Experimental Assessment of Possible Factors Associated with Tick-Borne Encephalitis Vaccine Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cells and Viruses
2.3. Infection of Ticks
2.4. Vaccination and Cyclophosphamide (cy) Treatment
2.5. Plaque Assay and 50% Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test (PRNT50)
2.6. Virus Titration in Mice
2.7. Sample Preparation and RNA Quantification (qRT-PCR)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Host-Related Factors of the Vaccine Failure in a Mouse Model
3.1.1. Influence of Mouse Strain and Sex on the Susceptibility to TBEV Infection and Efficacy of TBE Vaccine
3.1.2. Effect of Immunosuppression on TBE Vaccine Efficacy in BALB/c Mice
3.2. Virus-Related Factors of the Vaccine Failure in Mouse Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruzek, D.; Županc, T.A.; Borde, J.; Chrdle, A.; Eyer, L.; Karganova, G.; Kholodilov, I.; Knap, N.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Matveev, A.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and Russia: Review of pathogenesis, clinical features, therapy, and vaccines. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deviatkin, A.; Karganova, G.; Vakulenko, Y.; Lukashev, A. TBEV Subtyping in Terms of Genetic Distance. Viruses 2020, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domnich, A.; Panatto, D.; Arbuzova, E.K.; Signori, A.; Avio, U.; Gasparini, R.; Amicizia, D. Immunogenicity against Far Eastern and Siberian subtypes of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus elicited by the currently available vaccines based on the European subtype: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 2819–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, K.E.; Rosdahl, A.; Insulander, M.; Vene, S.; Lindquist, L.; Gredmark-Russ, S.; Askling, H.H. Tick-borne Encephalitis Vaccine Failures: A 10-year Retrospective Study Supporting the Rationale for Adding an Extra Priming Dose in Individuals Starting at Age 50 Years. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmit, R.; Postma, M.J. Review of tick-borne encephalitis and vaccines: Clinical and economical aspects. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2014, 14, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorob’eva, M.S.; El’Bert, L.B.; Grachev, V.P.; Lelikov, V.L.; Pervikov, I.V. Reactogenicity and immunological effectiveness of a concentrated, purified vaccine against tick-borne encephalitis. Vopr. Virusol. 1983, 28, 622–626. [Google Scholar]
- Vorovitch, M.F.; Maikova, G.B.; Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Romanenko, V.V.; Ankudinova, A.V.; Khapchaev, Y.K.; Karganova, G.G.; Ishmukhametov, A.A.; Drozdov, S.G. Immunogenicity and safety of the adult TBE vaccine Tick-E-Vac. Vopr. Virusol. 2017, 62, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, K.; Song, J.Y.; Park, S.-B.; Yang, J.; Schmitt, H.