Nitrogen Removal Performance and Metabolic Pathways Analysis of a Novel Aerobic Denitrifying Halotolerant Pseudomonas balearica Strain RAD-17
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultured Media
2.2. Bacteria Isolation and Identification
2.3. Nitrogen Removal Performance
2.4. Single-Factor Experiments
2.5. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.6. Bioaugmentation Performance Evaluation
2.7. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
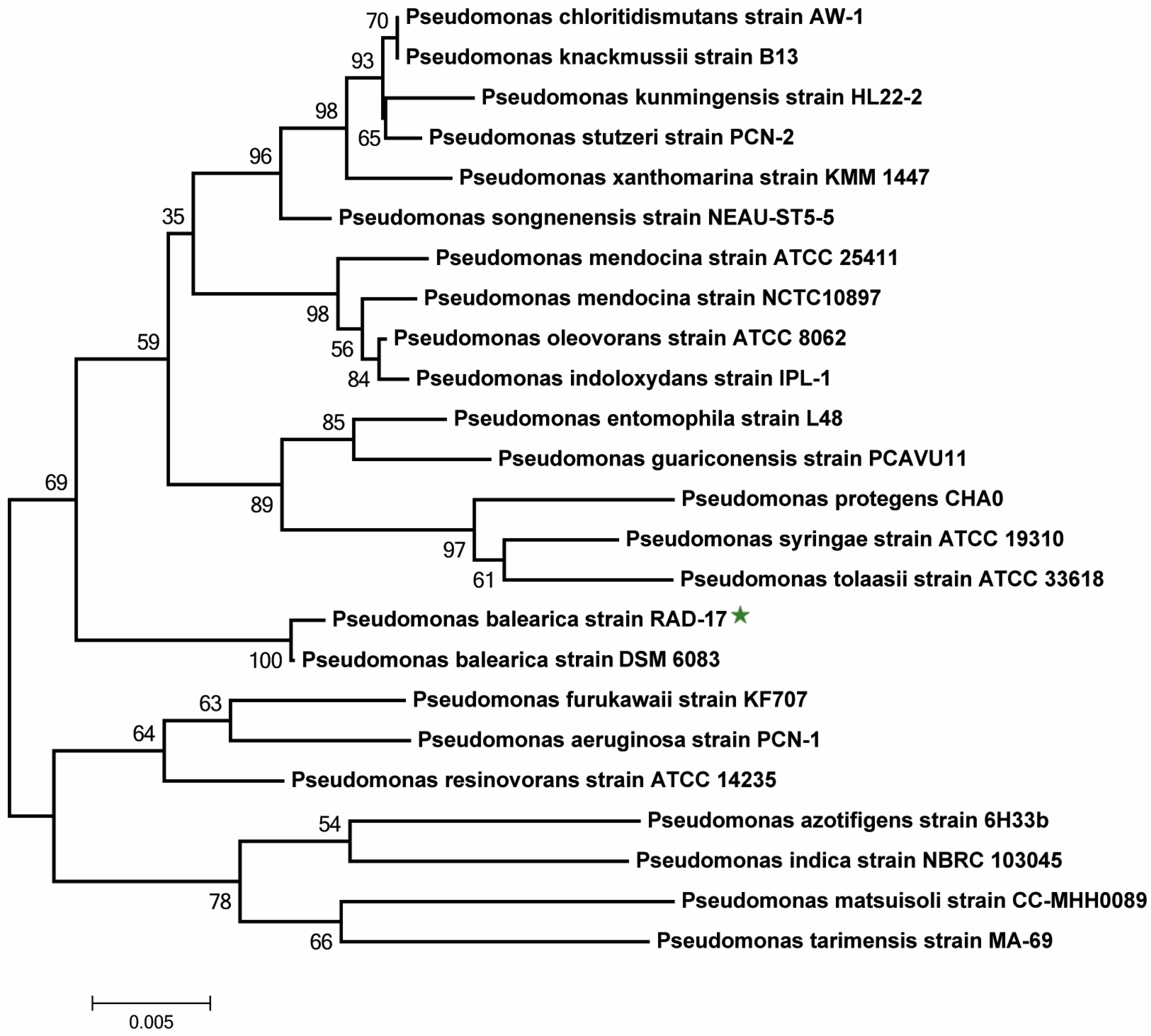
3.1. Bacteria Characteristics and Identification
3.2. Nitrogen Removal Performance
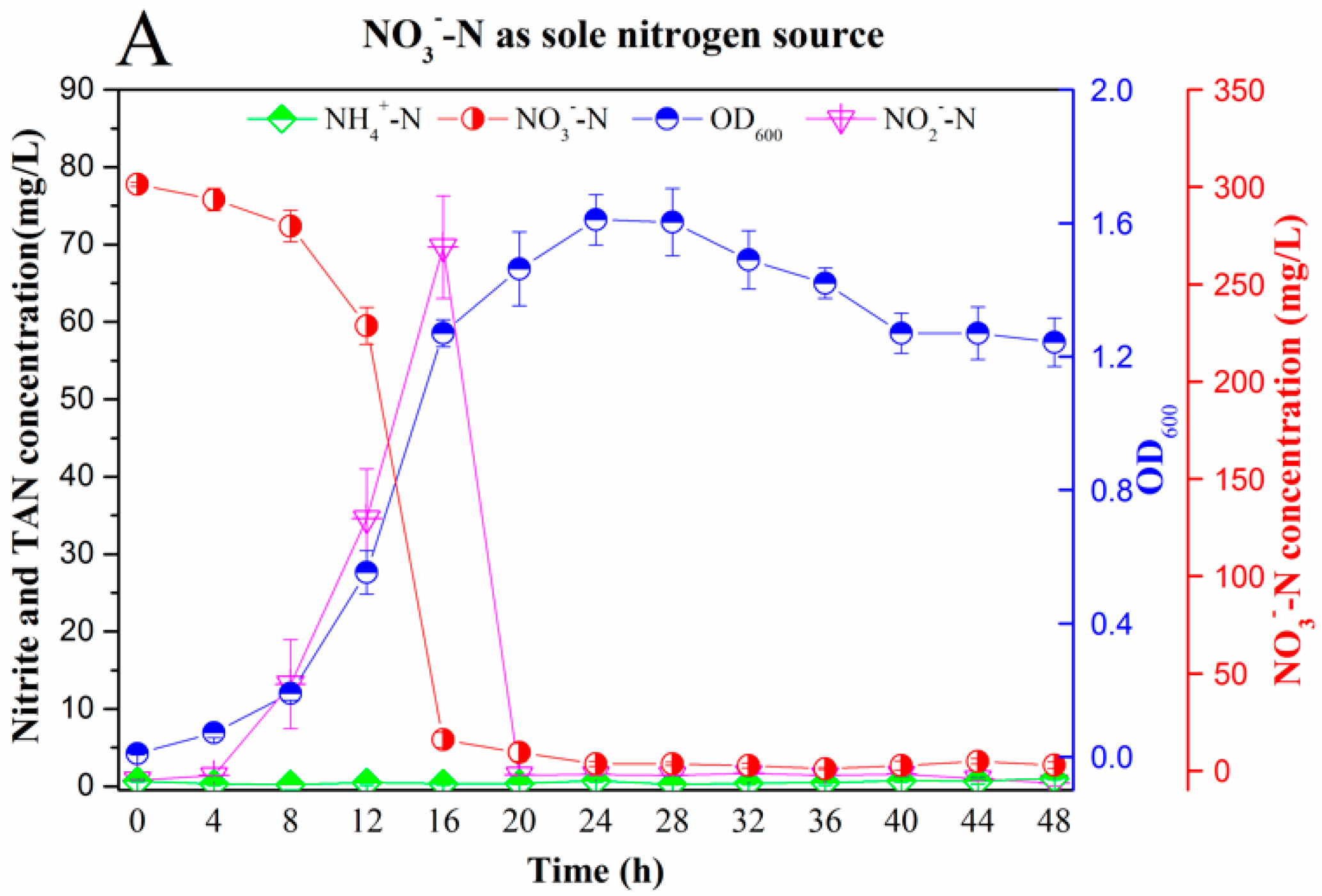
3.2.1. Nitrogen Removal Ability
3.2.2. Nitrogen Balance Analysis
3.2.3. Single Factor Experiments
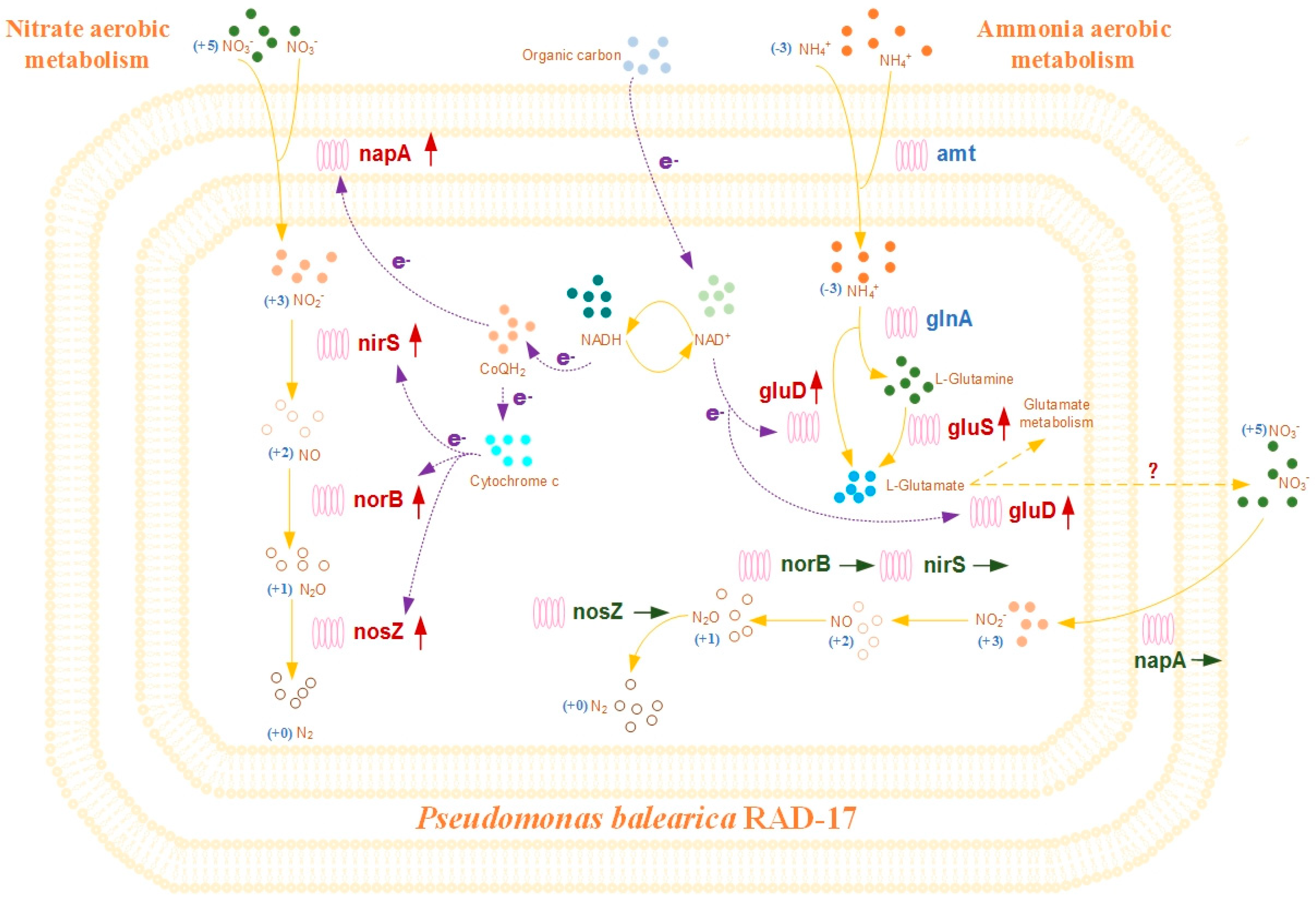
3.3. Nitrogen Metabolism Pathways Analysis
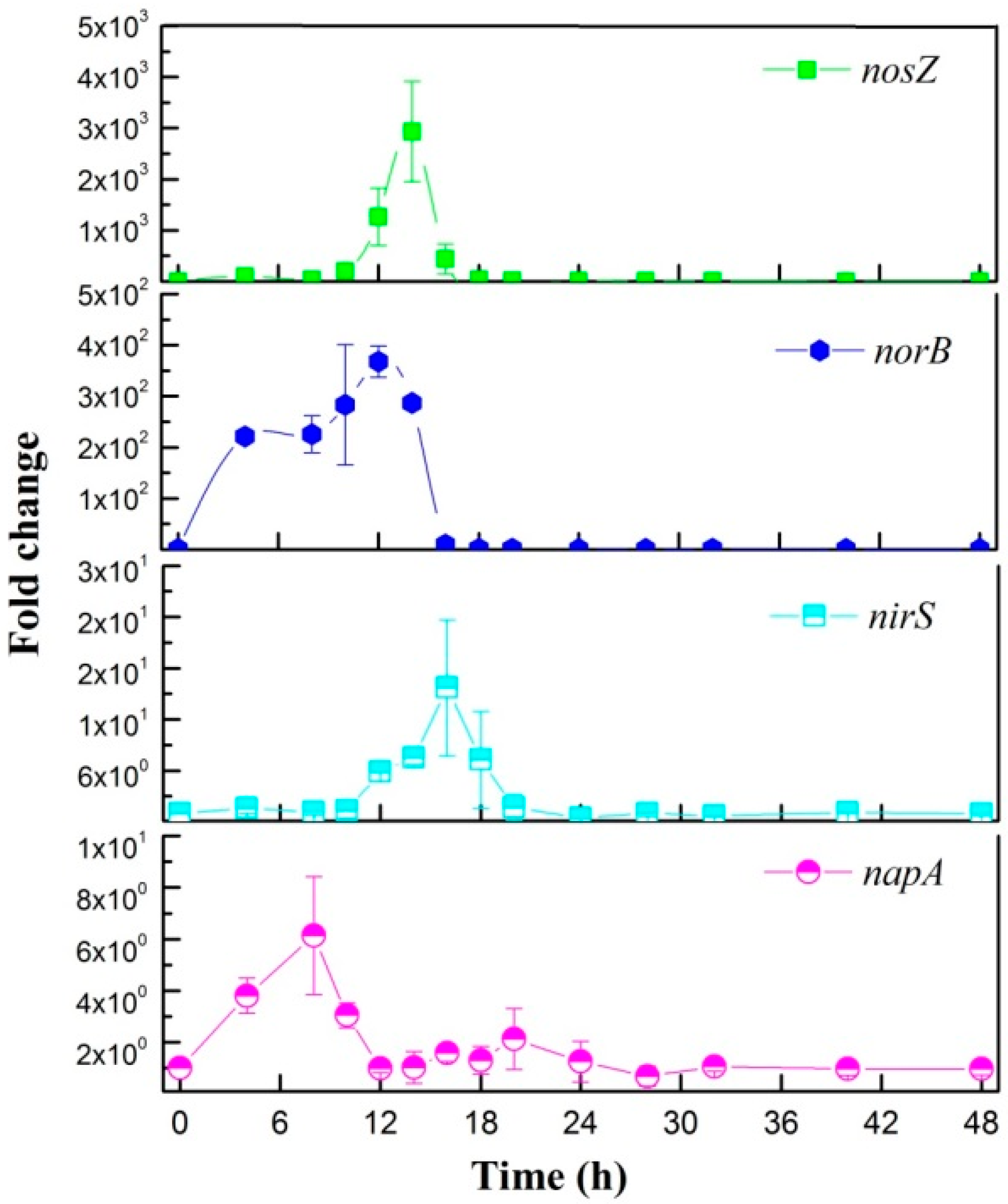
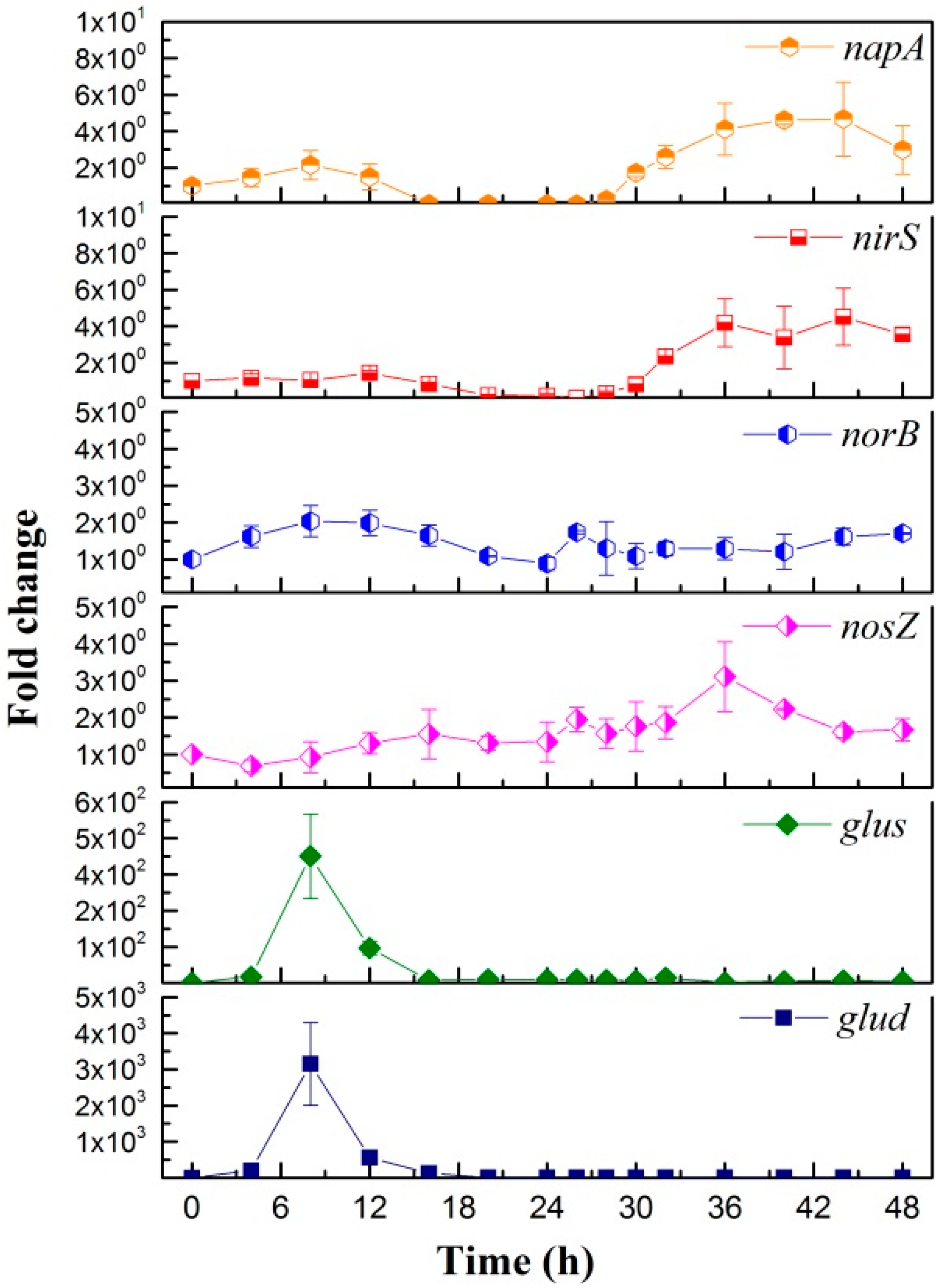
3.3.1. Aerobic Denitrification Pathway
3.3.2. Heterotrophic Ammonium Removal Pathway
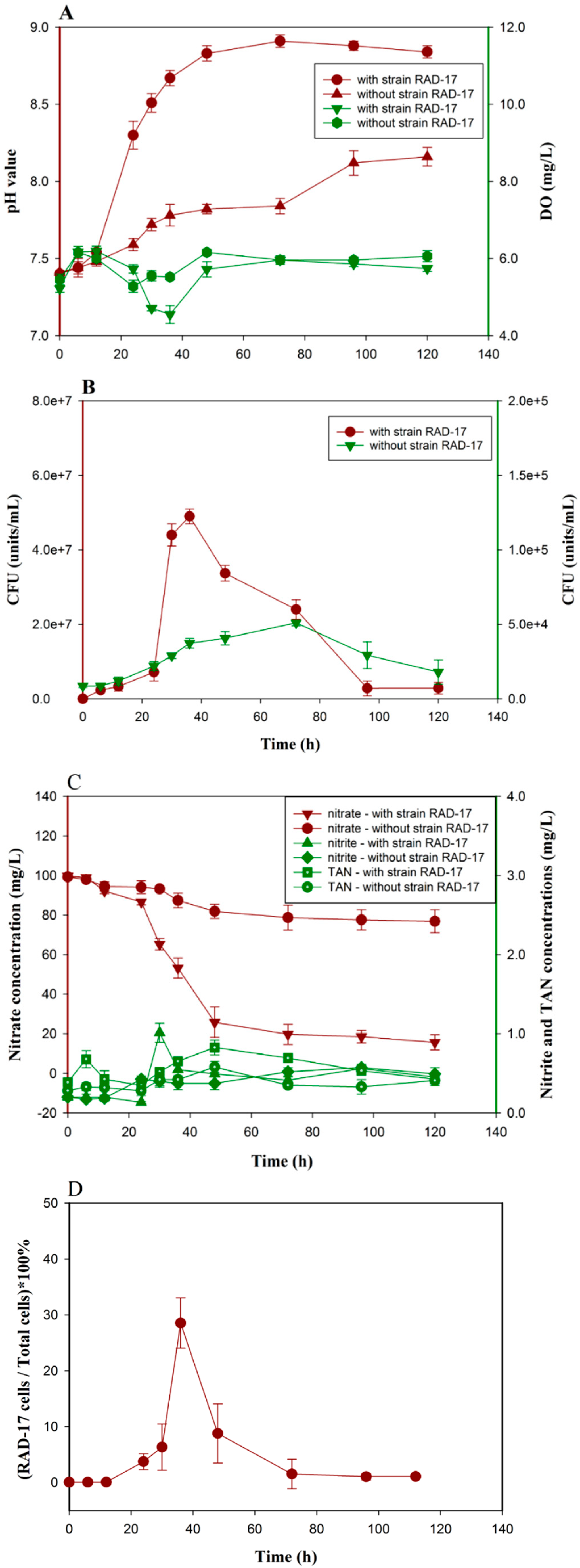
3.4. Bioaugmentation Performance Evaluation
3.5. Research Prospective
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winkler, M.K.H.; Straka, L. New directions in biological nitrogen removal and recovery from wastewater. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Chandran, K.; Stensel, D. Microbial ecology of denitrification in biological wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2014, 64, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.-M.; Deng, Y.-L.; Ruan, Y.-J.; Guo, X.-S.; Shi, M.-M.; Shen, J.-Z. Biological denitrification using poly (butylene succinate) as carbon source and biofilm carrier for recirculating aquaculture system effluent treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chu, L. Biological nitrate removal from water and wastewater by solid-phase denitrification process. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Liu, L.; Gao, M.; Zhang, L.; Tursun, H.; Wang, X. Effects of solid-phase denitrification on the nitrate removal and bacterial community structure in recirculating aquaculture system. Biodegradation 2016, 27, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.-J.; Deng, Y.-L.; Guo, X.-S.; Timmons, M.B.; Lu, H.