Extreme Weather Events Enhance DOC Consumption in a Subtropical Freshwater Ecosystem: A Multiple-Typhoon Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
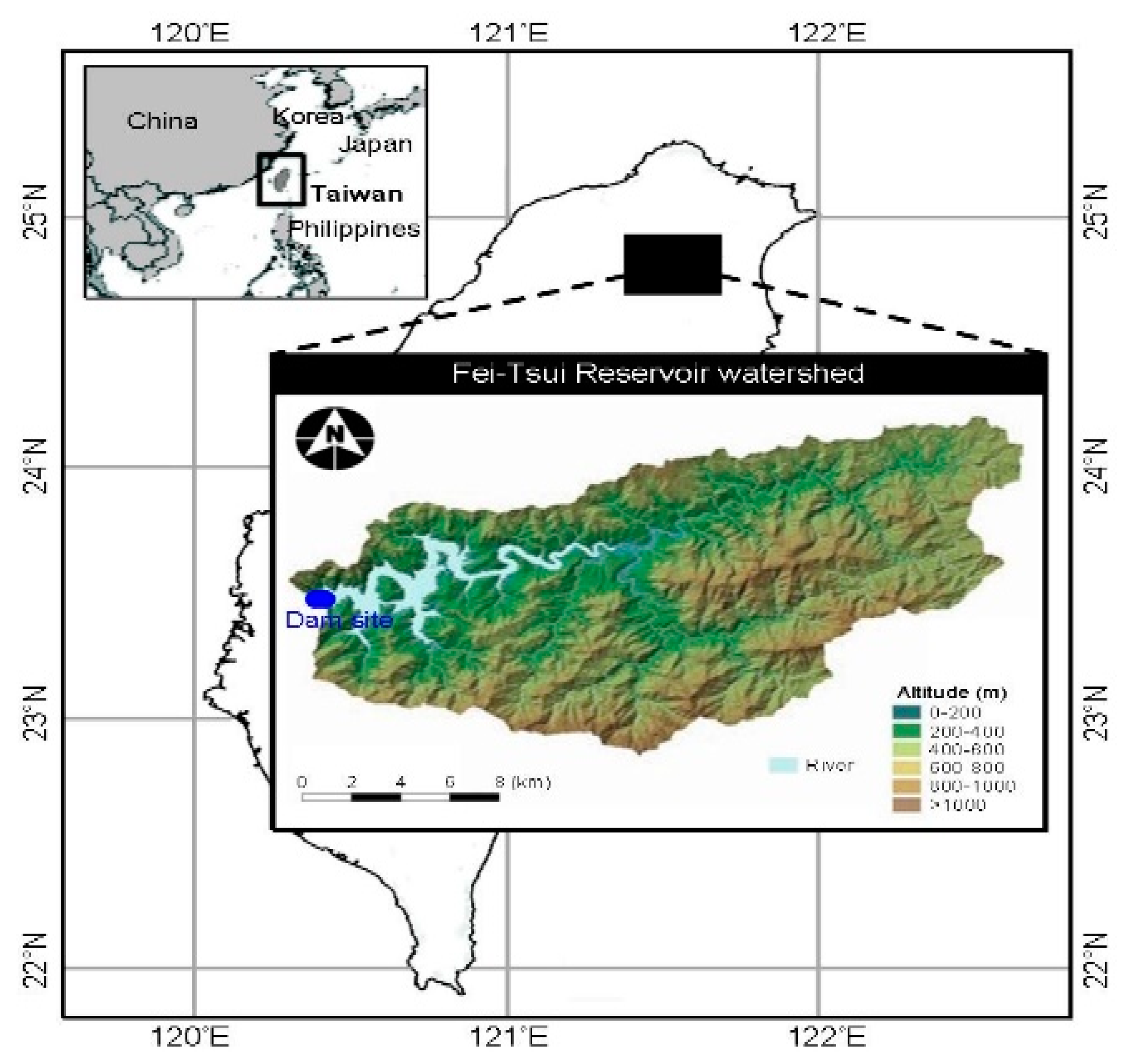
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Filed Sampling and Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
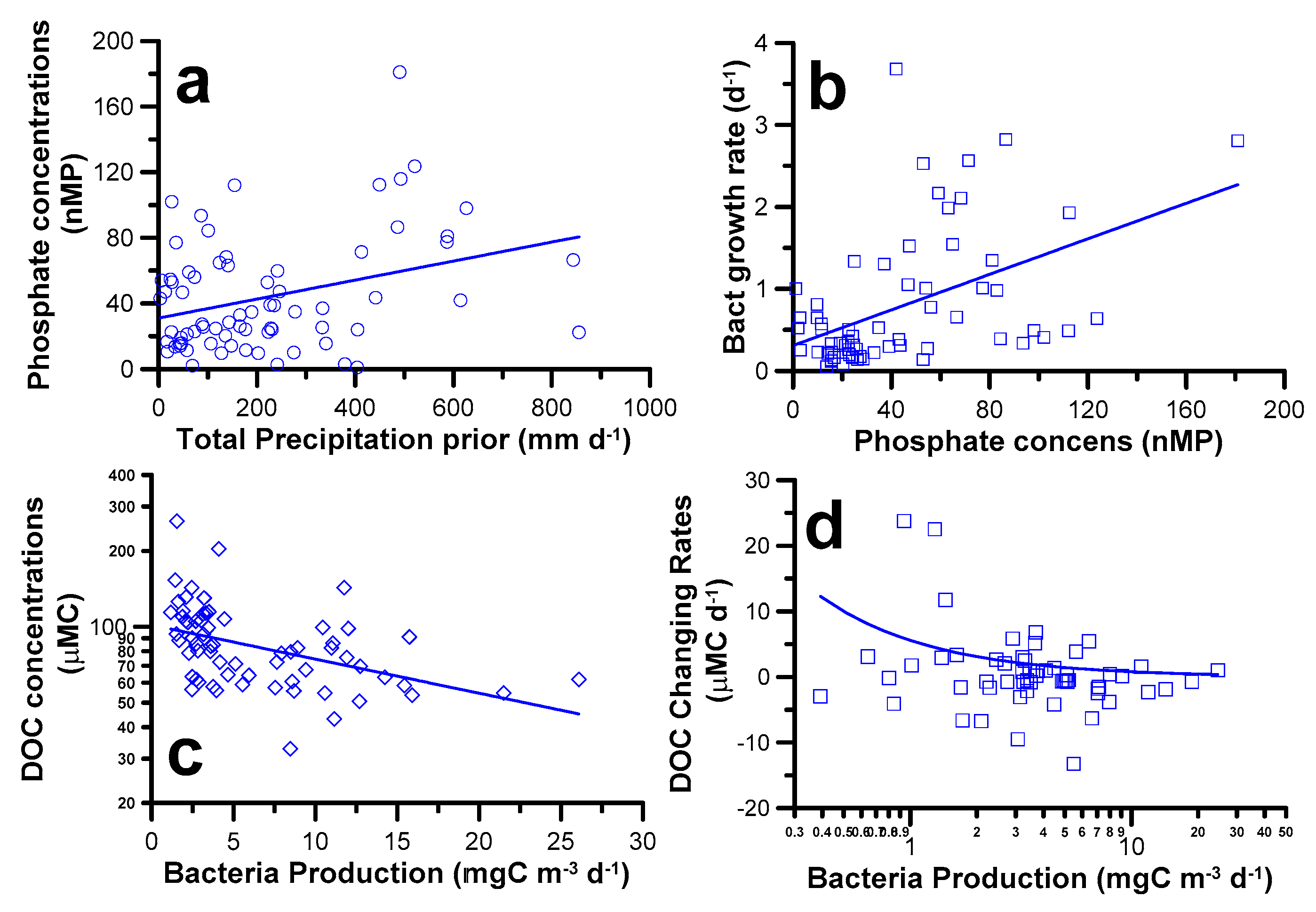
3. Results
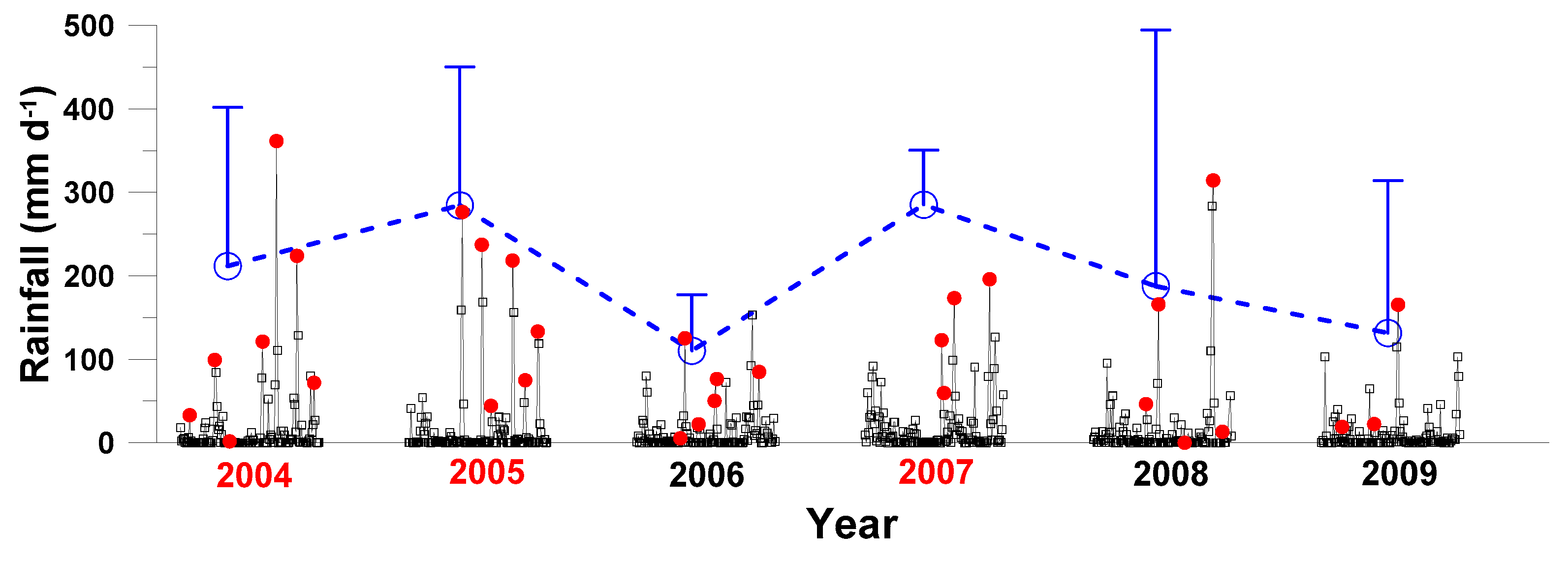
3.1. Precipitation Pattern and Typhoon Distribution
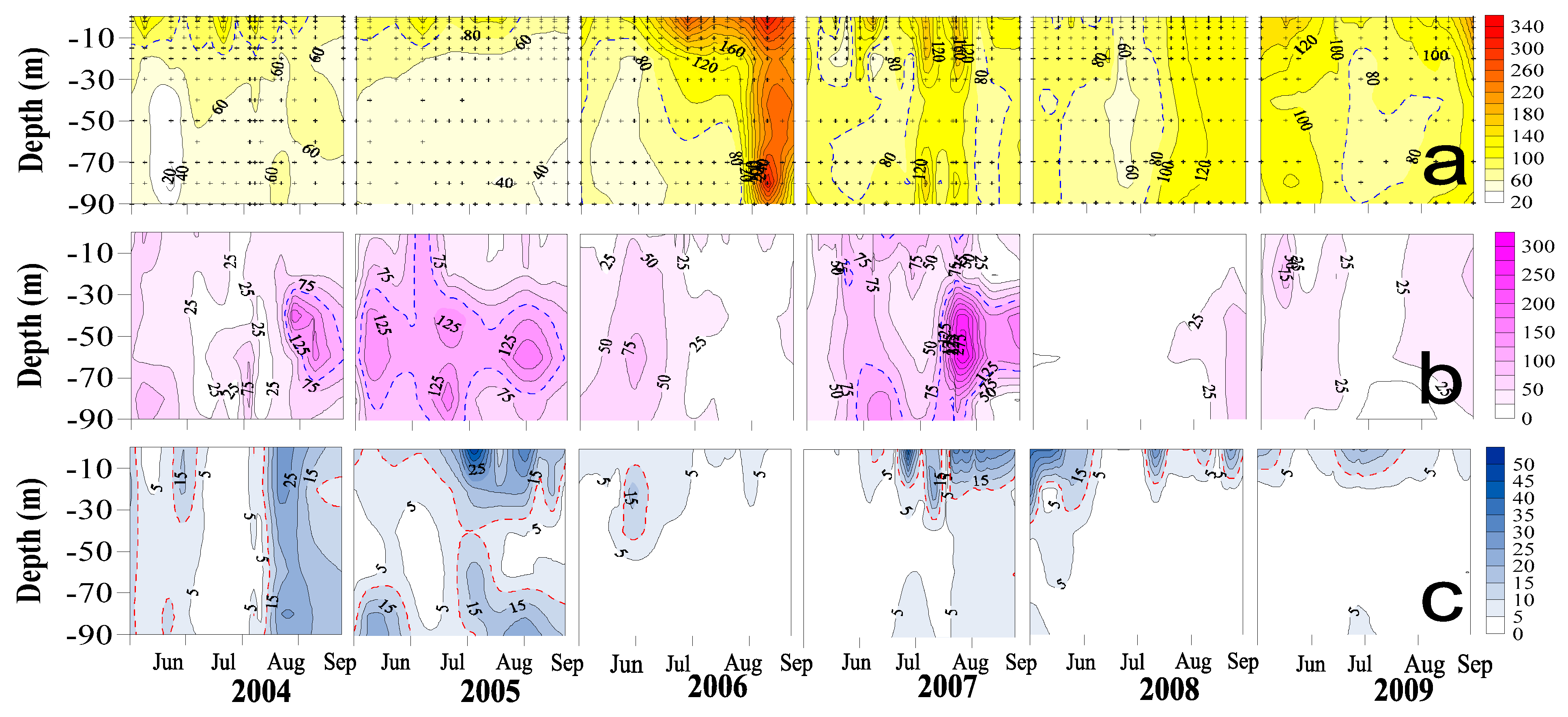
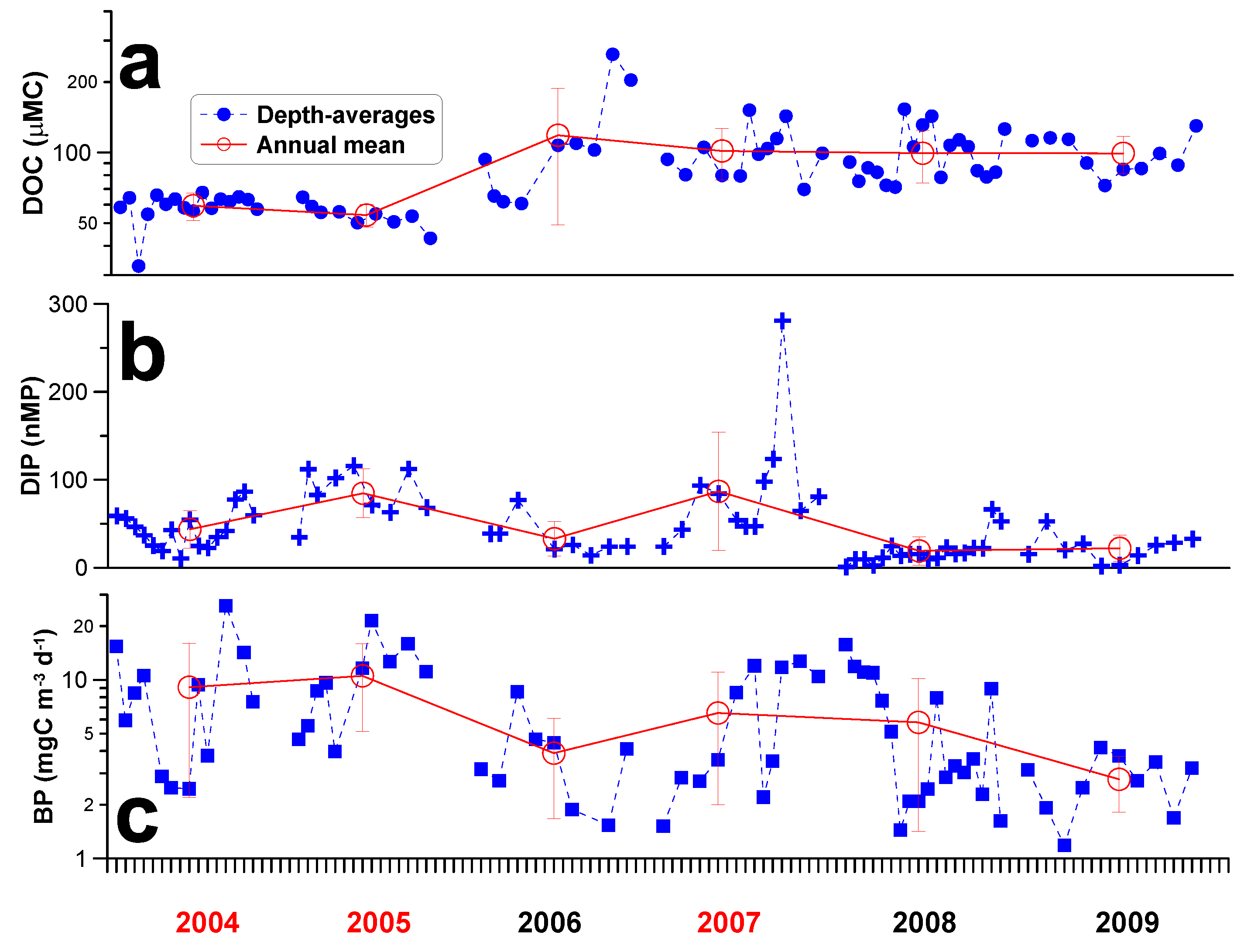
3.2. Depth Contours and Depth-Averages of Measurements
3.3. Statistical Relationships among Measurements
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecosystem Subjected to Multiple-Typhoon Impacts
4.2. DOC Long-Term Trend and Dynamics
4.3. Transportation of Limiting Mineral by Typhoon Rainfall
4.4. Potential Impacts and Feedback on C-Cycling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.C.; Fu, C.; Shiu, C.-J.; Chen, J.-P.; Wu, F. Temperature dependence of global precipitation extremes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Chiang, J.C.H.; Lan, C.-W.; Chung, C.-H.; Liao, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-J. Increase in the range between wet and dry season precipitation. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 436, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, P.J.; Holland, G.J.; Curry, J.A.; Chang, H.-R. Changes in Tropical Cyclone Number, Duration, and Intensity in a Warming Environment. Science 2005, 309, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, T.R.; Mcbride, J.l.; Chan, J.; Emanuel, K.; Holland, G.; Landsea, C.; Held, I.; Kossin, J.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sugi, M. Tropical cyclones and climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kotta, J.; Uuemaa, E.; Sobek, S.; Kutser, T.; Tranvik, L.J. Predicting lake dissolved organic carbon at a global scale. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-W. Particles dynamics in a deep reservoir triggered by typhoons. J. Hydrol. 