Transcriptomic Analysis of Testicular Gene Expression in Normal and Cryptorchid Horses
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Horse Testicular Tissue Collection
2.3. RNA Extraction and Quality Analysis
2.4. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Real-Time qPCR Verification of the mRNA Sequencing Results
3. Results
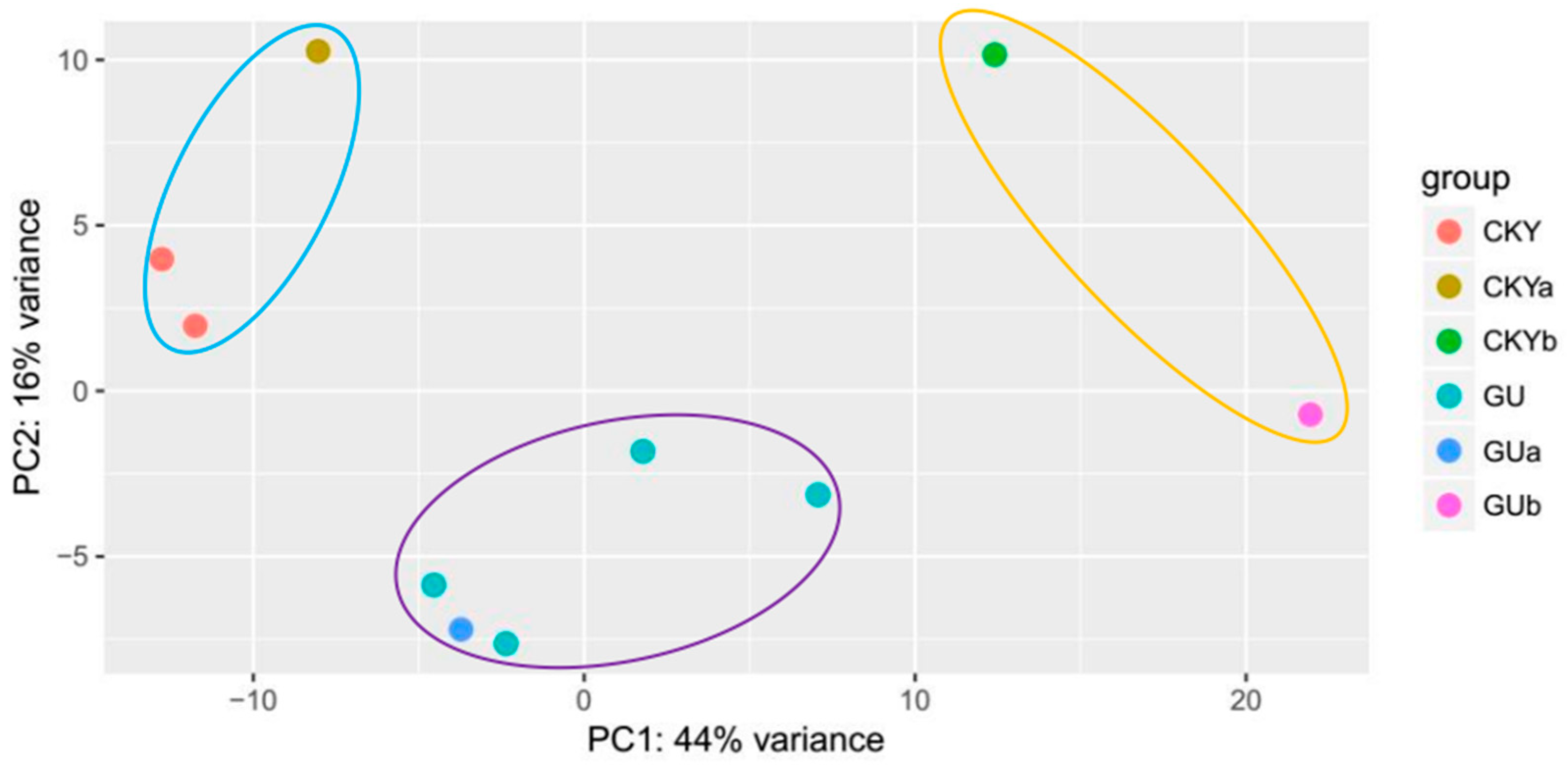
3.1. Overview of the Sequenced RNAs from Horse Testes
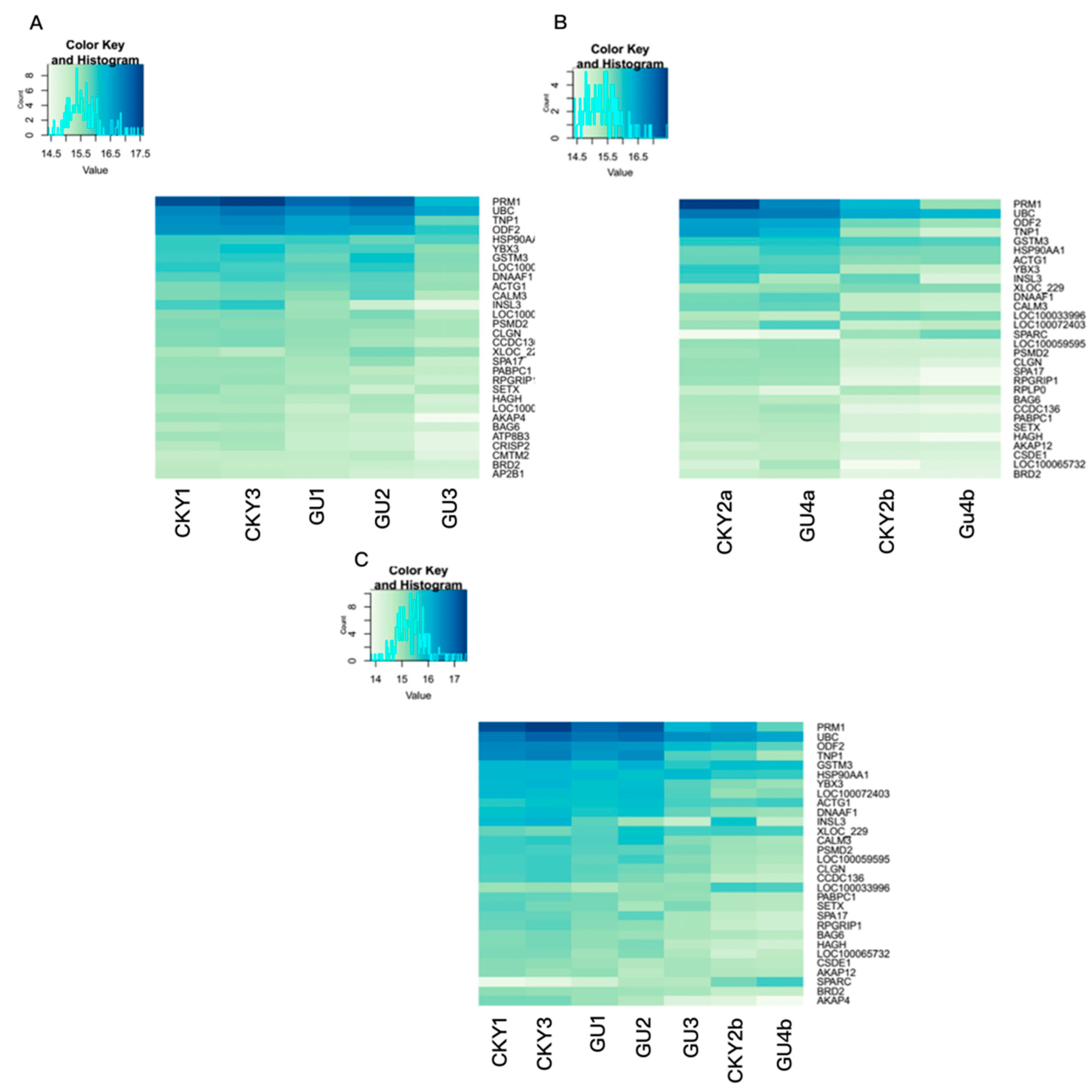
3.2. Top Genes Expressed in Horse Testicular Tissue
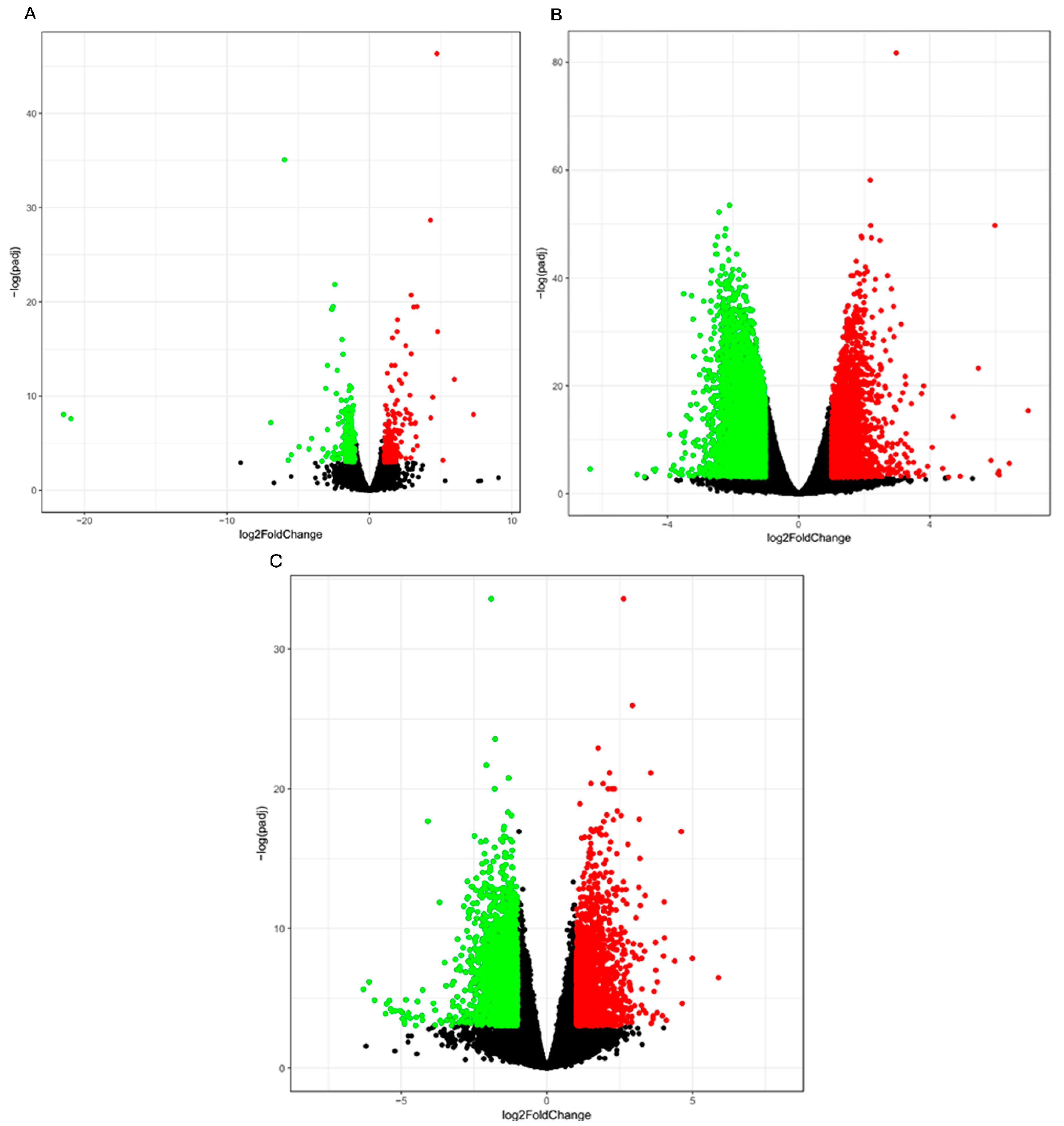
3.3. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
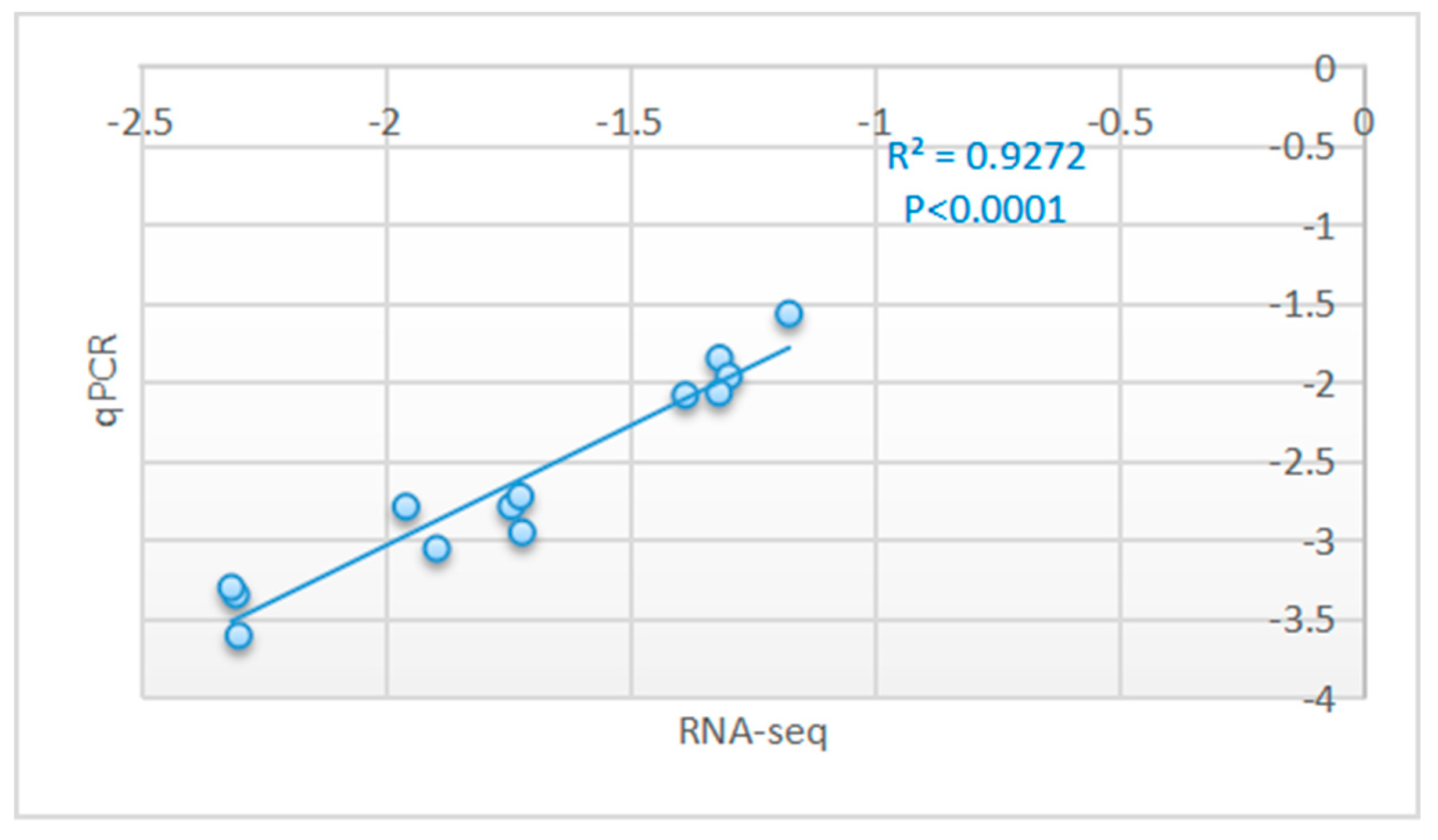
3.4. Real-Time qPCR Validation of the RNA-Seq Results
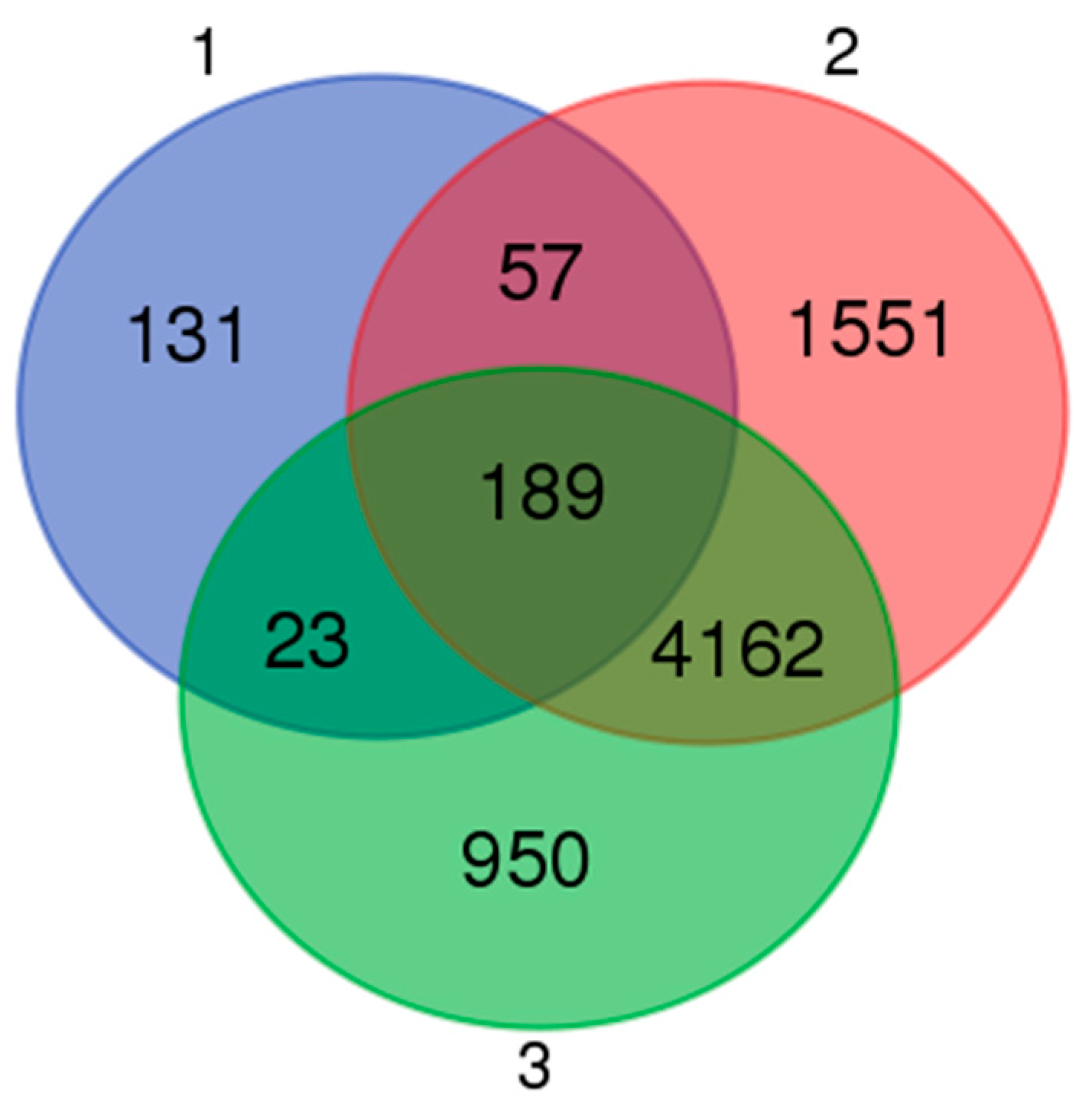
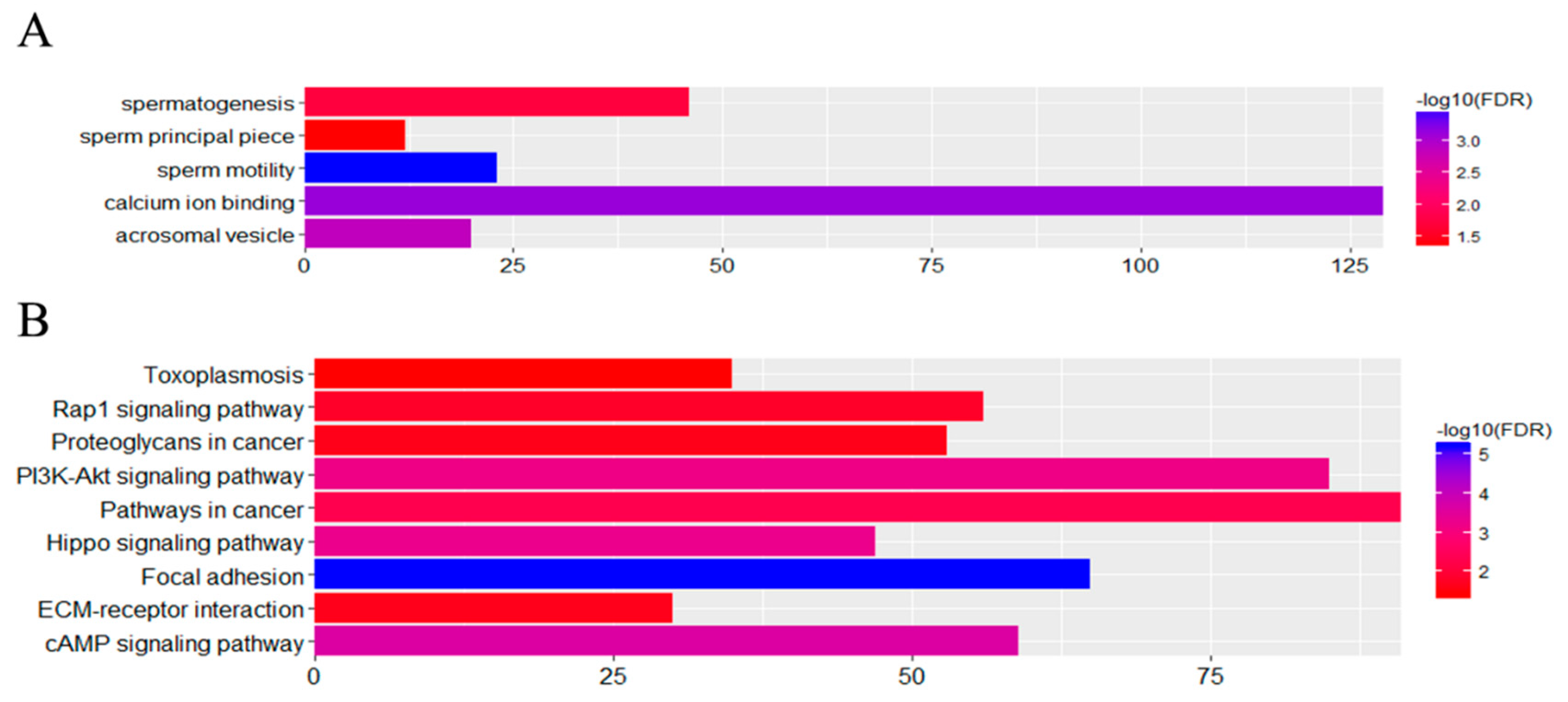
3.5. Functional Associations of the DEGs
3.6. Effects of Cryptorchidism on Gene Expression
3.7. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) May Cause Cryptorchidism in Horses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Eik-Nes, K.B. Secretion of testosterone by the eutopio and the cryptorchid testes in the same dog. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1966, 144, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, S.J. Fertility in cryptorchidism. Eur. J. Pediatrics 1987, 146 (Suppl. 2), S21–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, R.C.; Beard, C.M.; Kelalis, P.P.; Kurland, L.T. Malignant potential of the cryptorchid testis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1991, 66, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, J.M.; Baker, M.; Terada, M.; Zhou, B.; Paxton, G. Hormonal control of testicular descent and the cause of cryptorchidism. