Genomic Analysis of Carbapenemase-Producing Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals the Horizontal Spread of p18-43_01 Plasmid Encoding blaNDM-1 in South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Site and Sample Collection
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates
2.3.1. Culture Screening Methods
2.3.2. Detection and Identification of CPE Colonies
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (AST)
2.5. DNA Extraction Genome Sequencing and Analysis
2.6. WGS-Based Confirmation and Molecular Typing of K. Pneumoniae Isolates
2.7. WGS Identification of the Acquired and Chromosomal Mutations in the Isolates
2.8. WGS Identification of Mobile Genetic Elements (MGEs)/Genetic Support
2.9. Phylogenomic Analyses of the K. Pneumoniae Isolates (n = 10)
2.10. Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Identification, Confirmation and Phenotypic Analysis
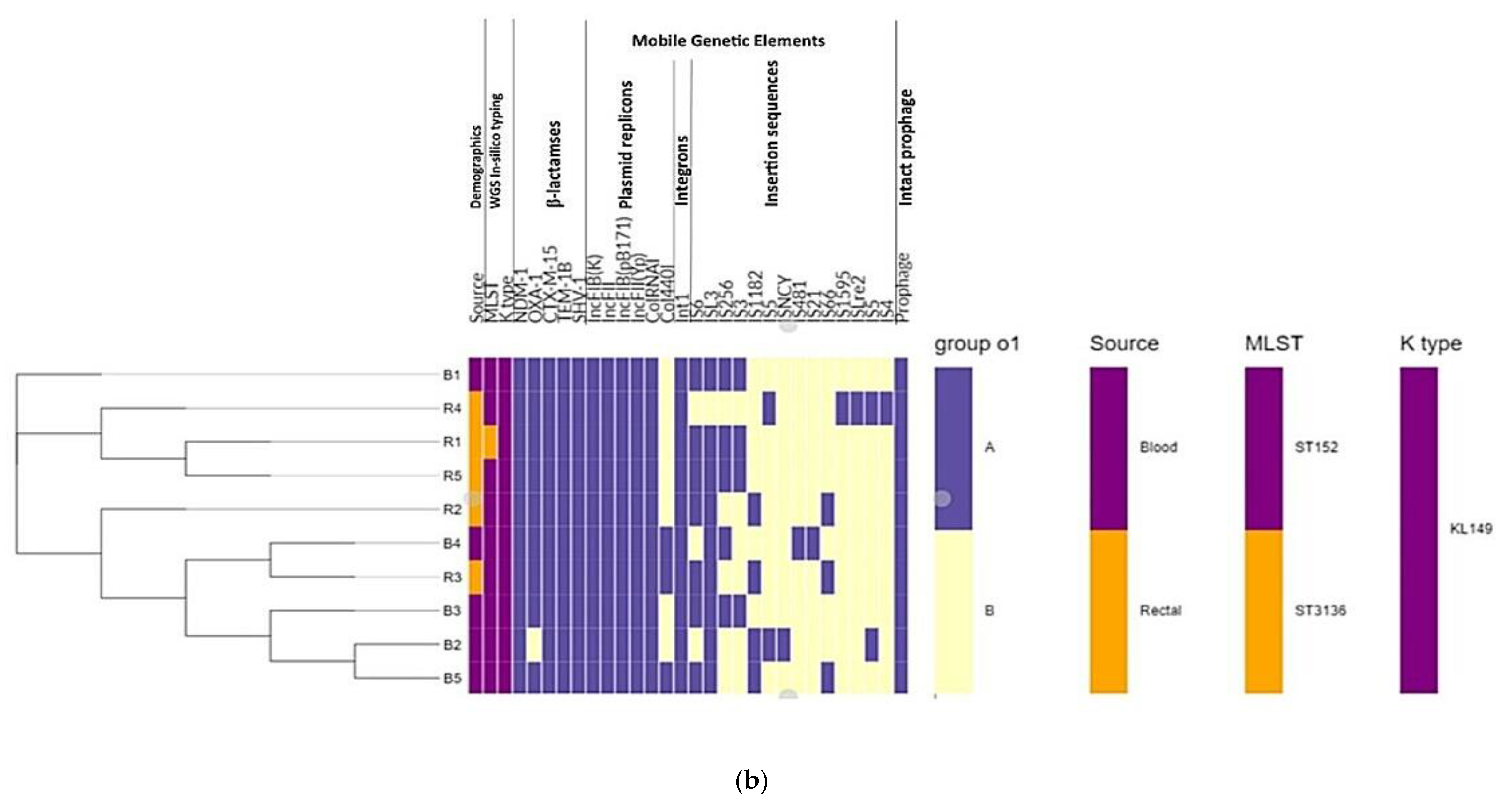
3.2. Genomic Confirmation and Resistance Profiling of β-Lactamases
3.3. WGS-Based Capsular Serotyping and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
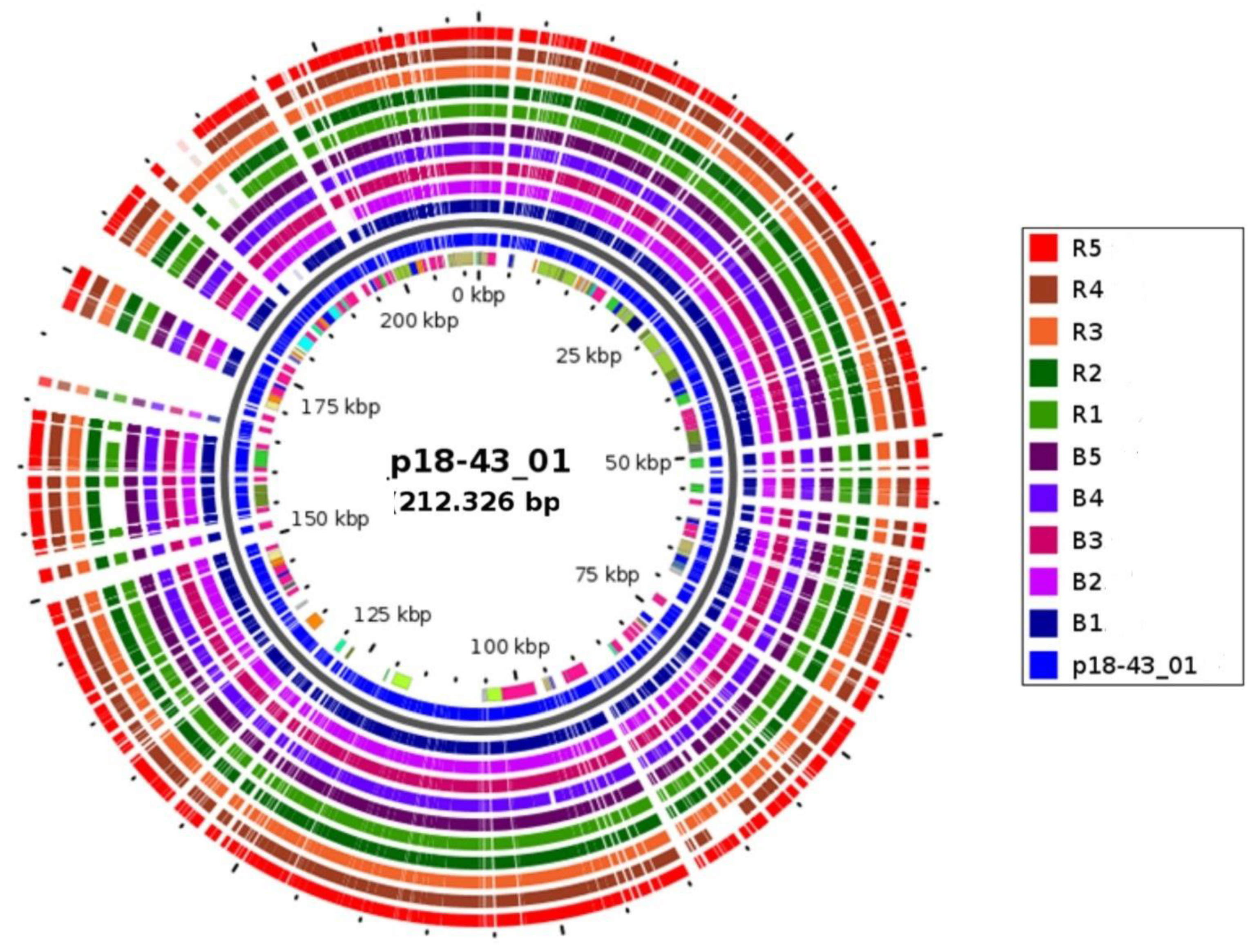
3.4. WGS Detection of Carbapenemase-Encoding BlaNDM-1 Plasmid Involved in Horizontal Spread
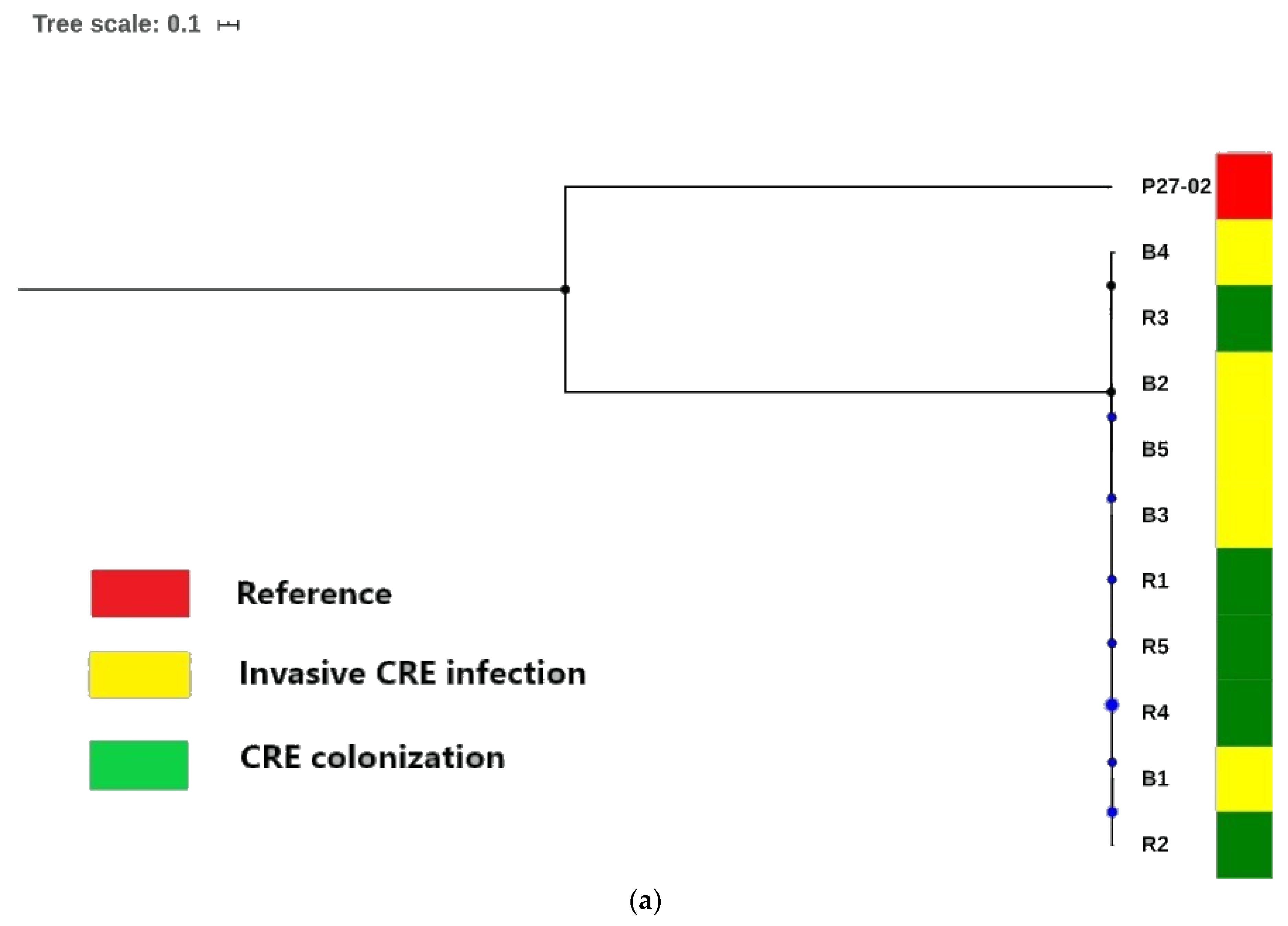
3.5. Phylogenomic Insights
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roca, I.; Akova, M.; Baquero, F.; Carlet, J.; Cavaleri, M.; Coenen, S.; Cohen, J.; Findlay, D.; Gyssens, I.; Heure, O.E.; et al. The global threat of antimicrobial resistance: Science for intervention. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, L.K.; Weinstein, R.A. The Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: The Impact and Evolution of a Global Menace. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S28–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Duin, D.; Doi, Y. The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2017, 8, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, R.A.; Burd, E.M.; Conly, J.; Limbago, B.M.; Poirel, L.; Segre, J.A.; Westblade, L.F. Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms: A Global Scourge. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codjoe, F.; Donkor, E. Carbapenem Resistance: A Review. Med. Sci. 2017, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlet, J.; Jarlier, V.; Harbarth, S.; Voss, A.; Goossens, H.; Pittet, D. Ready for a world without antibiotics? The Pensières Antibiotic Resistance Call to Action. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2012, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Bosch, A.; Bettiol, M.; Nossa González, D.L.; Erben, M.F.; Lamberti, Y. Novel guanidine compound against multidrug-resistant cystic fibrosis-associated bacterial species. Molecules 2018, 23, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Noonikara-Poyil, A.; Joshi, S.D.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Bugarin, A. New Urea Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboro, A.M.; Amoako, D.G.; Osei Sekyere, J.; Kumalo, H.M.; Khan, R.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane Restores the Activity of β-Lactam Antibiotics against Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae: Exploration of Potential Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02077-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboro, A.M.; Osei Sekyere, J.; Amoako, D.G.; Kumalo, H.M.; Khan, R.