Analysis of Bacterial Communities on North Sea Macroalgae and Characterization of the Isolated Planctomycetes Adhaeretor mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseimaritima multifibrata sp. nov., Rosistilla ulvae sp. nov. and Rubripirellula lacrimiformis sp. nov.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Sample Preparation
2.2. Isolation and Cultivation of Novel Strains
2.3. Determination of Temperature and pH Optima for Growth
2.4. Catalase and Cytochrome Oxidase Activity
2.5. Substrate Utilization
2.6. Cellular Fatty Acid Analysis
2.7. Algal Attachment Assay
2.8. DNA Isolation and Amplification for Sequence-Based Community Analysis
2.9. Amplicon Sequencing and Sequence Processing
2.10. Wide Field Microscopy
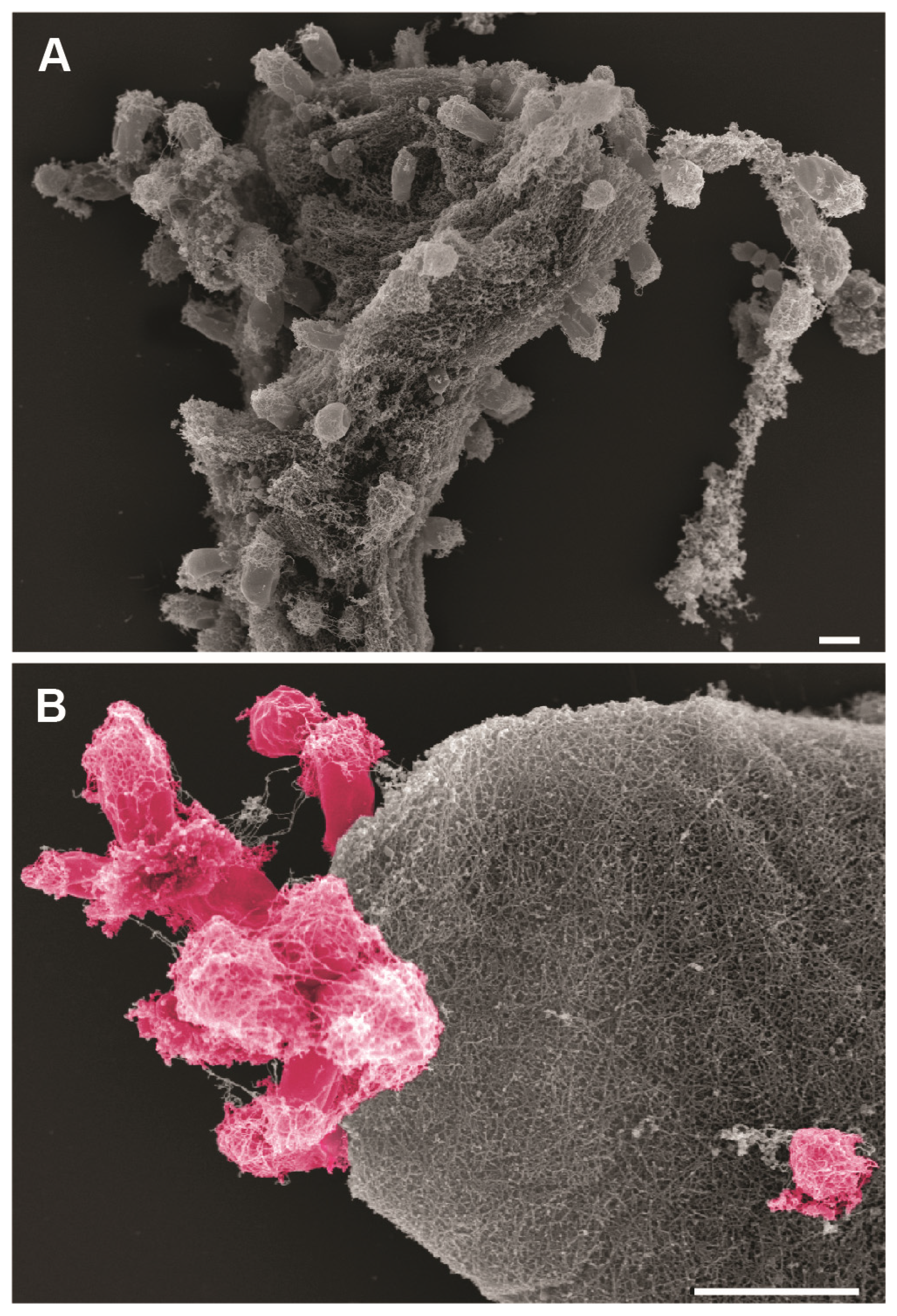
2.11. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of Bacteria, Biofilms on Algal Pieces and Algae Granules
2.12. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.13. Genome Information of the Isolated Strains
2.14. Construction of Phylogenetic Trees
2.15. Analysis of Phylogenetic Markers
2.16. Analysis of Genome-Encoded Features
3. Results
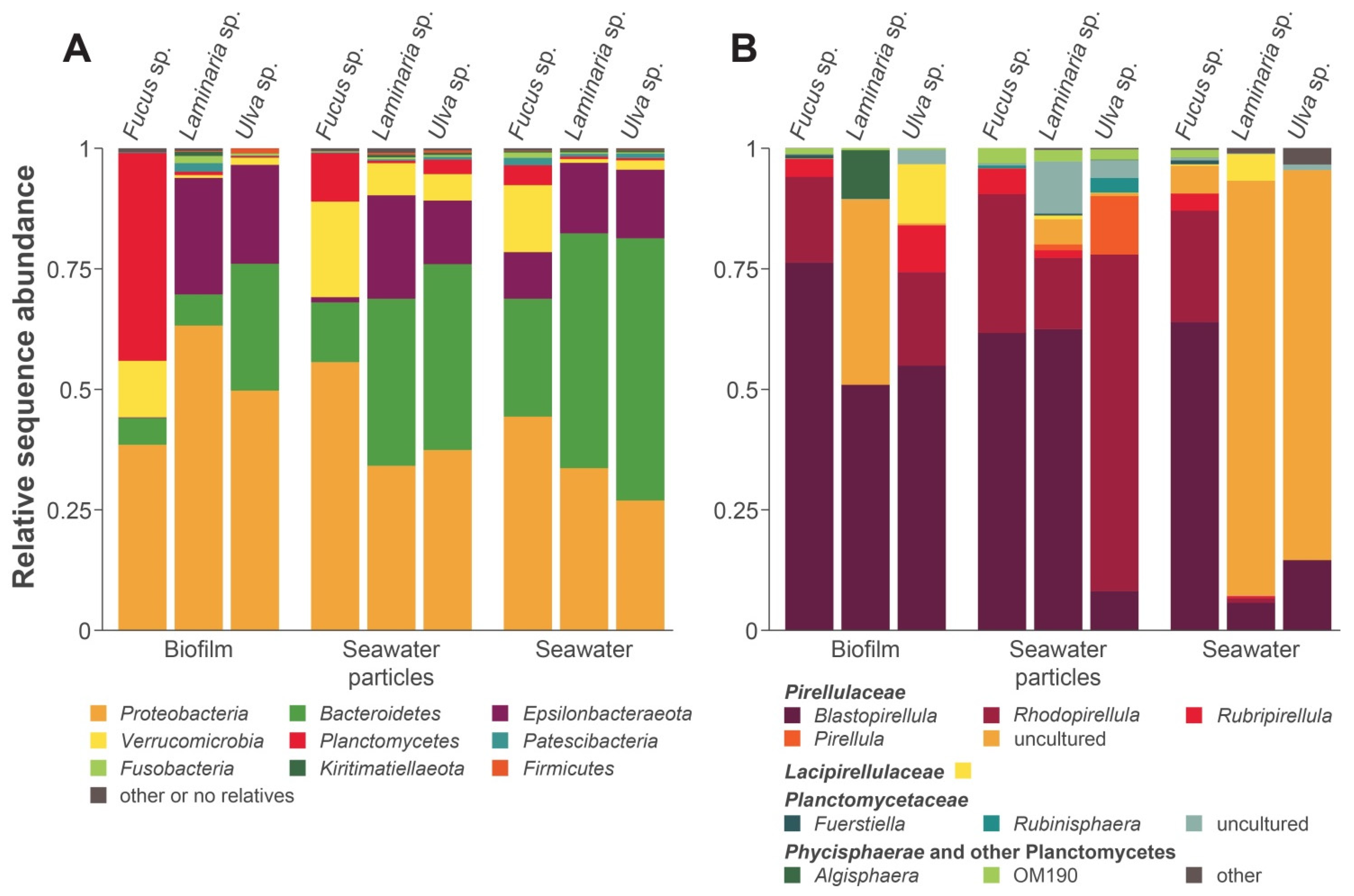
3.1. Bacterial Communities of North Sea Algae Surfaces
3.2. Cultivation-Dependent Targeted Isolation of Novel Planctomycetal Strains
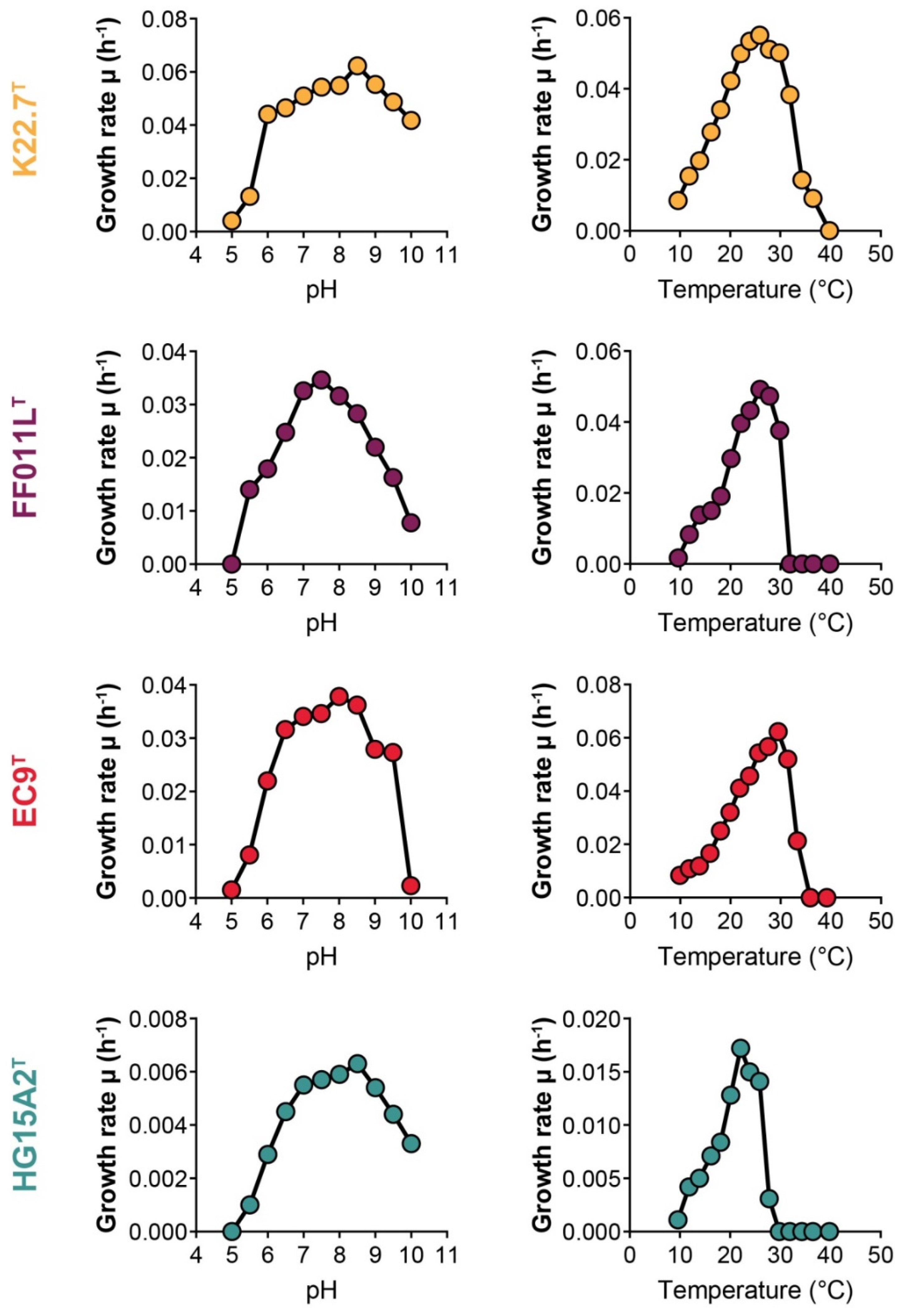
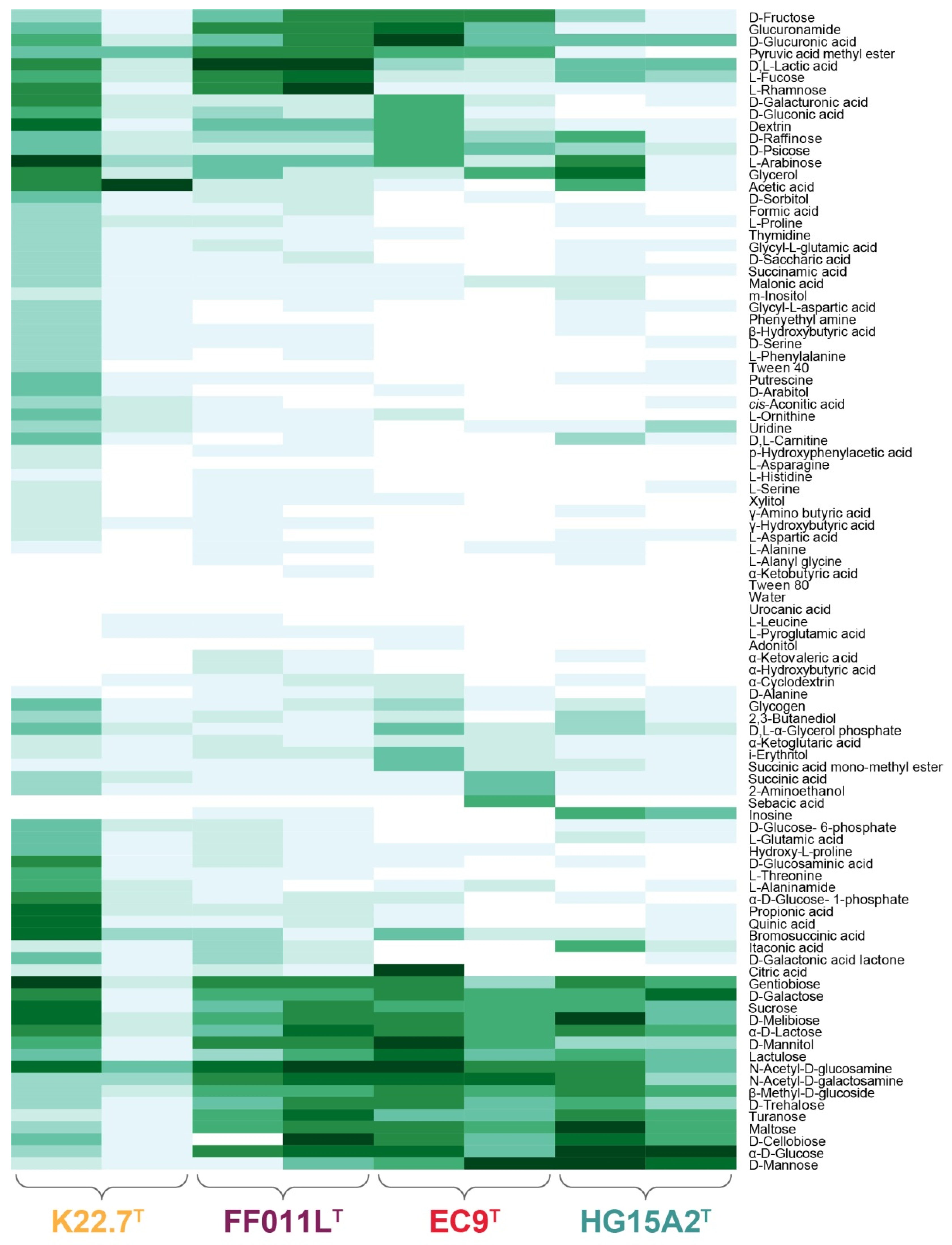
3.3. Physiological and Chemotaxonomic Characteristics of the Isolates
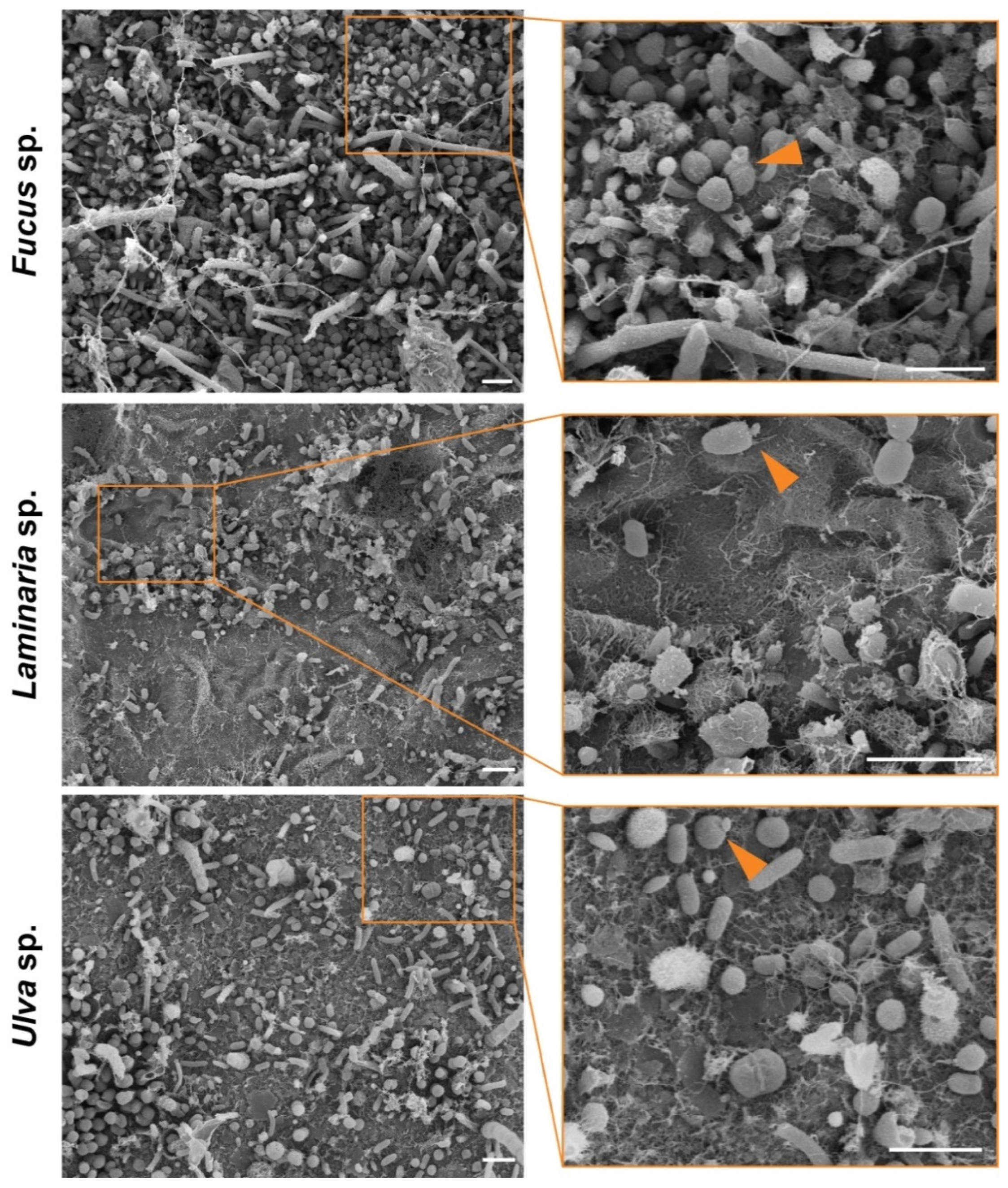
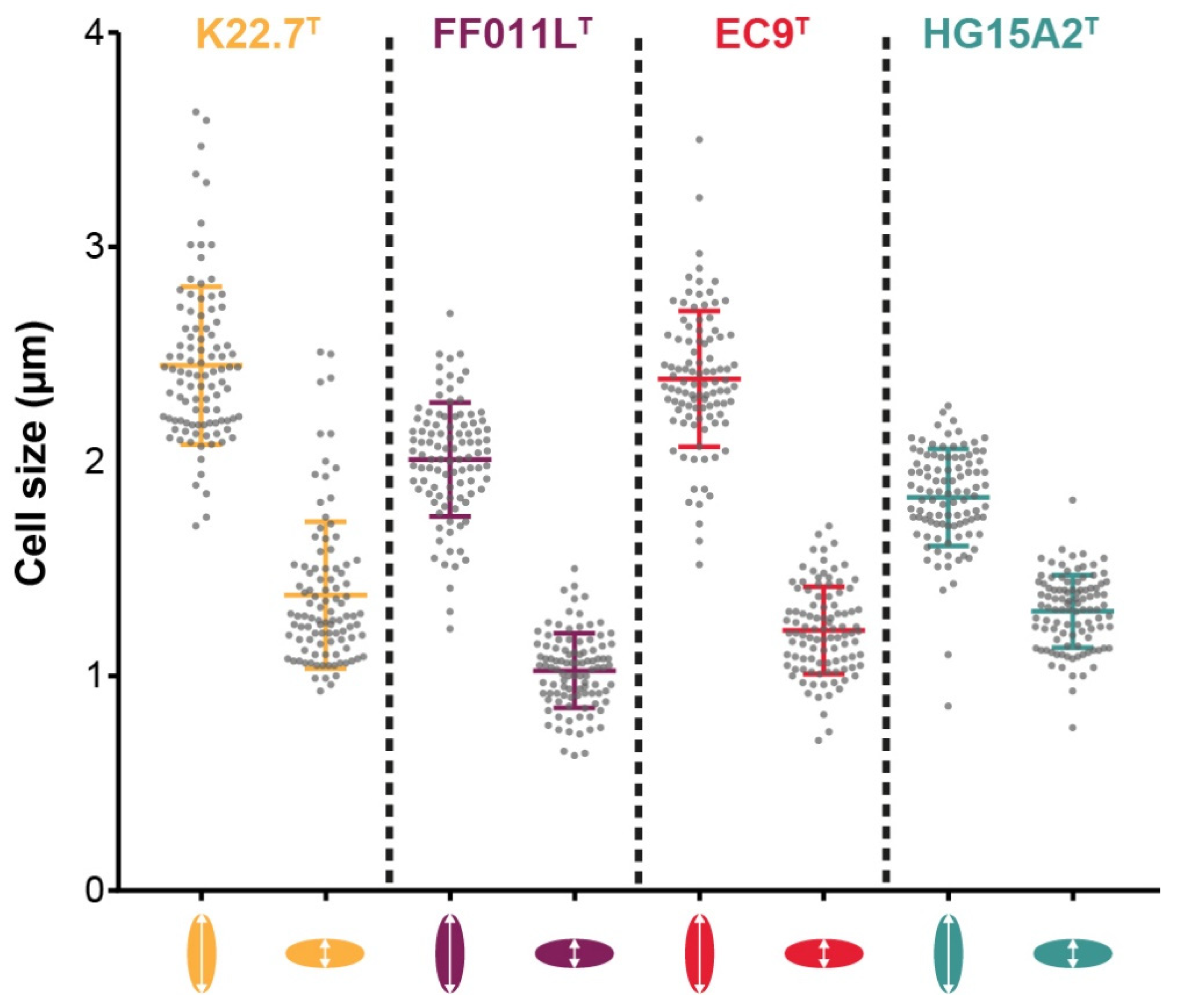
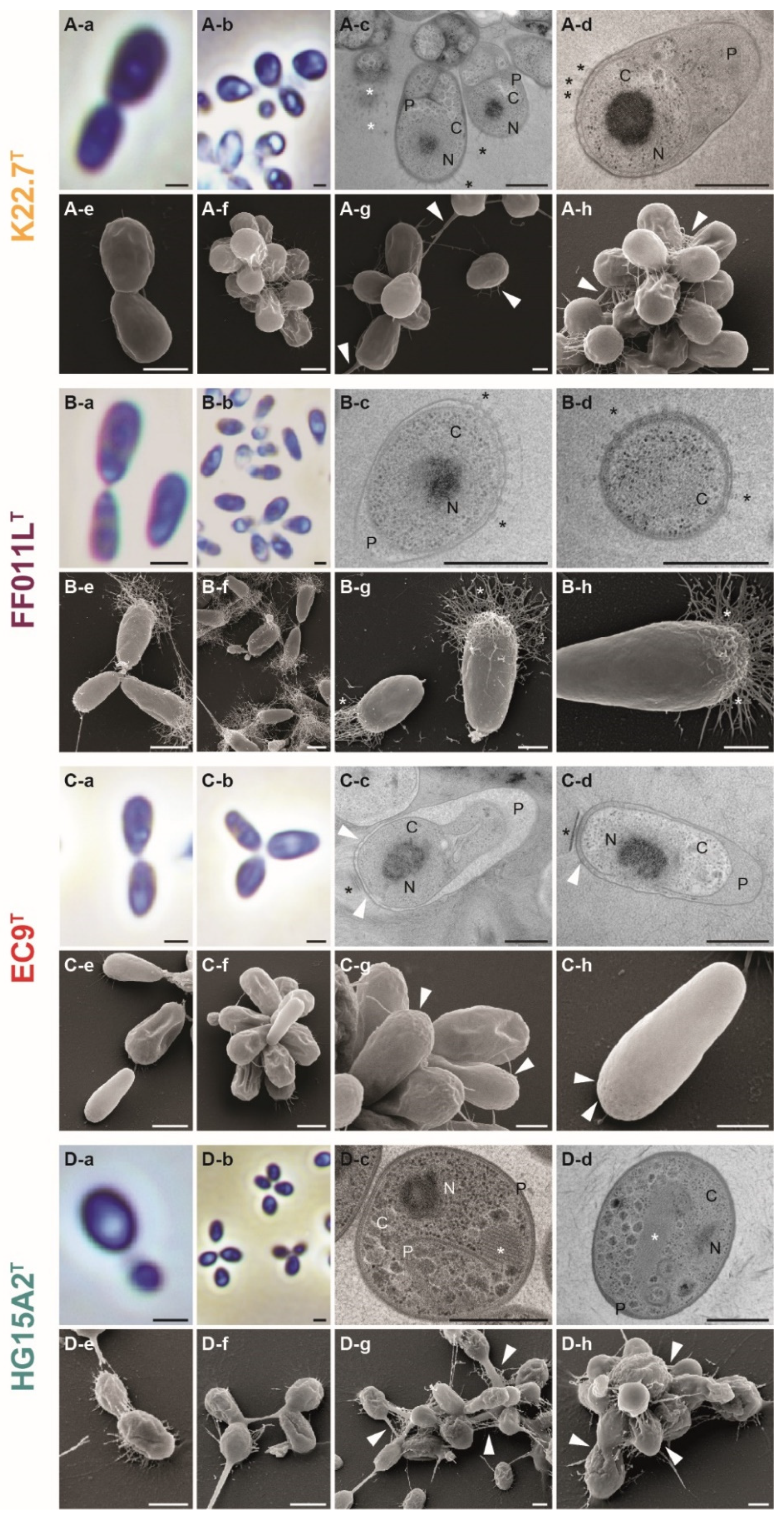
3.4. Morphology and Cell Biology
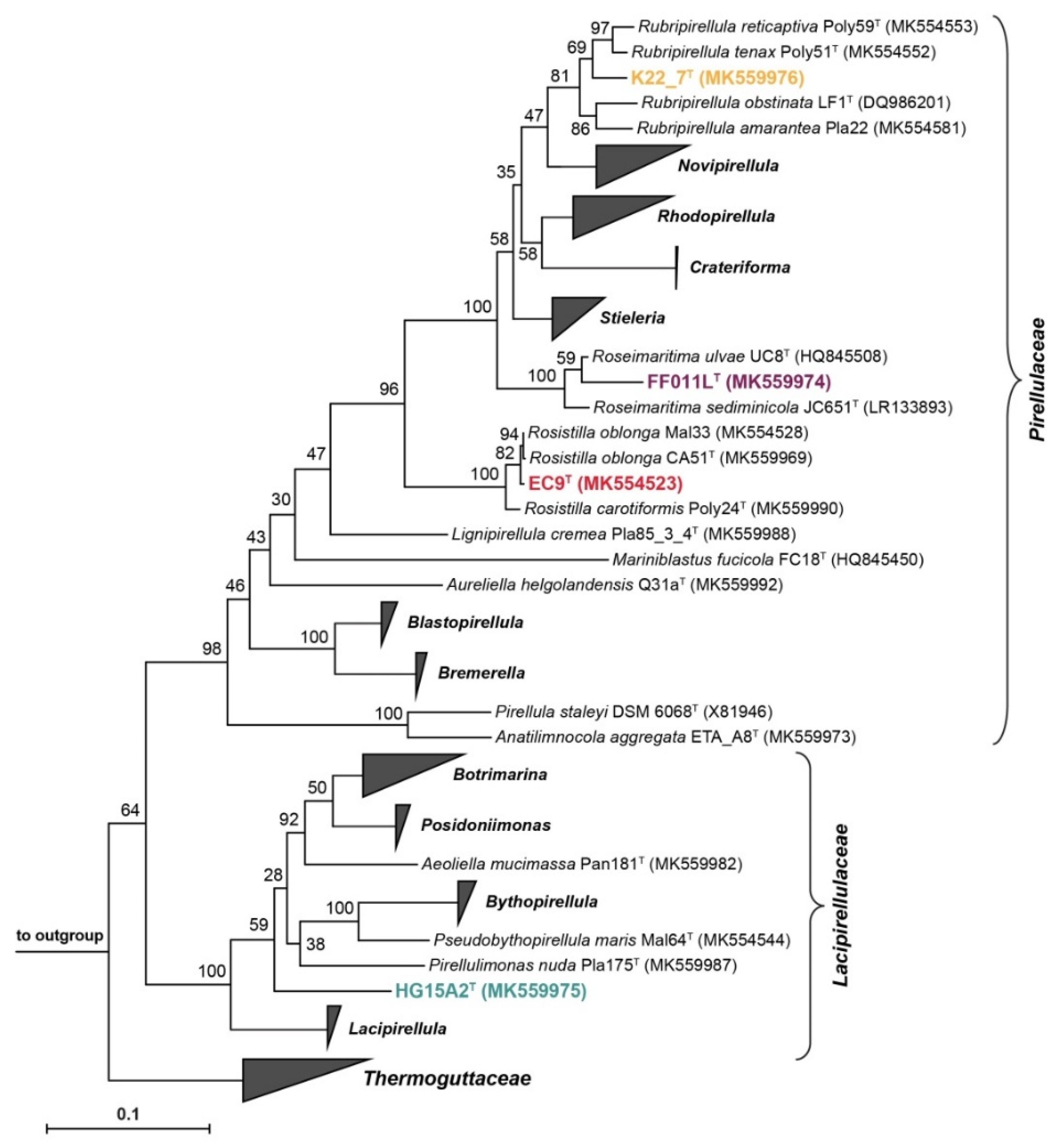
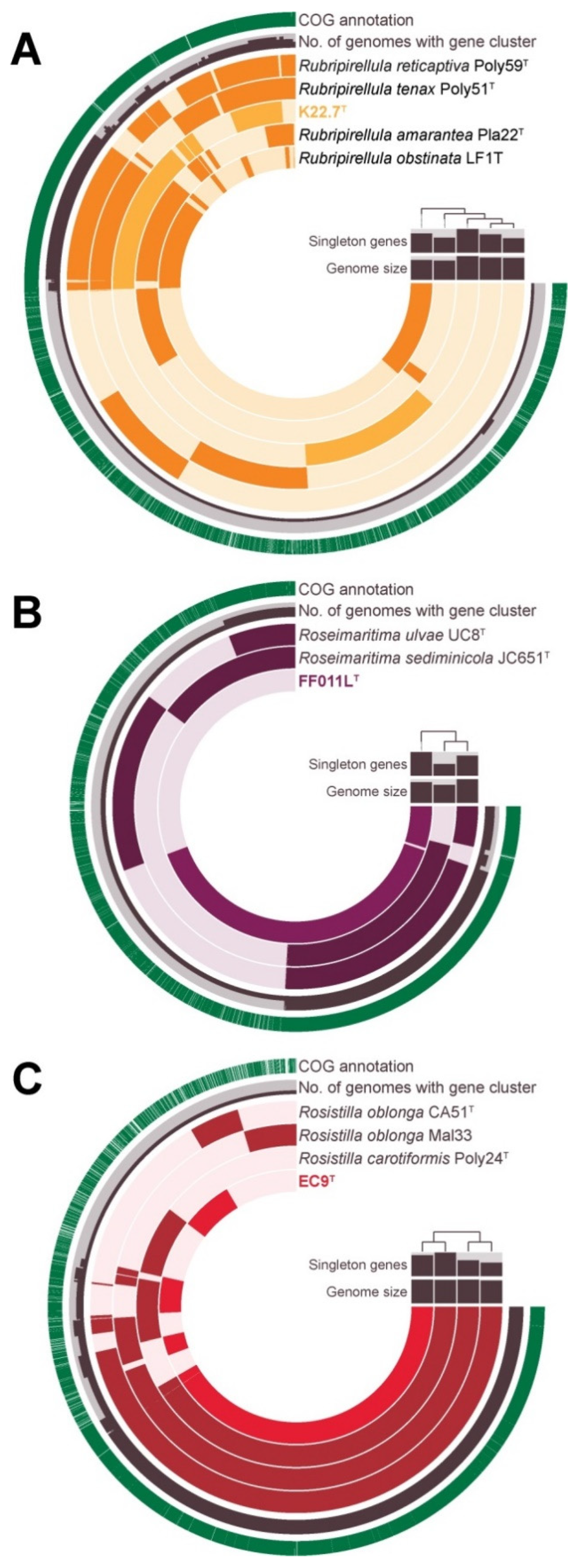
3.5. Phylogenetic Inference and Analysis of Genome-Encoded Features
3.6. Strain K22.7T and the Genus Rubripirellula
3.7. Strain FF011LT and the Genus Roseimaritima
3.8. Strain EC9T and the Genus Rosistilla
3.9. Strain HG15A2T and the Family Lacipirellulaceae
3.10. Genome-Based Analysis of Metabolic Features of the Novel Isolates
3.11. Conclusions
4. Genus and Species Protologues
4.1. Description of Adhaeretor gen. nov.
4.2. Description of Adhaeretor mobilis sp. nov.
4.3. Updated Description of Roseimaritima Bondoso et al. 2016
4.4. Description of Roseimaritima multifibrata sp. nov.
4.5. Description of Rosistilla ulvae sp. nov.