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 1994, 6, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, J.M. A biphasic model for the hormonal control of testicular descent. Lancet 1985, 326, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satokata, I.; Benson, G.; Maas, R. Sexually dimorphic sterility phenotypes in Hoxa10-deficient mice. Nature 1995, 374, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Steding, G.; Emmen, J.M.; Brinkmann, A.O.; Nayernia, K.; Holstein, A.F.; Engel, W.; Adham, I.M. Targeted disruption of the INSL3 gene causes bilateral cryptorchidism. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nef, S.; Parada, L.F. Cryptorchidism in mice mutant for INSL3. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, P.A.; Gorlov, I.P.; Sutherland, R.W.; Houston, J.B.; Harrison, W.R.; Boettger-Tong, H.L.; Bishop, C.E.; Agoulnik, A.I. A transgenic insertion causing cryptorchidism in mice. Genesis 2001, 30, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Houate, B.; Rouba, H.; Sibai, H.; Barakat, A.; Chafik, A.; Chadli el, B.; Imken, L.; Bogatcheva, N.V.; Feng, S.; Agoulnik, A.I.; et al. Novel mutations involving the INSL3 gene associated with cryptorchidism. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Schottler, P.; Engel, W.; Adham, I.M. Mouse Leydig insulin-like (Ley I-L) gene: Structure and expression during testis and ovary development. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 13, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresta, C.; Zuccarello, D.; Garolla, A.; Ferlin, A. Role of hormones, genes and environment in human cryptorchidism. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 560–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.; He, D.; Huang, H.; Cheng, Z. Genetic analysis of HOXA11 gene in Chinese patients with cryptorchidism. Andrologia 2017, 50, e12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthold, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Kolon, T.F.; Kollin, C.; Nordenskjöld, A.; Olivant Fisher, A.; Figueroa, T.E.; BaniHani, A.H.; Hagerty, J.A.; Gonzaléz, R.; et al. Pathway analysis supports association of nonsyndromic cryptorchidism with genetic loci linked to cytoskeleton dependent functions. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthold, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Kolon, T.F.; Kollin, C.; Nordenskjöld, A.; Olivant Fisher, A.; Figueroa, T.E.; BaniHani, A.H.; Hagerty, J.A.; Gonzalez, R.; et al. Phenotype specific association of the TGFBR3 locus with nonsyndromic cryptorchidism. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlin, A.; Garolla, A.; Bettella, A.; Bartoloni, L.; Vinanzi, C.; Roverato, A.; Foresta, C. Androgen receptor gene CAG and GGC repeat lengths in cryptorchidism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 152, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagraj, S.; Seah, G.J.; Farmer, P.J.; Davies, B.; Southwell, B.; Lewis, A.G.; Hutson, J.M. The development and anatomy of the gubernaculum in Hoxa11 knockout mice. J. Pediatric Surg. 2011, 46, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzemann, R.; Bottomly, D.; Darakjian, P.; Walter, N.; Iancu, O.; Searles, R.; Wilmot, B.; McWeeney, S. Genes, behavior and next-generation RNA sequencing. Genes Brain Behav. 2013, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, D.A.; McElhinney, L.M.; Ellis, R.J.; Horton, D.L.; Wise, E.L.; Leech, S.L.; David Lamballerie, X.; Fooks, A.R. Next generation sequencing of viral RNA genomes. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Cai, H.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H. Characterization of Transcriptional Complexity during Adipose Tissue Development in Bovines of Different Ages and Sexes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Schulz, M.H.; Richard, H.; Magen, A.; Klingenhoff, A.; Scherf, M.; Seifert, M.; Borodina, T.; Soldatov, A.; Parkhomchuk, D.; et al. A global view of gene activity and alternative splicing by deep sequencing of the human transcriptome. Science 2008, 321, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, H.; Schulz, M.H.; Sultan, M.; Nürnberger, A.; Schrinner, S.; Balzereit, D.; Dagand, E.; Rasche, A.; Lehrach, H.; Vingron, M.; et al. Prediction of alternative isoforms from exon expression levels in RNA-Seq experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, N.; Raudsepp, T.; Pearks Wilkerson, A.J.; O’Brien, P.C.