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. In vitro potentiation of carbapenems with tannic acid against carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae: Exploring natural products as potential carbapenemase inhibitors. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Endimiani, A.; Taracila, M.A.; Bonomo, R.A. Carbapenems: Past, Present, and Future. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4943–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanj, S.S.; Kanafani, Z.A. Current Concepts in Antimicrobial Therapy Against Resistant Gram-Negative Organisms: Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase–Producing Enterobacteriaceae, Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae, and Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queenan, A.M.; Bush, K. Carbapenemases: The versatile β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, H.; Du, H. Carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae: Detection and Antimicrobial Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, J.D.D.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a Key Pathogen Set for Global Nosocomial Dominance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5873–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaber, M.J.; Carmeli, Y. Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae: A potential threat. JAMA 2008, 300, 2911–2913. [Google Scholar]
- Fasciana, T.; Gentile, B.; Aquilina, M.; Ciammaruconi, A.; Mascarella, C.; Anselmo, A.; Fortunato, A.; Fillo, S.; Petralito, G.; Lista, F.; et al. Co-existence of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance in new Klebsiella pneumoniae clones emerging in south of Italy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Poirel, L. High Prevalence of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae among Hospitalized Children in Luanda, Angola. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6189–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangare, S.A.; Rondinaud, E.; Maataoui, N.; Maiga, A.I.; Guindo, I.; Maiga, A.; Camara, N.; Dicko, O.A.; Dao, S.; Diallo, S.; et al. Very high prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in bacteriemic patients hospitalized in teaching hospitals in Bamako, Mali. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrahim, A.; Djahmi, N.; Pujol, C.; Nedjai, S.; Bentakouk, M.C.; Kirane-Gacemi, D.; Dekhil, M.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Pantel, A. First Case of NDM-1-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Annaba University Hospital, Algeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussounda, M.; Diene, S.M.; Dos Santos, S.; Goudeau, A.; François, P.; van der Mee-Marquet, N. Emergence of blaNDM-7–producing enterobacteriaceaein Gabon, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesumirhewe, C.; Springer, B.; Lepuschitz, S.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W. Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Isolates from Edo State, Nigeria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, J.E.; Peirano, G.; Peer, A.K.; Govind, C.N.; Pitout, J.D.D. NDM-1–producing Enterobacteriaceae from South Africa: Moving towards endemicity? Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 79, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance Plasmid Families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Dortet, L.; Bernabeu, S.; Nordmann, P. Genetic Features of bla NDM-1 -Positive Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5403–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, R.F.; D’Souza, A.W.; Dantas, G. The rapid spread of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 29, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, T.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; Song, X.; Shen, Y.; Guo, T.; Kong, J.; Wang, M.; et al. The genetic structures of an extensively drug resistant (XDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae and its plasmids. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijon, D.; Curiao, T.; Baquero, F.; Coque, T.M.; Canton, R. Fecal Carriage of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae: A Hidden Reservoir in Hospitalized and Nonhospitalized Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1558–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaras, S.; Zarkotou, O.; Poulou, A.; Kristo, I.; Vrioni, G.; Themeli-Digalaki, K.; Tsakris, A. A Combined Disk Test for Direct Differentiation of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Surveillance Rectal Swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2986–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.D. A Decade of Development of Chromogenic Culture Media for Clinical Microbiology in an Era of Molecular Diagnostics. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 449–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: 27th Edition Informational Supplement M100-S27; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vasoo, S. Susceptibility Testing for the Polymyxins: Two Steps Back, Three Steps Forward? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; Sharma, A.N.; et al. CARD 2017: Expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lynch, K.H.; Dennis, J.J.; Wishart, D.S. PHAST: A Fast Phage Search Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siguier, P. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrenfeldt, J.; Skaarup, C.; Hasman, H.; Pedersen, A.G.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Bacterial whole genome-based phylogeny: Construction of a new benchmarking dataset and assessment of some existing methods. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.; Croucher, N.J.; Goater, R.J.; Abudahab, K.; Aanensen, D.M.; Harris, S.R. Phandango: An interactive viewer for bacterial population genomics. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F. bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsamy, Y.; Mlisana, K.P.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Singh, R.; Amoako, D.G.; Essack, S.Y. Whole-Genome Sequence of a Novel Sequence Type 3136 Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain Isolated from a Hospitalized Patient in Durban, South Africa. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e01300–e01318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, Y.; Hagiya, H.; Akeda, Y.; Aye, M.M.; Myo Win, H.P.; Sakamoto, N.; Shanmugakani, R.K.; Takeuchi, D.; Nishi, I.; Ueda, A.; et al. Dissemination of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae harbouring blaNDM or blaIMI in local market foods of Yangon, Myanmar. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R. Infections Caused by Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: An Update on Therapeutic Options. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Global Dissemination of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Genetic Context, Treatment Options, and Detection Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naparstek, L.; Carmeli, Y.; Chmelnitsky, I.; Banin, E.; Navon-Venezia, S. Reduced susceptibility to chlorhexidine among extremely-drug-resistant strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 81, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ye, L.; Wang, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L. Diverse prevalence of 16S rRNA methylase genes armA and rmtB amongst clinical multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malande, O.O.; Du Plessis, A.; Rip, D.; Bamford, C.; Eley, B. Invasive carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infection at a paediatric hospital: A case series. S. Afr. Med. J. 2016, 106, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Yi, J.; Ko, M.K.; Lee, S.O.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, K.-H. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae Acquisition in an Emergency Intensive Care Unit in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea: A Case-Control Study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, X. A 7-year surveillance of the drug resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae from a primary health care center. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2019, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, M.C.; Guimarães, T.; Duailibi, D.F.; Perondi, M.B.M.; Letaif, L.S.H.; Montal, A.C.; Rossi, F.; Cury, A.P.; Duarte, A.J.S.; Levin, A.S.; et al. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in patients admitted to the emergency department: Prevalence, risk factors, and acquisition rate. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 97, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, D.; Zmarlicka, M.; Nailor, M. Impact of the New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase on beta-lactam antibiotics. Infect. Drug Resist. 2015, 8, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboro, A.M.; Osei Sekyere, J.; Amoako, D.G.; Essack, S.Y.; Bester, L.A. Diversity and Proliferation of Metallo-β-Lactamases: A Clarion Call for Clinically Effective Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowman, W.; Sriruttan, C.; Nana, T.; Bosman, N.; Duse, A.; Venturas, J.; Clay, C.; Coetzee, J. NDM-1 has arrived: First report of a carbapenem resistance mechanism in South Africa. S. Afr. Med. J. 2011, 101, 873–875. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, T.; Sekyere, J.O.; Govinden, U.; Moodley, K.; Sivertsen, A.; Samuelsen, Ø.; Essack, S.Y.; Sundsfjord, A. Spread of Plasmid-Encoded NDM-1 and GES-5 Carbapenemases among Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Clinical Enterobacteriaceae in Durban, South Africa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02178-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei Sekyere, J. Current State of Resistance to Antibiotics of Last-Resort in South Africa: A Review From a Public Health Perspective. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekyere, J.O.; Govinden, U.; Essack, S. The Molecular Epidemiology and Genetic Environment of Carbapenemases Detected in Africa. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 22, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Maryam, L.; Zarrilli, R. Structure, Genetics and Worldwide Spread of New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase (NDM): A threat to public health. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei Sekyere, J.; Amoako, D.G. Carbonyl Cyanide m-Chlorophenylhydrazine (CCCP) Reverses Resistance to Colistin, but Not to Carbapenems and Tigecycline in Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyepong, N.; Govinden, U.; Owusu-Ofori, A.; Amoako, D.G.; Allam, M.; Janice, J.; Pedersen, T.; Sundsfjord, A.; Essack, S. Genomic characterization of multidrug-resistant ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from a Ghanaian teaching hospital. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 85, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei Sekyere, J.; Amoako, D.G. Genomic and phenotypic characterisation of fluoroquinolone resistance mechanisms in Enterobacteriaceae in Durban, South Africa. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Gorrie, C.; Jenney, A.; Follador, R.; Thomson, N.R.; Holt, K.E. Identification of Klebsiella capsule synthesis loci from whole genome data. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Lam, M.M.; Judd, L.M.; van Vinh Chau, N.; Dance, D.A.; Ip, M.; Karkey, A.; Ling, C.L.; Miliya, T.; et al. Genomic surveillance for hypervirulence and multi-drug resistance in invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae from south and southeast Asia. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Liu, H.; Dunstan, R.A.; Li, B.; Torres, V.V.L.; Cao, J.; Chen, L.; Wilksch, J.J.; Strugnell, R.A.; Lithgow, T.; et al. Extensively drug-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae causing nosocomial bloodstream infections in China: Molecular investigation of antibiotic resistance determinants, Informing therapy, and clinical outcomes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Seiffert, S.N.; Schwendener, S.; Perreten, V.; Endimiani, A. Differentiation of IncL and IncM Plasmids Associated with the Spread of Clinically Relevant Antimicrobial Resistance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, E.; Gužvinec, M.; Butić, I.; Krešić, S.; Crnek, S.Š.; Tambić, A.; Cornaglia, G.; Mazzariol, A. bla NDM-1 Carriage on IncR Plasmid in Enterobacteriaceae Strains. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahl, J.W.; Johnson, J.K.; Harris, A.D.; Phillippy, A.M.; Hsiao, W.W.; Thom, K.A.; Rasko, D.A. Genomic comparison of multi-drug resistant invasive and colonizing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from diverse human body sites reveals genomic plasticity. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako, D.G.; Somboro, A.M.; Abia, A.L.K.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Bester, L.; Essack, S.Y. Genomic analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from poultry and occupational farm workers in Umgungundlovu District, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polz, M.F.; Alm, E.J.; Hanage, W.P. Horizontal gene transfer and the evolution of bacterial and archaeal population structure. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubin, V.; Szöllősi, G.J. Horizontal Gene Transfer and the History of Life. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantere, T.; Kersten, S.; Hoischen, A. Long-Read Sequencing Emerging in Medical Genetics. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russotto, V.; Cortegiani, A.; Fasciana, T.; Iozzo, P.; Raineri, S.M.; Gregoretti, C.; Giammanco, A.; Giarratano, A. What Healthcare Workers Should Know about Environmental Bacterial Contamination in the Intensive Care Unit. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6905450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Burns, K.; Rodríguez Baño, J.; Borg, M.; Daikos, G.; Dumpis, U.; Lucet, J.C.; Moro, M.L.; Tacconelli, E.; Simonsen, G.S.; et al. Infection prevention and control measures and tools for the prevention of entry of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae into healthcare settings: Guidance from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bacterial Isolate * | MIC (mg/L) † | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Strain ID | Category | IMP | MEM | FEP | CXM | CTX | CAZ | CRO | FOX | AMP | AMC | TZP | AMX | GEN | AMK | CIP | ERT | SXT | TGC |
| 1 | B1 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | ≤0.5 |
| 2 | B2 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 2 |
| 3 | B3 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 1 |
| 4 | B4 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 2 |
| 5 | B5 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 2 |
| 6 | R1 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | 32 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 1 |
| 7 | R2 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | ≤0.5 |
| 8 | R3 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | 32 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 2 |
| 9 | R4 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 1 |
| 10 | R5 | XDR | ≥16 | ≥16 | 32 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥64 | ≥32 | ≥32 | ≥128 | ≥32 | ≥16 | ≥64 | ≥4 | ≥8 | ≥320 | 1 |
| Isolate * | Patient’s | Isolate’s | Carba NP † | β-Lactamase Genes | In-Silico Typing | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Strain ID | Sex | Age (Years) | Date | Source | MLST | K Typing | Allelic Types | ||
| 1 | B1 | M ‡ | 24 | 15/04/2017 | Blood | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 2 | B2 | F § | 14 | 29/01/2017 | Blood | + | NDM-1, ---------, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 3 | B3 | M | 30 | 03/01/2017 | Blood | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 4 | B4 | M | 15 days | 21/03/2017 | Blood | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 5 | B5 | - | 8 months | 25/04/2017 | Blood | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 6 | R1 | F | 61 | 20/05/2016 | Rectal | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST3136 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 7 | R2 | F | 72 | 18/07/2016 | Rectal | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 8 | R3 | M | 25 | 13/06/2016 | Rectal | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 9 | R4 | F | 21 | 11/07/2016 | Rectal | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| 10 | R5 | F | 66 | 27/07/2016 | Rectal | + | NDM-1, OXA-1, CTX-M-15, TEM-1B, SHV-1 | ST152 | KL149 | wzc:928, wzi:110 |
| Bacterial Strain | Carbapenemase 1 | Plasmids Structure 2 (% Identity) 3 | Plasmid Replicon Types | Plasmid MLST (Pmlsts) | Insertion Sequences | Intact Prophage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | ID | ||||||
| 1 | B1 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [100%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS6, ISL3, IS256, IS3 | 10 |
| 2 | B2 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [99%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS1182, IS5, ISNCY, ISL3 | 10 |
