Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Manifestations in Hospitalized Children with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Primary End-Point
3.2. Secondary End-Points
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Søndergaard, M.J.; Friis, M.B.; Hansen, D.S.; Jørgensen, I.M. Clinical manifestations in infants and children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz, M.H.; Benitez, A.J.; Winchell, J.M. Investigations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections in the United States: Trends in Molecular Typing and Macrolide Resistance from 2006 to 2013. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, E.R.; Foy, H.M.; Kenny, G.E.; Kronmal, R.A.; McMahan, R.; Clarke, E.R.; MacColl, W.A.; Grayston, J.T. Pneumonia Due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Its Incidence in the Membership of a Cooperative Medical Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1966, 275, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, T.P.; Balish, M.F.; Waites, K.B. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis and laboratory detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 956–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waites, K.B.; Talkington, D.F. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Its Role as a Human Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 697–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer Sauteur, P.M.; Unger, W.W.J.; van Rossum, A.M.C.; Berger, C. The Art and Science of Diagnosing Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguilera-Alonso, D.; López Ruiz, R.; Centeno Rubiano, J.; Morell García, M.; Valero García, I.; Ocete Mochón, M.D.; Montesinos Sanchis, E. Epidemiological and clinical analysis of community-acquired Mycoplasma pneumonia in children from a Spanish population, 2010–2015. An. Pediatr. Engl. Ed. 2019, 91, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, O.; Oster, Y.; Michael-Gayego, A.; Marans, R.S.; Averbuch, D.; Engelhard, D.; Moses, A.E.; Nir-Paz, R. The Clinical Presentation of Pediatric Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections—A Single Center Cohort. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrim, M.; Wolter, N.; Benitez, A.J.; Tempia, S.; du Plessis, M.; Walaza, S.; Moosa, F.; Diaz, M.H.; Wolff, B.J.; Treurnicht, F.K.; et al. Epidemiology and Molecular Identification and Characterization of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, South Africa, 2012–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadsby, N.J.; Reynolds, A.J.; McMenamin, J.; Gunson, R.N.; McDonagh, S.; Molyneaux, P.J.; Yirrell, D.L.; Templeton, K.E. Increased reports of Mycoplasma pneumoniae from laboratories in Scotland in 2010 and 2011—Impact of the epidemic in infants. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2012, 17, 20110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchley, C.S.; Berg, A.S.; Vahdani Benam, A.; Kvissel, A.K.; Leegaard, T.M.; Nakstad, B. Mycoplasma Pneumoniae: A Cross-sectional Population-based Comparison of Disease Severity in Preschool and School-age Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.S.; Yun, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Rhie, K.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, H.; Kwak, Y.H.; Kim, D.K.; Suh, D.I.; et al. Contribution of Co-detected Respiratory Viruses and Patient Age to the Clinical Manifestations of Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, T.M.; Schumacker, R.E. Multiple Regression Approach to Analyzing Contingency Tables: Post Hoc and Planned Comparison Procedures. J. Exp. Educ. 1995, 64, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waites, K.B. New concepts ofMycoplasma pneumoniae infections in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2003, 36, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defilippi, A.; Silvestri, M.; Tacchella, A.; Giacchino, R.; Melioli, G.; Di Marco, E.; Cirillo, C.; Di Pietro, P.; Rossi, G.A. Epidemiology and clinical features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beeton, M.L.; Zhang, X.-S.; Uldum, S.A.; Bébéar, C.; Dumke, R.; Gullsby, K.; Ieven, M.; Loens, K.; Nir-Paz, R.; Pereyre, S.; et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections, 11 countries in Europe and Israel, 2011 to 2016. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2020, 25, 1900112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youn, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-Y.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Rhim, J.-W.; Kang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, J.-C. Difference of clinical features in childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. BMC Pediatr. 2010, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardiner, S.J.; Gavranich, J.B.; Chang, A.B. Antibiotics for community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections secondary to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 1, CD004875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narita, M. Classification of Extrapulmonary Manifestations Due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection on the Basis of Possible Pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Isaacs, D.; Kesson, A. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in Australian children. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2005, 41, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, A.; Di Altobrando, A.; Parladori, R.; Biagi, C.; Balsamo, C.; Ghizzi, C.; Patrizi, A.; Lanari, M.; Neri, I. Duck-like lips: A new clinical feature for diagnosis of Mycoplasma-Induced Rash and Mucositis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 35, e225–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavan, T.N.; Mathes, E.F.; Frieden, I.; Shinkai, K. Mycoplasma pneumoniae–induced rash and mucositis as a syndrome distinct from Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme: A systematic review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 239–245.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D. Extra-pulmonary diseases related to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: Recent insights into the pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajantri, B.; Venkatram, S.; Diaz-Fuentes, G. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: A Potentially Severe Infection. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2018, 10, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, D.G.; Oski, F.A.; Orkin, S.H.; Fisher, D.E. (Eds.) Nathan and Oski’s Hematology and Oncology of Infancy and Childhood, 8th ed.; Elsevier, Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4557-5414-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Qiu, F.; Zhao, L.; Guo, W.; Yang, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, G. Impact and clinical profiles of Mycoplasma pneumoniae co-detection in childhood community-acquired pneumonia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagels, M.A.; Hugli, T.E. Mechanisms and mediators of neutrophilic leukocytosis. Immunopharmacology 1994, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxer, L.A.; Allen, J.M.; Baehner, R.L. Diminished polymorphonuclear leukocyte adherence. Function dependent on release of cyclic AMP by endothelial cells after stimulation of beta-receptors by epinephrine. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 66, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
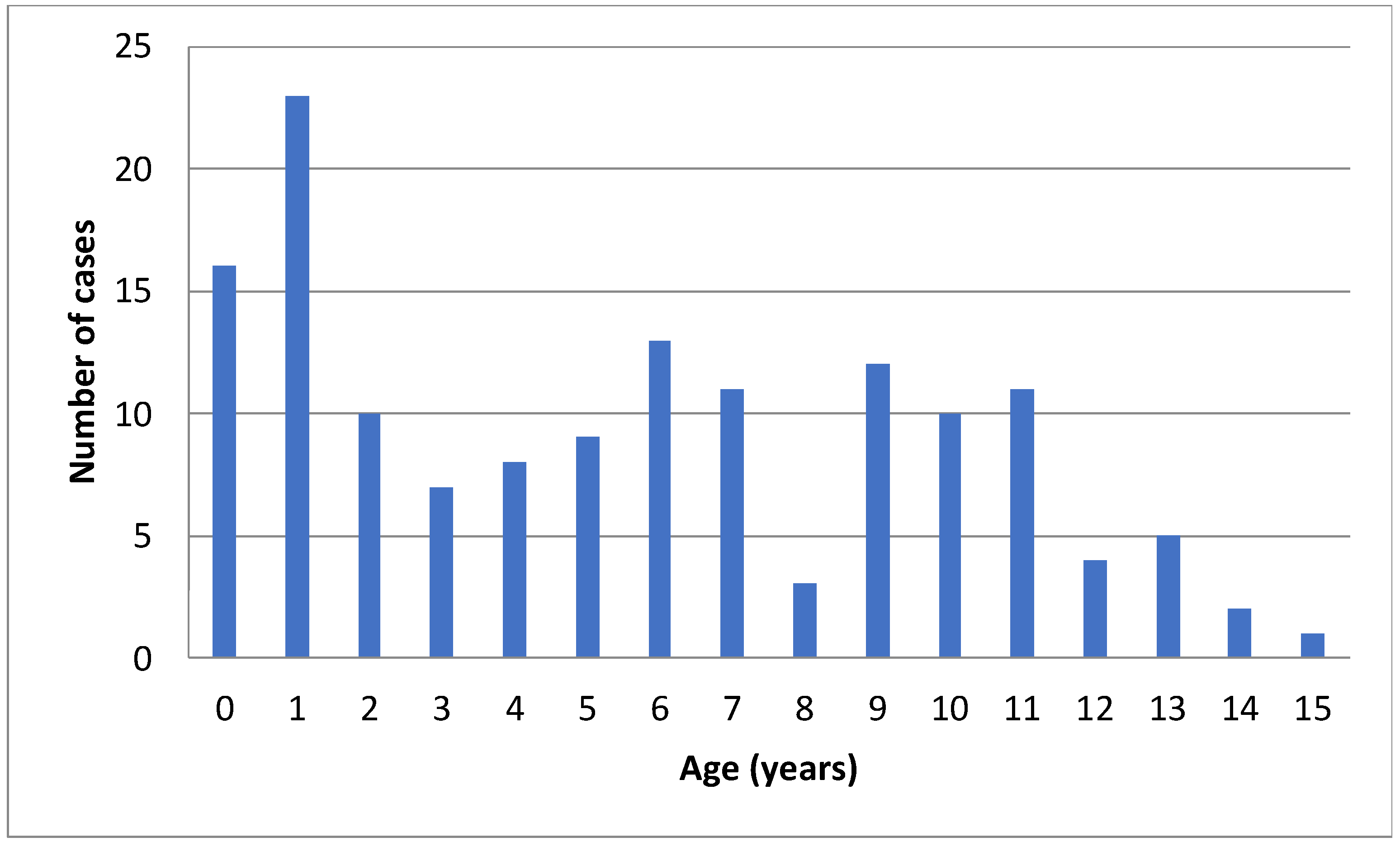
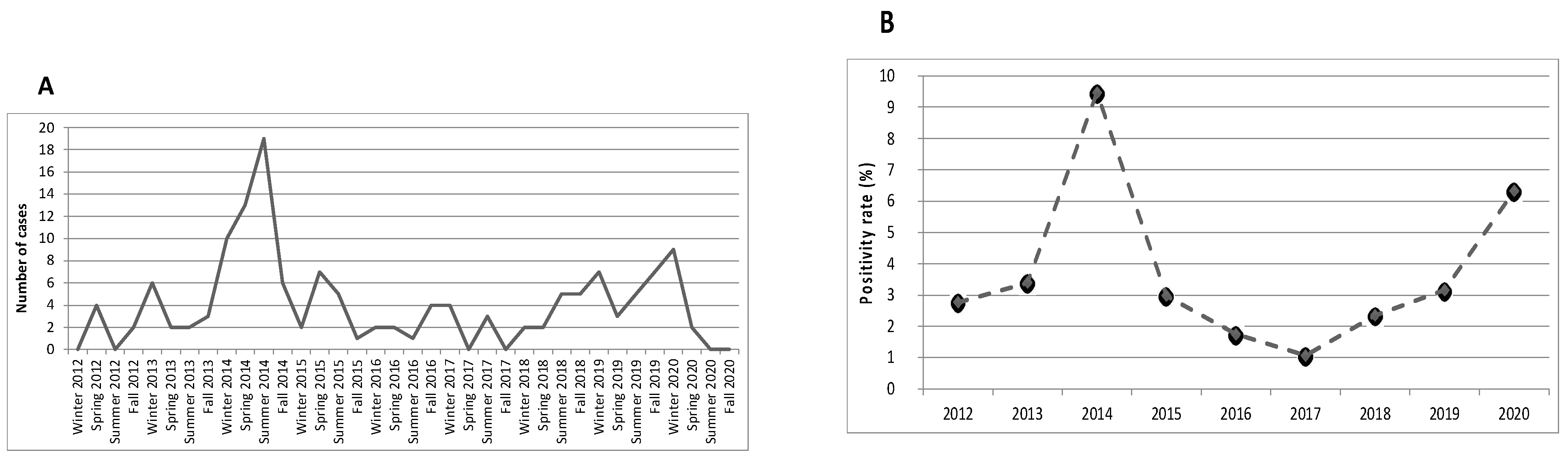
| Total n = 145 (100%) | <2 Years Old n = 39 (26.9%) | 2–5 Years Old n = 34 (23.4%) | ≥6 Years Old n = 72 (49.7%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and Anamnestic Data: | |||||
| Sex, n (%), male | 82 (56.6) | 26 (66.7) | 19 (55.9) | 37 (51.4) | 0.300 |
| Background disease°, n (%) | 34 (23.4) | 10 (25.6) | 7 (20.6) | 17 (23.6) | 0.878 |
| Season, n (%) | 0.079 | ||||
| Spring | 33 (22.8) | 8 (20.5) | 10 (29.4) | 15 (20.8) | |
| Summer | 40 (27.6) | 10 (25.6) | 6 (17.6) | 24 (33.3) | |
| Autumn | 33 (22.8) | 5 (12.8) | 12 (35.3) | 16 (22.2) | |
| Winter | 39 (26.9) | 16 (41) | 6 (17.6) | 17 (23.6) | |
| Time between symptoms onset and hospitalization, days (median, IQR) | 7.0 (4.0–10.0) | 5.0 (2.0–10.0) | 7.0 (4.0–12.2) | 7.0 (5.0–9.0) | 0.150 |
