The ComX Quorum Sensing Peptide of Bacillus subtilis Affects Biofilm Formation Negatively and Sporulation Positively
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Strain Construction
2.2. Growth Conditions
2.3. Biochemical Composition of Extracellular Polymers and CFU Counts Determination in Pellicle Biofilms
2.4. Spent Media Droplet Surface Wetting Assay
2.5. Pellicle Biofilm Bulk Fluorescence Measurements
2.6. Pellicle Biofilm Morphology, Hydrophobicity Estimation and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
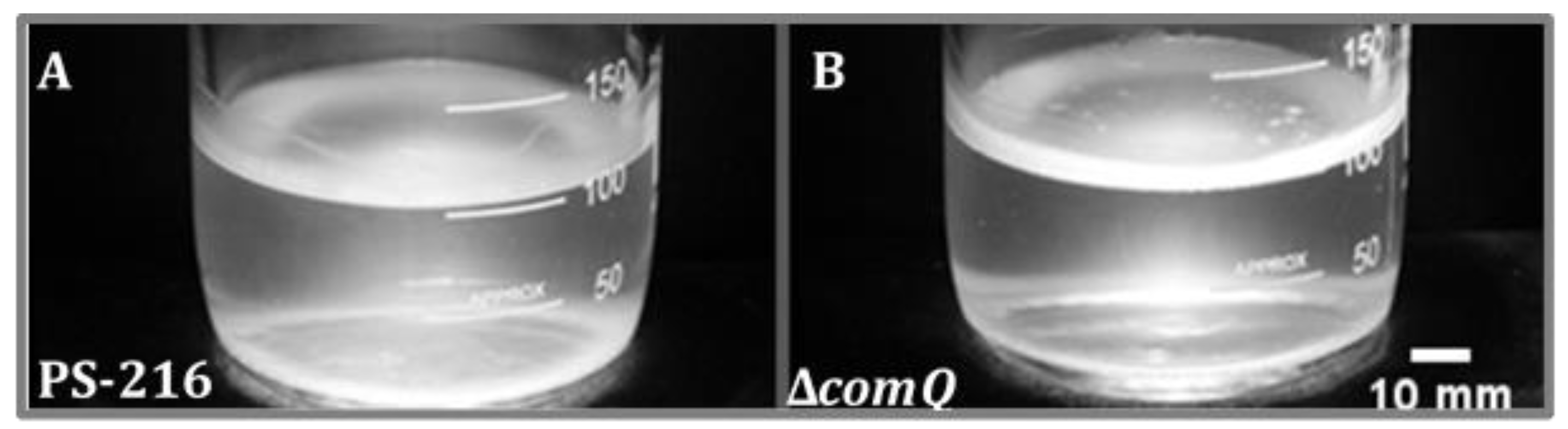
3.1. The Quorum Sensing ComQ Mutant Forms Thicker Pellicles than the Wild Type
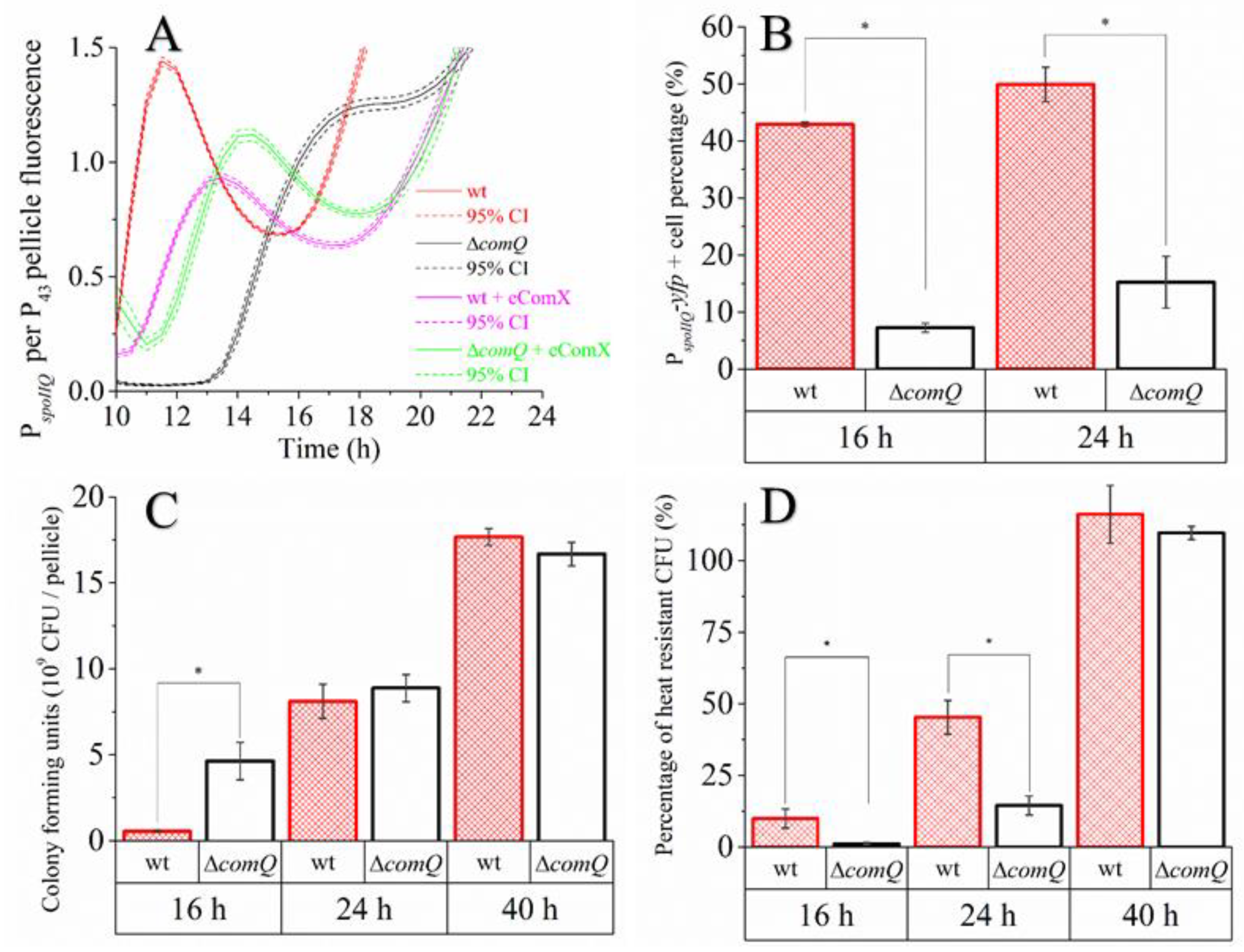
3.2. Expression of PepsA and PtapA Promoters Per Pellicle Is Higher in the QS Mutant than in the Wild Type Strain
3.3. The Quorum Sensing Mutant Pellicles Exhibit a Different Pellicle Morphology and Distributions of Cells with Active PepsA and PtapA Dependent Expression
3.4. PtapA But Not PepsA Dependent Expression Is More Active and in a More Substantial Portion of Cells in the ΔcomQ Mutant than in the Wild Type Strain
3.5. Extracellular Polymer Extracts of QS Mutant Pellicles Contain More Sugar and Protein
3.6. The QS Deficient Mutant Has Lower Spore Counts during the Early Stages of Biofilm Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: from the Natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, K.K. What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom-Ackermann, Z.; Ganin, H.; Kolodkin-Gal, I. Quorum-sensing Cascades Governing Bacterial Multicellular Communities. Isr. J. Chem. 2015, 56, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, T.G.; Fuqua, C. What’s in a name? The semantics of quorum sensing. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandic-Mulec, I.; Stefanic, P.; Van Elsas, J.D. Ecology of Bacillaceae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piggot, P.J.; Coote, J.G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol. Rev. 1976, 40, 908–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cairns, L.; Hobley, L.; Stanley-Wall, N.R. Biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis: new insights into regulatory strategies and assembly mechanisms. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragos, A.; Kiesewalter, H.; Martin, M.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Hartmann, R.; Wechsler, T.; Eriksen, C.; Brix, S.; Drescher, K.; Stanley-Wall, N.; et al. Division of Labor during Biofilm Matrix Production. Curr. Boil. 2018, 28, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abee, T.; Kovács, Á.T.; Kuipers, O.P.; Van Der Veen, S. Biofilm formation and dispersal in Gram-positive bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K. Gradual activation of the response regulator DegU controls serial expression of genes for flagellum formation and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, D.; Kolter, R. Extracellular signals that define distinct and coexisting cell fates in Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veening, J.-W.; Smits, W.K.; Kuipers, O.P. Bistability, Epigenetics, and Bet-Hedging in Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schultz, D.; Wolynes, P.G.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Onuchic, J.N. Deciding fate in adverse times: Sporulation and competence in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21027–21034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez, D.; Vlamakis, H.; Kolter, R. Biofilms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Boil. 2010, 2, a000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamara, M.; Spacapan, M.; Mandic-Mulec, I.; Stanley-Wall, N.R. Social behaviours by Bacillus subtilis: quorum sensing, kin discrimination and beyond. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 110, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dogsa, I.; Choudhary, K.S.; Marsetic, Z.; Hudaiberdiev, S.; Vera, R.; Pongor, S.; Mandic-Mulec, I. ComQXPA Quorum Sensing Systems May Not Be Unique to Bacillus subtilis: A Census in Prokaryotic Genomes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roggiani, M.; Dubnau, D. ComA, a phosphorylated response regulator protein of Bacillus subtilis, binds to the promoter region of srfA. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 3182–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogura, M. DNA microarray analysis of Bacillus subtilis DegU, ComA and PhoP regulons: an approach to comprehensive analysis of B.subtilis two-component regulatory systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 3804–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comella, N.; Grossman, A.D. Conservation of genes and processes controlled by the quorum response in bacteria: characterization of genes controlled by the quorum-sensing transcription factor ComA in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.; Rippa, V.; Mobarec, J.C.; Sauer, P.; Adlung, L.; Kolb, P.; Bischofs, I.B. The quorum-sensing regulator ComA from Bacillus subtilis activates transcription using topologically distinct DNA motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.M.A.; Marahiel, M.; Zuber, P. Identification of a genetic locus required for biosynthesis of the lipopeptide antibiotic surfactin in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 5662–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López, D.; Fischbach, M.A.; Chu, F.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Structurally diverse natural products that cause potassium leakage trigger multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 106, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López, D.; Vlamakis, H.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Paracrine signaling in a bacterium. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazazzera, B.A.; Kurtser, I.G.; McQuade, R.S.; Grossman, A.D. An Autoregulatory Circuit Affecting Peptide Signaling in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5193–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auchtung, J.; Lee, C.A.; Grossman, A.D. Modulation of the ComA-Dependent Quorum Response in Bacillus subtilis by Multiple Rap Proteins and Phr Peptides. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5273–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishii, H.; Tanaka, T.; Ogura, M. The Bacillus subtilis Response Regulator Gene degU Is Positively Regulated by CcpA and by Catabolite-Repressed Synthesis of ClpC. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 195, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Msadek, T.; Kunst, F.; Klier, A.; Rapoport, G. DegS-DegU and ComP-ComA modulator-effector pairs control expression of the Bacillus subtilis pleiotropic regulatory gene degQ. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 2366–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dogsa, I.; Brloznik, M.; Stopar, D.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Exopolymer Diversity and the Role of Levan in Bacillus subtilis Biofilms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, S.S.; González-Pastor, J.E.; Ben-Yehuda, S.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Fruiting body formation by Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11621–11626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearns, D.B.; Chu, F.; Branda, S.S.; Kolter, R.; Losick, R. A master regulator for biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 55, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.; Aguilar, C.