Prothrombin Time, Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, and Fibrinogen Reference Intervals for Inbred Strain 13/N Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) and Validation of Low Volume Sample Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals
2.3. Blood Collection
2.4. PT/aPTT
2.5. Fibrinogen
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Reference Intervals for Strain 13/N Guinea Pigs
3.2. Validation of the Low Volume Collection Approach
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Prescott, J.B.; Marzi, A.; Safronetz, D.; Robertson, S.J.; Feldmann, H.; Best, S.M. Immunobiology of Ebola and Lassa virus infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, M.; Geisbert, T.W. Ebola virus: The role of macrophages and dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl-Jensen, V.; Kurz, S.; Feldmann, F.; Buehler, L.K.; Kindrachuk, J.; DeFilippis, V.; da Silva Correia, J.; Früh, K.; Kuhn, J.H.; Burton, D.R.; et al. Ebola virion attachment and entry into human macrophages profoundly effects early cellular gene expression. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ströher, U.; West, E.; Bugany, H.; Klenk, H.D.; Schnittler, H.J.; Feldmann, H. Infection and activation of monocytes by Marburg and Ebola viruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11025–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welch, S.R.; Ritter, J.M.; McElroy, A.K.; Harmon, J.R.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Scholte, F.E.M.; Kobinger, G.P.; Bergeron, É.; Zaki, S.R.; Nichol, S.T.; et al. Fluorescent Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus illuminates tissue tropism patterns and identifies early mononuclear phagocytic cell targets in IFNAR-/- mice. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basler, C.F. Molecular pathogenesis of viral hemorrhagic fever. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher-Hoch, S.; McCormick, J.B.; Sasso, D.; Craven, R.B. Hematologic dysfunction in Lassa fever. J. Med. Virol. 1988, 26, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, B.H.; Dodd, K.A.; Erickson, B.R.; Albariño, C.G.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; McMullan, L.K.; Bergeron, E.; Ströeher, U.; Cannon, D.; Martin, B.; et al. Severe hemorrhagic fever in strain 13/N guinea pigs infected with Lujo virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahrling, P.B.; Frame, J.D.; Smith, S.B.; Monson, M.H. Endemic lassa fever in liberia. iii. characterization of lassa virus isolates. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 79, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgriff, T.M.; Jahrling, P.B.; Chen, J.P.; Hodgson, L.A.; Lewis, R.M.; Green, D.E.; Smith, J.I.; Jahrung, P.B.; Chen, J.P.; Hodgson, L.A.; et al. Studies of the coagulation system in arenaviral hemorrhagic fever: Experimental infection of strain 13 guinea pigs with Pichinde virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1987, 36, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronetz, D.; Strong, J.E.; Feldmann, F.; Haddock, E.; Sogoba, N.; Brining, D.; Geisbert, T.W.; Scott, D.P.; Feldmann, H. A recently isolated Lassa virus from Mali demonstrates atypical clinical disease manifestations and decreased virulence in cynomolgus macaques. