An Alcohol Dehydrogenase 3 (ADH3) from Entamoeba histolytica Is Involved in the Detoxification of Toxic Aldehydes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. E. histolytica Cell Culture and Generation of Transfectants
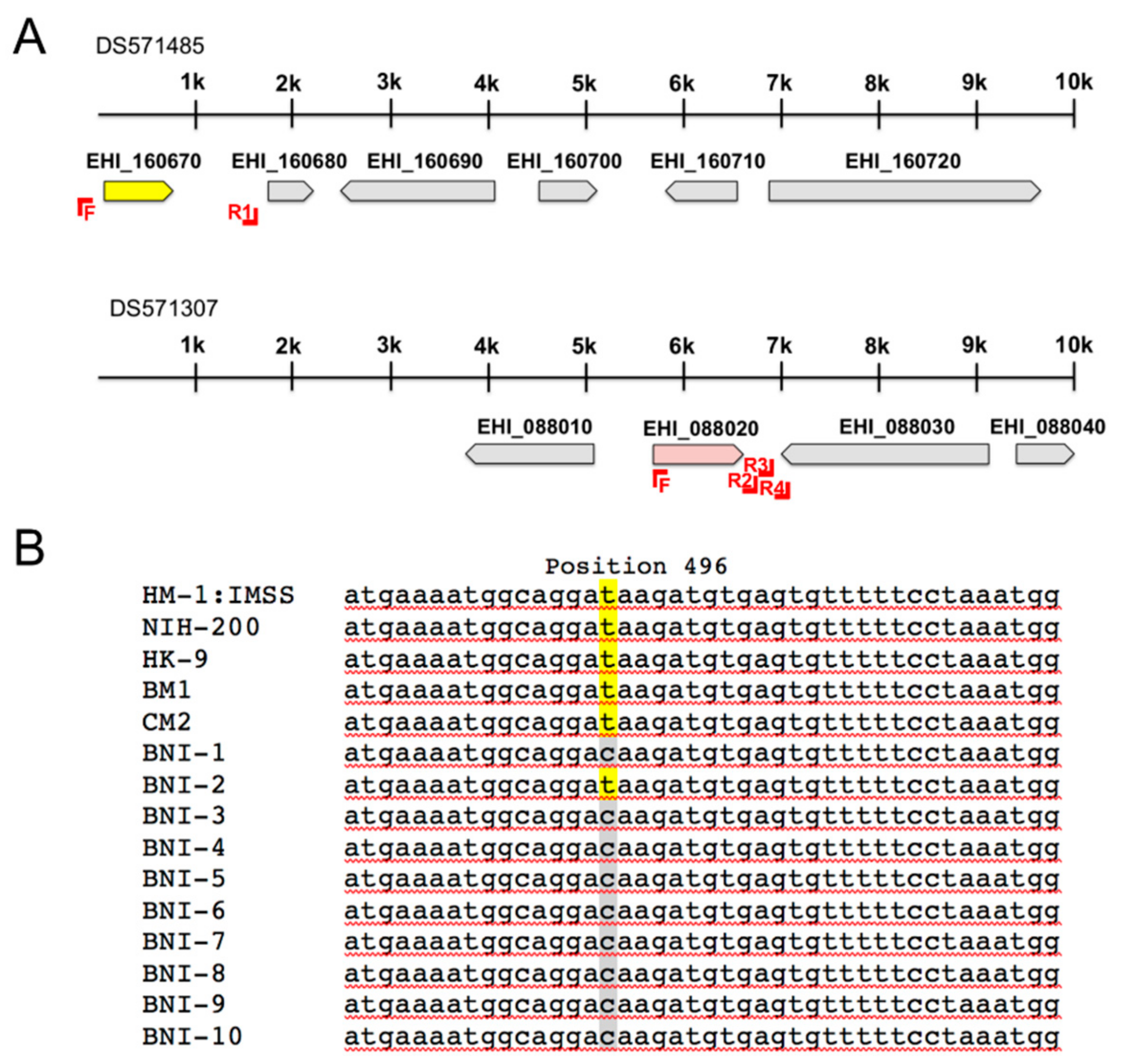
2.2. Amplification of adh3b Gene Locus
2.3. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real Time PCR
2.4. Protein Analyses
2.5. Determination of Hemolytic Activity
2.6. Cysteine Peptidase Assay
2.7. Erythrophagocytosis
2.8. Determination of Cell Division Rate
2.9. Motility
2.10. Determination of Amoeba Sizes
2.11. Recombinant Expression in E. coli and Purification of the Recombinant EhADH3Bb
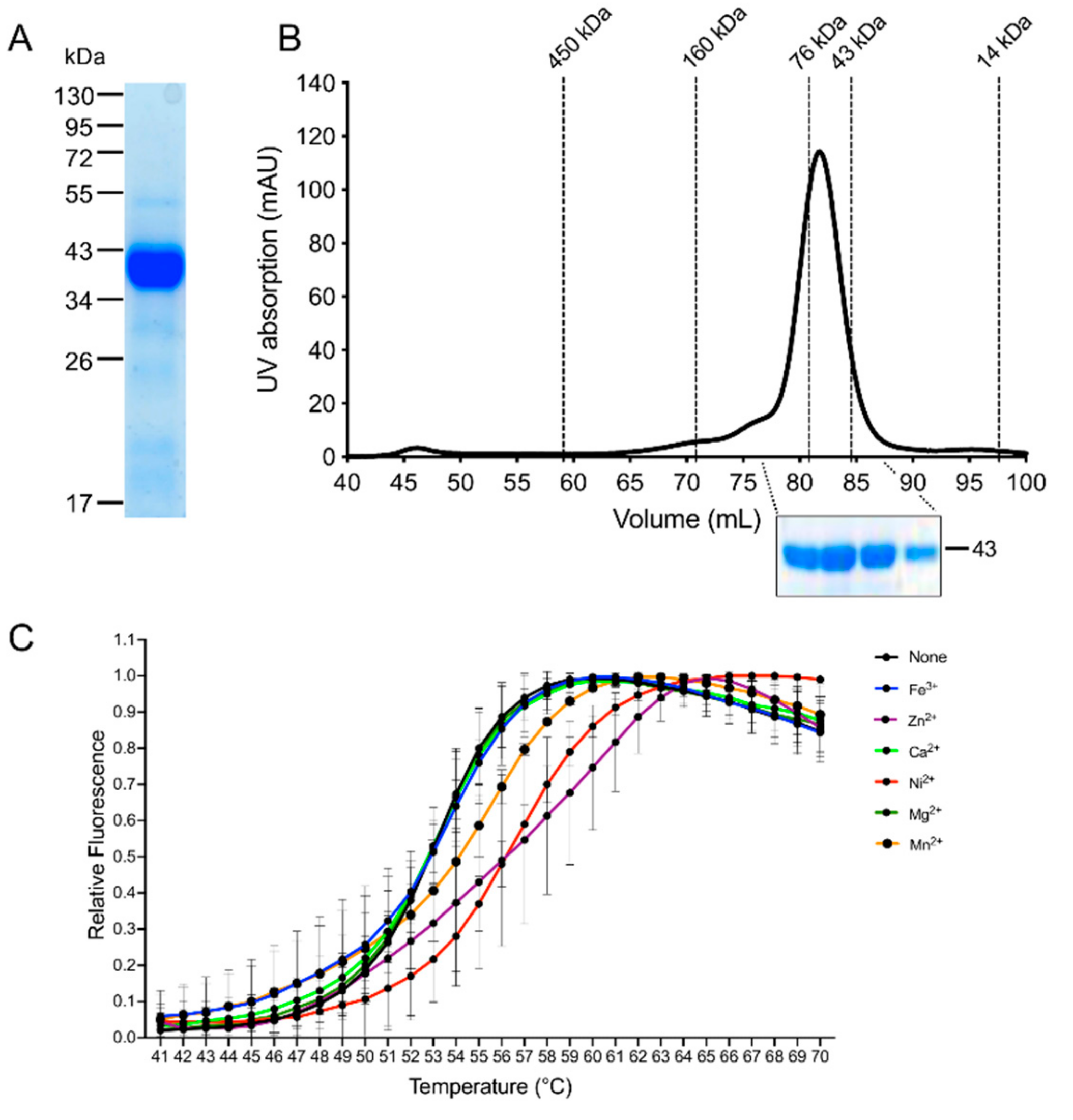
2.12. Size Exclusion Chromatography
2.13. Thermal Stabilization Assay
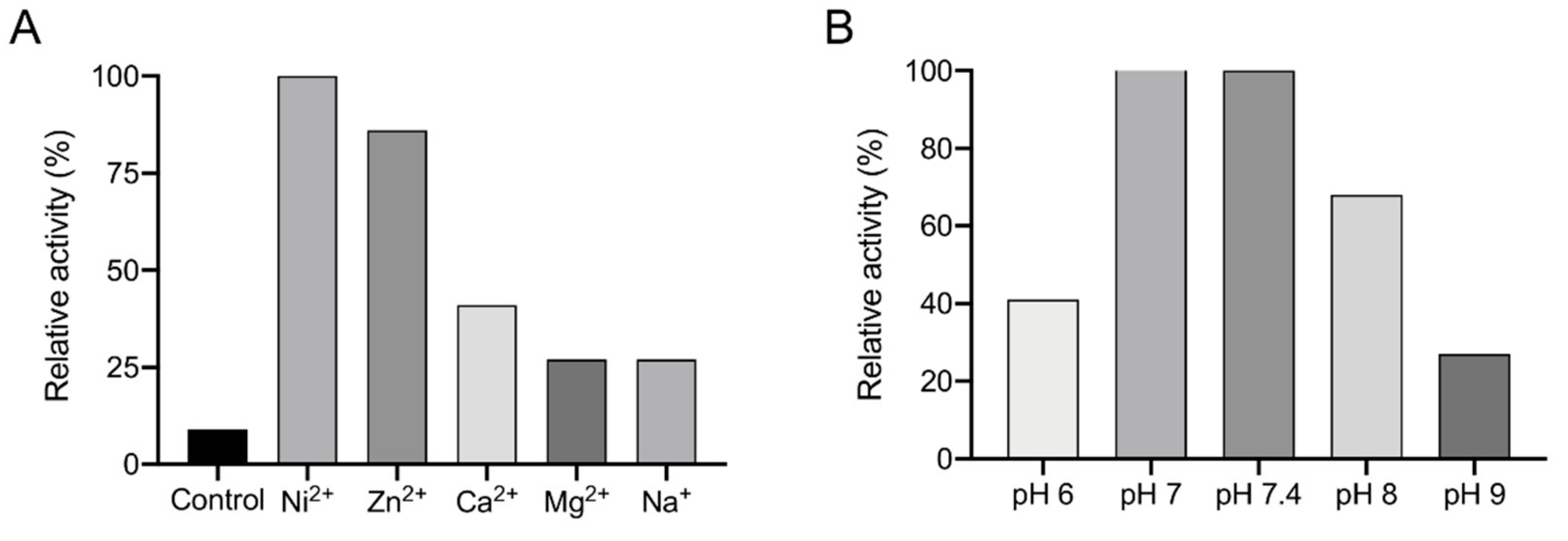
2.14. Enzymatic Assays
2.15. Generation of Polyclonal Antibodies
2.16. Immunofluorescence Assays (IFA)
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Analysis of E. histolytica ADHs
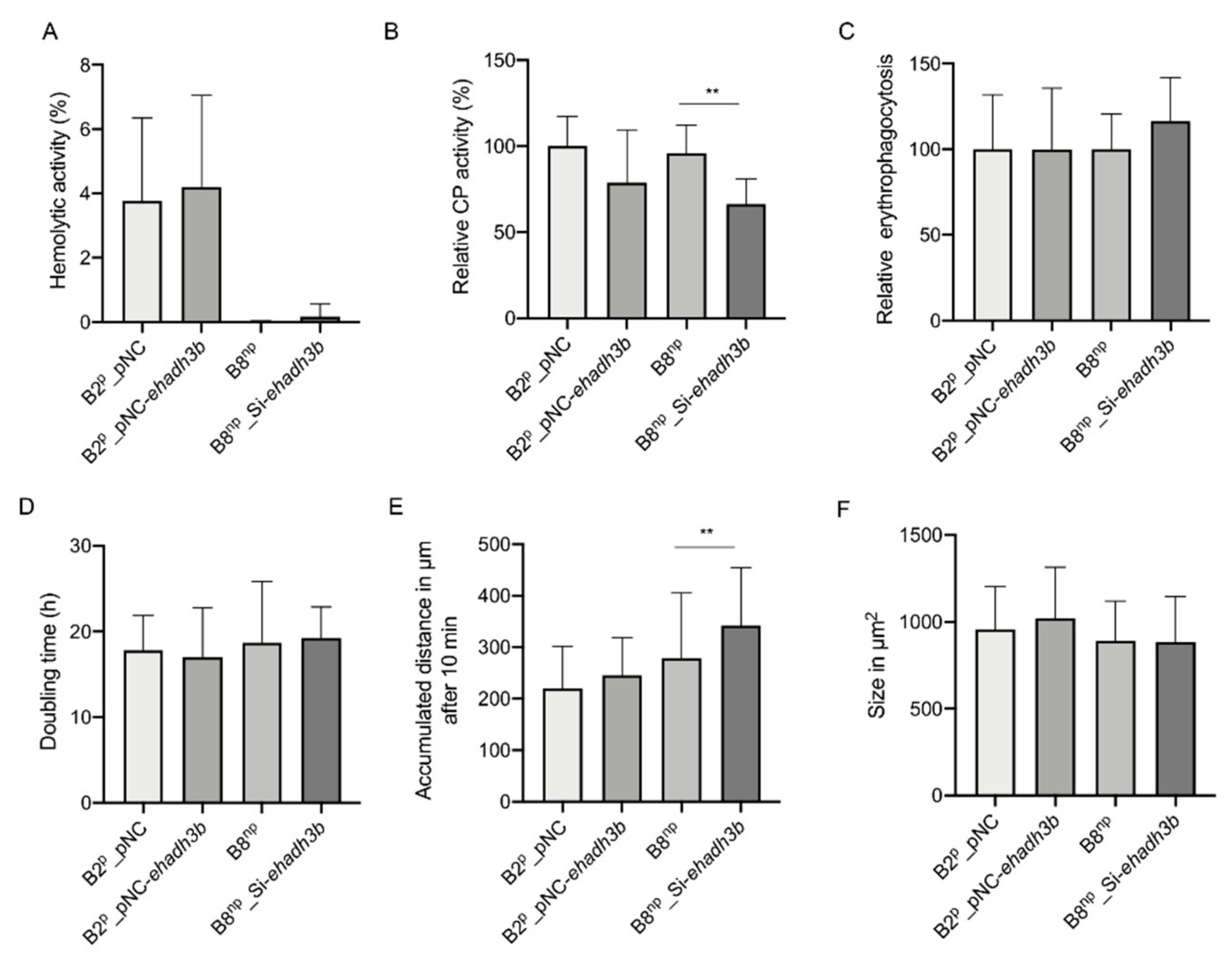
3.2. Phenotypical Characterization of ehadh3bb Overexpressing and Silencing Transfectants
3.3. Recombinant Expression and Determination of Co-Factor and Enzymatic Characterization of EhADH3B
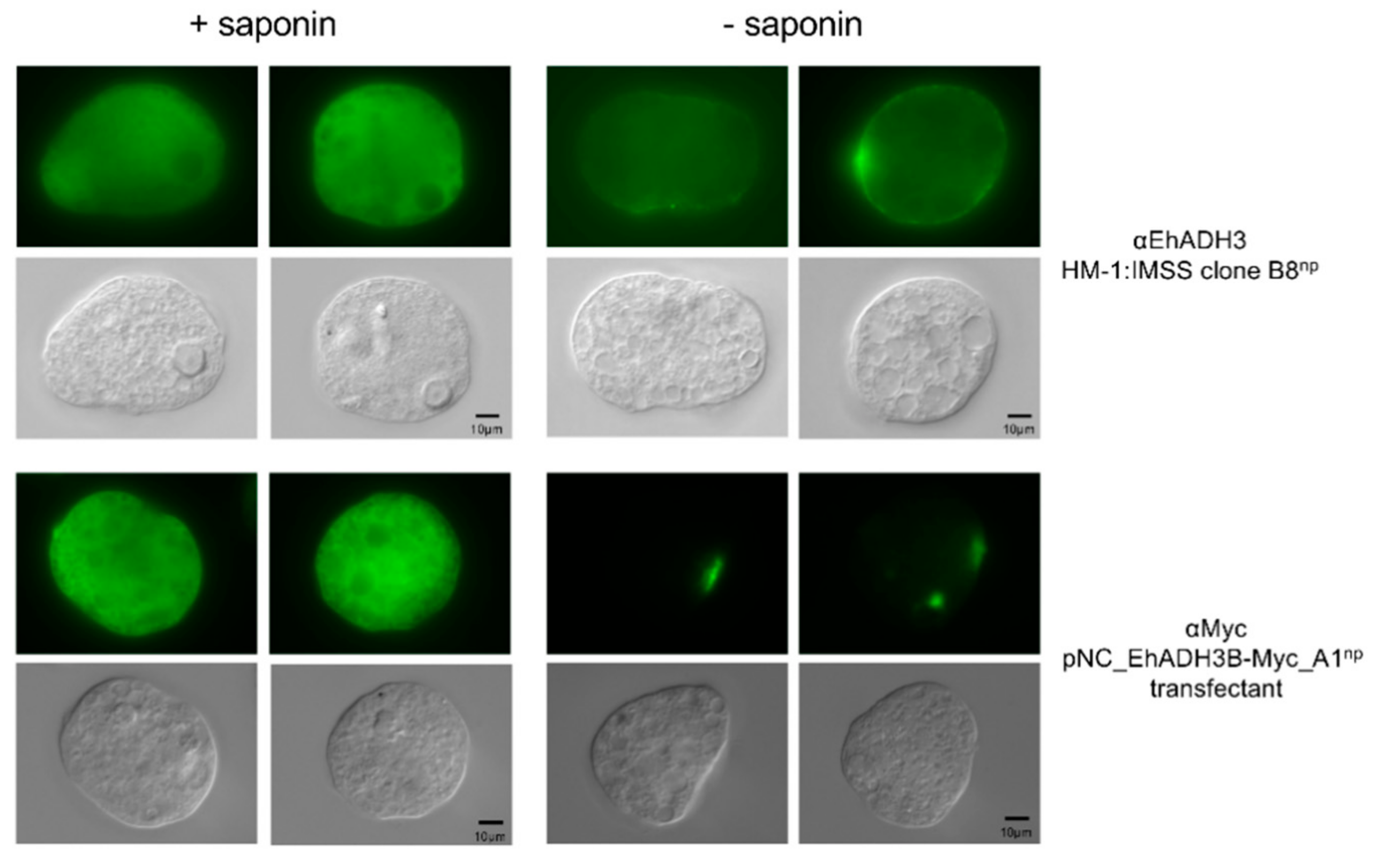
3.4. Localization of EhADH3Bb
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.E. Metabolism of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903. Adv. Parasitol. 1984, 23, 105–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.S.; Reeves, R.E. Pyruvate-to-ethanol pathway in Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem. J. 1978, 171, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M. Energy metabolism of protozoa without mitochondria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1988, 42, 465–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchhaus, I.; Tannich, E. Purification and molecular characterization