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Love, C.C.; Arnold, C.; Rakestraw, P.; Murphy, W.J.; Chowdhary, B.P. A gene catalogue of the euchromatic male-specific region of the horse Y chromosome: Comparison with human and other mammals. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Navarro, B.; Perez, G.; Jackson, A.C.; Hsu, S.; Shi, Q.; Tilly, J.L.; Clapham, D.E. A sperm ion channel required for sperm motility and male fertility. Nature 2001, 413, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Moran, M.M.; Navarro, B.; Chong, J.A.; Krapivinsky, G.; Krapivinsky, L.; Kirichok, Y.; Ramsey, I.S.; Quill, T.A.; Clapham, D.E. All four CatSper ion channel proteins are required for male fertility and sperm cell hyperactivated motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quill, T.A.; Sugden, S.A.; Rossi, K.L.; Doolittle, L.K.; Hammer, R.E.; Garbers, D.L. Hyperactivated sperm motility driven by CatSper2 is required for fertilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14869–14874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Reigada, D.; Mitchell, C.H.; Ren, D. CATSPER channel-mediated Ca2+ entry into mouse sperm triggers a tail-to-head propagation. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quill, T.A.; Ren, D.; Clapham, D.E.; Garbers, D.L. A voltage-gated ion channel expressed specifically in spermatozoa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12527–12531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Gao, B.; Wu, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, G.; Mao, J. Molecular cloning, spatial and temporal expression analysis of CatSper genes in the Chinese Meishan pigs. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.G.; Ding, X.F.; Liao, A.H.; Kong, X.B.; Xiong, C.L. Expression of CatSper family transcripts in the mouse testis during post-natal development and human ejaculated spermatozoa: Relationship to sperm motility. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 13, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambard, S.; Galeraud-Denis, I.; Martin, G.; Levy, R.; Chocat, A.; Carreau, S. Analysis and significance of mRNA in human ejaculated sperm from normozoospermic donors: Relationship to sperm motility and capacitation. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 10, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur, Y.; Breitbart, H. Mammalian sperm translate nuclear-encoded proteins by mitochondrial-type ribosomes. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, E.M.; Toshimori, K.; O’Brien, D.A. Fibrous sheath of mammalian spermatozoa. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisfalusi, M.; Miki, K.; Magyar, P.L.; O’Brien, D.A. Multiple glycolytic enzymes are tightly bound to the fibrous sheath of mouse spermatozoa. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 75, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Qu, W.; Goulding, E.H.; Willis, W.D.; Bunch, D.O.; Strader, L.F.; Perreault, S.D.; Eddy, E.M.; O’Brien, D.A. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase-S, a sperm-specific glycolytic enzyme, is required for sperm motility and male fertility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16501–16506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Willis, W.D.; Brown, P.R.; Goulding, E.H.; Fulcher, K.D.; Eddy, E.M. Targeted disruption of the Akap4 gene causes defects in sperm flagellum and motility. Dev. Biol. 2002, 248, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.R.; Miki, K.; Harper, D.B.; Eddy, E.M. A-kinase anchoring protein 4 binding proteins in the fibrous sheath of the sperm flagellum. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teves, M.E.; Sears, P.R.