New Insights into the Microbial Degradation of D-Cyphenothrin in Contaminated Water/Soil Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Medium
2.2. Isolation and Identification of D-Cyphenothrin-Degrading Bacterial Isolates
2.3. Optimization of Conditions for D-Cyphenothrin Degradation
2.4. Substrate Range of Strain HLJ-10 and Concentration Range of D-Cyphenothrin
2.5. Identification of Intermediate Metabolites of D-Cyphenothrin
2.6. Biodegradation of D-Cyphenothrin in Soils
2.7. Extraction method of D-Cyphenothrin
2.8. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
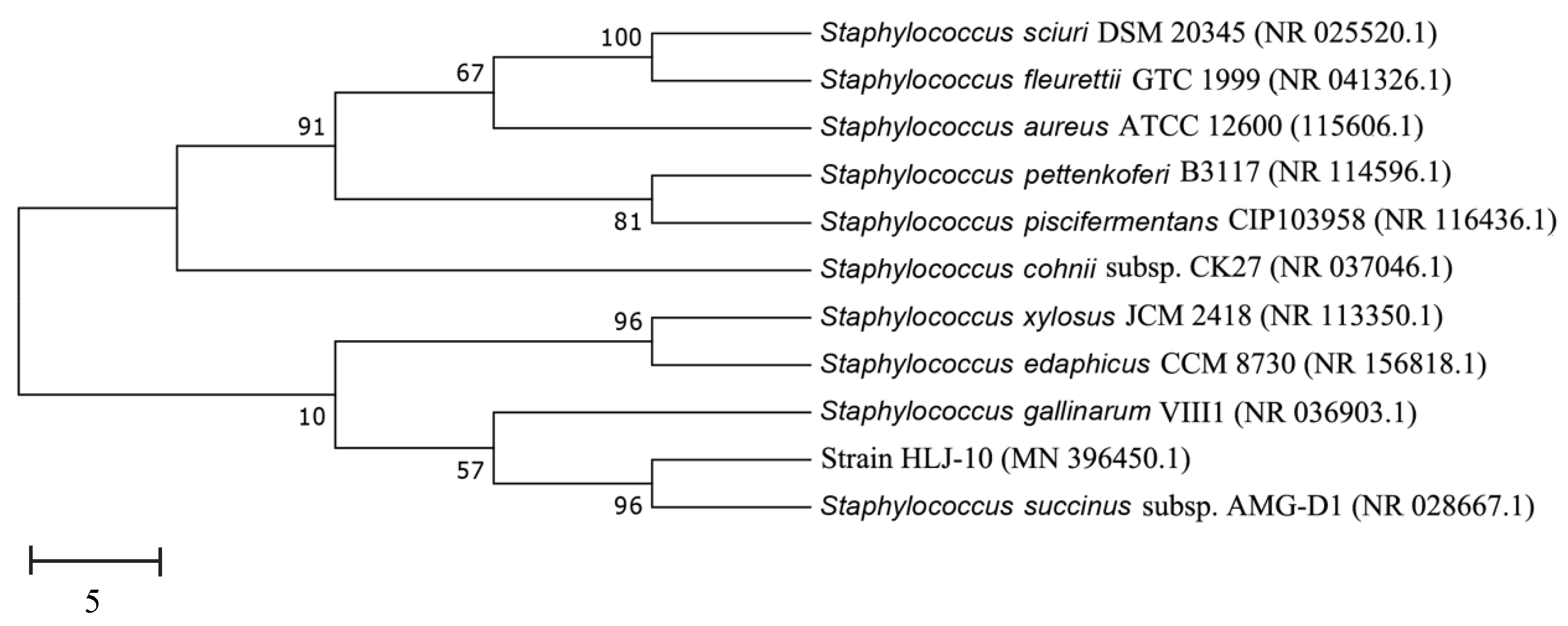
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of Strain HLJ-10
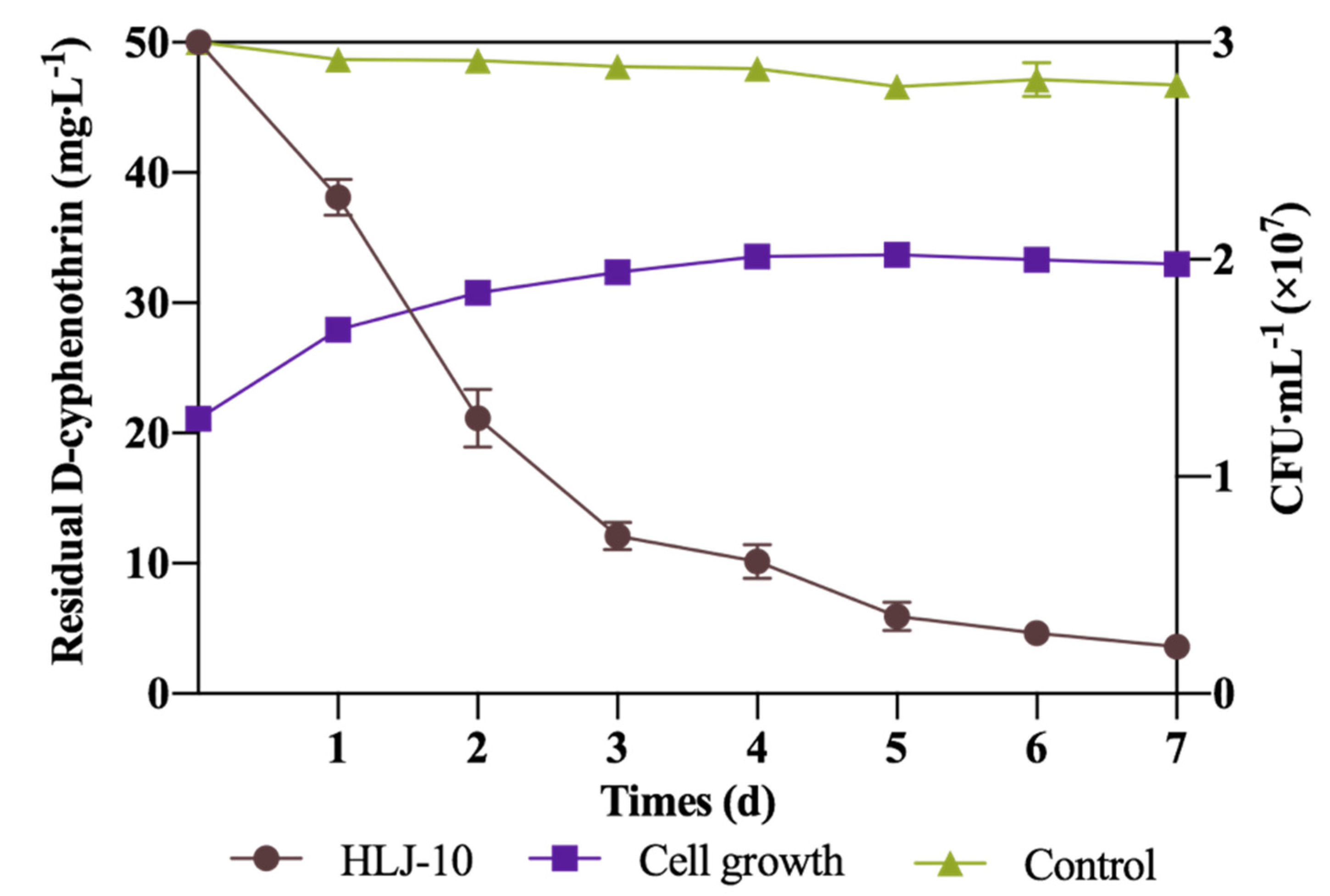
3.2. Growth of Isolate and Kinetic Analysis of Degradation Process
3.3. Optimization of D-Cyphenothrin Degradation Conditions
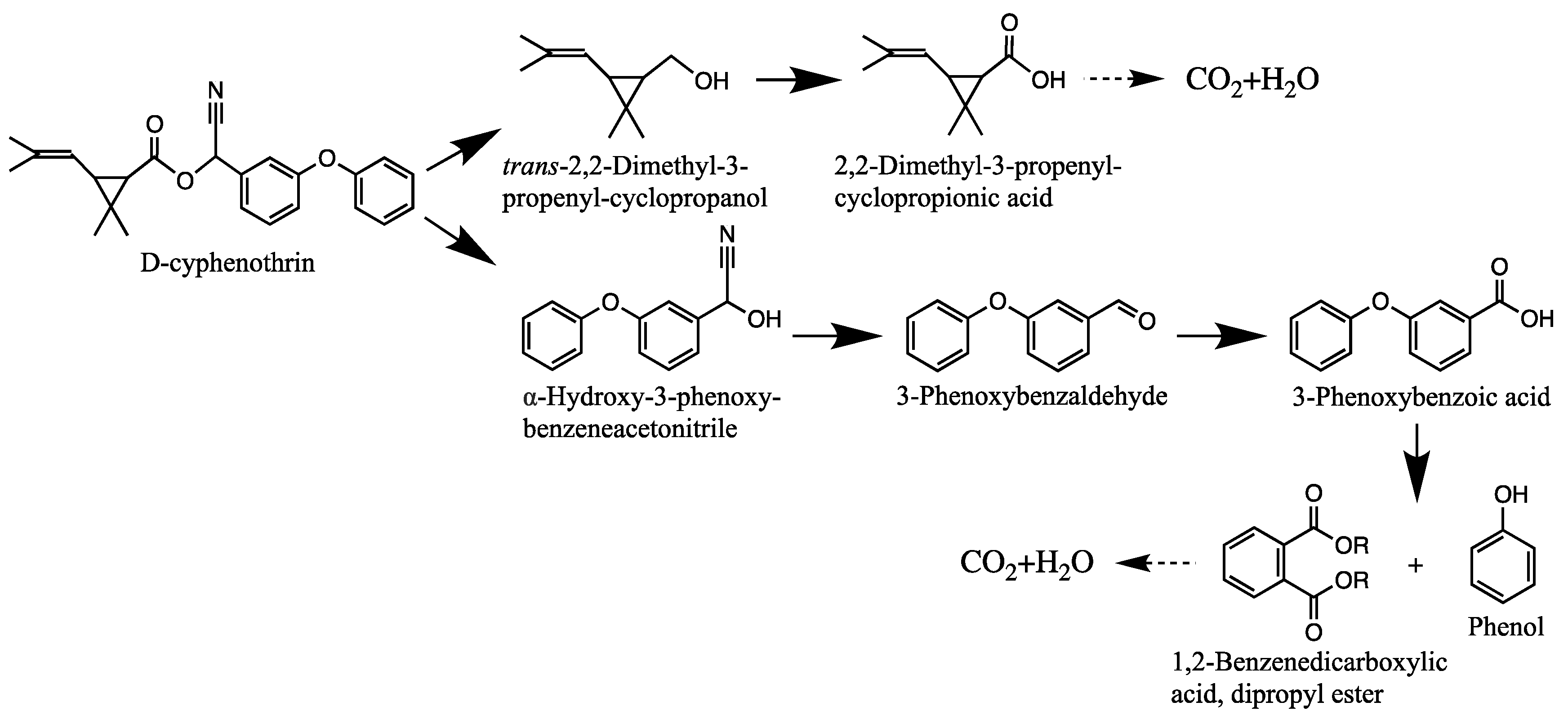
3.4. Degradation Products and Degradation Pathway of D-Cyphenothrin
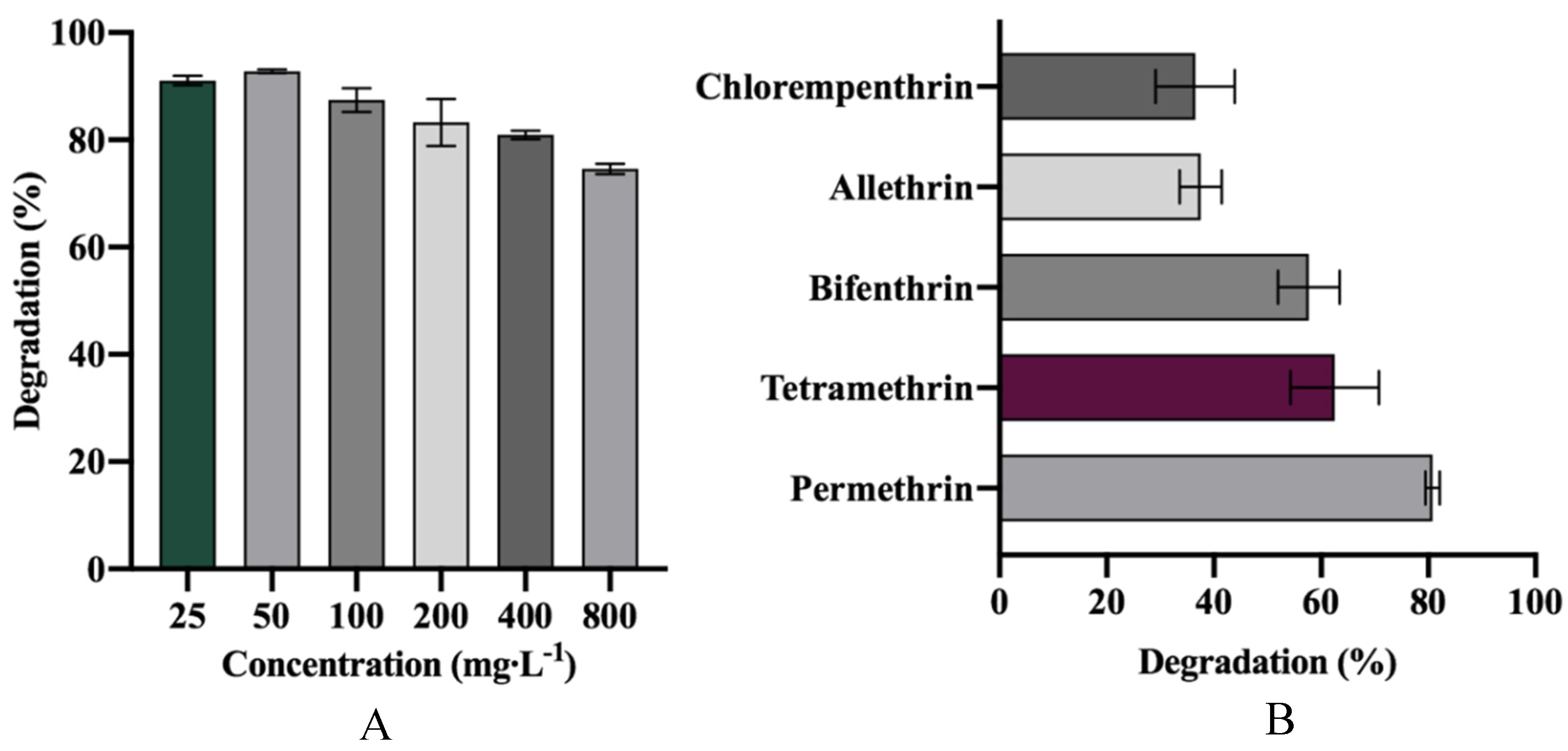
3.5. Degradation of Various SPs and Different Concentrations of D-Cyphenothrin
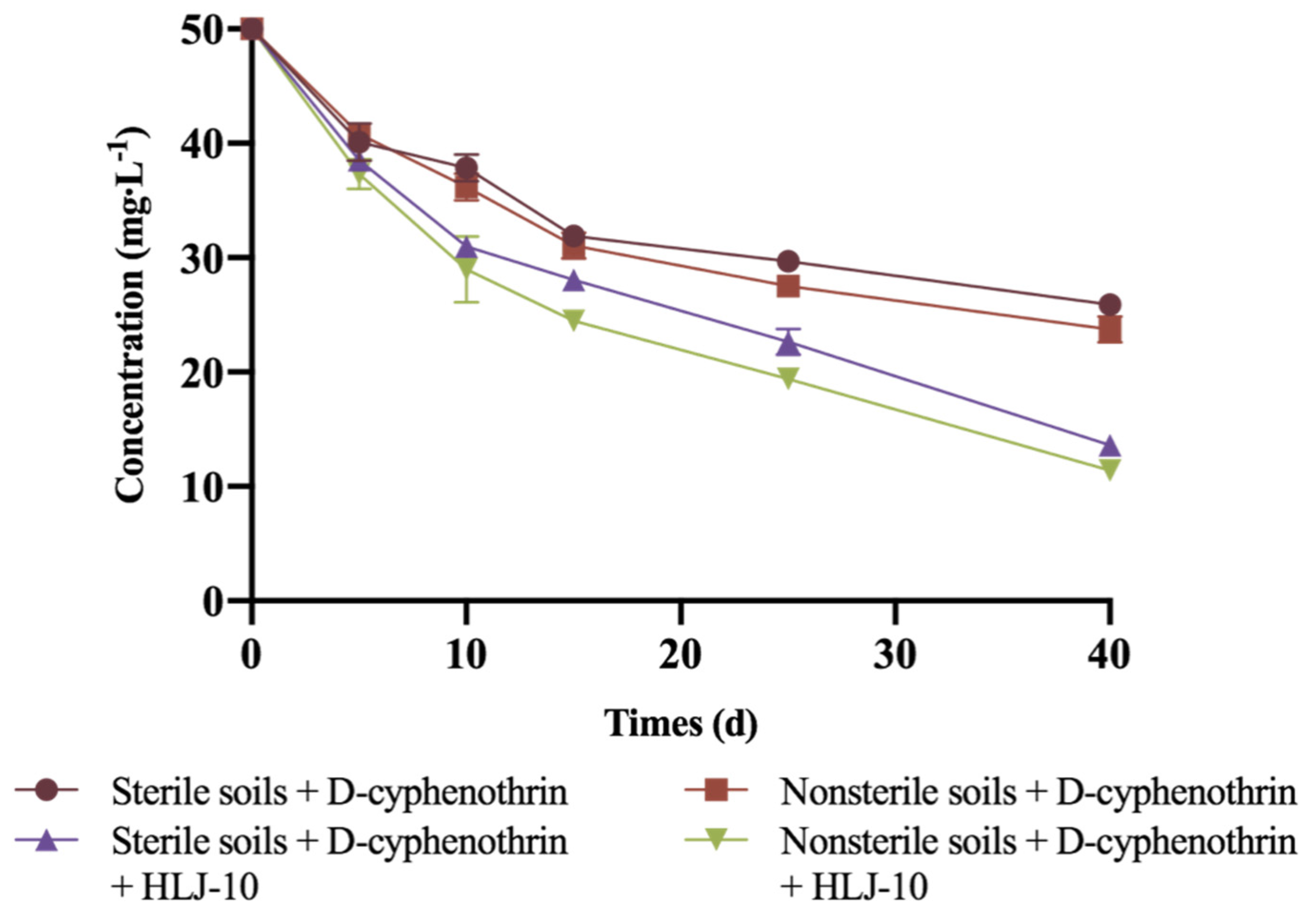
3.6. Biodegradation of D-Cyphenothrin in Soils
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Specifications and Evaluations for Public Health Pesticides, d,d,trans-Cyphenothrin. WHO 2005. Available online: https://www.who.int/whopes/en/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Beltran, J.; Peruga, A.; Pitarch, E.; Lopez, F.J.; Hernandez, F. Application of solid-phase microextraction for the determination of pyrethroid residues in vegetable samples by GC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendis, J.C.; Tennakoon, T.K.; Jayasinghe, C.D. Zebrafish embryo toxicity of a binary mixture of pyrethroid insecticides: D-tetramethrin and cyphenothrin. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stara, J.; Stejskal, V.; Nesvorna, M.; Plachy, J.; Hubert, J. Efficacy of selected pesticides against synanthropic mites under laboratory assay. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilak, R.; Agrawal, V.K.; Dutta, J. Field performance of cyphenothrin: An integrated insecticide strategy against German cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blatellidae). J. Vector. Borne. Dis. 2005, 42, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, H.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. New insights into the microbial degradation and catalytic mechanism of synthetic pyrethroids. