Cupriavidus sp. HN-2, a Novel Quorum Quenching Bacterial Isolate, is a Potent Biocontrol Agent Against Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
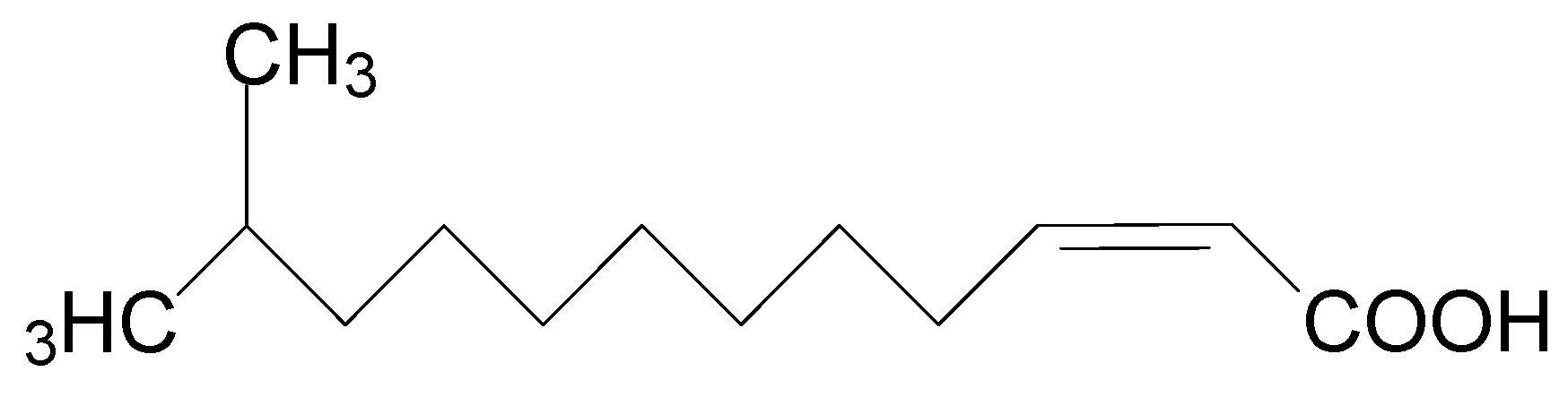
2.1. Chemicals and Plants
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.3. Isolation of DSF-Degrading Bacteria from Soil Samples
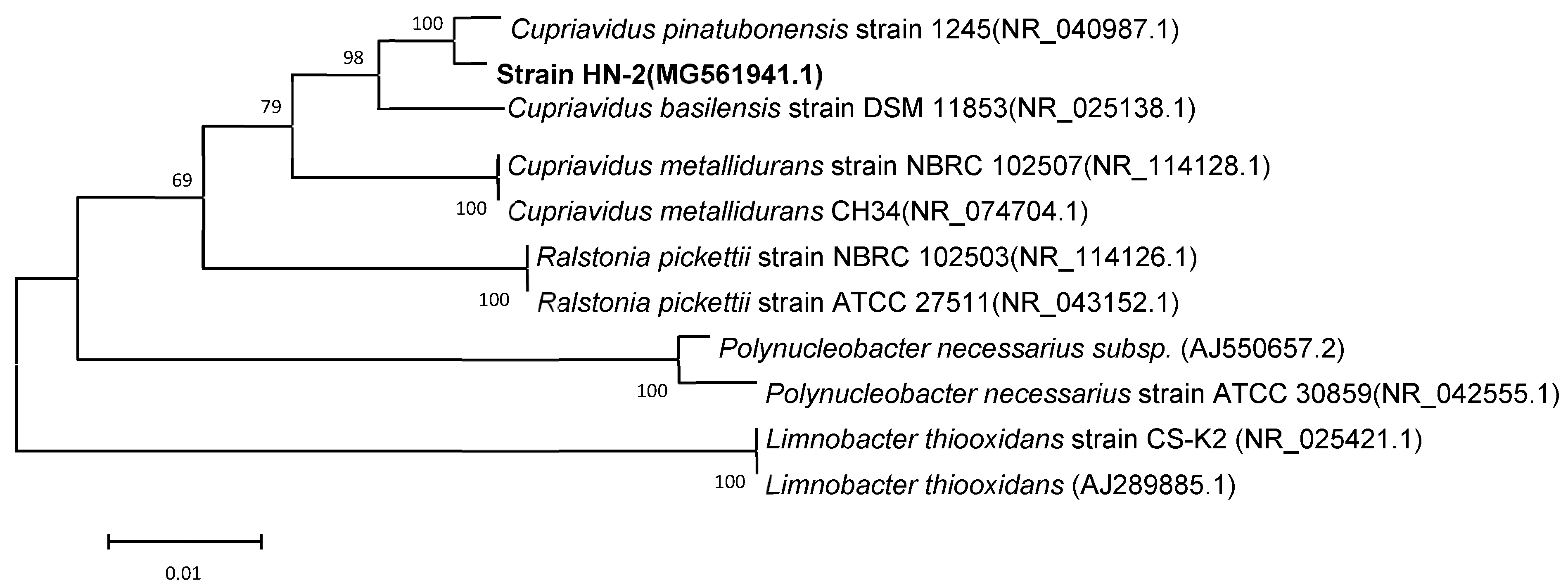
2.4. Identification of Strain HN-2
2.5. DSF Degradation Assays
2.6. Identification of DSF Degradation Products
2.7. Biocontrol Assay of Strain HN-2 Against Xcc
2.8. Data Analysis
2.9. GenBank Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Isolation, Screening, and Identification of DSF-Degrading Isolates
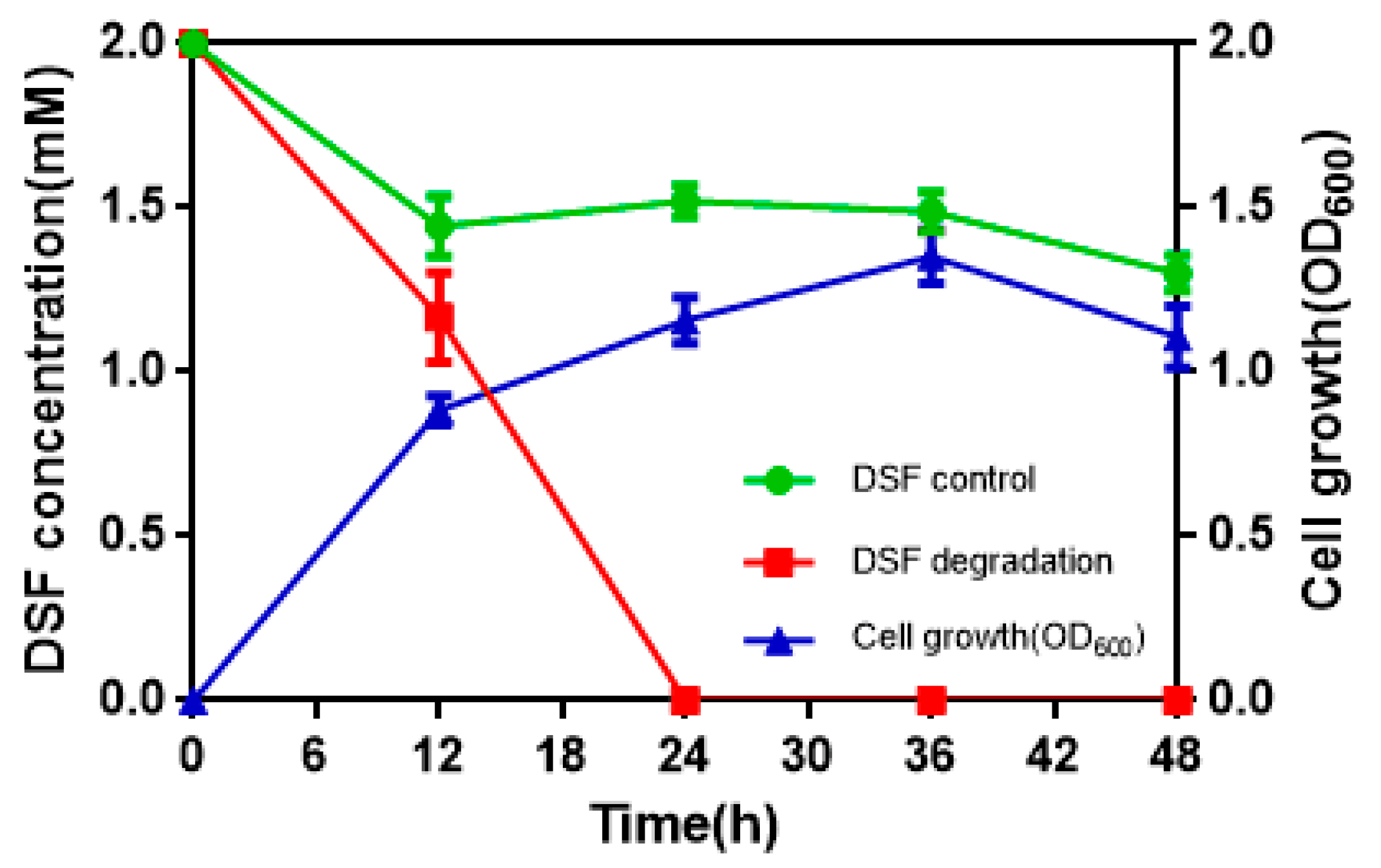
3.2. DSF Degradation Kinetics
3.3. Degrading Products and Degradation Pathway of DSF
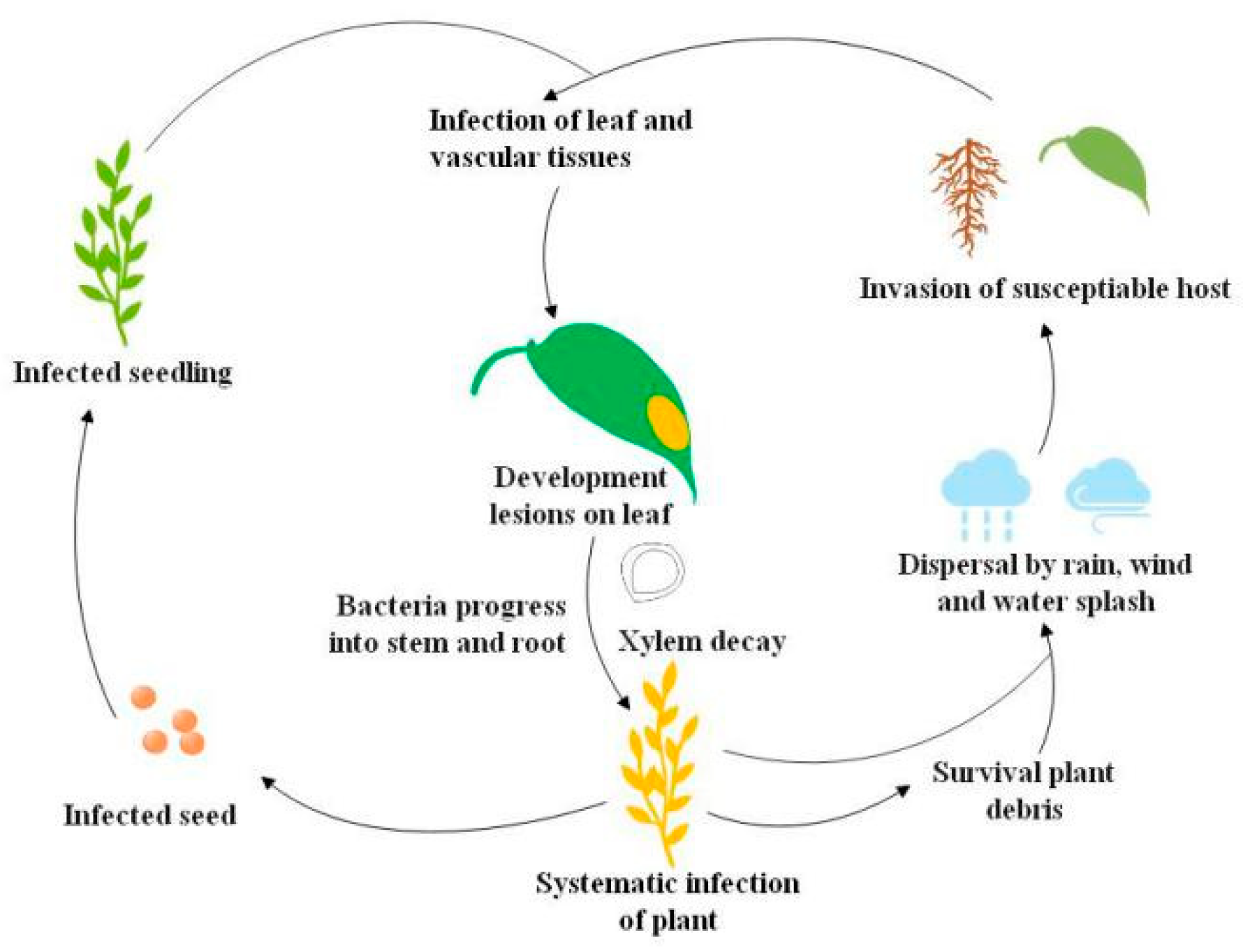
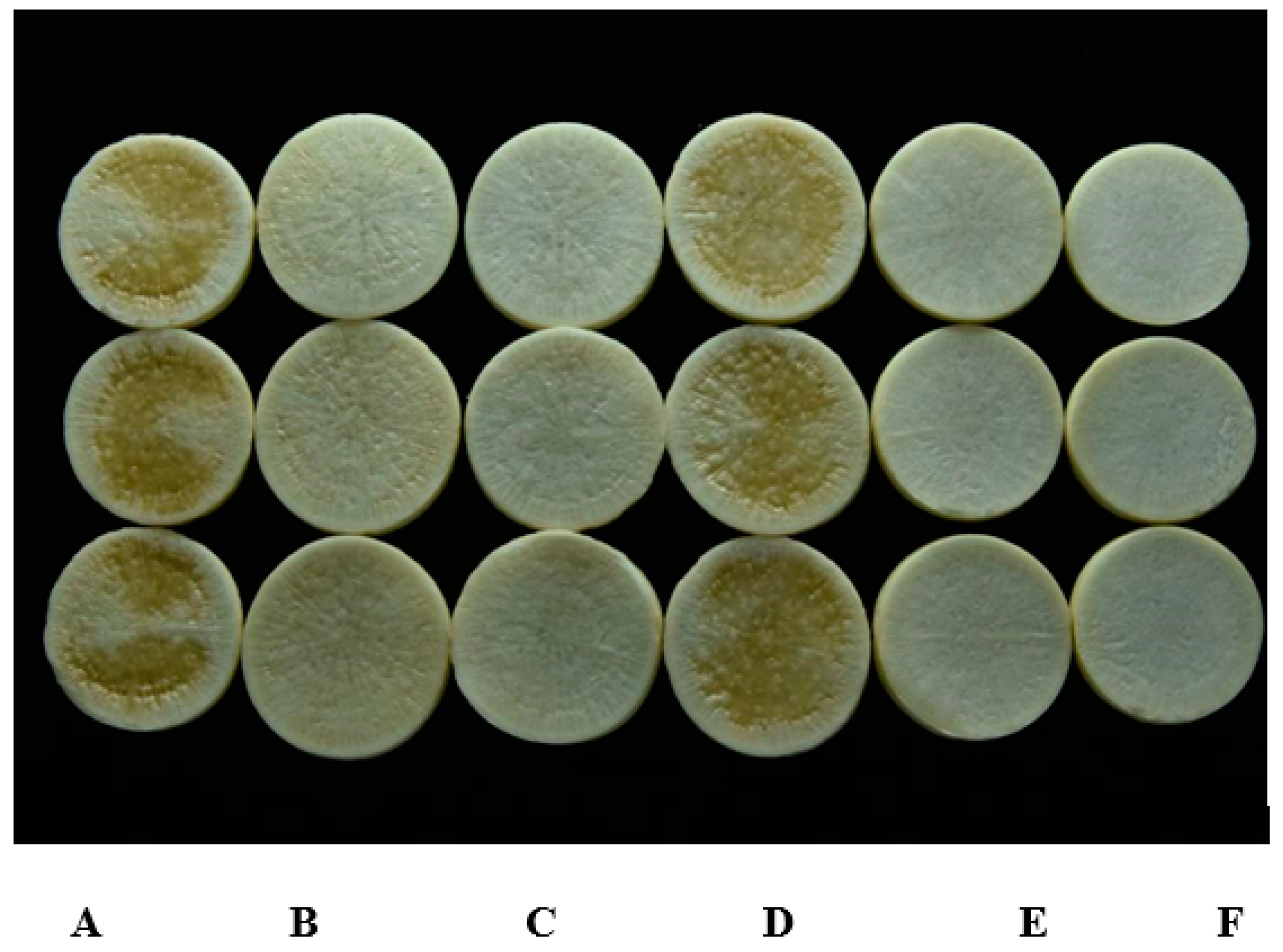
3.4. Biocontrol Potential of Isolate HN-2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez, A.M. Black Rot of Crucifers. In Mechanisms of Resistance to Plant Diseases; Slusarenko, A.J., Fraser, R.S.S., van Loon, L.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.H. Black rot: A continuing threat to world crucifers. Plant Dis. 1980, 64, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massomo, S.; Mabagala, R.; Swai, I.; Hockenhull, J.; Mortensen, C. Evaluation of varietal resistance in cabbage against the black rot pathogen, Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Tanzania. Crop Prot. 2004, 23, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derie, M.L. Black rot of crucifers in a