Abstract
The use of organic fertilizers constitutes a sustainable strategy to recycle nutrients, increase soil carbon (C) stocks and mitigate climate change. Yet, this depends largely on balance between soil C sequestration and the emissions of the potent greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N2O). Organic fertilizers strongly influence the microbial processes leading to the release of N2O. The magnitude and pattern of N2O emissions are different from the emissions observed from inorganic fertilizers and difficult to predict, which hinders developing best management practices specific to organic fertilizers. Currently, we lack a comprehensive evaluation of the effects of OFs on the function and structure of the N cycling microbial communities. Focusing on animal manures, here we provide an overview of the effects of these organic fertilizers on the community structure and function of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms in upland soils. Unprocessed manure with high moisture, high available nitrogen (N) and C content can shift the structure of the microbial community, increasing the abundance and activity of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms. Processed manure, such as digestate, compost, vermicompost and biochar, can also stimulate nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms, although the effects on the soil microbial community structure are different, and N2O emissions are comparatively lower than raw manure. We propose a framework of best management practices to minimize the negative environmental impacts of organic fertilizers and maximize their benefits in improving soil health and sustaining food production systems. Long-term application of composted manure and the buildup of soil C stocks may contribute to N retention as microbial or stabilized organic N in the soil while increasing the abundance of denitrifying microorganisms and thus reduce the emissions of N2O by favoring the completion of denitrification to produce dinitrogen gas. Future research using multi-omics approaches can be used to establish key biochemical pathways and microbial taxa responsible for N2O production under organic fertilization.
1. Introduction
Organic fertilizers (OFs) are being strongly incentivized as a core management strategy to improve soil health and mitigate climate change by several regional and national initiatives. The use of OFs, such as compost and manure, constitutes a direct input of C to the soil, which can be stabilized through physical, chemical, and biochemical mechanisms [1] contributing to long-term storage of C in soils (i.e., C sequestration) [2,3,4]. A review of field studies showed that between 2–16% of the C applied through OFs was sequestered in soil over a long-term (i.e., more than 10 years) [5]. Organic fertilizers supply various C compounds with different chemical compositions, from labile to recalcitrant, that can be used by soil microorganisms during the process of mineralization to increase their growth rates and biomass. Thus, OFs have strong, short- and long-term effects on the soil microbiome and are fundamental to support soil health by increasing microbial activity, microbial interactions and nutrient cycling [6,7,8]. During the mineralization of C compounds in OFs, microorganisms also release plant-available nutrients. Therefore, OFs can indirectly increase soil C storage by increasing net primary productivity and root litter and exudation, a mechanism, which has been recently found to contribute to most of the sequestered or stable C in soils [9,10]. Additional benefits of OFs for climate change mitigation are related to the off-site reduction of greenhouse gas emissions associated with landfilling of organic wastes [11] and recycling of plant-available nutrients, including nitrogen (N), the most limiting nutrient for plant growth. Nonetheless, several fields and incubation studies showed that applying OFs resulted in large releases of greenhouse gases, most importantly nitrous oxide (N2O) [12,13]. The release of N2O can offset the climate change mitigation benefits of OFs, particularly when soil C sequestration potential has reached its plateau [14,15].
Nitrous oxide is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 298 times larger than carbon dioxide (CO2) and contributes to ozone depletion in the stratosphere [16]. The emission of N2O results from complex soil biotic and abiotic processes that produce and consume this greenhouse gas before its release into the atmosphere [17]. Nitrous oxide is produced in soils mainly as a byproduct or intermediate product of the microbial processes of nitrification and denitrification. These processes are strongly dependent on the availability of ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3−) and labile C compounds and regulated by soil redox conditions, such as oxygen content and other soil physicochemical properties such as pH.
The use of fertilizers and manures in agricultural systems contributes to 23–31% of the global anthropogenic N2O emissions, most of which are released from soils after their application [18]. Organic fertilizers supply large amounts of inorganic N in both forms (i.e., NH4+ and NO3−) and, therefore, increase N2O production. Furthermore, organic fertilizers supply labile C compounds, which increase the activity of heterotrophic denitrifying microorganisms and trigger the emission of N2O [19,20,21,22]. The addition of OFs with high moisture content also promotes denitrification rates through changes in soil oxygen availability and redox conditions. Throughout the literature, it is observed that organic and inorganic fertilizers, when combined, resulted in higher N2O emissions per unit of N applied than if applied alone [12,23], showing that OFs have the potential to stimulate the release of N2O from previously applied inorganic N fertilizers. Nonetheless, several studies reported lower emissions from soil amended with organic than inorganic fertilizers or non-fertilized soils [24]. The production of N2O seems to differ depending on the type of OFs and their physicochemical properties, such as C: N ratio [25], with large differences, observed between plant-based vs. animal-based or composted vs. raw materials, as well as depending on soil conditions, such as soil texture, moisture, plant cover and quality [12,26]. Obviously, the effects of OFs on the microorganisms and processes of N2O emissions are far more complex than the effects produced by inorganic fertilizers.
Direct assessment of N2O emissions from soils is a challenge due to the extremely large spatial and temporal variability of the fluxes and the specialized analytical instrumentation required to detect and quantify this trace gas. Furthermore, accurately assessing N2O emissions requires high-frequency monitoring, which may become costly and time-intensive. Generally, rates of N2O production can reflect the changes in soil inorganic N pools. The relationship between N2O production, NH4+ and NO3− has been established and used in the well-known hole-in-the-pipe model [27] to assess N2O emissions. In this model, the specific microbial process responsible for the production of N2O can be determined by assessing soil moisture levels, with denitrification being the predominant process under high soil moisture (>60% water-filled pore space). This model has been validated in several natural and managed ecosystems, including agricultural systems with inorganic fertilizers input [28]. In this model, the ratio of N2O produced to the inorganic N applied is used to calculate fertilizer emission factors. However, although N2O production is triggered by rapid changes in soil inorganic N pools and moisture, N2O production may ultimately depend on the capacity of the soil microbial community to adapt to these instant changes in environmental conditions and cycle N efficiently. Given that OFs impact soil microorganisms in many different ways, their effect on N2O production pathways, rates and dynamics are different from those of inorganic fertilizers and cannot be estimated solely through N inputs or changes in soil inorganic N pools [29]. For example, by providing C and N substrates to nitrifiers and denitrifiers, OFs may increase the size and activity of their communities, and therefore, increase N2O production rates; however, by increasing the diversity of these microorganisms, OFs may as well increase the consumption of N2O [30]. As a result, N2O emissions after using OFs may be better predicted by the size, diversity, structure, and/or functionality of the entire N-cycling microbial community, which would regulate the size of the “holes in the pipe”.
Currently, using isotopic tracers and molecular techniques allow for a finer resolution in the study of the microbial processes leading to the production of N2O. PCR-based analysis of ribosomal RNA marker genes allows for the taxonomic identification of N-cycling microorganisms in soils and quantifying the structure of the nitrifying and denitrifying microbial communities [30]. This same approach can be used to study the functionality of the microbial community by determining the abundance and expression of the main genes involved in the synthesis of enzymes that regulate the N cycle. Furthermore, high-throughput metagenomics and meta-transcriptomics allow for the parallel assessment of the presence and expression of different functional genes involved in the N cycle, providing a comprehensive understanding of the effects of different types of fertilization treatments on microbial N transformations [31]. However, at present, the abundance and function of N cycling microorganisms are seldom used to predict N2O production from soils. Thus, integrating microbial parameters into predictive models remains a knowledge gap.
A better knowledge of the microbial processes responsible for the production and consumption of N2O concerning the characteristics of OFs may help developing best management practices that optimize the benefits through improved soil health while reducing negative environmental impacts. If microbial data improves model performance, analysis of soil microbial community paired with the analysis of OF characteristics could be used to estimate N2O emissions in a more cost-effective way than the continuous monitoring approach. Furthermore, if there is a strong microbial fingerprint for N2O reduction associated with using OFs, a tool can be developed to verify greenhouse gas reductions in C markets. Currently, we lack a comprehensive evaluation of the effects of OFs on the function and structure of the N cycling microbial communities.