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Pyrethroid-degrading microorganisms and their potential for the bioremediation of contaminated soils: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodaka, R.; Sugano, T.; Katagi, T. Degradation of esfenvalerate in illuminated water-sediment system. J. Pestic. Sci. 2009, 34, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S. Role of cytochrome P450 in mechanism of pyrethroid resistance. J. Pestic. Sci. 2004, 29, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakata, S.; Mikami, N.; Yamada, H. Degradation of pyrethroid optical isomers in soils. J. Pestic. Sci. 1992, 17, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pham, M.H.; Sebesvari, Z.; Tu, B.M.; Pham, H.V.; Renaud, F.G. Pesticide pollution in agricultural areas of Northern Vietnam: Case study in Hoang Liet and Minh Dai communes. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3344–3350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hadnagy, W.; Leng, G.; Sugiri, D.; Ranft, U.; Idel, H. Pyrethroids used indoors – Immune status of humans exposed to pyrethroids following a pest control operation – a one year follow-up study. Int. J. Hyg. Envir. Heal. 2003, 206, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Mohnssen, H. Chronic sequelae and irreversible injuries following acute pyrethroid intoxication. Toxicol. Lett. 1999, 107, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller-Winkler, R.; Hadnagy, W.; Leng, G.; Straube, E.; Idel, H. Immunological parameters in humans exposed to pesticides in the agricultural environment. Toxicol. Lett. 1999, 107, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.I. Vitamin E modulates reproductive toxicity of pyrethroid lambda-cyhalothrin in male rabbits. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Grand, R.; Dulaurent, S.; Gaulier, J.M.; Saint-Marcoux, F.; Moesch, C.; Lachatre, G. Simultaneous determination of five synthetic pyrethroid metabolites in urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application to 39 persons without known exposure to pyrethroids. