Production of Hydrophobic Zein-Based Films Bioinspired by The Lotus Leaf Surface: Characterization and Bioactive Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Lotus Leaves
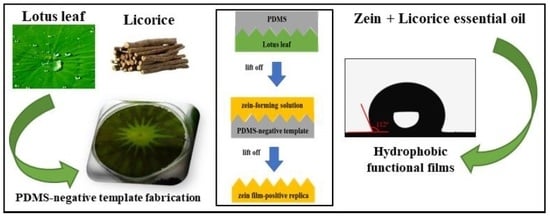
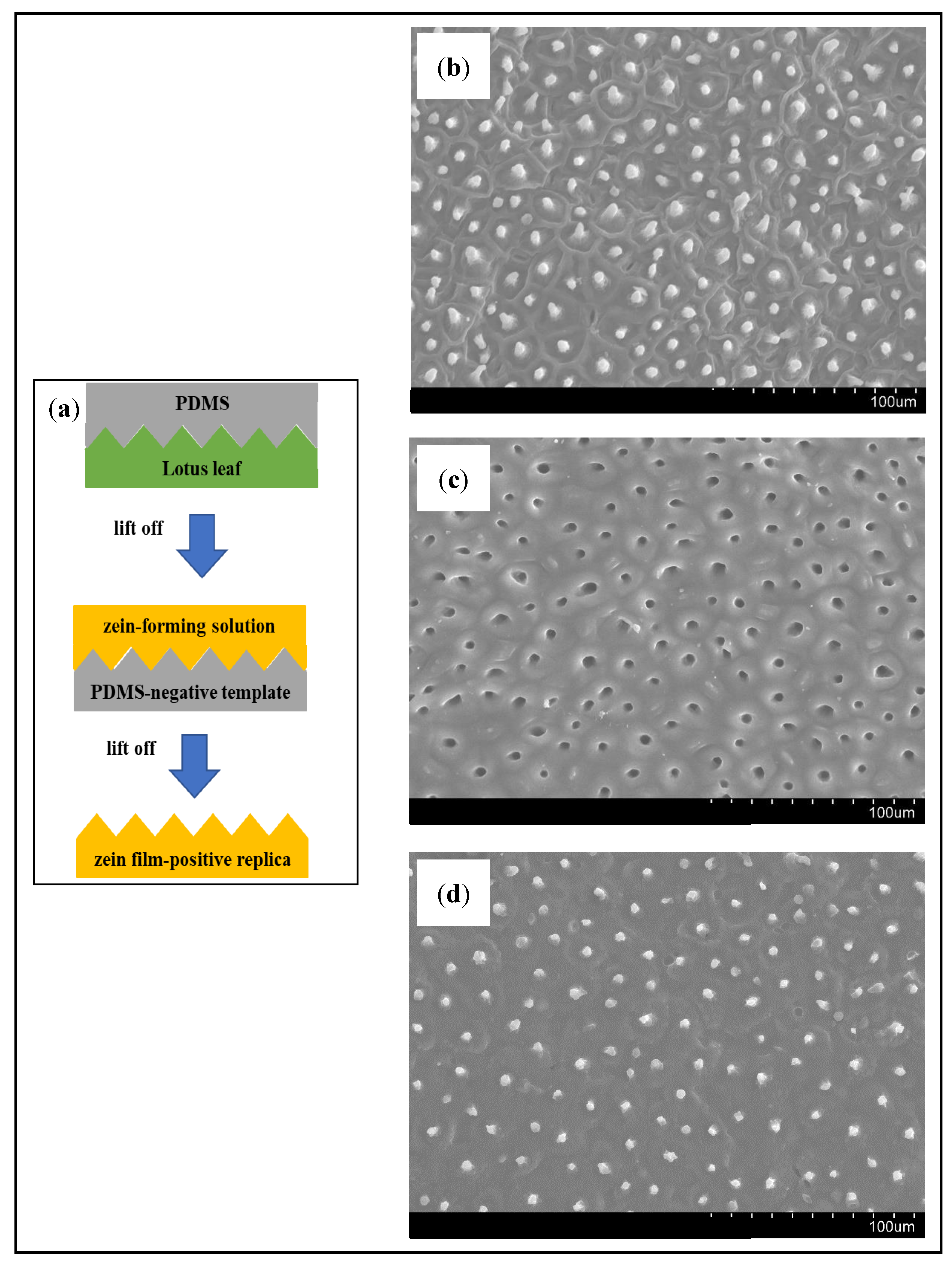
2.3. Negative Template Fabrication
2.4. Preparation of Zein-Based Films
2.5. Characterization of Films
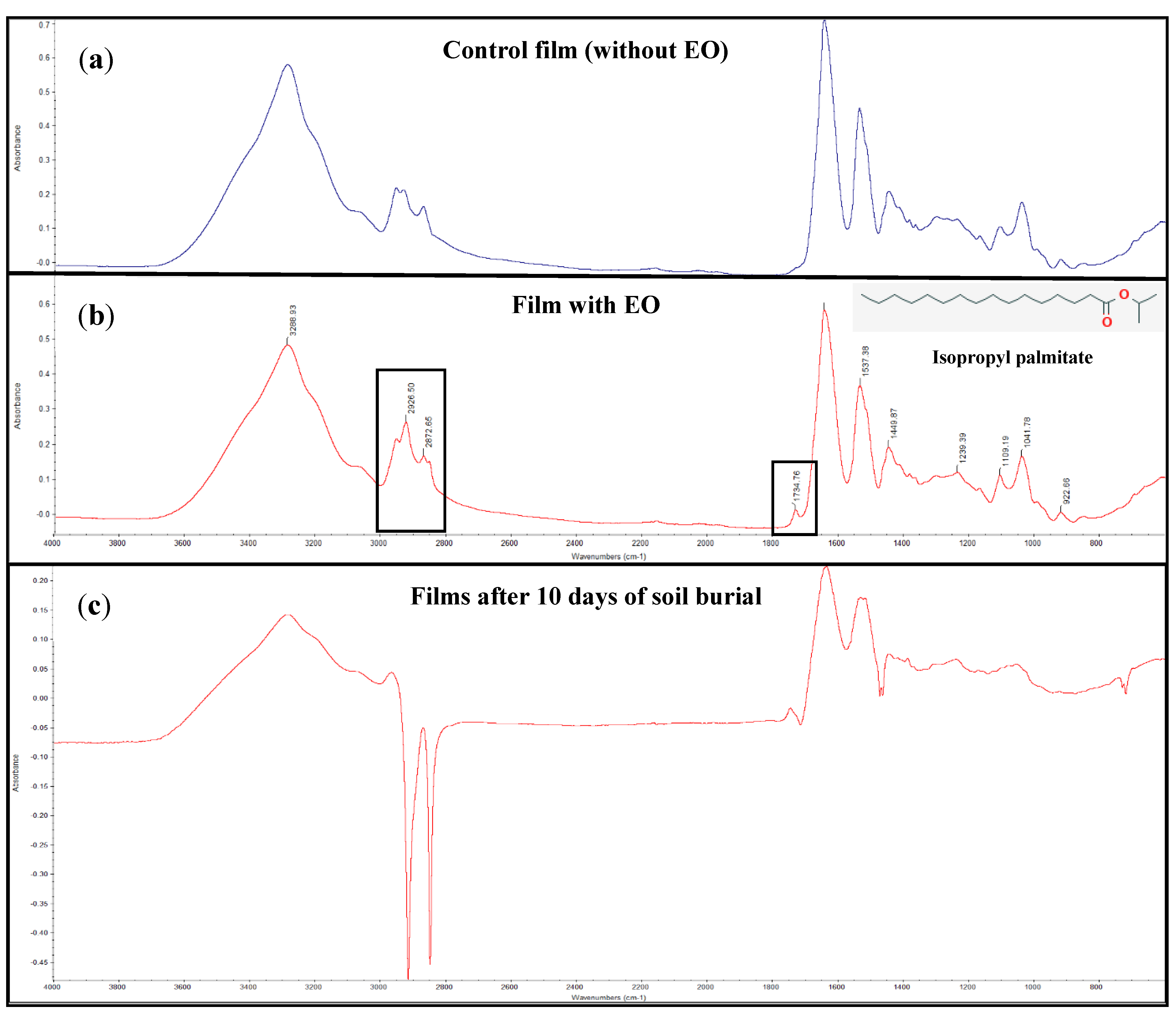
2.5.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
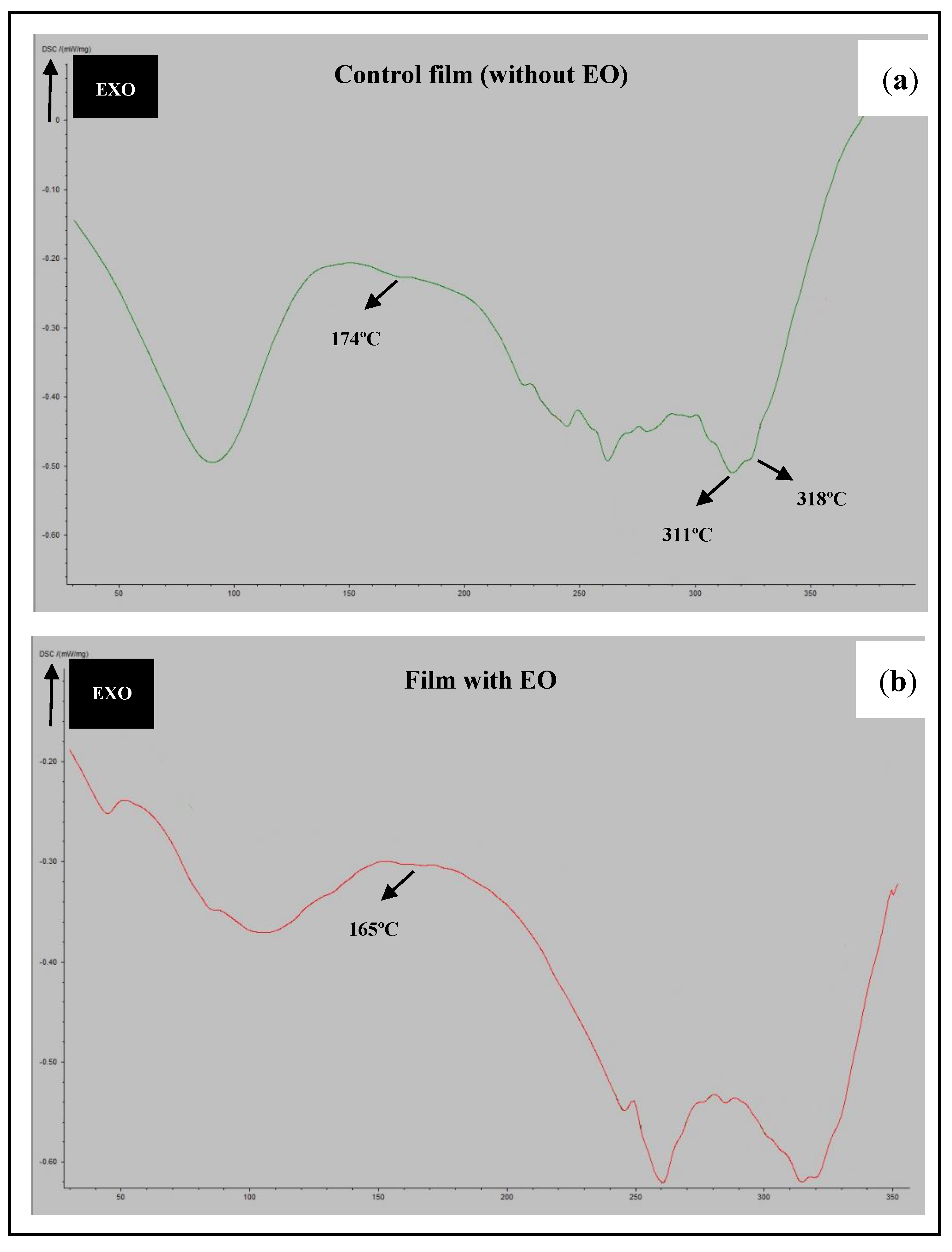
2.5.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.3. Grammage, Thickness and Mechanical Properties
2.5.4. Optical Properties
2.5.5. Barrier Properties: Water Vapor Permeability
2.5.6. Contact Angle Measurement
2.5.7. Water Solubility
2.5.8. Antioxidant Activity
2.5.9. Antibacterial Properties
2.5.10. Biodegradability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proof-of-Concept: Negative Template and Positive Replica
3.2. FTIR and DSC Analyses of The Films
3.3. Grammage, Thickness, Mechanical and Optical Properties of The Films
3.4. Barrier Properties: Water Vapor Permeability
3.5. Contact Angle and Water Solubility
3.6. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties
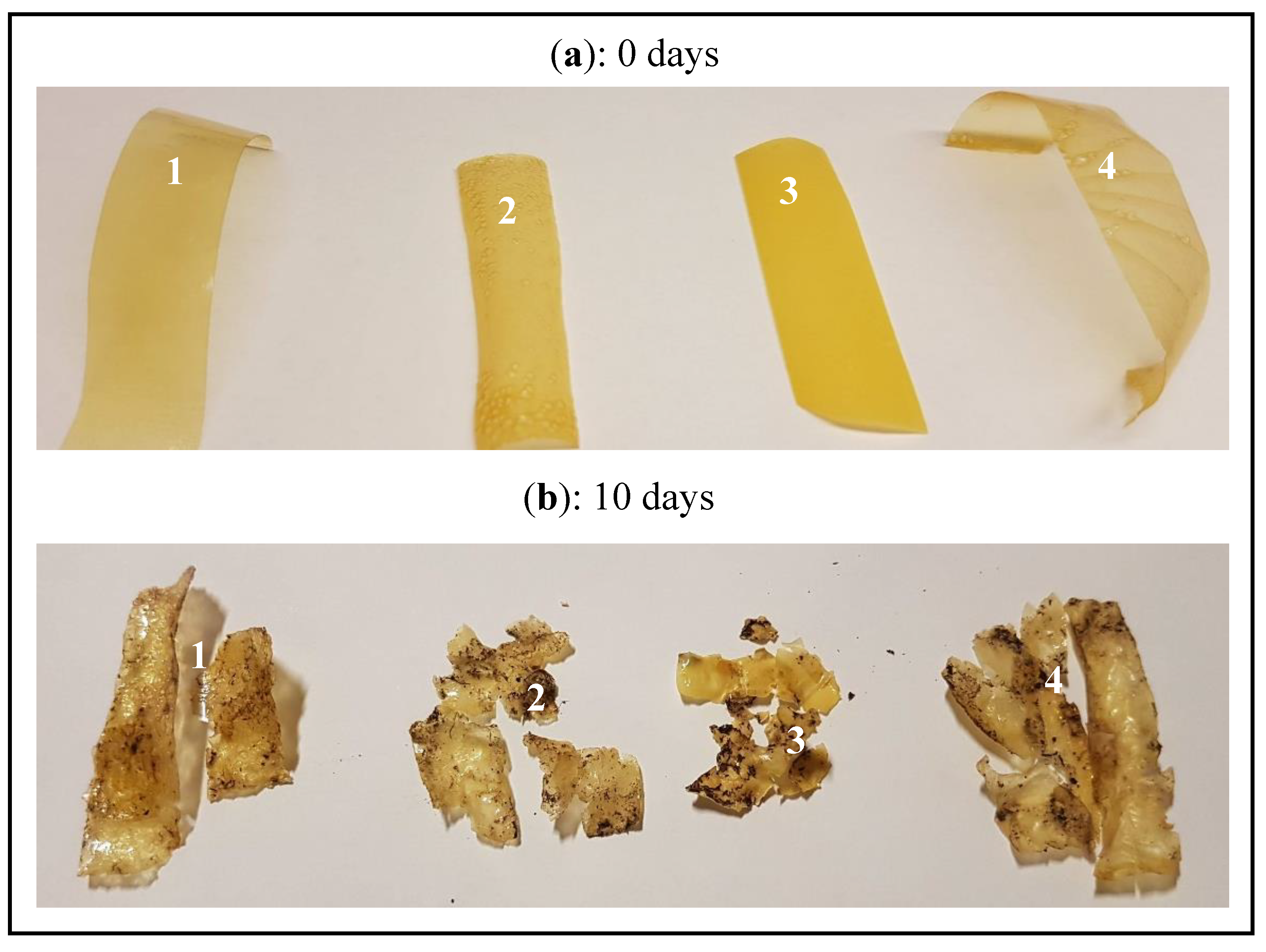
3.7. Biodegradability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribeiro-Santos, R.; Andrade, M.; Melo, N.R.; Sanches-Silva, A. Use of essential oils in active food packaging: Recent advances and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Velazquez, G.; Ramírez, J.A.; Vázquez, M. Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.L.; Song, K.B. Active gum karaya/Cloisite Na+ nanocomposite films containing cinnamaldehyde. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Mei, X.W.; Hu, Y.J.; Su, L.Y.; Bian, J.; Li, M.F.; Peng, F.; Sun, R.C. Fabrication of antimicrobial composite films based on xylan from pulping process for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Padua, G.W.; Wang, Y. Controlled formation of hydrophobic surfaces by self-assembly of an amphiphilic natural protein from aqueous