Here we provide an overview of the main microbial processes related to N2O production and summarize the current literature on assessing the effects of OFs on the abundance, diversity, community structure and function of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms in upland soils. We define organic fertilizers as naturally produced organic materials that are originated from different sources (e.g., animal and plant) and contain nutrients needed by plants. Organic fertilizers can be found in different degrees of decomposition or processing. Examples of unprocessed waste materials are raw manure, sewage sludge or industrial slurries of various types. Examples of processed materials are food waste hydrolysates, slaughter products (blood and feather meal), biochar, anaerobic digestates and composted materials. This review focuses on raw and processed animal manures with various physicochemical properties (i.e., plant-available N, C:N ratios). Based on the review, a framework of best management practices to minimize nutrient losses is proposed, and current challenges in research are discussed.
2. The N Cycle and Mechanisms Responsible for the Production and Consumption of N2O in Soils
The hole-in-the-pipe model [32] was groundbreaking in conceptualizing how microbial processes drive N2O emissions and remain the backbone of major biogeochemical process models that predict N2O emissions from soil to date [33]. However, new developments in molecular techniques to study soil microorganisms have revealed a diversity of microorganisms involved in N2O emissions much more complex than previously thought (Figure 1).
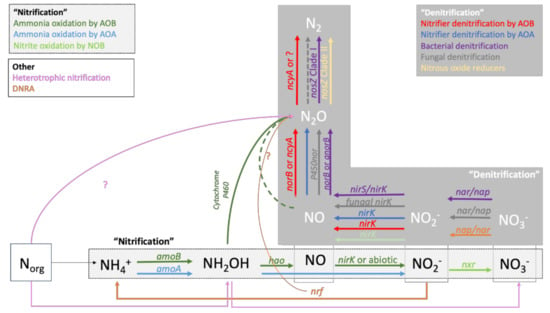
Figure 1.
Processes and enzymes involved in N2O production. Figure adapted from [34,35]. For full enzyme names, see Table 1.
Nitrification, referring to the oxidation of NH4+ to NO3−, was long assumed to be carried out by two distinct groups of autotrophic bacteria: ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB). It also has been proved that ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) can oxidize ammonia and that certain bacteria are capable of completing oxidation of NH4+ to NO3−, a process referred to as commammox [34]. A recently discovered cytochrome P460-mediated pathway explains the direct oxidation of NH2OH to N2O [35]. However, it is still unclear if this pathway only exists in AOB or if it also occurs in AOA. AOB is sensitive to low pH and favored in soils fertilized by single additions of high levels of inorganic NH3-based fertilizers, while AOA is dominant in acidic soils and grows preferentially when NH4+ is produced through mineralization of organic N [34].
Denitrification is traditionally known as the sequential reduction of NO3− to N2 by heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria and fungi, where N2O is one of the intermediate products [36]. Denitrification is stimulated by high NO3− concentrations, high availability of labile C, and low oxygen conditions. While stimulating denitrification and, therefore, N2O production, high labile C availability also stimulates the completion of denitrification and hence serves as a strategy to decrease N2O emissions through promoting N2O consumption [37]. The reduction of N2O to N2 is more sensitive to O2 exposure and low pH than the steps involved in reducing NO3− to N2O. The enzyme nosZ responsible for this reaction is known to be inhibited at low soil pH [38,39]. Therefore, agricultural practices that create anaerobic microhabitats and increase pH can promote N2O consumption [40,41]. The denitrification process was traditionally thought to be completed within a single organism, namely heterotrophic facultative anaerobic bacteria [36]. Nevertheless, a recent study has shown that denitrification is widespread and found among diverse genera of bacteria, archaea, fungi and other eukaryotes [42]. Moreover, denitrification was shown to be a truncated process, with many organisms capable of carrying out only a few of the various steps involved in NO3− reduction to N2 [42]. Denitrifying bacteria are found across several bacterial phyla, such as Proteobacteria, Nitrospira, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Chloroflexi, Nitrospirae and Verrucomicrobia [42]. Archaeal denitrifiers belong to the phyla Euryarcheota, Thaumarcheota and Crenarcheota [42]. Denitrification is also a widespread trait in fungi, being present in several species within the order Hypocreales, Eurotiales, Sordariales, Chetosphaeriales, Mucorales, Pleosporales, Glomerellales and Ophiostomatales [43].
A relatively well-studied example of this widespread occurrence of denitrifying enzymes is the process referred to as nitrifier denitrification, defined as the reduction of NO2− by ammonia oxidizers. This process may account for up to 100% of N2O emissions from NH4+ in soils and is more significant than classical denitrification under certain conditions [44]. Nitrifier identification is stimulated under NO2− accumulation, while N2O production via hydroxylamine oxidation is likely triggered by high NH3 and low NO2− in combination with high N oxidation rates [45]. Low O2 conditions favor nitrifier denitrification, but nitrifier denitrification may be more oxygen tolerant and less sensitive to pH change than classical denitrification [44]. The effect of C availability and source on nitrifier denitrification remains largely unknown [44]. An intriguing example of the truncated denitrification process is the recent discovery of a new clade of microorganisms that only possesses the denitrifying enzyme to reduce N2O to N2, raising the question of whether soil can be an effective sink of N2O rather than a source [46]. Factors that drive physiological and ecological responses of N2O reducing communities remain elusive. An improved understanding of niche differentiation between N2O producers and consumers could lead to innovative strategies to curb N2O emissions [42].
3. Methods to Study N2O Emissions and Underlying Processes in Soils
N2O emissions from soil can be studied using several methods that operate at varying scales, depending on the research question to be addressed (Figure 2). When the objective is to assess the global warming potential of contrasting management practices, quantification of the annual N2O budget is essential. N2O fluxes from the soil are notoriously variable in space and time, characterized by short-lived emission pulses in several days following disturbances, such as precipitation, tillage or fertilization [47]. This necessitates data to be collected at high temporal and spatial resolution. Eddy covariance is a micrometeorological method that quantifies N2O fluxes semi-continuously over a footprint that can encompass a few hectares [48]. While this method overcomes the challenges associated with measuring the high temporal and spatial variable N2O fluxes, the methodology is impractical in replicated controlled experiments with relatively small plot size, which are most suitable for assessing the effect of different OFs under field conditions. In these scenarios, N2O emissions are most commonly assessed using static flux chambers. Static flux chambers, typically ranging in footprint from 0.03–1 m2, are installed in each treatment plot. Gas samples are collected manually or automatically during chamber closure, which typically lasts up to an hour. Nitrous oxide fluxes for each sampling date are calculated based on the increase in N2O concentrations over time during chamber closure [49]. Whether measurements are based on eddy-covariance or static flux chambers, quantifying N2O budget at a field scale is costly and time-consuming, limiting the number of treatment combinations that can be assessed. Given the large diversity of feedstocks and characteristics of OFs and their interaction with varying soil properties, this imposes important constraints on research aimed to assess the effect of OFs on N2O emissions.
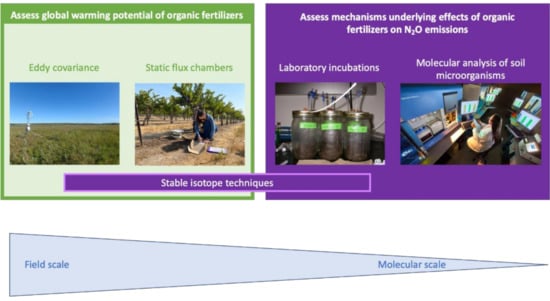
Figure 2.
Methodologies used to study nitrous oxide emissions from soils across different scales.