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 210, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Ranft, U.; Sugiri, D.; Hadnagy, W.; Berger-Preiss, E.; Idel, H. Pyrethroids used indoors - Biological monitoring of exposure to pyrethroids following an indoor pest control operation. Int. J. Hyg. Envir. Heal. 2003, 206, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chang, C.Q.; Deng, Y.Y.; An, S.W.; Dong, Y.H.; Zhou, J.N.; Hu, M.Y.; Zhong, G.H.; Zhang, L.H. Fenpropathrin biodegradation pathway in Bacillus sp. DG-02 and its potential for bioremediation of pyrethroid-contaminated soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, M.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Zhong, G.H.; Yang, L.; Rizwan-ul-Haq, M.; Han, H.T. Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a novel Ochrobactrum lupini DG-S-01. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, S. Recent advances in glyphosate biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 10, 5033–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Geng, P.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, M.Y. Bioremediation of beta-cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde contaminated soils using Streptomyces aureus HP-S-01. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, S.H.; Gao, Y.Q.; Hu, W.; Hu, M.Y.; Zhong, G.H. Isolation of a novel beta-cypermethrin degrading strain Bacillus subtilis BSF01 and its biodegradation pathway. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2849–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhan, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Characterization of a pyrethroid-degrading Pseudomonas fulva strain P31 and biochemical degradation pathway of D-phenothrin. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.B.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.W.; Cheng, F.X.; Luo, Y.H.; Cheng, J.E.; Ma, X.M. Degradation characteristics and pathway of fenpropathrin by Rhodopseudomonas sp. strain PSB07-6. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2009, 18, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Birolli, W.G.; Arai, M.S.; Nitschke, M.; Porto, A.L.M. The pyrethroid (±)-lambda-cyhalothrin enantioselective biodegradation by a bacterial consortium. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 156, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Żmijowska, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Enhancement of deltamethrin degradation by soil bioaugmentation with two different strains of Serratia marcescens. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sharma, A.; Chen, S. Enhanced cypermethrin degradation kinetics and metabolic pathway in Bacillus thuringiensis strain SG4. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolli, W.G.; Alvarenga, N.; Seleghim, M.H.; Porto, A.L. Biodegradation of the pyrethroid pesticide esfenvalerate by marine-derived fungi. Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolli, W.G.; Vacondio, B.; Alvarenga, N.; Seleghim, M.H.R.; Porto, A.L.M. Enantioselective biodegradation of the pyrethroid (+/-)-lambda-cyhalothrin by marine-derived fungi. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, Q.B.; Hu, M.Y.; Luo, J.J.; Weng, Q.F.; Lai, K.P. Isolation and characterization of a fungus able to degrade pyrethroids and 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8110–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Sugano, T.; Shibata, A.; Kodaka, R.; Fujisawa, T.; Katagi, T. Behavior of cyphenothrin in aquatic environment. J. Pestic. Sci. 2017, 42, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogorb, M.A.; Vilanova, E. Enzymes involved in the detoxification of organophosphorus, carbamate and pyrethroid insecticides through hydrolysis. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 128, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, K.; Song, J.; Shi, Y.; Yan, Y. Molecular cloning, purification and biochemical characterization of a novel pyrethroid-hydrolyzing carboxylesterase gene from Ochrobactrum anthropi YZ-1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.Q.; Lin, D.R.; Yao, K.; Yuan, H.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, J.L.; Zou, L.K.; Han, X.F.; Zhou, K.; He, L.; et al. Characterization of a novel beta-cypermethrin-degrading Aspergillus niger YAT strain and the biochemical degradation pathway of beta-cypermethrin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8187–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, H.; Wang, H.; Liao, L.; Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Kinetics and novel degradation pathway of permethrin in Acinetobacter baumannii ZH-14. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, J.J.; Hu, M.Y.; Lai, K.P.; Geng, P.; Huang, H.S. Enhancement of cypermethrin degradation by a coculture of Bacillus cereus ZH-3 and Streptomyces aureus HP-S-01. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Hao, X.; Huo, S.; Lin, W.; Xia, X.; Liu, K.; Duan, B. Isolation and identification of the Raoultella ornithinolytica-ZK4 degrading pyrethroid pesticides within soil sediment from an abandoned pesticide plant. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.C.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, H.; Liang, W.Q.; Luo, N.; Hu, J.M.; Lu, J.Q.; Luan, T.G.; et al. Molecular cloning, purification, and biochemical characterization of a novel pyrethroid-hydrolyzing esterase from Klebsiella sp. strain ZD112. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dong, Y.H.; Chang, C.Q.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhong, G.H.; Song, H.W.; Hu, M.Y.; Zhang, L.H. Characterization of a novel cyfluthrin-degrading bacterial strain Brevibacterium aureum and its biochemical degradation pathway. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, L.; Hu, M.; Liu, J. Biodegradation of fenvalerate and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a novel Stenotrophomonas sp. strain ZS-S-01 and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, S.E.; Maule, A.; Smith, A.R. Microbial transformation of the pyrethroid insecticides: Permethrin, deltamethrin, fastac, fenvalerate, and fluvalinate. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1988, 54, 2874–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Ding, J.; Xiao, Y.; Han, H.; Zhong, G. Sugarcane bagasse as support for immobilization of Bacillus pumilus HZ-2 and its use in bioremediation of mesotrione-contaminated soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10839–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, P.; Bhatt, K.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Chen, S. Esterase is a powerful tool for the biodegradation of pyrethroid insecticides. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Guo, P.; Hang, B.; Li, L.; He, J.; Li, S.P. Cloning of a novel pyrethroid-hydrolyzing carboxylesterase gene from Sphingobium sp. strain JZ-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5496–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Paraquat degradation from contaminated environments: Current achievements and perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Chen, S. Insight into microbial applications for the biodegradation of pyrethroid insecticides. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.X.; Wang, B.W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Tong, Z.F.; Wei, Y.J. Biodegradation and extracellular enzymatic activities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain GF31 on beta-cypermethrin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2015, 22, 13049–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Hou, Z.G.