solutions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5933–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.J.; Weng, Y.M. Novel edible composite films fabricated with whey protein isolate and zein: Preparation and physicochemical property evaluation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 101, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Shao, X.; Jiang, R.; Shen, Z.; Ma, Z. Mechanical and barrier properties of corn distarch phosphate-zein bilayer films by thermocompression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hönes, R.; Rühe, J. Extending the Lotus Effect: Repairing Superhydrophobic Surfaces after Contamination or Damage by CHic Chemistry. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8661–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Brugarolas, T.; Kang, S.M.; Park, B.J.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, D. Beauty of lotus is more than skin deep: Highly buoyant superhydrophobic films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7009–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latthe, S.S.; Terashima, C.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. Superhydrophobic surfaces developed by mimicking hierarchical surface morphology of lotus leaf. Molecules 2014, 19, 4256–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saison, T.; Peroz, C.; Chauveau, V.; Berthier, S.; Sondergard, E.; Arribart, H. Replication of butterfly wing and natural lotus leaf structures by nanoimprint on silica sol-gel films. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, Â.; Domingues, F.; Pereira, L. Metabolic changes after licorice consumption: A systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of clinical trials. Phytomedicine 2018, 39, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, Â.; Pereira, L.; Domingues, F.; Ramos, A. Development of a carboxymethyl xylan film containing licorice essential oil with antioxidant properties to inhibit the growth of foodborne pathogens. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensikat, H.J.; Ditsche-Kuru, P.; Barthlott, W. Scanning electron microscopy of plant surfaces: Simple but sophisticated methods for preparation and examination. Microsc. Sci. Technol. Appl. Educ. 2010, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, C.; Teixeira, G.; Monteiro, A. Leaf morphoanatomy of Portuguese autoctones white grapevine cultivars of different geographical origin. Xth Int. Terroir Congr. 2014, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hopf, R.; Bernardi, L.; Menze, J.; Zündel, M.; Mazza, E.; Ehret, A.E. Experimental and theoretical analyses of the age-dependent large-strain behavior of Sylgard 184 (10:1) silicone elastomer. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 60, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Jiang, L. Biomimic superhydrophobic surface with high adhesive forces. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6354–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiri, M.; Cerisuelo, J.; Domínguez, I.; López-Carballo, G.; Muriel-Gallet, V.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Zein films and coatings as carriers and release systems of Zataria multiflora Boiss. essential oil for antimicrobial food packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, M.R.; Castilho, M.S.M.; Veeck, A.P.L.; Rosa, C.G.; Noronha, C.M.; Maciel, M.V.O.B.; Barreto, P.M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial methylcellulose films containing Lippia alba extract and silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Piai, J.F.; Fajardo, A.R.; Fávaro, S.L.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Preparation and characterization of zein and zein-chitosan microspheres with great prospective of application in controlled drug release. J. Nanomater. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Â.; Duarte, A.; Sousa, S.; Ramos, A.; Domingues, F.C. Characterization and antimicrobial activity of cellulose derivatives films incorporated with a resveratrol inclusion complex. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Xu, T.; Gao, C.C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, X.; Tanh, X. Evaluations of physicochemical and biological properties of pullulan-based films incorporated with cinnamon essential oil and Tween 80. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, L.C.C.; Sousa, S.C.L.; Duarte, A.F.S.; Domingues, F.C.; Ramos, A.M.M. Development of carboxymethyl xylan films with functional properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casariego, A.; Souza, B.W.S.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Cruz, J.A.; Díaz, R.; Vicente, A.A. Chitosan/clay films’ properties as affected by biopolymer and clay micro/nanoparticles’ concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, P.; Pandey, J. Binary grafted chitosan film: Synthesis, characterization, antibacterial activity and prospects for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Lim, J.I.; Lee, B.R.; Mun, C.H.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.H. Preparation of lotus-leaf-like structured blood compatible poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(L-lactic acid) copolymer film surfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 114, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J. Facile method to prepare lotus-leaf-like super-hydrophobic poly(vinyl chloride) film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensikat, H.J.; Ditsche-Kuru, P.; Neinhuis, C.; Barthlott, W. Superhydrophobicity in perfection: The outstanding properties of the lotus leaf. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.B.; Corradini, E.; Forato, L.A.; Fujihara, R.; Filho, J.F.L. Microstructure and thermal and functional properties of biodegradable films produced using zein. Polímeros 2018, 28, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.M.; Padua, G.W. Properties and microstructure of plasticized zein films. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-García, M.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; Chanona-Pérez, J.; Mendoza-Madrigal, A.; Di Pierro, P.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Regalado-González, C.; Di Pierro, P.