Detection Methods for Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analytical Methods
- -
- if it is intended to detect the presence of the analyte in the sample, rapid methods can be used;
- -
- if it is intended to detect and quantify the analyte, quantitative methods must be used.
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Quantitative Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
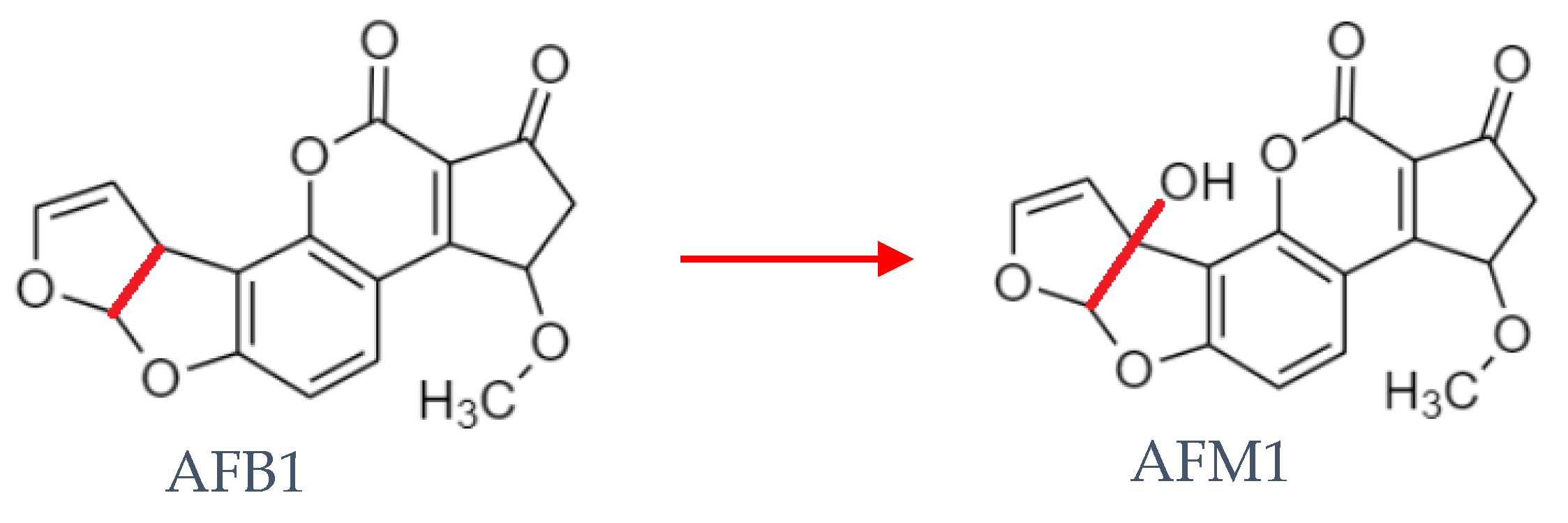
2.2.2. Extraction
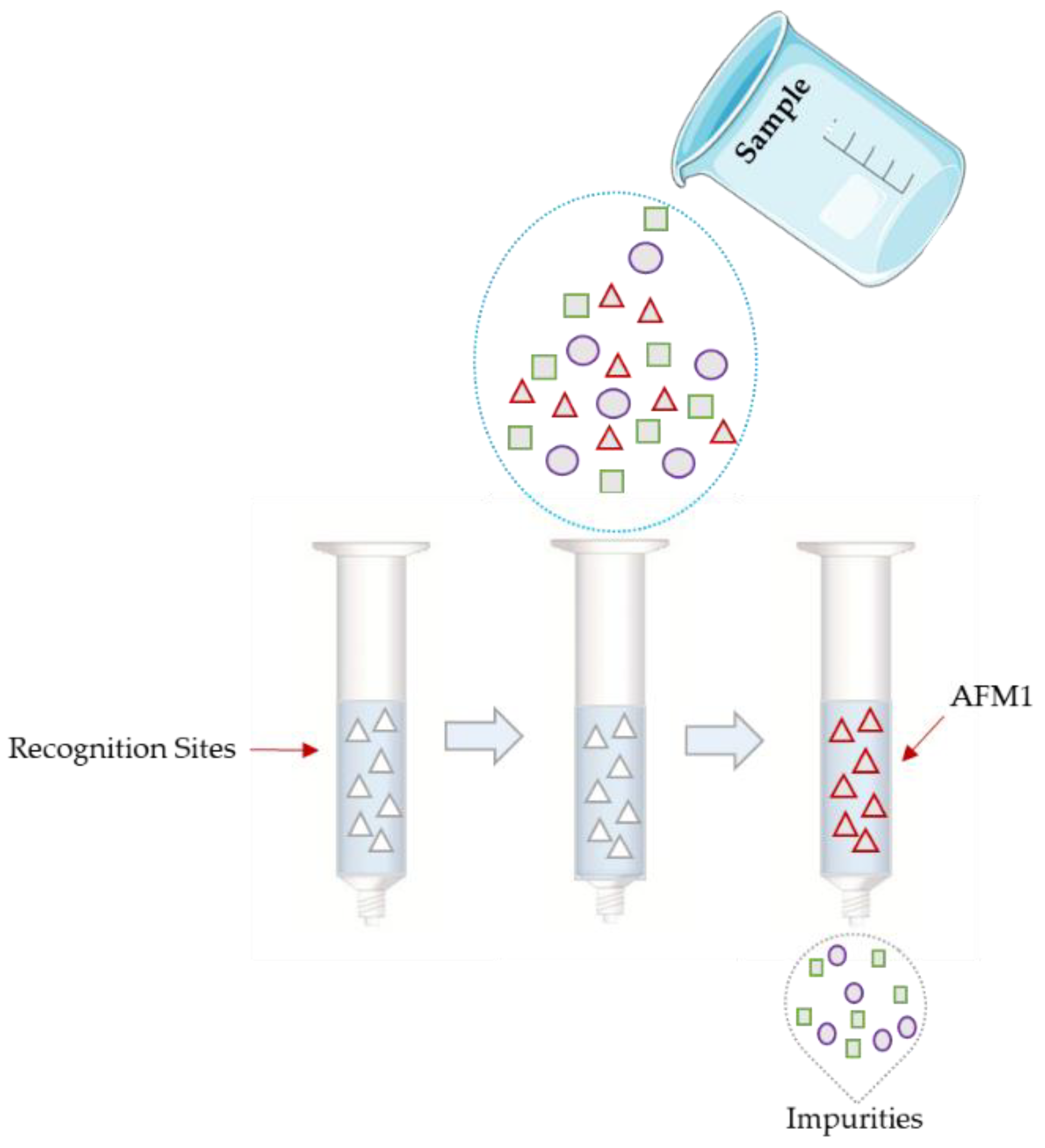
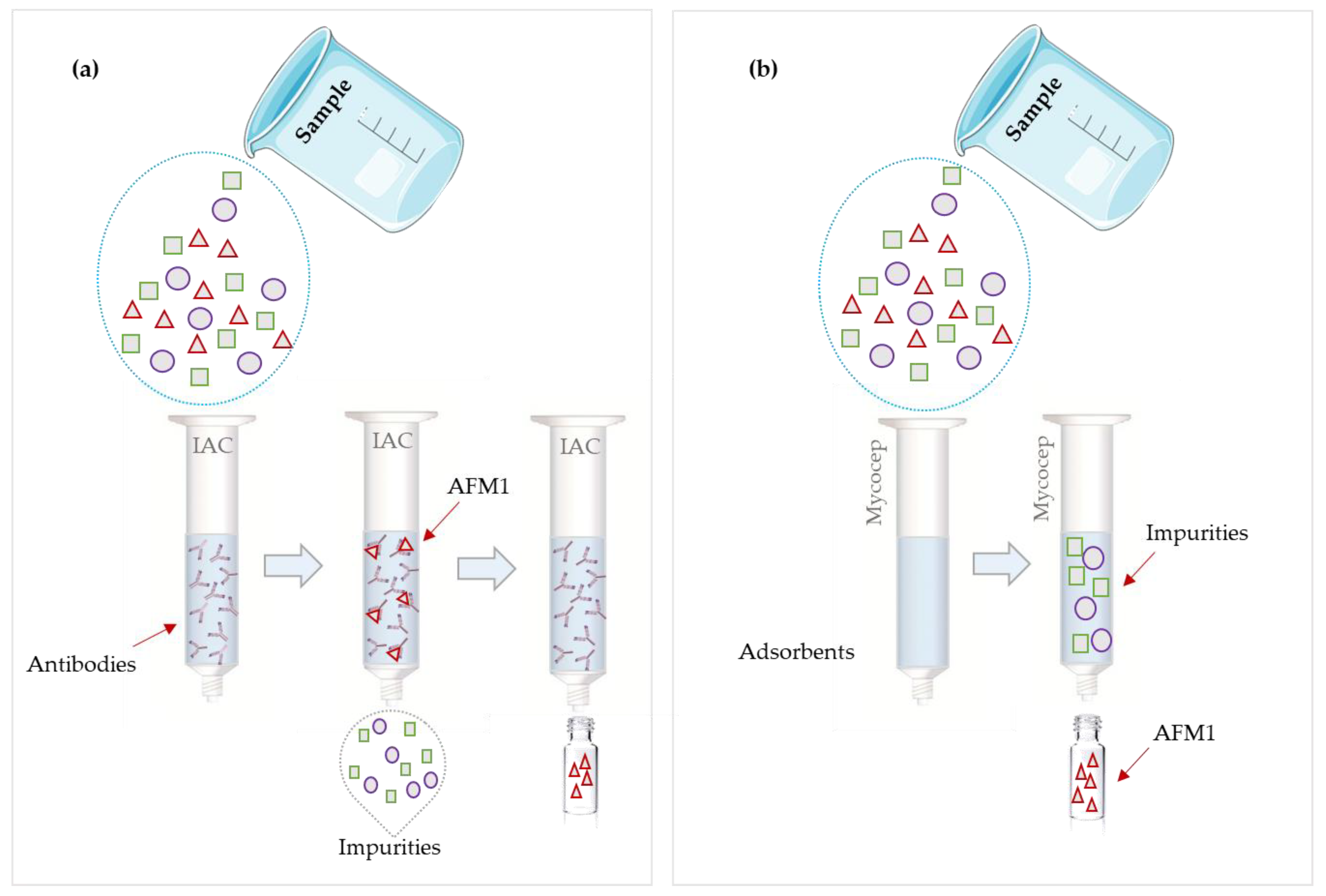
2.2.3. Clean-Up
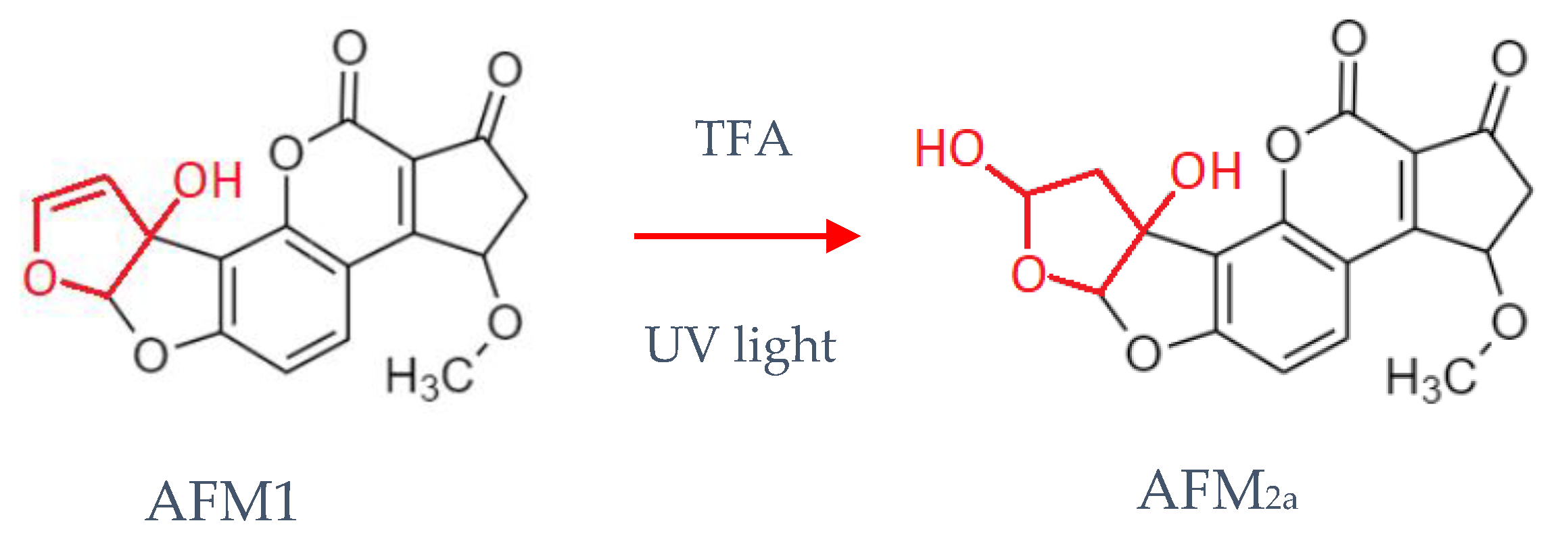
2.2.4. Quantification
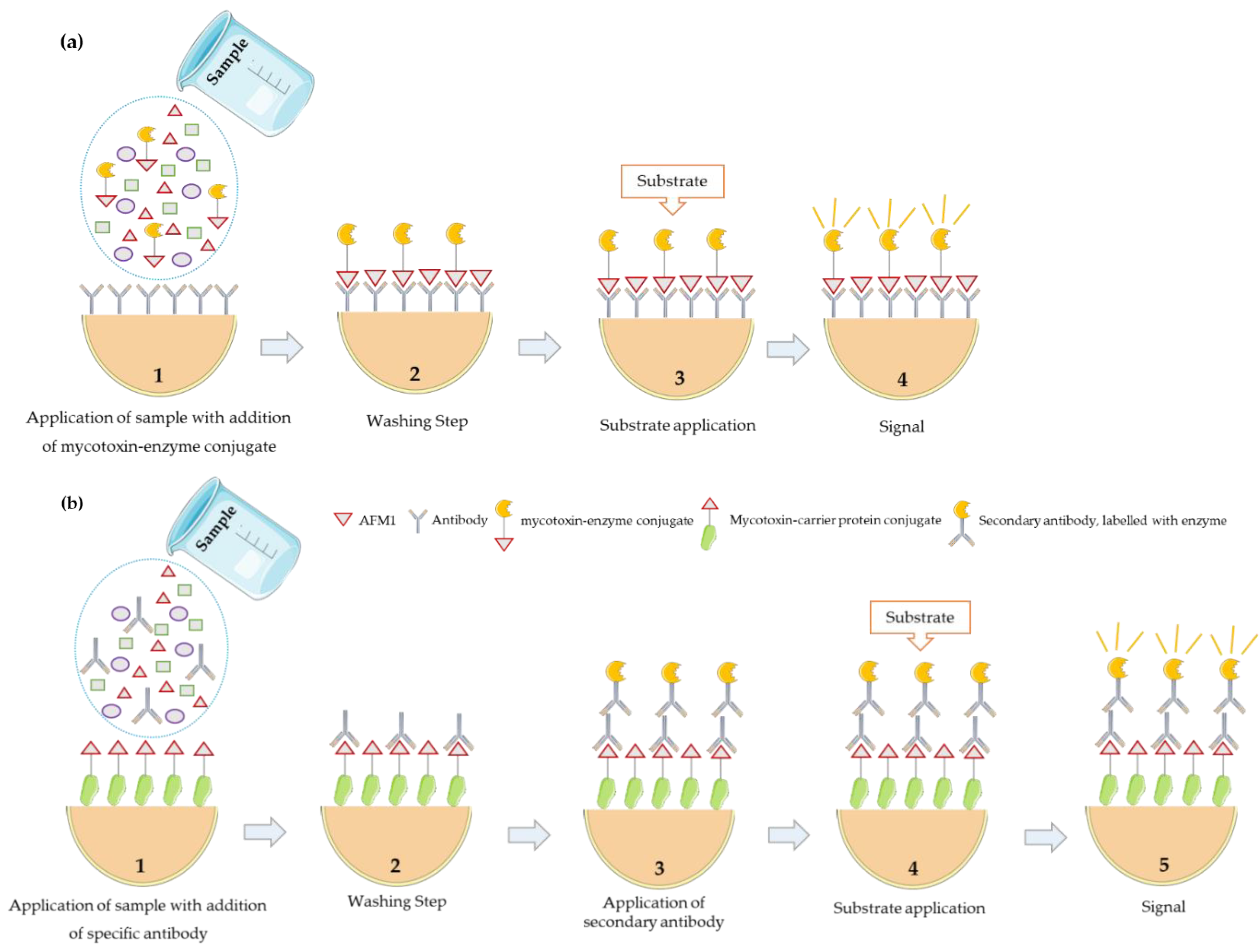
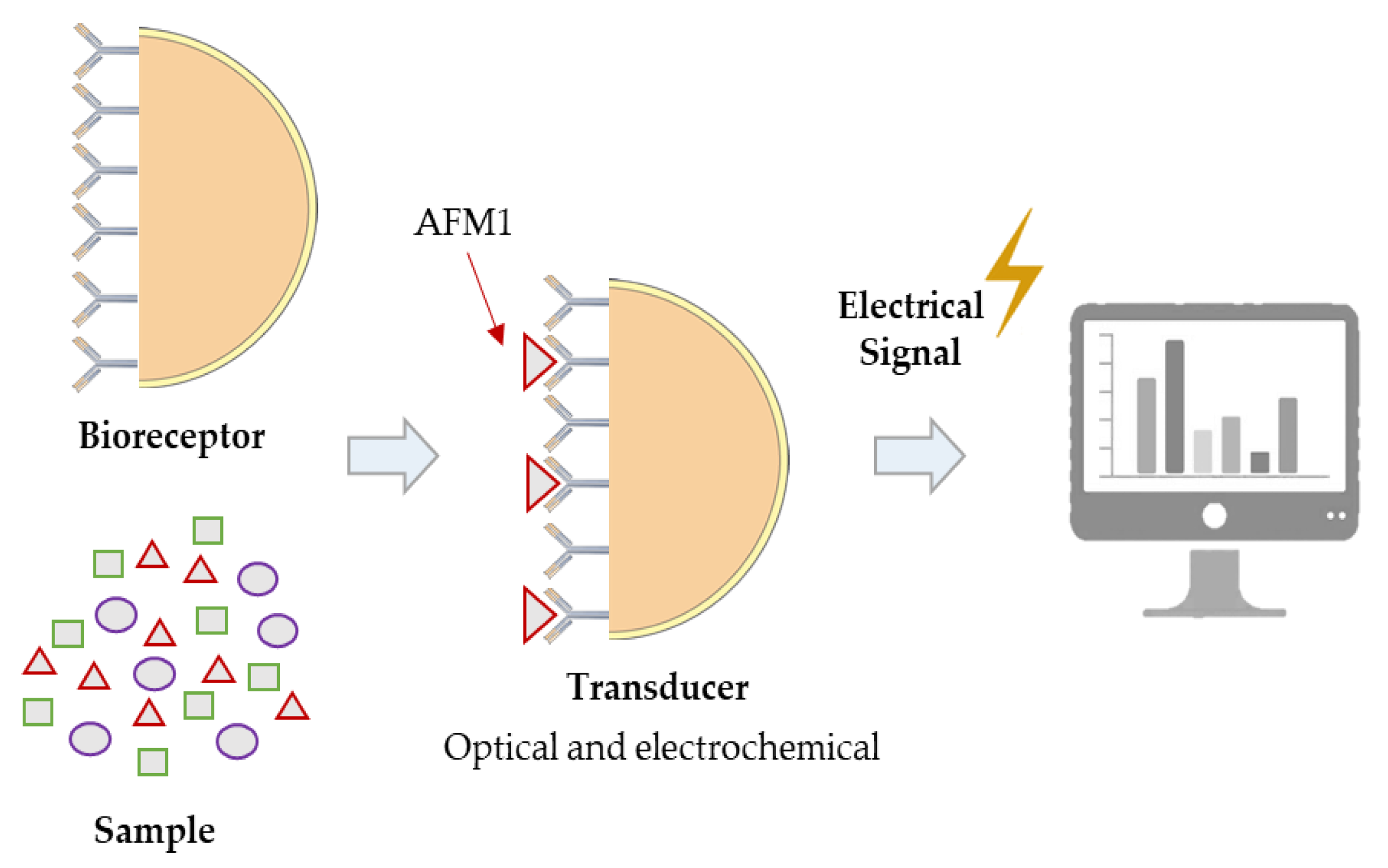
2.3. Rapid Methods
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Determination
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosielllo, L.; Lamberti, I. Biosensors for Aflatoxins Detection. In Aflatoxin—Detection Measurement and control; Torres-Pacheco, I., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 147–170. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, A.; Jinap, S.; Soleimany, F. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Mycotoxins. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009, 8, 202–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketney, O.; Santini, A.; Oancea, S. Recent aflatoxin survey data in milk and milk products: A review. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2017, 70, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25%. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetta, A.C. Aflatoxins: Their Measure and Analysis. In Aflatoxins—Detection, Measurement and Control; Torres-Pacheco, I., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Jinap, S.; Pirouz, A.A.; Ahmad Faizal, A.R. Aflatoxin M1in milk and dairy products, occurrence and recent challenges: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, A.; Bhat, R.V.; Bond, J.A.; Borghoff, S.J.; Bosch, F.X.; Carlson, G.P.; Castegnaro, M.; Cruzan, G.; Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Hass, U.; et al. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans: Some traditional herbal medicines, some mycotoxins, naphthalene and styrene. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2002, 82, 169–300. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, P.; Jha, S.N.; Kaur, J.; Borah, A.; Ramya, H.G. Detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk using spectroscopy and multivariate analyses. Food Chem. 2018, 238, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietri, A.; Fortunati, P.; Mulazzi, A.; Bertuzzi, T. Enzyme-assisted extraction for the HPLC determination of aflatoxin M1 in cheese. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC (European Comission). Commission Regulation (EU) No 165/2010 of 26 February 2010 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards aflatoxins. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 50, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa-Calderón, A.; Contreras-Medina, L.M.; Muñoz-Huerta, R.F.; Jesús Roberto Millán-Almaraz; González, R.G.G.; Torres-Pacheco, I. Methods for Detection and Quantification of Aflatoxins. In Aflatoxins –Detection, Measurement and Control; Torres-Pacheco, I., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I. Aflatoxin Measurement and Analysis. In Aflatoxins—Detection, Measurement and Control; Torres-Pacheco, I., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 129–160. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, T.B. Sampling for mycotoxins. In Mycotoxins in Food—Detection and Control; Magan, N., Olsen, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston/Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Benkerroum, N. Mycotoxins in dairy products: A review. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 62, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnollo, F.B.; Ganev, K.C.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Portela, J.B.; Cruz, A.G.; Granato, D.; Corassin, C.H.; Oliveira, C.A.F.; Sant’Ana, A.S. The occurrence and effect of unit operations for dairy products processing on the fate of aflatoxin M1: A review. Food Control 2016, 68, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC Comission Regulation (EC) No 401/2006 of 23 February 2006—Laying down the Methods of Sampling and Analysis for the Official Control of the Levels of Mycotoxins in Foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union. 9 May 2006. L70/12-34. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1581430639128&uri=CELEX:32006R0401 (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Al-Mossawei, M.T.; Al-Zubaidi, L.A.; Hamza, I.S.; Abduljaleel, S.Y. Detection of AFM 1 in Milk and Some Dairy Products in Iraq using different techniques. Adv. Life Sci. Technol. 