| 3 | B3 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [99%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS6, ISL3, IS256, IS3 | 10 |
| 4 | B4 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [100%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI, Col440I | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | ISL3, IS256, IS481, IS21 | 10 |
| 5 | B5 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [100%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI, Col440I | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS6, IS66, IS1182, ISL3 | 10 |
| 6 | R1 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [100%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171),IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS6, ISL3, IS256, IS3 | 10 |
| 7 | R2 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [99%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp),ColRNAI | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS6, IS66, IS1182, ISL3 | 10 |
| 8 | R3 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [99%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI, Col440I | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS6, IS66, IS1182, ISL3 | 10 |
| 9 | R4 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [100%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS1595, ISLre2, IS5, IS4 | 10 |
| 10 | R5 | NDM-1:bleMBL | p18-43_01-like [100%] | IncFIB(K), IncFII, IncFIB(pB171), IncFII(Yp), ColRNAI | IncF[K12:A-:B36] | IS6, ISL3, IS256, IS3 | 10 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramsamy, Y.; Mlisana, K.P.; Allam, M.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Ismail, A.; Singh, R.; Kisten, T.; Swe Han, K.S.; Muckart, D.J.J.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Carbapenemase-Producing Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals the Horizontal Spread of p18-43_01 Plasmid Encoding blaNDM-1 in South Africa. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010137
Ramsamy Y, Mlisana KP, Allam M, Amoako DG, Abia ALK, Ismail A, Singh R, Kisten T, Swe Han KS, Muckart DJJ, et al. Genomic Analysis of Carbapenemase-Producing Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals the Horizontal Spread of p18-43_01 Plasmid Encoding blaNDM-1 in South Africa. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(1):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010137
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamsamy, Yogandree, Koleka P. Mlisana, Mushal Allam, Daniel G. Amoako, Akebe L. K. Abia, Arshad Ismail, Ravesh Singh, Theroshnie Kisten, Khine Swe Swe Han, David J. Jackson Muckart, and et al. 2020. "Genomic Analysis of Carbapenemase-Producing Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals the Horizontal Spread of p18-43_01 Plasmid Encoding blaNDM-1 in South Africa" Microorganisms 8, no. 1: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010137
APA StyleRamsamy, Y., Mlisana, K. P., Allam, M., Amoako, D. G., Abia, A. L. K., Ismail, A., Singh, R., Kisten, T., Swe Han, K. S., Muckart, D. J. J., Hardcastle, T., Suleman, M., & Essack, S. Y. (2020). Genomic Analysis of Carbapenemase-Producing Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals the Horizontal Spread of p18-43_01 Plasmid Encoding blaNDM-1 in South Africa. Microorganisms, 8(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8010137








