Insights into the Potential of the Atlantic Cod Gut Microbiome as Biomarker of Oil Contamination in the Marine Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Quality Filtering of Sequence Data and Analysis
3. Results
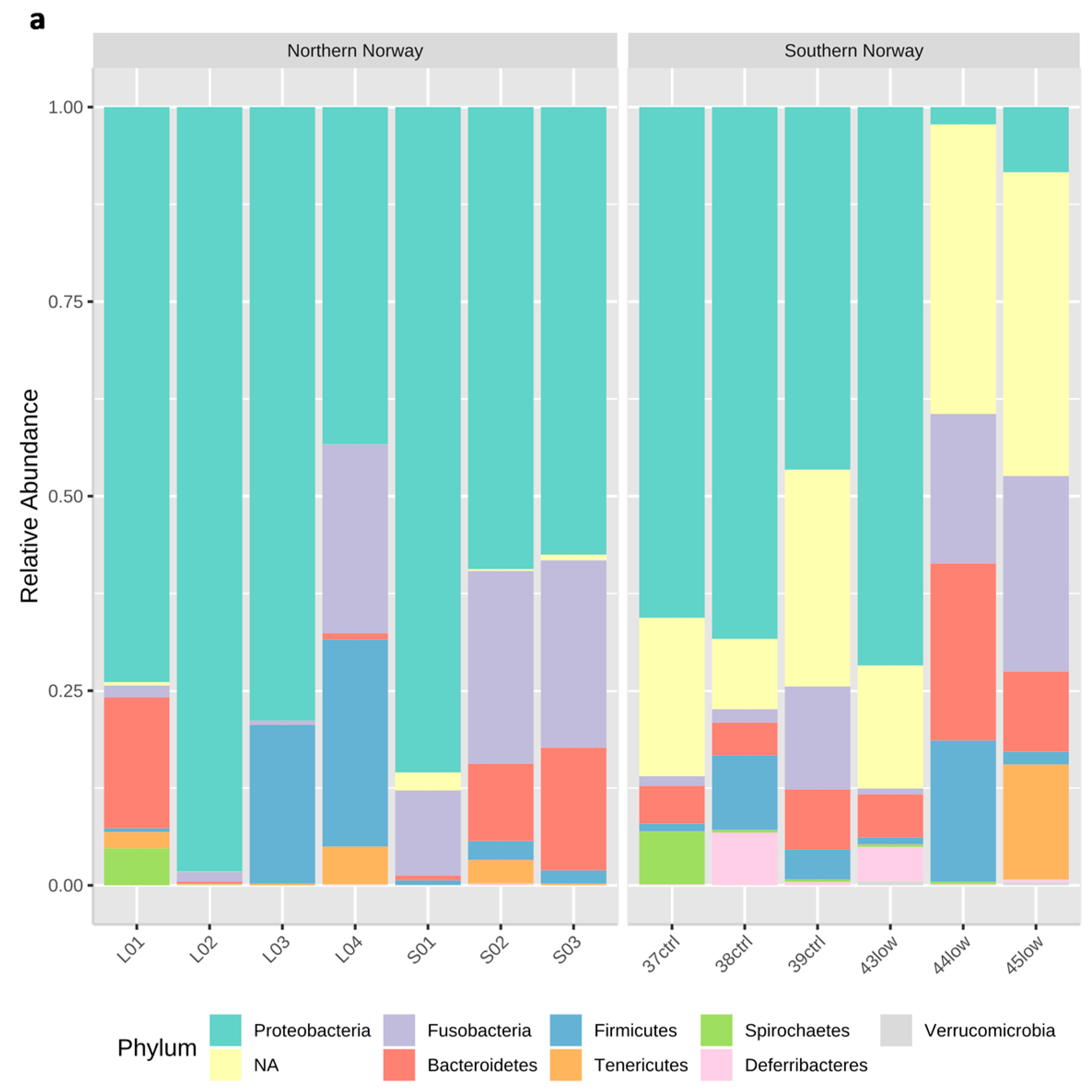
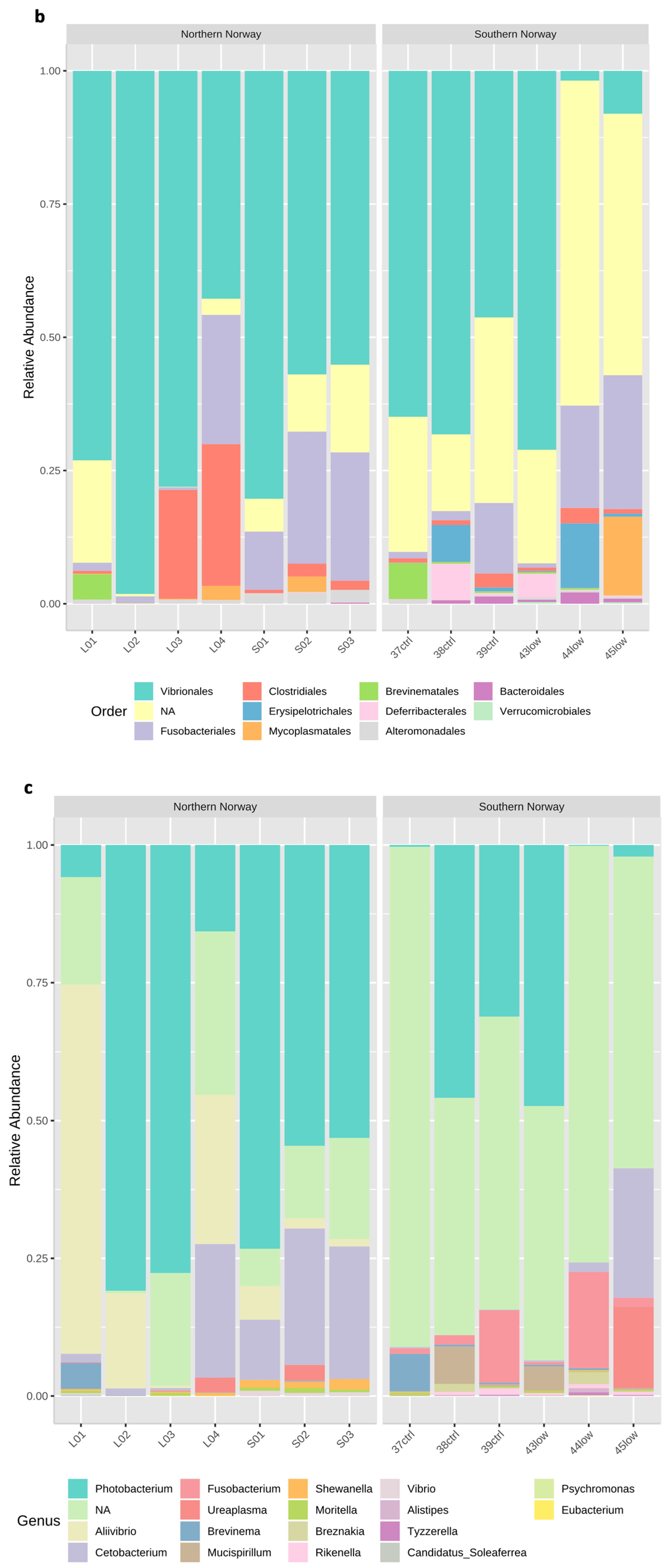
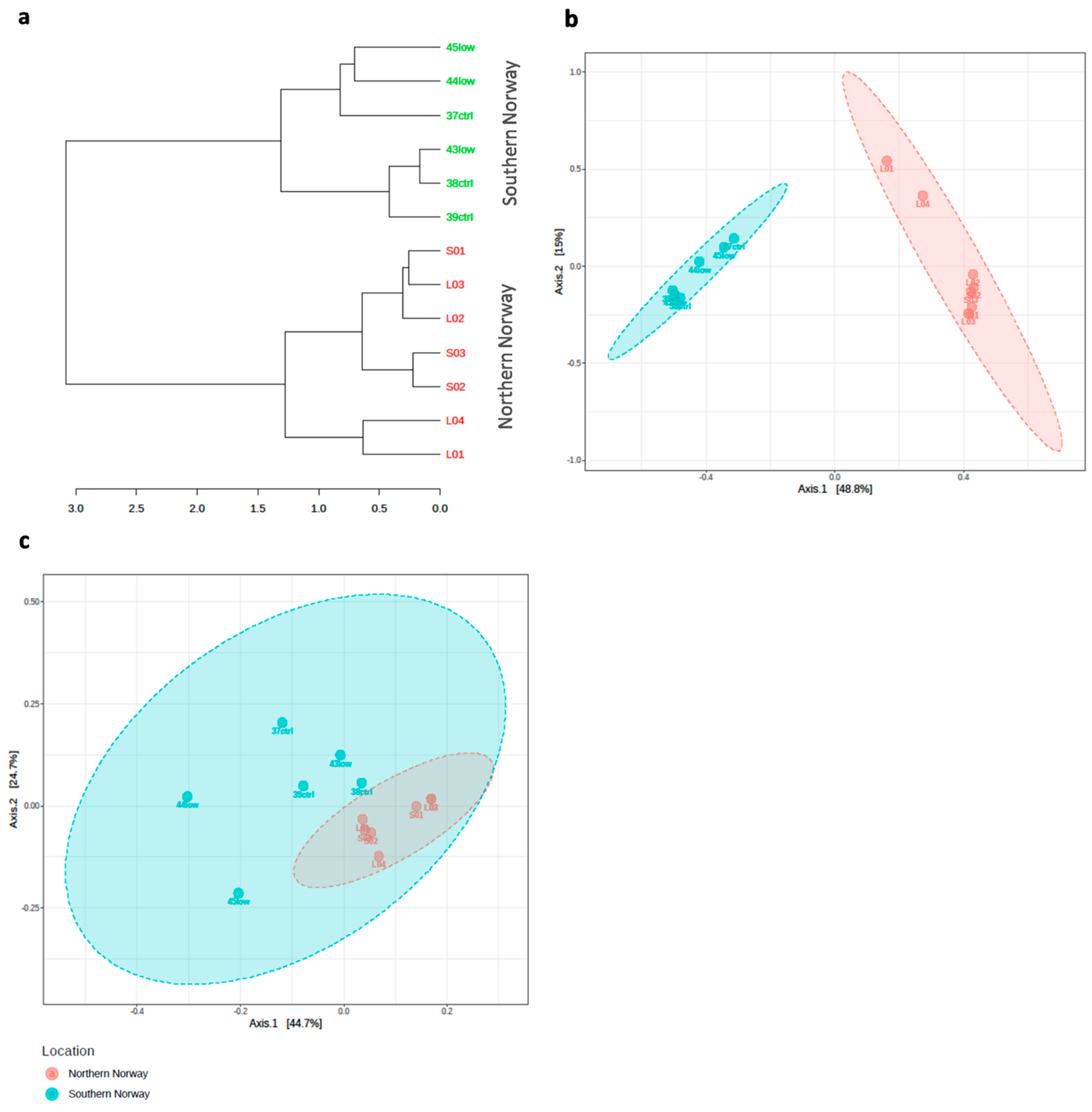
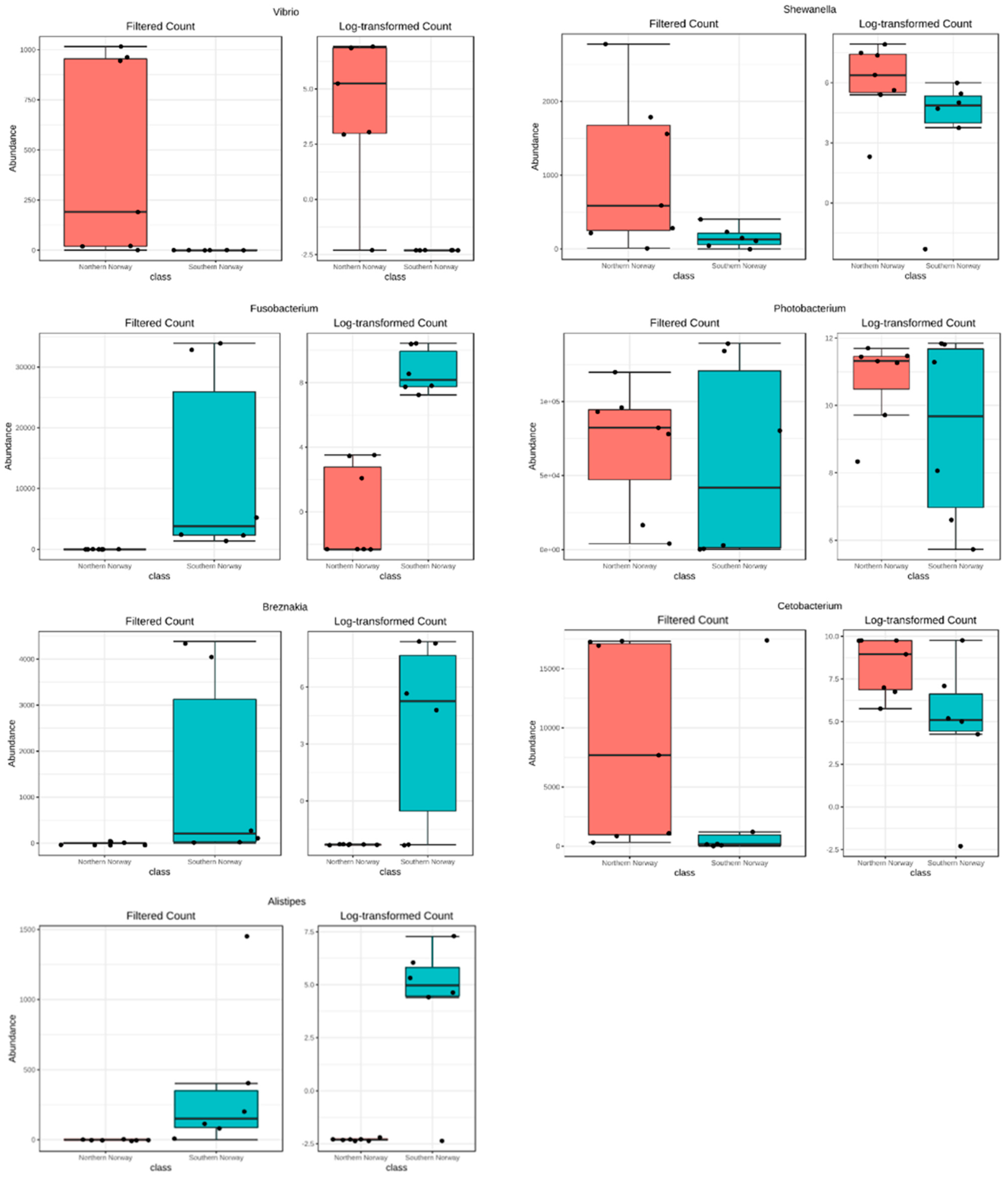
3.1. Overview of the bacterial community profiles
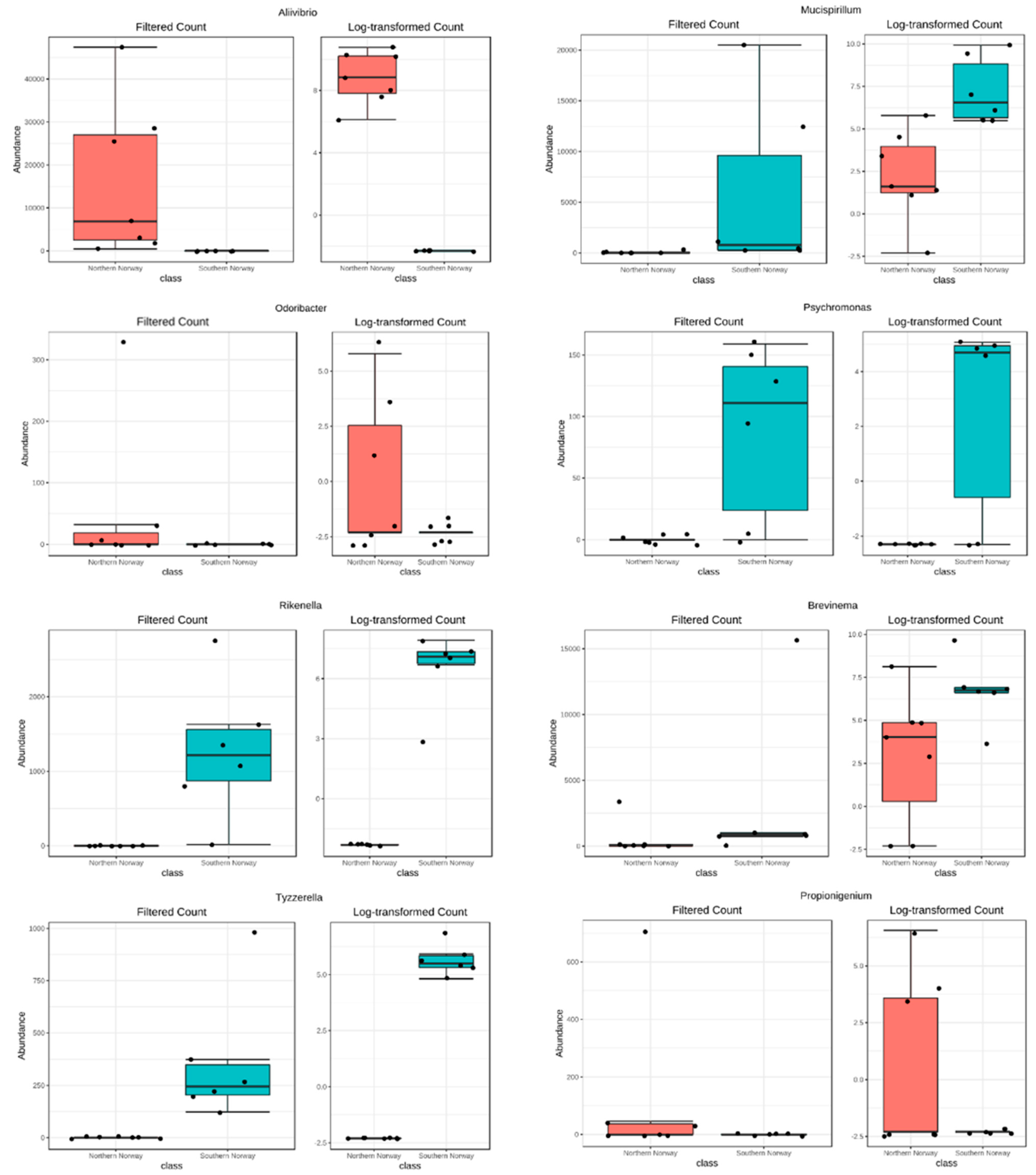
3.2. Differences in Most Abundant Gut Microbiota
3.3. Contribution of PAH Degraders Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawls, J.F.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I. Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4596–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Navarrete, P. 16S rDNA-based analysis of dominant bacterial populations associated with early life stages of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraune, S.; Bosch, T.C. Why bacteria matter in animal development and evolution. Bioessays 2010, 32, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, K.D.; Carey, H.V. A place for host-microbe symbiosis in the comparative physiologist’s toolbox. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3496–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Porchas, M.; Vargas-Albores, F. Microbial metagenomics in aquaculture: A potential tool for a deeper insight into the activity. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Sperstad, S.; Myklebust, R.; Refstie, S.; Krogdahl, Å. Characterisation of the microbiota associated with intestine of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.): The effect of fish meal, standard soybean meal and a bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Long, M.; Li, H.; Gatesoupe, F.-J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, D.; Li, A. Multi-omics analysis reveals a correlation between the host phylogeny, gut microbiota and metabolite profiles in cyprinid fishes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Hu, C.; Lam, P.K.S.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zhou, B. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota by chronic coexposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles and bisphenol A: Implications for host health in zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, C.; Lok-Shun Lai, N.; Zhang, W.; Hua, J.; Lam, P.K.S.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zhou, B. Acute exposure to PBDEs at an environmentally realistic concentration causes abrupt changes in the gut microbiota and host health of zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, X.