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Amyloid fibers provide structural integrity to Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2230–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terra, R.; Stanley-Wall, N.R.; Cao, G.; Lazazzera, B.A. Identification of Bacillus subtilis SipW as a Bifunctional Signal Peptidase That Controls Surface-Adhered Biofilm Formation. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamon, M.A.; Stanley, N.R.; Britton, R.A.; Grossman, A.D.; Lazazzera, B.A. Identification of AbrB-regulated genes involved in biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlamakis, H.; Chai, Y.; Beauregard, P.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 11, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Shao, W.; Perego, M.; Hoch, J.A. Multiple histidine kinases regulate entry into stationary phase and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Chu, F.; Kolter, R.; Losick, R. Bistability and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 67, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shafikhani, S.H.; Mandic-Mulec, I.; Strauch, M.A.; Smith, I.; Leighton, T. Postexponential Regulation of sin Operon Expression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, U.; Mandić-Mulec, I.; Smith, I. SinI modulates the activity of SinR, a developmental switch protein of Bacillus subtilis, by protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, F.; Kearns, D.B.; Branda, S.S.; Kolter, R.; Losick, R. Targets of the master regulator of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Iwano, M. BslA(YuaB) forms a hydrophobic layer on the surface of Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 85, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhamme, D.T.; Kiley, T.B.; Stanley-Wall, N.R. DegU co-ordinates multicellular behaviour exhibited by Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 65, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, N.R.; Lazazzera, B.A. Defining the genetic differences between wild and domestic strains of Bacillus subtilis that affect poly-γ-dl-glutamic acid production and biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garde, R.; Ibrahim, B.; Kovács, Á.T.; Schuster, S. Differential equation-based minimal model describing metabolic oscillations in Bacillus subtilis biofilms. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 190810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bettenworth, V.; Steinfeld, B.; Duin, H.; Petersen, K.; Streit, W.R.; Bischofs, I.B.; Becker, A. Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Bacterial Quorum Sensing Systems. J. Mol. Boil. 2019, 431, 4530–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, M.; Hahn, J.; Dubnau, D. Expression of competence genes in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spacapan, M.; Danevčič, T.; Mandic-Mulec, I. ComX-Induced Exoproteases Degrade ComX in Bacillus subtilis PS-216. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oslizlo, A.; Stefanic, P.; Vatovec, S.; Glaser, S.B.; Rupnik, M.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Exploring ComQXPA quorum-sensing diversity and biocontrol potential of Bacillus spp. isolates from tomato rhizoplane. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanic, P.; Kraigher, B.; Lyons, N.A.; Kolter, R.