MG-MLST: Characterizing the Microbiome at the Strain Level in Metagenomic Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. STRUCTURE Running Parameters
2.2. Selecting Representatives of Population Groups for the “Learning Sample” Set
2.3. Building Simulated Microbial Communities
2.4. Sample Preparation and 454 Sequencing
2.5. Metagenomic Shotgun MLST Data
2.6. Building Microbiome Allelic Profiles
2.7. MetaMLST Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Combination of MLST and STRUCTURE for Strain Identification and Quantification
3.2. Selection of “Learning Sample” Set
3.3. Using STRUCTURE to Determine Strain-Level Composition on Simulated Microbiome Data
3.4. Using MG-MLST to Determine Strain-Level Composition in MLST Amplicon Sequencing Data of Clinical Samples
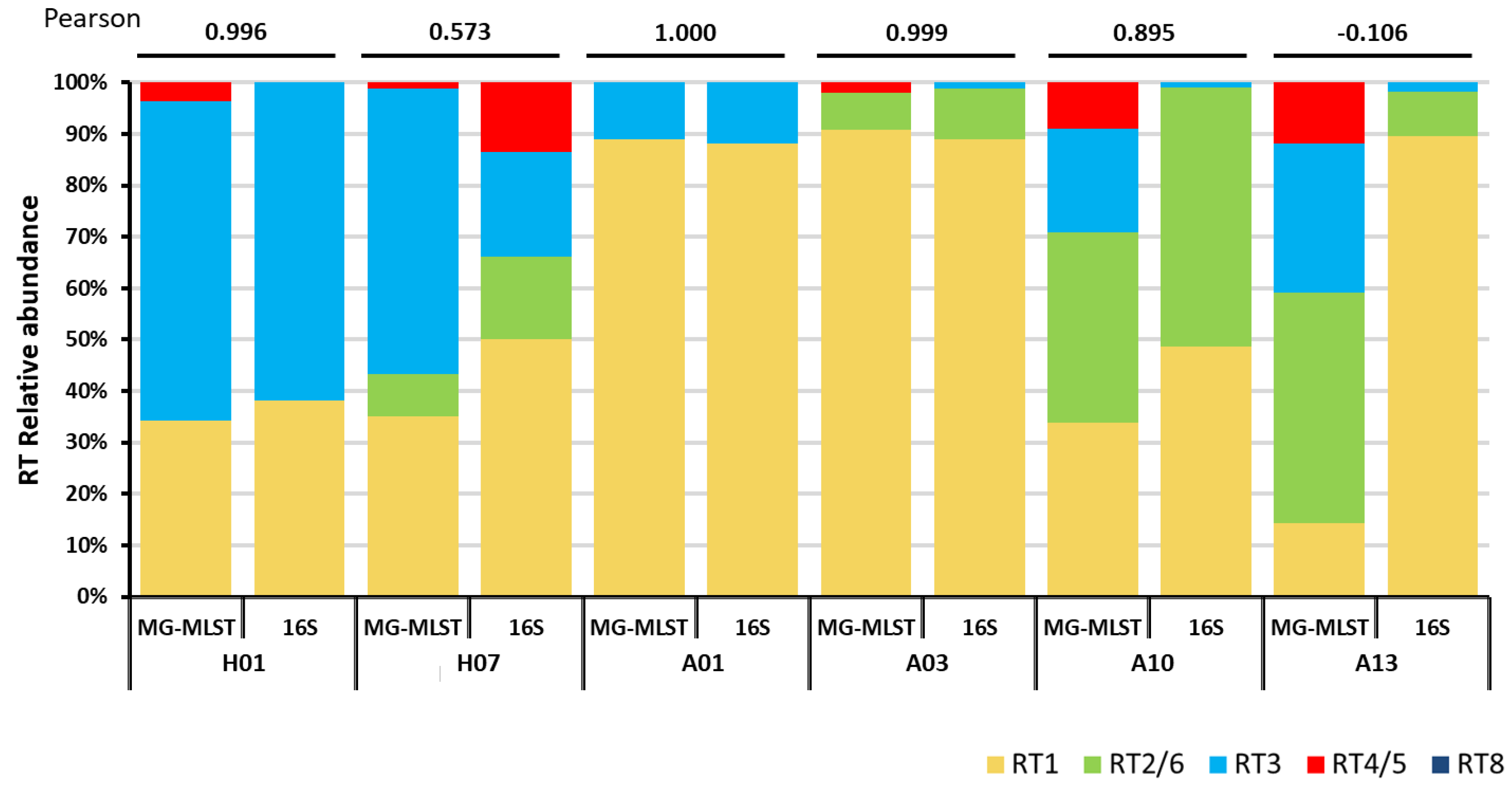
3.5. Using MG-MLST to Determine Strain-Level Composition in Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing Data of Clinical Samples
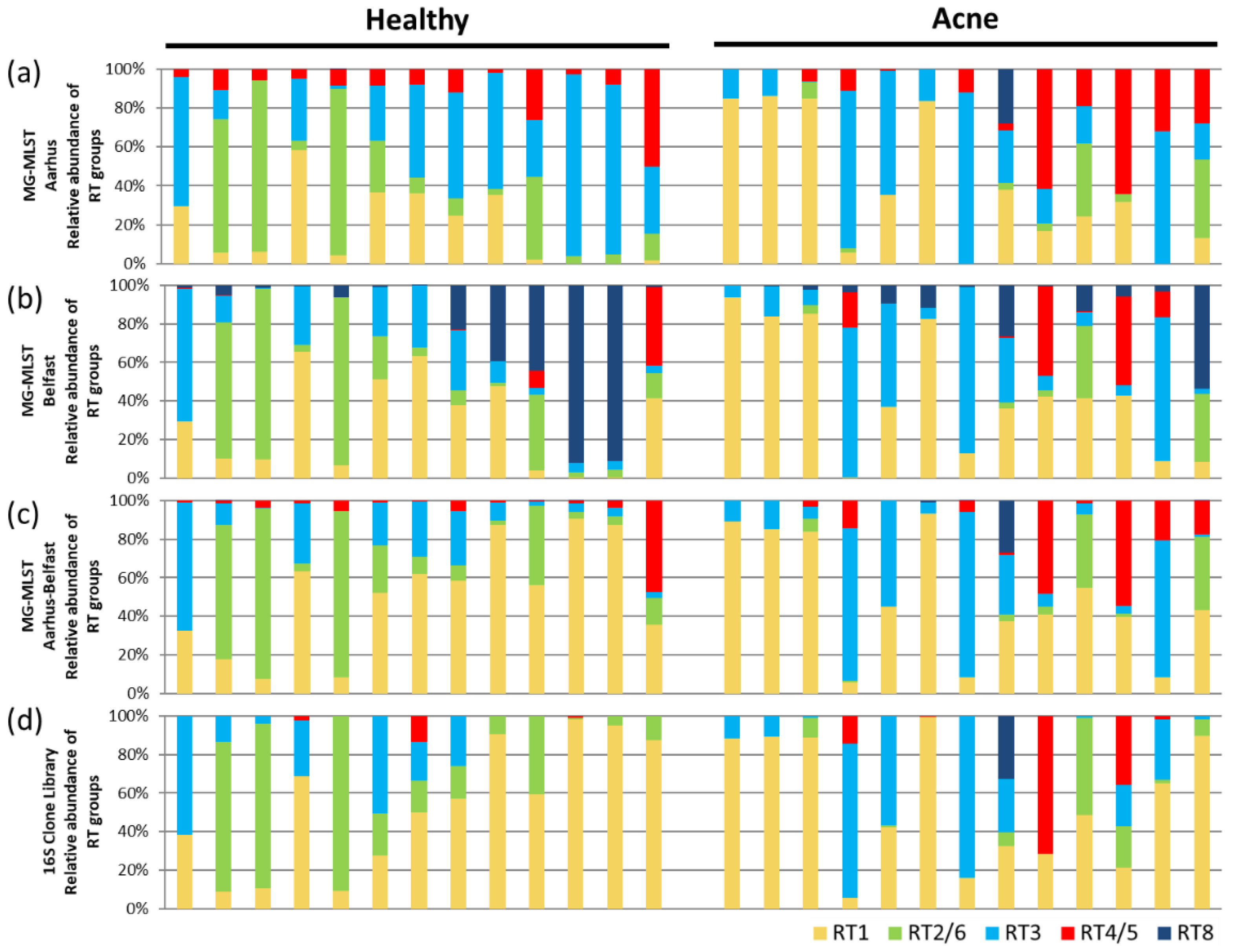
3.6. Using MG-MLST to Study Strain-Level Differences in the Skin Microbiome between Acne Patients and Healthy Individuals
3.7. Comparison between MG-MLST and MetaMLST
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruis, W.; Fric, P.; Pokrotnieks, J.; Lukás, M.; Fixa, B.; Kascák, M.; Kamm, M.A.; Weismueller, J.; Beglinger, C.; Stolte, M.; et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 2004, 53, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, P.I.; Gordon, C.A.; Chandler, W.L. Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolyticuraemic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Lomholt, H.B.; Kilian, M. Population genetic analysis of Propionibacterium acnes identifies a subpopulation and epidemic clones associated with acne. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, A.; Barnard, E.; Nagy, I.; Gao, A.; Tomida, S.; Li, H.; Eady, A.; Cove, J.; Nord, C.E.; Patrick, S. An expanded multilocus sequence typing scheme for propionibacterium acnes: Investigation of “pathogenic”, “commensal” and antibiotic resistant strains. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitz-Gibbon, S.; Tomida, S.; Chiu, B.-H.; Nguyen, L.; Du, C.; Liu, M.; Elashoff, D.; Erfe, M.C.; Loncaric, A.; Kim, J.; et al. Propionibacterium acnes strain populations in the human skin microbiome associated with acne. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2152–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloissnig, S.; Arumugam, M.; Sunagawa, S.; Mitreva, M.; Tap, J.; Zhu, A.; Waller, A.; Mende, D.R.; Kultima, J.R.; Martin, J.; et al. Genomic variation landscape of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2013, 493, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, M.C.; Bygraves, J.A.; Feil, E.; Morelli, G.; Russell, J.E.; Urwin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zurth, K.; Caugant, D.A.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing: A portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3140–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfo, M.; Tett, A.; Jousson, O.; Donati, C.; Segata, N. MetaMLST: Multi-locus strain-level bacterial typing from metagenomic samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Falush, D.; Wirth, T.; Linz, B.; Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Kidd, M.; Blaser, M.J.; Graham, D.Y.; Vacher, S.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; et al. Traces of human migrations in Helicobacter pylori populations. Science 2003, 299, 1582–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubisz, M.J.; Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomida, S.; Nguyen, L.; Chiu, B.-H.; Liu, J.; Sodergren, E.; Weinstock, G.M.; Li, H. Pan-genome and comparative genome analyses of propionibacterium acnes reveal its genomic diversity in the healthy and diseased human skin microbiome. mBio 2013, 4, e00003–e00013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasimatis, G.; Fitz-Gibbon, S.; Tomida, S.; Wong, M.; Li, H. Analysis of complete genomes of Propionibacterium acnes reveals a novel plasmid and increased pseudogenes in an acne associated strain. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 918320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, E.; Shi, B.; Kang, D.; Craft, N.; Li, H. The balance of metagenomic elements shapes the skin microbiome in acne and health. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittl, S.; Heckel, G.; Korczak, B.M.; Kuhnert, P. Source attribution of human Campylobacter isolates by MLST and fla-typing and association of genotypes with quinolone resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Liljander, A.; Kaspar, H.; Muriuki, C.; Fuxelius, H.-H.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E.; de Villiers, E.P.; Huber, C.A.; Frey, J.; Daubenberger, C.; et al. Camel Streptococcus agalactiae populations are associated with specific disease complexes and acquired the tetracycline resistance gene tetM via a Tn916-like element. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kodaman, N.; Pazos, A.; Schneider, B.G.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Mera, R.; Sobota, R.S.; Sicinschi, L.A.; Shaffer, C.L.; Romero-Gallo, J.; de Sablet, T.; et al. Human and Helicobacter pylori coevolution shapes the risk of gastric disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, A.; Gao, A.; Barnard, E.; Fink, C.; Murray, P.I.; Dowson, C.G.; Nagy, I.; Lambert, P.A.; Patrick, S. A novel multilocus sequence typing scheme for the opportunistic pathogen Propionibacterium acnes and characterization of type I cell surface-associated antigens. Microbiol. Read. Engl. 2011, 157, 1990–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, A.; Nagy, I.; Magyari, M.; Barnard, E.; Patrick, S. The opportunistic pathogen Propionibacterium acnes: Insights into typing, human disease, clonal diversification and CAMP factor evolution. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, M.; Scholz, C.F.P.; Lomholt, H.B. Multilocus sequence typing and phylogenetic analysis of Propionibacterium acnes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, C.F.P.; Jensen, A.; Lomholt, H.B.; Brüggemann, H.; Kilian, M. A novel high-resolution single locus sequence typing scheme for mixed populations of Propionibacterium acnes in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraal, L.; Abubucker, S.; Kota, K.; Fischbach, M.A.; Mitreva, M. The prevalence of species and strains in the human microbiome: A resource for experimental efforts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, T.-H.; Chai, J.; Pan, C. Sigma: Strain-level inference of genomes from metagenomic analysis for biosurveillance. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, O.E.; Bendall, M.; Manimaran, S.; Hong, C.; Clement, N.L.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Snell, Q.; Schaalje, G.B.; Clement, M.J.; Crandall, K.A.; et al. Pathoscope: Species identification and strain attribution with unassembled sequencing data. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Waldron, L.; Ballarini, A.; Narasimhan, V.; Jousson, O.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic microbial community profiling using unique clade-specific marker genes. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | MG-MLST | MetaMLST | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence Type (ST) Assigned | Ribotype (RT) Assigned | Relative Abundance of RT | Sequence Type (ST) Assigned | Ribotype (RT) Assigned | |