-X.; Ren, H.; Gao, S. Correlations of Gut Microbial Community Shift with Hepatic Damage and Growth Inhibition of Carassius auratus Induced by Pentachlorophenol Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11894–11902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, A.; Riiser, E.S.; Molland, H.S.; Star, B.; Haverkamp, T.H.A.; Sydnes, M.O.; Pampanin, D.M. Gastrointestinal microbial community changes in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) exposed to crude oil. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OSPAR Commission. Protecting and conserving the North-East Atlantic and its resources. Available online: https://www.ospar.org/ (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- OSPAR Commission. Assessment of the discharges, spills and emissions from offshore installations on the Norwegian Continental Shelf in 2012–2016. Available online: https://www.ospar.org/documents?d=38985 (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- NPD, Norwegian Petroleum Directorate Factpages. Available online: www.npd.no/en/ (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- Prince, R. The Microbiology of Marine Oil Spill Bioremediation. In Petroleum Microbiology; Ollivier, B., Magot, M., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 317–335. [Google Scholar]
- Pampanin, D.M.; Sydnes, M.O. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons a constituent of petroleum: Presence and influence in the aquatic environment. In Hydrocarbon; Kutcherov, V., Kolesnikov, A., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 83–118. [Google Scholar]
- Henner, P.; Schiavon, M.; Morel, J.L.; Lichtfouse, E. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) occurrence and remediation methods. Analusis 1997, 25, M56–M59. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (US) Committee on Oil in the Sea. Oil in the Sea III: Inputs. Fates and Effects; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Toxic Release Inventory Public Data Release. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/triinter/tridata/index.htm (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, P.P.; Yu, H. Photomutagenicity of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the US EPA priority pollutant list. Mutat. Res. 2004, 557, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aas, E.; Baussant, T.; Balk, L.; Liewenborg, B.; Andersen, O. PAH metabolites in bile, cytochrome P4501A and DNA adducts as environmental risk parameters for chronic oil exposure: A laboratory experiment with Atlantic cod. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 51, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, E.; Beyer, J.; Jonsson, G.; Reichert, W.; Andersen, O. Evidence of uptake, biotransformation and DNA binding of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in Atlantic cod and corkwing wrasse caught in the vicinity of an aluminium works. Mar. Environ. Res. 2001, 52, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.K.; Singh, O.V.; Jain, R.K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Environmental pollution and bioremediation. