Evaluation of a New Spike (S)-Protein-Based Commercial Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Consideration
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Establishment of A New SARS-CoV-2 Serological Test
2.4. Serological Testing for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
2.4.1. Commercial Assays
2.4.2. Live Virus Assay to Determine SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Activity (LVN)
2.4.3. Pseudovirus Assay to Determine SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Activity (PVN)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
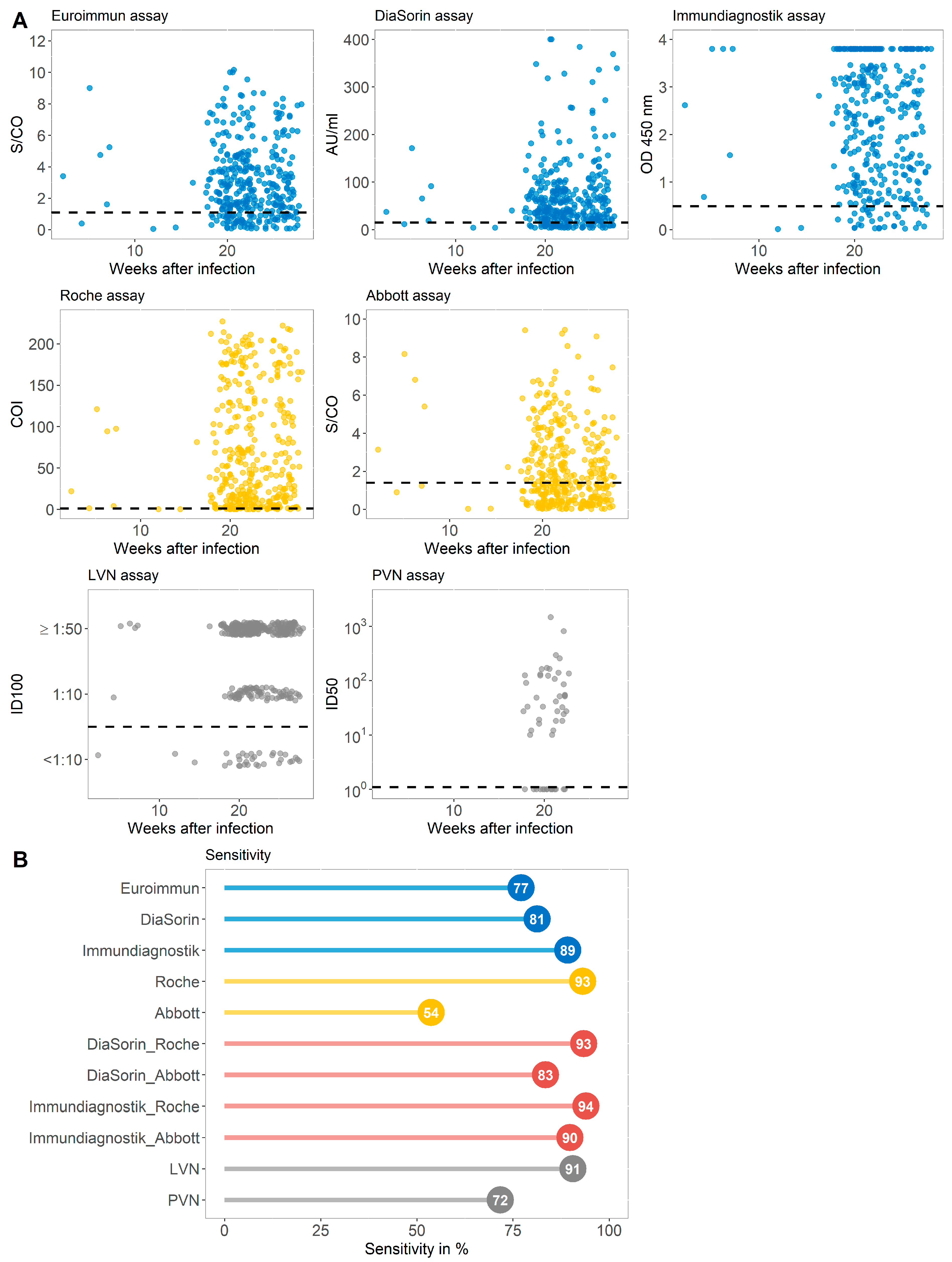
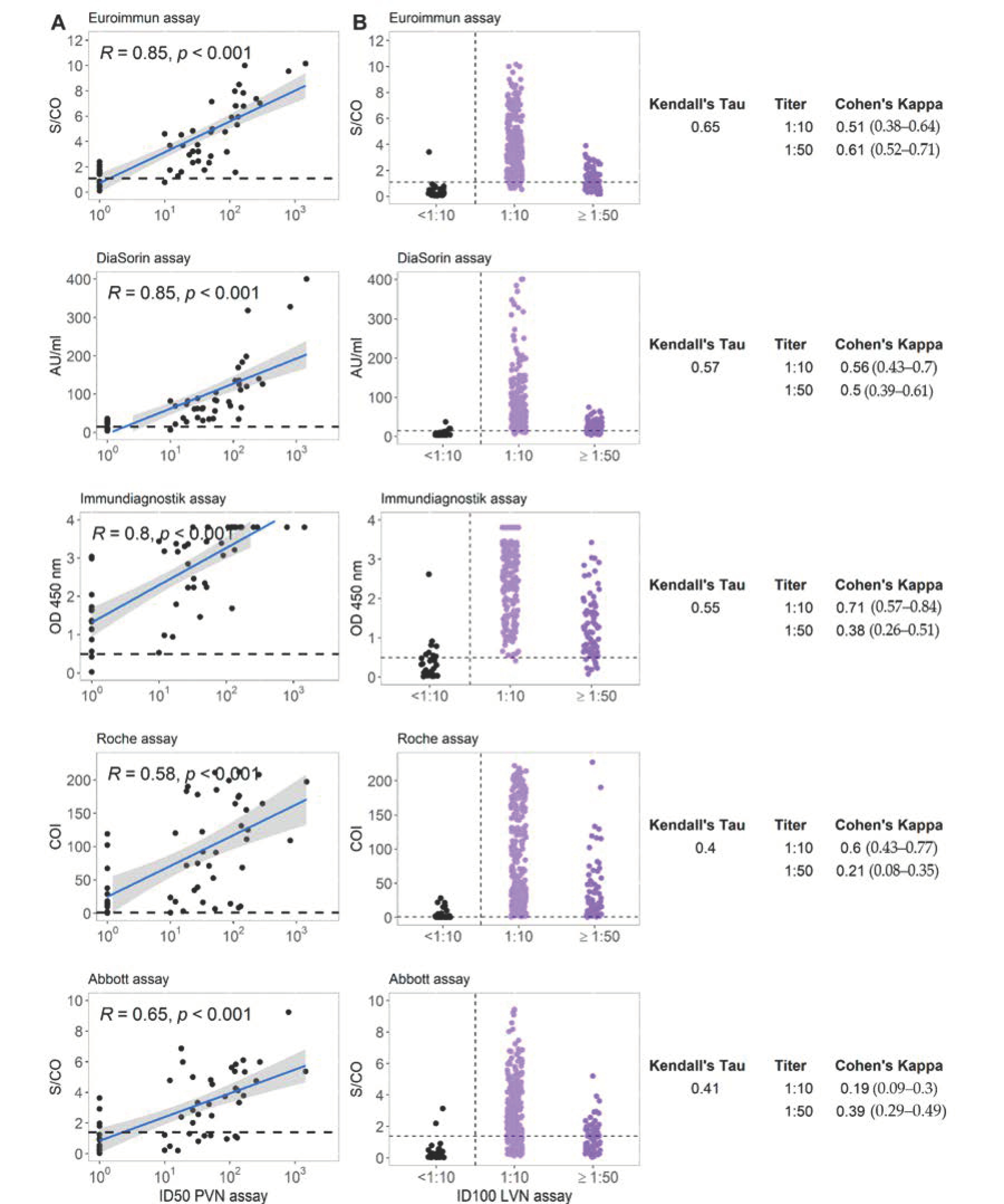
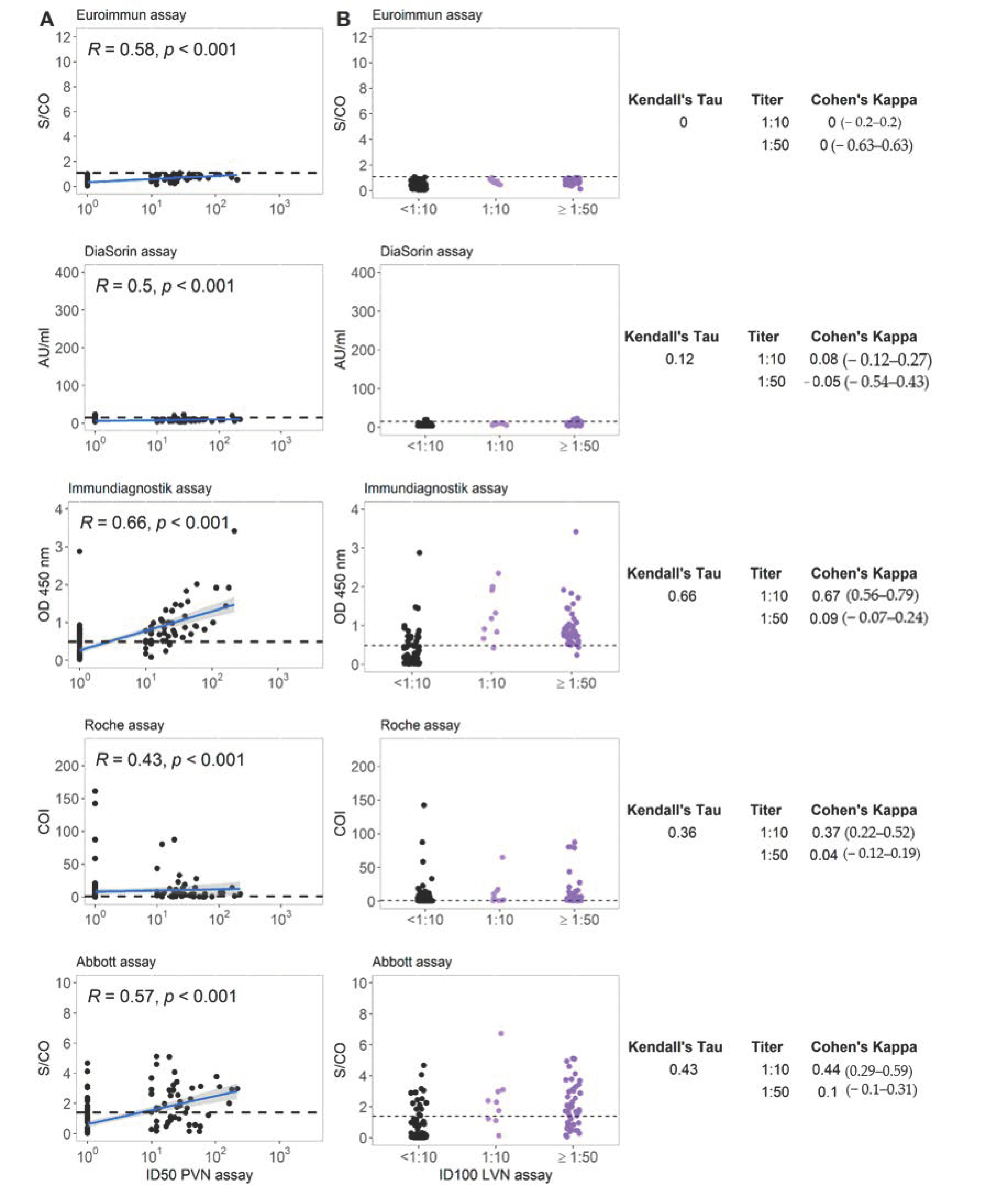
3.1. Sensitivity of Immundiagnostik IDK® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgG Assay in Comparison with Four Commercially Available Serological Tests and Two Virus-Neutralization Immunoassays in a Cohort with Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection (Group A)
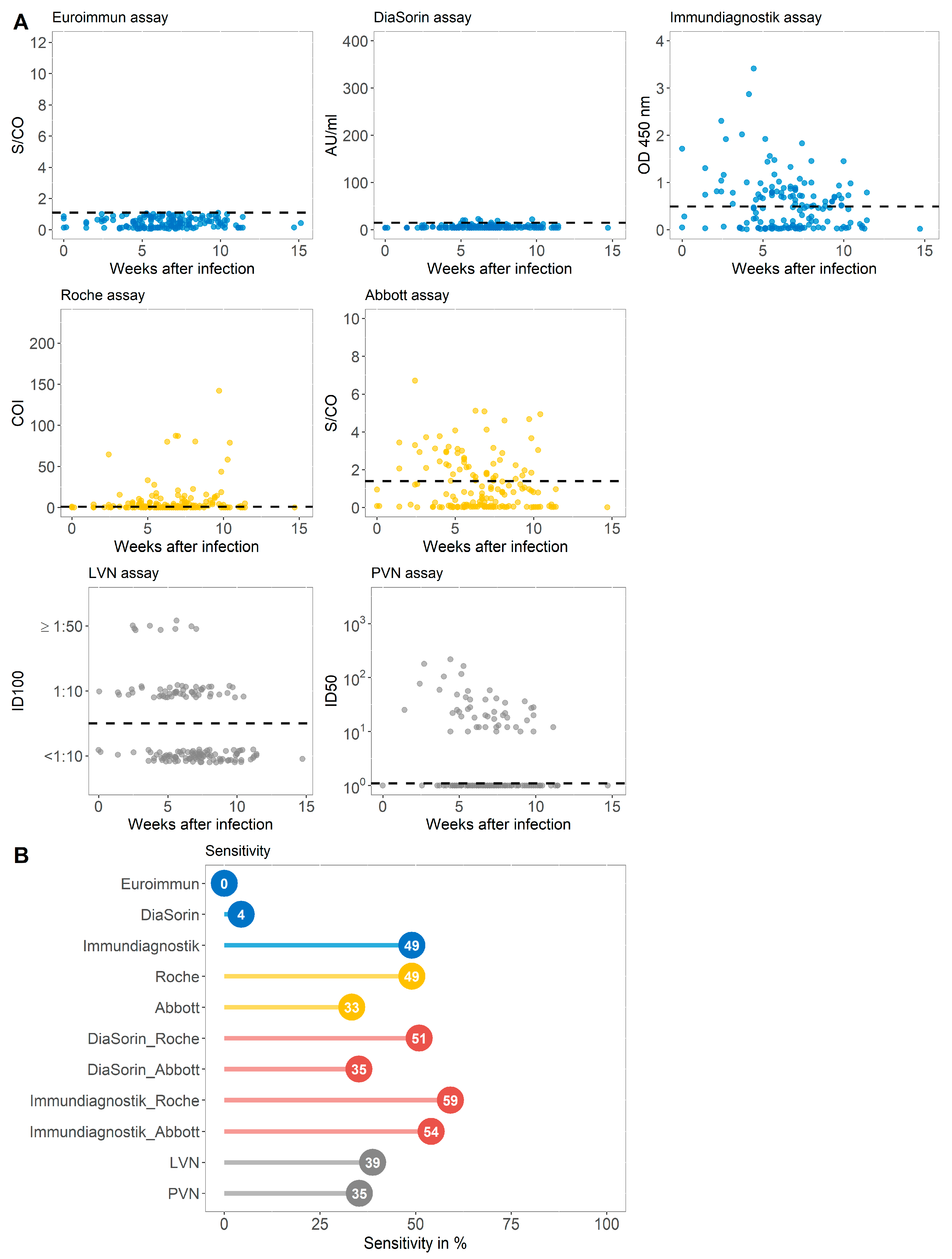
3.2. Sensitivity of Immundiagnostik IDK® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgG Assay and Three Commercially Available Serological Tests in a Cohort of COVID-19 Convalescent Subjects That Were Primarily Tested S1 IgG Non-Reactive (Group B)
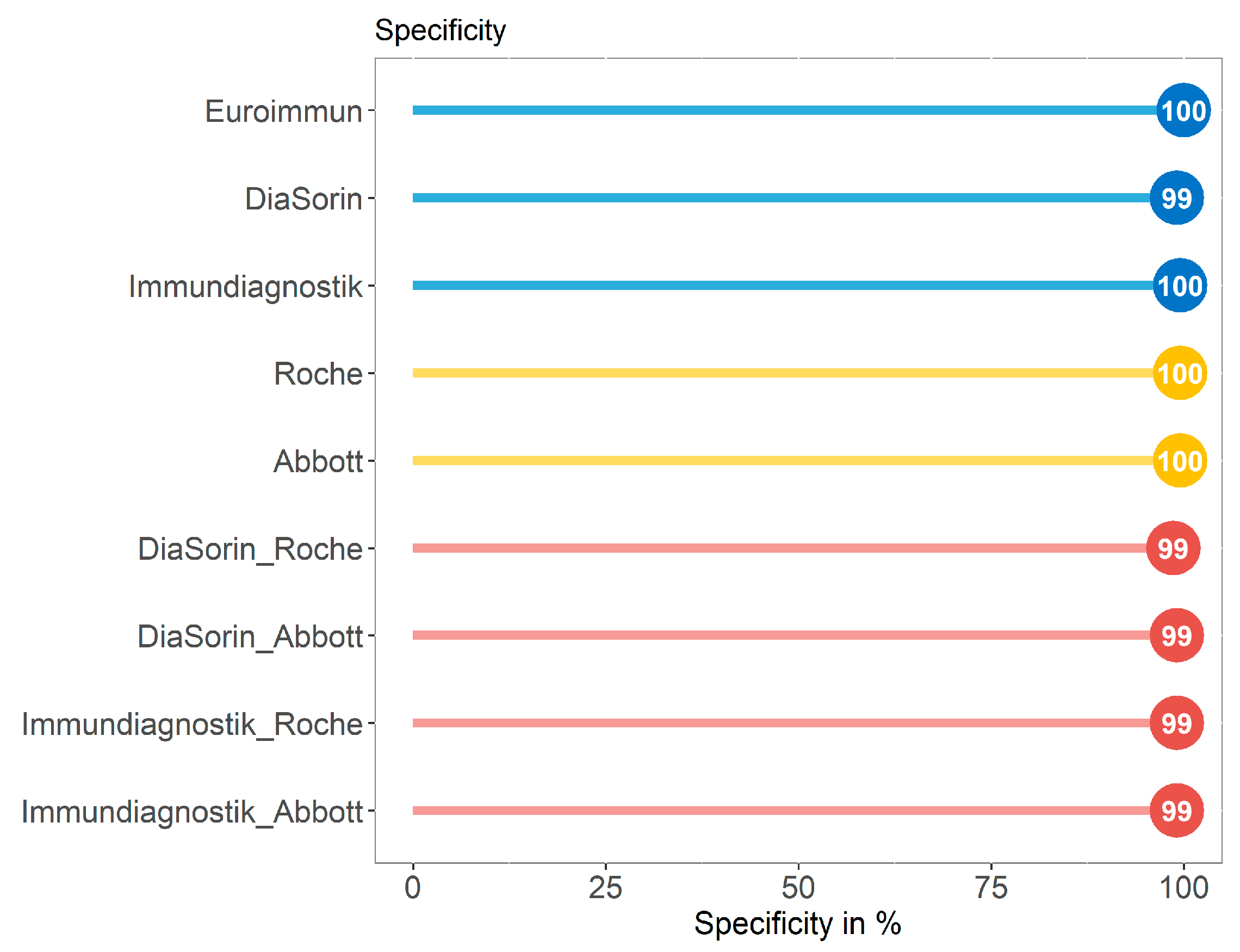
3.3. Specificity of Immundiagnostik IDK® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgG Assay in Comparison with Four Commercially Available Serological Tests in a SARS-CoV-2 Negative Control Group (Group C)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seow, J.; Graham, C.; Merrick, B.; Acors, S.; Pickering, S.; Steel, K.J.A.; Hemmings, O.; O’Byrne, A.; Kouphou, N.; Galao, R.P.; et al. Longitudinal observation and decline of neutralizing antibody responses in the three months following SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addetia, A.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.; Zhu, H.