2011, 406, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-C.; Hsu, T.-C.; Lee, T.-Y.; Shih, Y.-T.; Lin, C.Y.; Jien, S.-H.; Hein, T.; Zehetner, F.; Shiah, F.-K.; Huang, J.-C. Unusual Roles of Discharge, Slope and SOC in DOC Transport in Small Mountainous Rivers, Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.-F.; Hsu, T.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Kao, S.-J.; Wu, J.-T.; Lu, J.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Kuo, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Typhoon effects on DOC dynamics in a phosphate-limited reservoir. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jennings, E.; Jones, S.; Arvola, L.; Staehr, P.A.; Gaiser, E.; Jones, I.D.; Weathers, K.C.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Chiu, C.-Y.; De Eyto, E. Effects of weather-related episodic events in lakes: An analysis based on high-frequency data. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparber, K.; Dalton, C.; De Eyto, E.; Jennings, E.; Lenihan, D.; Cassina, F. Contrasting pelagic plankton in temperate Irish lakes: The relative contribution of heterotrophic, mixotrophic, and autotrophic components, and the effects of extreme rainfall events. Inland Waters 2015, 5, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.F.; Lai, C.-C.; Kuo, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, T.-Y.; Shiah, F.-K. Long Term Trends and Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) in a Subtropical Reservoir Basin. Water 2017, 9, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-C.; Liao, C.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Shih, Y.-T.; Huang, J.-C.; Zehetner, F.; Hein, T. Differences in N loading affect DOM dynamics during typhoon events in a forested mountainous catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.M.; Betts, R.A.; Jones, C.D.; Spal, S.A.; Totterdell, J.J. Acceleration of global warming due to carbon-cycle feedbacks in a coupled climate model. Nature 2000, 408, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimann, M.; Reichstein, M. Terrestrial ecosystem carbon dynamics and climate feedbacks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 451, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabine, C.L.; Feely, R.A.; Gruber, N.; Key, R.M.; Lee, K.; Bullister, J.L.; Wanninkhof, R.; Wong, C.S.; Wallace, D.W.R.; Tilbrook, B.; et al. The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO2. Science 2004, 305, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; McDowell, W.H.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Downing, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Plumbing the global carbon cycle: Integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I. Global biogeochemical cycles: Progress and problems. Mar. Chem. 1992, 39, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, D.A.; Carlson, C.A.; Repeta, D.J.; Schlitzer, R. Dissolved Organic Matter in the Ocean: A Controversy Stimulates New Insights. Oceanography 2009, 22, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.-P.; Kumar, H.; Smith, R.; Worrest, R. Effects on aquatic ecosystems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1998, 46, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Loiselle, S.A.; Striegl, R.G.; Ballatore, T.J.; Dillon, P.; Finlay, K.; Fortino, K.; Knoll, L.B.; et al. Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.R. The ocean’s foodweb, a changing paradigm. BioScience 1974, 24, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Fenchel, T.; Field, J.G.; Gray, J.; Meyer-Reil, L.; Thingstad, F. The Ecological Role of Water-Column Microbes in the Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1983, 10, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Agustí, S.; Vaqué, D.; Agawin, N.S.; Felipe, J.; Casamayor, E.O.; Gasol, J.M. Experimental test of bacteria-phytoplankton coupling in the Southern Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.R.; Wiebe, W.J. Temperature and substrates as interactive limiting factors for marine heterotrophic bacteria. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 23, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-W.; Kratz, T.K.; Hanson, P.C.; Kimura, N.; Liu, W.-C.; Lin, F.-P.; Chou, H.-M.; Wu, J.-T.; Chiu, C.-Y. Metabolic changes and the resistance and resilience of a subtropical heterotrophic lake to typhoon disturbance. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Hamasaki, K.; Tada, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Yoshiki, T.; Nakajima, R.; Imai, A.; Shimode, S.; Toda, T. Typhoon-induced response of phytoplankton and bacteria in temperate coastal waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, M.; Pace, M.; Cole, J. Regulation of planktonic bacterial growth rates: The effects of temperature and resources. Microb. Ecol. 1996, 31, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.M.; Stone, K.C.; Watts, D.W.; Johnson, M.H. Dissolved Phosphorus Transport during Storm and Base Flow Conditions from An Agriculturally Intensive Southeastern Coastal Plain Watershed. Trans. ASAE 2003, 46, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhanga, Q.; Blomquist, J.D. Watershed export of fine sediment, organic carbon, and chlorophyll-a to Chesapeake Bay: Spatial and temporal patterns in 1984–2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lu, Y.; Dash, P.; Das, P.; Li, J.; Capps, K.; Majidzadeh, H.; Elliott, M. Hurricane pulses: Small watershed exports of dissolved nutrients and organic matter during large storms in the Southeastern USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakour, H.; Lo, S.-L.; Lin, T.-F. Impacts of Typhoon Soudelor (2015) on the water quality of Taipei, Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.A.; Fowler, R.A.; Saros, J.E. Differences in the Effects of Storms on Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) in Boreal Lakes during an Early Summer Storm and an Autumn Storm. Water 2020, 12, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, G.; Parr, T.B.; Jeanneau, L.; Dupas, R.; Petitjean, P.; Akkal-Corfini, N.; Viaud, V.; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.; Denis, M.; Inamdar, S.; et al. Agricultural Practices and Hydrologic Conditions Shape the Temporal Pattern of Soil and Stream Water Dissolved Organic Matter. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 1325–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Tanoue, E. Dissolved Organic Matter in Oceanic Waters. J. Oceanogr. 2003, 59, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, T.; Bida, M.; Kenny, J.E. Trends in Levels of Allochthonous Dissolved Organic Carbon in Natural Water: A Review of Potential Mechanisms under a Changing Climate. Water 2014, 6, 2862–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalev, S.; Toor, G.S. Concentrations and Loads of Dissolved and Particulate Organic Carbon in Urban Stormwater Runoff. Water 2020, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puczko, K.; Jekatierynczuk-Rudczyk, E. Extreme Hydro-Meteorological Events Influence to Water Quality of Small Rivers in Urban Area: A Case Study in Northeast Poland. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasol, J.M.; Del Giorgio, P.A. Using flow cytometry for counting natural planktonic bacteria and understanding the structure of planktonic bacterial communities. Sci. Mar. 2000, 64, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, C.P.D. Optimization of Procedures for Counting Viruses by Flow Cytometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J.A.; Azam, F. Thymidine incorporation as a measure of heterotrophic bacterioplankton production in marine surface waters: Evaluation and field results. Mar. Biol. 1982, 66, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducklow, H.W.; Carlson, C.A. Oceanic Bacterial Production. In Advances in Microbial Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; Volume 12, pp. 113–181. [Google Scholar]
