The hns Gene of Escherichia coli Is Transcriptionally Down-Regulated by (p)ppGpp
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria Strains
2.2. DNA Manipulation and General Procedures
2.3. In Vitro Transcription
2.4. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays
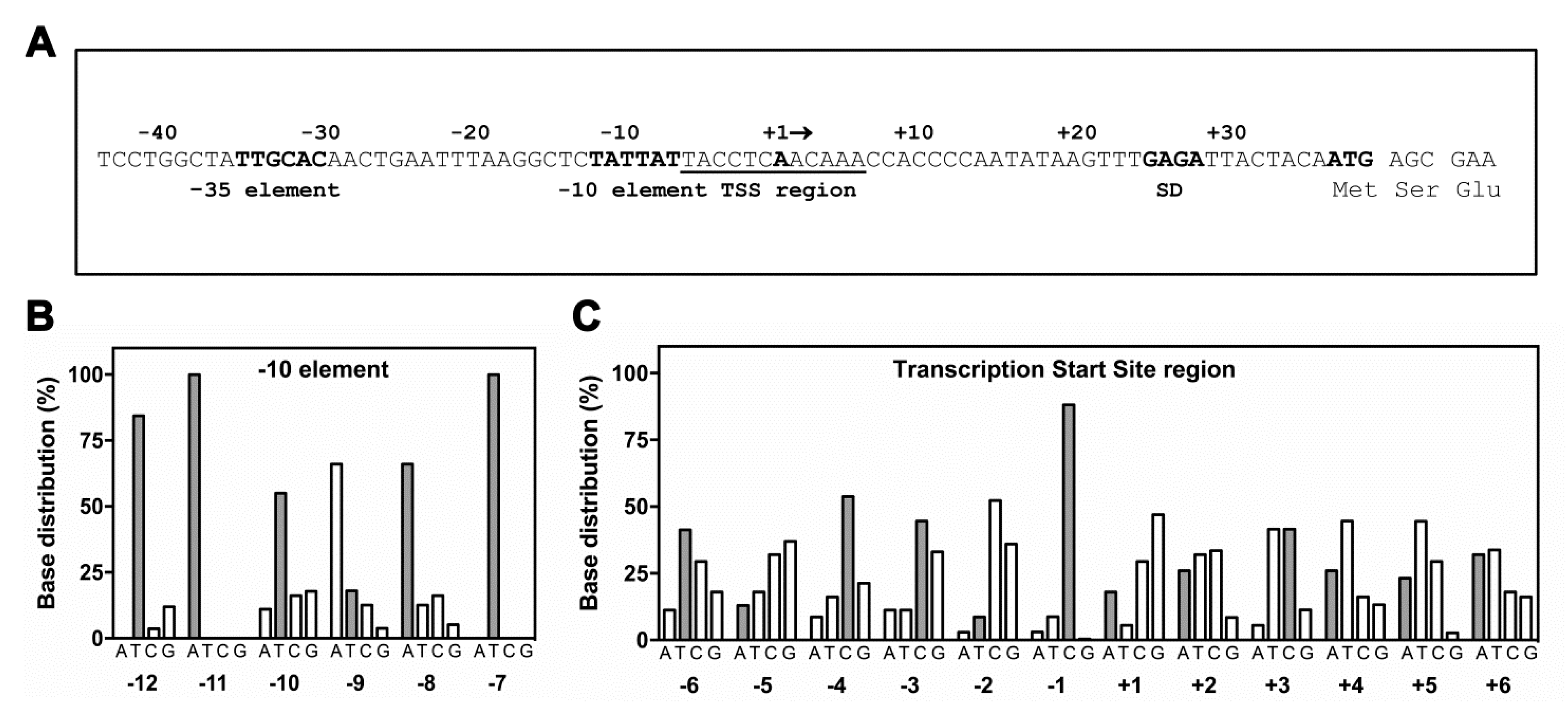
3. Results
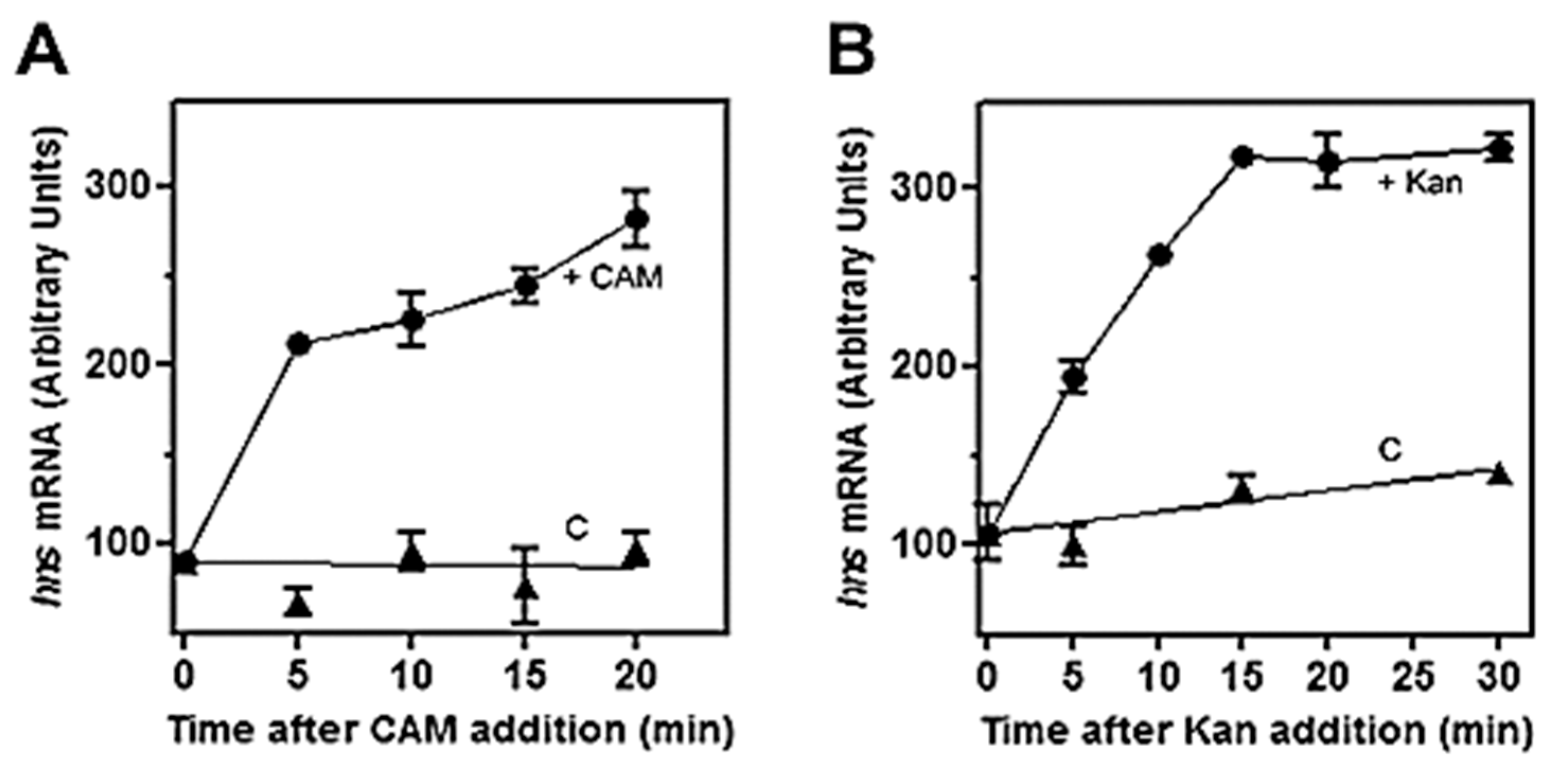
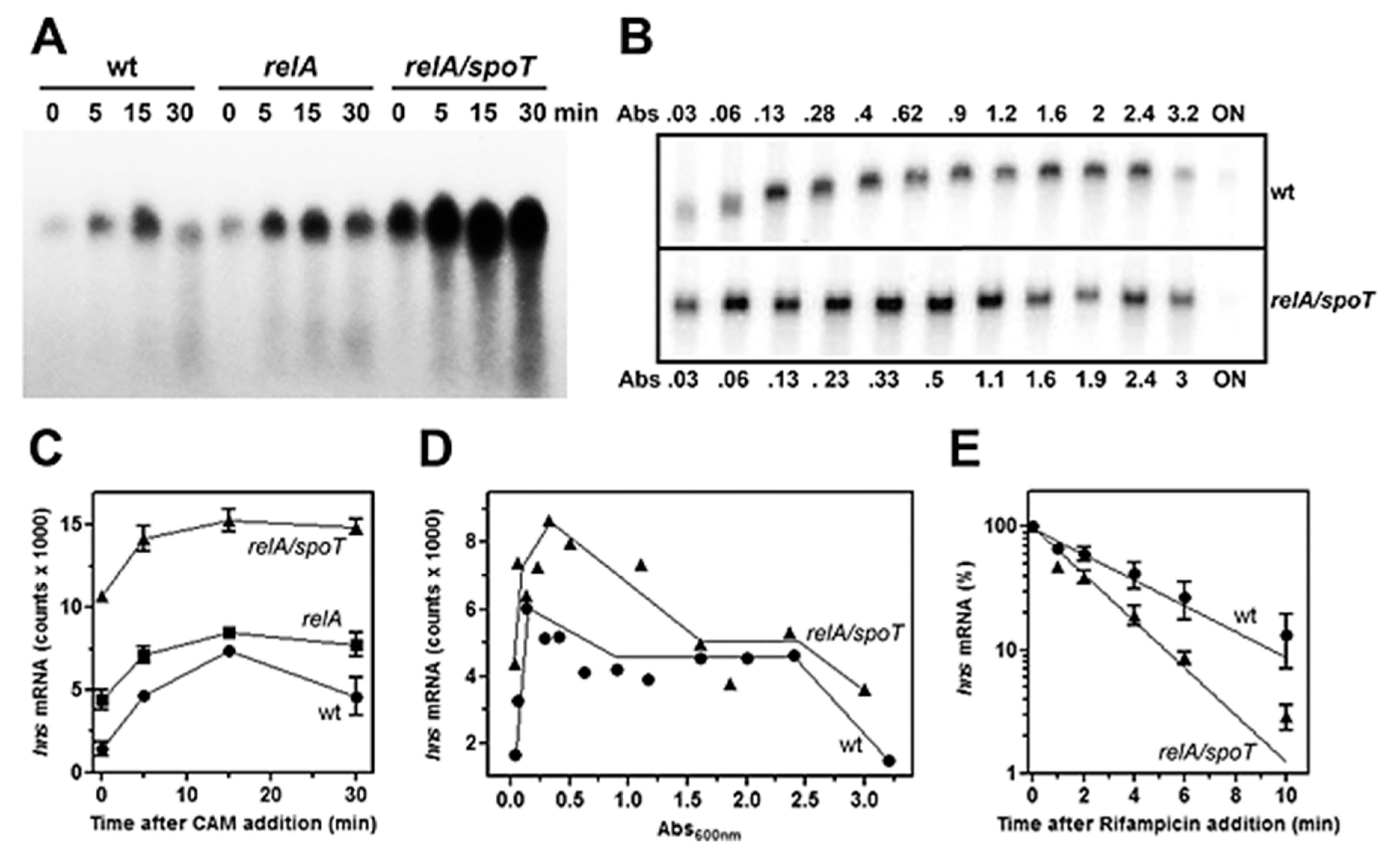
3.1. Low Levels of (p)ppGpp Stimulate hns Expression
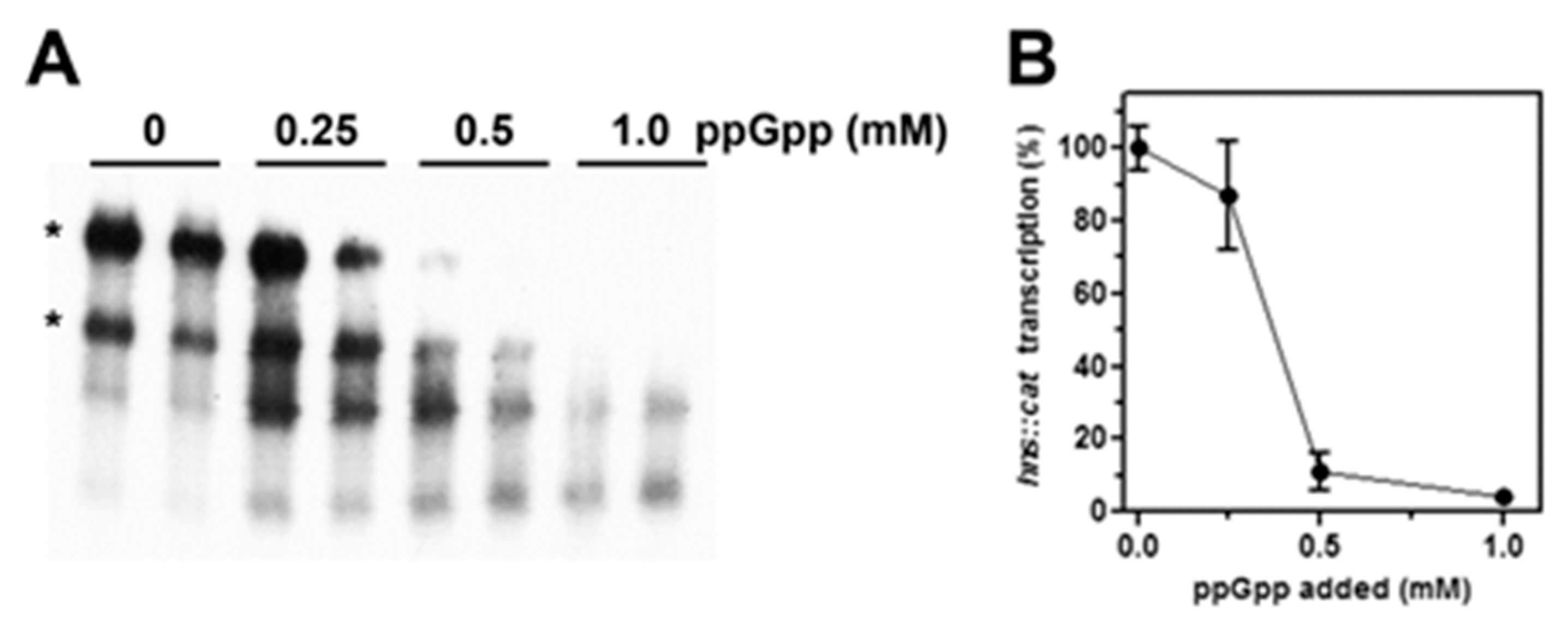
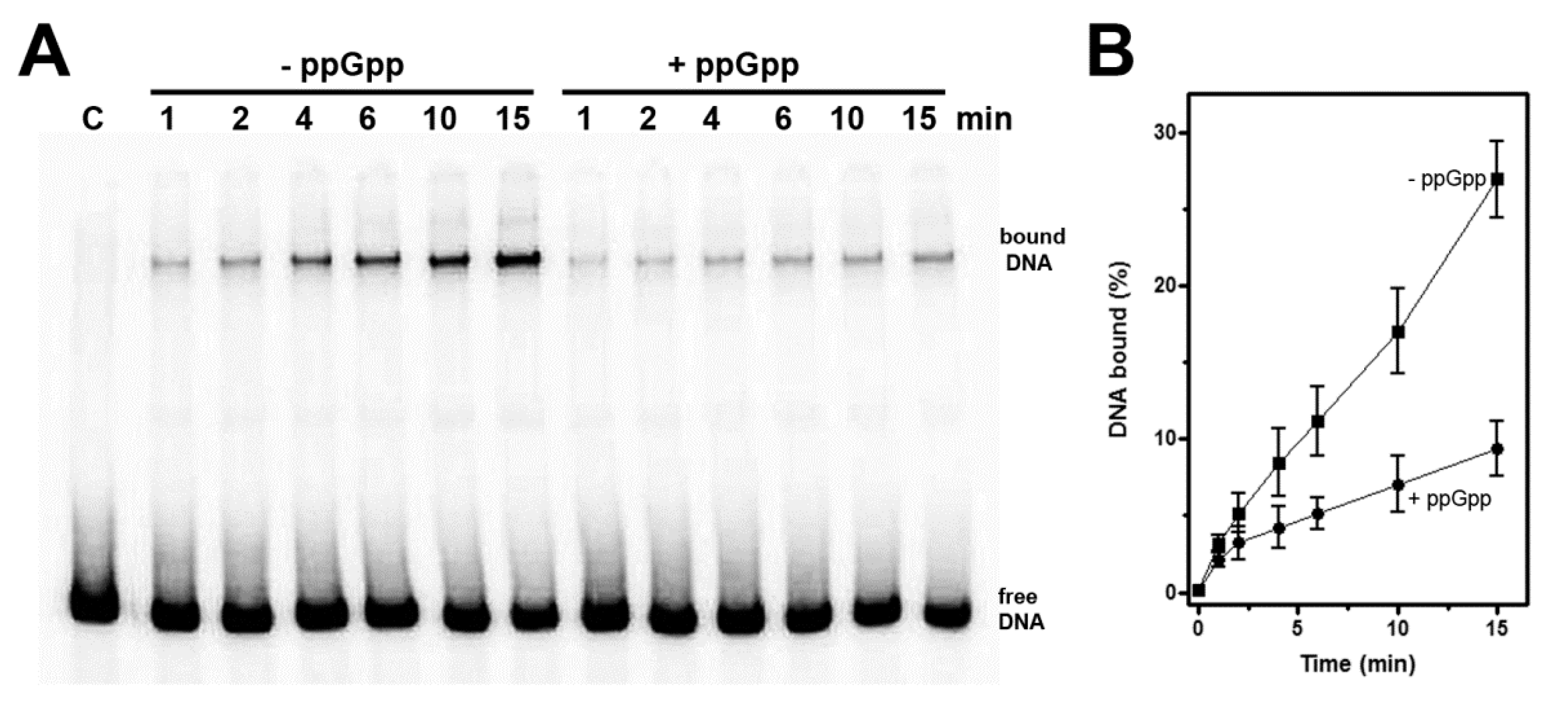
3.2. High Levels of (p)ppGpp Directly Repress hns Promoter
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potrykus, K.; Cashel, M. (p)ppGpp: Still magical? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Bittner, A.N.; Wang, J.D. Diversity in (p)ppGpp metabolism and effectors. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 24, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinchen, W.; Bange, G. The magic dance of the alarmones (p)ppGpp. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneau, S.; Hallez, R. Make and break the alarmone: Regulation of (p)ppGpp synthetase/hydrolase enzymes in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winther, K.S.; Roghanian, M.; Gerdes, K. Activation of the stringent response by loading of RelA tRNA complexes at the ribosomal A-site. Mol. Cell. 2018, 70, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauryliuk, V.; Atkinson, G.C.; Murakami, K.S.; Tenson, T.; Gerdes, K. Recent functional insights into the role of (p)ppGpp in bacterial physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, S.P.; Ross, W.; Gourse, R.L. Advances in bacterial promoter recognition and its control by factors that do not bind DNA. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourse, R.L.; Chen, A.Y.; Gopalkrishnan, S.; Sanchez-Vazquez, P.; Myers, A.; Ross, W. Transcriptional Responses to ppGpp and DksA. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, W.; Vrentas, C.E.; Sanchez-Vazquez, P.; Gaal, T.; Gourse, R.L. The magic spot: A ppGpp binding site on E. coli RNA polymerase responsible for regulation of transcription initiation. Mol. Cell. 2013, 50, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, W.; Sanchez-Vazquez, P.; Chen, AY.; Lee, JH.; Burgos, HL.; Gourse, R.L. ppGpp binding to a site at the RNAP-DksA interface accounts for its dramatic effects on transcription initiation during the stringent response. Mol. Cell. 2016, 62, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vazquez, P.; Dewey, C.N.; Kitten, N.; Ross, W.; Gourse, R.L. Genome-wide effects on Escherichia coli transcription from ppGpp binding to its two sites on RNA polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8310–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åberg, A.; Fernandez-Vazquez, J.; Cabrer-Panes, J.D.; Sanchez, A.; Balsalobre, C. Similar and Divergent Effects of ppGpp and DksA Deficiencies on Transcription in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3226–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pon, C.L.; Calogero, R.A.; Gualerzi, C.O. Identification, cloning, nucleotide sequence and chromosomal map location of hns, the structural gene for Escherichia coli DNA-binding protein H-NS. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1988, 212, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconi, M.; Gualtieri, M.T.; La Teana, A.; Losso, M.A.; Pon, C.L. Proteins from the prokaryotic nucleoid: Primary and quaternary structure of the15-kD Escherichia coli DNA binding protein H-NS. Mol. Microbiol. 1988, 2, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconi, M.; Higgins, N.P.; Spurio, R.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Expression of the gene encoding the major bacterial nucleoid protein H-NS is subject to transcriptional auto-repression. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 10, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorman, C.J. H-NS, the genome sentinel. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, S.C.; Dorman, C.J. Bacterial nucleoid-associated proteins, nucleoid structure and gene expression. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimsky, S.; Travers, A. Pervasive regulation of nucleoid structure and function by nucleoid-associated proteins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlung, T.; Ingmer, H. H-NS: A modulator of environmentally regulated gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Muramatsu, S.; Mizuno, T. An Escherichia coli protein that preferentially binds to sharply curved DNA. J. Biochem. 