-F.; Han, Z.-Y.; Ye, Z.-Y.; Shi, M.-M.; Zhu, S.-M. Simultaneous ammonium and nitrate removal in an airlift reactor using poly (butylene succinate) as carbon source and biofilm carrier. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Z.; Wei, C.; Wu, W. Nitrogen removal performance and functional genes distribution patterns in solid-phase denitrification sub-surface constructed wetland with micro aeration. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yang, F.; Yang, L. Biological denitrification with a novel biodegradable polymer as carbon source and biofilm carrier. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Z. Tertiary nitrogen removal for municipal wastewater using a solid-phase denitrifying biofilter with polycaprolactone as the carbon source and filtration medium. Water Res. 2016, 93, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giblin, A.E.; Tobias, C.R.; Song, B.; Weston, N.; Banta, G.T.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H. The importance of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) in the nitrogen cycle of coastal ecosystems. Oceanography 2013, 26, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, T.; Rensing, C.; Pepper, I.A.N. New approaches for bioaugmentation as a remediation technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 34, 447–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, T.; Gao, M.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Q. Bioaugmentation with Diaphorobacterpolyhydroxybutyrativorans to enhance nitrate removal in a poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)-supported denitrification reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumft, W.G. Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1997, 61, 533–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lv, P.-L.; Shi, L.-D.; Wang, Z.; Rittmann, B.; Zhao, H.-P. Methane oxidation coupled to perchlorate reduction in a membrane biofilm batch reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, H.; Zumft, W.G. Expression of denitrification enzymes in response to the dissolved oxygen level and respiratory substrate in continuous culture of Pseudomonas stutzeri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H. Aerobic denitrification: A review of important advances of the last 30 years. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2015, 20, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozkina, E.V.; Zvyagilskaya, R.A. Nitrate reductases: Structure, functions, and effect of stress factors. Biochemistry 2007, 72, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Strous, M. Denitrification and aerobic respiration, hybrid electron transport chains and co-evolution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2013, 1827, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Ma, B.; Timmons, M.B.; Lu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhao, H.; Yin, X. Multi-omics analysis reveals niche and fitness differences in typical denitrification microbial aggregations. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, P.; Hao, B.; Yu, Z. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by the bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeriYZN-001. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9866–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Ni, J.; Ma, T.; Li, C. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification at low temperature by a newly isolated bacterium, Acinetobacter sp. HA2. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, F. Ammonium assimilation: An important accessory during aerobic denitrification of Pseudomonas stutzeriT13. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Chen, G.; Yu, J.; Lin, F. Denitrification-potential evaluation and nitrate-removal-pathway analysis of aerobic denitrifier strain Marinobacterhydrocarbonoclasticus RAD-2. Water 2018, 10, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H. Aerobic denitrification by Pseudomonas stutzeriC3 incapable of heterotrophic nitrification. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 407–409. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Ma, F. Regulation of dissolved oxygen from accumulated nitrite during the heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification of Pseudomonas stutzeriT13. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3243–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, S.; Hao, H.; Chen, J. Characteristics and metabolic pathway of Alcaligenes sp. TB for simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9787–9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.L.; Ruan, Y.J.; Zhu, S.M.; Guo, X.S.; Han, Z.Y.; Ye, Z.Y.; Liu, G.; Shi, M.M. The impact of DO and salinity on microbial community in poly(butylene succinate) denitrification reactors for recirculating aquaculture system wastewater treatment. AMB Express. 2017, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garthright, W.E.; Blodgett, R.J. FDA’s preferred MPN methods for standard, large or unusual tests, with a spreadsheet. Food Microbiol. 2003, 20, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEPA. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Methods, 4th ed.; Chinese Environmental Science Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Su, J.; Wen, G.; Zhang, K. Nitrogen-removal efficiency of a novel aerobic denitrifying bacterium, Pseudomonas stutzeri strain ZF31, isolated from a drinking-water reservoir. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Effect of sulfamethoxazole on aerobic denitrification by strain Pseudomonas stutzeri PCN-1. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Li, Z.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ye, Q. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by Pseudomonas tolaasii Y-11 without nitrite accumulation during nitrogen conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, E.; Li, B.; He, R.; Yuan, H. Removal of nitrogen by heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification of a phosphate accumulating bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeriYG-24. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Liu, T.; Liu, G.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, A. Simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by the marine origin bacterium Pseudomonas sp. ADN-42. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 2000–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Kang, P.