Improvement of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 as a Cell Factory: IPTG-Inducible Plasmid Construction and Strain Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Media Formulations
2.2. Construction of pP79 and p79C Expression Plasmids
2.3. Sub-Cloning of Heterologous Genes into the Expression Plasmids
2.4. Preparation of pVS-lon and pVS-lacY Suicide Vectors
2.5. Transformation of KrPL and Selection of the lon and lacY+ Mutant Strains
2.6. gDNA Extraction from the Mutant Strains and Sequence Analysis
- lonA_SphI fw, lon_rv and lon_fw, lonB_EcoRI rv, for the analysis of lon mutants;
- lonY_fw, lacY_rv and lacY_fw, lonY_rv, for the analysis of lacY+ mutants.
2.7. Recombinant Production of the Reporter Proteins
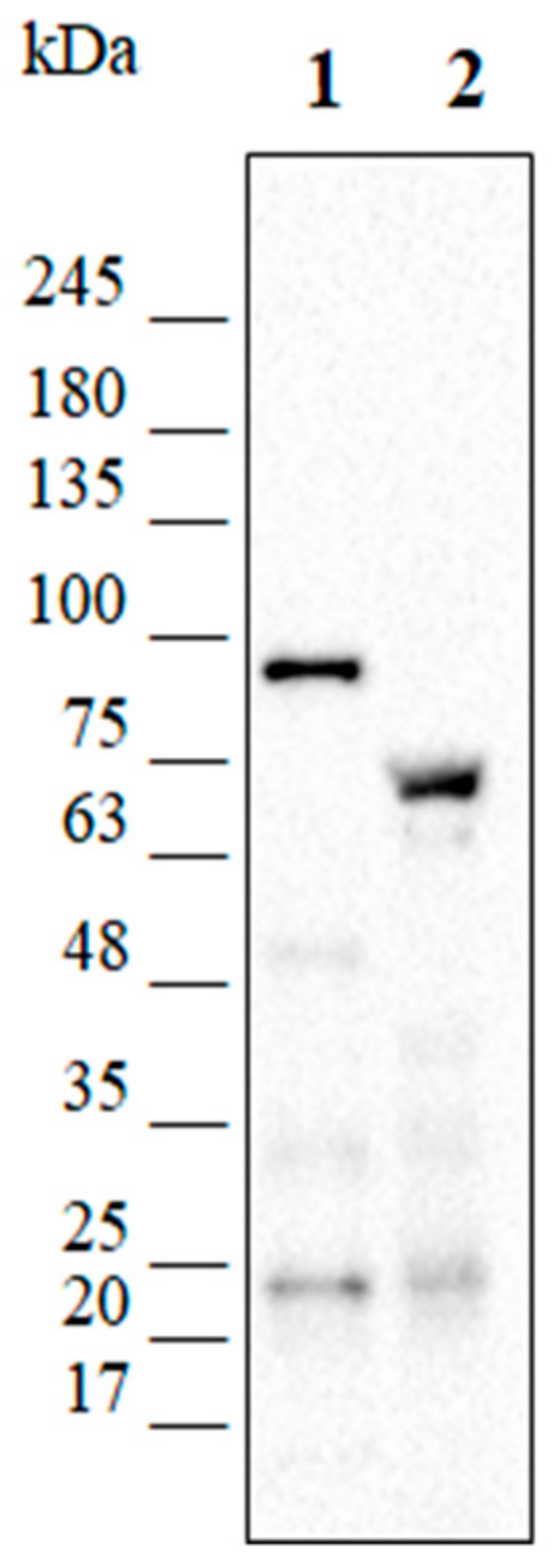
2.8. Analysis of the Production of the Recombinant Proteins
2.9. mRNA Extraction and qPCR
3. Results
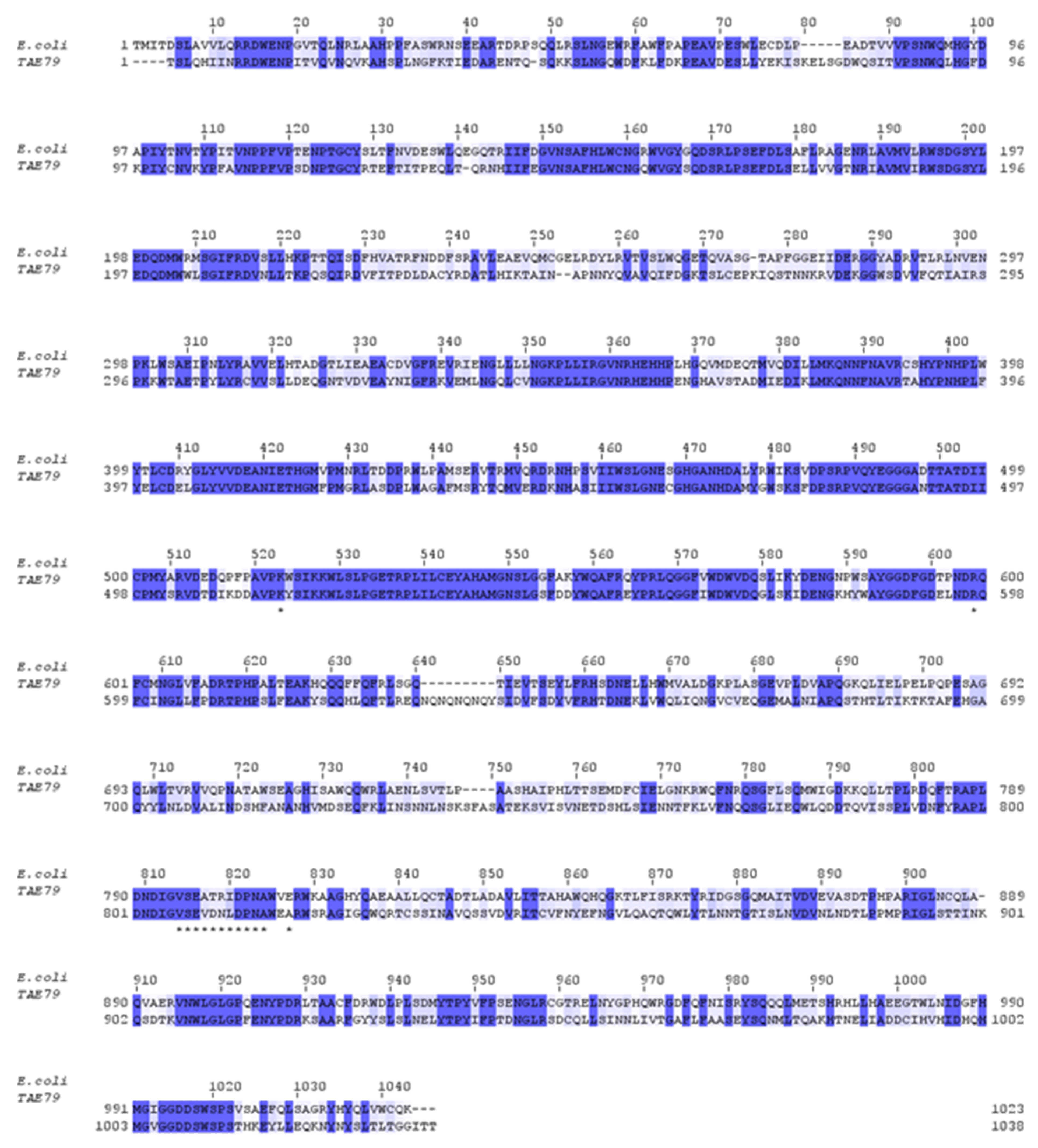
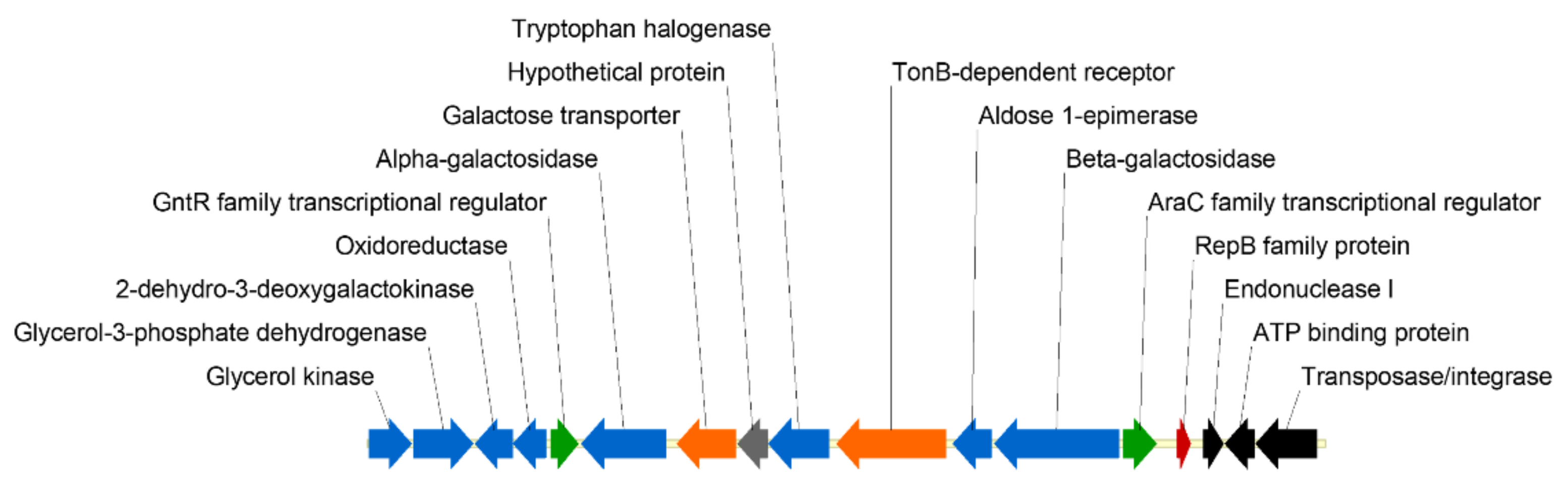
3.1. Analysis and Cloning of the PhTAE79 lacZ Expression Sequences
3.2. Quantification of pP79 Activity Using β-Galactosidase and R9-GFP Reporters
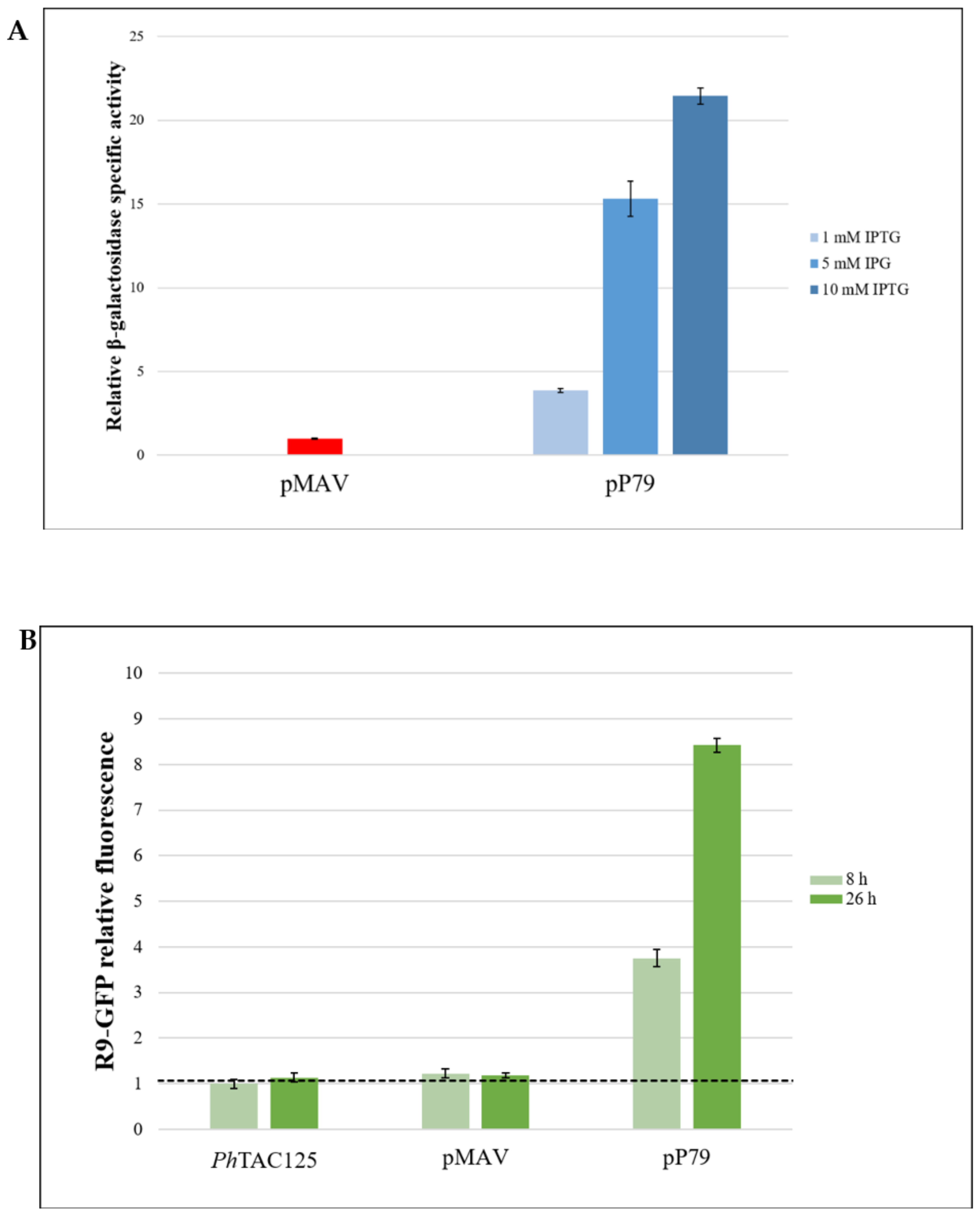
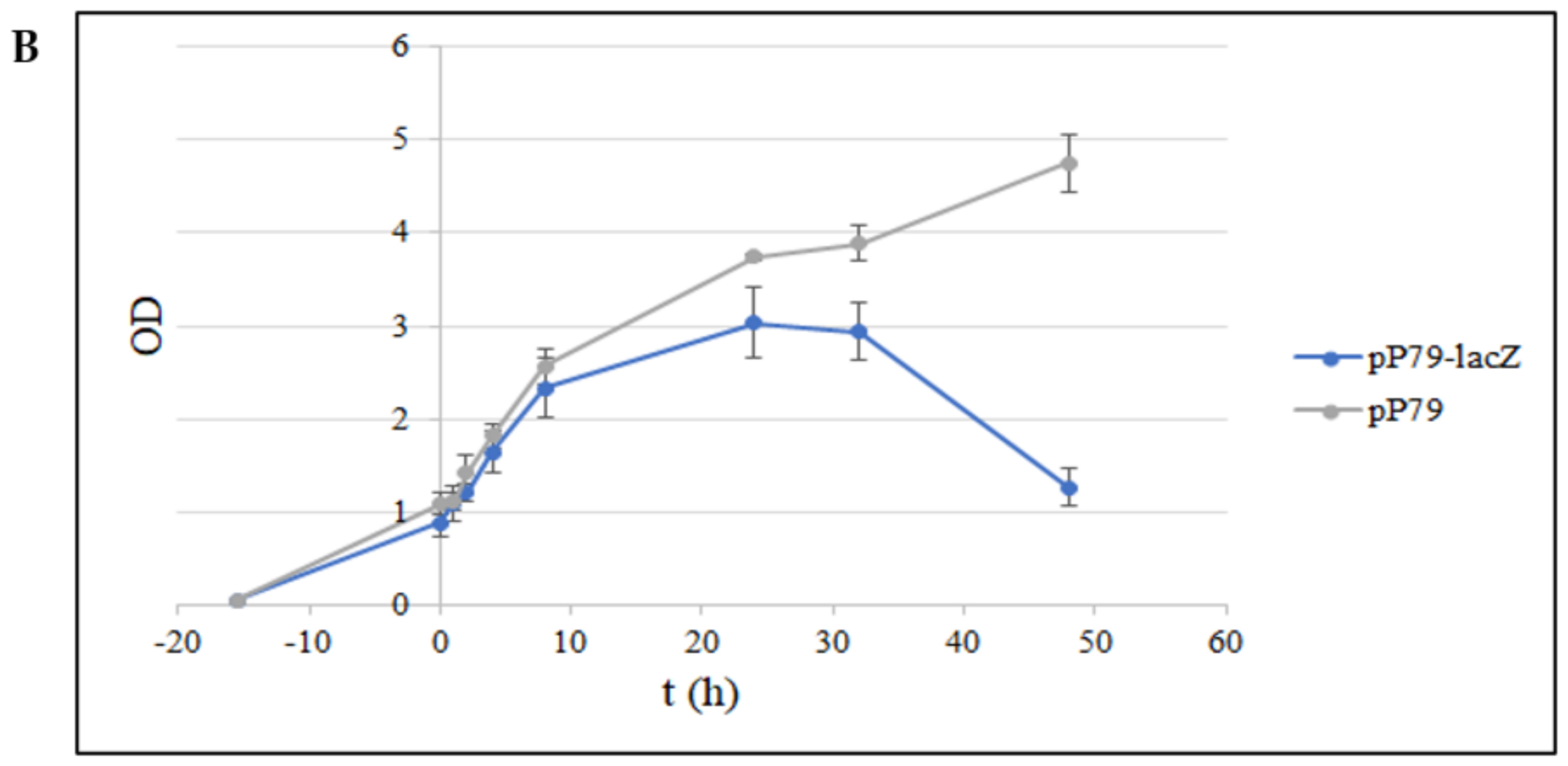
3.2.1. Comparison between pP79 and pMAV Efficiencies
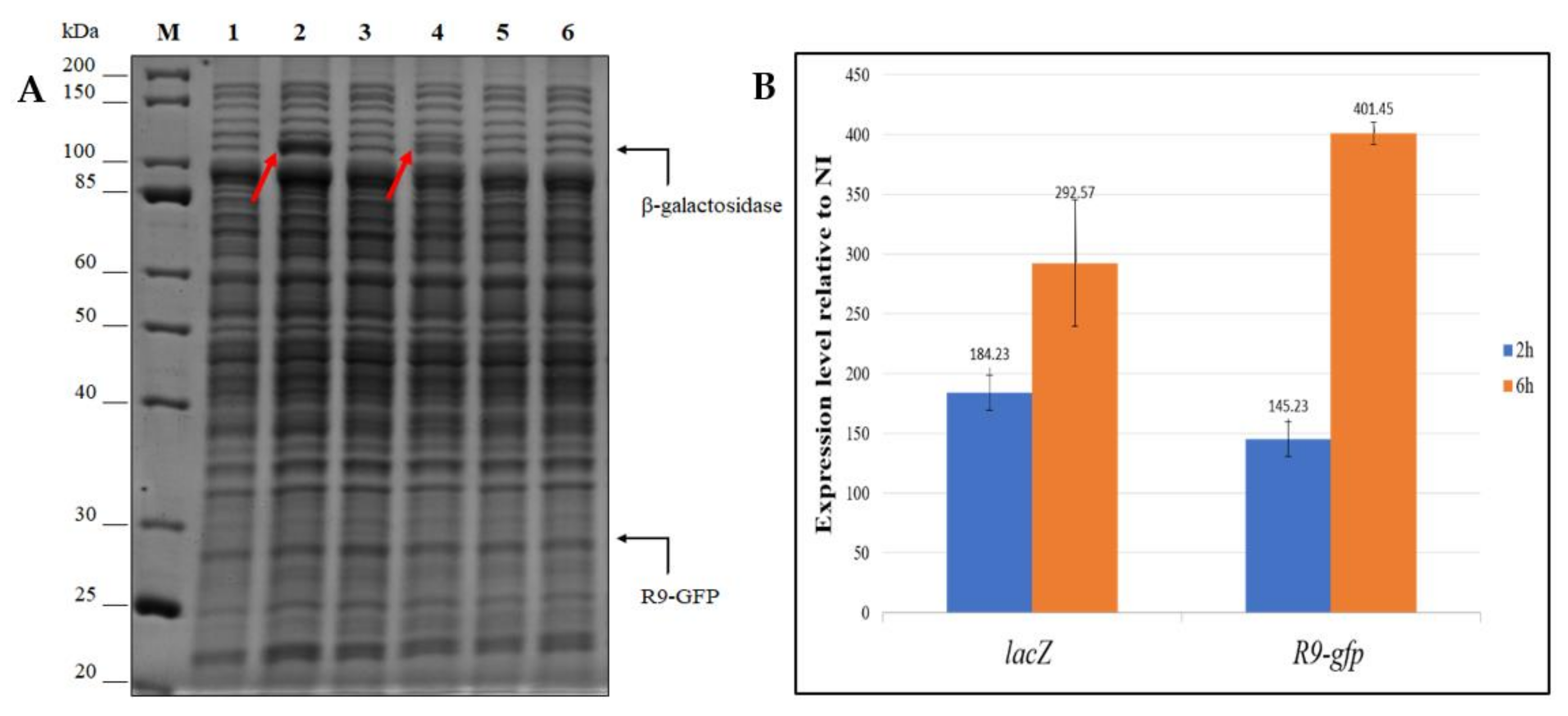
3.2.2. Evaluation of the Reliability of lacZ and R9-gfp as Reporter Systems
3.2.3. Influence of Medium Composition on pP79 Efficiency
3.3. Optimization of IPTG Transport Mechanism
3.3.1. Attempts in the Plasmidic Expression of a Lactose Permease
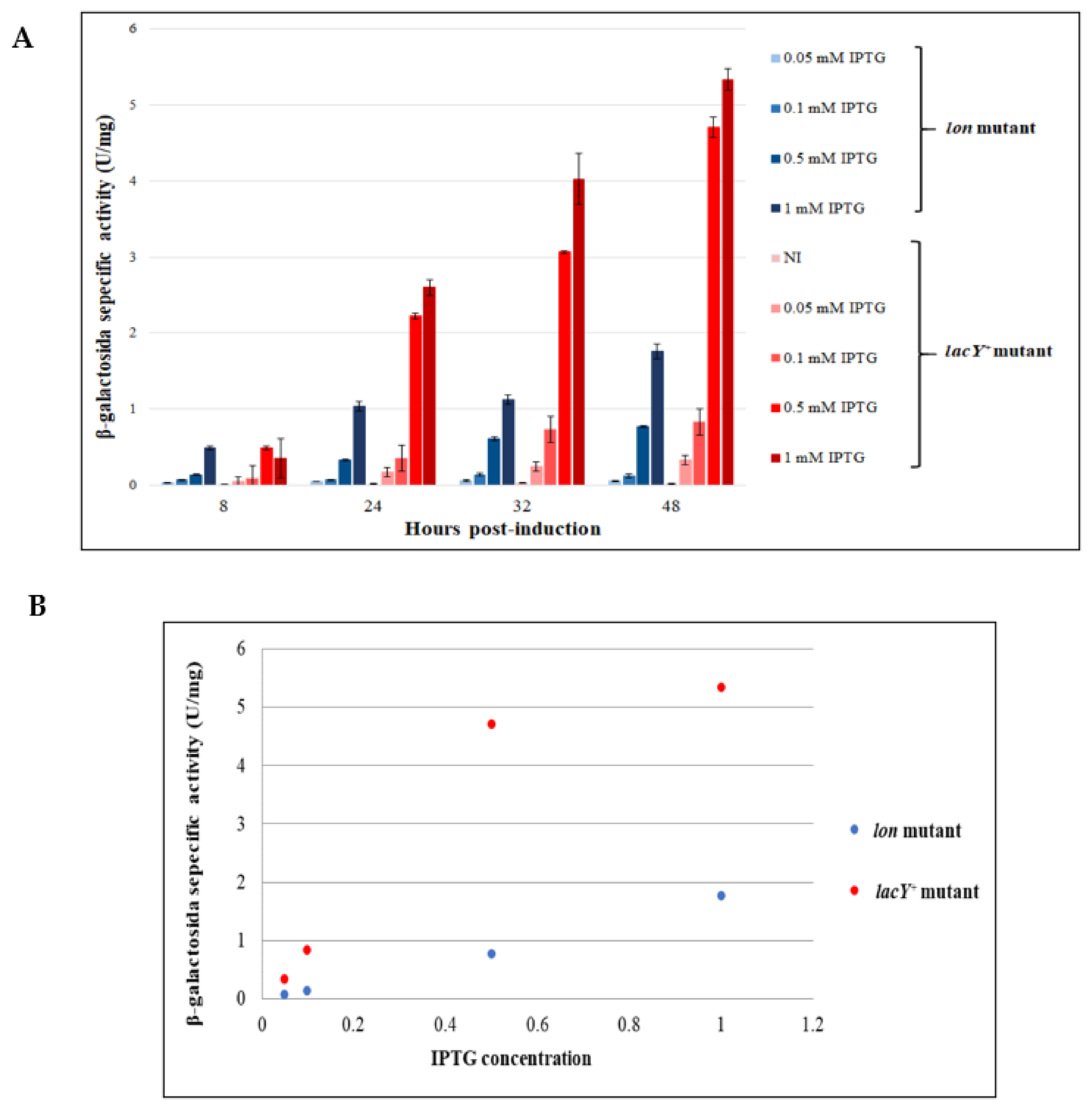
3.3.2. Construction of KrPL lon and lacY+ Mutant Strains
3.4. Comparison between the Performance of KrPL lon and KrPL lacY+ Strains
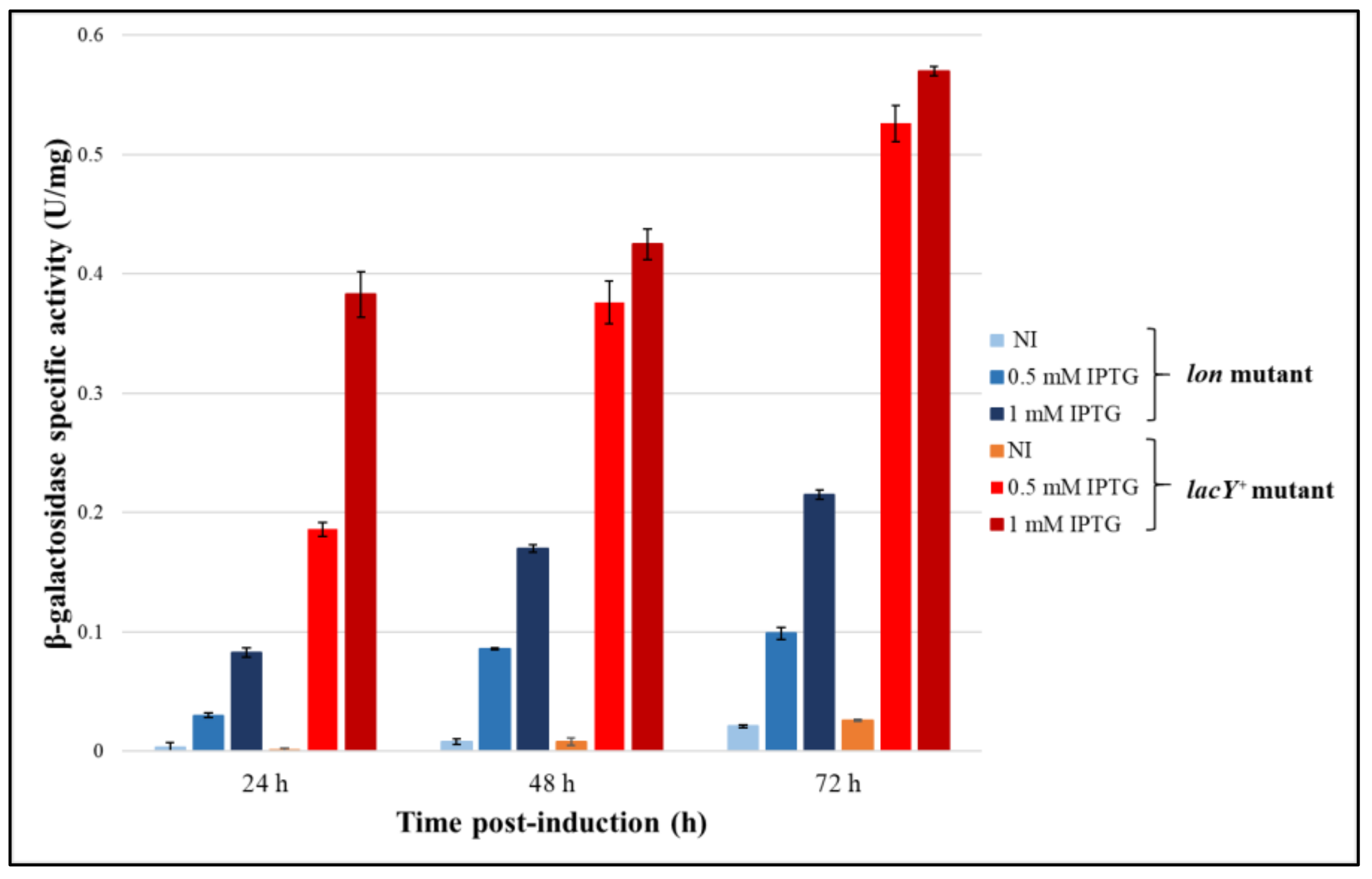
3.4.1. Evaluation of the Production Improvement at Different Temperatures
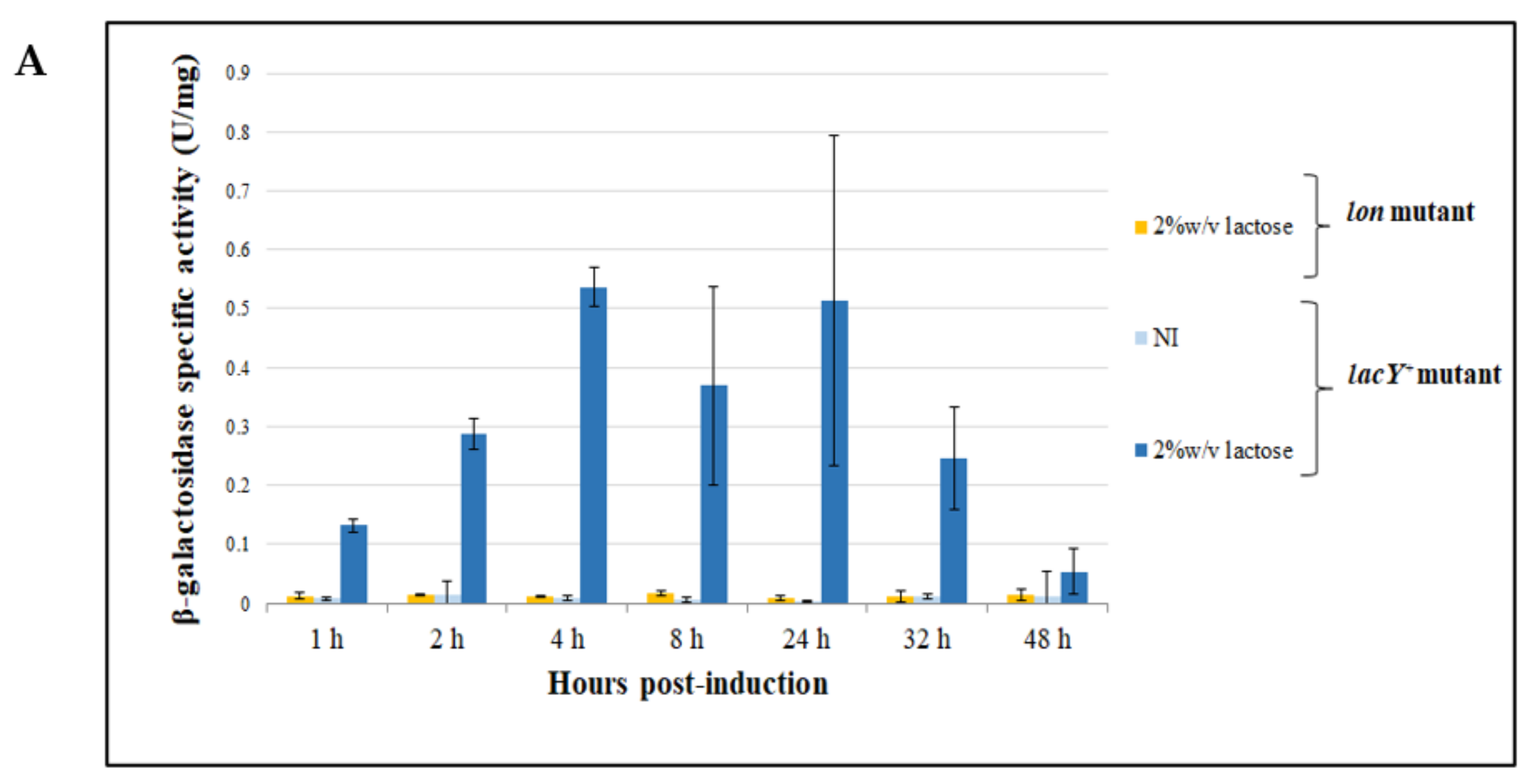
3.4.2. Evaluation of β-Galactosidase Production Using Lactose as an Inducer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Allolactose-Dependent AraC-Like Transcriptional Regulators Predicted on the Basis of β-galactosidases Features