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylland, K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) ecotoxicology in marine ecosystems. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2006, 69, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pinos, M.-C.; Vila-Costa, M.; Arrieta, J.M.; Morales, L.; González-Gaya, B.; Piña, B.; Dachs, J. Dysregulation of photosynthetic genes in oceanic Prochlorococcus populations exposed to organic pollutants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.S.; Johnson, L.L.; Olson, O.P.; Stehr, C.M.; Horness, B.H.; Collier, T.K.; McCain, B.B. Toxicopathic hepatic lesions as biomarkers of chemical contaminant exposure and effects in marine bottomfish species from the Northeast and Pacific Coasts, USA Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 37, 92–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, J.P.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. Oil spills and fish health: Exposing the heart of the matter. J. Expo Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, J.P.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. Defects in cardiac function precede morphological abnormalities in fish embryos exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 196, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incardona, J.P.; Carls, M.G.; Teraoka, H.; Sloan, C.A.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-independent toxicity of weathered crude oil during fish development. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatlen, K.; Sloan, C.A.; Burrows, D.G.; Collier, T.K.; Scholz, N.L.; Incardona, J.P. Natural sunlight and residual fuel oils are an acutely lethal combination for fish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 99, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-H.; Hicken, C.R.; Boyd, D.; Anulacion, B.F.; Carls, M.G.; Shim, W.J.; Incardona, J.P. Geologically distinct crude oils cause a common cardiotoxicity syndrome in developing zebrafish. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherr, G.N.; Fairbairn, E.; Whitehead, A. Impacts of Petroleum-Derived Pollutants on Fish Development. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 5, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayha, K.M.; Ortell, N.; Ryan, C.N.; Griffitt, K.J.; Krasnec, M.; Sena, J.; Ramaraj, T.; Takeshita, R.; Mayer, G.D.; Schilkey, F.; et al. Crude oil impairs immune function and increases susceptibility to pathogenic bacteria in southern flounder. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OSPAR. JAMP, Joint Assessment and Monitoring Program. Guidelines for Monitoring Contaminants in Biota. Available online: https://www.ospar.org/documents?d=32414 (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Sundt, R.C.; Ruus, A.; Jonsson, H.; Skarphéðinsdóttir, H.; Meier, S.; Grung, M.; Beyer, J.; Pampanin, D.M. Biomarker responses in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) exposed to produced water from a North Sea oil field: Laboratory and field assessments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahrgang, J.; Brooks, S.J.; Evenset, A.; Camus, L.; Jonsson, M.; Smith, T.J.; Lukina, J.; Frantzen, M.; Giarratano, E.; Renaud, P.E. Seasonal variation in biomarkers in blue mussel (Mytilus edulis), Icelandic scallop (Chlamys islandica) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua): implications for environmental monitoring in the Barents Sea. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 127, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holth, T.F.; Eidsvoll, D.P.; Farmen, E.; Sanders, M.B.; Martínez-Gómez, C.; Budzinski, H.; Burgeot, T.; Guilhermino, L.; Hylland, K. Effects of water accommodated fractions of crude oils and diesel on a suite of biomarkers in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 154, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, O.A.; Sheehan, D.; Gpksøyr, A. Alteration in the Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) hepatic thiol-proteome after methylmercury exposure. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2014, 77, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampanin, D.M.; Larssen, E.; Øysæd, K.B.; Sundt, R.C.; Sydnes, M.O. Study of the bile proteome of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua): Multi biological markers of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 101, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampanin, D.M.; Goff, J.L.; Skogland, K.; Marcucci, C.R.; Øysæd, K.B.; Lorentzen, M.; Jørgensen, K.B.; Sydnes, M.O. Biological effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and their first metabolic products in in vivo exposed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2016, 79, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oost, R.V.D.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiselbrecht, A.D.; Hedlund, B.P.; Tichi, M.A.; Staley, J.T. Isolation of marine polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading Cycloclasticus strains from the Gulf of Mexico and comparison of their PAH degradation ability with that of puget sound Cycloclasticus strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4703–4710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harayama, S.; Kasai, Y.; Hara, A. Microbial communities in oil-contaminated seawater. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, J.E.; Prakash, O.; Overholt, W.A.; Green, S.J.; Freyer, G.; Canion, A.; Delgardio, J.; Norton, N.; Hazen, T.C.; Hettel, M. Hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria and the bacterial community response in gulf of Mexico beach sands impacted by the deepwater horizon oil spill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7962–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, L.D.; Perez-Calderon, L.J.; Gontikaki, E.; Keith, L.; Gubry-Rangin, C.; Anderson, J.A.; Witte, U. Effect of spatial origin and hydrocarbon composition on bacterial consortia community structure and hydrocarbon biodegradation rates. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, T.; Morris, G.; Ellis, D.; Bowler, B.; Jones, M.; Salek, K.; Mulloy, B.; Teske, A. Hydrocarbon-degradation and MOS-formation capabilities of the dominant bacteria enriched in sea surface oil slicks during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2018, 135, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribicic, D.; Netzer, R.; Hazen, T.C.; Techtmann, S.M.; Drabløs, F.; Brakstad, O.G. Microbial community and metagenome dynamics during biodegradation of dispersed oil reveals potential key-players in cold Norwegian seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, F.; Streten, C.; Harries, S. A protocol for identifying suitable biomarkers to assess fish health: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, S.; Björkblom, C.; Jonsson, H.; Godal, B.F.; Liewenborg, B.; Lyng, E.; Pampanin, D.M. Biomarker quantification in fish exposed to crude oil as input to species sensitivity distributions and threshold values for environmental monitoring. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 125, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riiser, E.S.; Haverkamp, T.H.A.; Borgan, Ø.; Jakobsen, K.S.; Jentoft, S.; Star, B. A Single Vibrionales 16S rRNA Oligotype Dominates the Intestinal Microbiome in Two Geographically Separated Atlantic cod Populations. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ager, D.; Evans, S.; Li, H.; Lilley, A.K.; van der Gast, C.J. Anthropogenic disturbance affects the structure of bacterial communities. Environ Microbiol. 2010, 12, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: ftp://ftp.uvigo.es/CRAN/web/packages/dplR/vignettes/intro-dplR.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package Version 2.5–5. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 11 July 2019).