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J.; Jia, J.; Yan, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. ParacoccusversutusKS293 adaptation to aerobic and anaerobic denitrification: Insights from nitrogen removal, functional gene abundance, and proteomic profiling analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, X. Biological removal of nitrate and ammonium under aerobic atmosphere by Paracoccusversutus LYM. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrero-de Acuña, J.M.; Timmis, K.N.; Jahn, M.; Jahn, D. Protein complex formation during denitrification by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.-Y.; Ai, G.-M.; Miao, L.-L.; Liu, Z.-P. Characterization of a marine origin aerobic nitrifying–denitrifying bacterium. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-L.; Liu, Y.; Ai, G.-M.; Miao, L.-L.; Zheng, H.-Y.; Liu, Z.-P. The characteristics of a novel heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium, Bacillus methylotrophicus strain L7. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 108, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Linares, L.; Acquaviva, M.; Bertrand, J.-C.; Gauthier, M. Effect of sodium chloride concentration on growth and degradation of eicosane by the marine halotolerant bacterium Marinobacterhydrocarbonoclasticus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouesbet, G.; Blanco, C.; Hamelin, J.; Bernard, T. Osmotic adjustment in Brevibacteriumammoniumgenes: Pipecolic acid accumulation at elevated osmolalities. Microbiology 1992, 138, 959–965. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, G.-M.; Miao, L.-L.; Liu, Z.-P. Marinobacter strain NNA5, a newly isolated and highly efficient aerobic denitrifier with zero N2O emission. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh-Lakha, S.; Shannon, K.E.; Henderson, S.L.; Goyer, C.; Trevors, J.T.; Zebarth, B.J.; Burton, D.L. Effect of pH and temperature on denitrification gene expression and activity in Pseudomonas mandelii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 3903–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopoulos, G.; Sullivan, M.J.; Hartop, K.R.; Rowley, G.; Gates, A.J.; Watmough, N.J.; Richardson, D.J. Tuning the modular Paracoccus denitrificans respirome to adapt from aerobic respiration to anaerobic denitrification. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4953–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.C.; Ferguson, S.J.; Ludwig, B.; Page, M.D.; Richter, O.-M.H.; van Spanning, R.J.M. Molecular genetics of the genus Paracoccus: Metabolically versatile bacteria with bioenergetic flexibility. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 1046–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinchbeck, B.J.; Soriano-Laguna, M.J.; Sullivan, M.J.; Luque-Almagro, V.M.; Rowley, G.; Ferguson, S.J.; Roldán, M.D.; Richardson, D.J.; Gates, A.J. A dual functional redox enzyme maturation protein for respiratory and assimilatory nitrate reductases in bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, P.; Chen, Y.; Yao, R.; Zheng, Z.; Du, Q. New insight into the nitrogen metabolism of simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium in mRNA expression. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-W.; Bae, J.-H. Alkalinity requirements and the possibility of simultaneous heterotrophic denitrification during sulfur-utilizing autotrophic denitrification. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, H.-P.; Ji, J.-Y.; Zhou, X.-X.; Li, W. Bioaugmentation of nitrate-dependent anaerobic ferrous oxidation by heterotrophic denitrifying sludge addition: A promising way for promotion of chemoautotrophic denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | References |
|---|---|---|
| 16S rRNA | F: CCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG | This study |
| R: ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG | ||
| gluD | F: GCTATCGCATCCAGATGAAC | This study |
| R: CATCACTTCGTTGTCGCTC | ||
| gluS | F: CGCAACATCTTCTCCAACCC | This study |
| R: TTCTCCTCACCCCATTCGAC | ||
| napA | F: TTCATGGCCTGCTGTACCTG | This study |
| R: TCATCCTGGCGCAATCGAAC | ||
| nirS | F: TGGAAAGCCAGATGCAGCAC | This study |
| R: ACGCTCCTTGACGAAGTGGATG | ||
| norB | F: TTCTACAACCCCGAGAACC | This study |
| R: GCAATGATGACGTACAGCC | ||
| nosZ | F: CAACATCGACCAGATCGAAG | This study |
| R: TGCAGTAGTACCAGTGCAG |
| API 20NE Results | Strain RAD-17 |
|---|---|
| Oxidase test Nitrate reduction | − + |
| Arginine dihydrolase | − |
| Urease | − |
| β-Glucosidase | − |
| Protease | − |
| β-Galactosidase | − |
| Assimilation of | |
| Glucose | + |