| Treatment prior to hospitalization, n (%) | 0.039 | ||||
| No antibiotic | 63 (43.4) | 26 (67) * | 11 (32.3) | 26 (36.1) | |
| Empiric b-lactam | 64 (44.1) | 10 (25.6) | 19 (55.9) | 35 (48.6) | |
| Empiric macrolide | 10 (6.9) | 1 (2.6) | 3 (8.8) | 6 (8.3) | |
| Empiric b-lactam + macrolide | 8 (5.5) | 2 (5.1) | 1 (2.9) | 5 (6.9) | |
| Clinical Manifestations: | |||||
| Fever (≥38 °C), n (%) | 121 (83.4) | 31 (79.5) | 27 (79.4) | 63 (87.5) | 0.427 |
| Any respiratory manifestations, n (%) | 130 (89.7) | 34 (87.2) | 29 (85.3) | 67 (93.1) | 0.396 |
| Rhinitis, n (%) | 24 (16.6) | 14 (35.9) * | 4 (11.8) | 6 (8.3) | 0.001 |
| Pharyngitis, n (%) | 86 (59.3) | 22 (66.7) | 19 (55.9) | 41 (56.9) | 0.248 |
| Middle ear involvement, n (%) | 22 (15.2) | 11 (28.2) | 3 (8.8) | 8 (11.1) | 0.060 |
| Neck lymphadeonopathy, n (%) | 15 (10.3) | 4 (10.3) | 2 (5.9) | 9 (12.5) | 0.430 |
| Cough, n (%) | 113 (77.9) | 31 (79.5) | 24 (70.6) | 58 (80.6) | 0.494 |
| Chest pain, n (%) | 3 (2.1) | 0 | 0 | 3 (4.2) | 0.212 |
| Tachypnea, n (%) | 49 (33.8) | 22 (56.4) * | 13 (38.2) | 14 (19.4) * | <0.001 |
| Any findings on lung auscultation, n (%) | 108 (74.5) | 28 (71.8) | 26 (76.5) | 54 (75) | 0.892 |
| Extrapulmonary Manifestations: | |||||
| Any, n (%) | 74 (51.0) | 17 (43.6) | 19 (55.9) | 38 (52.8) | 0.529 |
| Involvement of 1 site, n (%) | 54 (37.2) | 14 (35.9) | 18 (52.9) | 22 (30.6) | |
| Involvement of 2 sites, n (%) | 16 (11) | 3 (7.7) | 1 (2.9) | 12 (16.7) | |
| Involvement of 3 sites, n (%) | 3 (0.1) | 0 | 0 | 3 (4.2) | |
| Involvement of 4 sites, n (%) | 1 (0.01) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.4) | |
| Cutaneous involvement: | 0.138 | ||||
| Any, n (%) | 21 (14.5) | 2 (5.1) | 5 (14.7) | 14 (19.4) | |
| Skin, n (%) | 16 (11.0) | 2 (5.1) | 4 (11.8) | 10 (13.9) | |
| Skin + mucous membranes, n (%) | 4 (2.8) | 0 | 0 | 4 (5.5) | |
| Retropharyngeal abscess, n (%) | 1 (0.7) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 0 | |
| Gastrointestinal involvement: | 0.681 | ||||
| Any, n (%) | 43 (29.6) | 13 (33.3) | 10 (29,4) | 20 (27.8) | |
| Nausea or vomit, n (%) | 22 (15.2) | 7 (17.9) | 5 (14.7) | 10 (13.9) | |
| Diarrhea, n (%) | 6 (4.1) | 3 (7.7) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (2.8) | |
| Abdominal pain, n (%) | 4 (2.7) | 0 | 2 (5.9) | 2 (2.8) | |
| More than 1 symptom, n (%) | 10 (6.9) | 2 (5.1) | 2 (5.9) | 6 (8.3) | |
| Serum transaminases elevation, n (%) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (2.6) | 0 | 0 | |
| Neurological involvement: | 0.006 | ||||
| Any, n (%) | 16 (11.0) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 15 (20.8) * | |
| Headache, n (%) | 12 (8.3) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 11 (15.3) * | |
| Other symptoms (weakness, dysesthesia, dystonic movements), n (%) | 4 (2.7) | 0 | 0 | 4 (5.5) | |