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.L.; Jerome, K.R.; Bloom, J.D.; Greninger, A.L. Neutralizing Antibodies Correlate with Protection from SARS-CoV-2 in Humans during a Fishery Vessel Outbreak with a High Attack Rate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajnberg, A.; Amanat, F.; Firpo, A.; Altman, D.R.; Bailey, M.J.; Mansour, M.; McMahon, M.; Meade, P.; Mendu, D.R.; Muellers, K. Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection persist for months. Science 2020, 370, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.C.; Freedberg, K.A.; Hyle, E.P.; Paltiel, A.D. Waiting for Certainty on Covid-19 Antibody Tests - At What Cost? N. Eng. J. Med. 2020, 383, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.S.; Case, J.B.; Franks, C.E.; Chen, R.E.; Anderson, N.W.; Henderson, J.P.; Diamond, M.S.; Gronowski, A.M.; Farnsworth, C.W. Association between SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and commercial serological assays. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, E.; Kuchipudi, S.V.; Christensen, P.A.; Eagar, T.; Yi, X.; Zhao, P.; Jin, Z.; Long, S.W.; Olsen, R.J.; Chen, J. Convalescent plasma anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein ectodomain and receptor-binding domain IgG correlate with virus neutralization. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6728–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FIND. SARS-COV-2 DIAGNOSTIC PIPELINESARS-COV-2 DIAGNOSTIC PIPELINE-COV-2 DIAGNOSTIC PIPELINE-COV-2 DIAGNOSTIC PIPELINE. Available online: http://www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline/?section=show-all#diag_tab (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Coste, A.T.; Jaton, K.; Papadimitriou-Olivgeris, M.; Greub, G.; Croxatto, A. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 serological tests with different antigen targets. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 134, 104690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Morishima, C.; Selke, S.; Zamora, D.; McGuffin, S.A.; Shapiro, A.E.; Campbell, V.L.; McClurkan, C.L.; Jing, L.; Gross, R.; et al. Clinical, laboratory, and temporal predictors of neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 among COVID-19 convalescent plasma donor candidates. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 131, e144930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muecksch, F.; Wise, H.; Batchelor, B.; Squires, M.; Semple, E.; Richardson, C.; McGuire, J.; Clearly, S.; Furrie, E.; Greig, N. Longitudinal Serological Analysis and Neutralizing Antibody Levels in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Convalescent Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National SARS-CoV-2 Serology Assay Evaluation Group. Performance characteristics of five immunoassays for SARS-CoV-2: A head-to-head benchmark comparison. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita, M.; Nishina, N.; Moriyama, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Uwamino, Y.; Nagata, M.; Aoki, W.; Masaki, K.; Ishii, M.; Saya, H. Incomplete humoral response including neutralizing antibodies in asymptomatic to mild COVID-19 patients in Japan. Virology 2021, 555, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, L.R.; Sami, S.; Vuong, N.; Pathela, P.; Weiss, D.; Morgenthau, B.M.; Henseler, R.A.; Daskalakis, D.C.; Atas, J.; Patel, A. Lack of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in a large cohort of previously infected persons. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa1685/5956137# (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Oved, K.; Olmer, L.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Wolf, T.; Supino-Rosin, L.; Prajgrod, G.; Shenhar, Y.; Payorsky, I.; Cohen, Y.; Kohn, Y. Multi-center nationwide comparison of seven serology assays reveals a SARS-CoV-2 non-responding seronegative subpopulation. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 29, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Norddahl, G.L.; Melsted, P.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Holm, H.; Eythorsson, E.; Arnthorsson, A.O.; Helgason, D.; Bjarnadottir, K.; Ingvarsson, R.F. Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Iceland. N. Eng. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanshylla, K.; Cristanziano, V.D.; Kleipass, F.; Dewald, F.; Schommers, P.; Gieselmann, L.; Gruell, H.; Schlotz, M.