| Arabinose | − |
| Mannose | − |
| Mannitol | − |
| N-acetyl-glucosamine | − |
| Maltose | + |
| Gluconate | + |
| Capric acid | + |
| Adipic acid | − |
| Malic acid | + |
| Citric acid | + |
| Phenylacetic acid | − |
| Substance | Initial TN (mg/L) | Final Nitrogen (mg/L) | Intracellular N | N Loss (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3−-N | NO2−-N | NH4+-N | Organic-N | ||||
| Nitrate | 30.56 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 3.23 ± 0.34 | 87.76 |
| Factor | Variations | Initial Nitrate (mg/L) | Final Nitrate (mg/L) | Final Nitrite (mg/L) | Final TAN (mg/L) | Growth (OD600) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/N ratios | 2 | 295.48 ± 0.60 | 149.00 ± 2.87 | 50.21 ± 1.52 | 8.61 ± 1.19 | 0.86 ± 0.16 |
| 5 | 298.42 ± 0.26 | 0.92 ± 0.80 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 1.88 ± 0.04 | 1.17 ± 0.10 | |
| 10 | 299.59 ± 0.37 | 8.17 ± 1.82 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 1.19 ± 0.03 | 1.43 ± 0.03 | |
| 15 | 301.51 ± 0.71 | 8.55 ± 5.10 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 1.02 ± 0.03 | 1.04 ± 0.25 | |
| 20 | 300.09 ± 0.71 | 23.41 ± 9.78 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.95 ± 0.00 | 1.09 ± 0.14 | |
| NaCl (‰) | 0 | 302.47 ± 0.19 | 3.14 ± 2.00 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.08 | 1.73 ± 0.08 |
| 2.5 | 299.78 ± 0.56 | 6.52 ± 1.37 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.06 | |
| 5 | 301.29 ± 0.24 | 9.37 ± 5.57 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 1.04 ± 0.08 | 1.30 ± 0.15 | |
| 15 | 300.36 ± 0.17 | 8.11 ± 4.29 | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | 1.40 ± 0.35 | |
| 25 | 301.46 ± 0.33 | 9.04 ± 4.11 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 1.66 ± 0.24 | |
| Carbon source | Fructose | 299.61 ± 0.22 | 205.59 ± 8.50 | 5.71 ± 4.08 | 29.13 ± 12.13 | 0.27 ± 0.03 |
| NaAC | 303.14 ± 0.11 | 2.39 ± 1.11 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 3.34 ± 0.33 | 1.99 ± 0.11 | |
| Lactin | 298.45 ± 0.27 | 296.90 ± 2.59 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | – | 0.69 ± 0.15 | |
| Glucose | 300.12 ± 0.09 | 4.71 ± 1.64 | 1.03 ± 0.03 | 2.23 ± 0.65 | 1.93 ± 0.05 | |