| Cardiovascular involvement: | 0.525 | ||||
| Any, n (%) | 4 (2.7) | 1 (2.6) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (2.8) | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 1 (0.7) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.4) | |
| Pericardial effusion, n (%) | 2 (1.4) | 1 (2.6) | 0 | 1 (1.4) | |
| Myopericarditis, n (%) | 1(0.7) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 0 | |
| Musculoskeletal involvement: | 0.927 | ||||
| Any, n (%) | 14 (9.6) | 4 (10.2) | 3 (8.8) | 7 (9.7) | |
| Arthralgia, n (%) | 5 (3.4) | 2 (5.1) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (2.8) | |
| Joint swelling, n (%) | 2 (1.4) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 1 (1.4) | |
| Myalgia + serum CK elevation, n (%) | 7 (4.8) | 2 (5.1) | 1 (2.9) | 4 (5.6) | |
| Genitourinary involvement: | 0.440 | ||||
| Macrohematuria, n (%) | 4 (2.8) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 3 (4.2) | |
| Laboratory Tests: | |||||
| WBC at admission (median, IQR) | 10,100 (7312–14,832) | 12,415 (8.932–17,020) * | 10,355 (8280–14,697) | 8285 (6380–13,355) * | 0.003 |
| Neutrophil count at admission (median, IQR) | 5795 (4250–9565) | 5200 (4442–9837) | 6570 (4685–8590) | 5760 (4200–10,062) | 0.750 |
| Lymphocyte count at admission (median, IQR) | 2226 (1492–3707) | 4645 (3387–5750) * | 2570 (1870–3340) * | 1705 (1152–2462) * | <0.001 |
| Platelet count at admission (median, IQR) | 325,000 (247,250–420,500) | 380,500 (300,250–473,250) * | 329,000 (277,250–420,750) | 283,000 (230,000–379,750) * | 0.003 |
| Hb at admission (median, IQR) | 12.4 (11.4–13.2) | 11.3 (10.7–12.2) | 12.0 (11.3–12.7) | 13.1 (12.3–13.8) * | <0.001 |
| CRP at admission (median, IQR) | 1.76 (0.76–5.15) | 1.07 (0.42–2.71) * | 2.77 (0.24–5.10) | 2.43 (0.99–6.61) * | 0.002 |
| Anti-MP IgM: | 0.043 | ||||
| Not performed, n (%) | 74 (51.0) | 28 (71.8) | 16 (47.1) | 30 (41.7) | |
| Negative, n (%) | 36 (24.8) | 6 (15.4) | 8 (23.5) | 22 (30.6) | |
| Positive, n (%) | 35 (24.1) | 5 (12.8) * | 10 (29.4) | 20 (27.8) | |
| CXR Findings: | |||||
| Not performed, n (%) | 24 (16.6) | 10 (25.6) | 6 (17.6) | 8 (11.1) | 0.013 |
| Negative for lung consolidation, n (%) | 13 (9.0) | 6 (15.4) | 1 (2.9) | 6 (8.3) | |
| Lung consolidation without pleural effusion, n (%) | 76 (52.4) | 22 (56.4) | 16 (47.1) | 38 (52.8) | |
| Lung consolidation with pleural effusion, n (%) | 32 (22.1) | 1 (2.6) * | 11 (32.4) | 20 (27.8) | |
| Hospital Course: | |||||
| Coinfection, n (%) | 0.070 | ||||
| Any | 19 (13.1) | 8 (21.1) | 6 (17.6) | 5 (6.9) | |
| Viral etiology | 16 (11.0) | 8 (21.1) | 5 (14.7) | 3 (4.1) | |
| Bacterial etiology | 3 (2.1) | 0 | 1 (2.9) | 2 (2.8) | |
| Treatment with macrolide in hospital, n (%) | 92 (63.4) | 14 (35.9) * | 20 (58.8) | 58 (80.6) * | <0.001 |