- Strock, K.E.; Saros, J.E.; Nelson, S.J.; Birkel, S.D.; Kahl, J.S.; McDowell, W. Extreme weather years drive episodic changes in lake chemistry: Implications for recovery from sulfate deposition and long-term trends in dissolved organic carbon. Biogeochemistry 2016, 127, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillela, M.; Rodriquez-Murillo, J. Long-term trends of organic carbon concentrations in freshwaters: Strength and weaknesses of existing evidence. Water 2014, 6, 1360–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucker, C.; Krause, K. Increasing dissolved organic carbon concentrations in freshwaters: What is the actual driver? iForest Biogeosciences For. 2010, 3, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, P.; Watkins, J.; Hansing, R. Nutrients, organic carbon and organic nitrogen in the upper water column of the Arctic Ocean: Implications for the sources of dissolved organic carbon. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1997, 44, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterloo, M.J.; Oliveira, S.M.; Drucker, D.P.; Nobre, A.D.; Cuartas, L.A.; Hodnett, M.G.; Langedijk, I.; Jans, W.W.P.; Tomasella, J.; De Araújo, A.C.; et al. Export of organic carbon in run-off from an Amazonian rainforest blackwater catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2581–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.C.; Wu, S.-C.; Lee, B.-S.; Hung, C.-C. Behavior of storm-induced suspension interflow in subtropical Feitsui Reservoir, Taiwan. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Inamdar, S. Extreme storms and changes in particulate and dissolved organic carbon in runoff: Entering un-charted waters? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forel, F.A. Les ravins sous-lacustres des fleuves glaciaires. Comptes Rendus Académie Sci. 1885, 101, 725–728. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, T.; Syvitski, J.P.; Migeon, S.; Faugères, J.-C.; Savoye, B. Marine hyperpycnal flows: Initiation, behavior and related deposits. A review. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 861–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R. On the Phosphorus Limitation Paradigm for Lakes. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Kao, S. Hyperpycnal Discharge of Fluvial Sediment to the Ocean: Impact of Super-Typhoon Herb (1996) on Taiwanese Rivers. J. Geol. 2005, 113, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtan, H.; Kamp-Nielsen, L.; Stuanes, A.O. Phosphorus in soil, water and sediment: An overview. Hydrobiologia 1988, 170, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Kadlec, R.H.; Flaig, E.; Gale, P.M. Phosphorus Retention in Streams and Wetlands: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 29, 83–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kitchell, J.F.; Pace, M.L. Pathways of organic carbon utilization in small lakes: Results from a whole-lake 13 C addition and coupled model. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, A.; Karlsson, J.; Jansson, M. Sources of carbon dioxide super saturation in clear water and humic lakes in northern Sweden. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; McDonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-C.; Ko, C.-Y.; Austria, E.; Shiah, F.-K. Extreme Weather Events Enhance DOC Consumption in a Subtropical Freshwater Ecosystem: A Multiple-Typhoon Analysis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061199
Lai C-C, Ko C-Y, Austria E, Shiah F-K. Extreme Weather Events Enhance DOC Consumption in a Subtropical Freshwater Ecosystem: A Multiple-Typhoon Analysis. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(6):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061199
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Chao-Chen, Chia-Ying Ko, Eleanor Austria, and Fuh-Kwo Shiah. 2021. "Extreme Weather Events Enhance DOC Consumption in a Subtropical Freshwater Ecosystem: A Multiple-Typhoon Analysis" Microorganisms 9, no. 6: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061199
APA StyleLai, C.-C., Ko, C.-Y., Austria, E., & Shiah, F.-K. (2021). Extreme Weather Events Enhance DOC Consumption in a Subtropical Freshwater Ecosystem: A Multiple-Typhoon Analysis. Microorganisms, 9(6), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061199