| Na-citrate | 301.09 ± 0.14 | 0.57 ± 0.27 | 0.51 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 1.86 ± 0.11 | |
| Rotation Speed (rpm) | 0 | 304.56 ± 0.15 | 19.16 ± 6.26 | 0.35 ± 0.11 | 1.01 ± 0.40 | 1.37 ± 0.06 |
| 50 | 302.42 ± 0.31 | 36.57 ± 4.53 | 1.07 ± 0.25 | 1.68 ± 0.57 | 0.76 ± 0.05 | |
| 100 | 301.77 ± 0.17 | 116.52 ± 9.91 | 13.74 ± 0.20 | 0.90 ± 0.65 | 1.07 ± 0.11 | |
| 150 | 299.46 ± 0.20 | 8.99 ± 1.33 | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 1.71 ± 0.29 | 2.00 ± 0.07 | |
| 200 | 301.26 ± 0.05 | 2.59 ± 0.94 | 0.53 ± 0.16 | 1.86 ± 0.93 | 2.19 ± 0.06 | |
| Temperature (°C) | 5 | 299.76 ± 0.16 | 298.57 ± 1.50 | – | 0.45 ± 0.29 | 0.74 ± 0.06 |
| 15 | 298.31 ± 0.09 | 7.79 ± 0.91 | 0.62 ± 0.06 | 1.63 ± 1.42 | 1.89 ± 0.18 | |
| 25 | 300.55 ± 0.11 | 2.28 ± 2.21 | 0.41 ± 0.07 | 2.49 ± 0.10 | 2.03 ± 0.25 | |
| 40 | 300.98 ± 0.17 | 18.51 ± 5.32 | 0.60 ± 0.18 | 2.50 ± 1.20 | 1.70 ± 0.15 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruan, Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Kong, D.; Lu, H.; Zhao, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cai, L. Nitrogen Removal Performance and Metabolic Pathways Analysis of a Novel Aerobic Denitrifying Halotolerant Pseudomonas balearica Strain RAD-17. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010072
Ruan Y, Taherzadeh MJ, Kong D, Lu H, Zhao H, Xu X, Liu Y, Cai L. Nitrogen Removal Performance and Metabolic Pathways Analysis of a Novel Aerobic Denitrifying Halotolerant Pseudomonas balearica Strain RAD-17. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuan, Yunjie, Mohammad J. Taherzadeh, Dedong Kong, Huifeng Lu, Heping Zhao, Xiangyang Xu, Yu Liu, and Lei Cai. 2020. "Nitrogen Removal Performance and Metabolic Pathways Analysis of a Novel Aerobic Denitrifying Halotolerant Pseudomonas balearica Strain RAD-17" Microorganisms 8, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010072
APA StyleRuan, Y., Taherzadeh, M. J., Kong, D., Lu, H., Zhao, H., Xu, X., Liu, Y., & Cai, L. (2020). Nitrogen Removal Performance and Metabolic Pathways Analysis of a Novel Aerobic Denitrifying Halotolerant Pseudomonas balearica Strain RAD-17. Microorganisms, 8(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010072