-J. Tick-borne encephalitis in Japan, Republic of Korea and China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K.; Holzmann, H.; Grgic-Vitek, M.; Kriz, B.; Essl, A.; Kundi, M. Vaccination and tick-borne encephalitis, central Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penyevskaya, N.A.; Rudakov, N.V.; Rudakova, S.A. Problematic Aspects of the Evaluation of the Epidemiological Effectiveness of Vaccination against Tick-BORNE Encephalitis. Epidemiol. Vaccine Prev. 2018, 17, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Romanenko, V.V.; Esiunina, M.S.; Kiliachina, A.S.; Pimenova, T.A. Massive immunization of the Sverdlovsk region population against tick-borne encephalitis, its epidemiological, clinical and immunological efficacy. Med. Virol. Trans. Chumakov IPVE 2006, 23, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Romanenko, V.V.; Esiunina, M.S.; Kiliachina, A.S. Experience in implementing the mass immunization program against tick-borne encephalitis in the Sverdlovsk Region. Vopr. Virusol. 2007, 52, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shcherbinina, M.S.; Barkhaleva, O.A.; Dorokhova, O.S.; Movsesyants, A.A. Effectiveness of Specific Prevention of Tick-Borne Encephalitis. Bioprep. Prev. Diagn. Treat. 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew-Baselli, A.; Konior, R.; Pavlova, B.G.; Fritsch, S.; Poellabauer, E.; Maritsch, F.; Harmacek, P.; Krammer, M.; Barrett, P.N.; Ehrlich, H.J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the modified adult tick-borne encephalitis vaccine FSME-IMMUN: Results of two large phase 3 clinical studies. Vaccine 2006, 24, 5256–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beran, J.; Douda, P.; Gniel, D.; Zent, O. Long-term immunity after vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis with Encepur® using the rapid vaccination schedule. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. Suppl. 2004, 293, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew-Baselli, A.; Poellabauer, E.-M.; Pavlova, B.G.; Fritsch, S.; Koska, M.; Bobrovsky, R.; Konior, R.; Ehrlich, H.J. Seropersistence of tick-borne encephalitis antibodies, safety and booster response to FSME-IMMUN® 0.5 ml in adults aged 18-67 years. Hum. Vaccines 2009, 5, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.J.; Pavlova, B.G.; Fritsch, S.; Poellabauer, E.M.; Loew-Baselli, A.; Obermann-Slupetzky, O.; Maritsch, F.; Cil, I.; Dorner, F.; Barrett, P.N. Randomized, phase II dose-finding studies of a modified tick-borne encephalitis vaccine: Evaluation of safety and immunogenicity. Vaccine 2003, 22, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorovitch, M.F.; Maikova, G.B.; Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Romanenko, V.V.; Karganova, G.G.; Ishmukhametov, A.A. Comparison of the Immunogenicity and Safety of Two Pediatric TBE Vaccines Based on the Far Eastern and European Virus Subtypes. Adv. Virol. 2019, 2019, 5323428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Rogova, Y.V.; Vorovitch, M.F.; Romanova, L.I.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Maikova, G.B.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Karganova, G.G. Protective immunity spectrum induced by immunization with a vaccine from the TBEV strain Sofjin. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2354–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maikova, G.B.; Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Vorovitch, M.F.; Rogova, U.V.; Karganova, G.G. Vaccines based on the Far-Eastern and European strains induce the neutralizing antibodies against all known tick-borne encephalitis virus subtypes. Vopr. Virusol. 2016, 61, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Morozova, O.V.; Bakhvalova, V.N.; Potapova, O.F.; Grishechkin, A.E.; Isayeva, E.I. A study of immunogenic and protective effects of inactivated vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) against modern TBE virus strains. Nac. Prior. Ross. 2011, 2, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Orlinger, K.K.; Hofmeister, Y.; Fritz, R.; Holzer, G.W.; Falkner, F.G.; Unger, B.; Loew-Baselli, A.; Poellabauer, E.-M.; Ehrlich, H.J.; Barrett, P.N.; et al. A tick-borne encephalitis virus vaccine based on the European prototype strain induces broadly reactive cross-neutralizing antibodies in humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollaritsch, H.; Paulke-Korinek, M.; Holzmann, H.; Hombach, J.; Bjorvatn, B.; Barrett, A. Vaccines and vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikova, G.B.; Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Rogova, Y.V.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Romanenko, V.V.; Esyunina, M.S.; Ankudinova, A.A.; Kilyachina, A.S.; Vorovitch, M.F.; et al. Ability of inactivated vaccines based on far-eastern tick-borne encephalitis virus strains to induce humoral immune response in originally seropositive and seronegative recipients. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, C.R.; Vene, S.; Insulander, M.; Lindquist, L.; Lundkvist, A.; Günther, G. Vaccine failures after active immunisation against tick-borne encephalitis. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2827–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogodina, V.V.; Levina, L.S.; Skrynnik, S.M.; Travina, N.S.; Kolesnikova, N.M.; Karmysheva, V.; Gerasimov, S.G.; Malenko, G.V.; Perminov, L.V. Tick-borne encephalitis with fulminant course and lethal outcome in patients after plural vaccination. Vopr. Virusol. 2013, 58, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pogodina, V.V.; Luchinina, S.V.; Stepanova, O.N.; Stenko, E.A.; Gorfinkel, A.N.; Karmysheva, V.Y.; Gerasimov, S.G.; Levina, L.S.; Chirkova, G.G.; Karan, L.S.; et al. Unusual case of lethal tick-borne encephalitis in patient vaccinated with vaccines produced from different viruses strains (the Chelyabinsk Region). Epidemiol. Infekc. Bolezn. 2015, 20, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Bogovič, P.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Jelovšek, M.; Lusa, L.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis in patients vaccinated against this disease. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotric-Furlan, S.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis after active immunization. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2008, 298, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Sabeena, S.P.; Varma, M.; Arunkumar, G. Current Understanding of the Pathogenesis of Dengue Virus Infection. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgič-Vitek, M.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Klavs, I. Tick-borne encephalitis after vaccination: Vaccine failure or misdiagnosis. Vaccine 2010, 28, 7396–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedermann, U.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; Wagner, A. Primary vaccine failure to routine vaccines: Why and what to do? Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkhash, A.V.; Babenko, V.N.; Kobzev, V.F.; Romaschenko, A.G.; Voevoda, M.I. Polymorphism of 2′-5’-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS) genes, associated with predisposition to severe forms of tick-borne encephalitis, in human populations of North Eurasia. Mol. Biol. 2010, 44, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzell, K.B.; Pauksens, K.; Rombo, L.; Knight, A.; Vene, S.; Askling, H.H. Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) vaccine to medically immunosuppressed patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective, open-label, multi-centre study. Vaccine 2016, 34, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erber, W.; Schmitt, H.-J. Self-reported tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) vaccination coverage in Europe: Results from a cross-sectional study. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner-Spitzer, E.; Poellabauer, E.-M.; Wagner, A.; Guzek, A.; Zwazl, I.; Seidl-Friedrich, C.; Binder, C.J.; Stiasny, K.; Kundi, M.; Wiedermann, U. Obesity and Sex Affect the Immune Responses to Tick-Borne Encephalitis Booster Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, T.; Ott, D.; Jakob, N.J.; Martinez-Torres, F.; Grond-Ginsbach, C.; Meyding-Lamadé, U. Clinical outcome and cerebrospinal fluid profiles in patients with tick-borne encephalitis and prior vaccination history. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobler, G.; Kaier, K.; Hehn, P.; Böhmer, M.; Kreusch, T.; Borde, J. Tick-borne encephalitis virus vaccination breakthrough infections in Germany: A retrospective analysis from 2001 to 2018. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1090.e7-1090.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevtsova, A.S.; Motuzova, O.V.; Kuragina, V.M.; Akhmatova, N.K.; Gmyl, L.V.; Kondrat’eva, Y.I.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Rogova, Y.V.; Litov, A.G.; Romanova, L.I.; et al. Lethal Experimental Tick-Borne Encephalitis Infection: Influence of Two Strains with Similar Virulence on the Immune Response. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.K.; Brandt, W.E.; Dalrymple, J.M. Chemical and Antigenic Structure of Flaviviruses. In The Togaviruses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 503–529. [Google Scholar]