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, J.; Lu, Z.B.; Zhao, X.F.; Sun, F.J.; Pan, H.Y. Biodegradation potential of deltamethrin by the Bacillus cereus strain Y1 in both culture and contaminated soil. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2016, 106, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, R.; Moreno-Ramon, H.; Albero, B.; Sanchez-Brunete, C.; Tadeo, J.L. Spatio-temporal distribution of pyrethroids in soil in Mediterranean paddy fields. J. Soil. Sediment. 2017, 17, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, K.M.; Weston, D.P.; Lydy, M.J.; Wellborn, G.A.; Poynton, H.C. Unintentional exposure to terrestrial pesticides drives widespread and predictable evolution of resistance in freshwater crustaceans. Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 748–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, P.; Huang, Y.; Rene, E.R.; Kumar, A.J.; Chen, S. Mechanism of allethrin biodegradation by a newly isolated Sphingomonas trueperi strain CW3 from wastewater sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Deng, Y.; Chang, C.; Lee, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, J.; He, F.; Hu, M.; Zhang, L.H. Pathway and kinetics of cyhalothrin biodegradation by Bacillus thuringiensis strain ZS-19. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pang, S.; Huang, Y.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Current approaches to and future perspectives on methomyl degradation in contaminated soil/water environments. Molecules 2020, 25, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cycoń, M.; Mrozik, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Bioaugmentation as a strategy for the remediation of pesticide-polluted soil: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 52–71. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. An overview of strobilurin fungicide degradation: Current status and future perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, Z.; Pang, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Insights into the biodegradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) using a microbial system. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 522. [Google Scholar]

| Independent Variables | Code | Code Levels of Variables | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Temperature (°C) | X1 | 25 | 30 | 35 |