- Dhariwal, A.; Chong, J.; Habib, S.; King, I.L.; Agellon, L.B.; Xia, J. MicrobiomeAnalyst: A web-based tool for comprehensive statistical, visual and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W180–W188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.; Vrbanac, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Aksenov, A.; Callewaert, C.; Debelius, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Kosciolek, T.; McCall, L.; McDonald, D.; et al. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman., F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods. 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Meth. 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrisse, F.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Noël, C.; Cagnon, C.; Dumbrell, A.J.; McGenity, T.J.; Duran, R. Variation of Oxygenation Conditions on a Hydrocarbonoclastic Microbial Community Reveals Alcanivorax and Cycloclasticus Ecotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Bai, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiao, L.; Zhou, H.; Shao, Z. Distribution of PAHs and the PAH-degrading bacteria in the deep-sea sediments of the high-latitude Arctic Ocean. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, D.; Ghosh, S.; Dutta, T.K.; Ahn, Y. Current state of knowledge in microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, S.P.; Guillou, H.; Ellero-Simatos, S. The gut microbiota: A major player in the toxicity of environmental pollutants? NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2016, 2, 16003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullam, K.E.; Essinger, S.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; O’Connor, M.P.; Rosen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Kilham, S.S.; Russell, J.A. Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: A meta-analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3363–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, K.A.; Meziti, A.; Mente, E.; Frentzos, A. Dietary differences are reflected on the gut prokaryotic community structure of wild and commercially reared sea bream (Sparus aurata). Microbiol. Open. 2014, 3, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarkasi, K.Z.; Abell, G.C.J.; Taylor, R.S.; Neuman, C.; Hatje, E.; Tamplin, M.L.; Katouli, M.; Bowman, J.P. Pyrosequencing-based characterization of gastrointestinal bacteria of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) within a commercial mariculture system. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehmann, K.; Hertkon, N.; Kettrup, A.A. Fluoranthene metabolism in Mycobacterium sp. strain KR20: Identify of pathway intermediates during degradation and growth. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2783–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahjoubi, M.; Jaouani, A.; Guesmi, A.; Ben-Amor, S.; Jouini, A.; Cherif, H.; Najjari, A.; Boudabous, A.; Koubaa, N.; Cherif, A. Hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria isolated from petroleum contaminated sites in Tunisia: Isolation, identification and characterization of the biotechnological potential. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, S.S.; Khanafer, M.M.; Al-Awadhi, H.A. Ability of the So-Called Obligate Hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria to utilize nonhydrocarbon substrates thus enhancing their activities despite their misleading name. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Golyshin, P.N.; Moore, E.R.; Abraham, W.R.; Lümsdorf, H.; Timmis, K.N. Alcanivorax borkumensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new, hydrocarbon-degrading and surfactant-producing marine bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Obligate oil-degrading marine bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2007, 18, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittel, A.; Kofoed, M.V.; Sørensen, K.B.; Ingvorsen, K.; Schramm, A. Succession of Deferribacteres and Epsilonproteobacteria through a nitrate-treated high temperature oil production facility. Syst. Appl Microbiol. 2012, 35, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, A.; Alsop, E.B.; Lomans, B.P.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Head, I.M.; Tsesmetzis, N. Succession in the petroleum reservoir microbiome through an oil field production lifecycle. ISME J. 2017, 1, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naether, D.J.; Slawtschew, S.; Stasik, S.; Engel, M.; Olzog, M.; Wick, L.Y.; Timmis, K.N.; Heipieper, H.J. Adaptation of the Hydrocarbonoclastic Bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis SK2 to Alkanes and Toxic Organic Compounds: A Physiological and Transcriptomic Approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4282–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golyshin, P.N.; Dos Santos, V.; Kaiser, O.; Ferrer, M.; Sabirova, Y.S.; Lunsdorf, H.; Chernikova, T.N.; Golyshina, O.V.; Yakimov, M.M.; Puhler, A.; et al. Genome sequence completed of Alcanivorax borkumensis, a hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium that plays a global role in oil removal from marine systems. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 106, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Shao, Z. Diversity of flavin-binding monooxygenase genes (almA) in marine bacteria capable of degradation long-chain alkanes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2012, 80, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Giuliano, L.; Gentile, G.; Crisafi, E.; Chernikova, T.N.; Abraham, W.-R.; Lünsdorf, H.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Oleispira antarctica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium isolated from Antarctic coastal sea water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppe, U.; Richnow, H.-H.; Michaelis, W.; Antranikian, G. Degradation of crude oil by an arctic microbial consortium. Extremophiles 2005, 9, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, I.M.; Jones, D.M.; Röling, W.F. 2006: Marine microorganisms make a meal of oil. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.C.; Dubinsky, E.A.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Piceno, Y.M.; Singh, N.; Jansson, J.K.; Probst, A.; Borglin, S.E.; Fortney, J.L. Deep-sea oil plume enriches indigenous oil-degrading bacteria. Science 2010, 330, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinsky, E.A.; Conrad, M.E.; Chakraborty, R.; Bill, M.; Borglin, S.E.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Mason, O.U.; Piceno, Y.M.; Reid, F.C.; Stringfellow, W.T.; et al. Succession of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria in the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10860–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, J.; Brejnrod, A.; Mortensen, M.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Stokholm, J.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.; Bisgaard, H.; Waage, J. Large-scale benchmarking reveals false discoveries and count transformation sensitivity in 16S rRNA gene amplicon data analysis methods used in microbiome studies. Microbiome 2016, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M. Statisticians issue warning on P values. Nature 2016, 531, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserstein, R.L.; Schirm, A.L.; Lazar, N.A. Moving to a World Beyond “p < 0.05”. Am. Stat. 2019, 73, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
| Area | Latitude | Longitude | Samples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Norway | Lofoten | 68°10′19″ N | 13°45′00″ E | 4 |
| Sørøya | 70°29′33″ N | 22°09′51″ E | 3 | |
| Southern Norway | Kvitsøy | 59°03′52″ N | 05°24′19″ E | 6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walter, J.M.; Bagi, A.; Pampanin, D.M. Insights into the Potential of the Atlantic Cod Gut Microbiome as Biomarker of Oil Contamination in the Marine Environment. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070209
Walter JM, Bagi A, Pampanin DM. Insights into the Potential of the Atlantic Cod Gut Microbiome as Biomarker of Oil Contamination in the Marine Environment. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(7):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070209
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalter, Juline M., Andrea Bagi, and Daniela M. Pampanin. 2019. "Insights into the Potential of the Atlantic Cod Gut Microbiome as Biomarker of Oil Contamination in the Marine Environment" Microorganisms 7, no. 7: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070209
APA StyleWalter, J. M., Bagi, A., & Pampanin, D. M. (2019). Insights into the Potential of the Atlantic Cod Gut Microbiome as Biomarker of Oil Contamination in the Marine Environment. Microorganisms, 7(7), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070209