4.6. Description of Rubripirellula lacrimiformis sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Labrenz, M. Marine Microbial Assemblages on Microplastics: Diversity, Adaptation, and Role in Degradation. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procopio, L. The role of biofilms in the corrosion of steel in marine environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial Surface Colonization and Biofilm Development in Marine Environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antunes, J.; Leao, P.; Vasconcelos, V. Marine biofilms: Diversity of communities and of chemical cues. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, M.M.; Sjøtun, K.; Øvreås, L. Seasonal dynamics of bacterial biofilms on the kelp Laminaria hyperborea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moss, J.A.; Nocker, A.; Lepo, J.E.; Snyder, R.A. Stability and change in estuarine biofilm bacterial community diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5679–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lee, O.O.; Tian, R.; Cao, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y.; Qian, P.Y. Adaptation of intertidal biofilm communities is driven by metal ion and oxidative stresses. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juhmani, A.S.; Vezzi, A.; Wahsha, M.; Buosi, A.; Pascale, F.; Schiavon, R.; Sfriso, A. Diversity and Dynamics of Seaweed Associated Microbial Communities Inhabiting the Lagoon of Venice. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachnit, T.; Blümel, M.; Imhoff, J.F.; Wahl, M. Specific epibacterial communities on macroalgae: Phylogeny matters more than habitat. Aquatic Biol. 2009, 5, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengst, M.B.; Andrade, S.; Gonzalez, B.; Correa, J.A. Changes in epiphytic bacterial communities of intertidal seaweeds modulated by host, temporality, and copper enrichment. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, R.; Kim, B.H.; Cho, D.H.; Oh, H.M.; Kim, H.S. Algae-bacteria interactions: Evolution, ecology and emerging applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florez, J.Z.; Camus, C.; Hengst, M.B.; Buschmann, A.H. A Functional Perspective Analysis of Macroalgae and Epiphytic Bacterial Community Interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.W. Bacterial Communities on Macroalgae. In Seaweed Biology—Novel Insights into Ecophysiology, Ecology and Utilization; Wiencke, C., Bischof, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hollants, J.; Leliaert, F.; De Clerck, O.; Willems, A. What we can learn from sushi: A review on seaweed-bacterial associations. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Yu, S.; Bai, J.; Qin, S. Community characteristics and ecological roles of bacterial biofilms associated with various algal settlements on coastal reefs. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachnit, T.; Meske, D.; Wahl, M.; Harder, T.; Schmitz, R. Epibacterial community patterns on marine macroalgae are host-specific but temporally variable. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, K.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Nilsson, R.H.; Kristiansson, E.; Alm Rosenblad, M.; Blanck, H.; Eriksson, K.M. Metagenomic sequencing of marine periphyton: Taxonomic and functional insights into biofilm communities. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Ding, W.; Li, Y.X.; Tam, C.; Bougouffa, S.; Wang, R.; Pei, B.; Chiang, H.; Leung, P.; Lu, Y.; et al. Marine biofilms constitute a bank of hidden microbial diversity and functional potential. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondoso, J.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Balague, V.; Gasol, J.M.; Harder, J.; Lage, O.M. Epiphytic Planctomycetes communities associated with three main groups of macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bondoso, J.; Balague, V.; Gasol, J.M.; Lage, O.M. Community composition of the Planctomycetes associated with different macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bengtsson, M.M.; Øvreås, L. Planctomycetes dominate biofilms on surfaces of the kelp Laminaria hyperborea. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J. Planctomycetes and macroalgae, a striking association. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J. Planctomycetes diversity associated with macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukunaga, Y.; Kurahashi, M.; Sakiyama, Y.; Ohuchi, M.; Yokota, A.; Harayama, S. Phycisphaera mikurensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine alga, and proposal of Phycisphaeraceae fam. nov., Phycisphaerales ord. nov. and Phycisphaerae classis nov. in the phylum Planctomycetes. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegand, S.; Jogler, M.; Jogler, C. On the maverick Planctomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 739–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.; Jang, J.H.; Kasai, H. Algisphaera agarilytica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel representative of the class Phycisphaerae within the phylum Planctomycetes isolated from a marine alga. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 105, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmers, J.; Frentrup, M.; Rast, P.; Jogler, C.; Kaster, A.K. Untangling Genomes of Novel Planctomycetal and Verrucomicrobial Species from Monterey Bay Kelp Forest Metagenomes by Refined Binning. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bondoso, J.; Albuquerque, L.; Lobo-da-Cunha, A.; da Costa, M.S.; Harder, J.; Lage, O.M. Rhodopirellula lusitana sp. nov. and Rhodopirellula rubra sp. nov., isolated from the surface of macroalgae. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondoso, J.; Albuquerque, L.; Nobre, M.F.; Lobo-da-Cunha, A.; da Costa, M.S.; Lage, O.M. Roseimaritima ulvae gen. nov., sp. nov. and Rubripirellula obstinata gen. nov., sp. nov. two novel planctomycetes isolated from the epiphytic community of macroalgae. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 38, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, O.M.; Albuquerque, L.; Lobo-da Cunha, A.; da Costa, M.S. Mariniblastus fucicola gen. nov., sp. nov. a novel planctomycete associated with macroalgae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqqas, M.; Salbreiter, M.; Kallscheuer, N.; Jogler, M.; Wiegand, S.; Heuer, A.; Rast, P.; Peeters, S.H.; Boedeker, C.; Jetten, M.S.M.; et al. Rosistilla oblonga gen. nov., sp. nov. and Rosistilla carotiformis sp. nov., isolated from biotic or abiotic surfaces in Northern Germany, Mallorca, Spain and California, USA. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1939–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, S.; Jogler, M.; Boedeker, C.; Heuer, A.; Peeters, S.H.; Kallscheuer, N.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Kaster, A.-K.; Rohde, M.; Jogler, C. Updates to the recently introduced family Lacipirellulaceae in the phylum Planctomycetes: Isolation of strains belonging to the novel genera Aeoliella, Botrimarina, Pirellulimonas and Pseudobythopirellula and the novel species Bythopirellula polymerisocia and Posidoniimonas corsicana. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1979–1997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salbreiter, M.; Waqqas, M.; Jogler, M.; Kallscheuer, N.; Wiegand, S.; Peeters, S.H.; Heuer, A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Boedeker, C.; Rast, P.; et al. Three Planctomycetes isolated from biotic surfaces in the Mediterranean Sea and the Pacific Ocean constitute the novel species Symmachiella dynata gen. nov., sp. nov. and Symmachiella macrocystis sp. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boersma, A.S.; Kallscheuer, N.; Wiegand, S.; Rast, P.; Peeters, S.H.; Mesman, R.J.; Heuer, A.; Boedeker, C.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Rohde, M.; et al. Alienimonas californiensis gen. nov. sp. nov., a novel Planctomycete isolated from the kelp forest in Monterey Bay. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Marin, E.; Wiegand, S.; Kallscheuer, N.; Jogler, M.; Peeters, S.H.; Heuer, A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Boedeker, C.; Rohde, M.; Devos, D.P.; et al. Thalassoglobus polymorphus sp. nov., a novel Planctomycete isolated close to a public beach of Mallorca Island. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogler, C.; Wiegand, S.; Boedeker, C.; Heuer, A.; Peeters, S.H.; Jogler, M.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Rohde, M.; Kallscheuer, N. Tautonia plasticadhaerens sp. nov., a novel species in the family Isosphaeraceae isolated from an alga in a hydrothermal area of the Eolian Archipelago. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wecker, P.; Klockow, C.; Ellrott, A.; Quast, C.; Langhammer, P.; Harder, J.; Glockner, F.O. Transcriptional response of the model planctomycete Rhodopirellula baltica SH1(T) to changing environmental conditions. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegner, C.E.; Richter-Heitmann, T.; Klindworth, A.; Klockow, C.; Richter, M.; Achstetter, T.; Glöckner, F.O.; Harder, J. Expression of sulfatases in Rhodopirellula baltica and the diversity of sulfatases in the genus Rhodopirellula. Mar. Genom. 2012, 9, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, S.; Jogler, M.; Boedeker, C.; Pinto, D.; Vollmers, J.; Rivas-Marin, E.; Kohn, T.; Peeters, S.H.; Heuer, A.; Rast, P.; et al. Cultivation and functional characterization of 79 planctomycetes uncovers their unique biology. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallscheuer, N.; Jeske, O.; Sandargo, B.; Boedeker, C.; Wiegand, S.; Bartling, P.; Jogler, M.; Rohde, M.; Petersen, J.; Medem, M.H.; et al. The planctomycete Stieleria maiorica Mal15T employs stieleriacines to alter the species composition in marine biofilms. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedeker, C.; Schuler, M.; Reintjes, G.; Jeske, O.; van Teeseling, M.C.; Jogler, M.; Rast, P.; Borchert, D.; Devos, D.P.; Kucklick, M.; et al. Determining the bacterial cell biology of Planctomycetes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallscheuer, N.; Rast, P.; Jogler, M.; Wiegand, S.; Kohn, T.; Boedeker, C.; Jeske, O.; Heuer, A.; Quast, C.; Glöckner, F.-O.; et al. Analysis of bacterial communities in a municipal duck pond during a phytoplankton bloom and isolation of Anatilimnocola aggregata gen. nov., sp. nov., Lacipirellula limnantheis sp. nov. and Urbifossiella limnaea gen. nov., sp. nov. belonging to the phylum Planctomycetes. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1379–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J. Bringing Planctomycetes into pure culture. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godinho, O.; Calisto, R.; Ovreas, L.; Quinteira, S.; Lage, O.M. Antibiotic susceptibility of marine Planctomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkema, D.; Schippers, K.; Maalcke, W.J.; Yang, Y.; Salim, S.; Blanch, H.W. Multiple approaches to enhance the cultivability of bacteria associated with the marine sponge Haliclona (gellius) sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2130–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rast, P.; Glockner, I.; Boedeker, C.; Jeske, O.; Wiegand, S.; Reinhardt, R.; Schumann, P.; Rohde, M.; Spring, S.; Glockner, F.O.; et al. Three Novel Species with Peptidoglycan Cell Walls form the New Genus Lacunisphaera gen. nov. in the Family Opitutaceae of the Verrucomicrobial Subdivision 4. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buddruhs, N.; Pradella, S.; Goker, M.; Pauker, O.; Pukall, R.; Sproer, C.; Schumann, P.; Petersen, J.; Brinkhoff, T. Molecular and phenotypic analyses reveal the non-identity of the Phaeobacter gallaeciensis type strain deposits CIP 105210T and DSM 17395. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63 Pt 11, 4340–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 6 November 2017).