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welch, S.R.; Scholte, F.E.M.; Albariño, C.G.; Kainulainen, M.H.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Wiggleton Guerrero, L.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Klena, J.D.; Nichol, S.T.; Spengler, J.R.; et al. The S genome segment is sufficient to maintain pathogenicity in intra-clade Lassa virus reassortants in a guinea pig model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, K.A.; Smith, M.A.; Twenhafel, N.A.; Larson, R.A.; Jones, K.F.; Allen, R.D.; Dai, D.; Chinsangaram, J.; Bolken, T.C.; Hruby, D.E.; et al. Evaluation of Lassa antiviral compound ST-193 in a guinea pig model. Antiviral Res. 2011, 90, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushko, P.; Geisbert, J.; Parker, M.; Jahrling, P.; Smith, J. Individual and bivalent vaccines based on alphavirus replicons protect guinea pigs against infection with Lassa and Ebola viruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11677–11685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cashman, K.A.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Wollen, S.E.; Shamblin, J.D.; Zelko, J.M.; Bearss, J.J.; Zeng, X.; Broderick, K.E.; Schmaljohn, C.S. DNA vaccines elicit durable protective immunity against individual or simultaneous infections with Lassa and Ebola viruses in guinea pigs. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, M.H.; Spengler, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Harmon, J.R.; Klena, J.D.; Nichol, S.T.; Albariño, C.G.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Use of a Scalable Replicon-Particle Vaccine to Protect Against Lethal Lassa Virus Infection in the Guinea Pig Model. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, M.H.; Spengler, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Harmon, J.R.; Scholte, F.E.M.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Nichol, S.T.; Albariño, C.G.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Protection from lethal Lassa disease can be achieved both before and after virus exposure by administration of single-cycle replicating Lassa virus replicon particles. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ye, C.; Cheng, B.; Nogales, A.; Iwasaki, M.; Yu, S.; Cooper, K.; Liu, D.X.; Hart, R.; Adams, R.; et al. A Lassa Fever Live-Attenuated Vaccine Based on Codon Deoptimization of the Viral Glycoprotein Gene. MBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genzer, S.C.; Huynh, T.; Coleman-Mccray, J.D.; Harmon, J.R.; Welch, S.R.; Spengler, J.R. Hematology and Clinical Chemistry Reference Intervals for Inbred Strain 13/n Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2019, 58, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargaden, M.; Singer, L. Anatomy, physiology, and behavior. In The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents; Suckow, M., Stevens, K., Wilson, R., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 575–602. [Google Scholar]