cabbage seed field in western Washington. Plant Dis. 1988, 72, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.Q.; Potnis, N.; Dow, M.; Vorholter, F.J.; He, Y.Q.; Becker, A.; Teper, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Bleris, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights into host adaptation, virulence and epidemiology of the phytopathogen Xanthomonas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; He, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, J.E.; Dong, Y.H.; He, C.; Wang, S.X.; Weng, L.X.; Xu, J.L.; Tay, L.; et al. A bacterial cell-cell communication signal with cross-kingdom structural analogues. F1000—Post-Publ. Peer Rev. Biomed. Lit. 2004, 51, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, K.L.; Chatterjee, S.; Ho, K.A.; Lindow, S.E. Virulence of plant pathogenic bacteria attenuated by degradation of fatty acid cell-to-cell signaling factors. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Coulthurst, S.J.; Pritchard, L.; Hedley, P.E.; Ravensdale, M.; Humphris, S.; Burr, T.; Takle, G.; Brurberg, M.-B.; Birch, P.R.J.; et al. Quorum sensing coordinates brute force and stealth modes of infection in the plant pathogen Pectobacterium atrosepticum. PLOS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Dong, Y.H. Quorum sensing and signal interference: diverse implications. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sluys, M.A.; Monteiro-Vitorello, C.B.; Camargo, L.E.; Menck, C.F.; Da Silva, A.C.; Ferro, J.A.; Oliveira, M.C.; Setubal, J.C.; Kitajima, J.P.; Simpson, A.J. Comparative genomic analysis of plant-associated bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2002, 40, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, K.B.; O’Connell, O.J.; McCarthy, Y.; Dow, J.M.; O’Toole, G.A.; Plant, B.J.; Ryan, R.P. Bacterial cis-2-unsaturated fatty acids found in the cystic fibrosis airway modulate virulence and persistence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ISME J. 2012, 6, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.G.; Marques, C.N.H. A fatty acid messenger is responsible for inducing dispersion in microbial biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Lim, A.; Lee, J.; Chen, S.; An, S.; Dong, Y.H.; Zhang, L.-H. Diffusible signal factor (DSF) quorum sensing signal and structurally related molecules enhance the antimicrobial efficacy of antibiotics against some bacterial pathogens. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, A.M.L.; Salmond, G.P.C. Quorum sensing in Erwinia species. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uroz, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Oger, P. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching: The Yin and Yang of bacterial communication. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Xu, J.L.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, L.H. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3526–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, F.; Reimmann, C.; Molina, L.; Michel, L.; Duffy, B.; Défago, G. Degradation of pathogen quorum-sensing molecules by soil bacteria: a preventive and curative biological control mechanism. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 45, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Uroz, S. Novel bacteria degrading N-acylhomoserine lactones and their use as quenchers of quorum-sensing-regulated functions of plant-pathogenic bacteria. Microbiology 2003, 149, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadja, B.; Latour, X.; Faure, D.; Chevalier, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Orange, N. Involvement of N-acylhomoserine lactones throughout plant infection by Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica (Pectobacterium atrosepticum). Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, D.; Dessaux, Y. Quorum sensing as a target for developing control strategies for the plant pathogen Pectobacterium. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 119, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessaux, Y.; Chapelle, E.; Faure, D. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching in soil ecosystems. Biocommun. Soil Microorg. 2011, 23, 339–367. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garge, S.S.; Nerurkar, A.S. Evaluation of quorum quenching Bacillus spp. for their biocontrol traits against Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum causing soft rot. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 9, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Harling, R. N-acyl-homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing blockage, a novel strategy for attenuating pathogenicity of Gram-negative bacterial plant pathogens. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 111, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.E.; Keshavan, N.D. Messing with bacterial quorum sensing. Microbiol. Mol. Boil. Rev. 2006, 70, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H. Quorum quenching and proactive host defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; Fouhy, Y.; Garcia, B.F.; Watt, S.A.; Niehaus, K.; Yang, L.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Dow, J.M. Interspecies signalling via the Stenotrophomonas maltophilia diffusible signal factor influences biofilm formation and polymyxin tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rossi, B.P.; Garcia, C.; Alcaraz, E.; Franco, M. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia interferes via the DSF-mediated quorum sensing system with Candida albicans filamentation and its planktonic and biofilm modes of growth. Rev. Argent. De Microbiol. 2014, 46, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.H.; Cámara, M.; He, Y.W. The DSF family of quorum sensing signals: Diversity, biosynthesis, and turnover. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, J.; Eberl, L.; Zhang, L.H. Structural and functional characterization of diffusible signal factor family quorum-sensing signals produced by members of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4675–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, J.; Tao, F.; Zhang, L.H. Listening to a new language: DSF-based quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Xuan, C.G.; Lu, C.H.; Guo, S.; Yu, J.F.; Asif, M.; Jiang, W.J.; Zhou, Z.G.; Luo, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.Q. AidB, a novel thermostable