References
- Duilio, A.; Madonna, S.; Tutino, M.L.; Pirozzi, M.; Sannia, G.; Marino, G. Promoters from a cold-adapted bacterium: Definition of a consensus motif and molecular characterization of UP regulative elements. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, R.; Rippa, V.; Sannia, G.; Marino, G.; Duilio, A. An effective cold inducible expression system developed in Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 127, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannino, F.; Giuliani, M.; Salvatore, U.; Apuzzo, G.A.; De Pascale, D.; Fani, R.; Fondi, M.; Marino, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E. A novel synthetic medium and expression system for subzero growth and recombinant protein production in Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 101, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilli, E.; Giuliani, M.; Tutino, M.L. General Secretory Pathway from marine Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Mar. Genom. 2008, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.; Parrilli, E.; Ferrer, P.; Baumann, K.; Marino, G.; Tutino, M.L. Process optimization for recombinant protein production in the psychrophilic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. Process. Biochem. 2011, 46, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.; Parrilli, E.; Sannino, F.; Apuzzo, G.A.; Marino, G.; Tutino, M.L. Recombinant production of a single-chain antibody fragment in Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4887–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmes, B.; Hartung, A.; Lalk, M.; Liebeke, M.; Schweder, T.; Neubauer, P. Fed-batch process for the psychrotolerant marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. Microb. Cell Factories 2010, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyoux, A.; Jennes, I.; Dubois, P.; Genicot, S.; Dubail, F.; François, J.M.; Baise, E.