- Quesenberry, K.; Donnelly, T.; Mans, C. Biology, husbandry, and clinical techniques of guinea pigs and chinchillas. In Ferrets, Rabbits, and Rodents; Quesenberry, K., Carpenter, J., Eds.; Saunders: St Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 279–294. [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt, C.E.; Brainard, B.M. Point of Care Assessment of Coagulation. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2016, 31, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasseville, V.G.; Hotchkiss, C.E.; Levesque, P.C.; Mankowski, J.L. Hematopoietic, Cardiovascular, Lymphoid and Mononuclear Phagocyte Systems of Nonhuman Primates. In Nohuman Primates in Biomedical Research (Volume 2: Diseases); Abee, C.R., Mansfield, K., Tardif, S., Morris, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 365. ISBN 9780123813664. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, M.; Schnaars, H.A.; Sibley, J.R.; Honor, D.J. Determination of plasma fibrinogen concentrations in beagle dogs, cynomolgus monkeys, New Zealand white rabbits, and Sprague-Dawley rats by using Clauss and prothrombin-time-derived assays. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adcock, D.M.; Kressin, D.C.; Marlar, R.A. Minimum specimen volume requirements for routine coagulation testing: Dependence on citrate concentration. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 109, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, J.; Sadler, M.A.; Witt, D.M. Impact of evacuated collection tube fill volume and mixing on routine coagulation testing using 2.5-mL (pediatric) tubes. Chest 2004, 126, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adcock, D.M. Collection, Transport, and Processing of Blood Specimens for Testing Plasma-Based Coagulation Assays and Molecular Hemostasis Assays: Approved Guideline, 5th ed; CLSI Document H21-A5; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Annapolis Junction, MD, USA; Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/hematology/documents/h21/ (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- Ebihara, H.; Zivcec, M.; Gardner, D.; Falzarano, D.; LaCasse, R.; Rosenke, R.; Long, D.; Haddock, E.; Fischer, E.; Kawaoka, Y.; et al. A Syrian golden hamster model recapitulating ebola hemorrhagic fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Safronetz, D.; Zivcec, M.; Lacasse, R.; Feldmann, F.; Rosenke, R.; Long, D.; Haddock, E.; Brining, D.; Gardner, D.; Feldmann, H.; et al. Pathogenesis and host response in Syrian hamsters following intranasal infection with Andes virus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, Y.-P.; Flick, M.J. Fibrinogen Is at the Interface of Host Defense and Pathogen Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaee, F.; Maas, A.; De Maat, M.P.M.; Verheijen, J.H.; Koopman, J. Effect of genetic background and diet on plasma fibrinogen in mice. Possible relation with susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2002, 164, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.; He, S.; Wei, H.; Kroeker, A.; Audet, J.; Leung, A.; Cutts, T.; Graham, J.; Kobasa, D.; Embury-Hyatt, C.; et al. Development and characterization of a guinea pig-adapted Sudan virus. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendenhall, M.; Russell, A.; Smee, D.F.; Hall, J.O.; Skirpstunas, R.; Furuta, Y.; Gowen, B.B. Effective oral favipiravir (T-705) therapy initiated after the onset of clinical disease in a model of arenavirus hemorrhagic fever. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, R.W.; Fenton, K.A.; Geisbert, J.B.; Ebihara, H.; Mire, C.E.; Geisbert, T.W. Comparison of the Pathogenesis of the Angola and Ravn Strains of Marburg Virus in the Outbred Guinea Pig Model. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, S258–S270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shifflett, K.; Marzi, A. Marburg virus pathogenesis-differences and similarities in humans and animal models. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahrling, P.B.; Smith, S.; Hesse, R.A.; Rhoderick, J.B. Pathogenesis of Lassa virus infection in guinea pigs. Infect. Immun. 1982, 37, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahrling, P.B. Protection of Lassa virus-infected guinea pigs with Lassa-immune plasma of guinea pig, primate, and human origin. J. Med. Virol. 1983, 12, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.T.; Jahrling, P.B.; Peters, C.J. Evidence for the involvement of sulfidopeptide leukotrienes in the pathogenesis of Pichinde virus infection in strain 13 guinea pigs. Prostaglandins. Leukot. Med. 1986, 24, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, R.H.; Green, D.E.; Maiztegui, J.I.; Peters, C.J. Viral strain dependent differences in experimental argentine hemorrhagic fever (Junin virus) infection of guinea pigs. Intervirology 1988, 29, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, W.C.; Geisbert, T.W.; Huggins, J.W.; Jahrling, P.B. Experimental infection of guinea pigs with Venezuelan hemorrhagic fever virus (Guanarito): A model of human disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 55, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Martin, B.E.; Nichol, S.T.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; Bird, B. Utility of oral swab sampling for Ebola virus detection in guinea pig model. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitagaki, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Sakurada, K.; Suwa, T.; Sasa, H. Age-related changes in haematology and serum chemistry of Weiser-Maples guineapigs (Cavia porcellus). Lab. Anim. 2005, 39, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, J.P.; Krigman, M.R. Selected procoagulants in the guinea pig. Am. J. Physiol. 1970, 218, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspareit, J.; Messow, C.; Edel, J. Blood coagulation studies in guineapigs (Cavia porcellus). Lab. Anim. 1988, 22, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. Clinical pathology of laboratory animals. In Animal Models in Toxicology; Gad, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; p. 819. [Google Scholar]