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Kin discrimination between sympatric Bacillus subtilis isolates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14042–14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doan, T.; Marquis, K.A.; Rudner, D.Z. Subcellular localization of a sporulation membrane protein is achieved through a network of interactions along and across the septum. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1767–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, J.E.; Kearns, D.B. MinJ (YvjD) is a topological determinant of cell division in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 1166–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, R.; Hofmeister, A. New shuttle vectors for ectopic insertion of genes into Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid 2004, 51, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Nikoloff, J.M.; Fu, G.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Xie, N.; Zheng, P.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D. Promoter Screening from Bacillus subtilis in Various Conditions Hunting for Synthetic Biology and Industrial Applications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, T.M.; Lord, N.D.; Paulsson, J.; Losick, R. Stochastic Switching of Cell Fate in Microbes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanic, P.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Social Interactions and Distribution of Bacillus subtilis Pherotypes at Microscale. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parashar, V.; Konkol, M.A.; Kearns, D.B.; Neiditch, M.B. A Plasmid-Encoded Phosphatase Regulates Bacillus subtilis Biofilm Architecture, Sporulation, and Genetic Competence. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansaldi, M.; Marolt, D.; Stebe, T.; Mandic-Mulec, I.; Dubnau, D. Specific activation of the Bacillus quorum-sensing systems by isoprenylated pheromone variants. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, G.; Suarez, N.I.; Bessio, M.; Ferreira, F.; Massaldi, H. Quantitative determination of pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide serotype 14 using a modification of phenol-sulfuric acid method. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 52, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaouteli, S.; Macphee, C.E.; Stanley-Wall, N.R. Just in case it rains: building a hydrophobic biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobley, L.; Ostrowski, A.; Rao, F.V.; Bromley, K.M.; Porter, M.; Prescott, A.R.; Macphee, C.E.; Van Aalten, D.; Stanley-Wall, N.R. BslA is a self-assembling bacterial hydrophobin that coats the Bacillus subtilis biofilm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13600–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Branda, S.S.; Chu, F.; Kearns, D.B.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. A major protein component of the Bacillus subtilis biofilm matrix. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrett, R.; Miras, M.; Mirouze, N.; Narechania, A.; Mandic-Mulec, I.; Dubnau, D. Genome Sequence of the Bacillus subtilis Biofilm-Forming Transformable Strain PS216. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dervaux, J.; Magniez, J.C.; Libchaber, A. On growth and form of Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Interface Focus 2014, 4, 20130051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bischofs, I.B.; Hug, J.A.; Liu, A.W.; Wolf, D.M.; Arkin, A.P. Complexity in bacterial cell-cell communication: Quorum signal integration and subpopulation signaling in the Bacillus subtilis phosphorelay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6459–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, Y.; Kolter, R.; Losick, R. Reversal of an epigenetic switch governing cell chaining in Bacillus subtilis by protein instability. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlamakis, H.; Aguilar, C.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Control of cell fate by the formation of an architecturally complex bacterial community. Genome Res. 2008, 22, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinberg, N.; Keren-Paz, A.; Hou, Q.; Doron, S.; Yanuka-Golub, K.; Olender, T.; Hadar, R.; Rosenberg, G.; Jain, R.; Cámara-Almirón, J.; et al. The extracellular matrix protein TasA is a developmental cue that maintains a motile subpopulation within Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaaw8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, R.; Solomon, J.; Grossman, A.D. Biochemical and genetic characterization of a competence pheromone from B. subtilis. Cell 1994, 77, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauregard, P.B.; Chai, Y.; Vlamakis, H.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Bacillus subtilis biofilm induction by plant polysaccharides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1621–E1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Gestel, J.; Vlamakis, H.; Kolter, R. New Tools for Comparing Microscopy Images: Quantitative Analysis of Cell Types in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 197, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lazazzera, A.; Solomon, B.; Grossman, J.M.A.D. An Exported Peptide Functions Intracellularly to Contribute to Cell Density Signaling in B. subtilis. Cell 1997, 89, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thérien, M.; Kiesewalter, H.T.; Auria, E.; Charron-Lamoureux, V.; Wibowo, M.; Maróti, G.; Kovács, Á.T.; Beauregard, P.B. Surfactin production is not essential for pellicle and root-associated biofilm development of Bacillus subtilis. Biofilm 2020, 2, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.; Dworkin, J. Recent progress in Bacillus subtilis sporulation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujita, M.; González-Pastor, J.E.; Losick, R. High- and Low-Threshold Genes in the Spo0A Regulon of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazazzera, A.B. Quorum Sensing and starvation: signals for entry into stationary phase. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, A.; Trauth, S.; Ziesack, M.; Nagler, K.; Bergeest, J.-P.; Rohr, K.; Becker, N.; Höfer, T.; Bischofs, I.B. Phenotypic memory in Bacillus subtilis links dormancy entry and exit by a spore quantity-quality tradeoff. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasperotti, A.; Brameyer, S.; Fabiani, F.; Jung, K. Phenotypic heterogeneity of microbial populations under nutrient limitation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 62, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veening, J.W.; Stewart, E.J.; Berngruber, T.W.; Taddei, F.; Kuipers, O.P.; Hamoen, L.W. Bet-hedging and epigenetic inheritance in bacterial cell development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4393–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossman, A.D. Genetic Networks Controlling the Initiation of Sporulation and the Development of Genetic Competence in Bacillus Subtilis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1995, 29, 477–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, E.A.; Kolter, R. Extracellular signaling and multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Strain Name | Background | Genome Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis strains | |||
| PS-216 | PS-216 | wt | [55] |
| BM1127 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ | [47] |
| BM1128 | PS-216 | amyE::PspoIIQ-yfp (Sp) | this work |