N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the bacterium Bosea sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Zhou, T.; Fan, X.; Bhatt, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Acinetobacter lactucae strain QL-1, a novel quorum quenching candidate against bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazelton, J.N.; Pfeufer, E.E.; Sweat, T.A.; Gardener, B.B.M.; Coenen, C. 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol alters plant root development. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, T.; Zhou, T.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Cupriavidus sp. HN-2, a Novel Quorum Quenching Bacterial Isolate, is a Potent Biocontrol Agent Against Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010045
Ye T, Zhou T, Li Q, Xu X, Fan X, Zhang L, Chen S. Cupriavidus sp. HN-2, a Novel Quorum Quenching Bacterial Isolate, is a Potent Biocontrol Agent Against Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Tian, Tian Zhou, Qiting Li, Xudan Xu, Xinghui Fan, Lianhui Zhang, and Shaohua Chen. 2020. "Cupriavidus sp. HN-2, a Novel Quorum Quenching Bacterial Isolate, is a Potent Biocontrol Agent Against Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris" Microorganisms 8, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010045
APA StyleYe, T., Zhou, T., Li, Q., Xu, X., Fan, X., Zhang, L., & Chen, S. (2020). Cupriavidus sp. HN-2, a Novel Quorum Quenching Bacterial Isolate, is a Potent Biocontrol Agent Against Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Microorganisms, 8(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010045