- Kopić, A.; Benamara, K.; Schuster, M.; Leidenmühler, P.; Bauer, A.; Glantschnig, H.; Höllriegl, W. Coagulation phenotype of wild-type mice on different genetic backgrounds. Lab. Anim. 2019, 53, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurata, M.; Sasayama, Y.; Yamasaki, N.; Kitazawa, I.; Hamada, Y.; Horii, I. Mechanism for shortening PT and APTT in dogs and rats--effect of fibrinogen on PT and APTT--. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 28, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Washington, I.M.; Hoosier, G. Van Clinical Biochemistry and Hematology. In The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents; Suckow, M.A., Stevens, K.A., Wilson, R.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 57–116. ISBN 9780123809209. [Google Scholar]
- Khokhlova, O.N.; Tukhovskaya, E.A.; Kravchenko, I.N.; Sadovnikova, E.S.; Pakhomova, I.A.; Kalabina, E.A.; Lobanov, A.V.; Shaykhutdinova, E.R.; Ismailova, A.M.; Murashev, A.N. Using Tiletamine-Zolazepam-Xylazine Anesthesia Compared to CO(2)-inhalation for Terminal Clinical Chemistry, Hematology, and Coagulation Analysis in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2017, 84, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, L.L.; Cheever, E.M.; Ellis, H.R.; Magnani, P.A.; Svenson, K.L.; Von Smith, R.; Bogue, M.A. Large-scale, high-throughput screening for coagulation and hematologic phenotypes in mice. Physiol. Genomics 2002, 11, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemini, C.; Jaimez, R.; Franco, Y. Gender and inter-species influence on coagulation tests of rats and mice. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.; Anderson, L.; Otto, G.; Pritchett-Corning, K.; Whary, M. (Eds.) Laboratory Animal Medicine, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9780124095274. [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle, R.F. Step-by-step evolution of vertebrate blood coagulation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2009, 74, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Doolittle, R.F. The evolution of vertebrate blood coagulation as viewed from a comparison of puffer fish and sea squirt genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7527–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doolittle, R.F. The structure and evolution of vertebrate fibrinogen: A comparison of the lamprey and mammalian proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1990, 281, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Adcock Funk, D.M.; Lippi, G. Pre-analytical Variables in Coagulation Testing Associated With Diagnostic Errors in Hemostasis. Lab. Med. 2012, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
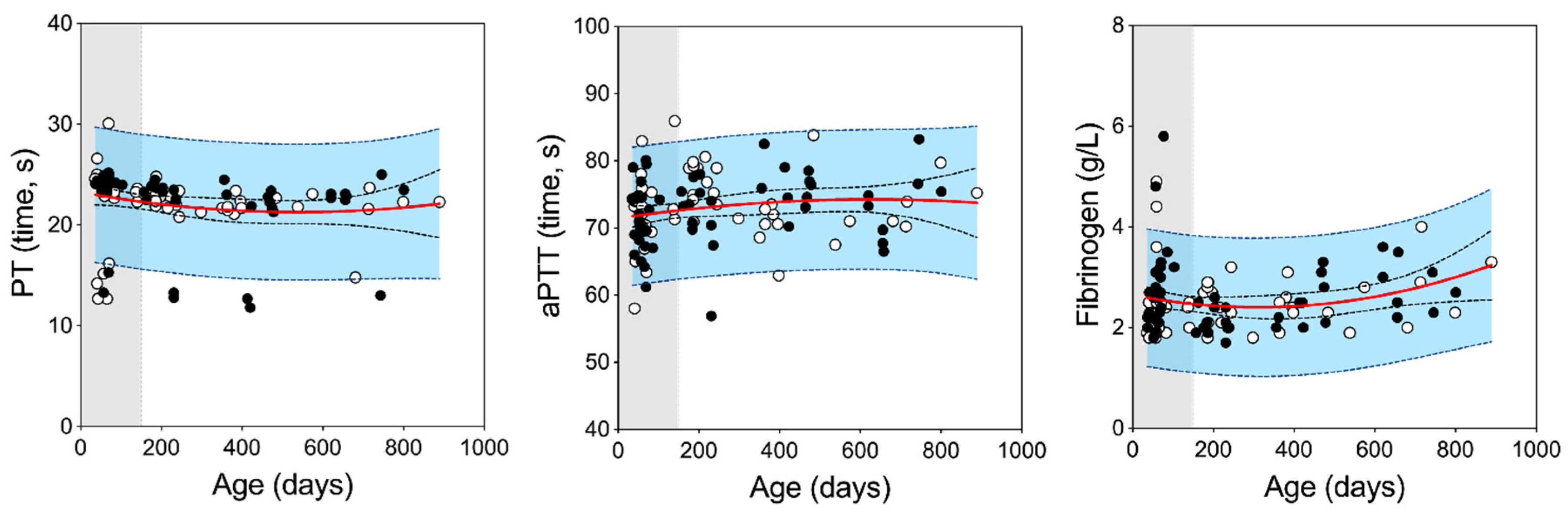
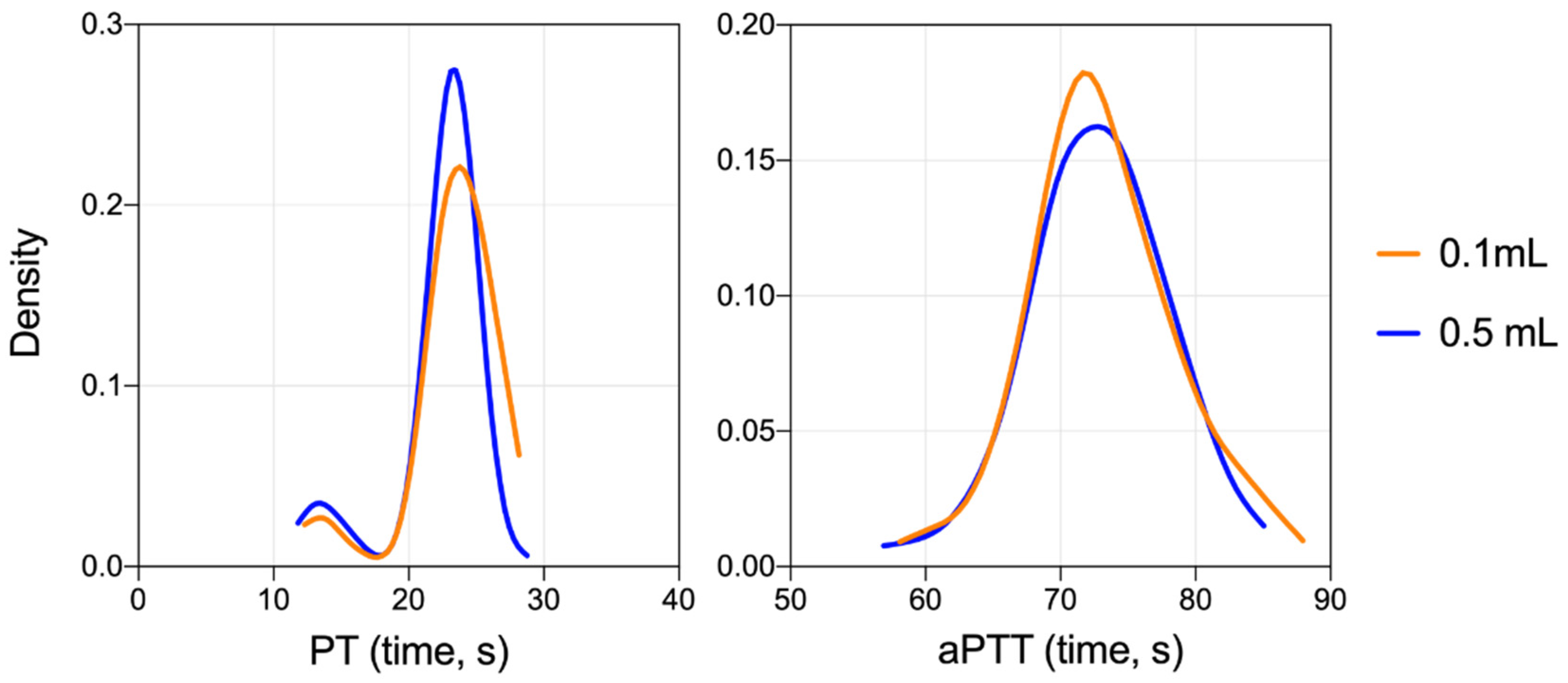
| Juvenile (Age ≤150 days) | ||||||||
| Analyte (unit) | n | Mean | SD | LRR | URR | Median | LIQ | UIQ |
| Female | ||||||||
| PT (time, s) | 25 | 22.66 | 4.30 | 14.24 | 31.09 | 23.6 | 23.1 | 24.7 |
| aPTT (time, s) | 23 | 72.03 | 4.94 | 62.35 | 81.70 | 72.1 | 70.2 | 74.7 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 25 | 2.45 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 3.97 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 2.5 |
| Male | ||||||||
| PT (time, s) | 26 | 23.07 | 3.07 | 17.05 | 29.10 | 24.1 | 23.5 | 24.2 |
| aPTT (time, s) | 26 | 70.71 | 4.96 | 60.98 | 80.44 | 69.8 | 67.3 | 74.2 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 27 | 2.75 | 0.88 | 1.03 | 4.47 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 3.1 |