| pH | X2 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| Inoculum size (OD) | X3 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.3 |
| Treatments | Regression Equation | k | R2 | t1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Ct = 49.8e−0.011t | 0.011 | 0.9830 | 63.0 |
| HLJ-10 | Ct = 50.2e−0.3896t | 0.3896 | 0.9659 | 1.8 |
| Run | X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 92.8 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 94.9 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 74.1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 94.9 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 91.6 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 77.4 |
| 7 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 85.9 |
| 8 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 82.9 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 96.9 |
| 10 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 88.1 |
| 11 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 73.4 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 85.1 |
| 13 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 79.2 |
| 14 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 74.9 |
| 15 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 90.0 |
| 16 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 77.6 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 92.8 |
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F-Value | p-Value* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 891.53 | 99.06 | 4.64 | 0.0277 |
| X1 | 1 | 20.48 | 20.48 | 0.9595 | 0.3599 |
| X2 | 1 | 35.28 | 35.28 | 1.65 | 0.2395 |
| X3 | 1 | 5.78 | 5.78 | 0.2708 | 0.6188 |
| X1X2 | 1 | 0.1600 | 0.1600 | 0.0075 | 0.9334 |
| X1X3 | 1 | 67.24 | 67.24 | 3.15 | 0.1192 |
| X2X3 | 1 | 5.29 | 5.29 | 0.2478 | 0.6339 |
| X1X1 | 1 | 240.33 | 240.33 | 11.26 | 0.0122 |
| X2X2 | 1 | 460.24 | 460.24 | 21.56 | 0.0024 |
| X3X3 | 1 | 5.62 | 5.62 | 0.2632 | 0.6237 |
| Residual | 7 | 149.41 | 21.34 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 3 | 137.56 | 45.85 | 15.48 | 0.0115 |
| Pure Error | 4 | 11.85 | 2.96 | ||
| Cor Total | 16 | 1040.94 |
| Code | RT (min) | m/z | Compound Structure | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 27.975 | 375 | 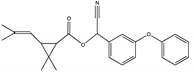 | (cis) D-cyphenothrin |