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Stumpf, R. Kinetics and correlates of the neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, E.; Leach, S.; Axelsson, H.; Nyström, K.; Norder, H.; Bemark, M.; Angeletti, D.; Lundgren, A.; Nilsson, S.; Andersson, L.M. Serum-IgG responses to SARS-CoV-2 after mild and severe COVID-19 infection and analysis of IgG non-responders. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Tang, X.J.; Shi, Q.L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.J. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, W.H.; Tenforde, M.W.; Stubblefield, W.B.; Feldstein, L.R.; Steingrub, J.S.; Shapiro, N.I.; Ginde, A.A.; Prekker, M.E.; Brown, S.M.; Peltan, I.D. Decline in SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies After Mild Infection Among Frontline Health Care Personnel in a Multistate Hospital Network—12 States, April-August 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Greenhouse, B.; Rodríguez-Barraquer, I. Are Seroprevalence Estimates for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Biased? J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1772–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.; Leviatan, S.; Segal, E. SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing for estimating COVID-19 prevalence in the population. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.P. What are protective antibody responses to pandemic SARS-CoV-2? J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6232–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, G.E.; Edwards, E.S.J.; Aui, P.M.; Varese, N.; Stojanovic, S.; McMahon, J.; Peleg, A.Y.; Boo, I.; Drummer, H.E.; Hogarth, P.M. Rapid generation of durable B cell memory to SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins in COVID-19 and convalescence. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabf8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.I.; Burbelo, P.D. Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Vaccines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, K.H.D.; Eguia, R.; Dingens, A.S.; Loes, A.N.; Malone, K.D.; Wolf, C.R.; Chu, H.Y.; Tortorici, M.A.; Veesler, D.; Murphy, M. Protocol and Reagents for Pseudotyping Lentiviral Particles with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein for Neutralization Assays. Viruses 2020, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppeta, L.; D’Alessandro, I.; Pietroiusti, A.; Somma, G.; Balbi, O.; Iannuzzi, I.; Magrini, A. Seroprevalence for vaccine-preventable diseases among Italian healthcare workers. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catry, E.; Jacqmin, H.; Dodemont, M.; Saad Albichr, I.; Lardinois, B.; de Fays, B.; Delaere, B.; Closset, M.; Laurent, T.; Denis, O. Analytical and clinical evaluation of four commercial SARS-CoV-2 serological immunoassays in hospitalized patients and ambulatory individuals. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 289, 114060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, K.A.; Meyer-Schwickerath, C.; Heger, E.; Knops, E.; Lehmann, C.; Rybniker, J.; Schommers, P.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Kurth, F.; Ramharter, M. RNAemia Corresponds to Disease Severity and Antibody Response in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Viruses 2020, 12, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Huang, B.; Wu, M.; Zhong, A.; Li, L.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, J. Dynamic changes in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during SARS-CoV-2 infection and recovery from COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Kaiser, T.; Pehnke, S.; Nickel, O.; Lübbert, C.; Kalbitz, S.; Arnold, B.; Ermisch, J.; Berger, L.; Schroth, S. Differences of SARS-CoV-2 serological test performance between hospitalized and outpatient COVID-19 cases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 511, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, G.P.; Dioni, L.; Favero, C.; Cantone, L.; Macchi, C.; Delbue, S.; Bonzini, M.; Montomoli, E.; Bollati, V.; Consortium, U. Serological follow-up of SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic subjects. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflüger, L.S.; Bannasch, J.H.; Brehm, T.T.; Pfefferle, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Nörz, D.; van der Meirschen, M.; Kluge, S.; Haddad, M.; Pischke, S. Clinical evaluation of five different automated SARS-CoV-2 serology assays in a cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 130, 104549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, K.; Gunsolus, I.L. Comparison of the Clinical Performances of the Abbott Alinity IgG, Abbott Architect IgM, and Roche Elecsys Total SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, L.; Saso, A.; Torres, A.; Lam, T.; Hatcher, J.; Thistlethwayte, R.; Harris, M.; Best, T.; Johnson, M.; Wagstaffe, H. Humoral Response Dynamics Following Infection with SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, T.; Alter, G. Dissecting antibody-mediated protection against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soresina, A.; Moratto, D.; Chiarini, M.; Paolillo, C.; Baresi, G.; Focà, E.; Bezzi, M.; Baronio, B.; Giacomelli, M.; Badolato, R. Two X-linked agammaglobulinemia patients develop pneumonia as COVID-19 manifestation but recover. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, V.; Denolly, S.; Vogrig, M.; Boson, B.; Siret, E.; Rigaill, J.; Pillet, S.; Grattard, F.; Gonzalo, S.; Verhoeven, P.; et al. A longitudinal study of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients reveals a high correlation between neutralizing antibodies and COVID-19 severity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, S.F.; O’Donnell, D.; Stoesser, N.E.; Matthews, P.C.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; Marsden, B.D.; Cox, S.; James, T.; Warren, F. Antibody Status and Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Care Workers. N. Eng. J. Med. 2020, 384, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.J.; Lyke, K.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Raabe, V.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A. Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults. Nature 2020, 586, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsinger, L.L.; Ransegnola, B.P.; Jin, D.K.; Muecksch, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Bao, W.; George, P.J.; Rodriguez, M.; Tricoche, N.; Schmidt, F. Serological Assays Estimate Highly Variable SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Activity in Recovered COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kekäläinen, E.; Ahava, M.J.; Loginov, R.; Kallio-Kokko, H.; Vapalahti, O.; Jarva, H.; Kurkela, S.; Lappalainen, M. Performance of six SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays in comparison with microneutralisation. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia, A.; Torres, I.; Latorre, V.; Francés-Gómez, C.; Albert, E.; Gozalbo-Rovira, R.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Buesa, J.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Geller, R. Inference of SARS-CoV-2 spike-binding neutralizing antibody titers in sera from hospitalized COVID-19 patients by using commercial enzyme and chemiluminescent immunoassays. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrews, K.M.; Dowlatshahi, D.P.; Dai, J.; Becker, L.M.; Hensel, J.; Snowden, L.M.; Leveille, J.M.; Brunner, M.R.; Holden, K.W.; Hopkins, N.S. Heterogeneous antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain and nucleocapsid with implications for COVID-19 immunity. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokal, A.; Chappert, P.; Barba-Spaeth, G.; Roeser, A.; Fourati, S.; Azzaoui, I.; Vandenberghe, A.; Fernandez, I.; Meola, A.; Bouvier-Alias, M. Maturation and persistence of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 memory B cell response. Cell 2021, 184, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
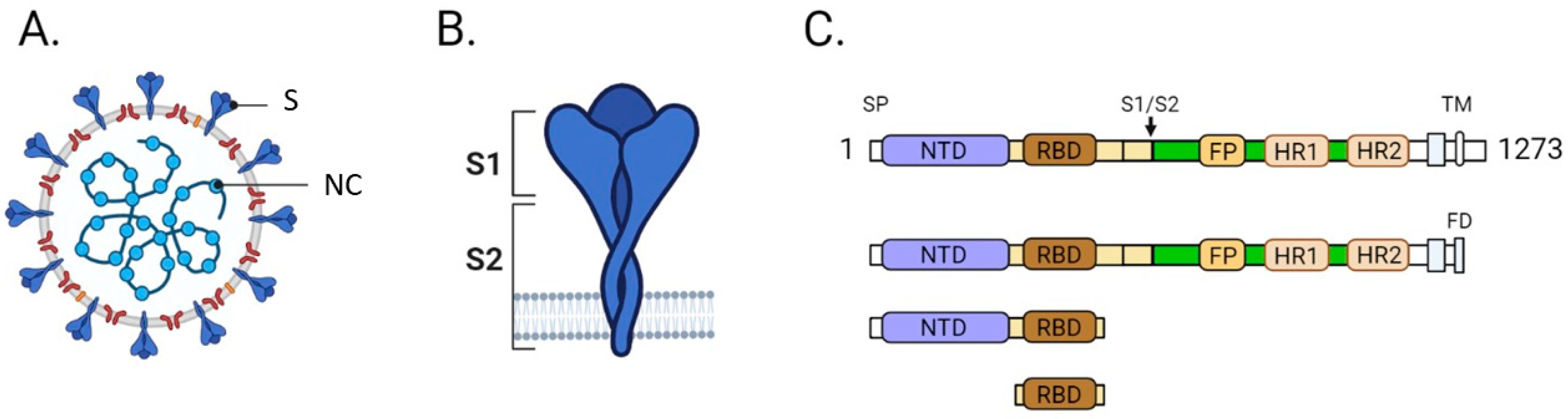
| Company | Assay | Method | Platform | Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbott | SARS-CoV-2 IgG | CMIA | Alinity I (Abbott) | NC |
| DiaSorin | LIAISON® SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 IgG | CLIA | Liaison XL (DiaSorin) | S1/S2 |
| Euroimmun | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG | ELISA | Euroimmun Analyzer I (Euroimmun) | S1 |