| H01 | 6,7,25,27,28,30 | 2/6 | 0.869 | 7 | 6 |
| H02 | 6,7,25,27,28,30 | 2/6 | 0.704 | 30 | 2 |
| H03 | 6,7,25,27,28,30 | 2/6 | 0.886 | 100 | New |
| H04 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.656 | New | New |
| H05 | 2 | 3 | 0.691 | 2 | 3 |
| H06 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.511 | 5 | 1 |
| H07 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.634 | New | New |
| H08 | 1,5 | 1 3 | 0.378 0.316 | New | New |
| H09 | 1,5 | 1 8 | 0.477 0.395 | 4 | 8 |
| H10 | 4,13,21 | 8 2/6 | 0.443 0.393 | New | New |
| H11 | 4,13,21 | 8 | 0.922 | 4 | 8 |
| H12 | 4,13,21 | 8 | 0.912 | 4 | 8 |
| H13 | 1,5 | 1 4/5 | 0.414 0.409 | 115 | 1 |
| A01 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.935 | 1 | 1 |
| A02 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.840 | New | New |
| A03 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.851 | 53 | New |
| A04 | 2,22,23,24,36,91 | 3 | 0.779 | 2 | 3 |
| A05 | 2 | 3 | 0.537 | New | New |
| A06 | 1,5 | 1 | 0.825 | New | New |
| A07 | 2 | 3 | 0.862 | New | New |
| A08 | 6,7,25,27,28,30 | 1 | 0.360 | New | New |
| A09 | 3,10,11,17,70 | 4/5 1 | 0.468 0.423 | New | New |
| A10 | 1,5 | 1 2/6 | 0.414 0.377 | New | New |
| A11 | 3,10,11,17,70 | 4/5 1 | 0.460 0.426 | New | New |
| A12 | 2,22,23,24,36,91 | 3 | 0.747 | 22 | 3 |
| A13 | 4,13,21 | 8 | 0.538 | New | New |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bangayan, N.J.; Shi, B.; Trinh, J.; Barnard, E.; Kasimatis, G.; Curd, E.; Li, H. MG-MLST: Characterizing the Microbiome at the Strain Level in Metagenomic Data. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050684
Bangayan NJ, Shi B, Trinh J, Barnard E, Kasimatis G, Curd E, Li H. MG-MLST: Characterizing the Microbiome at the Strain Level in Metagenomic Data. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(5):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050684
Chicago/Turabian StyleBangayan, Nathanael J., Baochen Shi, Jerry Trinh, Emma Barnard, Gabriela Kasimatis, Emily Curd, and Huiying Li. 2020. "MG-MLST: Characterizing the Microbiome at the Strain Level in Metagenomic Data" Microorganisms 8, no. 5: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050684
APA StyleBangayan, N. J., Shi, B., Trinh, J., Barnard, E., Kasimatis, G., Curd, E., & Li, H. (2020). MG-MLST: Characterizing the Microbiome at the Strain Level in Metagenomic Data. Microorganisms, 8(5), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050684