of the NAD(+)-dependent acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase from Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem. J. 1994, 303, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, E.; Stanley, S.L., Jr. Structural analysis of the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase activity of Entamoeba histolytica alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (EhADH2), a member of the ADHE enzyme family. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2004, 137, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Foster, L.; Clark, D.; Li, E.; Stanley, S.L., Jr. The bifunctional Entamoeba histolytica alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (EhADH2) protein is necessary for amebic growth and survival and requires an intact C-terminal domain for both alcohol dahydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20136–20143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Lopez, M.; Bermudez-Cruz, R.M.; Avila, E.E.; de la Garza, M. Acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase-2 (EhADH2) and clathrin are involved in internalization of human transferrin by Entamoeba histolytica. Microbiology 2011, 157, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.E.; Montalvo, F.E.; Lushbaugh, T.S. Nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase: The enzyme from Entamoeba histolytica and some inhibitors. Int. J. Biochem. 1971, 2, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.S.; Chang, C.J. Purification and properties of NADP-linked, alcohol dehydrogenase from Entamoeba histolytica. J. Parasitol. 1982, 68, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Shen, P.S.; Descoteaux, S.; Pohl, J.; Bailey, G.; Samuelson, J. Cloning and expression of an NADP(+)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase gene of Entamoeba