2016, 41, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Shuib, N.S.; Makahleh, A.; Salhimi, S.M.; Saad, B. Determination of aflatoxin M 1 in milk and dairy products using high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence with post column photochemical derivatization. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1510, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.R.; Hong, S.Y.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, K.R.; Kim, M.; Chung, S.H. Aflatoxin M1 levels in dairy products from South Korea determined by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 55, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pamela, A.; Miriam, H.; Filomena, E.; Teresa, C.M.; Antonio, M.; Antonio, L.; Antonia, S. Fungal mycobiota and mycotoxin risk for traditional artisan Italian cave cheese. Food Microbiol. 2019, 78, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Michlig, N.; Repetti, M.R.; Chiericatti, C.; García, S.R.; Gaggiotti, M.; Basílico, J.C.; Beldoménico, H.R. Multiclass Compatible Sample Preparation for UHPLC–MS/MS Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw Milk. Chromatographia 2016, 79, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrbić, B.; Antić, I.; Živančev, J. Presence of aflatoxin M1 in white and hard cheese samples from Serbia. Food Control 2015, 50, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iha, M.H.; Barbosa, C.B. Rosa Maria Duarte Favaro Chromatographic Method for the Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Cheese, Yogurt, and Dairy Beverages. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.M.; Corrêa, B.; Rosim, R.E.; Kobashigawa, E.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Distribution and stability of aflatoxin M1 during processing and storage of Minas Frescal cheese. Food Control 2012, 24, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Taherimaslak, Z.; Rashidi, S. Enhanced spectrofluorimetric determination of aflatoxin M1 in liquid milk after magnetic solid phase extraction. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 128, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regal, P.; Díaz-Bao, M.; Barreiro, R.; Cepeda, A.; Fente, C. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in food analysis: Clean-up and chromatographic improvements. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2012, 10, 766–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Kant, K.; Chidambara, V.A.