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C. Cold-Adapted β-Galactosidase from the Antarctic Psychrophile Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Voorde, I.; Goiris, K.; Syryn, E.; Bussche, C.V.D.; Aerts, G. Evaluation of the cold-active Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis β-galactosidase enzyme for lactose hydrolysis in whey permeate as primary step of d-tagatose production. Process. Biochem. 2014, 49, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Médigue, C.; Krin, E.; Pascal, G.; Barbe, V.; Bernsel, A.; Bertin, P.N.; Cheung, F.; Cruveiller, S.; D’Amico, S.; Duilio, A.; et al. Coping with cold: The genome of the versatile marine Antarctica bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilli, E.; De Vizio, D.; Cirulli, C.; Tutino, M.L. Development of an improved Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 strain for recombinant protein secretion at low temperature. Microb. Cell Factories 2008, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmes, B.; Kock, H.; Glagla, S.; Albrecht, D.; Voigt, B.; Markert, S.; Gardebrecht, A.; Bode, R.; Danchin, A.; Feller, G.; et al. Cytoplasmic and Periplasmic Proteomic Signatures of Exponentially Growing Cells of the Psychrophilic Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktisTAC125. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fondi, M.; Maida, I.; Perrin, E.; Mellera, A.; Mocali, S.; Parrilli, E.; Tutino, M.L.; Lió, P.; Fani, R. Genome-scale metabolic reconstruction and constraint-based modelling of the Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutino, M.L.; Duilio, A.; Parrilli, E.; Remaut, E.; Sannia, G.; Marino, G. A novel replication element from an Antarctic plasmid as a tool for the expression of proteins at low temperature. Extremophiles 2001, 5, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Giaquinto, L.; Duilio, A.; Sannia, G.; Feller, G.; Marino, G. Secretion of α-Amylase from Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAB23: Two Different Pathways in Different Hosts. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5814–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, E.; Roldán, M.; Diez-Gil, C.; Unzueta, U.; Domingo-Espín, J.; Cedano, J.; Conchillo, O.; Ratera, I.; Veciana, J.; Daura, X.; et al. Protein nanodisk assembling and intracellular trafficking powered by an arginine-rich (R9) peptide. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gurtu, V.; Kain, S.R. An Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein Allows Sensitive Detection of Gene Transfer in Mammalian Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 227, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigbo, P.; Guzmán, E.; Romeu, A.; Garcia-Vallve, S. OPTIMIZER: A web server for optimizing the codon usage of DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W126–W131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusano, A.M.; Parrilli, E.; Duilio, A.; Sannia, G.; Marino, G.; Tutino, M.L. Secretion of psychrophilic α-amylase deletion mutants in Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 258, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.; Parrilli, E.; Pezzella, C.; Rippa, V.; Duilio, A.; Marino, G.; Tutino, M.L. A Novel Strategy for the Construction of Genomic Mutants of the Antarctic Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2011, 824, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, E.; Fondi, M.; Orlandini, V.; Perrin, E.; Maida, I.; De Pascale, D.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Giudice, A.L.; Filloux, A.; et al. The pangenome of (Antarctic) Pseudoalteromonas bacteria: Evolutionary and functional insights. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Colarusso, A.; Olombrada, M.; Parrilli, E.; Patrignani, A.; Tutino, M.L.; Toll-Riera, M. New insights on Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 genome organization and benchmarks of genome assembly applications using next and third generation sequencing technologies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crameri, A.; Whitehorn, E.A.; Tate, E.; Stemmer, W.P. Improved Green Fluorescent Protein by Molecular Evolution Using DNA Shuffling. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, E.; Ghini, V.; Giovannini, M.; Di Patti, F.; Cardazzo, B.; Carraro, L.; Fagorzi, C.; Turano, P.; Fani, R.; Fondi, M. Diauxie and co-utilization of carbon sources can coexist during bacterial growth in nutritionally complex environments. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocali, S.; Chiellini, C.; Fabiani, A.; Decuzzi, S.; De Pascale, D.; Parrilli, E.; Tutino, M.L.; Perrin, E.; Bosi, E.; Fondi, M.; et al. Ecology of cold environments: New insights of bacterial metabolic adaptation through an integrated genomic-phenomic approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.H.; Knudsen, S.; Sørensen, S.J. The effect of the lacY gene on the induction of IPTG inducible promoters, studied in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Curr. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilibaris, V.; Maenhaut-Michel, G.; Van Melderen, L. Biological roles of the Lon ATP-dependent protease. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Melderen, L.; Aertsen, A. Regulation and quality control by Lon-dependent proteolysis. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigentini, I.; Merico, A.; Tutino, M.L.; Compagno, C.; Marino, G. Optimization of recombinant human nerve growth factor production in the psychrophilic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 127, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unzueta, U.; Vázquez, F.; Accardi, G.; Mendoza, R.; Toledo-Rubio, V.; Giuliani, M.; Sannino, F.; Parrilli, E.; Abasolo, I.; Schwartz, S.; et al. Strategies for the production of difficult-to-express full-length eukaryotic proteins using microbial cell factories: Production of human alpha-galactosidase A. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5863–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlebnikov, A.; Keasling, J. Effect of lacY Expression on Homogeneity of Induction from the Ptac and Ptrc Promoters by Natural and Synthetic Inducers. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbudak, E.M.; Thattai, M.; Lim, H.N.; Shraiman, B.I.; Van Oudenaarden, A. Multistability in the lactose utilization network of Escherichia coli. Nature 2004, 427, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, T.; Biliouris, K.; Kaznessis, Y.N.; Beisel, C.L. Bacterial sugar utilization gives rise to distinct single-cell behaviours. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, T.; Biliouris, K.; Boykin, K.E.; Kaznessis, Y.N.; Beisel, C.L. Trade-offs in Engineering Sugar Utilization Pathways for Titratable Control. ACS Synth. Biol. 2014, 4, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Castané, A.; Vine, C.E.; Caminal, G.; López, C. Evidencing the role of lactose permease in IPTG uptake by Escherichia coli in fed-batch high cell density cultures. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 157, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, L.M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stülke, J.; Hillen, W. Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubellini, F.; Verdon, G.; Karpowich, N.K.; Luff, J.D.; Boël, G.; Gauthier, N.; Handelman, S.K.; Ades, S.E.; Hunt, J.F. Physiological Response to Membrane Protein Overexpression inE. coli. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Melderen, L.; Gottesman, S. Substrate sequestration by a proteolytically inactive Lon mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6064–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, S.; Collins, T.; Marx, J.-C.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C. Psychrophilic microorganisms: Challenges for life. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, M.; Dimanta, I.; Gavare, M.; Strazdina, I.; Liepins, J.; Juhna, T.; Kalnenieks, U. Hydrogen-producing Escherichia coli strains overexpressing lactose permease: FT-IR analysis of the lactose-induced stress. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2014, 61, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juers, D.H.; Matthews, B.W.; Huber, R.E. LacZ β-galactosidase: Structure and function of an enzyme of historical and molecular biological importance. Protein Sci. 2012, 21, 1792–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalik, V.K.; Guimaraes, J.C.; Cambray, G.; Lam, C.; Christoffersen, M.J.; Mai, Q.