histolytica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10188–10192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelson, J.; Zhang, W.W.; Kumar, A.; Descoteaux, S.; Shen, P.S.; Bailey, G. Primary structures of alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase genes of Entamoeba histolytica. Arch. Med. Res. 1992, 23, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.A.; Baez-Camargo, M.; Delgadillo, D.M.; Orozco, E. Cloning and expression of an Entamoeba histolytica NAPD+(-)dependent alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1306, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Hara, Y.; Kimoto, T.; Okuno, Y.; Minekawa, Y.; Nakabayashi, T. Cloning and expression of a putative alcohol dehydrogenase gene of Entamoeba histolytica and its application to immunological examination. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1996, 3, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Clark, C.G.; Townsend, R.R.; Stanley, S.L., Jr. Proteomic comparison of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar and the role of E. histolytica alcohol dehydrogenase 3 in virulence. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.; Rosenthal, B.; Samuelson, J. Early lateral transfer of genes encoding malic enzyme, acetyl-CoA synthetase and alcohol dehydrogenases from anaerobic prokaryotes to Entamoeba histolytica. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, J.E.; Wang, A.; Field, J.; Morrison, H.G.; McArthur, A.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Loftus, B.J.; Samuelson, J. Evidence for lateral transfer of genes encoding ferredoxins, nitroreductases, NADH oxidase, and alcohol dehydrogenase 3 from anaerobic prokaryotes to Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba histolytica. Eukaryot. Cell 2002, 1, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, B.M.; Stanley, S.L., Jr.; Yong, T.S.; Ali, M.; Yang, W.; Diedrich, D.L.; Torian, B.E. Surface localization, regulation, and biologic properties of the 96-kDa alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenase (EhADH2) of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Biller, L.; Matthiesen, J.; Kuhne, V.; Lotter, H.; Handal, G.; Nozaki, T.; Saito-Nakano, Y.; Schumann, M.; Roeder, T.; Tannich, E.; et al. The Cell Surface Proteome of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Fehling, H.; Matthiesen, J.; Lorenzen, S.; Schuldt, K.; Bernin, H.; Zaruba, M.; Lender, C.; Ernst, T.; Ittrich, H.; et al. Overexpression of differentially expressed genes identified in non-pathogenic and pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica clones allow identification of new pathogenicity factors involved in amoebic liver abscess formation. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiesen, J.; Lender, C.; Haferkorn, A.; Fehling, H.; Meyer, M.; Matthies, T.; Tannich, E.; Roeder, T.; Lotter, H.; Bruchhaus, I. Trigger-induced RNAi gene silencing to identify pathogenicity factors of Entamoeba histolytica. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.S.; Harlow, D.R.; Cunnick, C.C. A new medium for axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1978, 72, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, L.; Schmidt, H.; Krause, E.; Gelhaus, C.; Matthiesen, J.; Handal, G.; Lotter, H.; Janssen, O.; Tannich, E.; Bruchhaus, I. Comparison of two genetically related Entamoeba histolytica cell lines derived from the same isolate with different pathogenic properties. Proteomics 2009, 9, 4107–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leippe, M.; Sievertsen, H.J.; Tannich, E.; Horstmann, R.D. Spontaneous release of cysteine proteinases but not of pore-forming peptides by viable Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitology 1995, 111, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.G.; Alsmark, U.C.; Tazreiter, M.; Saito-Nakano, Y.; Ali, V.; Marion, S.; Weber, C.; Mukherjee, C.; Bruchhaus, I.; Tannich, E.; et al. Structure and content of the Entamoeba histolytica genome. Adv. Parasitol. 