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, W.; van Reesema, L.; Costanzo, R.M.; Davis, C.W.; Knowles, M.R.; Strauss, J.F., 3rd; et al. Sperm-Associated Antigen 6 (SPAG6) Deficiency and Defects in Ciliogenesis and Cilia Function: Polarity, Density, and Beat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.W.; Ossipova, O.; Ioannou, A.; Sokol, S.Y. Prickle3 synergizes with Wtip to regulate basal body organization and cilia growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaul, N.; Wang, R.; Sperry, A.O. PPP1R42, a PP1 binding protein, regulates centrosome dynamics in ARPE-19 cells. Biol. Cell 2013, 105, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Bases | Total Mapped Reads | Multiple Mapped Reads | Uniquely Mapped Reads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKY1 | 61,721,592 | 59,762,158 | 8,700,950,792 | 52,179,635 (87.31%) | 813,963 (1.36%) | 50,385,369 (84.31%) |
| CKY2a | 77,719,686 | 75,527,312 | 10,936,704,233 | 66,175,695 (87.62%) | 1,074,061 (1.42%) | 63,821,947 (84.50%) |
| CKY2b | 72,480,272 | 70,588,360 | 10,234,970,744 | 62,176,229 (88.08%) | 1,002,706 (1.42%) | 60,005,651 (85.01%) |
| CKY3 | 92,420,914 | 88,846,736 | 12,869,802,573 | 78,285,911 (88.11%) | 1,305,326 (1.47%) | 75,421,193 (84.89%) |
| GU1 | 74,459,300 | 72,055,254 | 10,494,742,859 | 63,316,272 (87.87%) | 994,823 (1.38%) | 61,130,797 (84.84%) |
| GU2 | 73,099,626 | 70,758,154 | 10,296,493,984 | 61,319,858 (86.66%) | 1,017,616 (1.44%) | 59,085,846 (83.50%) |
| GU3 | 79,108,430 | 76,613,632 | 11,153,734,663 | 67,734,267 (88.41%) | 1,113,341 (1.45%) | 65,306,502 (85.24%) |
| GU4a | 73,056,308 | 70,657,318 | 10,241,905,462 | 60,878,044 (86.16%) | 980,165 (1.39%) | 58,722,122 (83.11%) |
| GU4b | 65,345,248 | 63,299,092 | 9,212,135,314 | 55,446,209 (87.59%) | 869,078 (1.37%) | 53,551,478 (84.60%) |
| GU5 | 62,041,338 | 59,931,894 | 8,714,823,986 | 52,460,612 (87.53%) | 831,832 (1.39%) | 50,626,486 (84.47%) |