| Oxygen therapy, n (%) | 18 (12.4) | 9 (23.1) * | 4 (11.8) | 5 (6.9) | 0.048 |
| Intravenous fluid therapy, n (%) | 125 (86.2) | 37 (94.9) | 30 (88.2) | 58 (80.6) | 0.105 |
| Length of hospital stay, days (median, IQR) | 5.0 (3.0–6.0) | 5.0 (4.0–8.0) * | 4.0 (3.0–6.0) | 5.0 (3.0–6.0) * | 0.036 |
| Total n = 145 (100%) | No Extrapulmonary Manifestations n = 71 (49%) | Extrapulmonary Manifestations n = 74 (51%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and Anamnestic data: | ||||
| Sex, n (%), male | 82 (56.6) | 41 (57.7) | 41 (55.4) | 0.776 |
| Age, n (%) | 0.529 | |||
| <2 years old | 39 (26.9) | 22 (31) | 17 (26.9) | |
| 2–5 years old | 34 (23.4) | 15 (21.1) | 19 (25.7) | |
| ≥6 years old | 72 (47.9) | 34 (47.9) | 38 (51.4) | |
| Background disease *, n (%) | 34 (23.4) | 19 (26.8) | 15 (20.3) | 0.356 |
| Season, n (%) | 0.618 | |||
| Spring | 33 (22.8) | 13 (18.3) | 20 (27) | |
| Summer | 40 (27.6) | 21 (29.6) | 19 (25.7) | |
| Autumn | 33 (22.8) | 16 (22.5) | 17 (23) | |
| Winter | 39 (26.9) | 21 (29.6) | 18 (24.3) | |
| Time between symptoms onset and hospitalization, days (median, IQR) | 7.0 (4.0–10.0) | 7.0 (4.0–11.0) | 6.0 (4.0–9.0) | 0.158 |
| Treatment prior to hospitalization, n (%) | 0.455 | |||
| No antibiotic | 63 (43.4) | 28 (39.4) | 35 (47.3) | |
| Empiric b-lactam | 64 (44.1) | 36 (50.7) | 28 (37.8) | |
| Empiric macrolide | 10 (6.9) | 4 (5.6) | 6 (8.1) | |
| Empiric b-lactam + macrolide | 8 (5.5) | 3 (4.2) | 5 (6.8) | |
| Clinical Manifestations: | ||||
| Fever (≥38 °C), n (%) | 121 (83.4) | 61 (85.9) | 60 (81.1) | 0.434 |
| Any respiratory manifestations, n (%) | 130 (89.7) | 67 (94.4) | 63 (85.1) | 0.068 |
| Rhinitis, n (%) | 24 (16.6) | 17 (23.9) * | 7 (9.5) | 0.019 |
| Pharyngitis, n (%) | 86 (59.3) | 43 (60.6) | 43 (58.1) | 0.842 |
| Middle ear involvement, n (%) | 22 (15.2) | 11 (15.5) | 11 (14.9) | 0.740 |
| Neck lymphadeonopathy, n (%) | 15 (10.3) | 7 (9.9) | 8 (10.8) | 0.584 |
| Cough, n (%) | 113 (77.9) | 67 (94.4) * | 46 (62.2) | <0.001 |
| Chest pain, n (%) | 3 (2.1) | 2 (2.8) | 1 (1.4) | 0.535 |
| Tachypnea, n (%) | 49 (33.8) | 26 (36.6) | 23 (31.1) | 0.481 |
| Any findings on lung auscultation, n (%) | 108 (74.5) | 59 (83.1) * | 49 (66.2) | 0.020 |
| Laboratory Tests: | ||||
| WBC at admission (median, IQR) | 10,100 (7312–14,832) | 10,050 (7782–14,877) | 10,260 (6790–14,787) | 0.897 |
| Neutrophil count at admission (median, IQR) | 5795 (4250–9565) | 5735 (4405–8950) | 5890 (4215–10,272) | 0.815 |
| Lymphocyte count at admission (median, IQR) | 2226 (1492–3707) | 2595 (1225–4457) | 2190 (1560–3305) | 0.608 |
| Platelet count at admission (median, IQR) | 325,000 (247,250–420,500) | 329,000 (241,750–428,000) | 313,500 (257,750–417,500) | 0.783 |