Various soil incubation procedures have been used to study potential N2O emissions under laboratory conditions, including potential denitrification and denitrifier enzyme activity [50]. The procedures are rather poorly standardized across studies but do allow for comparisons within studies across a wider range of treatment combinations at a relatively low cost. Laboratory incubation studies are also commonly used to study mechanisms underlying N2O emissions. For example, soil can be incubated at varying moisture conditions to favor certain processes underlying N2O emissions, or selective inhibitors, such as acetylene or fungicides, can be used to block certain production or consumption pathways [51,52]. Mechanisms underlying N2O emissions can also be assessed using stable isotopes, either through using isotopically enriched tracer material or based on natural isotopic abundance, including the position of 15 N within the N2O molecule, referred to as site preference [53,54]. The enriched tracer method requires the addition of isotopically enriched substrate, which can be a challenge in the case of OFs. Isotopic natural abundance method can be employed at the laboratory or the field scale, but using the changes of isotopic signatures at the natural abundance level to distinct production pathways is a challenge as well due to the overlapping isotopic signatures among different N2O production and consumption processes.
The mechanistic understanding of N2O emissions following OF amendments can be enhanced by assessing the abundance of the microorganisms involved in N2O emissions. Over the last decade, studies have evaluated the effects of OFs on N cycling and N2O emissions by quantifying the abundance of the microorganisms involved in nitrification and denitrification via real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) of marker genes or by measuring the abundances of the functional genes coding the enzymes involved in the production and consumption of N2O (Table 1) [55]. Similarly, the diversity of nitrifying or denitrifying microorganisms has been successfully studied using DGGE fingerprinting, high throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA or genes encoding N cycling enzymes [56].

Table 1.
Summary of the enzymes and microbial domains involved in the different steps of the N cycle.
Nitrifying soil organisms are typically studied based on RNA or DNA sequences of amoA genes encoding the enzyme ammonia monooxygenase [57,58]. Regarding denitrification, many enzymes are involved in the reduction of NO3− to N2 (Figure 1). However, denitrifying microorganisms are most commonly studied based on the nirK and nirS genes encoding the nitrite reductases or nosZ genes encoding the N2O reductases. NirK is commonly observed in denitrifiers and nitrifiers, while nirS is thought to be exclusively found in denitrifiers [42]. It is important to note that bacterial, fungal and archaeal nitrifying and denitrifying enzymes require different primers to anneal properly with the target organisms’ DNA or RNA. Likewise, nosZ in the newly discovered clade of N2O reducers referred to as Clade II nosZ cannot be identified by primers designed for classical denitrifiers that possess Clade I nosZ. Studies that only include primers for Clade I nosZ or only assess bacterial DNA or RNA may gravely overlook the important changes in the structure, abundance and diversity of microorganisms that drive the response of N2O emissions to OFs.
4. Sources of Organic Fertilizers and N2O Emissions
Organic fertilizers are commonly used as nutrient sources in small-scale crop-livestock integrated systems. The use of OFs is an important practice to maintain or improve soil health and fertility in organic production systems where no synthetic nutrient sources are allowed [59]. Furthermore, in recent years, scientific evidence on the role of soil organic matter in soil health and climate change mitigation, together with an increasing emphasis on the circular economy, has reinvigorated the interest in using OFs in agriculture at large, including conventional and industrial large-scale crop productions. As a result, a small but steady increase in using organic waste-based fertilizers has been observed over the last two decades [60].
Confined animal feeding operations are the greatest sources of organic waste worldwide. Cattle manure is the animal waste produced in the largest amount in most countries, followed by poultry and pig manure [61]. Cattle manure production has increased steadily by 5%, as consumption of beef and milk increased globally. India is currently the largest producer of cattle manure, with 172 Tg y−1, followed by the USA (77 Tg y−1) and China (69 Tg y−1) [61]. Animal manures are sources of plant nutrients, such as organic and inorganic N. The total N excreted in animal manure globally ranges from 81.5 to 128.3 Tg y−1 [62]. Only in 2011, 120 Tg of manure N were excreted, an amount which was similar or larger than the total synthetic fertilizer N requirements worldwide [63]. Nevertheless, it should also be highlighted that the type and amount of N in animal manures vary largely. Manures are heterogeneous materials made of a mixture of animal feces and urine, which make up for different proportions of easily available N (urea, NH4+ and NO3−) and organic N (undigested protein, amino acids, urea and nucleic acids mostly). The actual proportion of inorganic and organic N depends on the animal species, livestock diet, N excretion rates, livestock bedding, and how the manure has been treated and processed [64,65]. For instance, the total N content in poultry manure is generally higher than in cattle (beef or dairy) or pig manure, while liquid manures have lower amounts of organic N and higher proportions of NH4+ when compared to solid manures [65]. For the same type of animal manure, bedding materials and manure processing and storage methods strongly influence the total amount and form of N, resulting in large differences between farm operations even in the same region [12]. For example, manure that has been processed aerobically through composting, vermicomposting or simply aging, contains relatively lower organic N and higher NO3− than raw manure. On the other hand, manure that has been processed anaerobically, such as digester has relatively high organic N content with NH4+ dominates the inorganic N pool.
Despite the nutrient value of organic waste materials, it is well-known that mismanagement of OFs can lead to low N use efficiency and large losses to the environment, including the release of N2O after their application. A recent meta-analysis estimated that between 0.02 ± 0.13% and 1.21 ± 0.14% of the N in the applied OFs is emitted as N2O [29]. Depending on the usage and management of OFs, they can contribute to a significant portion of a region’s greenhouse gas budget. In India, it is estimated that 15,309 Gg CO2- Ceq per year are directly emitted as N2O from cattle manure, representing about 20% of the annual N2O emissions in the country. In the USA, cattle manure generates 6837 Gg CO2- Ceq as N2O per year, accounting for 2.2% of the total national emissions [61]. Nevertheless, throughout the literature, it is shown that emission factors can vary substantially depending on the physicochemical properties of the OF [29] and environmental conditions [66]. This suggests that a more detailed study on how OFs and their physicochemical properties affect soil microbial processes controlling N2O emissions is necessary.
5. Effects of Organic Fertilizers on Nitrifying and Denitrifying Soil Microorganisms
It is well known that the overall community structure of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms is strongly regulated by changes in substrate availability (NH4+, NO and NO3−), nutrient stoichiometry, labile C and soil physicochemical conditions, such as O2, pH or temperature [30,67]. By supplying inorganic N, C compounds and changing soil physicochemical properties, OFs can strongly shape the abundance and diversity of N cycling microorganisms in soils.
5.1. Effects of Raw Manure on the Structure and Activity of the Nitrifying and Denitrifying Community
Raw organic materials, such as animal manures, provide large inputs of NH4+ to a soil that directly impact the structure of the nitrifying community. NH4+ can also be released gradually through the mineralization of organic N in the manure after its application [31]. Ammonia oxidizers are particularly sensitive to the supply of NH4+ since they are lithoautotrophic microorganisms. Thus, animal manures typically increase the abundance and activity of ammonia oxidizers, leading to overall high nitrification rates [56,68]. While mineralization kinetics of organic N depends on environmental conditions and C:N ratios of the manure, nitrification of NH4+ proceeds relatively quickly, especially under high temperature and oxygen availability. As a result, all the easily available N can be nitrified within a few days to a few weeks, depending on soil texture and temperature, leading to subsequent peaks in N2O emissions [12,69].
The functional gene responsible for ammonia oxidation, the first step of nitrification, is amoA. The abundance of amoA gene copies is positively correlated with higher N2O emissions [70]. Higher nitrification rates lead to increased availability of NH2OH, NO and NO3− (substrates for N2O production), as well as promote oxygen consumption, which can evoke denitrification and the subsequent release of N2O. In fact, several examples in the literature indicated increases in denitrification rates and abundance of the genes encoding for the denitrification enzymes after repeated application of raw manure (Table 2). Hallin et al. [71] reported that 50 years of cattle manure application increased the abundance of narG (encoding nitrate reductase), nirK and nosZ (encoding nitrite reductases) in Sweden. Similarly, in a laboratory incubation experiment, Cui et al. [72] observed that a soil that received pig manure for 30 years had a higher N2O emission baseline than an unfertilized control and an inorganically fertilized treatment; these higher emissions were positively correlated with the abundance of nirK, nirS and nosZ, the genes encoding nitrite and N2O reductases. Most likely, these high emissions were driven by the supply of organic C compounds that promoted microbial activity, consuming O2 and stimulating heterotrophic denitrification [73].