-A.; Tran, A.B.; Paull, M.; Keasling, J.D.; Arkin, A.P.; et al. Precise and reliable gene expression via standard transcription and translation initiation elements. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, K.; Martinez, V.; Toddo, S.; Guntur, S.; Herrgård, M.J.; Elofsson, A.; Nørholm, M.H.H.; Daley, D.O. Enhanced Protein Production in Escherichia coli by Optimization of Cloning Scars at the Vector–Coding Sequence Junction. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boel, G.; Letso, R.; Neely, H.; Price, W.N.; Wong, K.-H.; Su, M.; Luff, J.D.; Valecha, M.; Everett, J.K.; Acton, T.B.; et al. Codon influence on protein expression in E. coli correlates with mRNA levels. Nature 2016, 529, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsch, N.; Homuth, G.; Schweder, T. Suitability of different β-galactosidases as reporter enzymes in Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 93, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesei, G.; Vazdar, M.; Jensen, M.R.; Cragnell, C.; Mason, P.E.; Heyda, J.; Skepö, M.; Jungwirth, P.; Lund, M. Self-association of a highly charged arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11428–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.; Gulati, N.; Kaul, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Nagaich, U. Protein Based Nanostructures for Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. 2018, 2018, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaki, T.; Sriram, S.M.; Park, K.S.; Kwon, Y.T. The N-end rule pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, M.T.P.; Sánchez-García, L.; Sánchez-Chardi, A.; Roldan, M.; Unzueta, U.; Serna, N.; Cano-Garrido, O.; Azzoni, A.R.; Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Villaverde, A.; et al. Protein nanoparticles are nontoxic, tuneable cell stressors. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, A.H.; Liu, H.; Melville, S.B. Construction and Characterization of a Lactose-Inducible Promoter System for Controlled Gene Expression in Clostridium perfringens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, K.; Trowell, S.C. Highly Sensitive and Selective Biosensor for a Disaccharide Based on an AraC-Like Transcriptional Regulator Transduced with Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12986–12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.; Caron, K.; Nebl, T.; Peat, T.S. Structures of the Transcriptional Regulator BgaR, a Lactose Sensor. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2019, 75, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, R.W.; Lo, S.; Jancewicz, L.J.; Dugdale, M.L.; Huber, R.E. Structural Explanation for Allolactose (Lac Operon Inducer) Synthesis by LacZ β-Galactosidase and the Evolutionary Relationship between Allolactose Synthesis and the Lac Repressor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12993–13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colarusso, A.; Lauro, C.; Calvanese, M.; Parrilli, E.; Tutino, M.L. Improvement of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 as a Cell Factory: IPTG-Inducible Plasmid Construction and Strain Engineering. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101466
Colarusso A, Lauro C, Calvanese M, Parrilli E, Tutino ML. Improvement of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 as a Cell Factory: IPTG-Inducible Plasmid Construction and Strain Engineering. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(10):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101466
Chicago/Turabian StyleColarusso, Andrea, Concetta Lauro, Marzia Calvanese, Ermenegilda Parrilli, and Maria Luisa Tutino. 2020. "Improvement of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 as a Cell Factory: IPTG-Inducible Plasmid Construction and Strain Engineering" Microorganisms 8, no. 10: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101466
APA StyleColarusso, A., Lauro, C., Calvanese, M., Parrilli, E., & Tutino, M. L. (2020). Improvement of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 as a Cell Factory: IPTG-Inducible Plasmid Construction and Strain Engineering. Microorganisms, 8(10), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101466