| Immundiagnostik | IDK® anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG | ELISA | DYNEX DSX (Dynex Technologies) | S1 |
| Roche | Elecsys® anti-SARS-CoV-2 pan-Ig | ECLIA | Cobas 8000 (Roche) | NC |
| Parameters | Group A, n = 363 | Group B, n = 169 |
|---|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 200 (55.24) | 103 (60.95) |
| Male, n (%) * | 162 (44.75) | 66 (39.05) |
| Age in years, mean ± SD | 44.09 ± 12.86 | 42.69 ± 12.86 |
| Days after disease onset, median (IQR) | 154 (141–176) | 47 (35–56) |
| Asymptomatic, n (%) | 15 (5.90) | 20 (16.00) |
| Mild, n (%) | 228 (89.77) | 100 (80.00) |
| Severe, n (%) ** | 11 (4.33) | 5 (4.00) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eberhardt, K.A.; Dewald, F.; Heger, E.; Gieselmann, L.; Vanshylla, K.; Wirtz, M.; Kleipass, F.; Johannis, W.; Schommers, P.; Gruell, H.; et al. Evaluation of a New Spike (S)-Protein-Based Commercial Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040733
Eberhardt KA, Dewald F, Heger E, Gieselmann L, Vanshylla K, Wirtz M, Kleipass F, Johannis W, Schommers P, Gruell H, et al. Evaluation of a New Spike (S)-Protein-Based Commercial Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(4):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040733
Chicago/Turabian StyleEberhardt, Kirsten Alexandra, Felix Dewald, Eva Heger, Lutz Gieselmann, Kanika Vanshylla, Maike Wirtz, Franziska Kleipass, Wibke Johannis, Philipp Schommers, Henning Gruell, and et al. 2021. "Evaluation of a New Spike (S)-Protein-Based Commercial Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG" Microorganisms 9, no. 4: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040733
APA StyleEberhardt, K. A., Dewald, F., Heger, E., Gieselmann, L., Vanshylla, K., Wirtz, M., Kleipass, F., Johannis, W., Schommers, P., Gruell, H., Brensing, K. A., Müller, R.-U., Augustin, M., Lehmann, C., Koch, M., Klein, F., & Di Cristanziano, V. (2021). Evaluation of a New Spike (S)-Protein-Based Commercial Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG. Microorganisms, 9(4), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9040733