- Gritsun, T.S.; Lisak, V.M.; Liapustin, V.N.; Korolev, M.B.; Lashkevich, V.A. Slowly-sedimenting hemagglutinin of the tick-borne encephalitis virus. Vopr. Virusol. 1989, 34, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Schalich, J.; Allison, S.L.; Stiasny, K.; Mandl, C.W.; Kunz, C.; Heinz, F.X. Recombinant subviral particles from tick-borne encephalitis virus are fusogenic and provide a model system for studying flavivirus envelope glycoprotein functions. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4549–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, T.C.; Diamond, M.S. Degrees of maturity: The complex structure and biology of flaviviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, K.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Pierson, T.C. Combined effects of the structural heterogeneity and dynamics of flaviviruses on antibody recognition. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11726–11737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, K.A.; Pierson, T.C. The Many Faces of a Dynamic Virion: Implications of Viral Breathing on Flavivirus Biology and Immunogenicity. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliphant, T.; Nybakken, G.E.; Austin, S.K.; Xu, Q.; Bramson, J.; Loeb, M.; Throsby, M.; Fremont, D.H.; Pierson, T.C.; Diamond, M.S. Induction of epitope-specific neutralizing antibodies against West Nile virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11828–11839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueva, E.V.; Tuchynskaya, K.K.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Sedenkova, K.N.; Averina, E.B.; Palyulin, V.A.; Karganova, G.G. Spectrum of antiviral activity of 4-aminopyrimidine N-oxides against a broad panel of tick-borne encephalitis virus strains. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2020, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogodina, V.V.; Bochkova, N.G.; Karan’, L.S.; Frolova, M.P.; Trukhina, A.G.; Malenko, G.V.; Levina, L.S.; Platonov, A.E. Sravnitel’nyĭ analiz virulentnosti sibirskogo i dal’nevostochnogo podtipov virusa kleshchevogo entsefalita Comparative analysis of virulence of the Siberian and Far-East subtypes of the tick-born encephalitis virus. Vopr. Virusol. 2004, 49, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tonteri, E.; Jääskeläinen, A.E.; Tikkakoski, T.; Voutilainen, L.; Niemimaa, J.; Henttonen, H.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild rodents in winter, Finland, 2008–2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, O.V.; Panov, V.V.; Bakhvalova, V.N. Innate and adaptive immunity in wild rodents spontaneously and experimentally infected with the tick-borne encephalitis virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2020, 80, 104187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayasaka, D.; Nagata, N.; Fujii, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Sata, T.; Suzuki, R.; Gould, E.A.; Takashima, I.; Koike, S. Mortality following peripheral infection with tick-borne encephalitis virus results from a combination of central nervous system pathology, systemic inflammatory and stress responses. Virology 2009, 390, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreil, T.R.; Maier, E.; Fraiss, S.; Attakpah, E.; Burger, I.; Mannhalter, J.W.; Eibl, M.M. Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis virus, a flavivirus, prevents disease but not infection, although viremia is undetectable. Vaccine 1998, 16, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletnev, A.G.; Karganova, G.G.; Dzhivanyan, T.I.; Lashkevich, V.A.; Bray, M. Chimeric Langat/Dengue viruses protect mice from heterologous challenge with the highly virulent strains of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Virology 2000, 274, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinton, M.A.; Perelygin, A.A. Genetic resistance to flaviviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2003, 60, 43–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tigabu, B.; Juelich, T.; Bertrand, J.; Holbrook, M.R. Clinical evaluation of highly pathogenic tick-borne flavivirus infection in the mouse model. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, O.A.; Burenkova, L.A.; Karganova, G.G. Different tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) prevalences in unfed versus partially engorged ixodid ticks—Evidence of virus replication and changes in tick behavior. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health Animal Research Advisory Committee. In Guidelines for Survival Bleeding of Mice and Rats. 2019. Available online: http://oacu.od.nih.gov/ARAC/survival.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2019).
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of Estimating Fifty Per Cent Endpoind. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernokhaeva, L.L.; Rogova, Y.V.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Romanova, L.I.; Osolodkin, D.I.; Vorovitch, M.F.; Karganova, G.G. Experimental Evaluation of the Protective Efficacy of Tick-Borne Encephalitis (TBE) Vaccines Based on European and Far-Eastern TBEV Strains in Mice and in Vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.J.; Bögel, K. Laboratory techniques in rabies: Methods of calculation. Monogr. Ser. World Heal. Organ. 1973, 23, 321–335. [Google Scholar]
- Schwaiger, M.; Cassinotti, P. Development of a quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay with internal control for the laboratory detection of tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) RNA. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2003, 27, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, L.I.; Gmyl, A.P.; Dzhivanian, T.I.; Bakhmutov, D.V.; Lukashev, A.N.; Gmyl, L.V.; Rumyantsev, A.A.; Burenkova, L.A.; Lashkevich, V.A.; Karganova, G.G. Microevolution of tick-borne encephalitis virus in course of host alternation. Virology 2007, 362, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gmyl, A.P.; Korshenko, S.A.; Belousov, E.V.; Khitrina, E.V.; Agol, V.I. Nonreplicative homologous RNA recombination: Promiscuous joining of RNA pieces? RNA 2003, 9, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.A.; Hanson, R.P. Influence of sex and age on natural resistance to St. Louis encephalitis virus infection in mice. Infect. Immun. 1974, 9, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, M.E.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Rodenhuis, S.; Beijnen, J.H. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Cyclophosphamide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 1135–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockman, G.D.; Heim, L.R.; South, M.A.; Trentin, J.J. Differential effects of cyclophosphamide on the B and T cell compartments of adult mice. J. Immunol. 