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; et al. Physical, structural, barrier, and antifungal characterization of chitosan-zein edible films with added essential oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuselvi, L.; Dhathathreyan, A. Contact angle hysteresis of liquid drops as means to measure adhesive energy of zein on solid substrates. Pramana 2006, 66, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillon, V.; Debeaufort, F.; Blond, G.; Capelle, M.; Voilley, A. Factors affecting the moisture permeability of lipid-based edible films: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dumont, M.J. Review: Bio-based films from zein, keratin, pea, and rapeseed protein feedstocks. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1915–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAFUS—Everything Added to Food: A Food Additivie Database. Available online: http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/∼dms/eafus.html (accessed on 14 September 2018).
- SCOGS—Select Committee on Gras Substances. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=SCOGS&sort=Sortsubstance&order=ASC&startrow=1&type=basic&search=licorice (accessed on 20 July 2018).
- Saito, H.E.; Harp, J.R.; Fozo, E.M. Enterococcus faecalis Responds to Individual Exogenous Fatty Acids Independently of Their Degree of Saturation or Chain Length. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 84, e01633-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoshevich, L.; Cossart, P. Listeria monocytogenes: towards a complete picture of its physiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 16, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramescu, R.E.; Ghica, M.V.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.; Prisada, R.; Popa, L. Superhydrophobic natural and artificial Surfaces-A structural approach. Materials 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Properties | Films | p-Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polystyrene Petri Dishes | Lotus Negative Template | ||||
| Without EO a | With EO b | Without EO c | With EO d | ||