Table 2.
Effects of manure-based organic fertilizers on the main microbial enzymes involved in the processes of nitrification and denitrification, based on the literature reported in the main text. Upward pointing arrows designate a predominantly positive effect; downward pointing arrows designate a negative effect; question marks indicate that not enough is known to draw conclusions.
Raw animal feces often contain variable amounts of C, such as undigested cellulose, a relatively labile source of C [65]. Labile C generally constitutes up to 35% of the total C in manure [37]. Additionally, cattle and poultry are typically raised on concrete floors with bedding materials such as straw or woodchips. Therefore, manure is frequently mixed with variable amounts of bedding material which supplies additional C and contains compounds of higher recalcitrance like lignin. While highly recalcitrant C can reduce N2O emissions by promoting N immobilization, relatively labile sources of C such as cellulose stimulate the release of N2O by promoting denitrification [80]. Nevertheless, it has been observed that labile C in animal manure might promote the reduction of N2O to N2 by increasing the abundance of nosZ bearing bacteria, therefore, decreasing the overall emissions of this greenhouse gas [37]. The reduction of N2O to N2 is directly affected by soil pH since nosZ is inhibited by acidic soil conditions. Several studies have observed that the long-term application of inorganic fertilizers induces soil acidity, leading to increasing N2O emissions. Conversely, long-term application of organic fertilizers, such as manures, can reduce acidification and thus reduce N2O emissions [81].
Finally, another physicochemical parameter that drives N transformations in the soil is moisture. Liquid manures generally create anaerobic conditions rapidly and trigger N2O emissions [12]. In addition to the observed changes in microbial community function, animal manures change the structure and diversity of the nitrifying and denitrifying communities. Several studies showed that the dominance of nitrifying microorganisms switched towards ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) after short- or long-term application of animal manures as it has been established that AOA is known to grow preferentially from mineralized NH4 [72,82,83]. However, this phenomenon seems to occur only in soils with low pH and substrate availability. In the soils with inorganic N additions or relatively high pH, AOB is still the main players [82,83], as reported by Lin et al. [68], who observed a shift from AOA to AOB accompanied by an increase in pH of an acidic soil after 44 years of pig manure and inorganic N additions. Microorganisms carrying nirK and nirS denitrifying genes are also sensitive to pH change and, as mentioned earlier, to changes in C availability [84]. Consequently, several studies showed that the structure of the denitrifying community is directly affected by manure inputs as compared to soils with no fertilizer inputs or with inorganic fertilizers [67,85]. Yin et al. [86] reported that 28 years of continuous application of pig manure significantly increased denitrification potential by increasing the abundance of nirS genes, then the same unfertilized soil, but not nirK. In a three-year field experiment, Huang et al. [67] observed that fertilization with cattle manure increased the abundance of nirS-harboring bacteria from the genera Rubrivivax, Bradyrhizobium, Ideonella, Azoarcus and Polymophum, resulting in significant changes in the overall structure of the soil-denitrifying community than the non-fertilized soil. These changes were significantly correlated to the C: N ratio of the manure, highlighting the importance of C in microbial denitrification.
5.2. Effects of Processed Manure on the Structure and Activity of the Nitrifying and Denitrifying Communities
Many approaches have been adopted to process organic waste materials, such as anaerobic digestion or pyrolysis, to obtain bioenergy, and composting or vermicomposting to produce biofertilizers. Often, waste materials are first processed through anaerobic digestion and followed up by composting, serving a dual purpose. These processes likely change the physicochemical properties of animal manures that have different impacts on soil microbiome and N2O emissions.
Anaerobic digestion is the degradation of organic substrates by a consortium of anaerobic microorganisms [87]. Both solid and liquid manure can be processed through anaerobic digestion to generate biogas (a mixture of CH4 and CO2) and digestate. Digestates are characterized by the lower amount of available C, higher relative amounts of recalcitrant compounds (such as lignin or non-hydrolyzable lipids), and higher NH4 +: total N ratio as compared to the initial manure [88,89]. This high amount of NH4 +, together with the high pH that is generally found in digestates, increases the risk of ammonia volatilization, a major concern for N losses and human health [89]. On the other hand, the literature shows contrasting data on the effects of anaerobic digestates on soil N2O emissions as compared to raw manure (Table 2). For example, in an incubation study, Cayuela et al. [90] observed that digestates produced from cattle or pig manure resulted in lower soil N mineralization rates and N2O emissions than the initial feedstocks. Similar results were observed by Grave et al. [91] in a field study comparing raw and anaerobically digested pig slurry, and the differences were attributed to the low content of volatile solids and labile C compounds in the digested slurry. In contrast, Saunders et al. [74] observed that in a laboratory incubation, cumulative soil N2O emissions were more than five times higher in the digestate than the raw cattle manure treatments. These contrasting results seem to be directly correlated to the physicochemical properties of the digestates, most importantly the contents of available C and NO3−. Saunders et al. [74] showed that in the soils amended with digestate, higher N2O emissions were generally correlated with higher abundances of amoA, narG, and nosZ and high N substrate availability in the digested manure, compared to raw manure.
Composting promotes the accelerated microbial decomposition of organic waste materials under aerobic conditions. Composting, which can take up to several months, is characterized by an initial 2-week thermophilic stage, where decomposition of labile compounds proceeds at very high rates [92]. During this phase, heat is generated, which allows for the sanitization of the waste material. Subsequently, the amount of labile compounds decreases and the microbial decomposition slows down, and the composting enters into the maturation phase [93]. As a result, compared with the initial feedstock, the final product of composting (i.e., compost) is more stable with a lower proportion of labile organic C and N compounds, higher NO3−/NH4+ ratio, and lower C:N ratio [93]. Accordingly, composted manure typically has different effects on the structure and function of the soil microbiome than raw manure [7,94]. Compost application to soils has been shown to induce short-term increases in the abundance of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms, resulting in N2O production [30]. Similarly, long-term application of compost increases the abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and denitrifying microorganisms (nosZ, nirK, nirS) than inorganic fertilizers (Table 2) [75]. Yet, N2O emissions from composts were comparatively lower than raw manures due to a lower input of easily available organic C and slower nitrification and denitrification rates associated with compost compared to raw manure [29,95]. Nevertheless, the addition of composted swine manure (rich in available organic N and recalcitrant C) to a clay loam inceptisol had similar cumulative N2O emissions as the untreated swine slurry. This shows that the differences in N2O emissions between raw and composted manure may be dependent on the type of manure, especially the availability of dissolved organic N and C in the manure [24].
Similar to compost, vermicompost is a stabilized organic fertilizer with a lower proportion of labile organic C and N compounds, higher NO3−/NH4+ ratio, and lower C:N ratio compared to raw manure [92]. During the vermicomposting process, earthworms graze on microorganisms, shaping the structure of the microbial community and increasing nitrification rates [96]. Typically, soils amended with vermicompost have a different microbial community structure than soils amended with raw or composted manures, including differences in AOB [6,97]. In a column incubation experiment, Liu et al. [78] observed that applying vermicompost amendment to a saline-alkaline soil increased nitrification rates by increasing archaeal and bacterial amoA gene copy numbers than a non-amended control. Nevertheless, nitrite-reducing bacteria were inhibited by the vermicompost, as shown by the decreased nirS and nirK gene copy numbers after its application. This, together with the increase in nosZ gene copies, suggests that using vermicompost may not lead to large N2O emissions, compared to raw manure or other organic amendments. Rodriguez et al. [21] reported that soil amended with vermicomposted biosolids produced less N2O emissions than soil with raw biosolids, although this depended on the moisture: at high soil moisture, N2O emissions were high regardless of the type of soil amendments.