1990, 108, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, B.R.; Li, Y.; Cote, A.; Weirauch, M.T.; Ding, P.; Hughes, T.R.; Navarre, W.W.; Xia, B.; Liu, J. Structural basis for recognition of AT-rich DNA by unrelated xenogeneic silencing proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10690–10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spurio, R.; Falconi, M.; Brandi, A.; Pon, L.C.; Gualerzi, C.O. The oligomeric structure of nucleoid protein H-NS is necessary for recognition of intrinsically curved DNA and for DNA bending. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahramanoglou, C.; Seshasayee, A.S.; Prieto, A.I.; Ibberson, D.; Schmidt, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Benes, V.; Fraser, G.M.; Luscombe, N.M. Direct and indirect effects of H-NS and Fis on global gene expression control in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2073–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Valk, R.A.; Vreede, J.; Qin, L.; Moolenaar, G.F.; Hofmann, A.; Goosen, N.; Dame, R.T. Mechanism of environmentally driven conformational changes that modulate H-NS DNA-bridging activity. eLife 2017, 6, e27369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahul Hameed, U.F.; Liao, C.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Huser, F.; Aljedani, S.S.; Zhao, X.; Momin, A.A.; Melo, F.A.; Guo, X.; Brooks, C.; et al. H-NS uses an autoinhibitory conformational switch for environment-controlled gene silencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2666–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihama, A.; Kori, A.; Koshio, E.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, H.; Shimada, T.; Makinoshima, H.; Iwata, A.; Fujita, N. Intracellular concentrations of transcription factors in Escherichia coli: 65 species with known regulatory functions. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Bridier, A.; Briandet, R.; Ishihama, A. Novel roles of LeuO in transcription regulation in E. coli: Genome antagonistic interplay with the universal silencer H-NS. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 82, 376–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarre, W.W.; McClelland, M.; Libby, S.J.; Fang, F.C. Silencing of xenogeneic DNA by H-NS-facilitation of lateral gene transfer in bacteria by a defense system that recognizes foreign DNA. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1456–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Xia, B.; Liu, J.; Navarre, W.W. Silencing of foreign DNA in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, A.; Giangrossi, M.; Giuliodori, A.M.; Falconi, M. An Interplay among FIS, H-NS, and Guanosine Tetraphosphate Modulates Transcription of the Escherichia coli cspA Gene under Physiological Growth Conditions. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammack, K.A.; Wade, H.E. The sedimentation behaviour of ribonuclease-active and -inactive ribosomes from bacteria. Biochem. J. 1965, 96, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarubbi, E.; Kenneth, E.R.; Cashel, M. Basal ppGpp level adjustment shown by new spoT mutants affect steady state growth rates and rrnA ribosomal promoter regulation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1988, 213, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Kalman, M.; Ikehara, K.; Zemel, S.; Glaser, G.; Cashel, M. Residual guanosine 3’,5’-bispyrophosphate synthetic activity of relA null mutants can be eliminated by spoT null mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 5980–5990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wright, B.E.; Minnick, M.F. Reversion rates in a leuB auxotroph of Escherichia coli K-12 correlate with ppGpp levels during exponential growth. Microbiology 1997, 143, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedin, K.; Witte, A.; Reisinger, G.; Lubitz, W.; Bläsi, U. Evaluation of the E. coli rrnB P1 promoter and phage-derived lysis genes for the use in a biological containment system: A concept study. J. Biotechnol. 1995, 39, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual; CSHL Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brandi, A.; Giangrossi, M.; Paoloni, S.; Spurio, R.; Giuliodori, A.M.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional events trigger de novo infB expression in cold stressed Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4638–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurio, R.; Dürrenberger, M.; Falconi, M.; La Teana, A.; Pon, C.L.; Gualerzi, C.O. Lethal overproduction of the Escherichia coli nucleoid protein H-NS: Ultramicroscopic and molecular autopsy. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1992, 231, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarubbi, E.; Rudd, K.E.; Xiao, H.; Ikehara, K.; Kalman, M.; Cashell, M. Characterization of the spoT gene of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 15074–15082. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gross, C.; Engbaek, F.; Flammang, T.; Burgess, R. Rapid micromethod for the purification of Escherichia coli Ribonucleic Acid Polymerase and the preparation of bacterial extracts active in ribonucleic acid synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 1976, 128, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, A.; Kimura, A.; Osawa, S. Effects of some antibiotics on the stringent control of RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1975, 139, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryals, J.; Little, R.; Bremer, H. Control of rRNA and tRNA syntheses in Escherichia coli by guanosine tetraphosphate. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 151, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamming, J.; Geert, A.B.; Gruber, M. E. coli RNA polymerase-rRNA promoter interaction and the effect of ppGpp. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 3947–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommais, F.; Krin, E.; Laurent-Winter, C.; Soutourina, O.; Malpertuy, A.; Le Caer, J.P.; Danchin, A.; Bertin, P. Large-scale monitoring of pleiotropic regulation of gene expression by the prokaryotic nucleoid-associated protein, H-NS. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconi, M.; Brandi, A.; La Teana, A.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Pon, C.L. Antagonistic involvement of FIS and H-NS proteins in the transcriptional control of hns expression. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconi, M.; Colonna, B.; Prosseda, G.; Micheli, G.; Gualerzi, C.O. Thermoregulation of Shigella and Escherichia coli EIEC pathogenicity. A temperature-dependent structural transition of DNA modulates accessibility of virF promoter to transcriptional repressor H-NS. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 7033–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, C.; Nieto, J.M.; Paytubi, S.; Falconi, M.; Gualerzi, C.O.; Juárez, A. Temperature- and H-NS-dependent regulation of a plasmid-encoded virulence operon expressing Escherichia coli hemolysin. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5058–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloin, C.; McKenna, S.; Dorman, C.J. Molecular dissection of VirB a key regulator of the virulence cascade of Shigella flexneri. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15333–15344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walthers, D.; Carrol, R.K.; Navarre, W.W.; Libby, S.J.; Fang, F.C.; Kenney, L.J. The response regulator SsrB activates expression of diverse Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 promoters and counters silencing by the nucleoid-associated protein H-NS. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 65, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.N.; Giangrossi, M.; Prosseda, G.; Brandi, A.; Di Martino, M.L.; Colonna, B.; Falconi, M. A multifactor regulatory circuit involving H-NS, VirF and an antisense RNA modulates transcription of the virulence gene icsA of Shigella flexneri. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8122–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, M.D.; Mobley, H.L. Regulation of Expression of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Nonfimbrial Adhesin TosA by PapB Homolog TosR in Conjunction with H-NS and Lrp. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, M.; Wagner, R. Guanosine 3′,5′-bis(diphosphate) (ppGpp)-dependent inhibition of transcription from stringently controlled Escherichia coli promoters can be explained by an altered initiation pathway that traps RNA polymerase. FEBS 1997, 247, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łyżeń, R.; Maitra, A.; Milewska, K.; Kochanowska-Łyżeń, M.; Hernandez, V.J.; Szalewska-Pałasz, A. The dual role of DksA protein in the regulation of Escherichia coli pArgX promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 