, J.C.; Mullan, B.P.; Pluske, J.R.; Kim, I.H. Vitamin E and omega-3 fatty acids independently attenuate plasma concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines and prostaglandin E2 in Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide-challenged growing-finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Wei, H. Oregano essential oil improves intestinal morphology and expression of tight junction proteins associated with modulation of selected intestinal bacteria and immune status in a pig model. BioMed Res. Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, C.; Branciari, R.; Pacetti, D.; Miraglia, D.; Ranucci, D.; Acuti, G.; Balzano, M.; Frega, N.G.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M. Dietary oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) aqueous extract improves oxidative stability and consumer acceptance of meat enriched with CLA and n-3 PUFA in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, A.V.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, R.T. Oxidative Stress and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review of Upstream and Downstream Antioxidant Therapeutic Options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Phenolics and polyphenolics in foods, beverages and spices: Antioxidant activity and health effects—A review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 820–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chishti, S.; Kaloo, Z.A.; Sultan, P. Medicinal importance of genus Origanum: A review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytother. 2013, 5, 170–177. [Google Scholar]
- Leyva-López, N.; Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Vazquez-Olivo, G.; Heredia, J.B. Essential oils of Oregano: Biological activity beyond their antimicrobial properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallverdù-Queralt, A.; Regueiro, J.; Martìnez-Huèlamo, M.; Alvarenga, J.F.; Leal, L.N.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. A comprehensive study on the phenolic profile of widely used culinary herbs and spices: Rosemary, thyme, oregano, cinnamon, cumin and bay. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutièrrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Picos-Salas, M.A.; Leyva-Lopez, N.; Criollo-Mendoza, M.S.; Vazquez-Olivo, G.; Hereida, J.B. Flavonoids and phenolic acids from oregano: Occurence, biological activity and health benefits. Plants 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkan, B.; Balkan, S.; Aydogdu, H.; Guler, N.; Ersoy, H.; Aşkin, B. Evaluation of antioxidant activities and antifungal activity of different plants species against pink mold rot-causing Trichothecium roseum. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.J.W.; Skandamis, P.N.; Coote, P.J.; Nychas, G.J.E. A study of the minimum inhibitory concentration and mode of action of oregano essential oil, thymol and cavacrol. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Hao, L.; Qipeng, Y.; Chunfang, L. In vitro antimicrobial effects and mechanism of action of selected plant essential oil combinations against four food-related microorganisms. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar]
- Scocco, P.; Forte, C.; Franciosini, M.P.; Mercati, F.; Casagrande-Proietti, P.; Dall’Aglio, C.; Acuti, G.; Tardella, F.M.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M. Gut complex carbohydrates and intestinal microflora in broiler chickens fed with oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) aqueous extract and Vitamin E. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.J.; Tullis, R.E. The effects of diet and digestive cycle on the gastrointestinal tract pH values in the goldfish, Carrassius auratus L., Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambique(Peters), and channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque). J. Fish Biol. 1984, 25, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajak, B.; Danguy, A. Characterization of sugar moieties and oligosaccharide sequences in the diastal intestinal epithelium of the rainbow trout by means of lecithin histochemistry. J. Fish Biol. 1993, 43, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scocco, P.; Menghi, G.; Ceccarelli, P. Histochemical differentiation of glycoconjugates occurring in the tilapine intestine. J. Fish Biol. 1997, 51, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedini, V.; Dall’Aglio, C.; Parillo, F.; Scocco, P. A lectin histochemical study of the oesophagus of shi drum. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedini, V.; Dall’Aglio, C.; Parillo, F.; Scocco, P. Glycoconjugate distribution in gastric fundic mucosa of Umbrina cirrosa L. revealed by lectin histochemistry. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 66, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scocco, P.; Pedini, V. Equine mandibular gland: In situ characterisation of sialoderivatives. Equine Vet. J. 2006, 38, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scocco, P.; Pedini, V. Localization of influenza virus sialoreceptors in equine respiratory tract. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 973–978. [Google Scholar]
- Scocco, P.; Pedini, V. Histochemical characterisation of complex carbohydrates expressed in the alimentary tract of chickens. Vet. J. 2010, 185, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, T.; Kaneko, Y. Novel hyaluronidase from streptomyces. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 198, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Hirano, K. The histochemistry of hyaluronic acid-containing mucosubstances. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1973, 21, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werling, D. The clinical significance of sialoderivates in the search for novel means of antipathogen therapy. Equine Vet. J. 2006, 38, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuw-Ameronge, A.V.; Bolscher, J.G.M.; Veerman, E.C.I. Salivary mucins: Protective functions in relation to their diversity. Glycobiology 1995, 5, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.P.; Banerjee, S.; Brown, T.R. Bcl-2 Protein Expression Correlates with Cell Survival and Androgen Independence in Rat Prostatic Lobes. Endocrinology 2002, 5, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciosini, M.P.; Casagrande-Proietti, P.; Forte, C.; Beghelli, D.; Acuti, G.; Zanichelli, D.; dal Bosco, A.; Castellini, C.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M. Effects of oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) and rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) aqueous extracts on broiler performance, immune function and intestinal microbial population. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2016, 44, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Aglio, C.; Scocco, P.; Maranesi, M.; Petrucci, L.; Acuti, G.; De Felice, E.; Mercati, F. Immunohistochemical identification of resistin in the uterus of ewes subjected to different diets: Preliminary results. Eur. J. Histochem. 2019, 63, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearse, A.G.E. Histochemistry, Theoretical and Applied; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Aglio, C.; Polisca, A.; Cappai, M.G.; Mercati, F.; Troisi, A.; Pirino, C.; Scocco, P.; Maranesi, M. Immunohistochemistry detected and localized cannabinoid receptor type 2 in bovine fetal pancreas at late gestation. Eur. J. Histochem. 2017, 61, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercati, F.; Scocco, P.; Maranesi, M.; Acuti, G.; Petrucci, L.; Cocci, P.; Renzi, A.; De Felice, E.; Dall’Aglio, C. Apelin system detection in the reproductive apparatus of ewes grazing on semi-natural pasture. Theriogenology 2019, 139, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Wang, A.Y. Significance of increased apoptosis and Bax expression in human small intestinal adenocarcinoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 57, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.C. Proapoptotic multidomain Bcl-2/Bax-family proteins: Mechanisms, physiological roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.N.; Theiss, A.L. Gut bacteria signaling to mithocondria in intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gut Microbes 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, J.; Hung, M.; Pandey, S. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in dividing fibroblasts involves activation of p38 MAP kinase and over-expression of Bax: Resistance of quiescent cells to oxidative stress. Apoptosis 2003, 8, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartron, P.F.; Oliver, L.; Mayat, E.; Meflah, K.; Vallette, F.M. Impact of pH on Bax alpha conformation, oligomerisation and mitochondrial integration. FEBS Lett. 2004, 578, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Component | Phase 1 (from 30 to 90 kg) | Phase 2 (from 90 to 120 kg) | Phase 3 (from 120 to 180 kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Degermed corn | 48 | 49.92 | 51 |