| A2 | 28.050 | 375 | 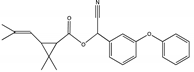 | (trans) D-cyphenothrin |
| B | 23.160 | 156 | 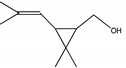 | trans-2,2-Dimethyl-3-propenyl-cyclopropanol |
| C | 23.144 | 172 | 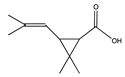 | 2,2-Dimethyl-3-propenyl-cyclopropionic acid |
| D | 23.399 | 154 | 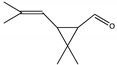 | trans-2,2-Dimethyl-3-propenyl-cyclopropionaldehyde |
| E | 16.814 | 227 | 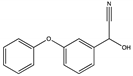 | α-Hydroxy-3-phenoxy-benzeneacetonitrile |
| F | 16.765 | 198 | 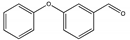 | 3-Phenoxybenzaldehyde |
| G | 26.634 | 232 | 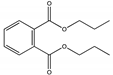 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, dipropyl ester |
| Treatments | Regression Equation | k | R2 | t1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sterile soils + D-cyphenothrin | Ct = 50.3e−0.011t | 0.0124 | 0.9302 | 55.9 |
| Nonsterile soils + D-cyphenothrin | Ct = 51.8e−0.3896t | 0.015 | 0.942 | 46.2 |
| Sterile soils + D-cyphenothrin + HLJ-10 | Ct = 51.2e−0.3896t | 0.0283 | 0.9878 | 24.5 |
| Nonsterile soils + D-cyphenothrin + HLJ-10 | Ct = 52.1e−0.3896t | 0.0323 | 0.9899 | 21.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pang, S.; Bhatt, P.; Rene, E.R.; Kumar, A.J.; Chen, S. New Insights into the Microbial Degradation of D-Cyphenothrin in Contaminated Water/Soil Environments. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040473
Huang Y, Lin Z, Zhang W, Pang S, Bhatt P, Rene ER, Kumar AJ, Chen S. New Insights into the Microbial Degradation of D-Cyphenothrin in Contaminated Water/Soil Environments. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(4):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040473
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yaohua, Ziqiu Lin, Wenping Zhang, Shimei Pang, Pankaj Bhatt, Eldon R. Rene, Alagarasan Jagadeesh Kumar, and Shaohua Chen. 2020. "New Insights into the Microbial Degradation of D-Cyphenothrin in Contaminated Water/Soil Environments" Microorganisms 8, no. 4: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040473
APA StyleHuang, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, W., Pang, S., Bhatt, P., Rene, E. R., Kumar, A. J., & Chen, S. (2020). New Insights into the Microbial Degradation of D-Cyphenothrin in Contaminated Water/Soil Environments. Microorganisms, 8(4), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040473