10316–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traxler, M.F.; Summers, S.M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Zacharia, V.M.; Hightower, G.A.; Smith, J.T.; Conway, T. The global, ppGpp-mediated stringent response to amino acid starvation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 1128–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spassky, A.; Rimsky, S.; Garreau, H.; Buc, H. H1a, an E. coli DNA-binding protein which accumulates in stationary phase, strongly compacts DNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 5321–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersch, P.; Schmidt, K.; Bremer, E. Synthesis of the Escherichia coli K-12 nucleoid-associated DNA-binding protein H-NS is subjected to growth-phase control and autoregulation. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 8, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, A.; Dorman, C.J. Coupling of Escherichia coli hns mRNA levels to DNA synthesis by autoregulation: Implications for growth phase control. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 18, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, E.; Sclavi, B. Gene Regulation by H-NS as a Function of Growth Conditions Depends on Chromosomal Position in Escherichia coli. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feklistov, A.; Darst, S.A. Structural basis for promoter -10 element recognition by the bacterial RNA polymerase σ subunit. Cell 2011, 147, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, A.A. Promoter sequence for stringent control of bacterial ribonucleic acid synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 1980, 141, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleghorn, M.L.; Davydova, E.K.; Basu, R.; Rothman-Denes, L.B.; Murakami, K.S. X-ray crystal structures elucidate the nucleotidyl transfer reaction of transcript initiation using two nucleotides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3566–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, J.T.; Chandrangsu, P.; Ross, W.; Gourse, R.L. Open complex scrunching before nucleotide addition accounts for the unusual transcription start site of E. coli ribosomal RNA promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1787–E1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, C.W.; Ross, W.; Martin-Tumasz, S.; Toulokhonov, I.; Vrentas, C.E.; Rutherford, S.T.; Lee, J.H.; Butcher, S.E.; Gourse, R.L. Direct interactions between the coiled-coil tip of DksA and the trigger loop of RNA polymerase mediate transcriptional regulation. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2634–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perederina, A.; Svetlov, V.; Vassylyeva, M.N.; Tahirov, T.H.; Yokoyama, S.; Artsimovitch, I.; Vassylyev, D.G. Regulation through the secondary channel-structural framework for ppGpp-DksA synergism during transcription. Cell 2004, 118, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.J.; Barker, M.M.; Ross, W.; Schneider, D.A.; Webb, C.; Foster, J.W.; Gourse, R.L. DksA: A critical component of the transcription initiation machinery that potentiates the regulation of rRNA promoters by ppGpp and the initiating NTP. Cell 2004, 118, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.W. Promoter-specific control of E. coli RNA polymerase by ppGpp and a general transcription factor. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Villers, C.L.; Lee, J.H.; Ross, W.; Gourse, R.L. Allosteric control of Escherichia coli rRNA promoter complexes by DksA. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandi, A.; Giangrossi, M.; Fabbretti, A.; Falconi, M. The hns Gene of Escherichia coli Is Transcriptionally Down-Regulated by (p)ppGpp. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101558
Brandi A, Giangrossi M, Fabbretti A, Falconi M. The hns Gene of Escherichia coli Is Transcriptionally Down-Regulated by (p)ppGpp. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(10):1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101558
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandi, Anna, Mara Giangrossi, Attilio Fabbretti, and Maurizio Falconi. 2020. "The hns Gene of Escherichia coli Is Transcriptionally Down-Regulated by (p)ppGpp" Microorganisms 8, no. 10: 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101558
APA StyleBrandi, A., Giangrossi, M., Fabbretti, A., & Falconi, M. (2020). The hns Gene of Escherichia coli Is Transcriptionally Down-Regulated by (p)ppGpp. Microorganisms, 8(10), 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101558