| Barley | 20.25 | 21.06 | 21.53 |
| Wheat | 6.75 | 7.02 | 7.17 |
| Soybean oil meal | 22.15 | 19.2 | 16.5 |
| Calcium carbonate | 1.25 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Di-calcium phosphate | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Mineral vitamin premix | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Sodium chlorine | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Lysine | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Methionine | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Conjugated Linoleic Acid | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Pig Duodenum | CTR | EXP | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histochemical Treatment | Goblet Cells | Duodenal Glands | Goblet Cells | Duodenal Glands | Goblet Cells | Duodenal Glands |
| AB pH2.5 | 1/2 | 0.5/1 | 2 | 0.5/1 | * | ns |
| Sial-AB | 1/2 | 0 | 1/2 | 0 | ns | ns |
| KOH-Sial-AB | 1/2 | 0 | 0.5/1 | 0 | * | ns |
| AB pH1 | 1 | 0 | 0.5/1 | 0 | * | ns |
| AB pH0.5 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | * | ns |
| PAS | 1/2 a | 1 | 1 a | 1 | ns | ns |
| 2 b | 2 b | ns | ||||
| AB/PAS | B1/R0 a | B0/1/R1 | B2/R0 a | B0/1/R1 | ** | ns |
| B2/R1 b | B2/R2 b | * | ||||
| LID | 1/2 | 0.5/1 | 2 | 0.5/1 | * | ns |
| HID | 1 | 0 | 0.5/1 | 0 | * | ns |
| PIG COLON | CTR | EXP | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Histochemical Treatments | |||
| AB pH2.5 | 2 | 2 | ns |
| Sial-AB | 2 | ½ | * |
| KOH-Sial-AB | 2 | ½ | * |
| AB pH1 | 1 | 0.5/1 | ns |
| AB pH0.5 | 1 | 0.5/1 | * |
| PAS | 1 | 1 | ns |
| AB/PAS | B2/R0 | B2/R0/1 | * |
| LID | 2 | 2 | ns |
| HID | 1 | 0.5/1 | * |
| Intestinal Tract | Diet | Secretory Structure | AB pH 2.5 vs. Sial-AB | Sial-AB vs. KOH-Sial-AB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duodenum | CTR | Goblet cells | 0.821 | 0.821 |
| EXP | Goblet cells | 0.011 | 0.011 | |
| CTR | Duodenal glands | 0.007 | 1.000 | |
| EXP | Duodenal glands | 0.008 | 1.000 | |
| Colon | CTR | Goblet cells | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| EXP | Goblet cells | 0.015 | 1.000 |
| Diet | Complex Carbohydrates Produced by Duodenal Goblet Cells | Complex Carbohydrates Produced by Duodenal Glands | Complex Carbohydrates Produced by Colon Goblet Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTR | Heparin/heparansulphate-like GAGs Hyaluronic acid/chondroitin-like GAGs | Neutral and sialilated not C4 acetylated glycoproteins | Heparin/heparansulphate-like GAGs Hyaluronic acid/chondroitin-like GAGs |
| EXP | Sialilated glycoproteins with and without C4 acetylated SA Heparin/heparansulphate-like GAGs Chondroitinsulphate A/B/C-like GAGs | Neutral and sialilated not C4 acetylated glycoproteins | Heparin/heparansulphate-like GAGs Hyaluronic acid/chondroitin-like GAGs Sialilated glycoproteins not C4 acetylated |
| IntestinalTract | CTR | EXP | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duodenum | 2 | 0.5 | * |
| Colon | 2 | 0.5 | * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercati, F.; Dall’Aglio, C.; Acuti, G.; Faeti, V.; Tardella, F.M.; Pirino, C.; De Felice, E.; Scocco, P. Oregano Feed Supplementation Affects Glycoconjugates Production in Swine Gut. Animals 2020, 10, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010149
Mercati F, Dall’Aglio C, Acuti G, Faeti V, Tardella FM, Pirino C, De Felice E, Scocco P. Oregano Feed Supplementation Affects Glycoconjugates Production in Swine Gut. Animals. 2020; 10(1):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010149
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercati, Francesca, Cecilia Dall’Aglio, Gabriele Acuti, Valerio Faeti, Federico Maria Tardella, Carolina Pirino, Elena De Felice, and Paola Scocco. 2020. "Oregano Feed Supplementation Affects Glycoconjugates Production in Swine Gut" Animals 10, no. 1: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010149
APA StyleMercati, F., Dall’Aglio, C., Acuti, G., Faeti, V., Tardella, F. M., Pirino, C., De Felice, E., & Scocco, P. (2020). Oregano Feed Supplementation Affects Glycoconjugates Production in Swine Gut. Animals, 10(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010149