| Grammage (g/m2) | 107.30 ± 5.33 | 145.10 ± 18.64 | 128.55 ± 3.35 | 167.21 ± 1.41 | 0.088 ab 0.023 cd 0.020 ac 0.176 bd |
| Thickness (µm) | 118.70 ± 10.70 | 119.33 ± 13.92 | 156.67 ± 29.66 | 166.67 ± 10.99 | 0.914 ab 0.460 cd 0.024 ac < 0.001 bd |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 14.20 ± 2.08 | 9.60 ± 0.55 | 6.82 ± 0.57 | 5.31 ± 0.62 | 0.054 ab 0.063 cd 0.022 ac 0.001 bd |
| Elongation (%) | 2.51 ± 0.36 | 2.44 ± 0.36 | 3.13 ± 0.22 | 2.21 ± 0.38 | 0.823 ab 0.032 cd 0.076 ac 0.489 bd |
| Elastic modulus (MPa) | 927.12 ± 110.02 | 353.21 ± 20.21 | 172.49 ± 25.49 | 257.97 ± 31.80 | 0.111 ab 0.177 cd 0.079 ac 0.149 bd |
| Transparency (%) | 94.89 ± 0.45 | 63.78 ± 2.56 | 82.38 ± 0.98 | 69.92 ± 1.56 | 0.050 ab 0.033 cd 0.037 ac 0.203 bd |
| L* (lightness) | 25.99 ± 0.47 | 62.35 ± 1.65 | 46.67 ± 1.41 | 56.85 ± 0.44 | 0.019ab 0.066 cd 0.027ac 0.167 bd |
| a* (redness) | −1.43 ± 0.07 | 0.04 ± 0.39 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 2.69 ± 1.01 | 0.158 ab 0.263 cd 0.003 ac 0.199 bd |
| b* (yellowness) | 10.74 ± 1.95 | 37.70 ± 1.51 | 26.49 ± 1.70 | 42.73 ± 2.31 | 0.010 ab 0.036 cd 0.027 ac 0.230 bd |
| Properties | Films | p-Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polystyrene Petri Dishes | Lotus Negative Template | ||||
| Without EO a | With EO b | Without EO c | With EO d | ||
| WVTR (g/(m2.day)) | 31.53 ± 3.38 | 30.33 ± 3.04 | 27.23 ± 0.68 | 27.23 ± 4.73 | 0.672 ab 0.991 cd 0.156 ac 0.402 bd |
| WVP (g/(Pa.day.m)) (×10−6) | 2.74 ± 0.167 | 2.74 ± 0.274 | 3.58 ± 0.049 | 4.46 ± 0.178 | 1.000 ab 0.009 cd 0.009 ac 0.002 bd |
| Properties | Films | p-Values | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polystyrene Petri Dishes | Lotus Negative Template | ||||||||
| Without EO A | With EO B | Without EO C | With EO D | ||||||
| Lower Side a | Upper Side | Lower Side b | Upper Side | Lower Side (Lotus Replica) c | Upper Side d | Lower Side (Lotus Replica) e | Upper Side f | ||
| Contact angle (°) | 48.27 ± 3.76 | 31.49 ± 1.05 | 71.80 ± 8.60 | 69.92 ± 3.02 | 81.95 ± 8.74 | 65.15 ± 3.11 | 112.50 ± 3.48 | 58.04 ± 5.71 | 0.009 ab < 0.001 ce < 0.001 ac 0.001 be 0.001 cd < 0.001 ef |