| average | 73,145,271 | 70,803,991 | 10,285,626,461 | 61,997,273 (87.53%) | 1,000,291 (1.41%) | 59,805,739 (84.45%) |
| Gene | NCBI Accession Number | Exon | Nucleotide | Protein | Genotype | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Horse | Cryptorchid Horse | |||||
| LOC102147809 | XM_005602655.2 | exon 1 | c.A14G | p.E5G | AA | AG |
| ZNF37A | XM_005602647.2 | exon 5 | c.T450A | p.H150Q | TT | TA |
| DDX60L | XM_014737782.1 | exon 22 | c.G2747A | p.R916Q | GG | GA |
| FNIP2 | XM_005607793.2 | exon 13 | c.C2612T | p.T871M | GG | GA |
| c.C2231T | p.T744I | GG | GA | |||
| C3H16orf46 | XM_001501937.3 | exon 3 | c.G62C | p.S21T | CC | CG |
| GK2 | NM_001256933.1 | exon 1 | c.A230G | p.E77G | AA | AG |
| BMP2K | XM_014738530.1 | exon 10 | c.C1109T | p.T370M | GG | GA |
| PNPLA8 | XM_005609080.2 | exon 10 | c.C2110T | p.P704S | GG | GA |
| ALDH9A1 | XM_001492799.4 | exon 1 | c.C125T | p.A42V | CC | CT |
| LOC100058290 | XM_001495326.4 | exon 7 | c.C479G | p.A160G | GG | GC |
| GPSM2 | XM_001493568.5 | exon 14 | c.G2006A | p.S669N | CC | CT |
| TMEM198 | XM_001494150.4 | exon 1 | c.G242T | p.R81L | GG | GT |
| LOC102148548 | XM_014741362.1 | exon 3 | c.G2650A | p.D884N | CC | CT |
| c.G2627C | p.R876T | CC | CG | |||
| c.G2068A | p.V690M | CC | CT | |||
| c.A1679T | p.E560V | TT | TA | |||
| c.A1648G | p.M550V | TT | TC | |||
| c.C581T | p.P194L | GG | GA | |||
| c.A437T | p.Q146L | TT | TA | |||
| c.A369T | p.L123F | TT | TA | |||
| c.T362C | p.M121T | AA | AG | |||
| c.A354C | p.E118D | TT | TG | |||
| c.G278A | p.S93N | CC | CT | |||
| PPP1R42 | XM_005613086.2 | exon 8 | c.A799G | p.I267V | AA | GG |
| TMEM68 | NM_001309262.1 | exon 1 | c.A70G | p.I24V | AA | AG |
| HACE1 | XM_014734298.1 | exon 20 | c.A2257G | p.M753V | TT | TC |
| FBF1 | XM_005597144.2 | exon 9 | c.C614T | p.P205L | CC | CT |
| ABCA9 | XM_001916991.3 | exon 8 | c.T974C | p.V325A | TT | TC |
| HIRIP3 | XM_014730026.1 | exon 4 | c.A958G | p.K320E | TT | TC |