2007, 65, 51–190. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, E.E.; Martinez-Alcaraz, E.R.; Barbosa-Sabanero, G.; Rivera-Baron, E.I.; Arias-Negrete, S.; Zazueta-Sandoval, R. Subcellular localization of the NAD+-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase in Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. J. Parasitol. 2002, 88, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Li, E.; Kairong, T.; Stanley Jr, S.L. Entamoeba histolytica has an alcohol dehydrogenase homologous to the multifunctional adhE gene product of Escherichia coli, Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1994, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elleuche, S.; Fodor, K.; Klippel, B.; von der Heyde, A.; Wilmanns, M.; Antranikian, G. Structural and biochemical characterisation of a NAD(+)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase from Oenococcus oeni as a new model molecule for industrial biotechnology applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 8963–8975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarboe, L.R. YqhD: A broad-substrate range aldehyde reductase with various applications in production of biorenewable fuels and chemicals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleuche, S.; Fodor, K.; von der Heyde, A.; Klippel, B.; Wilmanns, M.; Antranikian, G. Group III alcohol dehydrogenase from Pectobacterium atrosepticum: Insights into enzymatic activity and organization of the metal ion-containing region. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4041–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Song, J.M.; Park, M.Y.; Park, H.M.; Sun, J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, J.S. Structures of iron-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase 2 from Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 with and without NAD+ cofactor. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 407, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.F.; Fewson, C.A. Molecular characterization of microbial alcohol dehydrogenases. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1994, 20, 13–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzenbacher, G.; Alvarez, K.; Van Den Heuvel, R.H.; Versluis, C.; Spinelli, S.; Campanacci, V.; Valencia, C.; Cambillau, C.; Eklund, H.; Tegoni, M. Crystal structure of E.coli alcohol dehydrogenase YqhD: Evidence of a covalently modified NADP coenzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, N.; Rangel, P.; Hernandez-Munoz, R.; Perez-Montfort, R. Purification of alcohol dehydrogenase from Entamoeba histolytica and Saccharomyces cerevisiae using zinc-affinity chromatography. Protein Expr. Purif. 1997, 10, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, A.; Perdrizet, G.; Paz, Y.M.C.G.; Lanfranchi, R.; Phay, M. Effects of iron depletion on Entamoeba histolytica alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (EhADH2) and trophozoite growth: Implications for antiamoebic therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, J.M.; Arenas, F.A.; Pradenas, G.A.; Sandoval, J.M.; Vasquez, C.C. Escherichia coli YqhD exhibits aldehyde reductase activity and protects from the harmful effect of lipid peroxidation-derived aldehydes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7346–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorokhov, Y.L.; Shindyapina, A.V.; Sheshukova, E.V.; Komarova, T.V. Metabolic methanol: Molecular pathways and physiological roles. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 603–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Onodera, M.; Hasegawa, T. Toxicity of formaldehyde in experimental animals--concentrations of the chemical in the elution from dishes of formaldehyde resin in some vegetables. Keio J. Med. 1975, 24, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dhareshwar, S.S.; Stella, V.J. Your prodrug releases formaldehyde: Should you be concerned? No! J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Accession Number (AmoebaDB) | Length (aa) | ADH Type (Homology) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| EhADH1 | |||
| EHI_023110 | 366 | Type 1, Zn-dependent | [11,12] |
| EHI_042260 | 343 | Type 1, Zn-dependent | |
| EHI_107210 | 367 | Type 1, Zn-dependent | |
| EhADH2 | |||
| EHI_150490 | 870 | Bifunctional ADHE | [5,6,7,18,26,27] |
| EHI_160940# | 870 | Bifunctional ADHE | |
| EHI_024240 | 829 1 | Bifunctional ADHE | |
| EhADH3 | |||
| EHI_198760 (EhADH3A) | 384 | Fe-ADH | [13,14,15] |
| EHI_088020 (EhADH3Ba) | 382 | Fe-ADH | [20] |
| EHI_160670 (EhADH3Bb) | 382 2 | Fe-ADH | [20] |
| EHI_125950 (EhADH3C) | 383 | Fe-ADH | |
| EHI_192470 (EhADH3D) | 382 | Fe-ADH | |
| Undetermined | |||
| EHI_000410 | 360 | Fe-ADH superfamily | |
| EHI_166490 | 419 1 | Bifunctional ADHE EHI_150490: 52% (C-terminus) | |
| EhADH1 | |||||
| EHI_023110 | EHI_042260 | EHI_107210 | |||
| EHI_023110 | × | 24% | 66% | ||
| EHI_042260 | × | 25% | |||
| EHI_107210 | × | ||||
| EhADH2 | |||||
| EHI_150490 | EHI_160940 | EHI_024240 1 | |||
| EHI_150490 | × | 99% | 97% | ||
| EHI_160940 | × | 97% | |||
| EHI_024240 | × | ||||
| EhADH3 | |||||
| EHI_088020 | EHI_160670 | EHI_198760 | EHI_125950 | EHI_192470 | |
| EHI_088020 | × | 100% | 70% | 55% | 78% |
| EHI_160670 | × | 70% | 55% | 78% | |
| EHI_198760 | × | 55% | 69% | ||
| EHI_125950 | × | 57% | |||
| EHI_192470 | × |
| Gene | Expression Level | Fold Change | Padj | Product | qPCT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B2p_pNC | B2p pNC-ehadh3bb | B8np | B8np-Si-ehadh3bb | ||||
| EHI_088020/EHI_160670 | 312 | 4081 | 13 | 9.4 × 10−34 | EhADH3Ba/b | 1 | 0.02 ± 0.008 **** |
| EHI_198760 | 10,423 | 12,377 | 1.2 | 1 | EhADH3A | 1 | 0.935 ± 0.18 |