- Miller, L.T. Single derivatization method for routine analysis of bacterial whole-cell fatty acid methyl esters, including hydroxy acids. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1982, 16, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuykendall, L.D.; Roy, M.A.; apos Neill, J.J.; Devine, T.E. Fatty Acids, Antibiotic Resistance, and Deoxyribonucleic Acid Homology Groups of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1988, 38, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, L.; Bernad, A.; Lazaro, J.M.; Martin, G.; Garmendia, C.; Salas, M. Highly efficient DNA synthesis by the phage phi 29 DNA polymerase. Symmetrical mode of DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 8935–8940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, F.B.; Hosono, S.; Fang, L.; Wu, X.; Faruqi, A.F.; Bray-Ward, P.; Sun, Z.; Zong, Q.; Du, Y.; Du, J.; et al. Comprehensive human genome amplification using multiple displacement amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5261–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muyzer, G.; de Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartram, A.K.; Lynch, M.D.; Stearns, J.C.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Neufeld, J.D. Generation of multimillion-sequence 16S rRNA gene libraries from complex microbial communities by assembling paired-end illumina reads. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizhong, L.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Jogler, C.; Glöckner, F.O.; Kolter, R. Characterization of Planctomyces limnophilus and development of genetic tools for its manipulation establish it as a model species for the phylum Planctomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5826–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kallscheuer, N.; Jogler, M.; Wiegand, S.; Peeters, S.H.; Heuer, A.; Boedeker, C.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Rohde, M.; Jogler, C. Three novel Rubripirellula species isolated from plastic particles submerged in the Baltic Sea and the estuary of the river Warnow in northern Germany. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandargo, B.; Jeske, O.; Boedeker, C.; Wiegand, S.; Wennrich, J.-P.; Kallscheuer, N.; Jogler, M.; Rohde, M.; Jogler, C.; Surup, F. Stieleriacines, N-Acyl Dehydrotyrosines From the Marine Planctomycete Stieleria neptunia sp. nov. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedysh, S.N.; Kulichevskaya, I.S.; Beletsky, A.V.; Ivanova, A.A.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Damste, J.S.S.; Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V. Lacipirellula parvula gen. nov., sp. nov., representing a lineage of planctomycetes widespread in low-oxygen habitats, description of the family Lacipirellulaceae fam. nov. and proposal of the orders Pirellulales ord. nov., Gemmatales ord. nov. and Isosphaerales ord. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126050. [Google Scholar]
- Storesund, J.E.; Ovreas, L. Diversity of Planctomycetes in iron-hydroxide deposits from the Arctic Mid Ocean Ridge (AMOR) and description of Bythopirellula goksoyri gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel Planctomycete from deep sea iron-hydroxide deposits. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Gaurav, K.; Jagadeeshwari, U.; Deepshikha, G.; Ch, S. Roseimaritima sediminicola sp. nov., a new member of Planctomycetaceae isolated from Chilika lagoon. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2616–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallscheuer, N.; Wiegand, S.; Heuer, A.; Rensink, S.; Boersma, A.S.; Jogler, M.; Boedeker, C.; Peeters, S.H.; Rast, P.; Jetten, M.S.M.; et al. Blastopirellula retiformator sp. nov. isolated from the shallow-sea hydrothermal vent system close to Panarea Island. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rensink, S.; Wiegand, S.; Kallscheuer, N.; Rast, P.; Peeters, S.H.; Heuer, A.; Boedeker, C.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Rohde, M.; Jogler, M.; et al. Description of the novel planctomycetal genus Bremerella, containing Bremerella volcania sp. nov., isolated from an active volcanic site, and reclassification of Blastopirellula cremea as Bremerella cremea comb. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodkina, G.B.; Panteleeva, A.N.; Beskorovaynaya, D.A.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Slobodkin, A.I. Thermostilla marina gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic, facultatively anaerobic planctomycete isolated from a shallow submarine hydrothermal vent. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodkina, G.B.; Kovaleva, O.L.; Miroshnichenko, M.L.; Slobodkin, A.I.; Kolganova, T.V.; Novikov, A.A.; van Heerden, E.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. Thermogutta terrifontis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Thermogutta hypogea sp. nov., thermophilic anaerobic representatives of the phylum Planctomycetes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65 Pt 3, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Matsuo, Y.; Kasai, H.; Lee, M.-K. Phylogenetic and taxonomic analyses of Rhodopirellula caenicola sp. nov., a new marine Planctomycetes species isolated from Iron Sand. J. Phylogenetics Evol. Biol. 2014, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, M.; Richter-Heitmann, T.; Klindworth, A.; Wegner, C.-E.; Frank, C.S.; Harder, J.; Glöckner, F.O. Permanent draft genomes of the Rhodopirellula maiorica strain SM1. Mar. Genom. 2014, 13, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesner, H.; Rensmann, C.; Tindall, B.J.; Gade, D.; Rabus, R.; Pfeiffer, S.; Hirsch, P. Taxonomic heterogeneity within the Planctomycetales as derived by DNA-DNA hybridization, description of Rhodopirellula baltica gen. nov., sp. nov., transfer of Pirellula marina to the genus Blastopirellula gen. nov. as Blastopirellula marina comb. nov. and emended description of the genus Pirellula. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54 Pt 5, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, G.; Uppada, J.; Ahmed, S.; Sasikala, C.; Venkata Ramana, C. Descriptions of Roseiconus nitratireducens gen. nov. sp. nov. and Roseiconus lacunae sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 203, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.; Findeiss, S.; Steiner, L.; Marz, M.; Stadler, P.F.; Prohaska, S.J. Proteinortho: Detection of (co-)orthologs in large-scale analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castresana, J. Selection of Conserved Blocks from Multiple Alignments for Their Use in Phylogenetic Analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 1, gkz239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bondoso, J.; Harder, J.; Lage, O.M. rpoB gene as a novel molecular marker to infer phylogeny in Planctomycetales. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The enveomics collection: A toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Preprints 2016, 4, e:1900v1. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.L.; Xie, B.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhou, J.; Oren, A.; Zhang, Y.Z. A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Steinke, K.; Villebro, R.; Ziemert, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 5.0: Updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W81–W87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eren, A.M.; Esen, O.C.; Quince, C.; Vineis, J.H.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Delmont, T.O. Anvi’o: An advanced analysis and visualization platform for ’omics data. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmont, T.O.; Eren, A.M. Linking pangenomes and metagenomes: The Prochlorococcus metapangenome. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spring, S.; Bunk, B.; Sproer, C.; Schumann, P.; Rohde, M.; Tindall, B.J.; Klenk, H.P. Characterization of the first cultured representative of Verrucomicrobia subdivision 5 indicates the proposal of a novel phylum. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2801–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castelle, C.J.; Brown, C.T.; Anantharaman, K.; Probst, A.J.; Huang, R.H.; Banfield, J.F. Biosynthetic capacity, metabolic variety and unusual biology in the CPR and DPANN radiations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.T.; Hug, L.A.; Thomas, B.C.; Sharon, I.; Castelle, C.J.; Singh, A.; Wilkins, M.J.; Wrighton, K.C.; Williams, K.H.; Banfield, J.F. Unusual biology across a group comprising more than 15% of domain Bacteria. Nature 2015, 523, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawes, J.C.; Neilan, B.A.; Brown, M.V.; Clark, G.F.; Johnston, E.L. Elevated nutrients change bacterial community composition and connectivity: High throughput sequencing of young marine biofilms. Biofouling 2016, 32, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dogs, M.; Wemheuer, B.; Wolter, L.; Bergen, N.; Daniel, R.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Rhodobacteraceae on the marine brown alga Fucus spiralis are abundant and show physiological adaptation to an epiphytic lifestyle. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Clemente, R.; Igeño, M.I.; Población, A.G.; Guijo, M.I.; Merchán, F.; Blasco, R. Study of pH changes in media during bacterial growth of several environmental strains. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2018, 2, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verniere, C.; Pruvost, O.; Civerolo, E.L.; Gambin, O.; Jacquemoud-Collet, J.P.; Luisetti, J. Evaluation of the Biolog Substrate Utilization System To Identify and Assess Metabolic Variation among Strains of Xanthomonas campestris pv. Citri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeske, O.; Jogler, M.; Petersen, J.; Sikorski, J.; Jogler, C. From genome mining to phenotypic microarrays: Planctomycetes as source for novel bioactive molecules. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.E.; Korber, D.R.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraan, S. Algal Polysaccharides, Novel Applications and Outlook. In Carbohydrates—Comprehensive Studies on Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2012; pp. 489–524. [Google Scholar]