1973, 110, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Hoover, S.K.; Barrett, S.K.; Turk, T.M.; Lee, T.C.; Bear, H.D. Cyclophosphamide and abrogation of tumor-induced suppressor T cell activity. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 1990, 31, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, R.; Ferrara, F.; Müller, C.; Dreyer, A.Y.; McLeod, D.D.; Fricke, S.; Boltze, J. Immunosuppression for in vivo research: State-of-the-art protocols and experimental approaches. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 146–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyan, X.-H.; Lin, Y.-P.; Gao, T.; Chen, R.-Y.; Fan, Y.-M. Immunosuppressive effect of cyclophosphamide on white blood cells and lymphocyte subpopulations from peripheral blood of Balb/c mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandl, C.W.; Ecker, M.; Holzmann, H.; Kunz, C.; Heinz, F.X. Infectious cDNA clones of tick-borne encephalitis virus European subtype prototypic strain Neudoerfl and high virulence strain Hypr. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, E.; Sheldon, J.; Perales, C. Viral quasispecies evolution. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2012, 76, 159–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litov, A.G.; Deviatkin, A.A.; Goptar, I.A.; Dedkov, V.G.; Gmyl, A.P.; Markelov, M.L.; Shipulin, G.A.; Karganova, G.G. Evaluation of the population heterogeneity of TBEV laboratory variants using high-throughput sequencing. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinigaglia, L.; Gracias, S.; Décembre, E.; Fritz, M.; Bruni, D.; Smith, N.; Herbeuval, J.-P.; Martin, A.; Dreux, M.; Tangy, F.; et al. Immature particles and capsid-free viral RNA produced by Yellow fever virus-infected cells stimulate plasmacytoid dendritic cells to secrete interferons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchinskaya, K.; Volok, V.; Illarionova, V.; Kovaleva, O. Development of a method for assessing the structural heterogeneity of a population of different strains of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Patogenez 2018, 16, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K. The Antigenic Structure of Zika Virus and Its Relation to Other Flaviviruses: Implications for Infection and Immunoprophylaxis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00055-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.D.; Mukherjee, S.; Edeling, M.A.; Dowd, K.A.; Austin, S.K.; Manhart, C.J.; Diamond, M.S.; Fremont, D.H.; Pierson, T.C. The Fc region of an antibody impacts the neutralization of West Nile viruses in different maturation states. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13729–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, S.-M. The Interplay of Dengue Virus Morphological Diversity and Human Antibodies. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrier, M.V.; Kaufmann, B.; Nybakken, G.E.; Lok, S.-M.; Warren, J.T.; Chen, B.R.; Nelson, C.A.; Kostyuchenko, V.A.; Holdaway, H.A.; Chipman, P.R.; et al. Structural basis for the preferential recognition of immature flaviviruses by a fusion-loop antibody. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3269–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Décembre, E.; Assil, S.; Hillaire, M.L.B.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Screaton, G.R.; Davidson, A.D.; Dreux, M. Sensing of immature particles produced by dengue virus infected cells induces an antiviral response by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
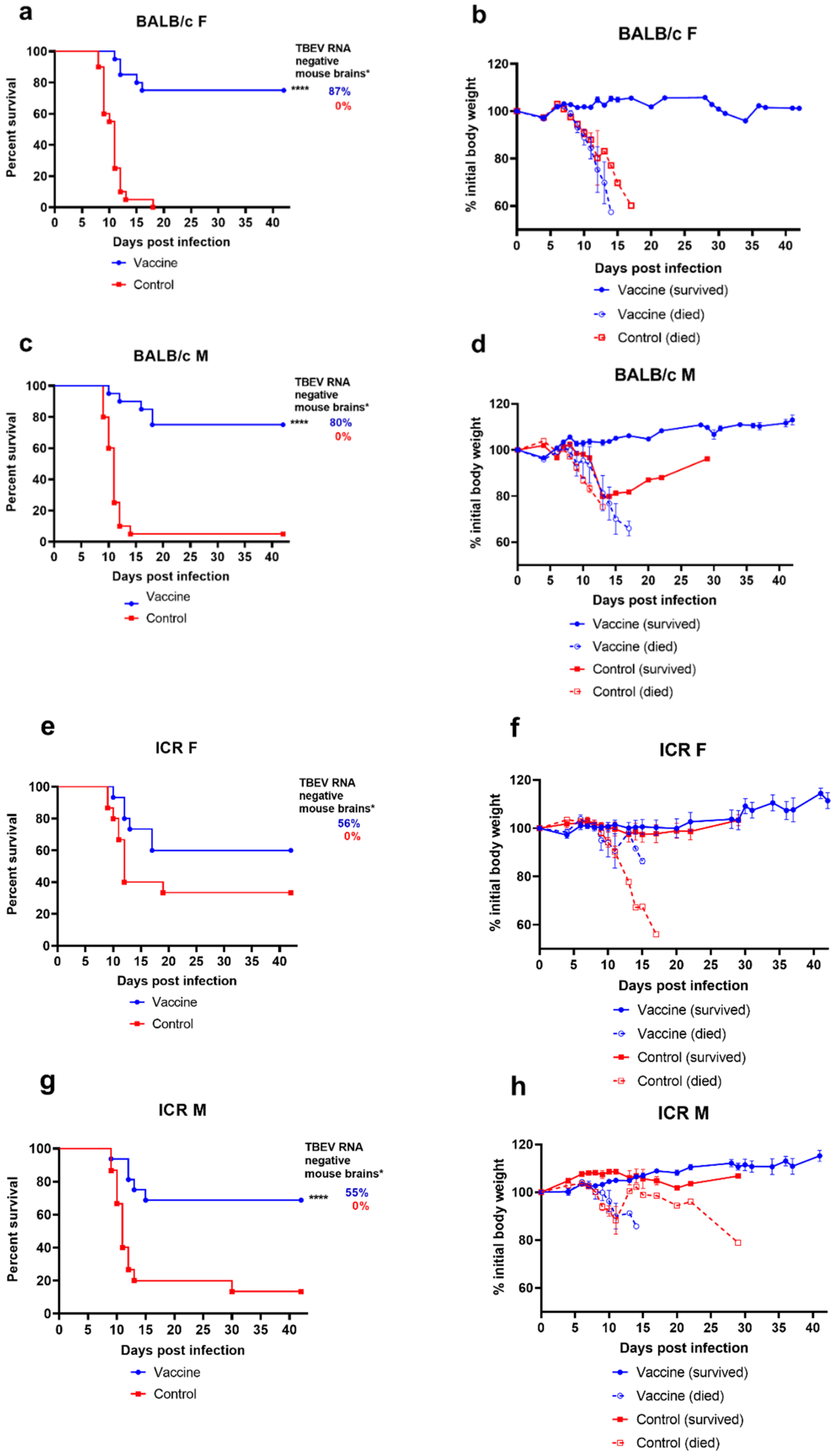
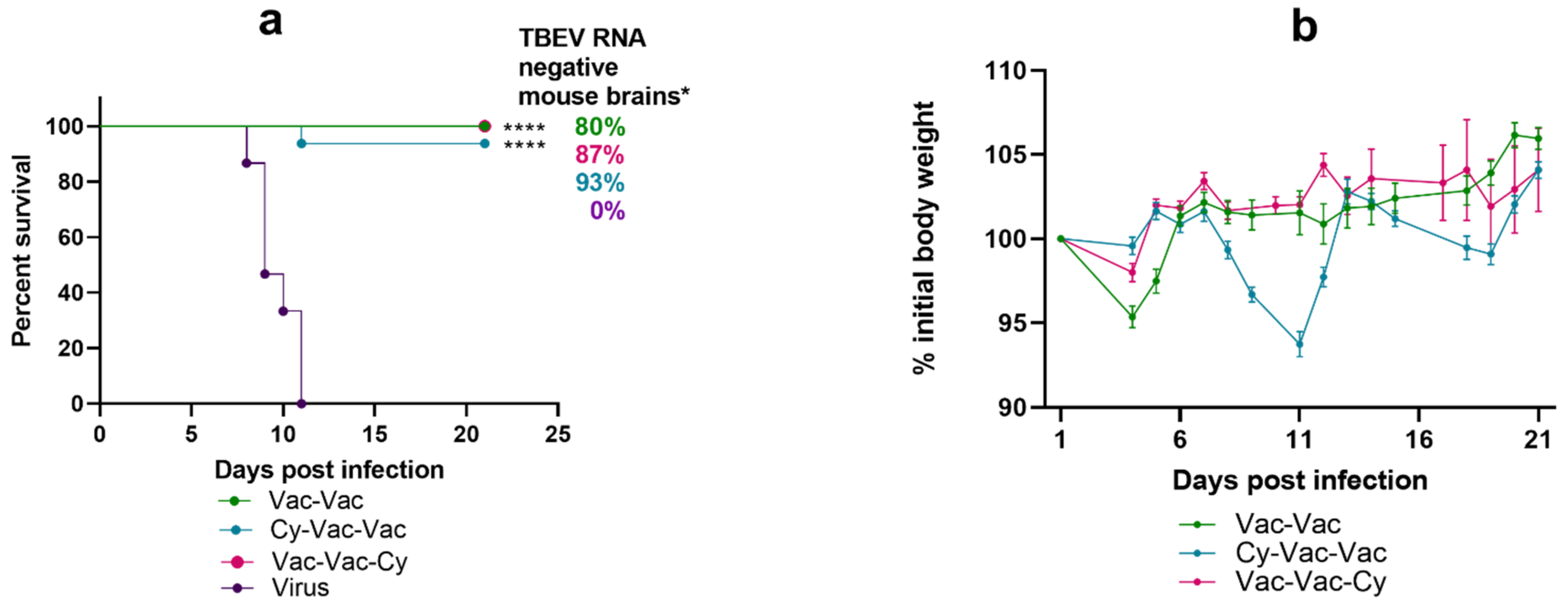
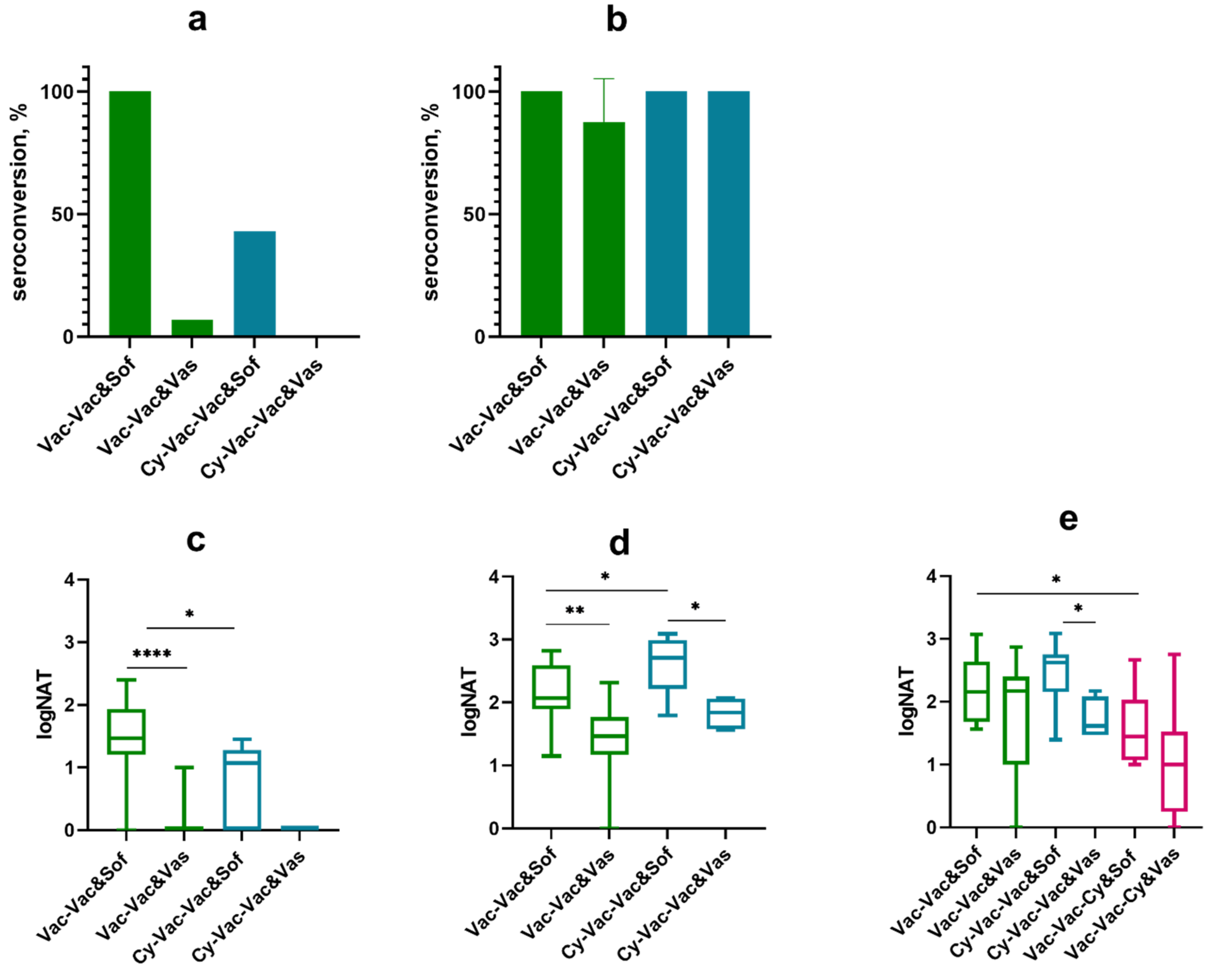
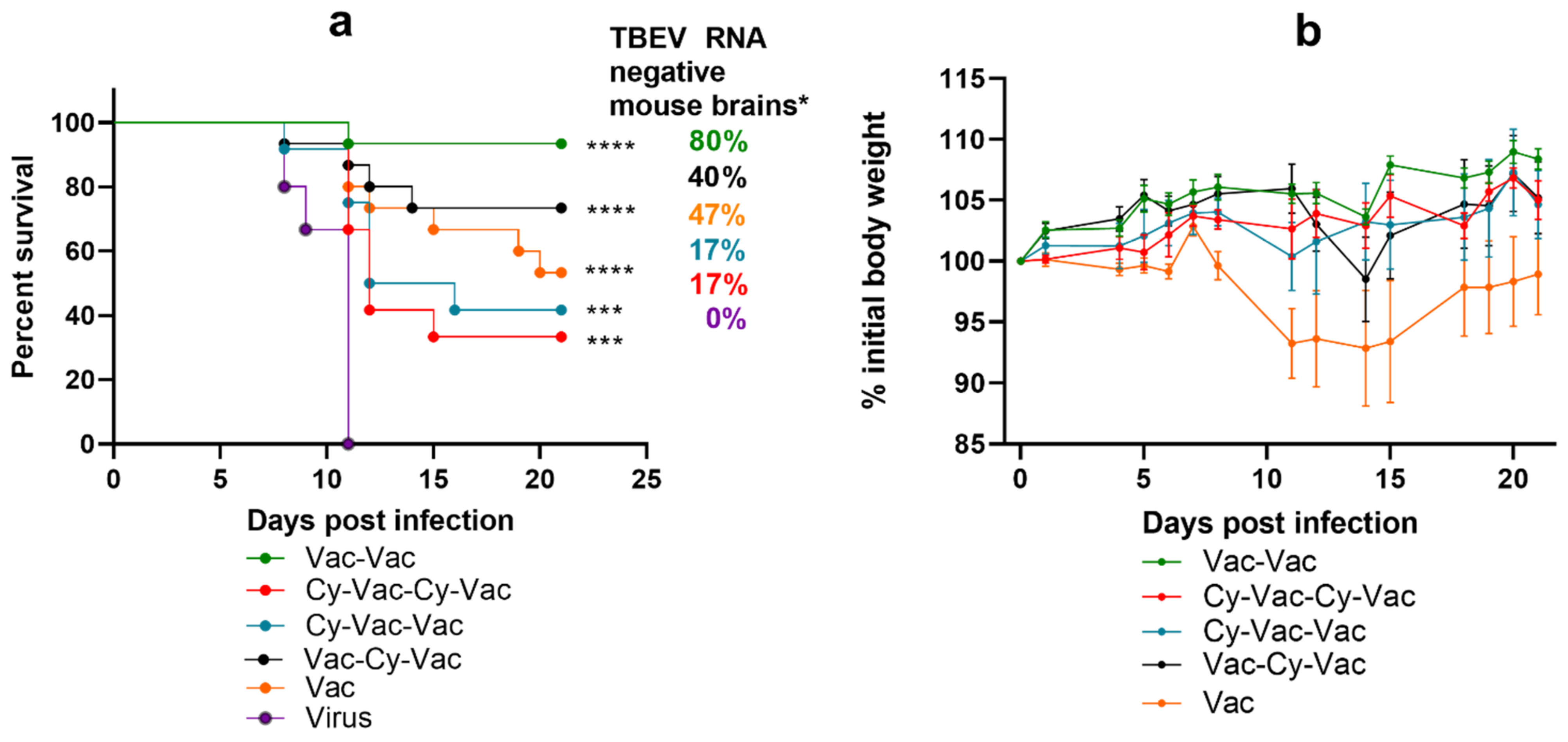
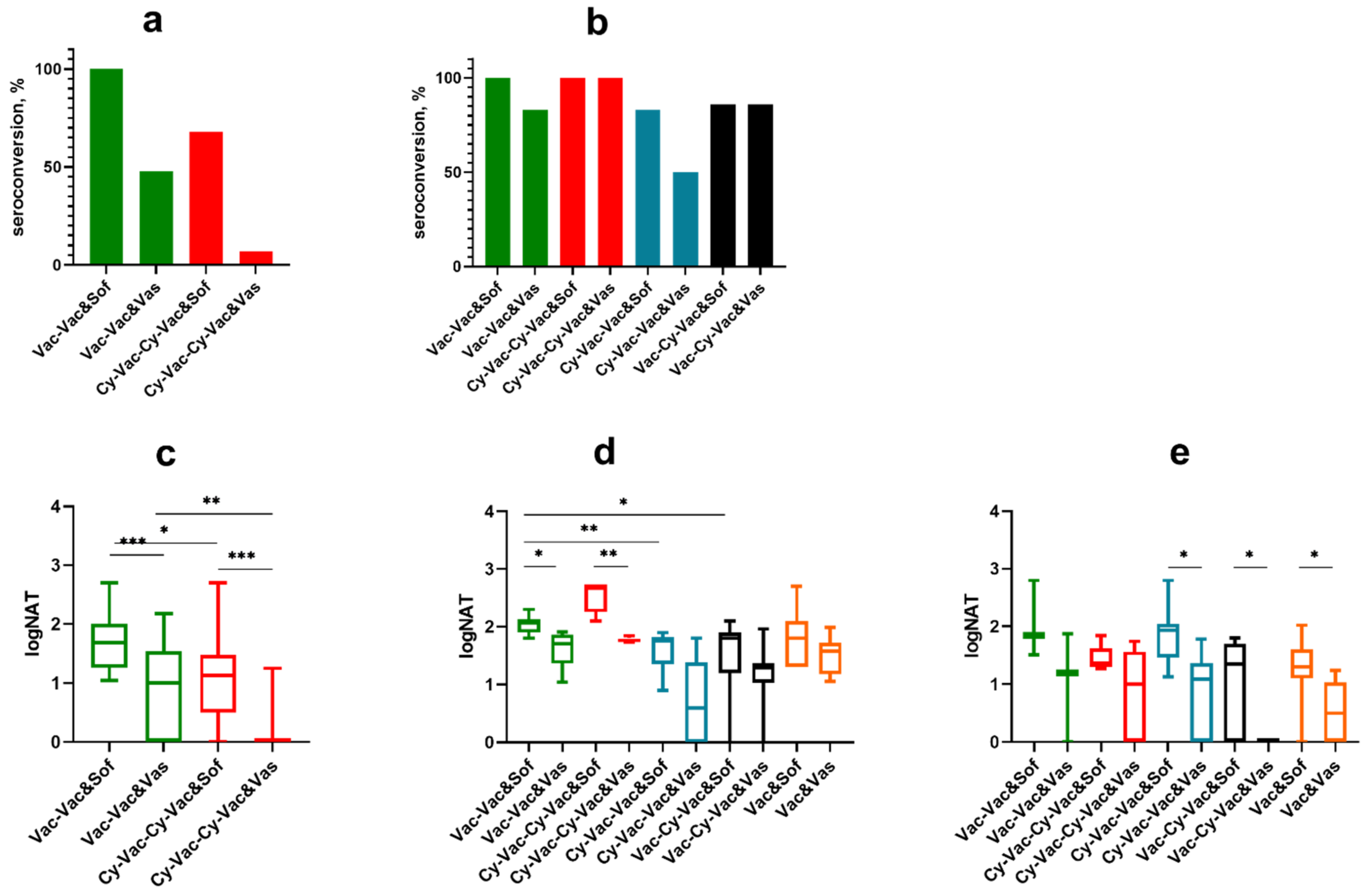
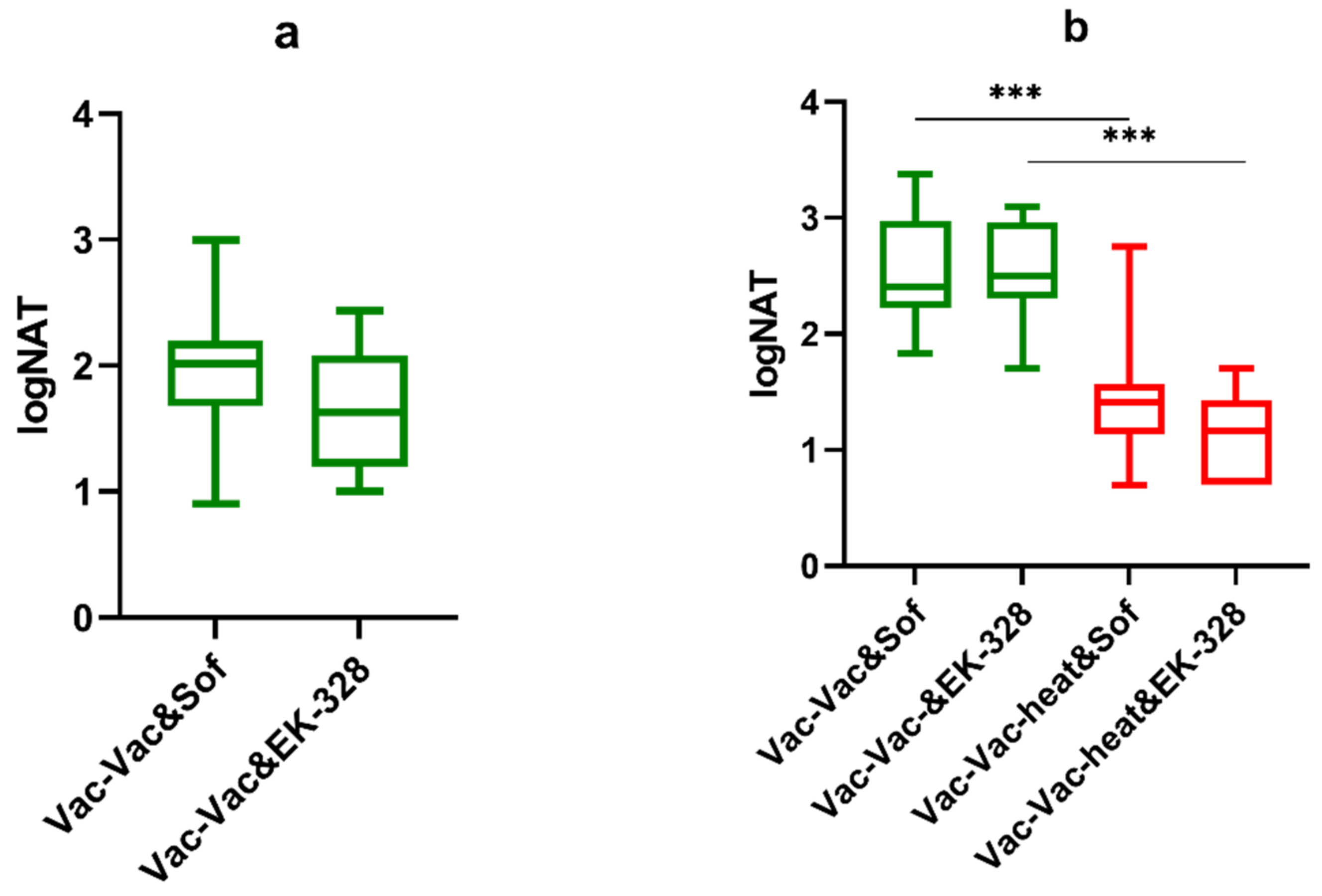
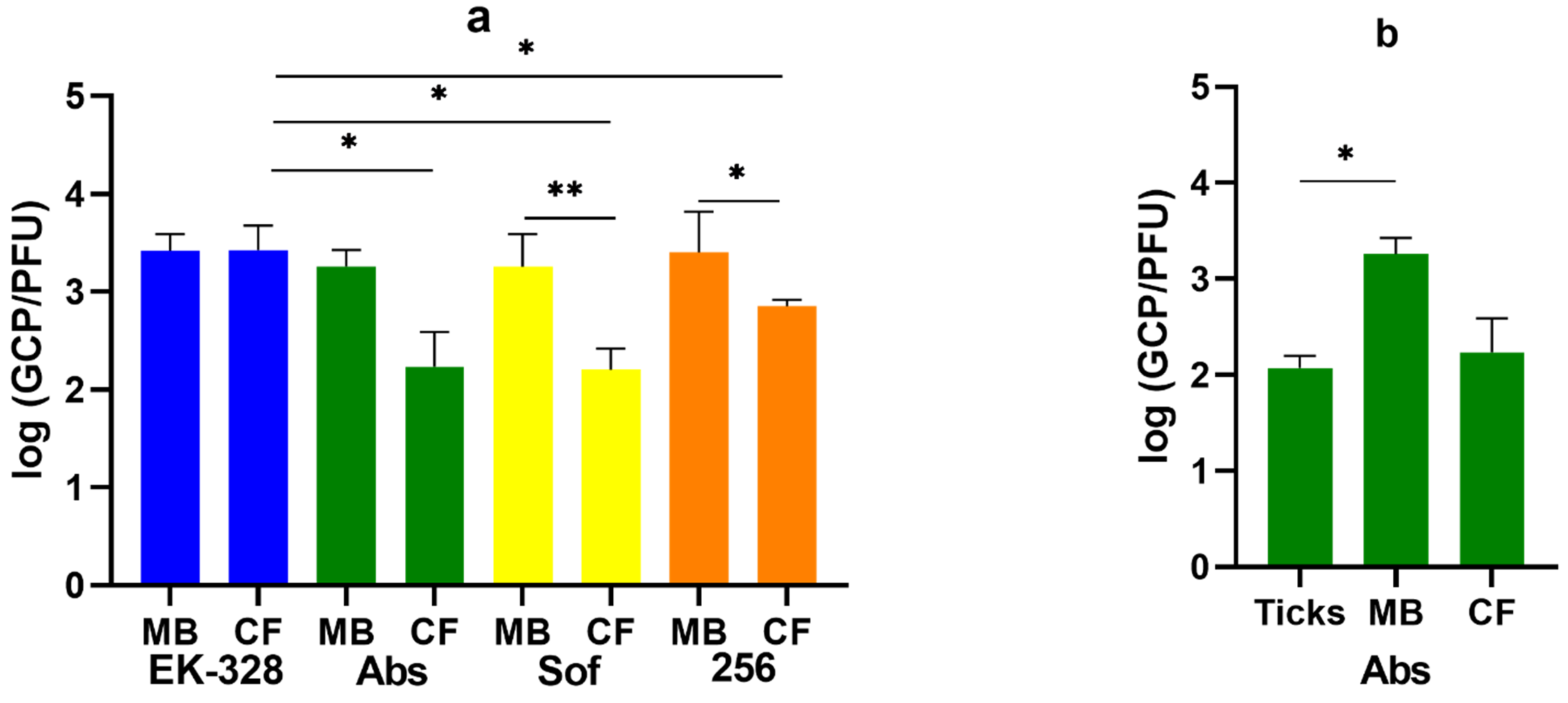
| TBEV Strain | Region and Year of Isolation | Source of Isolate | Passage History * | GenBank Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Far Eastern Subtype | ||||
| SofjinKGG | Primorsky Krai, 1937 | Brain of deceased TBE patient | МхР1М3P1 | GU121963 |
| Siberian subtype | ||||
| Vasilchenko | Novosibirsk region, 1961 | Blood of TBE patient | МхМ2V1 | L40361 |
| EK-328 | Estonia, 1972 | I. persulcatus ticks | M6P1M6P2 | DQ486861 |
| European Subtype | ||||
| 256 | Belarus, 1940 | I. ricinus tcks | MxM6 | AF091014 |
| Absettarov | Leningrad region, Russia, 1951 | blood of a TBE patient | MxM5 | KU885457 |
| TBEV Strain | Passage History * | LD50 | PFU | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Far Eastern Subtype | ||||
| Sofjin KGG | P1M2 | 100 | 130,000 | 350,000 |
| Siberian Subtype | ||||
| Vasilchenko | хМ2V1 | 100 | 5,000 | 60,000 |
| EK-328 | М6P1М4 | 100 | 1000 | |
| European Subtype | ||||
| Absettarov | Mx | 100 | 10,000 | 1,000,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuchynskaya, K.; Volok, V.; Illarionova, V.; Okhezin, E.; Polienko, A.; Belova, O.; Rogova, A.; Chernokhaeva, L.; Karganova, G. Experimental Assessment of Possible Factors Associated with Tick-Borne Encephalitis Vaccine Failure. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061172
Tuchynskaya K, Volok V, Illarionova V, Okhezin E, Polienko A, Belova O, Rogova A, Chernokhaeva L, Karganova G. Experimental Assessment of Possible Factors Associated with Tick-Borne Encephalitis Vaccine Failure. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(6):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061172
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuchynskaya, Ksenia, Viktor Volok, Victoria Illarionova, Egor Okhezin, Alexandra Polienko, Oxana Belova, Anastasia Rogova, Liubov Chernokhaeva, and Galina Karganova. 2021. "Experimental Assessment of Possible Factors Associated with Tick-Borne Encephalitis Vaccine Failure" Microorganisms 9, no. 6: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061172
APA StyleTuchynskaya, K., Volok, V., Illarionova, V., Okhezin, E., Polienko, A., Belova, O., Rogova, A., Chernokhaeva, L., & Karganova, G. (2021). Experimental Assessment of Possible Factors Associated with Tick-Borne Encephalitis Vaccine Failure. Microorganisms, 9(6), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061172