| Adult (Age 151–900 days) | ||||||||
| Analyte (unit) | n | Mean | SD | LRR | URR | Median | LIQ | UIQ |
| Female | ||||||||
| PT (time, s) | 28 | 22.10 | 1.69 | 18.79 | 25.42 | 22.3 | 21.7 | 23.0 |
| aPTT (time, s) | 28 | 74.16 | 4.67 | 65.01 | 83.31 | 73.7 | 71.0 | 78.9 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 27 | 2.52 | 0.53 | 1.49 | 3.55 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.9 |
| Male | ||||||||
| PT (time, s) | 31 | 21.44 | 3.97 | 13.65 | 29.22 | 22.9 | 21.9 | 23.5 |
| aPTT (time, s) | 31 | 73.50 | 5.18 | 63.34 | 83.66 | 74.5 | 70.2 | 76.6 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 28 | 2.46 | 0.51 | 1.47 | 3.46 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.8 |
| Variable | Group | Mean Diff | SD Diff | n | t-Stat | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | All | 0.99 | 4.56 | 108 | 2.26 | 0.026 |
| Juveniles | 1.79 | 4.83 | 50 | 2.62 | 0.012 | |
| Adults | 0.30 | 4.24 | 58 | 0.55 | 0.588 | |
| Females | 0.66 | 4.23 | 52 | 1.12 | 0.269 | |
| Males | 1.30 | 4.87 | 56 | 2.00 | 0.050 | |
| aPTT | All | 0.82 | 9.18 | 106 | 0.92 | 0.360 |
| Juveniles | 2.16 | 6.60 | 48 | 2.27 | 0.028 | |
| Adults | −0.29 | 10.80 | 58 | −0.21 | 0.838 | |
| Females | 0.32 | 6.51 | 50 | 0.35 | 0.728 | |
| Males | 1.26 | 11.08 | 56 | 0.85 | 0.397 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Condrey, J.A.; Flietstra, T.; Nestor, K.M.; Schlosser, E.L.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Genzer, S.C.; Welch, S.R.; Spengler, J.R. Prothrombin Time, Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, and Fibrinogen Reference Intervals for Inbred Strain 13/N Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) and Validation of Low Volume Sample Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081127
Condrey JA, Flietstra T, Nestor KM, Schlosser EL, Coleman-McCray JD, Genzer SC, Welch SR, Spengler JR. Prothrombin Time, Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, and Fibrinogen Reference Intervals for Inbred Strain 13/N Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) and Validation of Low Volume Sample Analysis. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(8):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081127
Chicago/Turabian StyleCondrey, Jillian A., Timothy Flietstra, Kaitlyn M. Nestor, Elizabeth L. Schlosser, JoAnn D. Coleman-McCray, Sarah C. Genzer, Stephen R. Welch, and Jessica R. Spengler. 2020. "Prothrombin Time, Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, and Fibrinogen Reference Intervals for Inbred Strain 13/N Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) and Validation of Low Volume Sample Analysis" Microorganisms 8, no. 8: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081127
APA StyleCondrey, J. A., Flietstra, T., Nestor, K. M., Schlosser, E. L., Coleman-McCray, J. D., Genzer, S. C., Welch, S. R., & Spengler, J. R. (2020). Prothrombin Time, Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, and Fibrinogen Reference Intervals for Inbred Strain 13/N Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus) and Validation of Low Volume Sample Analysis. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081127