- Pengzhan, Y.; Quanbin, Z.; Ning, L.; Zuhong, X.; Yanmei, W.; Zhi’en, L. Polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) and preliminary studies on their antihyperlipidemia activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 15, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Bourgougnon, N.; Deslandes, E. Chapter 8—Carbohydrates From Seaweeds. In Seaweed in Health and Disease Prevention; Fleurence, J., Levine, I., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J.; Lobo-da-Cunha, A. Insights into the ultrastructural morphology of novel Planctomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, T.; Kallscheuer, N.; Wiegand, S.; Boedeker, C.; Peeters, S.H.; Jogler, M.; Heuer, A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Rohde, M.; Jogler, C. Calycomorphotria hydatis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel species in the family Planctomycetaceae with conspicuous subcellular structures. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niftrik, L.A.; Fuerst, J.A.; Sinninghe Damste, J.S.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.; Strous, M. The anammoxosome: An intracytoplasmic compartment in anammox bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 233, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niftrik, L. Cell biology of unique anammox bacteria that contain an energy conserving prokaryotic organelle. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, N.M.; Neumann, S.; Mesman, R.J.; Ferousi, C.; Keltjens, J.T.; Jetten, M.S.; Kartal, B.; van Niftrik, L. Immunogold Localization of Key Metabolic Enzymes in the Anammoxosome and on the Tubule-Like Structures of Kuenenia stuttgartiensis. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, V.A.; Salzer, R.; Averhoff, B.; Kuhlbrandt, W. Structure of a type IV pilus machinery in the open and closed state. Elife 2015, 4, e07380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, L.; Forest, K.T.; Maier, B. Type IV pili: Dynamics, biophysics and functional consequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, T.; Wiegand, S.; Boedeker, C.; Rast, P.; Heuer, A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Schuler, M.; Becker, S.; Rohde, C.; Muller, R.W.; et al. Planctopirus ephydatiae, a novel Planctomycete isolated from a freshwater sponge. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Konstantinidis, K.T. MyTaxa: An advanced taxonomic classifier for genomic and metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Oh, H.S.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64 Pt 2, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H.; Whitman, W.B.; Euzeby, J.; Amann, R.; Rossello-Mora, R. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Vaddavalli, R.; Siripuram, S.; Eedara, R.V.V.; Yadav, S.; Rabishankar, O.; Lodha, T.; Chintalapati, S.; Chintalapati, V. Planctopirus hydrillae sp. nov., an antibiotic producing Planctomycete isolated from the aquatic plant Hydrilla and its whole genome shotgun sequence analysis. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallscheuer, N.; Jogler, M.; Wiegand, S.; Peeters, S.H.; Heuer, A.; Boedeker, C.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Rohde, M.; Jogler, C. Rubinisphaera italica sp. nov. isolated from a hydrothermal area in the Tyrrhenian Sea close to the volcanic island Panarea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panter, F.; Garcia, R.; Thewes, A.; Zaburannyi, N.; Bunk, B.; Overmann, J.; Gutierrez, M.V.; Krug, D.; Müller, R. Production of a Dibrominated Aromatic Secondary Metabolite by a Planctomycete Implies Complex Interaction with a Macroalgal Host. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallscheuer, N.; Moreira, C.; Airs, R.; Llewellyn, C.A.; Wiegand, S.; Jogler, C.; Lage, O.M. Pink- and orange-pigmented Planctomycetes produce saproxanthin-type carotenoids including a rare C45 carotenoid. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santana-Molina, C.; Rivas-Marin, E.; Rojas, A.M.; Devos, D.P. Origin and Evolution of Polycyclic Triterpene Synthesis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1925–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damsté, J.S.S.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Schouten, S.; Fuerst, J.A.; Jetten, M.S.; Strous, M. The occurrence of hopanoids in planctomycetes: Implications for the sedimentary biomarker record. Org. Geochem. 2004, 35, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Marin, E.; Stettner, S.; Gottshall, E.Y.; Santana-Molina, C.; Helling, M.; Basile, F.; Ward, N.L.; Devos, D.P. Essentiality of sterol synthesis genes in the planctomycete bacterium Gemmata obscuriglobus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, L.E. Assembly of aryl-capped siderophores by modular peptide synthetases and polyketide synthases. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, G.; Dai, S.; Xie, L.; Li, X. Polyketide antibiotics produced by polyketide synthase in streptomyces—A review. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2009, 49, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Tanikawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Matsuyama, T. Serratia marcescens gene required for surfactant serrawettin W1 production encodes putative aminolipid synthetase belonging to nonribosomal peptide synthetase family. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 49, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Feature | K22.7T | FF011LT | EC9T | HG15A2T |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arrangement of cells | Rosettes and aggregates | Rosettes and aggregates | Rosettes and aggregates | Rosettes and aggregates |
| Cell size (µm) | 2.5 ± 0.4 × 1.4 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.3 × 1.0 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.3 × 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 × 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| Cell shape | pear | pear | elongated pear | egg |
| Isolation source | Fucus sp. biofilm | Laminaria sp. biofilm | Ulva sp. biofilm | Laminaria sp. biofilm |
| Isolation method | Biofilm plating | Floating filter assay | Enrichment cultivation | Biofilm plating |
| Colony color | pink | pink to red | red | cream |
| Respiration | aerobic | aerobic | aerobic | aerobic |
| Oxidase activity | + | + | + | + |
| Catalase activity | + | + | + | + |
| Temperature range (°C) | 10–37 | 12–30 | 10–33 | 12–28 |
| Topt (°C) | 26 | 26 | 30 | 22 |
| pH range | 5.5–10.0 | 5.5–10.0 | 5.5–9.5 | 5.5–10.0 |
| pHopt | 8.5 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.5 |
| Growth rate at Topt | 0.053 | 0.049 | 0.062 | 0.018 |
| Generation time (h) at Topt | 13.0 | 14.1 | 11.1 | 38.7 |
| Major fatty acid component (%) | C18:1 ω9c (42.5) | C18:1 ω9c (55.1) | C16:0 (37.3) | C18:1 ω9c (34.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiegand, S.; Rast, P.; Kallscheuer, N.; Jogler, M.; Heuer, A.; Boedeker, C.; Jeske, O.; Kohn, T.; Vollmers, J.; Kaster, A.-K.; et al. Analysis of Bacterial Communities on North Sea Macroalgae and Characterization of the Isolated Planctomycetes Adhaeretor mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseimaritima multifibrata sp. nov., Rosistilla ulvae sp. nov. and Rubripirellula lacrimiformis sp. nov. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071494
Wiegand S, Rast P, Kallscheuer N, Jogler M, Heuer A, Boedeker C, Jeske O, Kohn T, Vollmers J, Kaster A-K, et al. Analysis of Bacterial Communities on North Sea Macroalgae and Characterization of the Isolated Planctomycetes Adhaeretor mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseimaritima multifibrata sp. nov., Rosistilla ulvae sp. nov. and Rubripirellula lacrimiformis sp. nov. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(7):1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071494
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiegand, Sandra, Patrick Rast, Nicolai Kallscheuer, Mareike Jogler, Anja Heuer, Christian Boedeker, Olga Jeske, Timo Kohn, John Vollmers, Anne-Kristin Kaster, and et al. 2021. "Analysis of Bacterial Communities on North Sea Macroalgae and Characterization of the Isolated Planctomycetes Adhaeretor mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseimaritima multifibrata sp. nov., Rosistilla ulvae sp. nov. and Rubripirellula lacrimiformis sp. nov." Microorganisms 9, no. 7: 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071494
APA StyleWiegand, S., Rast, P., Kallscheuer, N., Jogler, M., Heuer, A., Boedeker, C., Jeske, O., Kohn, T., Vollmers, J., Kaster, A.-K., Quast, C., Glöckner, F. O., Rohde, M., & Jogler, C. (2021). Analysis of Bacterial Communities on North Sea Macroalgae and Characterization of the Isolated Planctomycetes Adhaeretor mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseimaritima multifibrata sp. nov., Rosistilla ulvae sp. nov. and Rubripirellula lacrimiformis sp. nov. Microorganisms, 9(7), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071494