| BM1129 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ amyE::PspoIIQ-yfp (Sp) | this work |
| BM1625 | PS-216 | amyE::PspoIIQ-yfp (Sp) sacA::P43-mKate2 (Cm) | this work |
| BM1626 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ amyE::PspoIIQ-yfp (Sp) sacA::P43-mKate2 (Cm) | this work |
| BM1613 | PS-216 | amyE::PtapA-yfp (Sp) sacA::P43-mKate2 (Cm) | this work |
| BM1614 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ amyE::PtapA-yfp (Sp) sacA::P43-mKate2 (Cm) | this work |
| BM1629 | PS-216 | sacA::P43-mKate2 (Kan) | this work |
| BM1630 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ sacA::P43-mKate2 (Kan) | this work |
| BM1631 | PS-216 | amyE::PepsA-gfp (Cm) sacA::P43-mKate2 (Kan) | this work |
| BM1622 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ amyE::PepsA-gfp (Cm) sacA::P43-mKate2 (Kan) | this work |
| DK1042 | NCIB 3610 | comIQ12L | [56] |
| BM1667 | NCIB 3610 | ΔcomQ comIQ12L | this work |
| BM1623 | NCIB 3610 | comIQ12L amyE::PepsA-gfp (Cm) | this work |
| BM1624 | NCIB 3610 | comIQ12L ΔcomQ amyE::PepsA-gfp (Cm) | this work |
| YC164 | NCIB 3610 | amyE::PepsA-gfp (Cm) | [37] |
| BM1103 | PS-216 | amyE::PepsA-gfp (Cm) | this work |
| BM1458 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ amyE::PepsA-gfp (Cm) | this work |
| BM1115 | PS-216 | amyE::PtapA-yfp (Sp) | [49] |
| BM1126 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ amyE::PtapA-yfp (Sp) | this work |
| BM1097 | PS-216 | amyE::Phyperspank-mKate2 (Cm) | [51] |
| BM1044 | PS-216 | srfA::Tn917 (mls) | [48] |
| BM1673 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ srfA::Tn917 (mls) | this work |
| DL722 | 3610 | amyE::PsrfAA-yfp (Sp) | [24] |
| BM1454 | PS-216 | amyE::PsrfAA-yfp (Sp) | this work |
| BM1455 | PS-216 | ΔcomQ amyE::PsrfAA-yfp (Sp) | this work |
| Escherichia coli strain | |||
| ED367 | BL-21 (DE3) | pET22(b)—comQ comX from B. subtilis 168 (Amp) | [57] |
| Plasmid Name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| pKM3 | amyE::PspoIIQ-yfp (Sp, Amp) | [50] |
| Pkm3-p43-yfp | amyE::P43-yfp (Sp, Amp) | [49] |
| pSac-Kan | sacA::kan (Amp) | [52] |
| pSac-Cm | sacA::cat (Amp) | [52] |
| pEM1071 | sacA::P43-yfp (Cm, Amp) | this work |
| pMS7 | sacA::P43-mKate2 (Cm, Amp) | this work |
| pMS17 | sacA::P43-mKate2 (Kan, Amp) | this work |
| pMiniMAD2-updowncomQ | pMiniMAD2 with updown comQ between EcoRI and SalI sites (Mls, Amp) | [47] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Špacapan, M.; Danevčič, T.; Štefanic, P.; Porter, M.; Stanley-Wall, N.R.; Mandic-Mulec, I. The ComX Quorum Sensing Peptide of Bacillus subtilis Affects Biofilm Formation Negatively and Sporulation Positively. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081131
Špacapan M, Danevčič T, Štefanic P, Porter M, Stanley-Wall NR, Mandic-Mulec I. The ComX Quorum Sensing Peptide of Bacillus subtilis Affects Biofilm Formation Negatively and Sporulation Positively. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(8):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081131
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠpacapan, Mihael, Tjaša Danevčič, Polonca Štefanic, Michael Porter, Nicola R. Stanley-Wall, and Ines Mandic-Mulec. 2020. "The ComX Quorum Sensing Peptide of Bacillus subtilis Affects Biofilm Formation Negatively and Sporulation Positively" Microorganisms 8, no. 8: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081131
APA StyleŠpacapan, M., Danevčič, T., Štefanic, P., Porter, M., Stanley-Wall, N. R., & Mandic-Mulec, I. (2020). The ComX Quorum Sensing Peptide of Bacillus subtilis Affects Biofilm Formation Negatively and Sporulation Positively. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081131