| ANKRD31 | XM_014730406.1 | exon 11 | c.G1451T | p.R484L | GG | GT |
| exon 15 | c.A2804G | p.Y935C | AA | AG | ||
| exon 19 | c.T3918A | p.H1306Q | TT | TA | ||
| c.C3922T | p.R1308W | CC | CT | |||
| RMDN2 | XM_005600050.2 | exon 2 | c.A13G | p.T5A | TT | TC |
| VWA8 | XM_001493030.5 | exon 41 | c.G5224A | p.A1742T | GG | GA |
| CCDC168 | XM_014732045.1 | exon 3 | c.A16781G | p.E5594G | TT | TC |
| c.C14732G | p.P4911R | GG | GC | |||
| c.A10753T | p.N3585Y | TT | TA | |||
| c.G10363A | p.E3455K | CC | CT | |||
| POM121L2 | XM_001495084.5 | exon 1 | c.A397C | p.T133P | TT | TG |
| SKIV2L | XM_001492580.3 | exon 9 | c.C833T | p.P278L | CC | CT |
| XPO5 | XM_005603953.2 | exon 19 | c.A1996G | p.I666V | TT | TC |
| MMP9 | NM_001111302.1 | exon 9 | c.A1414G | p.T472A | AA | AG |
| PSD3 | XM_001488201.5 | exon 2 | c.G144A | p.M48I | CC | CT |
| PRICKLE3 | XM_001495412.5 | exon 8 | c.G1222T | p.A408S | CC | AA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, H.; Dong, H.; Chen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Dang, R.; Lei, C. Transcriptomic Analysis of Testicular Gene Expression in Normal and Cryptorchid Horses. Animals 2020, 10, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010102
Han H, Dong H, Chen Q, Gao Y, Li J, Li W, Dang R, Lei C. Transcriptomic Analysis of Testicular Gene Expression in Normal and Cryptorchid Horses. Animals. 2020; 10(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Haoyuan, Hong Dong, Qiuming Chen, Yuan Gao, Jun Li, Wantao Li, Ruihua Dang, and Chuzhao Lei. 2020. "Transcriptomic Analysis of Testicular Gene Expression in Normal and Cryptorchid Horses" Animals 10, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010102
APA StyleHan, H., Dong, H., Chen, Q., Gao, Y., Li, J., Li, W., Dang, R., & Lei, C. (2020). Transcriptomic Analysis of Testicular Gene Expression in Normal and Cryptorchid Horses. Animals, 10(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010102