| Hb at admission (median, IQR) | 12.4 (11.4–13.2) | 12.4 (11.4–13.2) | 12.4 (11.4–13.3) | 0.503 |
| CRP at admission (median, IQR) | 1.76 (0.76–5.15) | 2.26 (0.78–5.36) | 1.53 (0.68–4.85) | 0.350 |
| Positive anti-MP IgM, n (%) | 35 (24.1) | 17 (23.9) | 18 (24.3%) | 0.792 |
| CXR Findings: | ||||
| Not performed, n (%) | 24 (16.6) | 8 (11.3) | 16 (21.6) | 0.180 |
| Negative for lung consolidation, n (%) | 13 (9.0) | 7 (9.9) | 6 (8.1) | |
| Lung consolidation without pleural effusion, n (%) | 76 (52.4) | 36 (50.7) | 40 (54.1) | |
| Lung consolidation with pleural effusion, n (%) | 32 (22.1) | 20 (28.2) | 12 (16.2) | |
| Hospital Course: | ||||
| Coinfection, n (%): | 0.540 | |||
| Any | 19 (13.1) | 8 (11.3) | 11 (14.9) | |
| Viral etiology | 16 (11.0) | 6 (8.5) | 10 (13.5) | |
| Bacterial etiology | 3 (2.1) | 2 (2.8) | 1 (1.4) | |
| Treatment with macrolide in hospital, n (%) | 92 (63.4) | 48 (67.6) | 44 (59.5) | 0.309 |
| Oxygen therapy, n (%) | 18 (12.4) | 10 (14.1) | 8 (10.8) | 0.550 |
| Intravenous fluid therapy, n (%) | 125 (86.2) | 67 (94.4) * | 58 (78.4) | 0.005 |
| Length of hospital stay, days (median, IQR) | 5.0 (3.0–6.0) | 5.0 (3.0–6.0) | 5.0 (3.0–6.0) | 0.892 |
| Any Extrapulmonary Manifestations | Cutaneous Involvement | Gastrointestinal Involvement | Neurological Involvement | Cardiovascular Involvement | Musculoskeletal Involvement | Genitourinary Involvement | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | IC 95% | p-Value | OR | IC 95% | p-Value | OR | IC 95% | p-Value | OR | IC 95% | p-Value | OR | IC 95% | p-Value | 0R | IC 95% | p-Value | 0R | IC 95% | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.0 | 0.9–1.1 | 0.425 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.2 | 0.486 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.1 | 0.738 | 1.3 | 1.1–1.5 | <.001 | 1.0 | 0.8–1.3 | 0.924 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.1 | 0.985 | 1.2 | 0.9–1.5 | 0.176 |
| Sex | 1.1 | 0.6–2.1 | 0.776 | 1.5 | 0.6–3.9 | 0.374 | 0.5 | 0.2–1.1 | 0.088 | 0.8 | 0.3–2.2 | 0.612 | 1.3 | 0.2–9.6 | 0.789 | 1.8 | 0.6–5.6 | 0.282 | 1.3 | 0.2– 9.6 | 0.789 |
| Prior empiric antibiotic treatment | 1.0 | 0.7–1.5 | 0.981 | 7.0 | 2.4- 21.0 | 0.000 | 0.4 | 0.1–1.6 | 0.208 | 1.8 | 0.4–6.9 | 0.420 | 0 | --- | 0.999 | 2.1 | 0.5–8.4 | 0.291 | 2.4 | 0.2–24.7 | 0.453 |
| Respiratory manifestations | 0.3 | 0.1–1.1 | 0.078 | 0.5 | 0.2–1.3 | 0.158 | 1.2 | 0.5–2.7 | 0.685 | 0.7 | 0.2–2.2 | 0.578 | 0 | --- | 0.998 | 0.4 | 0.1–1.3 | 0.126 | 0.3 | 0.1–2.4 | 0.277 |
| WBC at admission | 1.0 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.806 | 1.0 | 1.0–1.1 | 0.626 | 1.1 | 1.0–1.1 | 0.062 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.1 | 0.887 | 0.9 | 0.7–1.1 | 0.443 | 0.8 | 0.7–1.0 | 0.033 | 1.0 | 0.8–1.2 | 0.847 |