Another alternative for the valorization of animal manure is combustion through pyrolysis to produce energy and biochar. Biochar produced from manure is a source of stable C that contributes to long-term C sequestration and improvements in soil fertility due to its nutrient content, high surface area, porosity and high pH, although production temperature can cause substantial variability in these physicochemical properties [98]. Due to its chemical stability, manure biochar typically results in lower N2O emissions than raw or composted manure [99]. Biochar also influences N2O emissions indirectly by changing the amount of inorganic N available in the soil. Typically, the high adsorption capacity of biochar reduces inorganic N availability and N2O production. Nevertheless, between 1 and 20% of the organic N in manure biochar can be mineralized in the short term and subsequently increase the nitrification rate. Biochars with lower aromaticity also have higher amounts of available C that can increase denitrification rates (nirK, nirS, and nosZ) and N2O emissions [79] (Table 2). Additionally, the observed effects are dependent on biochar interactions with soil texture, pH, moisture and soil N [100,101]. N2O emissions tend to be higher in acidic, coarse-textured soils at high soil moisture or in fine-textured soils at low moisture conditions [100]. Finally, increases in soil pH induced by the typically alkaline biochars can induce changes in the dominance and diversity of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms [98].
5.3. Management Strategies to Reduce N2O Emissions from Soils Amended with Manure-Based Organic Fertilizers
As mentioned earlier, the microbial processes that lead to the production of N2O in soils are largely regulated by substrate availability. Thus, regulating N2O emissions requires tight control of inorganic N in soils. The 4R of fertilizer management is a decision-making tool that helps growers to reduce nutrient (mainly N) losses. The 4R strategy uses information on crop N requirements, fertilizer and soil N content to establish the right N source, the right application rate, right timing and placement. Following the 4R principles, a careful evaluation of the amount of inorganic N provided by a specific OF is necessary to reduce N2O emissions. Furthermore, the amount of labile C also needs to be taken into account due to its role in stimulating denitrification. The availability of N and C depends on the type of animal manure but also on the processing approach used. Generally, raw manures contain high amounts of available C and N than processed manures (compost, vermicompost and digestates) and should be managed carefully to avoid evoking emissions [13]. Calculating the right rate of fertilizer requires adjusting inputs to satisfy plant needs taking into account the nutrients already available in the soil. For raw manures, the right application rate is sometimes calculated based on P and K rather than N due to the larger amount of these two plant macronutrients in the manure relative to the plant’s needs and the risk of overapplication. Yet, care should be taken to match the addition of large amounts of immediately available N with plant needs. It is expected that, in addition to the immediately available inorganic N, a substantial amount of N in OFs will become available to the crop through the mineralization of organic compounds. Thus, to calculate the right rate of OFs, immediately and potentially available N (PAN) need to be both taken into consideration [102].
Biochar, with its high surface area and adsorptive capacity, has the potential to reduce the amount of available N in manure-based OFs and subsequently lower N2O emissions. Yuan et al. [103] observed that mixing composted manure with biochar reduced denitrifier abundance, as shown by lower nirK abundances and resulted in lower N2O emissions compared with the composted manure alone. Several recent studies showed that inorganic N availability and N2O emissions from OFs could also be effectively reduced through the use of nitrification inhibitors. Nguyen et al. [104] showed that 3,4-dimethyl pyrazole phosphate reduced the N2O emissions from the soil after the application of cattle manure by 60%. Vallejo et al. [24] reported that the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide reduced N2O emissions from soil amended with pig manure and composted pig manure by 83% and 77%, respectively. Nevertheless, Duan et al. [105] suggested that nitrification inhibitors are not as efficient in reducing N2O emissions as biochar since they may stimulate denitrification.
A good understanding of the fertilizer mineralization temporal dynamics is also required to match nutrient release with crop needs and optimize nutrient use efficiency. Processed manures, such as compost, have a higher proportion of stable organic compounds that provide a gradual and steady release of N. Thus, a single application at pre-plant is recommended to allow enough time for these OFs to release mineral N [106]. On the other hand, to avoid large emissions of N2O, split applications are recommended for certain unprocessed manure-based OFs with high concentrations of inorganic N, such as liquid manure [12]. Lastly, research showed that N2O emissions are also affected by the manure placement method. Depending on the cropping system, manure can be applied to the soil surface, incorporated or injected into the sub-surface. N2O emissions are typically higher when manure is injected into soils than surface application, due to higher chances of contact between manure and soil microorganisms that produce N2O, as well as creating anaerobic conditions at the injection sites, which are further enhanced by high soil moisture [107]. Nevertheless, Velthof et al. [13] observed that manure N2O emissions decreased with injection depth, which was attributed to the larger diffusion path and the larger chance for the produced N2O to be reduced to N2 while transported to the soil surface.
In addition to controlling N inputs, N availability can be managed through practices that promote microbial N immobilization and tighten the N cycle. Agroecological management and the overall improvement of soil health through long-term compost application can reduce soil N losses such as N2O emissions [108,109]. Several studies showed that the repeated application of composted manure induced changes in soil physicochemical properties and microbial communities, which may help reduce emission peaks in response to the pulses of available N and C associated with a single fertilizer application. Long-term repeated compost additions increase the diversity, activity and abundance of denitrifiers (as shown by higher nirS, nirK, and nosZ gene abundance), allowing for completed denitrification to proceed and resulting in comparatively lower N2O emissions than the soils without any compost inputs [70,76,77]. It has been suggested that C accumulation in soils due to compost inputs allows for denitrification to be completed, and promotes the immobilization of surplus N, therefore, reducing N2O emissions [110]. Identification of the microbial species responsible for N2O reduction under long-term compost additions would open the door to microbiome engineering. The abundance and/or presence of these species could be used to improve predictions of N2O emissions under organic fertilization and verify greenhouse gas reductions in C markets.
The promotion of beneficial plant-microbe interactions is also a fundamental component of agroecological management that contributes to improving plant nutrient use efficiency and decreasing N losses. For instance, symbiosis with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), a widespread fungal symbiont capable of colonizing most terrestrial plants, increases plant N and water uptake, therefore, indirectly driving soil N and moisture changes. As a consequence, AMF colonization typically reduces N2O emissions [111] and has a strong impact on N2O− related microorganisms, such as reducing nirK and increasing nosZ gene abundances [112]. No-till or reduced-till promotes C sequestration and the AMF colonization [113], thus potentially promoting various pathways to mitigate N2O emissions. Nevertheless, several studies showed higher nitrification and denitrification rates and N2O emissions in no to than tilled soils in the first 10 years following practice conversion [91,114], which were attributed to the increased water-filled pore space and N availability than tilled soils [91,115].
6. Conclusions, Future Directions and Research Needs
Organic fertilizers have strong impacts on the structure and function of nitrifying and denitrifying microorganisms. Several fields and incubation studies show increases in the abundance of genes responsible for nitrification (amo) and denitrification (narG, nirS, nirK, nosZ) after applying organic fertilizers, which result in N2O emissions. These changes in soil microorganisms are related to the supply of N substrates for nitrification and denitrification, the supply of labile C that stimulates heterotrophic denitrification, and the modification of soil conditions (e.g., change pH and oxygen availability).
Nevertheless, the large heterogeneity in the physicochemical properties of OFs due to the different feedstocks and processing methods results in extremely variable effects on soil microorganisms and N2O emissions. Typically, unprocessed manure with high moisture content can produce a short-term increase in N2O emissions, especially when plant N demand is low. Nonetheless, processed and highly stable OFs, such as composted manure and biochar, result in N2O emissions that are comparatively lower than raw manure and inorganic N fertilizers. Thus, a good understanding of the specific chemical composition of OFs is needed to minimize negative environmental impacts. Furthermore, published research shows that agroecological soil management can help in tightening the N cycle to reduce N losses through N2O emissions. Interestingly, long-term application of OFs and the buildup of soil C stocks may contribute to N retention as microbial or stabilized organic N while increasing the abundance of denitrifying microorganisms and thus reduce the production of N2O by favoring the completion of denitrification to produce N2.