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D.; Sun, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation and biosensing in food analysis: Progress and perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Bao, M.; Regal, P.; Barreiro, R.; Fente, C.A.; Cepeda, A. A facile method for the fabrication of magnetic molecularly imprinted stir-bars: A practical example with aflatoxins in baby foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1471, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and Easy Multiresidue Method Employing Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and “ispersive Solid-Phase Extraction” for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Produce. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Huertas-Pérez, J.F.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Gámiz-Gracia, L. Mycotoxin Analysis: New Proposals for Sample Treatment. Adv. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, B. QuEChERS Purification Combined with Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Simultaneous Quantification of 25 Mycotoxins in Cereals. Toxins 2016, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dou, X.-W.; Zhang, C.; Logrieco, A.; Yang, M.-H. A Review of Current Methods for Analysis of Mycotoxins in Herbal Medicines. Toxins 2018, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Boyd, S.A.; Li, H. Comparison of accelerated solvent extraction and quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe method for extraction and determination of pharmaceuticals in vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1404, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Izzo, L.; Gaspari, A.; Graziani, G.; Mañes, J.; Ritieni, A. Simultaneous Determination of AFB1 and AFM1 in Milk Samples by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Beverages 2018, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetta, A.C.; Di Giuseppe, L.; Giammarco, M.; Fusaro, I.; Simonella, A.; Gramenzi, A.; Formigoni, A. High-performance liquid chromatography with post-column derivatisation and fluorescence detection for sensitive determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk and cheese. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1083, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarimehmetoglu, B.; Kuplulu, O.; Haluk Celik, T. Detection of aflatoxin M1 in cheese samples by ELISA. Food Control 2004, 15, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norian, R.; Mahmoudi, R.; Porfarzaneh, A.; Mashatian, F.; Kaboudari, A. Determination of aflatoxin M 1 levels in raw milk samples using ELISA and high-performance liquid chromatography in Qazvin, Iran. J. Mycol. Res. 2015, 2, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso, F.; Fremy, J.M.; Bevis, S.; Dragacci, S. Joint IDF-IUPAC-IAEA(FAO) interlaboratory validation for determining aflatoxin M1 in milk by using immunoaffinity clean-up before thin-layer chromatography. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk Yilmaz, S.; Altinci, A. Incidence of aflatoxin M1 contamination in milk, white cheese, kashar and butter from Sakarya, Turkey. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. AOAC Official Method 2000.08. In Aflatoxin M1 in Liquid Milk, Immunoaffinity Column by Liquid Chromatography, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Mulunda, M.; Ngoma, L.; Mathe, N.; Motsei, L.; Bakunzi, F. A Decade of Aflatoxin M1 Surveillance in Milk and Dairy Products in Developing Countries (2001-2011): A Review. In Mycotoxin and Food Safety in Developing Countries Techniques; Makun, H.A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 39–60. [Google Scholar]
- De Saeger, S. Determining Mycotoxins and Mycotoxigenic Fungi in Food and Feed; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2011; p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- Fallah, A.A. Aflatoxin M1 contamination in dairy products marketed in Iran during winter and summer. Food Control 2010, 21, 1478–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkar, A. A study on the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in raw milk produced in Sarab city of Iran. Food Control 2005, 16, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazi, A.; Ince, S.; Temamogullari, F. Survey of the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in cheeses produced by dairy ewe’s milk in Urfa city, Turkey. Ankara Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2010, 57, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, C.; Venâncio, A. Fate of aflatoxin M1 in cheese whey processing. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 2067–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iha, M.H.; Barbosa, C.B.; Okada, I.A.; Trucksess, M.W. Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in dairy products in Brazil. Food Control 2011, 22, 1971–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaj, A.; Meyer, K.; Berisha, B.; Arbneshi, T.; Haziri, A. Aflatoxin M 1 contamination of raw cow’s milk in five regions of Kosovo during 2016. Mycotoxin Res. 2018, 34, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campone, L.