| Neutrophil count at admission | 1.0 | 1.0–1.1 | 0.425 | 1.0 | 1.0–1.1 | 0.598 | 1.1 | 1.0–1.1 | 0.019 | 1.0 | 1.0–1.1 | 0.360 | 0.9 | 0.7–1.2 | 0.545 | 0.8 | 0.6–1.0 | 0.023 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.2 | 0.806 |
| Lymphocyte count at admission | 0.9 | 0.8–1.0 | 0.221 | 1.0 | 0.8–1.2 | 0.734 | 0.9 | 0.8–1.1 | 0.392 | 0.6 | 0.4–1.0 | 0.040 | 0.9 | 0.6–1.5 | 0.740 | 0.9 | 0.7–1.2 | 0.617 | 0.5 | 0.2–1.5 | 0.219 |
| Platelet count at admission | 1.0 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.805 | 1.0 | 1.0–1.1 | 0.279 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.611 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.1 | 0.531 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.637 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.195 |
| Hb at admission | 1.1 | 0.9–1.4 | 0.283 | 1.3 | 0.9–1.8 | 0.193 | 1.0 | 0.7–1.2 | 0.714 | 2.4 | 1.4–4.0 | 0.001 | 1.4 | 0.6–3.2 | 0.379 | 1.0 | 0.7–1.5 | 0.958 | 1.0 | 0.5–2.0 | 0.957 |
| CRP at admission | 1.0 | 0.9–1.1 | 0.970 | 1.0 | 1.0–1.2 | 0.348 | 1.0 | 0.9–1.1 | 0.474 | 1.1 | 1.0–1.2 | 0.154 | 0.9 | 0.7–1.3 | 0.567 | 0.8 | 0.7–1.0 | 0.130 | 1.0 | 0.8–1.3 | 0.9 |
| Coinfections | 1.1 | 0.5–2.5 | 0.780 | 1.1 | 0.3–4.2 | 0.873 | 1.3 | 0.6–3.0 | 0.531 | 0.4 | 0.1–3.3 | 0.399 | 2.3 | 0.2–22.9 | 0.490 | 1.1 | 0.3–5.4 | 0.899 | 0 | --- | 0.998 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biagi, C.; Cavallo, A.; Rocca, A.; Pierantoni, L.; Antonazzo, D.; Dondi, A.; Gabrielli, L.; Lazzarotto, T.; Lanari, M. Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Manifestations in Hospitalized Children with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122553
Biagi C, Cavallo A, Rocca A, Pierantoni L, Antonazzo D, Dondi A, Gabrielli L, Lazzarotto T, Lanari M. Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Manifestations in Hospitalized Children with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(12):2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122553
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiagi, Carlotta, Alessandra Cavallo, Alessandro Rocca, Luca Pierantoni, Davide Antonazzo, Arianna Dondi, Liliana Gabrielli, Tiziana Lazzarotto, and Marcello Lanari. 2021. "Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Manifestations in Hospitalized Children with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection" Microorganisms 9, no. 12: 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122553
APA StyleBiagi, C., Cavallo, A., Rocca, A., Pierantoni, L., Antonazzo, D., Dondi, A., Gabrielli, L., Lazzarotto, T., & Lanari, M. (2021). Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Manifestations in Hospitalized Children with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection. Microorganisms, 9(12), 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122553