Despite the recent interest in engineering the soil microbiome to increase agricultural sustainability, we still lack a fundamental mechanistic understanding of how OFs affect the N cycle in soils. Current literature investigating N2O emissions from OFs mostly focuses on the broad processes of nitrification and denitrification without providing a clear resolution on the specific microbial taxa and N transformations responsible for N2O emissions. Given that the N cycle is mostly composed of narrow processes, which are supported only by few microbial taxa [116], changes in the diversity of soil microorganisms imposed by OFs may have important consequences on N cycling and N2O production, as the rate of N2O production or reduction varies by taxa. High-throughput sequencing has been instrumental in revealing how fertilizer management practices drive microbial diversity and composition, but due to the large uncertainty in the physiology and N2O production rates of key N cycling microorganisms, assessment of microbial functions may be more important [30,117]. Thus, future research needs to determine if the structure can be used to predict microbial function, and a multi-omics approach can be used to establish key biochemical pathways and microbial taxa responsible for N2O production [117,118].
Another major challenge is integrating microbial processes into terrestrial ecosystems and biogeochemical models for the prediction of N2O emissions with different scenarios of land use [119]. Nitrous oxide production in soils is spatially variable due to the patchy distribution of N in soils and the existence of a great diversity of microenvironments and conditions within a soil profile. Temporal variability in N2O production is associated with changes in N inputs, soil moisture and oxygen availability, all of which are affected by OFs. This complicates accurately simulating and scaling up of these processes, resulting in large uncertainties in the model estimates of N2O responses to OFs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and C.D.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L. and C.D; writing—review and editing, C.L., C.D. and X.Z.-B.; visualization, C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) Healthy Soils Initiative (Grant 17-0624-000-HS).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter: Implications for C-Saturation of Soils. Plant Soil 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gong, W. The Role of Chemical and Organic Fertilizers on Yield, Yield Variability and Carbon Sequestration—Results of a 19-Year Experiment. Plant Soil 2010, 331, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautges, N.E.; Chiartas, J.L.; Gaudin, A.C.M.; O’Geen, A.T.; Herrera, I.; Scow, K.M. Deep Soil Inventories Reveal That Impacts of Cover Crops and Compost on Soil Carbon Sequestration Differ in Surface and Subsurface Soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 3753–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, B.S.; Singh, K.; Dheri, G.S.; Balwinder-Kumar. Carbon Sequestration and Soil Carbon Pools in a Rice? Wheat Cropping System: Effect of Long-Term Use of Inorganic Fertilizers and Organic Manure. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 128, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Blanco, J.; Lazcano, C.; Christensen, T.H.; Muñoz, P.; Rieradevall, J.; Møller, J.; Antón, A.; Boldrin, A. Compost Benefits for Agriculture Evaluated by Life Cycle Assessment. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Revilla, P.; Domínguez, J. Short-Term Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Microbial Community Structure and Function: A Field Study with Sweet Corn. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.; Zhu, C.; Xue, C.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y.; Peng, C.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q. Insight into How Organic Amendments Can Shape the Soil Microbiome in Long-Term Field Experiments as Revealed by Network Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gil, J.C.; Plaza, C.; Soler-Rovira, P.; Polo, A. Long-Term Effects of Municipal Solid Waste Compost Application on Soil Enzyme Activities and Microbial Biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Bradford, M.A. Microbial Formation of Stable Soil Carbon Is More Efficient from Belowground than Aboveground Input. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryals, R.; Silver, W.L. Effects of Organic Matter Amendments on Net Primary Productivity and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Annual Grasslands. Ecol. Appl. 2013, 23, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLonge, M.S.; Ryals, R.; Silver, W.L. A Lifecycle Model to Evaluate Carbon Sequestration Potential and Greenhouse Gas Dynamics of Managed Grasslands. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 962–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Tsang, A.; Doane, T.A.; Pettygrove, G.S.; Horwath, W.R.; Burger, M. Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Forage Systems Fertilized with Liquid Dairy Manure and Inorganic Fertilizers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 225, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthof, G.L.; Kuikman, P.J.; Oenema, O. Nitrous Oxide Emission from Animal Manures Applied to Soil under Controlled Conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugato, E.; Leip, A.; Jones, A. Mitigation Potential of Soil Carbon Management Overestimated by Neglecting N2O Emissions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenet, B.; Gabrielle, B.; Chenu, C.; Arrouays, D.; Balesdent, J.; Bernoux, M.; Bruni, E.; Caliman, J.; Cardinael, R.; Chen, S.; et al. Can N2O Emissions Offset the Benefits from Soil Organic Carbon Storage? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 27, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- van Groenigen, J.W.; Huygens, D.; Boeckx, P.; Kuyper, T.W.; Lubbers, I.M.; Rütting, T.; Groffman, P.M. The Soil N Cycle: New Insights and Key Challenges. SOIL 2015, 1, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syakila, A.; Kroeze, C. The Global Nitrous Oxide Budget Revisited. Greenh. Gas Meas. Manag. 2011, 1, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrance, R.; Johnson, J.C.; Newton, G.L.; Williams, R.G. Denitrification from Soils of a Year-Round Forage Production System Fertilized with Liquid Dairy Manure. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Silva, L.C.R.; Doane, T.A.; Wu, N.; Horwath, W.R. Quantifying the Effects of Green Waste Compost Application, Water Content and Nitrogen Fertilization on Nitrous Oxide Emissions in 10 Agricultural Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, V.; de los Valdez-Perez, M.A.; Luna-Guido, M.; Ceballos-Ramirez, J.M.; Franco-Hernández, O.; van Cleemput, O.; Marsch, R.; Thalasso, F.; Dendooven, L. Emission of Nitrous Oxide and Carbon Dioxide and Dynamics of Mineral N in Wastewater Sludge, Vermicompost or Inorganic Fertilizer Amended Soil at Different Water Contents: A Laboratory Study. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 49, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Müller, C.; Cai, Z. Heterotrophic Nitrification of Organic N and Its Contribution to Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Boumans, L.J.M.; Batjes, N.H. Modeling Global Annual N2O and NO Emissions from Fertilized Fields: N2O and no Emissions from Fertilizers. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 28-1–28-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, A.; Skiba, U.; Garciatorres, L.; Arce, A.; Lopezfernandez, S.; Sanchezmartin, L. Nitrogen Oxides Emission from Soils Bearing a Potato Crop as Influenced by Fertilization with Treated Pig Slurries and Composts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2782–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Hu, F.; Shi, W. Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions Following Crop Residue Addition: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2956–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu-Barker, X.; Doane, T.A.; Horwath, W.R. Role of Green Waste Compost in the Production of N2O from Agricultural Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Keller, M.; Erickson, H.E.; Verchot, L.V.; Veldkamp, E. Testing a Conceptual Model of Soil Emissions of Nitrous and Nitric Oxides. BioScience 2000, 50, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Verchot, L.V. Testing the Hole-in-the-Pipe Model of Nitric and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Soils Using the TRAGNET Database. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.; Rochette, P.; Whalen, J.K.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Bertrand, N. Global Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors from Agricultural Soils after Addition of Organic Amendments: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braker, G.; Conrad, R. Diversity, Structure, and Size of N2O-Producing Microbial Communities in Soils—What Matters for Their Functioning? In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 75, ISBN 978-0-12-387046-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Y.; Norton, J.M. Short-Term Nitrogen Fertilization Affects Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Mineralization Functions in an Agricultural Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 86, e02278-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestone, M.K.; Davidson, E.A. Microbiological basis of NO and N2O production and consumption in soil. In Exchange of Trace Gases between Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Atmosphere; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Soils: How Well Do We Understand the Processes and Their Controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, J.I.; Hink, L.; Gubry-Rangin, C.; Nicol, G.W. Nitrous Oxide Production by Ammonia Oxidizers: Physiological Diversity, Niche Differentiation and Potential Mitigation Strategies. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caranto, J.D.; Vilbert, A.C.; Lancaster, K.M. Nitrosomonas europaea Cytochrome P460 Is a Direct Link between Nitrification and Nitrous Oxide Emission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14704–14709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, R. Denitrification. Microbiol. Rev. 1982, 46, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.N.; Zebarth, B.J.; Dandie, C.E.; Burton, D.L.; Goyer, C.; Trevors, J.T. Influence of Liquid Manure on Soil Denitrifier Abundance, Denitrification, and Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-W.; Chen, D.; He, J.-Z. Microbial Regulation of Terrestrial Nitrous Oxide Formation: Understanding the Biological Pathways for Prediction of Emission Rates. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.J.; Giannopoulos, G.; Pretty, J.; Baggs, E.M.; Richardson, D.J. Biological Sources and Sinks of Nitrous Oxide and Strategies to Mitigate Emissions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ŠImek, M.; Cooper, J.E. The Influence of Soil PH on Denitrification: Progress towards the Understanding of This Interaction over the Last 50 Years: Soil PH and Denitrification. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2002, 53, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Mørkved, P.T.; Frostegård, Å.; Bakken, L.R. Denitrification Gene Pools, Transcription and Kinetics of NO, N2O and N2 Production as Affected by Soil PH: Gene Transcription, Gas Kinetics as Affected by Soil PH. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 72, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallin, S.; Philippot, L.; Löffler, F.E.; Sanford, R.A.; Jones, C.M. Genomics and Ecology of Novel N2O-Reducing Microorganisms. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Spor, A.; Edel-Hermann, V.; Heraud, C.; Breuil, M.-C.; Bizouard, F.; Toyoda, S.; Yoshida, N.; Steinberg, C.; Philippot, L. N2O Production, a Widespread Trait in Fungi. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrage-Mönnig, N.; Horn, M.A.; Well, R.; Müller, C.; Velthof, G.; Oenema, O. The Role of Nitrifier Denitrification in the Production of Nitrous Oxide Revisited. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, A3–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlin, P.; Mohn, J.; Joss, A.; Emmenegger, L.; Siegrist, H. Mechanisms of N2O Production in Biological Wastewater Treatment under Nitrifying and Denitrifying Conditions. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domeignoz-Horta, L.A.; Putz, M.; Spor, A.; Bru, D.; Breuil, M.C.; Hallin, S.; Philippot, L. Non-Denitrifying Nitrous Oxide-Reducing Bacteria—An Effective N2O Sink in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénault, C.; Grossel, A.; Mary, B.; Roussel, M.; Léonard, J. Nitrous Oxide Emission by Agricultural Soils: A Review of Spatial and Temporal Variability for Mitigation. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, W.; Merbold, L. Eddy Covariance for Quantifying Trace Gas Fluxes from Soils. SOIL 2015, 1, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B.; Venterea, R.T. USDA-ARS GRACEnet Project Protocols, Chapter 3. Chamber-Based Trace Gas Flux Measurements. In Sampling Protocols; Follett, R.F., Ed.; USDA-ARS: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Burger, M.; Doane, T.A.; Horwath, W.R. Ammonia Oxidation Pathways and Nitrifier Denitrification Are Significant Sources of N2O and NO under Low Oxygen Availability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, E.J.; Baggs, E.M. Contributions of Nitrification and Denitrification to N2O Emissions from Soils at Different Water-Filled Pore Space. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Yuan, H.; Dong, W.; Hu, C.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, Y. Relationship between Soil Properties and the Bias of N2O Reduction by Acetylene Inhibition Technique for Analyzing Soil Denitrification Potential. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 66, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decock, C.; Six, J. How Reliable Is the Intramolecular Distribution of 15N in N2O to Source Partition N2O Emitted from Soil? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.M. A Review of Stable Isotope Techniques for N2O Source Partitioning in Soils: Recent Progress, Remaining Challenges and Future Considerations. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenstein, M.D.; Vilgalys, R.J. Quantitative Analyses of Nitrogen Cycling Genes in Soils. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Fujii, T.; Morimoto, S.; Lin, X.; Yagi, K.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J. Community Structure of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria under Long-Term Application of Mineral Fertilizer and Organic Manure in a Sandy Loam Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintie, A.T.; Heichen, R.S.; Cromack, K.; Myrold, D.D.; Bottomley, P.J. Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria along Meadow-to-Forest Transects in the Oregon Cascade Mountains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-D.; Wells, G.F.; Bae, H.; Criddle, C.S.; Francis, C.A. Occurrence of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea in Wastewater Treatment Plant Bioreactors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.M.; Jay-Russell, M.T.; Millner, P.D.; Shade, J.; Misiewicz, T.; Sorge, U.S.; Hutchinson, M.; Lilley, J.; Pires, A.F.A. Assessment of Biological Soil Amendments of Animal Origin Use, Research Needs, and Extension Opportunities in Organic Production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupton, S. Markets for Waste and Waste–Derived Fertilizers. An Empirical Survey. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 55, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Tian, G.; Naidu, R.; Kunhikrishnan, A. Role of Organic Amendment Application on Greenhouse Gas Emission from Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, P.; Ramankutty, N.; Bennett, E.M.; Donner, S.D. Characterizing the Spatial Patterns of Global Fertilizer Application and Manure Production. Earth Interact. 2010, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Ma, L.; Oenema, O. Global Animal Production and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Flows. Soil Res. 2017, 55, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Wrage, N.; Velthof, G.L.; van Groenigen, J.W.; Dolfing, J.; Kuikman, P.J. Trends in Global Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Animal Production Systems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2005, 72, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sharifi, M. Novel Practices and Smart Technologies to Maximize the Nitrogen Fertilizer Value of Manure for Crop Production in Cold Humid Temperate Regions. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 153, pp. 1–85. ISBN 978-0-12-817404-3. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Mei, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M. Response of N2O Emission to Manure Application in Field Trials of Agricultural Soils across the Globe. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J.; Xie, D.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer by Organic Materials Changed the Abundance, Diversity, and Activity of NirS-Type Denitrifying Bacterial Communities in a Vegetable Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 152, 103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ye, G.; Luo, J.; Di, H.J.; Liu, D.; Fan, J.; Ding, W. Nitrosospira Cluster 8a Plays a Predominant Role in the Nitrification Process of a Subtropical Ultisol under Long-Term Inorganic and Organic Fertilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01031-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, D.M.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Spoelstra, J. Stable Isotopes Reveal Rapid Cycling of Soil Nitrogen after Manure Application. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ju, X. Linkage between N2O Emission and Functional Gene Abundance in an Intensively Managed Calcareous Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallin, S.; Jones, C.M.; Schloter, M.; Philippot, L. Relationship between N-Cycling Communities and Ecosystem Functioning in a 50-Year-Old Fertilization Experiment. ISME J. 2009, 3, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, P.; Fan, F.; Yin, C.; Song, A.; Huang, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Wakelin, S.A.; et al. Long-Term Organic and Inorganic Fertilization Alters Temperature Sensitivity of Potential N2O Emissions and Associated Microbes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surey, R.; Lippold, E.; Heilek, S.; Sauheitl, L.; Henjes, S.; Horn, M.A.; Mueller, C.W.; Merbach, I.; Kaiser, K.; Böttcher, J.; et al. Differences in Labile Soil Organic Matter Explain Potential Denitrification and Denitrifying Communities in a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 153, 103630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, O.E.; Fortuna, A.-M.; Harrison, J.H.; Cogger, C.G.; Whitefield, E.; Green, T. Gaseous Nitrogen and Bacterial Responses to Raw and Digested Dairy Manure Applications in Incubated Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11684–11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Friman, V.-P.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q. Long-Term Fertilization Regimes Drive the Abundance and Composition of N-Cycling-Related Prokaryotic Groups via Soil Particle-Size Differentiation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatti, E.; Goyer, C.; Zebarth, B.J.; Burton, D.L.; Giovannetti, L.; Viti, C. Short-Term Effects of Mineral and Organic Fertilizer on Denitrifiers, Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Denitrification in Long-Term Amended Vineyard Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambreville, C.; Hallet, S.; Nguyen, C.; Morvan, T.; Germon, J.