| Water solubility (%) | 20.33 ± 1.45 | 23.41 ± 2.18 | 22.38 ± 0.73 | 22.38 ± 1.57 | 0.118 AB 0.546 CD 0.122 AC 1.000 BD | ||||
| Weight loss (%) | 61.97 ± 3.16 | 56.61 ± 1.18 | 63.72 ± 2.82 | 47.66 ± 3.31 | 0.181 AB 0.003 CD 0.955 AC 0.031 BD | ||||
| Properties | Films | p-values | |||
| Polystyrene Petri Dishes | Lotus Negative Template | ||||
| Without EO a | With EO b | Without EO c | With EO d | ||
| % Inhibition (β-carotene bleaching test) | 3.45 ± 0.26 | 29.00 ± 1.67 | 5.91 ± 0.64 | 22.36 ± 1.29 | <0.001ab <0.001cd 0.011ac 0.007bd |
| Diameters of inhibition zones (mm) | Without EO a | With EO b | Without EO c | With EO d | p-values |
| E. faecalis ATCC 29219 | 6.45 ± 0.24 | 7.68 ± 0.39 | 6.52 ± 0.36 | 7.74 ± 0.40 | 0.015 ab 0.018 cd 0.795 ac 0.861 bd |
| L. monocytogenes LMG 16779 | 6.58 ± 0.33 | 8.25 ± 0.42 | 6.64 ± 0.35 | 8.46 ± 0.39 | 0.007 ab 0.004 cd 0.840 ac 0.560 bd |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luís, Â.; Domingues, F.; Ramos, A. Production of Hydrophobic Zein-Based Films Bioinspired by The Lotus Leaf Surface: Characterization and Bioactive Properties. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7080267
Luís Â, Domingues F, Ramos A. Production of Hydrophobic Zein-Based Films Bioinspired by The Lotus Leaf Surface: Characterization and Bioactive Properties. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(8):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7080267
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuís, Ângelo, Fernanda Domingues, and Ana Ramos. 2019. "Production of Hydrophobic Zein-Based Films Bioinspired by The Lotus Leaf Surface: Characterization and Bioactive Properties" Microorganisms 7, no. 8: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7080267
APA StyleLuís, Â., Domingues, F., & Ramos, A. (2019). Production of Hydrophobic Zein-Based Films Bioinspired by The Lotus Leaf Surface: Characterization and Bioactive Properties. Microorganisms, 7(8), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7080267