| EHI_125950 | 6319 | 6578 | 1.0 | 1 | EhADH3C | 1 | 0.465 ± 0.12 **** |
| EHI_192470 | 128 | 132 | 1.0 | 1 | EhADH3D | 1 | 0.01 ± 0 **** |
| EHI_022490 | 15 | 52 | 3.5 | 0.0033 | AIG family protein | ||
| EHI_144490 | 309 | 746 | 2.4 | 0.0033 | Hypothetical protein | ||
| EHI_176590 | 28 | 96 | 3.4 | 0.0046 | AIG family protein | ||
| EHI_062960 | 10 | 37 | 3.7 | 0.0205 | Hypothetical protein | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
König, C.; Meyer, M.; Lender, C.; Nehls, S.; Wallaschkowski, T.; Holm, T.; Matthies, T.; Lercher, D.; Matthiesen, J.; Fehling, H.; et al. An Alcohol Dehydrogenase 3 (ADH3) from Entamoeba histolytica Is Involved in the Detoxification of Toxic Aldehydes. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101608
König C, Meyer M, Lender C, Nehls S, Wallaschkowski T, Holm T, Matthies T, Lercher D, Matthiesen J, Fehling H, et al. An Alcohol Dehydrogenase 3 (ADH3) from Entamoeba histolytica Is Involved in the Detoxification of Toxic Aldehydes. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(10):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101608
Chicago/Turabian StyleKönig, Constantin, Martin Meyer, Corinna Lender, Sarah Nehls, Tina Wallaschkowski, Tobias Holm, Thorben Matthies, Dirk Lercher, Jenny Matthiesen, Helena Fehling, and et al. 2020. "An Alcohol Dehydrogenase 3 (ADH3) from Entamoeba histolytica Is Involved in the Detoxification of Toxic Aldehydes" Microorganisms 8, no. 10: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101608
APA StyleKönig, C., Meyer, M., Lender, C., Nehls, S., Wallaschkowski, T., Holm, T., Matthies, T., Lercher, D., Matthiesen, J., Fehling, H., Roeder, T., Reindl, S., Rosenthal, M., Metwally, N. G., Lotter, H., & Bruchhaus, I. (2020). An Alcohol Dehydrogenase 3 (ADH3) from Entamoeba histolytica Is Involved in the Detoxification of Toxic Aldehydes. Microorganisms, 8(10), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101608