-C.; Philippot, L. Structure and Activity of the Denitrifying Community in a Maize-Cropped Field Fertilized with Composted Pig Manure or Ammonium Nitrate: Effect of Fertilization Regime on Denitrifiers. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 56, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Saline-Alkali Soil Applied with Vermicompost and Humic Acid Fertilizer Improved Macroaggregate Microstructure to Enhance Salt Leaching and Inhibit Nitrogen Losses. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Luo, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Easily Mineralizable Carbon in Manure-Based Biochar Added to a Soil Influences N2O Emissions and Microbial-N Cycling Genes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Reichel, R.; Islam, M.S.; Wissel, H.; Amelung, W.; Brüggemann, N. Chemical Composition of High Organic Carbon Soil Amendments Affects Fertilizer-Derived N2O Emission and Nitrogen Immobilization in an Oxic Sandy Loam. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Sheng, L. Effects of Long-Term Application of Organic Fertilizer on Improving Organic Matter Content and Retarding Acidity in Red Soil from China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Liang, G.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; He, P.; Zhou, W. Different Roles of Rhizosphere Effect and Long-Term Fertilization in the Activity and Community Structure of Ammonia Oxidizers in a Calcareous Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fornara, D.; Wasson, E.A.; Wang, D.; Ren, G.; Christie, P.; Jia, Z. Effects of 44 Years of Chronic Nitrogen Fertilization on the Soil Nitrifying Community of Permanent Grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 91, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, J.; Melichová, T.; Vaněk, D.; Picek, T.; Šantrůčková, H. Effect of PH and Dissolved Organic Matter on the Abundance of NirK and NirS Denitrifiers in Spruce Forest Soil. Biogeochemistry 2010, 101, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolsing, M.; Prieme, A. Observation of High Seasonal Variation in Community Structure of Denitrifying Bacteria in Arable Soil Receiving Artificial Fertilizer and Cattle Manure by Determining T-RFLP of Nir Gene Fragments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Fan, F.; Song, A.; Cui, P.; Li, T.; Liang, Y. Denitrification Potential under Different Fertilization Regimes Is Closely Coupled with Changes in the Denitrifying Community in a Black Soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5719–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insam, H.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Ascher, J. Manure-Based Biogas Fermentation Residues—Friend or Foe of Soil Fertility? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Terruzzi, L.; Scaglia, B.; Adani, F. Composting of the Solid Fraction of Digestate Derived from Pig Slurry: Biological Processes and Compost Properties. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of Anaerobic Digestion on Digestate Nutrient Availability and Crop Growth: A Review: Digestate Nutrient Availability. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; Oenema, O.; Kuikman, P.J.; Bakker, R.R.; Van GROENIGEN, J.W. Bioenergy By-Products as Soil Amendments? Implications for Carbon Sequestration and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. GCB Bioenergy 2010, 2, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grave, R.A.; da Nicoloso, R.S.; Cassol, P.C.; da Silva, M.L.B.; Mezzari, M.P.; Aita, C.; Wuaden, C.R. Determining the Effects of Tillage and Nitrogen Sources on Soil N2O Emission. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Domínguez, J. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Composting and Vermicomposting for the Biological Stabilization of Cattle Manure. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Lazcano, C.; Domínguez, J. The Evaluation of Stability and Maturity during the Composting of Cattle Manure. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Huang, S.; Sha, C.; Wu, J.; Cui, C.; Su, J.; Ruan, J.; Tan, J.; Tang, H.; Xue, J. Changes of Bacterial Community in Arable Soil after Short-Term Application of Fresh Manures and Organic Fertilizer. Environ. Technol. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lang, M.; Li, C.; Hao, X. Nitrous Oxide and Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Soils Amended with Compost and Manure from Cattle Fed Diets Containing Wheat Dried Distillers’ Grains with Solubles. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 97, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.; Aira, M.; Kolbe, A.R.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Pérez-Losada, M. Changes in the Composition and Function of Bacterial Communities during Vermicomposting May Explain Beneficial Properties of Vermicompost. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Juárez, M.F.-D.; Zangerle, M.; Insam, H. Effects of Digestate on Soil Chemical and Microbiological Properties: A Comparative Study with Compost and Vermicompost. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K. Biochemical Cycling of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Biochar-Amended Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Christel, W.; Bruun, S.; Jensen, L.S. The Different Effects of Applying Fresh, Composted or Charred Manure on Soil N2O Emissions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; van Zwieten, L.; Singh, B.P.; Jeffery, S.; Roig, A.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Biochar’s Role in Mitigating Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol Pereira, E.I.; Léchot, J.; Feola Conz, R.; da Silva Cardoso, A.; Six, J. Biochar Enhances Nitrous Oxide Reduction in Acidic but Not in Near-Neutral pH Soil. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Diaz, D.A.; Sawyer, J.E.; Mallarino, A.P. Poultry Manure Supply of Potentially Available Nitrogen with Soil Incubation. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, W.; Williams, D.; Walker, J.T.; Shi, W. Is Biochar-Manure Co-Compost a Better Solution for Soil Health Improvement and N2O Emissions Mitigation? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.V.; Wu, D.; Kong, X.; Bol, R.; Petersen, S.O.; Jensen, L.S.; Liu, S.; Brüggemann, N.; Glud, R.N.; Larsen, M.; et al. Effects of Cattle Slurry and Nitrification Inhibitor Application on Spatial Soil O2 Dynamics and N2O Production Pathways. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Z. Mechanisms of Mitigating Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Vegetable Soil Varied with Manure, Biochar and Nitrification Inhibitors. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 278, 107672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazicki, P.; Geisseler, D.; Lloyd, M. Nitrogen Mineralization from Organic Amendments Is Variable but Predictable. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderZaag, A.C.; Jayasundara, S.; Wagner-Riddle, C. Strategies to Mitigate Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Land Applied Manure. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2011, 166–167, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Hollander, A.D.; Steenwerth, K.; Jackson, L.E. Tightly-Coupled Plant-Soil Nitrogen Cycling: Comparison of Organic Farms across an Agricultural Landscape. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, E.; Lassaletta, L.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Garnier, J.; Vallejo, A. The Potential of Organic Fertilizers and Water Management to Reduce N2O Emissions in Mediterranean Climate Cropping Systems. A Review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, A.; Fortuna, A.-M.; Cihacek, L.J.; Bary, A.I.; Cogger, C.G. Use of Biological Indicators of Soil Health to Estimate Reactive Nitrogen Dynamics in Long-Term Organic Vegetable and Pasture Systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Barrios-Masias, F.H.; Jackson, L.E. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Effects on Plant Water Relations and Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions under Changing Moisture Regimes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, S.F.; Plantenga, F.; Neftel, A.; Jocher, M.; Oberholzer, H.-R.; Köhl, L.; Giles, M.; Daniell, T.J.; van der Heijden, M.G. Symbiotic Relationships between Soil Fungi and Plants Reduce N2O Emissions from Soil. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Jackson, L.E.; Loeher, M.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Ecological Intensification and Arbuscular Mycorrhizas: A Meta-Analysis of Tillage and Cover Crop Effects. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, M.; Krause, H.-M.; Spangler, S.; Kandeler, E.; Behrens, S.; Kappler, A.; Mäder, P.; Gattinger, A. Tillage System Affects Fertilizer-Induced Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquina, S.; Pérez, T.; Donoso, L.; Giuliante, A.; Rasse, R.; Herrera, F. NO, N2O and CO2 Soil Emissions from Venezuelan Corn Fields under Tillage and No-Tillage Agriculture. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 101, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Bennett, J. Nitrogen Mineralization: Challenges of a Changing Paradigm. Ecology 2004, 85, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P. The Known and the Unknown in Soil Microbial Ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, J.K.; Hofmockel, K.S. Soil Microbiomes and Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, E.B.; Knelman, J.E.; Schindlbacher, A.; Siciliano, S.; Breulmann, M.; Yannarell, A.; Beman, J.M.; Abell, G.; Philippot, L.; Prosser, J.; et al. Microbes as Engines of Ecosystem Function: When Does Community Structure Enhance Predictions of Ecosystem Processes? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).