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Celano, R.; Pagano, I.; Di Sanzo, R.; Carabetta, S.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L. Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples from Italy analysed by online-SPE UHPLC-MS/MS. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campone, L.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Celano, R.; Pagano, I.; Russo, M.; Rastrelli, L. Rapid and automated analysis of aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products by online solid phase extraction coupled to ultra-high-pressure-liquid-chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Li, W.-J.; Peng, K.-Y. Determination of Aflatoxin M 1 in Milk and Milk Powder Using High-Flow Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography−Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8474–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, C.; Foglia, P.; Pastorini, E.; Samperi, R.; Laganà, A. Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric confirmatory method for determining aflatoxin M1 in cow milk: Comparison between electrospray and atmospheric pressure photoionization sources. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1101, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.C.; Zheng, N.; Zheng, B.Q.; Wen, F.; Cheng, J.B.; Han, R.W.; Xu, X.M.; Li, S.L.; Wang, J.Q. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin M1, ochratoxin A, zearalenone and α-zearalenol in milk by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymery, N.; Vasseur, V.; Coton, M.; Mounier, J.; Jany, J.L.; Barbier, G.; Coton, E. Filamentous fungi and mycotoxins in Cheese: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matabaro, E.; Ishimwe, N.; Uwimbabazi, E.; Lee, B.H. Current Immunoassay Methods for the Rapid Detection of Aflatoxin in Milk and Dairy Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.O.; Vaz, A.; Rodrigues, P.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Venâncio, A.; Peres, A.M. Thin Films Sensor Devices for Mycotoxins Detection in Foods: Applications and Challenges. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, T.; Lacorn, M.; FLannery, J.; Benzinger, J.; Bird, P.; CroWLey, E.; Goins, D.; Agin, J.; NutriSciences, M.; De Paris, R.; et al. Validation of the RIDASCREEN ® FAST Milk Kit. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- r-Biopharm RIDASCREEN ® Aflatoxin M1 Art. No. R1121 Cheese 2015, 2. Available online: https://food.r-biopharm.com/products/ridascreen-aflatoxin-m1/ (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Motawee, M.M.; McMahon, D.J. Fate of aflatoxin M1 during manufacture and storage of feta cheese. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi Sani, A.; Khezri, M.; Moradnia, H. Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk by ELISA Technique in Mashad (Northeast of Iran). ISRN Toxicol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, H.R.; Riazipour, M.; Kamkar, A.; Shaldehi, H.R.; Mozaffari Nejad, A.S. Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in white cheese samples from Tehran, Iran. Food Control 2012, 23, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdovenko, M.M.; Lu, C.C.; Yu, F.Y.; Sakharov, I.Y. Development of ultrasensitive direct chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, L.; Bhand, S. Fluorimetric immunoassay for multianalysis of aflatoxins. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 584964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameil, S.; Schubert, P.; Grundmann, P.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E. Use of 3-(4- hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid as electron donating compound in a potentiometric aflatoxin M1-immunosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 661, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, B.D.; Falco, A.; Ibba, P.; Cantarella, G.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Development of Flexible Dispense-Printed Electrochemical Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Detection in Milk. Sensors 2019, 19, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; Grecco, R.; Badea, M.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. An electrochemical immunosensor for aflatoxin M1 determination in milk using screen-printed electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, N.M.; Bostan, H.B.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Youssefi, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Karimi, G. Ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 and its major metabolite aflatoxin M1 using aptasensors: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 99, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Khabbaz, H.; Dadmehr, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Mohamadnejad, J. Aptamer-based Colorimetric and Chemiluminescence Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Foods Samples. Acta Chim. Slov. 2015, 62, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sharma, R.; Singh, D. Immobilized aptamer on gold electrode senses trace amount of aflatoxin M1. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouati, A.; Catanante, G.; Nunes, G.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.-L. Label-Free Aptasensors for the Detection of Mycotoxins. Sensors 2016, 16, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.H.; Tran, L.D.; Do, Q.P.; Nguyen, H.L.; Tran, N.H.; Nguyen, P.X. Label-free detection of aflatoxin M1 with electrochemical Fe3O4/polyaniline-based aptasensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M. Aptasensor. In Encyclopedia of Astrobiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
| Country | Milk (µg/L) | Dairy Products (µg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 0.05 | 0.50 (milk products); 0.25 (cheese) |
| Brazil | 0.5 | 5 (milk powder); 2.5 (cheese) |
| China | 0.5 | 0.5 (milk products) |
| Egypt | 0 | 0 |
| EU | 0.05 0.025 (food products meant for infants and young children) Austria 0.01 (pasteurized infant milk) France 0.03 (for children ˂3 years) | Italy 0.25 (soft cheese); 0.45 (hard cheese) Austria 0.020 (butter); 0.25 (cheese); 0.40 (milk powder) The Netherlands 0.020 (butter); 0.020 (cheese) |
| Honduras | 0.05 | 0.250 (cheese) |
| Iran | 0.05 | 0.50 (milk powder); 0.020 (butter and butter milk); 0.250 (cheese) |
| Nigeria | 1 | - |
| Switzerland | 0.05 | 0.25 (cheese) |
| Turkey | 0.05 | 0.25 (cheese) |
| USA | 0.5 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaz, A.; Cabral Silva, A.C.; Rodrigues, P.; Venâncio, A. Detection Methods for Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020246
Vaz A, Cabral Silva AC, Rodrigues P, Venâncio A. Detection Methods for Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(2):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020246
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaz, Andreia, Ana C. Cabral Silva, Paula Rodrigues, and Armando Venâncio. 2020. "Detection Methods for Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products" Microorganisms 8, no. 2: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020246
APA StyleVaz, A., Cabral Silva, A. C., Rodrigues, P., & Venâncio, A. (2020). Detection Methods for Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products. Microorganisms, 8(2), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020246





